Features of calculations
Calculating the power of a heating radiator is associated with a number of problems. The fact is that during the heating season the temperature outside the window is constantly changing, and accordingly the heat loss differs. So at 30 degrees below zero and a strong north wind, they will be much greater than at -5 degrees, and even in calm weather.
Many property owners are concerned that incorrectly calculated thermal power of heating radiators can lead to the fact that in frosty weather the house will be cold, and in warm weather they will have to keep the windows wide open all day and thus heat the street (for more details: “Calculating the power of heating radiators - how calculate it yourself").
However, there is a concept called a temperature graph.
Due to this, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system changes depending on the weather outside. As the outside air temperature rises, the heat transfer of each battery section increases. And if so, then with respect to any heating equipment we can talk about the average value of heat transfer. As for residents of private households, after installing a modern electric or gas heating unit or heating using heat pumps, they do not have to worry about the temperature of the coolant circulating in the circuit of the heating structure.
Thermal equipment created using the latest technologies allows you to control it using thermostats and adjust the power of the batteries according to needs. Having a modern boiler does not require control over the coolant temperature, but to install heating radiators, power calculations will still be required.
Glazing, window area and orientation
Windows can account for 10% to 35% of heat loss. The specific indicator depends on three factors: the nature of the glazing (coefficient A), the area of the windows (B) and their orientation (C).
Dependence of the coefficient on the type of glazing:
- triple glass or argon in a double package – 0.85;
- double glass – 1;
- single glass – 1.27.
The amount of heat loss directly depends on the area of window structures. Coefficient B is calculated based on the ratio of the total area of window structures to the area of the heated room:
- if windows make up 10% or less of the total area of the room, B = 0.8;
- 10-20% – 0,9;
- 20-30% – 1;
- 30-40% – 1,1;
- 40-50% – 1,2.
And the third factor is the orientation of the windows: heat losses in a room facing south are always lower than in a room facing north. Based on this, we have two coefficients C:
- windows in the north or west - 1.1;
- windows on the south or east side - 1.
Required thermal power of the radiator
When calculating a heating battery, you definitely need to know the required thermal power to make it comfortable to live in the house. How to calculate the power of a heating radiator or other heating devices for heating an apartment or house is of interest to many consumers.
- The method according to SNiP assumes that 100 watts are required per “square” of area. But in this case, a number of nuances should be taken into account:
- heat loss depends on the quality of thermal insulation. For example, to heat an energy-efficient house equipped with a heat recovery system with walls made of sip panels, the thermal power required will be less than 2 times; - the creators of sanitary norms and rules, when developing them, were guided by a standard ceiling height of 2.5-2.7 meters, but this parameter can be equal to 3 or 3.5 meters; - this option, which allows you to calculate the power of a heating radiator and heat transfer, is only correct subject to an approximate temperature of 20°C in the apartment and 20°C outside. A similar picture is typical for settlements located in the European part of Russia. If the house is located in Yakutia, much more heat will be required. - The calculation method based on volume is not considered complicated. For each cubic meter of room, 40 watts of thermal power is required. If the room dimensions are 3x5 meters and the ceiling height is 3 meters, then 3x5x3x40 = 1800 watts of heat will be required. And although the errors associated with the height of the premises have been eliminated in this calculation option, it is still not accurate.
- A refined method of calculation by volume, taking into account a larger number of variables, gives a more realistic result. The basic value remains the same 40 watts per cubic meter of volume.
General information on the calculation results
- Number of radiator sections
- Amount of heat required for heating
- Amount of heat generated by the radiator
- Amount of heat generated by one section
— Calculated number of radiator sections, ensuring the necessary heat flow for sufficient heating of the room at the given parameters.
— General heat loss of the room, taking into account the characteristics of the room and the functioning of the heating system.
— The total heat flow from all sections of the radiator released into the room at a given coolant temperature.
— The actual heat flow emitted by one section of the radiator, taking into account the characteristics of the heating system.
The calculator is working in test mode.
Which radiators have the best heat transfer?
As can be seen from the table below, which compares the heat transfer of heating batteries, bimetallic heating radiators have the highest power. They are a ribbed aluminum body, inside of which there is a durable welded frame made of metal tubes designed for the flow of coolant.
This type of heating equipment is perfect for installation in a private house with an individual system, as well as for a centralized heating system. The main disadvantage of such products is their high cost. However, the best heat transfer of bimetallic heating radiators often allows you to make a choice in their direction.
Ways to increase heat transfer

There are several ways to increase the heat transfer of heating devices:
- Regular wet cleaning to clean the surface of the batteries. The cleaner they are, the higher their level of heat transfer.
- Equally important is the correct painting of the radiator, especially for cast iron appliances. The fact is that multi-layer applied paint prevents effective heat transfer. Before you start painting the heating radiator, you should remove the old layer. No less effective is the use of special enamels intended for pipelines and heating devices, since they have low resistance to heat transfer.
- To ensure maximum power, these devices must be installed correctly.
- Among the main mistakes made during installation, experts note: – tilting the battery; – installing the device too close to the floor or wall; – blocking access to radiators with furnishings and installing inappropriate reflective screens.
- To increase the efficiency of heating batteries, it would not hurt to inspect their internal cavity. Often, in the process of connecting heating radiators to the system, burrs are formed, due to which, during operation, blockages are formed that prevent the free movement of the coolant.
- You can place a heat-reflecting screen made of foil material on the wall behind the heating device.
Comparison by other characteristics
One feature of battery operation – inertia – has already been mentioned above. But in order for the comparison of heating radiators to look objective, in addition to heat transfer, other important parameters should be taken into account:
- working and maximum coolant pressure;
- amount of water held;
- weight.
The operating pressure limitation determines whether the heating device can be installed in multi-storey buildings, where the height of water lifting by network pumps can reach hundreds of meters. The parameter does not matter for private houses, where the pressure in the system is low, maximum 3 Bar.
Comparing the capacity of radiators can give an idea of the total amount of water in the network that will have to be heated. Well, the weight of the product is important when choosing the installation location and method of attaching the battery.
As an example, below is a comparison table of the characteristics of various heating radiators of the same size:
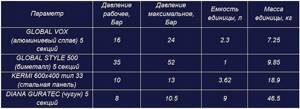
Note. In the table, a heating device consisting of 5 sections is taken as 1 unit, except for the steel one, which is a single panel.
How to choose the right number of sections
The heat output of bimetallic heating devices is indicated in the data sheet. Based on this data, all necessary calculations are made. In cases where the heat transfer value is not indicated in the documents, these data can be viewed on the official websites of the manufacturer or used in the calculations the average value. For each individual room, its own calculation must be carried out.
To calculate the required number of bimetal sections, you need to take into account several factors. The heat transfer parameters of bimetal are slightly higher than those of cast iron (taking into account the same operating conditions. For example, let the coolant temperature be 90 ° C, then the power of one section of bimetal is 200 W, of cast iron - 180 W).
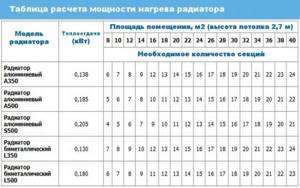
Radiator heating power calculation table
If you are planning to replace a cast-iron radiator with a bimetallic one, then with the same dimensions, the new battery will heat a little better than the old one. And this is good. It is worth considering that over time the heat transfer will be slightly less due to blockages inside the pipes. Batteries become clogged with deposits that appear due to metal contact with water.
Therefore, if you decide to replace it, then calmly take the same number of sections. Sometimes batteries are installed with a small margin in one or two sections. This is done to avoid loss of heat transfer due to clogging. But if you are purchasing batteries for a new room, you cannot do without calculations.
Dependence of the degree of heat transfer on the connection method
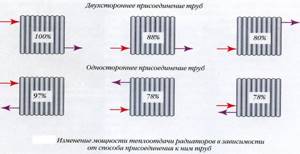
The heat transfer of heating radiators is affected not only by the material of manufacture and the temperature of the coolant circulating through the pipes, but also by the chosen option for connecting the device to the system:
- The connection is direct one way
. It is the most favorable in relation to the thermal power indicator. For this reason, the calculation of the heat transfer of a heating radiator is performed precisely with a direct connection. - Diagonal connection
. It is used if you plan to connect a radiator to the system in which the number of sections exceeds 12. This method allows you to minimize heat loss. - Bottom connection
. It is used when the battery is connected to a floor screed in which the heating system is hidden. As the calculation of the heat transfer of the radiator shows, with such a connection, the loss of thermal energy does not exceed 10%. - Single pipe connection
. The least profitable method in terms of thermal power. Heat transfer losses with a single-pipe connection most often reach 25 - 45%.
Features of connecting radiators

Connecting batteries to the heating system is of great importance only with natural circulation .
In this case, the principle is that all radiators are completely filled with coolant and do not form counter currents. But when using forced circulation, this factor does not matter.
Calculation of steel panel heating radiators. Varieties
Types of steel heating radiators
Let's consider panel-type steel radiators, which vary in size and power level. Devices can consist of one, two or three panels. Another important design element is fins (corrugated metal plates). To achieve certain thermal output values, several combinations of panels and fins are used in the design of the devices. Before choosing the most suitable device for high-quality room heating, you need to familiarize yourself with each type.
Main types of steel radiators
Steel panel batteries are available in the following types:
Type 10. Here the device is equipped with only one panel. Such radiators are light in weight and have the lowest power.
Steel heating radiators type 10
Type 11. Consists of one panel and a fin plate. The batteries are slightly heavier and larger than the previous type, and have higher thermal power parameters.
Steel panel radiator type 11
- Type 21. The radiator has two panels, between which there is a corrugated metal plate.
- Type 22. The battery consists of two panels, as well as two fin plates. The device is similar in size to type 21 radiators, however, compared to them, they have greater thermal power.
Steel panel radiator type 22
Type 33. The design consists of three panels. This class is the most powerful in terms of thermal output and the largest in size. In its design, 3 fin plates are attached to three panels (hence the type number - 33).
Steel panel radiator type 33
Determining the number of radiators for single-pipe systems
There is another very important point: all of the above is true for a two-pipe heating system, when a coolant with the same temperature enters the input of each radiator. A single-pipe system is considered much more complex: there, increasingly colder water flows to each subsequent heating device. And if you want to calculate the number of radiators for a one-pipe system, you need to recalculate the temperature every time, and this is difficult and time-consuming. Which exit? One of the possibilities is to determine the power of the radiators as for a two-pipe system, and then, in proportion to the drop in thermal power, add sections to increase the heat transfer of the battery as a whole.
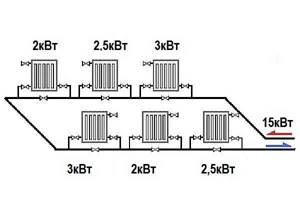
In a single-pipe system, increasingly colder water flows to each radiator
Let's explain with an example. The diagram shows a single-pipe heating system with six radiators. The number of batteries was determined for two-pipe wiring. Now we need to make an adjustment. For the first heating device everything remains the same. The second one receives coolant with a lower temperature. We determine the % drop in power and increase the number of sections by the corresponding value. In the picture it turns out like this: 15kW-3kW=12kW. We find the percentage: the temperature drop is 20%. Accordingly, to compensate, we increase the number of radiators: if 8 pieces were needed, there will be 20% more - 9 or 10 pieces. This is where knowing the room will come in handy: if it’s a bedroom or a children’s room, round up, if it’s a living room or other similar room, round down. You also take into account the location relative to the cardinal directions: in the north you round up, in the south you round down.

In single-pipe systems, it is necessary to add sections to radiators located further along the branch
This method is clearly not ideal: after all, it turns out that the last battery in the branch will have to be simply enormous in size: judging by the diagram, a coolant with a specific heat capacity equal to its power is supplied to its input, and in practice it is unrealistic to remove all 100%. Therefore, usually when determining the power of a boiler for single-pipe systems, they take a certain reserve, install shut-off valves and connect radiators through a bypass so that the heat transfer can be adjusted and thus compensate for the drop in coolant temperature. One thing follows from all this: the number and/or size of radiators in a single-pipe system must be increased, and more and more sections must be installed as you move away from the beginning of the branch.
Increased heat transfer efficiency
When the radiator heats the internal air of the room, intense heating of the external wall in the area behind the radiator also occurs. This leads to additional unjustified heat losses.
To increase the efficiency of heat transfer from the radiator, it is proposed to fence off the heating device from the outer wall with a heat-reflecting screen.
The market offers many modern insulating materials with a heat-reflecting foil surface. The foil protects the warm air heated by the battery from contact with the cold wall and directs it inside the room.
For proper operation, the boundaries of the installed reflector must exceed the dimensions of the radiator and protrude 2-3 cm on each side. The gap between the heating device and the thermal protection surface should be left 3-5 cm.
To make a heat-reflecting screen, we can recommend isospan, penofol, alufom. A rectangle of the required dimensions is cut out of the purchased roll and fixed on the wall at the location where the radiator is installed.
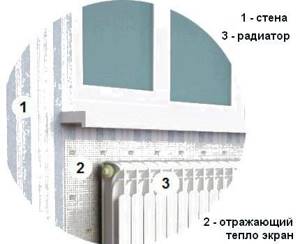
It is best to fix the screen that reflects the heat of the heating device on the wall with silicone glue or liquid nails
It is recommended to separate the insulation sheet from the external wall with a small air gap, for example, using a thin plastic grid.
If the reflector is joined from several parts of insulating material, the joints on the foil side must be sealed with metallized adhesive tape.
This must be taken into account when installing heating devices
The value obtained using the calculator is indicative
In addition, you need to take into account that the characteristics declared by the manufacturer are not always confirmed in practice. This means that it is better to accept 10% more sections for installation, rounding up to the whole part
If you are worried that the room will be too hot in winter, then install a valve on the radiator that regulates the amount of circulating coolant. It will also help save time if it is necessary to replace one of the sections.
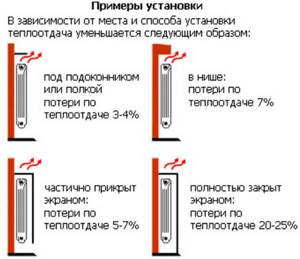
Distances must be strictly maintained within the established limits:
- The width of the assembled window sections must be at least 70%. This means that it is better to install more sections with lower thermal power.
- The distance from the top of the device to the window sill should be within 100-120 mm. Otherwise, it will be much more difficult to predict the magnitude of the heat flow.
- In order not to heat the street, radiators must be at least 50 mm away from the wall.
- A distance of 100 mm must be maintained between the floor plane and the bottom point of the heating device.
We hope that this material will be useful when carrying out repair work or installing a new water heating system.
Brick barbecues do not have to be huge monsters that cost a lot of money to build. They can be compact, neat, and easily fit into the design of any area.
Most importantly, they can be relatively inexpensive. In this article we provide examples of brick barbecues that will easily decorate your summer kitchen
No one is immune from this. The conveniences that we have long been accustomed to when living in urban environments sooner or later show their downside. Does the water not drain away, threateningly filling more than half the volume of the toilet bowl? What to do if it gets clogged? You can call a plumber, or you can solve the problem yourself. Fortunately, there are enough options to solve the problem.
Are you preparing to build an extension to your home? Have you decided to add a second floor? Perhaps the old foundation of the house scares you with an abundance of cracks and uncharacteristic distortion? All this indicates the need to strengthen the foundation. We have tried to summarize data that will be useful in resolving this issue.










