Formula for calculating hood power
For the calculation, parameters such as kitchen area, ceiling height, and a coefficient of 12 are used. According to sanitary standards, this is how many times per hour the air in the kitchen should be renewed. As a result, the formula for calculating the hood power looks like this:
Q = S (room area) × H (room height) × 12
Example: for a kitchen with an area of about 10 m² and a ceiling height of about 2.5 m, you will need a hood with a capacity of approximately 390-400 m³/h. Does the apartment have high 3-meter ceilings? With an area of 10 m², in this case you will need equipment with a capacity of about 470 m³/h.
The procedure for calculating the exhaust hood
To calculate the required hood performance, you need to know the parameters of the stove.
In the calculation given below as an example, the characteristics of a gas stove from the Slovenian manufacturer Gorenje (model GI633E35WKB) were used. Please note that the brand and model of the stove were chosen arbitrarily.
You may also find useful information on how to hang a hood over a gas stove, discussed in our other article.

The hood is not capable of performing any 10-fold change of air in the kitchen. To calculate its power, you need to know the heat output and dimensions of the stove
The calculations made below were carried out according to the methodology of RNP "ABOK" 7.3-2007 . Despite the “industrial” purpose of this method (ventilation of hot catering shops), its formulas can be used to calculate the parameters of a domestic kitchen hood.
When cooking food, the stove generates heat that needs to be recovered (exhausted). The heat generated by the stove creates convection air currents above it, which simplifies the operation of the exhaust hood. But it is impossible to completely eliminate air pollution arising above the stove by relying only on convection.
Stage #1 - calculation of total thermal power
Volatile particles generated during cooking are delivered to the hood or panel by convection air flow. It is the heat developed by the burners that provides the volumes of air for elimination. Therefore, it is necessary to calculate their total thermal power.
To determine it, the formula is used:
QT=q1+q2+q3+q4,
Here q is the rated thermal power of one burner, kW.
The model of kitchen stove under consideration has four gas burners on the surface; their thermal powers must be summed up.
We consider: QT=1.9+1.9+1.0+3.5=8.3 kW . The resulting heat output value is valid when cooking on all burners simultaneously, which is rare.
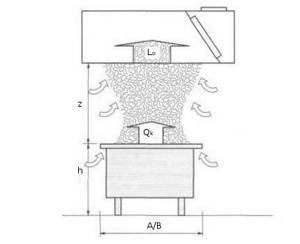
The power of a kitchen hood directly depends on the thermal parameters of the stove. It is the burners that form the convection flow that requires exhaust hood. Legend: Lo – air flow, A/B – width and depth of the slab, h – height of the slab, Z – height from the slab to the hood, Qk – total thermal power of the convective flow
In principle, it is possible to take into account the heat emission of only three burners with the highest heat output. But let's leave it like that, just in case.
To calculate the hood power, it is necessary to determine the air flow ( Lo ) based on the parameters of the kitchen stove. However, the air flow formula requires calculating intermediate parameters - the hydraulic diameter of the plate surface ( D ), air flow in the convective flow ( Lki ) and volume flow of combustion products ( Lri ).
Also in the calculation process, coefficients developed by specialists of NP "ABOC" are used. The coefficient values were selected according to parameters suitable for household stoves.
Stage #2 - calculation of hydraulic diameter and flow
Let's start calculating the hydraulic diameter and convective air flow. The first parameter is determined by the formula:
D=2*A*B/(A+B),
Where:
- A – width of the kitchen stove, m;
- B – kitchen stove length, m.
We substitute the width and length of the gas stove model selected for the approximate calculation: D=2*0.6*0.6/(0.6+0.6)=0.6 m .

Among other things, the choice of hood power is related to the upcoming location of the device. The more free space around the umbrella, the more powerful the hood should be. For a device located in a corner, a correction factor of 0.8 is entered, for an “island” system 1.1
To determine the volume of convective flow, it is necessary to first find out the share of convective heat release of our slab. It is calculated using the formula:
Qk=QT*KЯ*KK,
Where:
- QT – plate power defined above, kW;
- KYa is the fraction of sensible heat released from the thermal power of kitchen equipment. For a domestic stove, the value taken is 250 W/kW;
- KK is the fraction of convective heat release in relation to the sensible heat release of kitchen equipment. The accepted value is 0.5.
We substitute the numerical data into the formula, counting: Qk=8.3*250*0.5=1037.5 W. Let's move on and start calculating the convective air flow.
The formula is as follows:
Lki=k*Qk1/3*(z+1.7*D)5/3*r,
Where:
- k – coefficient obtained experimentally by specialists of NP “ABOC”. It is taken equal to 5·10-3;
- Qk – the share of convective heat release of the slab calculated above, W;
- z – distance from the surface of the stove to the exhaust hood, m. The minimum vertical distance of the hood from the gas stove is 0.75 m;
- D – hydraulic diameter of the tile surface, m. The formula for its calculation and an example of calculation are presented above;
- r is a correction factor, the value of which depends on the conditions of placement of the hood (see the table image above). In our example, the position of the exhaust hood “next to the wall” will be selected, with a coefficient value of 0.75 (due to the conditional “proximity” of cabinet furniture next door, which is usually for kitchens).
We determine the convective flow rate by substituting numerical data into the formula:
Lki=5·10-3*1037.51/3*(0.75+1.7*0.6)5/3*0.75= 0.061 m3/s
As the calculation results show, the air flow as a result of convection over the stove is quite intense. Taking these data into account, you will be able to choose the right power of the exhaust unit.
Stage #3 - calculating the power of the exhaust hood
An electric stove does not emit combustion products during cooking, because The burners are heated without open combustion - thanks to the heaters. But gas burners produce combustion products and the hood will have to remove them.
Formula for calculating volumetric flow rate for methane combustion products:
Lri=3.75*10-7*QT,
Here QT is the installed power of the kitchen stove, kW. This parameter was previously found by us.
We enter its data into the formula and get: Lri=3.75*10-7*8.3= 3.1125*10-6 .
It is clear from the example that the volumetric flow rate of combustion products of a household gas stove is small. Therefore, when determining the parameters of a kitchen hood, it is permissible to neglect them.
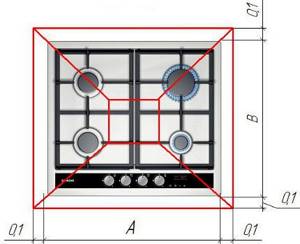
The edges of the hood should extend slightly beyond the boundaries of the slab. A is the width of the hood, B is the depth of the hood. An overhang of 100 mm is enough to prevent the convective flow from the stove from mixing with the atmosphere of the house
So, it’s time to calculate the air flow for our stove. This is the determining parameter when choosing a hood.
The formula for calculating it:
Lo=Lki+Lri,
Where:
- Lki – value of air flow from the convective flow rising above the slab, m3/s;
- Lri – data on the volumetric flow rate of natural gas combustion products in the stove burners, m3/s.
All that remains is to enter the data and calculate the required air flow, rounding the result to three decimal places: Lo=0.061+3.1125*10-6=0.061 m3/s . We found the air flow in cubic meters per second, but to select the model of the exhaust hood we need cubic meters per hour (L).
To convert m3/s to m3/h, multiply the resulting air flow (Lo) by the number of seconds in one hour and by the hydraulic diameter of the plate (D)/L=0.061*3600*0.6=131.76 m3/h .
Thus, the sufficient maximum power of the exhaust hood for the Gorenje gas stove model shown in the example, with rounding “in reserve”, will be 150 m3/h. Greater power is simply not needed - a waste of electricity.
What else is important to consider when choosing
The device cannot constantly operate at its limit. This will mean its rapid wear. Therefore, the calculation result should be increased by another 15-20%. This “gap” will allow the device not to be damaged by maximum load. It is better to choose a hood with several power levels. The operation of the last most powerful stage should be limited in time - like with Miele hoods. Their most intensive mode lasts no more than 10 minutes. After which the technique automatically moves to a lower level.
There are other factors due to which the number will have to be recalculated again. One of them is the type of hob.
If you have a gas hob, gas combustion products will be released into the air. In this case, instead of 12, you should substitute the number 20 into the formula for calculating the hood power - the equipment should work harder. If the kitchen has an electric stove, then this will not be necessary. When working with such burners, only cooking fumes are released into the air. The coefficient can be left the same or slightly increased if you cook often or if you have a large stove.
The frequency of cooking and their volume also matter. When the apartment has a spacious kitchen, but most often one burner is occupied on the stove, there will be no point in a powerful hood. A productive hood is needed by those who cook in large quantities every day.
Another important point is the noise level. Obviously, more powerful kitchen hoods make more noise. However, their noise level should not exceed 50 dB, otherwise the operation of the device will interfere with the residents of the apartment/house. In some models this point is thought out. Miele offers devices with noise reduction. It involves sound insulation for the motor, chimney and fireplace hood.
Hood dimensions as an indicator of performance
When calculating the power of a kitchen hood, it is logical to assume that the larger the exhaust surface of the device, the greater the volume of air it can pass during operation. Accordingly, small (built-in or folding) hood models have low performance indicators, while large dome hoods have the highest performance.

This is the only external factor by which you can “determine” the power of the device by eye. However, today this approach cannot be called correct. Modern hoods can be highly efficient even with a compact design. An example of this is T-shaped and inclined hoods, which, in the absence of an impressive dome, do an excellent job of ventilating even spacious rooms.
What is the difference between a hood and ventilation?
The ventilation system is a network of channels built into the walls with an exit to the outside of the building for exhaust air exhaust from the room. The influx of fresh air occurs naturally through door and window openings.
According to sanitary standards, this air exchange system must be installed in all residential premises. But it is not very effective and, even more so, is not able to localize and remove odors, fumes, soot and other “delights” of everyday life. To prevent them, forced ventilation is installed - an exhaust hood. It collects all the vapors from the hob and directs them through the air duct to the ventilation system.
How does a kitchen hood work?
The hood design of any model is not particularly complicated. Its working panel hides a grease filter, which is responsible for rough air purification. The mesh of the filter cartridge traps airborne fat particles. This component is required for any type of exhaust devices. It prevents grease from settling on the internal parts of the mechanism, thereby extending the service life of the device.
Immediately behind the filters there are fans that remove contaminated air through the air duct into the ventilation duct. The fans are connected to motors designed specifically for use in hoods. To make the operation of the device quieter, manufacturers are trying to introduce various innovations, from coating the blades with Teflon to insulating the motor in an individual housing. Sometimes two turbines are installed, operating at lower power and, accordingly, quieter.
Exhaust device
According to the principle of operation, they are all similar to a vacuum cleaner, but with different functions. Modern exhaust devices come in different designs, depending on their purpose - some only remove polluted air, while others filter it and return it back already purified. According to the cleaning method, they are divided into flow-through, recirculation and combined, which combine both options.
- Flow hoods are equipped with metal or plastic pipes (round, square, corrugated) for connection to the ventilation system, which can be rigid or flexible. The lower parts of the device consist of filters (grease traps) that trap soot and grease. They are hidden behind decorative panels. Fans and special motors are located inside. Behind them there is an air duct connected to ventilation.
- Recirculation units operate autonomously, without connection to ventilation, and therefore do not have pipes, which is why they look more aesthetically pleasing. Inside their cases, after the fans, there are replaceable, very thin carbon filters. For rough cleaning, the filters are made of durable aluminum and can be simply washed with detergents. Externally, the principle of the housing structure is the same as that of flow-through ones.
The exhaust system operates from the electrical network. Everything is very simple - plug it in, press the button with the selected mode (indicated by numbers 1-3), the engine picks up speed. The most convenient hoods to connect are those with touch screens or remote control (using a remote control or voice commands).
Regulatory requirements
Existing sanitary standards determine the requirements for kitchen exhaust devices without linking them to specific models. At the same time, they proceed from the fact that they are not intended to organize ventilation of the room, but serve solely to remove contaminated air from the stove. The ceiling area is also inaccessible to them, which forces them to choose a model that can only serve the space above the hob, for example, or above a regular gas stove.
The performance of hoods is linked to sanitation requirements as follows:
- An indicator of effective operation is considered to be a mode when the air in the kitchen is renewed at least 10 times in one hour.
- The average indicator for various rooms used in calculations is selected from the range of 10-15 times.
- For standard kitchens it is taken equal to 12 units.
If the owners constantly smoke in this place, the required performance of the unit increases by 15-30 percent.
How to calculate the power of a kitchen hood
Content
- Why do you need power calculation?
- Factors affecting power calculation
- Slab type
- Kitchen location
- Recommended power
- Power calculation
- What to pay attention to
- Hood type
- Noise level
- Finally
Properly calculated hood power plays a significant role when purchasing a device. Specific odors during cooking and frying food, fumes, burning, smoke - all this is removed using this device. However, this is only possible when its performance matches the required characteristics.
In order not to purchase just an elegant kitchen accessory instead of a working apparatus, before going to the store you need to calculate the power of the hood. And to correctly calculate the formula, you need to understand the design and operating principle of the exhaust device. All the necessary information can be found in this article.
Kitchen hood power
Now let's talk a little about the power of a kitchen hood. We have already talked about what this is above. We will talk specifically about the amount of energy consumed, which is measured in kilowatts.
As already mentioned, the power of the hood motor does not always have a significant impact on the performance of the device. Based on this indicator, it is first of all worth assessing energy consumption: the lower the power, the less electricity the device will consume. It should also be taken into account that overly powerful motors produce quite a lot of noise.
Why do you need power calculation?
The performance of the engine will determine how much exhaust air the hood can replace in an hour, and it is measured in cubic meters. The main task of this device is to eliminate specific odors in the kitchen, as well as timely removal of fat, soot, and fumes that are inevitably present when cooking and frying food.
How to calculate a kitchen hood so that the performance complies with the conditions of SNiP. Having selected and installed a hood of the required power, the costs for it will be compensated over time by saving detergents.
Recommended power
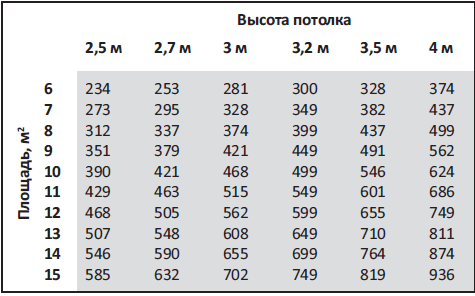
The greater the power of the kitchen hood, the sooner the air above the stove in the kitchen is cleaned. Productivity can be quickly calculated using the table below.
Exhaust device performance
In small kitchens it is allowed to install low-power exhaust devices with a capacity of 200-300 m³/h. The price of these devices is relatively small and they perform their task under certain conditions: cooking occurs no more than two or three times a day and in small volumes. For more frequent cooking, it is better to use a classic hood with a power of 600 m³/h.
On a note! The productivity of the device is indicated in m³/h. Sometimes it is called power. However, this value cannot be used as power consumption, which is defined in watts (W).
Productivity must comply with SNiP standards. During an hour of operation, air is replaced approximately 10-12 times. For calculations, as a rule, they take the number 12. If household members often smoke in the kitchen, then the productivity of the unit increases by 20-30%.
Additional functions
Modern household appliances are equipped with many auxiliary functions. When choosing a hood, you should pay attention to the ease of use.
- Touch control panels increase the cost, but are preferable to slider ones, as they are less susceptible to contamination and look more aesthetically pleasing.

- All models have a lighting function. It is better if the hood is equipped with halogen lamps. They have a more pleasant light and less color distortion than incandescent or fluorescent lamps.

By carefully calculating the required power of a kitchen hood and carefully choosing its model, you can guarantee not only comfortable conditions in the food preparation area, but also a long service life of the purchased equipment.
Power calculation
As is already known, to quickly calculate the performance of the device, use the following formula:
P – calculated power value;
S – area of the room;
H – ceiling height;
12 – replacement of air mass in the kitchen according to SNiP.
This formulation is suitable for relatively small volumes of air in the room, up to 40 m³. It is used to determine the lowest extraction power. In practice, this value may vary, as it is influenced by other aspects: the type of hob and air circulation, the composition of the family and the location of the kitchen.
For a clear example, let’s give a calculation of the performance of a hood for a kitchen measuring 12 m2.
Kitchen hood performance and features of its calculation
Choosing a hood for the kitchen should begin with determining the technical characteristics of the device you like. Many users do not study this issue well enough, paying attention only to the dimensions and design of the device. As a result, they acquire a device that is too weak, which cannot cope with the air masses in the room, or, on the contrary, it is too powerful, creating noise and consuming a lot of electricity. To avoid these problems, you need to know how to calculate the hood in accordance with the dimensions and features of the kitchen.

Among the technical characteristics, special attention should be paid to the power and performance of the device. These indicators reflect the volume of air masses that the hood passes through itself over a certain time, as well as the energy spent on this process. If you correctly calculate the volume of air in the room and take into account additional factors, you can accurately determine how much time the appliance needs to fully ventilate the kitchen. This will allow you not to make a mistake when choosing an exhaust device and subsequently use it as efficiently and economically as possible. In this material we will tell you how to calculate the power of a kitchen hood so that it successfully copes with the ventilation of the room.
What to pay attention to
When selecting a device, first of all, you need to find out whether there is a possibility of connection to exhaust ventilation. If the room has this throughput channel, it’s very good. If there is no possibility of connection, you will have to purchase a hood with special filters built into the device.
Hood type
Devices are divided according to the principle of operation, and more specifically, according to the method of removing air flow from the hob.
There are two types of exhaust devices:
- flow-through;
- recirculating
- The first type of device is designed to connect it to a ventilation duct and discharge exhaust air outside. Moreover, such hoods can be combined. They can remove the air flow to the street, or they can immediately return it back, after passing it through filters.
Such modes are chosen at the will of the owner; generally, the second option is convenient to use in winter, so as not to cool the kitchen with the flow of cold air during replacement. Before connecting the hood, you need to check the draft in the channel; to do this, just bring the flame of a candle or match to the hole and make sure whether it deviates towards the channel.
If the draft in the well is weak, then you need to clean it first, otherwise the hood will not fully cope with its task. Another option is to move a separate ventilation duct outside with further insulation.
- The second type, recirculation, is equipped with a filter system, and such devices do not need to be connected to the ventilation duct. In these hoods, the purification of the air mass takes place in two stages. First, mesh filter elements remove particles of fat, burning, and scale.
Then the air mass undergoes a second cleaning through activated carbon, after which all unpleasant odors disappear and then the air returns back to the kitchen. During operation of the unit, filters provide resistance to air circulation, and this must also be taken into account when calculating performance. It is recommended to increase the indicator for such units by approximately 20-30%.
Noise level
When purchasing a hood for your kitchen, you need to pay attention to its noise level, since the sounds produced by different household appliances can cause your discomfort. How to find out the noise level from the installed device? This indicator is indicated in the instructions from the manufacturer. Modern hoods have a noise value from 30 to 70 dB.
An acceptable indicator according to SNiP is considered to be a level from 30 to 45 dB. If the digital value of the hood is higher, its operation will be loud. The more massive the walls of the exhaust device body, the quieter it will work, since all sounds will be absorbed inside the device.
Sometimes manufacturers soundproof the outside of the unit using various sound-absorbing materials. And also in some models, instead of one, two fans with lower power are built-in, which significantly affects the overall noise level towards a decrease.
As a result of such design changes, modern hoods have the lowest noise levels.
When choosing a quiet appliance for the kitchen, experts recommend paying attention to the following aspects:
- Performance. The more powerful the device, the more efficiently it will move the air. Therefore, it will create more noise when operating this way. Therefore, you should not purchase a hood with a power exceeding that calculated for a given room.
- Number of operating modes. Choose a kitchen hood with several modes. This way you can reduce noise by setting the process to a minimum value. When choosing, you do not need to buy a model with a noise level greater than 45 dB.
- Noise level value. Periodically clean the first stage filters and promptly change the second stage carbon filter elements, since when they are dirty they also significantly increase the noise level.
Noise level at different device performance
When a large volume of air passes through the exhaust ducts, a sound naturally arises, which increases when the motor operates with high power. In residential areas, noise can interfere with the comfort of the kitchen and even penetrate into other rooms. Therefore, it is very important to choose a hood of such power that the noise level during its operation does not exceed permissible limits.
Small hoods with low power have the lowest noise levels - their values do not exceed 40–45 decibels. This is a fairly comfortable level for constant operation of the device in automatic mode. However, when choosing such a model, you will have to sacrifice the efficiency of its operation.
Kitchen hoods with high power have high noise levels and can create discomfort when working in small spaces. Experts recommend turning these devices “on full” only in emergencies; for daily use, set the settings to average. Then the hood will not make loud sounds during operation.