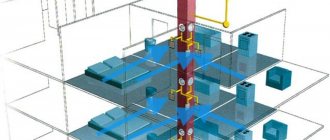
The kitchen space must be equipped with a high-quality ventilation system in order to ventilate the room in a timely manner. Exhaust pipes differ in the material of manufacture and methods of installation of the system. In our article we will look at different installation options and show clear examples in completed projects.
Using a hood in the kitchen, you will be able to remove unpleasant odors during the cooking process and normalize the air temperature in the room.
The minimum concentration of fats in the air will allow you to do cosmetic repairs at home much less frequently.
Plastic air duct
Advantages:
- The plastic box conceals noise when the hood is operating (this effect is especially important for small apartments);
- The surface does not accumulate dirt inside. Such ventilation systems are characterized by good throughput due to smooth walls.
Plastic pipes can be round or rectangular.

Additionally, you should purchase special adapters:
- L-shaped (at least three);
- adapter connecting the ventilation duct to the hood.
To ensure the tightness of the system, a special agent is used to treat the joints between the elements.
Use of ventilation pipes in everyday life
Residential buildings must have ventilation. In the process of breathing, a person emits carbon dioxide and moisture, cooking - moisture, soot, fat, carbon dioxide, sanitary appliances - a lot of moisture. Moisture settles on walls and furniture, which leads to the formation of mold. Carbon dioxide and combustion products, odors from cooking lead to rapid fatigue, irritation of the respiratory tract, deterioration of well-being, and decreased performance. Some of the substances formed during frying are carcinogens.
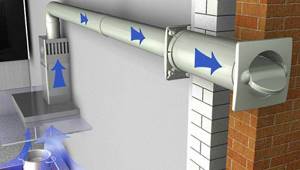
In old Soviet-built houses with small apartments and loose doors, ventilation in the kitchen and bathroom simultaneously removed some of the air from the living rooms. Ventilation ducts were built into the building structure. In private houses, ventilation was not provided at all - the situation with carbon dioxide was saved by a stove with a chimney: the air for firing the stove was taken from the house and removed, along with the products of fuel combustion, outside the living space. Fresh air entered houses and apartments through leaks in wooden windows and doors. The smoke and soot simply settled on the walls and ceiling - they had to be whitewashed every year.
In modern houses, in addition to the hood, additional ventilation systems are often installed - exhaust and supply and exhaust. In passive and energy-efficient houses, supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery is a mandatory component of the house design.
Corrugation
This type of air duct is installed when it is difficult to create a duct with several elbows in a room. Plastic and aluminum are used for manufacturing. Steel corrugations can withstand high temperatures, but the cost of such pipes is much higher than their analogues.
Advantages:
- Choosing corrugation will allow you to save on kitchen furnishings;
- Easy installation;
- No additional adapters needed.
To correctly measure the length of the corrugation, you need to stretch it, getting rid of folds.
To install a corrugated pipe, you will need grids with fittings and clamps.

Tips for choosing
When choosing a pipe type, they are guided primarily by aesthetic considerations. Before making a choice, it is determined whether the box will be mounted openly or covered with furniture, a box, a false wall, or a suspended ceiling.
Corrugated shiny pipes spoil the kitchen interior; more often, when laying air ducts openly, smooth plastic pipes are chosen - they are easy to clean and can be painted in the desired colors - white or colored to match the ceiling or walls. Rectangular and square boxes fit better into the interior; round plastic boxes have minimal resistance to air flow.
When laying hidden, corrugated pipes are chosen - they are easier to install, no adapters or corners are needed, they are easier to bend when avoiding obstacles and for turning. Masking metal pipes will require additional costs. If problems arise, it will be difficult to get to the hidden pipe.
Diameter and shape
The diameter of the round pipe should be equal to the diameter of the outlet pipe of the kitchen hood.
Round boxes provide minimal resistance to air movement.
The ideal shape for an air duct is straight. Sharp corners when installing air ducts are unacceptable.

Dimensions and cross-section
The cross-section of a square or rectangular pipe must be equal in area to the cross-section of the round hood pipe. Narrowing the cross-section will lead to deterioration in system performance, fan overload, increased noise, vibration and loosening of fasteners. It is better to take a pipe with a slightly larger cross-sectional area. A large excess of the cross-section will lead to increased costs and difficulties with masking the pipe.
A slight narrowing of the cross-section is permissible only if the fan power is taken “with a reserve” and the hood is rarely turned on at maximum power.
The optimal length of the air duct is no more than 3 meters. If the duct length is longer, the fan power must be increased.
Diameters of corrugated pipes used in domestic ventilation: 100 mm, 125 mm, 150 mm.
Dimensions of plastic boxes: 8080 mm, 100100 mm, 125125 mm, 55110 mm, 50120 mm, 60204 mm, 90220 mm.
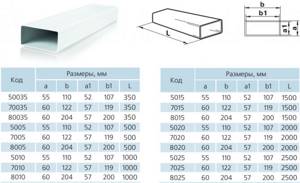
Diameters of plastic pipes: 100 mm, 125 mm, 150 mm, 200 mm.
Calculation of the minimum required size
Calculation of the cross-section of the hood duct is not necessary. The cross-section should be equal to the cross-section of the hood outlet pipe. If the hood was purchased with a power reserve and it is not planned to turn it on at maximum power, then the cross-section can be narrowed.
The minimum cross section is calculated using the formula:
Smin=Srab *(QrabQmax), where
- Smin is the minimum possible cross section.
- Srab is the nameplate section of the exhaust pipe.
- Qwork is the required volume of air removed.
- Qmax - maximum volume of air removed (according to the hood's passport).
- Qwork is calculated using the formula:
- Qwork = kitchen volume x 12 times x 1.3 per m³.
In accordance with sanitary standards, 12 is the air exchange coefficient (the air in the kitchen should be changed 12 times per hour), 1.3 is the power loss coefficient in the air duct and ventilation shaft.
Selecting the diameter
The main rule when determining the diameter or cross-sectional dimensions for a pipe is an exact match with the opening of the hood itself. This condition directly affects the efficiency of the ventilation system.
Let's look at different sections:
1. Round . The size increment is 1 cm. The minimum diameter is 8 cm, the maximum is 30 cm. The most commonly used sections are: 18, 20, 24 cm.
2. Rectangular. Basically, this cross-section involves the use of a low-power hood.
Size range:
• 5x10 cm; • 8x15 cm; • 15x20 cm (rarely used in practice).
An adapter is often required for installation, because Almost all hoods have a round hole.
Preparing for installation
Before installation, all dimensions must be checked. The diameter of the duct must be exactly the same as the diameter of the hole in the hood. If the diameter of the duct is smaller, then due to resistance, the retraction force will be weak.
In addition, during installation you need to pay attention to the bending angles of the air duct. To prevent high resistance, each duct bend angle should not be more than 90 degrees.
To avoid reverse draft from the ventilation shaft to the kitchen utensils, it is necessary to install a check valve. We proceed directly to the installation of the ventilation pipe.
Air duct masking
Installation above upper cabinets
This option is ideal for those sets in which the hood is located as close as possible to the ventilation hole.

A plastic rectangular box is located above the upper modules and is visually almost invisible due to the height of the headset.

To hide the pipe, you can also use a decorative box after the repair work is completed. Case color may vary. This design is suitable for integrating spotlights.
Inside modules
The built-in model is the most aesthetic option. The hood occupies the interior space of the cabinet and is pulled out only during use.

Installation above ceiling level
The entire ventilation system is hidden under the suspended ceiling. In this case, the pipe is hidden completely, regardless of the layout of the modules.

Closed facades completely hide the equipment.

Routing of the box before installation of the gypsum board ceiling.

A two-level ceiling that helps disguise the communications of the exhaust system.

Why ventilation and exhaust are different things
According to sanitary standards, living quarters are equipped with ventilation. The entrance is located in the non-residential part, where most of the factors unfavorable for humans are formed. People use kitchen equipment, wash, bathe, smoke, use the toilet. The processes generate an abundance of moisture and odor; ventilation is designed to remove unnecessary things. When the subsystem of a living space is faulty, the laundry dries in the bathroom for 2-3 days, the ceiling and walls become covered with condensation. Over time, the problem causes the growth of fungus, mold - a separate matter. Smoke, the smoke will spread throughout the premises. This is what malfunctioning ventilation leads to.
Most people are familiar with the problem of upper floors. There are three ways to bring the ventilation duct outside:
- The channel penetrates the floors, goes, bypassing the attic, to the roof in the form of a pipe covered from above.
- In the attic, the channels are combined into boxes and go out together.
- The air is exhausted into the attic, from where it enters the street.
With the first method there are no problems. To ensure that air exits the apartment to the street, it must travel 2 meters through the pipe; the height of the attic space is that much. However, a reliable method is unsuitable for high-rise buildings; unfortunately, new developments suffer from the problem of upper floors.
When air comes out of a vertical shaft, it hits the roof of the attic or box. A traffic jam is created. The air continues to press and seek exits. One is a pipe going outside, the other is a ventilation hole in the kitchen of the residents of the top floor. The two meters mentioned above are not gained for the thickness of the ceiling. All year round people are harassed by reverse thrust. We will breathe what air we have collected from the other floors.
There is no simple solution to the problem:
- Firstly, you can increase the height of the box against which the air flow hits. And two or three times. But this is done by the construction team in agreement with government agencies.
- Secondly, you can separate the upper floor ventilation duct from the rest. It is fraught with construction work and will require thermal and hydro insulation of a new passage.
You see how many problems and nuances a working ventilation network has. Refining the duct with kitchen hood air ducts will also add complexity. Remember the video we discussed. If it happened on the top floor, the kitchen stove will collect odors from the lower floors and ventilation will be disrupted.
If the upper floor has a separate exit, the height should be increased so that the length becomes 2 meters.