Here you will learn:
- Electric convectors
- Water convectors
- Oil radiators
- Water heating radiators
- Comparison and conclusions
Convector heaters, radiators and oil radiators are actively used to heat rooms for various purposes. Differing in design and method of heat supply, they allow you to create efficient heating systems. Convector or radiator, which is better - such questions are often puzzled by people who want to create an autonomous heating system. It is difficult to answer this question, since the specified equipment is designed for use in a wide variety of conditions.
In this comparative review we will cover the following equipment:
- Electric convectors;
- Water convectors;
- Oil radiators;
- Radiators for water heating systems.
At the same time, we’ll find out which of these is better – let’s go through the list in order.
What distinguishes a convector from a radiator
The described devices are a type of heating devices. They can work independently or as elements of a heating system. The main difference between a convector and a radiator is the design and operating principle of the devices.
Radiator
It is a unit with a sectional metal body. All free space in the sections is filled with coolant. Water, special mineral oil or antifreeze liquid are used as a coolant.
The operating principle of the unit is based on the thermal radiation method. Under the influence of a heat source, the coolant is heated. This source is the heating element.
An increase in coolant temperature leads to heating of the surface of the device body. The heated body releases heat into the surrounding space. Under the influence of thermal radiation, the heating level in the room increases.
The coolant temperature is monitored by a built-in thermal sensor. Automation turns the device on and off when the set values are reached. The heating of the working fluid is controlled using a built-in thermostat.
Convector
To answer how a heating convector differs from a radiator, let’s consider the operating principle of the device.
The operation of the device is based on the convection of air masses in the room. It is an installation with a panel-type metal casing. The housing contains a heating element with a thermostat. The thermostat is used to regulate the heating temperature.
The housing has an open space at the bottom. Through it, a flow of cold air enters the housing. The heating element heats the cold air to a predetermined level. Heated air currents rush upward.
To accelerate and direct the warm air flow, special blinds are used in the device body.
Warm air masses displace cold air in the upper part of the room. The flow of cold air falls down. Below it again enters the device body. The working cycle of air movement is repeated.
The set temperature level in the room is controlled by a thermal sensor. Triggering of the sensor leads to automatic switching on and off of the device. Adjustment of the specified parameters is carried out using a mechanical or electronic control unit.
The difference between water heating radiators
The design of radiators intended for water heat supply systems has much in common with oil-based devices, but they differ in that they are heated not by hot oil, but by using coolant circulating through pipes and batteries.
Water radiators are equipment for arranging permanent heating. The scope of their use is autonomous or centralized heating systems. They are better than oil units because they do not consume electricity. And if the coolant is heated by an economical gas boiler, then financial costs for heating are minimal.
Water radiators are superior to oil models due to increased reliability. They are easy to clean and can provide body space for large spaces. Heating a larger area is the main advantage of water heating systems.
Once they are connected into a single structure, it is possible to uniformly adjust the heating temperature simultaneously in all rooms. Equipping water radiators with thermostatic valves allows for individual temperature control in each room.
The advantages of such devices:
- high heat transfer coefficient;
- environmental cleanliness;
- increased power for some models.
The disadvantages of water radiators include:
- First of all, what is the difference between a convector and a radiator - this is the compactness of the first devices, for example, in-floor or miniature plinth models;
- radiators are more expensive than convectors;
- their bodies can be very hot, unlike convectors.
Advantages and disadvantages of convectors
The answer to the question of which is better, a convector or a radiator, allows us to obtain an analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of both types of systems.
The advantages of the devices include:
- Autonomous operation mode.
- Low level of heating of the housing surface (up to +70 ᵒC).
- Quick heating of cold air (1-1.5 minutes).
- Lack of coolant and pipelines.
- Possibility of combining devices into one network.
- Convenient control of one or several devices simultaneously.
- Simplicity of design and installation of the installation.
- Quiet and environmentally friendly.
- Explosion and fire safety.
- Modern design.
The disadvantages are:
- Large amount of electricity used.
- High cost of multifunctional installations.
- Low level of electrical safety.
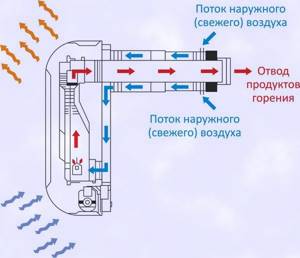
Distinctive characteristics of electric convectors
Mobile models on casters can be used in the absence of central heating during periods when there are not yet severe frosts. Of course, a compact heater cannot replace the main system; it can only heat a small space.
Such devices are well suited for temporary heating: there is no point in turning on the boiler, for example, if 1-2 rooms in a large building need heat. Electric heaters, including convector types, cope well with this. This is also economical in that the space heating units can be turned off several hours before departure if the walls, windows and doors retain heat well.

Electric convector heater
There are basic criteria by which one can judge the effectiveness of a mobile electric convector with a cooler and a conventional heating device operating on a familiar heating circuit.
Table 1
| Characteristic | Water radiator | Electric convector |
| Safety | Warm surface | Warm air flow |
| Lifetime | Up to 30-50 years | On average 10 years |
| Thermal output | Doesn't give off heat until it warms up | Air heating starts immediately |
| Economical | Efficiency depends on the metal and coolant | Power and energy consumption are adjustable |
| Dimensions and mobility | Takes up space in a window sill or on the wall | Install anywhere |
| Price | Installation starts from 2000 rubles. | No installation required |
But there is also a significant drawback: working from the network is expensive, especially when using electric convectors. It is recommended to install multi-tariff meters (day/night) to minimize energy costs.
Advantages and disadvantages of radiators
The advantages of these devices include:
- Ease of Management.
- Ease of movement.
- Affordable price.
- Easy to care and maintain.
The disadvantages are:
- High level of heating of the housing surface (up to +100 ᵒС…+120 ᵒС).
- High fire hazard.
- Heavy weight.
The listed pros and cons will help buyers determine what is better to use in the apartment - a convector or a radiator.
What to choose?
To understand which device is better for specific conditions of use, an oil heater or a convector, it is necessary to compare them according to various parameters.
It is important to consider the design of the device, since units of the same type, but of different brands, can differ significantly in quality, ease of use, durability and safety
Compactness
Convectors, like radiators, are available in floor-mounted and wall-mounted models. However, the dimensions of the convector are usually slightly smaller
When choosing a portable convector or oil radiator for temporary use, you should also pay attention to the weight of the product. The weight of convectors does not exceed 10 kg, while oil heaters weigh 18-25 kg

Convector type wall heater
Room heating speed
An electric convector will outperform a conventional oil heater in terms of warming up speed, since it quickly reaches the operating heat transfer mode. However, a radiator equipped with a built-in fan will take some time to warm up, but then in a short time it will warm up the entire volume of air in the room due to forced circulation. The convector has a lower heating temperature and works only due to natural air exchange.
Safety
Most convector models are equipped with protection against voltage surges, overheating, and are equipped with position sensors that turn off the unit when it falls or tilts.
Economy class oil-filled radiators may not have any protection, so their operation is possible only with constant monitoring. More expensive models also have a rollover sensor.
The surface of a working convector heats up to approximately 60°C; it is impossible to get burned on this heating device. The metal body of the oil cooler heats up to 85°C, and if touched, you can get burned. If there are children in the house, choose a model with a protective casing.
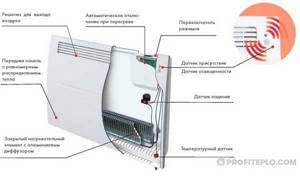
The device of a modern convector heater
If you imagine an emergency situation, then if the convector malfunctions, a short circuit may occur. A malfunctioning oil cooler can also lead to a short circuit, and in addition there is a risk of hot oil leaking.
From a safety point of view, the best option is a convector.
Environmental friendliness
According to this parameter, the devices are equivalent and safe for health. In both cases, during operation, oxygen in the room is not burned, and dust is not burned. The paint and varnish external coating does not emit harmful substances when heated.
Oil radiators without a fan differ only in that they raise dust particles into the air to a lesser extent, since they are characterized by relatively low convection efficiency.
Heating of large areas
If you need to warm up a large room well, several heating devices are used. In this case, a separate socket is required for each oil radiator.

Oil radiators with and without fan
Convectors installed in the same or different rooms are combined into a single heating network, which is equipped with a rheostat - this allows to reduce electrical energy consumption.
Comfort
Heating devices of both types operate silently (with the exception of radiators equipped with a fan) and do not emit unpleasant odors. High-end models are designed for programming the operating mode, setting the on and off time.
Oil radiators do not dry out the air; in addition, they can be additionally equipped with a humidifier.
When choosing a convector, please note that heat during convection is distributed unevenly - the difference in air temperatures near the floor and under the flow can reach 10°C. In addition, devices of this type are not suitable for dusty rooms and areas
Cost and durability
When assessing the pros and cons of heaters, it is necessary to compare the service life and cost of the products.

Oil heaters come in different sizes
Convectors are designed for 20-25 years of use. These are reliable, repairable devices. Oil radiators leak after several years of operation (up to 10 years) due to the formation of microcracks. Such heaters cannot be repaired and must be replaced with new ones.
The cost of both convectors and radiators depends on the brand and characteristics of a particular model. On average, oil heaters are cheaper when comparing units of different types, but with the same power and functionality. Products from well-known brands are highly expensive, but inexpensive analogues usually have a short service life.
Technical characteristics and cost of heaters
The main characteristics and cost of heating radiators and convectors are given in the table.
| Model name | Specifications | Manufacturer country | Cost, rub. |
| Radiators | |||
| Ballu BOH/CL-05WRN 1000 | Number of modes – 3. Number of sections – 5. Power, kW – 1.0. Heating area, m2 – 15. Control – mechanical. Thermostat - yes. Weight, kg – 4.2. | Russia | 1 990 |
| Vitek VT-1709 W | Number of modes – 3. Number of sections – 9. Power, kW – 2.0. Heating area, m2 – 20. Control – mechanical. Thermostat - yes. Weight, kg – 6.5. Functions: * shutdown when overturning; * overheat protection. | China | 3 990 |
| De Longhi TRRS0920C | Number of modes – 3. Number of sections – 9. Power, kW – 2.0. Heating area, m2 – up to 24. Control – mechanical. Thermostat - yes. Weight, kg – 12. Functions: * frost protection. | China | 8 990 |
| Convectors | |||
| Ballu BEC/EM-1000 | Number of modes – 2. Power, kW – 1.0. Heating area, m2 – up to 15. Control – mechanical. Thermostat - yes. Weight, kg – 3.0. Functions: * shutdown when overturning; * overheat protection. | Russia | 1 990 |
| Electrolux ECH/B-1500 E | Number of modes – 5. Power, kW – 1.5. Heating area, m2 – up to 20. Control – electronic. Thermostat - yes. Weight, kg – 3.0. Functions: * shutdown when overheating; * frost protection. | China | 5 790 |
| Bork R704 | Number of modes – 3. Power, kW – 1.0. Heating area, m2 – up to 20. Control – electronic. Thermostat - yes. Weight, kg – 5.6. Functions: * touch screen; * automatic maintaining heat; * shutdown when overturning; * protection from children; * overheat protection; * remote control. | China | 12 890 |
Comparison of tabular data shows a slight increase in the cost of convectors. This is due to the increasing degree of automation and the presence of a large number of useful functions.
The final assessment of whether convectors or heating radiators is better will be made by comparing the operating and maintenance features of the devices.
Which heating devices are better?
- Technical characteristics of radiators
- Oil radiators for heating
- Technical features of convectors
- How are convectors used?
- Which is better to choose?
When it comes to heating a home, the first question that arises is which device to choose. According to the principle of operation, all heating devices are divided into two large categories: convectors and radiators.

According to the principle of operation, heating devices are divided into convectors and radiators. To choose the device that is suitable for you, you need to familiarize yourself with their characteristics.
Therefore, when it comes to the question of what is better to choose for heating a house, a radiator or a convector, the first thing you need to do is carefully study all the available advantages and disadvantages of such heating devices, and then make a decision. In order to install such devices, you must have the following tools:
The principle of operation of convectors is based on the fact that they heat a room through a flow of air, which heats up when it passes through the body of the heating device. Radiators heat the room by radiating heat from the surface body.
Features of operation of radiators and convectors
Each of the types of installations under consideration has individual characteristics. Comfortable operation of devices is determined by the number of useful functions.
Radiators
These heaters provide quick heating of rooms. The automatic regulator ensures stable temperature in the room. The coolants used have high thermal conductivity.
For ease of movement, many devices are equipped with wheels. Transfer to another location using the built-in handle. To protect against tipping, side stops are used. A wall-mounted heated towel rail is used to dry small items. On the end side of the control unit there is space for the power cable.
Convectors
The devices have a convenient control system. The main element of this system is a mechanical or electronic thermostat.
The mechanical thermostat is easy to use. Manually operated units have low cost. The main disadvantages are noisy operation and low accuracy of temperature setting. The adjustment step of the mechanical thermostat does not exceed 5 ᵒC.
An electronic thermostat allows you to set the temperature with an accuracy of 0.1 ᵒC. Such devices have several operating modes. It is possible to change settings and program operating modes. Quiet operation allows the use of electrical appliances in bedrooms.
A large number of useful functions in the question of what is better for an apartment - a convector or a radiator - make the difference in favor of devices of the first type. These devices have the following convenient features:
- frost protection;
- Keypad lock;
- economy mode;
- remote control;
- Internet connection.
The “Freeze Protection” function allows you to autonomously maintain the indoor temperature at a level of +5 ᵒС…+7 ᵒС. Used in country houses and in houses without central heating.
Water convectors
Convector heating equipment can operate not only by consuming electricity, but also by using coolant moving through the heating system. Water is heated by different boilers - gas, electric, solid fuel, liquid or universal.
The water convector heating radiator has a simple internal structure, so there are no problems associated with operation. This device is capable of quickly heating rooms.
Powerful heat exchangers are installed in such convectors. Consumers can choose models with exchangers made of steel or non-ferrous metals.
The latest modifications of converter heating batteries, produced using aluminum and copper, are more expensive equipment, but they have an important advantage - resistance to external and internal corrosion processes. The coolant moves through copper pipes, and the air is heated due to the presence of aluminum fins.
Water convector heating batteries are produced in the following standard solutions:
- wall-mounted - in this case, the devices are placed on the walls, usually under window blocks;
- floor - installation is carried out under panoramic windows or openings with low window sills that do not reach the floor;
- built-in - the equipment is installed in niches inside the walls; this type of convectors is purchased if they want to make the heating system invisible;
- in-floor - such devices best prevent the formation of condensation on a panoramic window.
Safety first
The types of devices being compared are classified as high-risk heating devices. The devices are equipped with built-in overheating protection. When the maximum temperature is reached, the device automatically turns off.
Electrical devices have an increased risk of electric shock. To prevent injury, it is necessary to strictly comply with fire and electrical safety requirements.
Some models are used in rooms with high humidity. To protect against damage, the devices have a high degree of sealing.
Baseboard heating with compact radiators
Low and compact heating devices are placed along the baseboard around the perimeter of the room. This system has an interesting feature - it uses the property of warm air that rises along a vertical surface to not form intense convection. The flow “sticks” to the wall, heats it, and then due to radiation and slight mixing of the air, the room is heated.
The effectiveness of this solution is achieved only if the heat transfer is correctly calculated: if the length of the plinth elements exceeds 15 m, then it is necessary to install a distribution manifold so that the coolant does not cool down at the far end of the radiator. The big advantage of the system is the ability to maintain the temperature within 40-50 ° C for good heating, since the area of the heat source is large. A noticeable drawback is the impossibility of installing furniture along the walls, since heat transfer will be sharply reduced. The price of a baseboard heating radiator is higher than the cost of traditional products. Maintenance of the system is not difficult; installation is possible without recessing it into the walls. Mainly used in public buildings with open baseboards.










