Why is it important to know the cooling power of an air conditioner?
The cooling power (CO) of an air conditioner is the most important technical parameter on which the efficiency of the device in a particular room depends. If the power is not enough, the air conditioner will not be able to create comfortable coolness, and at the same time it will work for wear, which will lead to rapid breakdowns of the equipment.
An air conditioner with more cooling capacity than required for a particular room will create a lot of noise and will not be used to its full potential. This, of course, will not lead to premature breakdowns of the equipment, but it may turn out to be an unwise purchase with overpayment for a high-power device and its installation.
And in order not to overpay extra money and buy a good air conditioner that will create a comfortable temperature in a particular room, you need to correctly calculate the optimal cooling power of the device.
How to calculate power using calculators
If you have neither the desire nor the time to do calculations, then you can use the services of some Internet resources that have special calculators. In theory, of all the methods, this should combine the optimal simplicity/accuracy ratio, but in practice, not everything is so simple. We don’t know what algorithms are embedded in the program code, we don’t know which heat sources are taken into account and which are not. Some resources, based on the results of verification, provide indicators with a significant margin, which will force you to overpay when purchasing.
Calculator for calculating air conditioner power by room area
Skip to calculations
For these reasons, we recommend using calculators only for rough calculations. If you are not “scared” by the power reserve, then calculators will help you quickly calculate the level of ventilation and other characteristics that you have not even thought about.
These resources will also help you choose the type of air conditioner depending on the room in which it will be installed.
Video - Calculation of air conditioner power
Methods for calculating air conditioner power
Each air conditioner has a marking from the manufacturer, where the MO parameter is indicated. Before you go shopping for a split system, you need to do a small calculation of the optimal power using a special formula, using the parameter of the room area or its volume.
Air conditioner labeling options:
- 0.7 – MO 2 kW;
- 0.9 – MO 2.5-2.6 kW;
- 10 - MO 2.9 kW;
- 12 – MO up to 3.5 kW.
Calculation of air conditioner by room area
The air conditioner is calculated based on the area of the room using a simple formula: 1 kW = 10 m2. To calculate MO, you need to divide the total area of the room by 10 and round the result. For example, the area of a 1-room apartment is 24.5 m2. We divide this figure by 10 and get the optimal power of the device - 2.45 kW. In this case, it is optimal to purchase a 2.5 kW air conditioner.
The minimum power parameter for split systems is 2 kW, optimal for installation in rooms up to 20 square meters. m.
Calculation of air conditioner power by room volume
You can more accurately calculate the optimal MO of an air conditioner based on the volume of the room. In this case, the calculation uses the specific cold parameter per 1 sq. m.
Power density value ( q) :
- room on the sunny side - 40 W/m3;
- average room illumination – 30 W/m3;
- darkened room – 20 W/m3.
MO calculation formula: Q1 = qx V
Q1 – device power;
q – specific parameter;
V is the volume of the room.
Since the room also contains household appliances and people that generate heat, the amount of heat generated by people and household appliances is added to the result. Calculation formula: Q1+ Q2+Q3= Q
The rate of heat generated from a person is 0.1 kW, from a computer – 0.3 kW, from household appliances and office equipment – 30% of power consumption.
Markings from manufacturers
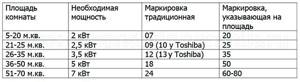
A split system of the same model is produced for different areas (accordingly, different capacities). Manufacturers label devices by cooling capacity expressed in kBTU (1000 BTU/h = 293 W). Based on this marking, you can judge whether this air conditioner is suitable for the needs of the future owner or not:
07 – power is 2 kW. On average, such a device can be placed in a room with an area of 18-20 square meters;- 09 – air conditioners 2.5-2.6 kW. Suitable for rooms up to 26 square meters;
- 12 is the most powerful option among household air conditioners (3.5 kW). This split system can be installed in rooms up to 35 square meters. Marking 12 – the air conditioner is designed for the area of a large room with high ceilings.
Some manufacturers use other values - for example, Toshiba also labels BTU with numbers 10 and 13 (they are slightly more powerful than “nines” and “twos”, respectively). And, for example, Mitsubishi in their markings use numbers corresponding to the area of the room - 20, 25, 35 (which is similar to “sevens”, “nines” and “twos”, respectively).
Below is a table that shows the required cooling capacity for a certain area of the room. Please note that this table takes into account only standard ceiling heights, low light levels, and the minimum number of equipment and people .
I would like to add that split systems with a power of less than 4 kW are suitable for apartments. Devices with higher power (18, 24, 36, 48 kBTU) are more often used for industrial buildings, gyms, and offices with a huge amount of heat-generating equipment. If you are planning to install such a “split”, then I recommend reading the article - how effective is a large air conditioner in an apartment.

Since many people confuse cooling power and power consumption, I recommend reading an article on how to distinguish between these concepts. And this article talks about labeling in more detail.
What happens if you choose the wrong power?
If you select a split system without taking into account the characteristics of the home, then unpleasant consequences are possible later.
If the air conditioner is not powerful enough, then the owner will have:
- poor quality cooling;
- overheating and breakdown of the device;
- additional costs for repairs and maintenance.
A device that is not powerful enough will simply not be able to perform its functions in a room that is too large and warm.
If the air conditioner is too powerful, then:
- the cost of the device and installation will be higher;
- the noise from the “split” will be louder;
- The device's potential will not be fully utilized.
Increased power will not lead to premature failure of the device, but owners will be forced to overpay for the “conder” and will get used to the “excessive” noise. If the number of people or working household appliances in the room constantly changes, the sun actively appears only at a certain time of day, it is recommended to choose a split system with a function for adjusting to the environment (automatic mode, which is found in almost every modern device). Such devices are capable of maintaining a comfortable climate in homes without much human intervention - the algorithm itself selects the optimal parameters.
Leave your comments and share the link to this article with your friends!
How to calculate without a calculator
Calculation of the cooling power of an air conditioner without a calculator is performed using the simple formulas published above.
For example, a buyer wants to calculate the exact power of the device based on the volume of the room. First, he needs to determine the value of V, the volume of the room, by multiplying the parameter of the height, length and width of the room.
Next, the specific power parameter is multiplied by the area and the parameter of the amount of heat from devices and people is added to the resulting result. The resulting value is rounded.
Air conditioners all new for 2021
How to choose the right split system
So, let's summarize everything we talked about during today's article. Suppose that you have chosen your optimal calculation method, and you have obtained a certain value, let it be 2.4 kW for a room size of 20 m² - let’s slightly reduce the result from the example given earlier, since we have one person resting, and the second one also sitting at the computer and makes a minimum of movements.
Technically, all calculations were performed correctly, but the fact that the device cannot constantly operate at full capacity has not yet been taken into account - this is an extreme operating mode. To relieve the equipment from additional loads, 10-15% of the reserve is added to the obtained result, 20% is possible, but then the point in accurate calculations is a little lost. We consider that 15% of 2.4 is 0.36. In total, the figure rises to 2.76 kW.

Air conditioning - a device for maintaining and setting a certain temperature in a room
From the data given earlier, it becomes clear that an option of at least nine will be required. This situation can confuse many people, since the air conditioner will consume a lot of energy. There is no need to worry, since the efficiency of split systems is quite high, since freon condenses and steam generation occurs. In fact, this results in energy consumption reduced by 2.5-3 times.
Prices for freon for refilling air conditioners
Freon
So, we looked at different methods for calculating the power of split systems. The material is presented in a clear and easy-to-learn form. We hope you find it useful!
Finishing the toilet with PVC panels will greatly simplify the improvement of the interior of the toilet. In a special article, we’ll look at how to finish wall panels in a bathroom, and we’ll also figure out how to choose the right material.
Video - How not to make a mistake when choosing an air conditioner
Examples of calculation and selection of air conditioner
Let's give a simple example of calculating the MO of an air conditioner.
Initial data:
- room area – 30 sq. m.;
- 1 person resides;
- The room contains several household appliances with a power consumption of 165 W (computer, TV and refrigerator).
- medium-light room.
Calculation:
- Q1 = S * h * q / 1000 = 30 sq. m * 2.70 m * 30 / 1000 = 2.45 kW.
- We calculate the heat flow of household appliances. Since the computer and TV operate at different times, for the calculation we take one of the devices that generates the greatest amount of heat. For example, a computer is 0.3 kW. Calculation: 0.165 kW x 0.3 = 0.05 kW.
- Heat gain from a person – Q2 = 0.1 kW.
- Now let’s calculate the general parameter of heat inflows from household appliances. Let's add the heat gain of the PC to the maximum power consumption of the refrigerator. Calculation: 0.05 kW + 0.3 kW = 0.35 kW. This means Q3 = 0.35 kW.
- Now let's calculate the optimal power of the equipment using the formula: Q = Q1 + Q2 + Q3 = 2.45 kW + 0.1 kW + 0.35 kW = 2.9 kW.
In this case, the optimal air conditioner power parameter will be 2.9 kW. In the standard range of split equipment with different MO parameters, we choose the most approximate option.
Correspondence between model ranges and air conditioner power in BTU and kW
| The lineup | BTU | kW |
| 7 | 7000 BTU | 2.1 kW |
| 9 | 9000 BTU | 2.6 kW |
| 12 | 12000 BTU | 3.5 kW |
| 18 | 18000 BTU | 5.3 kW |
| 24 | 24000 BTU | 7.0 kW |
| 28 | 28000 BTU | 8.2 kW |
| 36 | 36000 BTU | 10.6 kW |
| 42 | 42000 BTU | 12.3 kW |
| 48 | 48000 BTU | 14.0 kW |
| 54 | 54000 BTU | 15.8 kW |
| 56 | 56000 BTU | 16.4 kW |
| 60 | 60000 BTU | 17.6 kW |
Calculation of power consumption and energy costs

As mentioned above, the cooling power of an air conditioner exceeds the power consumption by several times.
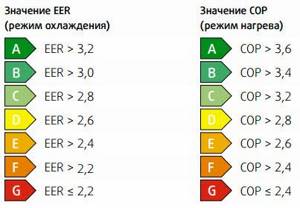
The ratio of these values is called the energy efficiency of the air conditioner and is designated in the specifications by the abbreviation “EER”.
Thus, if the air conditioner’s passport states EER = 3 (usually this value ranges from 2.5 to 4), then the device will consume Q/3 of electricity during the hottest period of the year.
Multiplying this value by the operating time - 8 hours, we get the daily electricity costs in kWh.
Device power consumption
The characteristics of air conditioners indicate two types of power: consumed and produced. They determine different operating parameters of the equipment. Power consumption is the amount of energy required for the operation of the device. Its value depends on the energy efficiency of the split system. Class A air conditioners consume 60-70% less electricity than class G models.
Comparing the values of power consumption and generation, it is easy to notice that less energy is consumed than is produced. For example, a 700 W air conditioner produces 2000 W (2 kW) of cold. The efficiency of the installation is 300%.
The peculiarity of the operation of climate control equipment is the transfer of heat using a refrigerant. Electrical energy is converted into mechanical energy. Installations that regulate the microclimate do not produce cold, but remove excess heat from the room.
The ratio of power consumption to cooling capacity is the main indicator of the energy efficiency of climate control equipment. It is designated by the EER coefficient. In household appliances its value is 2.5-4. For heating, a similar formula and COP coefficient are derived. Its parameters are in the range of 2.8-5.
The performance of equipment also has two parameters: cooling and heating. The temperature reduction mode is used more often, so we focus on it. The heating output of the split is 3.6-5.5 kW per 1 kW of electricity consumed. The indicator is higher than in the cold. The difference is explained by the absence of heat loss on the main line.
Most models are not designed to operate at outdoor temperatures below -5°. In the off-season, heating a room with an air conditioner will cost less than an electric heater.
Choosing an air conditioner for an apartment
When choosing an air conditioner for a residential apartment, you should first of all calculate the required power.
After making all the calculations, you can choose the type of air conditioner. The global market offers any type of air conditioners with optimal power and in different price categories. Due to the great abundance of products, the question arises, what kind of air conditioner is needed in an apartment? Let's look at the main types of air conditioners offered for home use:
Split system.
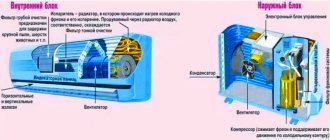
The device consists of 2 parts: an internal unit located inside the room and an external unit mounted outside. They are connected by pipes in which freon refrigerant circulates. This type of equipment can operate on an area from 10 to 120 sq.m.
Advantages: Aesthetic appearance of the indoor unit, low noise level, high power, the ability to install the indoor unit anywhere in the room, additional functions such as air humidification, ionizer, heating, filtration, etc.
Disadvantages: The cost of this type of device is quite high, the need for professional installation, the need to refill the refrigerant some time after the start of operation.
Floor mobile air conditioner.
It is a mobile box with a pipe. The pipe is inserted into a vent or window to remove warm air. The best option for renters and travelers.
Advantages: Mobility, ease of use, equipment does not require installation, low price category.
Disadvantages: Quite bulky and noisy, requires a hole for the pipe, lower power compared to split systems, the need to constantly monitor the level of condensate and timely emptying of the tray for it.
Window.
The simplest and cheapest type of equipment. It is used in the absence of plastic windows in the apartment.
Advantages: Low price, good power, ease of installation.
Disadvantages: Produces a lot of noise, takes up a lot of space on the window, which leads to a decrease in the level of light illumination in the room.
Multi-split system.
An ideal solution for the entire apartment. If there are several rooms, it is possible to install several internal units and one external one. The number of indoor units can be from 2 to 4.
Air conditioning or climate control
From the cooling system for an apartment or house, we smoothly move on to the issue of combating heat in the car interior. There are two cooling systems available for the car - air conditioning or climate control. These are not the same thing, and the differences between the devices are as follows:
- An air conditioner is a device for cooling air. It works on the principle of a refrigerator, but this approach increases fuel consumption and reduces the power of the machine. However, the equipment copes with the cooling function perfectly.
- Climate control is about more than just cooling the air. It maintains the set temperature for 24 hours, while the “smart” system takes into account both sunlight and outside temperature. When outside air enters the cabin, the climate control filters it.
In general, climate control is just an improved air conditioner
However, it is important to remember that such a system costs an order of magnitude more. Before deciding which is better to choose - air conditioning or climate control, draw up a budget that you are willing to spend on a cooling system in your car
By the way, climate control is now being introduced into residential premises. In so-called “smart homes”, climate control maintains the set temperature continuously, and in different rooms it differs depending on the set parameters. Its only drawback is its very high price.
Air conditioner characteristics
The use of energy by a split system depends on the operating modes, therefore, in order to understand the essence, we need to consider this aspect in more detail. Every air conditioner has a heat pump that moves warm air from one room to another, for example from a house to the street.
It needs some amount of electrical energy to work. To determine this value, you need to understand that there are two parameters: consuming and cooling (heating) performance. These indicators are usually indicated in the accompanying instructions for the device.
The power consumption of the air conditioner indicates how much electricity will be consumed from the line, and the cooling (heating) power indicates how much the system produces the required energy. This information is individually indicated in the device manual, but is indicated in the form of heat (COP) or cold (EER) indicators.
And the higher this digital value, the lower the energy consumption will be. At the same time, you need to be aware that the numbers written by the manufacturer may differ from the actual ones. This happens because when testing air conditioners at the factory, all calculations were made with the doors and window frames closed. In everyday life, as practice shows, conditions do not always correspond to test tests.
Determining the numerical values for EER and COP facilitates familiarization with energy efficiency categories. The most economical air conditioner consumption will be in category A. There are seven gradations in the table, and the last class is marked G.
Additional aspects
There are some other factors that influence the energy consumption during operation of the air conditioner:
- Compressor capabilities. At low speeds, less energy is consumed. The most economical in this regard are inverter air conditioners.
- The temperature difference between the external and internal environment. Electrical energy consumption will vary depending on the temperature difference indoors and outdoors. The costs of a split system for heating a room in 10-degree frost will be much higher than for creating coolness in the room in summer.
- Loads during cooling of air conditioners.
- Additional split system modes.
The change in temperature occurs due to the circulation of the coolant by the compressor, the transformation of the refrigerant and different pressures in the system.
During operation, after reaching the set temperature, the split system goes into the standby stage. As soon as the thermometer goes beyond the readings set on it, the air conditioner starts working again.
Consequently, the air conditioner does not always function, but periodically. While it is waiting, it essentially does not use electricity. The applied current is consumed only for the operation of the control network. And when a split system operates, the compressor consumes the most current, followed by the fan.
How to calculate the performance of an appliance for a room
For small rooms, a good option is a mobile air conditioner. At the same time, no special knowledge of how to use it is required: you just need to place it in the room at your discretion and plug it into a power outlet. But it must be borne in mind that it has a relatively small power, only up to 4 kW. Therefore, before calculating the performance of the device, you need to take into account not only the area, but also other features:
- Illumination of the room.
- Location. From the north or south side of the world.
- Heat radiation from electrical appliances.
- Heat radiation from living people.
How to calculate power using additional parameters can be seen from the table. But first, we give the formula for calculation: Q=Q1+Q2+Q3, where (see in the table)
| Q1 - heat gain from windows and walls | Q1=S×h×g/1000, while S – room size (m2) H – height G – coefficient equal to 30-40 W/m³, depending on illumination |
| Q2-sum of heat radiation from people | 0.1 – at rest 0.2 – under load |
| Q3 – heat radiation from electrical appliances | 0.3 – from a computer 0.2 – from a TV |
For example:
There is a room measuring 27 m2, height 3.0 m, the windows face south. The volume of the room will be 81 m2, we take the heat gain with the highest value of 40 W/m³. Taking these data into account, the following performance will be required: 40 W/m³×81m³=3.24 kW. We round up and get 3 kW.