What is partial pressure
Air is a mixture of gases. It contains the most nitrogen - 78 percent. Also, oxygen is contained in the form of molecules \(O_{2}\) and \(O_{3}\) - ozone, it makes up 21 percent. The remaining gases, including inert gases and carbon dioxide, make up 1 percent. Air pressure is the sum of the pressures of each gas entering the air.
Let's explain this with a simple example. Let's consider a container, for example, an ordinary three-liter glass jar for preservation. When there is no food in the jar, its volume is entirely taken up by air. The air pressure in the jar will be equal to atmospheric pressure. Seal the jar with a lid. Suppose we have the ability to separately filter each gas from the air.
We will conduct the following experiment:
- First, let's measure the air pressure in the jar.
- Then, we pump out all the gases from the jar, except one. This individual gas at the same temperature occupies the entire volume that was previously occupied by the gas mixture. Using a pressure gauge, measure the pressure created by the remaining gas. The pressure of the remaining gas is called partial pressure.
- Next, let’s return the gases pumped out earlier to the jar.
- After this, we filter out some other gas, leaving it in the jar and pumping out all other gases. We will measure the partial pressure of the remaining gas with a pressure gauge.
Having done this experiment several times, we will obtain the partial pressures of all the gases that make up the air.
Notes:
- Partial from the Italian "parzio" - part. This means a part of something whole.
- Manometer – a device for measuring pressure (link).
- Bodies in a gaseous state occupy the entire volume offered to them. As gases are removed, the mass of the substance in the jar will decrease. But the remaining gas will occupy the entire volume of the jar, creating pressure on its walls.
The relationship between the total pressure and the partial pressures of all gases in the mixture can be described using mathematics as follows:
\[\large \boxed{ P_{\text{general}} = P_{1} + P_{2} + P_{3} + \ldots + P_{n} }\]
\(\large P_{\text{total}} \left(\text{Pa} \right) \) – pressure of the gas mixture (total pressure);
\(\large P_{1} \left(\text{Pa} \right) \) – partial pressure of the first gas;
\(\large P_{2} \left(\text{Pa} \right) \) – partial pressure of the second gas;
Each gas makes its own contribution to the total pressure of the mixture. This contribution is called the gas partial pressure.
If we add up the partial pressures of all the gases, we get the air pressure that we measured at the beginning of the experiment, before we started pumping the gases out of the can.
In what units is absolute humidity measured?
Every molecule has mass. The more molecules of steam, the greater the mass of steam in each cubic meter of air.
Mass in volume is density. Therefore, absolute humidity is indicated using water vapor density.
The density of steam is related to its partial pressure. The greater the vapor density, the greater its partial pressure. Therefore, absolute humidity can also be indicated using the partial pressure of water vapor.
The more vapor molecules in each cubic meter of air, the greater the absolute humidity.
In what units is relative humidity measured?
The degree of air humidity depends on whether the water vapor in the air is close or far away, and on the state of saturation. If the steam is close to saturation, the relative humidity is high. And if the steam is far from saturation, the relative humidity is low.
Relative humidity is usually measured as a percentage, since we describe relative values using fractions.
Important! Measure the air temperature first and then measure the relative humidity!
Note: Relative value means fractional. A percentage is a fraction with 100 as its denominator.
How to maintain relative humidity in your home
We have already decided how to measure the humidity level in the room; now we just need to figure out how to restore the optimal humidity level.
If the humidity is low
Ventilate the room.
However, this method cannot always significantly improve the state of the home microclimate, since in the summer the street air can be dry.
Also, when ventilating in the traditional way, dangerous microbes, allergens, dust, harmful gases and unpleasant odors can enter the apartment. But if you keep the windows constantly closed, then there is a high probability of encountering another problem in maintaining the microclimate - stuffiness (high levels of carbon dioxide).
High-quality ventilation is also important when ventilating rooms. A valve can provide fresh air into the room, but it will not be enough to ventilate a room inhabited by more than one person. The air passing through the supply and exhaust valve is not heated and not cleaned.
A breather will help you easily deal with the stuffiness and not let dangerous “guests” from the street into your house. This is a supply ventilation device that takes air from the street, heats it, cleans it and supplies it to the room.
- Regularly wet clean
rooms. - Install an aquarium at home.
Keeping fish in an aquarium at home can also affect air humidity. But remember that you need to take care of the fish and keep the aquarium clean. - water containers
on window sills or near heating radiators . - A humidifier
is a good option for your home. This device will cope with dry home air, improve the microclimate and prevent the development of respiratory diseases. - Climate control equipment (air conditioner, breather, air purifier, Danfoss Eco thermostat)
complete with a MagicAir base station will help not only track the microclimate conditions in the house, but also maintain optimal performance.
The base station collects information from room air about temperature, humidity and carbon dioxide concentration. All indicators are displayed on the smartphone screen in the MagicAir application.
If the humidity is high
The other side of the coin is that there is too much moisture in the air.
- Do not dry clothes in the apartment.
It is best to do this on the balcony. - After taking water procedures, when the air humidity in the bathroom can reach 100%, you need to ventilate
. With good ventilation, it will be enough to open the door to the bathroom and the window closest to the bathroom or turn on the breather. - You can purchase a special device for absorbing moisture
. The operating principle of this device is the opposite of the air humidification process: a built-in fan drives moist air through the device. There is also an evaporator inside, which turns moisture into condensate, which flows into a special container.
If you get into the habit of constantly maintaining optimal air humidity at the required level, this will help reduce the risk of developing respiratory diseases and cases of allergic reactions. Normalized humidity has a beneficial effect on the skin, protecting it from drying out and premature aging.
Formula for calculating relative humidity
The numerator is the vapor density available at the time of measurement.
The denominator is the maximum vapor density corresponding to the available temperature (that is, the saturated vapor density).
If the vapor density is maximum, then the vapor is called saturated. The higher the temperature, the greater the maximum vapor density.
\[\large \boxed{ \varphi = \frac{\rho_{0}}{\rho_{max}} }\]
\( \large \varphi \) – relative humidity;
\(\large \rho_{0} \left( \frac{\text{kg}}{\text{m}^{3}}\right) \) – measured density of water vapor in the air, i.e. absolute humidity;
\(\large \rho_{max} \left( \frac{\text{kg}}{\text{m}^{3}}\right) \) – the maximum density of water vapor in the air, which can be at measured temperature, i.e. saturated vapor density;
Sometimes it is more convenient to write the formula in this form:
\[\large \boxed{ \rho_{0} = \varphi \cdot \rho_{max} }\]
How is air humidity measured?
You can find out the amount of moisture using available means: a lighted candle, a fir cone, a glass of water, or the condition of the leaves of a homemade moisture-loving plant. Such methods have been used for a long time, but they determine only approximate values.
Accurate readings can be obtained with a regular thermometer. This method is long and not very convenient, since it requires compliance with certain instructions, without which the data obtained will have a significant error.
Modern moisture meters are safe and fit harmoniously into the interior. Therefore, they can be used in any room to create a comfortable microclimate

To objectively measure water vapor in the air, special instruments are used that convert data on temperature and vapor concentration.
Such devices include:
- Hygrometers.
- Psychrometers.
Devices with different operating principles show values with varying degrees of error. Some of the devices provide accurate data on the moisture content in the air, others allow for error.
There are instruments that record absolute values, and there are meters that reflect relative values. Therefore, before choosing a hygrometer, it is necessary to study the operating principle of the devices and take into account the conditions in which the device will be used.
The absolute value reflects the weight of water vapor in a cubic meter of air. The value is indicated in grams, kilograms per cubic meter. Such a value will not tell an ordinary person anything, so the unit of measurement is usually considered to be relative air humidity.
Relative humidity is the ratio of steam to air. The maximum possible amount of vapor in the air is 100%, the remaining values are displayed relative to the maximum value.
To calculate the relative amount of moisture in the air, each device is equipped with a temperature sensor. Some devices broadcast additional temperature data, which is convenient since you don’t need to buy an additional thermometer

According to SNiP 2.04.05-91, relative air humidity should remain within 30-60%. In climatically humid areas, with outdoor vapor content greater than 75%, the values will be slightly higher.
What is dew point
If you cool moist air, you can bring the vapor in the air to saturation. At the same time, you can notice how dew appears on smooth surfaces. The appearance of dew will occur at a certain temperature. This temperature is called the dew point.
The dew point is the temperature at which the relative humidity becomes 100%. At this temperature, moisture condenses from the air: dew falls, it rains, or, for example, glass fogs up.
Humidity measuring instruments
Instruments that can be used to measure humidity are called hygrometers. There are several types of such devices: hair, condensation, psychrometric.
Hair hygrometer
A hair hygrometer uses the property of hair to change its length when humidity changes. The higher the air humidity, the longer the hair becomes. Usually they use hair from a horse's mane or long human hair. One end of the hair is fixed to the body of the device, and the other is attached to the arrow (Fig. 1). Using the scale of the device, you can determine the relative humidity of the air.
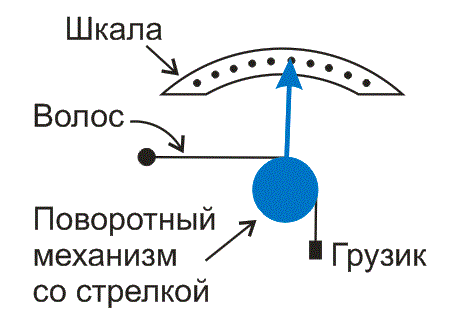
Rice. 1. The hair hygrometer consists of a scale, a rotary mechanism with a pointer and a hair
Condensation hygrometer
A dew point condensation hygrometer helps determine the absolute humidity of the air.
First, determine the dew point using the thermometer built into the device. Then, using a table containing the density and partial pressure of water vapor at various temperatures, the absolute humidity of the air is determined.
If the air temperature and absolute humidity are known, the relative air humidity can be additionally calculated.
The design of a condensation hygrometer is shown in Figure 2.
A small metal box contains a tube with a bulb and a thermometer. The front thin wall of the box is polished to make it easier to observe the condensation of water droplets. A metal ring that stiffens the thin front wall is attached through a spacer for thermal insulation.
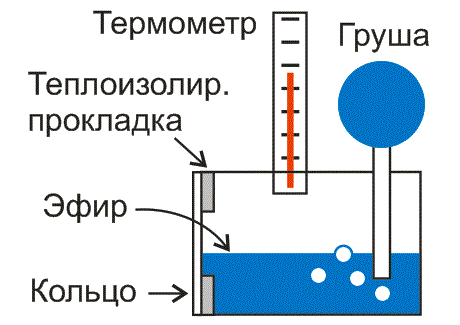
Rice. 2. A condensation hygrometer contains a thermometer and a bulb immersed in a container with a rapidly evaporating liquid, the container has a polished wall on which water from the air can condense
The device is used like this: Pour a quickly evaporating liquid (alcohol, ether, etc.) into the box and blow air through the box with a pear. Thus, they cause rapid evaporation of the liquid and a decrease in temperature in the box. At the same time, dew appears on the polished front wall of the box. A thermometer allows you to measure the temperature at which the dew condensed. The appearance of dew indicates that the steam has become saturated.
Absolute air humidity is determined from a table that contains the density and partial pressure of water vapor at various temperatures.
Psychrometric hygrometer
Such a device for measuring relative humidity is called a psychrometer for short. It consists of two identical thermometers mounted on a holder (Fig. 3). The bottom of one of the thermometers is immersed in a small container containing a few milliliters of water. Usually a psychrometric table is applied to the body of this device. Thanks to this table, by reading the readings of two thermometers, you can determine the relative humidity of the air.
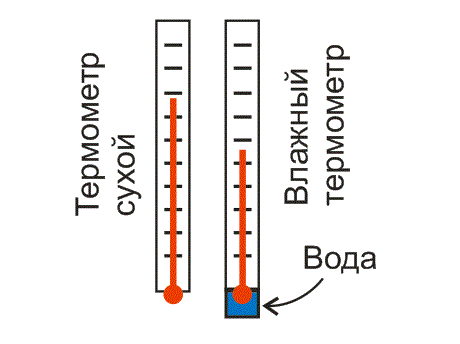
Rice. 3. The psychrometric hygrometer consists of a dry and wet thermometer
Homemade psychrometer
To make a homemade psychrometer, you need to take two identical household alcohol thermometers.
At the bottom of each thermometer there is a ball of liquid. This liquid expands as temperature increases. Excess liquid from the ball rises through a thin tube, next to which the divisions of the temperature scale are marked. Typically, tinted alcohol (alcohol thermometer) or mercury (mercury thermometer) is used as such a liquid.
The ball of one of the thermometers should be wrapped in a piece of cotton wool or a small cloth moistened with water at room temperature. We will agree to call this thermometer “wet.”
You don't need to do anything with the second thermometer. We will call this thermometer a “dry” thermometer.
Let's place these thermometers close to each other. After a few minutes, the homemade psychrometer will be ready to measure humidity.
We know that the temperature of a liquid decreases as it evaporates (link). Therefore, the wet bulb reading will always be less than the dry bulb reading. The drier the air, the greater the difference between thermometer readings. Because in dry air the rate of evaporation (link) of water increases.
Let's record the readings of dry and wet thermometers. Relative air humidity can be found using a psychrometric table.
Operating principle and types of devices
The operation of hygrometers is based on variations in the physical parameters of various materials. When the amount of vapor in the air changes, the properties change: density, weight, length and other operating parameters of the substances. By recording changes in the physical characteristics of materials, it is possible to draw conclusions about the amount of vapor in the air.
Hair and film moisture meters
The simplest mechanisms of devices, analyzing the physical properties of materials, make it possible to accurately determine the amount of vapor in the air.
The hair device consists of synthetic defatted hair, a base with a scale, a pointer and a pulley. When the vapor increases or decreases, the tension force of the hair changes, the pulley rotates, changing the position of the arrow on the scale with values.
Rare and exclusive models of hair hygrometers operate exclusively according to the laws of mechanics, and therefore do not require an external power source

This meter operates in the range from 30 to 80%. Nowadays it is practically not used, since there are other models that have a larger range of operation.
In a film moisture meter , the sensing element is an organic film attached to a pulley. When the humidity indicator changes, the film tension increases or decreases, which leads to the movement of the pulley, which changes the angle of the arrow.
The pointer moves along the arc-shaped dial, showing the percentage of air humidity in the room.
Both mechanisms operate according to the laws of mechanics, so they can accurately measure moisture in rooms where the temperature is low, down to 0 ° C.
Weight and condensation meters
Using a weighing hygrometer, you can determine the absolute humidity of the air. This device is used for laboratory experiments, so it is not suitable for indoor use at home.
The condensation meter summarizes the most accurate data. The design of such a device consists of a flat surface on which moisture settles, a thermometer that determines the moment of condensation formation, and a beam of light that detects the appearance of the first condensation. The operating range of the meter is from 0 to 100%.
The condensing device has large dimensions. To activate the device, a rubber bulb is used, so such moisture meters are used only in laboratories

These mechanisms generate results with high accuracy, which is necessary for research, but not as home air humidity meters.
Mechanical and electrical devices
A mechanical or ceramic moisture meter works through electrical resistance of the mass. Since the ceramic mass contains silicon and kaolin with metal particles, the resulting mixture changes resistance after a change in air humidity.
Due to this, with different steam contents, the arrow on the device changes position, reflecting the air humidity.
This operating mechanism allows ceramic devices to be made compact, which is why they are in demand for measuring air humidity in the home.
An electronic or room hygrometer is a modern high-speed device for determining indoor air humidity.
The following operating principles can be used in the design:
- measurement of electrical conductivity of ambient air;
- optoelectronic method, with dew point measurement;
- measurement of electrical resistance of polymers and salts;
- analysis of condensate capacity.
The digital moisture meter works using microcircuits, so calculations are made within a few seconds, and the output data has minimal error.
Accurate readings from an electronic hygrometer are possible in the absence of a draft. Some models allow fluctuations of up to 2 m/s, to take this into account, you must first read the technical documentation

When determining air humidity with devices of this type, it is necessary to take into account the ambient temperature. The slightest deviations from stationary conditions affect the final indicators, therefore, before direct measurement, street doors must be closed for 15 minutes.
In addition to temperature fluctuations, the operation of devices is affected by the proximity of heating devices. Therefore, when placing hygrometers of any type, take into account the proximity of radiators and place them on the opposite wall or table, located at a considerable distance from the heaters.
What is a psychrometric table
The psychrometric table (Fig. 4 and Fig. 5) contains values of relative air humidity. These values are related to the dry bulb readings and the difference between the dry and wet bulb readings.
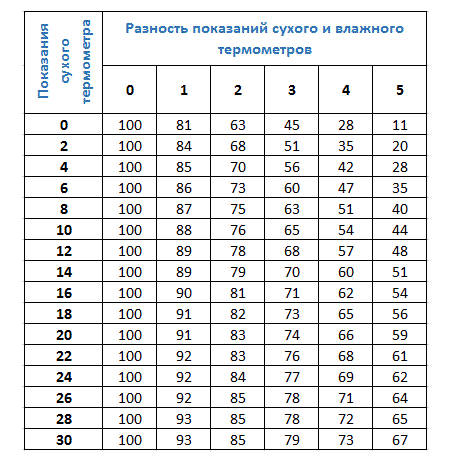
Rice. 4. Psychrometric table, part 1
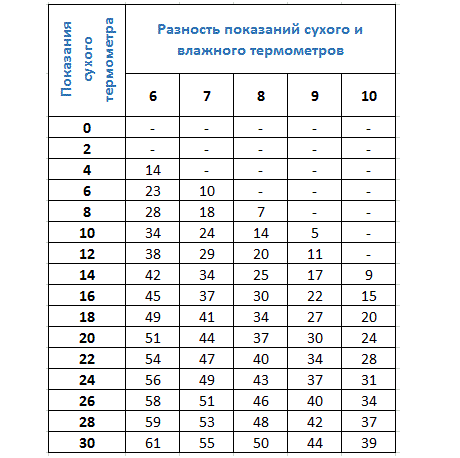
Rice. 5. Psychrometric table, part 2
The presence of water vapor in the air affects the rate of evaporation. The higher the temperature and the less steam in the air, the faster the water evaporates, the greater the difference between the readings of the dry and wet thermometers.
Voting for the best air quality meter
Which air quality meter would you choose or recommend?
Testo 435-4
0.00 % ( 0 )
CEM DT-9881
5.56 % ( 1 )
Fluke 975V
11.11 % ( 2 )
CEM DT-968
22.22 % ( 4 )
AMTAST AMF062
16.67 % ( 3 )
AirVisual Node
11.11 % ( 2 )
TION MagicAir
0.00 % ( 0 )
Xiaomi Smartmi PM 2.5 Air Detector
22.22 % ( 4 )
LifeControl MCLH-08
5.56 % ( 1 )
Table - dependence of saturated vapor density on temperature
This table (Fig. 6 and Fig. 7) contains the density and partial pressure of water vapor at various temperatures. Using such a table, knowing the absolute humidity and air temperature, you can calculate the relative humidity.
Absolute air humidity is usually indicated using water vapor density.
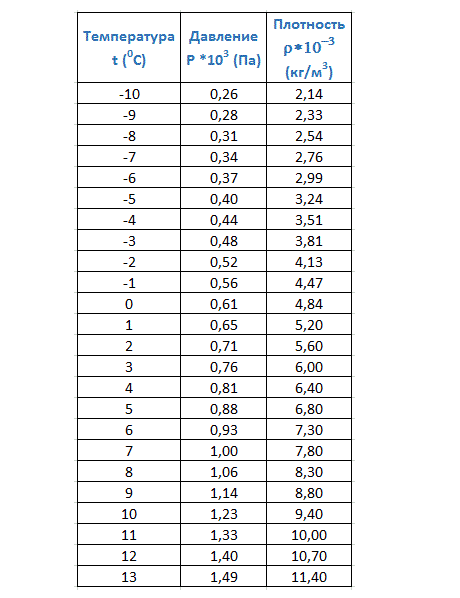
Rice. 6. Density and partial pressure of water vapor at different temperatures, part 1
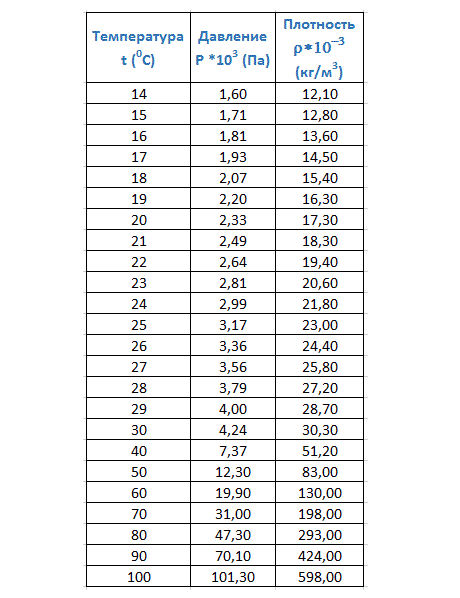
Rice. 7. Density and partial pressure of water vapor at different temperatures, part 2
The Tale of a Little Wizard and a Magic Bucket
The concept of air humidity is easy to explain with the help of a fairy tale.
In a certain kingdom there lived a little wizard. His name was Air. And he had a magic bucket.
The magic was that the size of the bucket depended on the temperature. The higher the temperature, the larger the bucket became, increasing in size.
Note: In this analogy, absolute humidity is the amount of water poured into the bucket. And relative humidity is the proportion that the poured water occupies in relation to the entire volume of the bucket.
Suppose that at a certain temperature the volume of the bucket is 10 liters. Pour 5 liters of water into a bucket. This is half a bucket, that is, the relative humidity will be 50%. Since 5/10 = 0.50 = 50%
We do not change the amount of water poured, which means that the mass and volume of water does not change.
Let's say the temperature has increased. The size of the bucket will increase with increasing temperature. Let's assume that the bucket has grown so much that its volume is now 15 liters.
This means that now the relative humidity will be equal to
5/15 = 0,33 = 33%
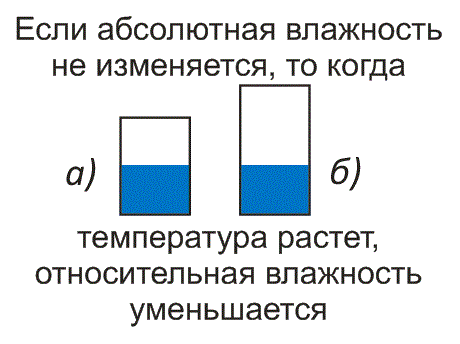
Rice. 8. As temperature increases, relative humidity decreases
If absolute humidity does not change when temperature rises, relative humidity decreases.
Let us now assume that the temperature has dropped. This means that the volume (size) of the bucket will decrease. If, for example, the volume of the bucket decreases to 8 liters, then the relative humidity will be
5/8 = 0,625 = 62,5%
That is, absolute humidity has not changed, but relative humidity has increased.
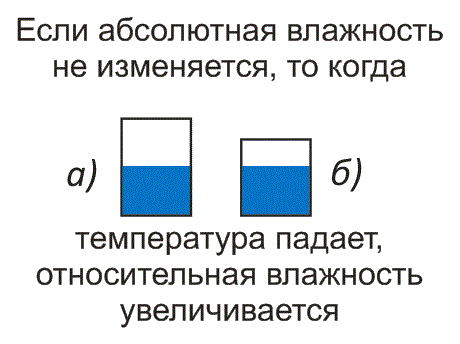
Rice. 9. As temperature decreases, relative humidity increases
If absolute humidity does not change when the temperature falls, relative humidity rises.
As the temperature drops further, the volume of the bucket will continue to decrease. At a certain temperature, it may happen that the volume of the reduced bucket coincides with the volume of water poured.
Suppose the volume of the bucket decreases to 5 liters. And the amount of water in the bucket is also 5 liters. The relative humidity will be 100%.
5/5 = 1,0 = 100%
The temperature at which the size of the bucket matches the amount of water poured is called the dew point.

Rice. 10. By reducing the temperature of humid air we can achieve steam saturation and dew point. Relative humidity at this temperature will be 100%
If the temperature continues to drop, the magic bucket will continue to shrink. Excess water will spill out. We say in such cases: “precipitation is falling,” or “it is raining.”
Note: Relative humidity cannot exceed 100%. When relative humidity is 100%, excess water vapor from the air condenses, resulting in precipitation - rain or dew.
What is air humidity
There are several units for measuring relative air humidity. 1. Absolute humidity is the amount of water per unit volume of air, A (g/m3). 2. To determine the second unit of measurement, you need to carefully look at the picture showing the movement of water molecules in a closed vessel filled with water to a certain level. After some time, two processes in this vessel: evaporation and condensation of water molecules will align and we will get saturated water vapor, which creates a pressure on the walls of the vessel equal to the pressure of saturated water vapor, Ps(Pa). There are always water molecules in the air, but their concentration is lower than above the water surface. They, just like other air molecules, create pressure. This pressure, created specifically by water molecules, is called the partial pressure of water vapor, P(Pa). The ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor to the saturated pressure of water vapor, expressed as a percentage, is called relative air humidity:
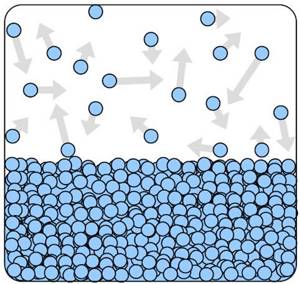
From the definition it follows that above the surface of the water the relative humidity of the air is 100%. And vice versa, at 100% air humidity, moisture condensation is observed. The pressure of saturated water vapor increases with increasing temperature. If you increase the temperature in an isolated room with 100% humidity, the relative humidity will drop sharply. 3. The third unit follows from the second unit of measurement. If you reduce the temperature in a closed volume with a certain humidity, the relative humidity of the air will increase. At a certain temperature, the relative humidity will become 100%. This temperature is called dew point temperature. For negative temperatures there is a dew point - the frost point. The definition itself suggests one of the ways to determine air humidity in a certain volume. You need to slowly cool an object while controlling its temperature. The temperature at which a water film of condensed water molecules appears on an object will be equal to the dew point temperature in a given volume. Below are expressions for calculating the pressure of saturated water vapor above the surface of water Psw and ice Psi depending on temperature:

Values of saturated vapor pressure above the surface of water (Psw) and ice (Psi)
Table 1.
| T, ° C | psw, Pa | psi, Pa | T, ° C | psw, Pa | psi, Pa | T, ° C | psw, Pa | psi,Pa |
| -50 | 6,453 | 3,924 | -33 | 38,38 | 27,65 | -16 | 176,37 | 150,58 |
| -49 | 7,225 | 4,438 | -32 | 42,26 | 30,76 | -15 | 191,59 | 165,22 |
| -48 | 8,082 | 5,013 | -31 | 46,50 | 34,18 | -14 | 207,98 | 181,14 |
| -47 | 9,030 | 5,657 | -30 | 51,11 | 37,94 | -13 | 225,61 | 198,45 |
| -46 | 10,08 | 6,38 | -29 | 56,13 | 42,09 | -12 | 244,56 | 217,27 |
| -45 | 11,24 | 7,18 | -28 | 61,59 | 46,65 | -11 | 264,93 | 237,71 |
| -44 | 12,52 | 8,08 | -27 | 67,53 | 51,66 | -10 | 286,79 | 259,89 |
| -43 | 13,93 | 9,08 | -26 | 73,97 | 57,16 | -9 | 310,25 | 283,94 |
| -42 | 15,48 | 10,19 | -25 | 80,97 | 63,20 | -8 | 335,41 | 310,02 |
| -41 | 17,19 | 11,43 | -24 | 88,56 | 69,81 | -7 | 362,37 | 338,26 |
| -40 | 19,07 | 12,81 | -23 | 96,78 | 77,06 | -6 | 391,25 | 368,84 |
| -39 | 21,13 | 14,34 | -22 | 105,69 | 85,00 | -5 | 422,15 | 401,92 |
| -38 | 23,40 | 16,03 | -21 | 115,32 | 93,67 | -4 | 455,21 | 437,68 |
| -37 | 25,88 | 17,91 | -20 | 125,74 | 103,16 | -3 | 490,55 | 476,32 |
| -36 | 28,60 | 19,99 | -19 | 136,99 | 113,52 | -2 | 528,31 | 518,05 |
| -35 | 31,57 | 22,30 | -18 | 149,14 | 124,82 | -1 | 568,62 | 563,09 |
| -34 | 34,83 | 24,84 | -17 | 162,24 | 137,15 | 0 | 611,65 | 611,66 |
Values of saturated vapor pressure above a flat water surface (Psw)
Table 2.
| T, ° C | psw, Pa | T, ° C | psw, Pa | T, ° C | psw, Pa | T, ° C | psw, Pa |
| 0 | 611,65 | 26 | 3364,5 | 52 | 13629,5 | 78 | 43684,4 |
| 1 | 657,5 | 27 | 3568,7 | 53 | 14310,3 | 79 | 45507,1 |
| 2 | 706,4 | 28 | 3783,7 | 54 | 15020,0 | 80 | 47393,4 |
| 3 | 758,5 | 29 | 4009,8 | 55 | 15759,6 | 81 | 49344,8 |
| 4 | 814,0 | 30 | 4247,6 | 56 | 16530,0 | 82 | 51363,3 |
| 5 | 873,1 | 31 | 4497,5 | 57 | 17332,4 | 83 | 53450,5 |
| 6 | 935,9 | 32 | 4760,1 | 58 | 18167,8 | 84 | 55608,3 |
| 7 | 1002,6 | 33 | 5036,0 | 59 | 19037,3 | 85 | 57838,6 |
| 8 | 1073,5 | 34 | 5325,6 | 60 | 19942,0 | 86 | 60143,3 |
| 9 | 1148,8 | 35 | 5629,5 | 61 | 20883,1 | 87 | 62524,2 |
| 10 | 1228,7 | 36 | 5948,3 | 62 | 21861,6 | 88 | 64983,4 |
| 11 | 1313,5 | 37 | 6282,6 | 63 | 22878,9 | 89 | 67522,9 |
| 12 | 1403,4 | 38 | 6633,1 | 64 | 23936,1 | 90 | 70144,7 |
| 13 | 1498,7 | 39 | 7000,4 | 65 | 25034,6 | 91 | 72850,8 |
| 14 | 1599,6 | 40 | 7385,1 | 66 | 26175,4 | 92 | 75643,4 |
| 15 | 1706,4 | 41 | 7787,9 | 67 | 27360,1 | 93 | 78524,6 |
| 16 | 1819,4 | 42 | 8209,5 | 68 | 28589,9 | 94 | 81496,5 |
| 17 | 1939,0 | 43 | 8650,7 | 69 | 29866,2 | 95 | 84561,4 |
| 18 | 2065,4 | 44 | 9112,1 | 70 | 31190,3 | 96 | 87721,5 |
| 19 | 2198,9 | 45 | 9594,6 | 71 | 32563,8 | 97 | 90979,0 |
| 20 | 2340,0 | 46 | 10098,9 | 72 | 33988,0 | 98 | 94336,4 |
| 21 | 2488,9 | 47 | 10625,8 | 73 | 35464,5 | 99 | 97795,8 |
| 22 | 2646,0 | 48 | 11176,2 | 74 | 36994,7 | 100 | 101359,8 |
| 23 | 2811,7 | 49 | 11750,9 | 75 | 38580,2 | ||
| 24 | 2986,4 | 50 | 12350,7 | 76 | 40222,5 | ||
| 25 | 3170,6 | 51 | 12976,6 | 77 | 41923,4 |
Relative humidity at negative temperature Ψi
correction factor k = psw / psi.
Values of the correction factor “k” at different temperatures:
Table 3.
| T,⁰С | 0 | -10 | -20 | -30 | -40 |
| 0 | 1 | 1,104 | 1,219 | 1,347 | 1,489 |
| -1 | 1,01 | 1,115 | 1,231 | 1,361 | 1,504 |
| -2 | 1,02 | 1,126 | 1,243 | 1,374 | 1,519 |
| -3 | -1,03 | 1,137 | 1,256 | 1,388 | 1,534 |
| -4 | 1,04 | 1,148 | 1,269 | 1,402 | 1,549 |
| -5 | 1,05 | 1,16 | 1,281 | 1,416 | 1,565 |
| -6 | 1,061 | 1,171 | 1,294 | 1,43 | 1,58 |
| -7 | 1,071 | 1,183 | 1,307 | 1,445 | 1,596 |
| -8 | 1,082 | 1,195 | 1,32 | 1,459 | 1,612 |
| -9 | 1,093 | 1,207 | 1,334 | 1,474 | 1,628 |
Values of absolute gas humidity with relative humidity of water 100% at different temperatures
Table 4.
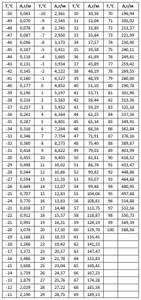
Why control air humidity?
It is necessary to measure and control the level of air humidity in a wide variety of situations:
- in meteorology - to predict the weather;
- in agriculture - in greenhouses and greenhouses it is necessary to maintain air humidity that is comfortable for the plants being grown;
- in the warehouses of grocery stores - so that products do not spoil before their expiration date;
- in car boxes - to prevent corrosion on the metal surfaces of cars, mechanisms and spare parts for them;
- in residential premises - a comfortable level of relative air humidity for humans is in the range from 40 to 60 percent;
- in libraries and museums - to preserve books and valuable works of art for many centuries;
Effect of dry air
During human life, a certain amount of moisture evaporates from the surface of his skin. Excessively dry indoor air promotes the activation of this process, which may result in signs of dehydration:
- Drying of the skin and mucous membranes, which can lead to cracking. The most common negative consequence is the occurrence of infectious diseases due to the easier penetration of infectious agents through cracks.
- Wrinkling of the skin, peeling of the epidermis. This implies that the rate of wound healing depends on the level of environmental humidity.
In addition, in an excessively dry room, the amount of dust increases, which can cause a negative reaction in the form of allergies.

The reasons for indoor humidity falling below normal levels are:
- operation of heating devices, including heated floors;
- frosty weather in winter.
If a problem of dry air in a residential area is detected, and subsequently, it is recommended to take preventive measures in order to prevent a recurrence of the unpleasant situation.
conclusions
- Partial pressure is the pressure of one gas in a mixture. Partial - from the Italian "parzio" - part of something whole.
- If we add up all the partial pressures, we get the total pressure of the gas mixture.
- Air is a mixture of gases. Air pressure is the sum of the partial pressures of all the gases that make up air.
- The air, even at subzero temperatures, contains water vapor. By measuring the amount of this steam, we will measure the humidity of the air.
- The higher the temperature, the more water vapor the air can hold. Of course, if you add this water vapor to the air.
- There are two types of air humidity - absolute and relative.
- Absolute humidity is indicated using water vapor density or using partial pressure of water vapor.
- Instruments for measuring humidity are called hygrometers. Condensation, hair and psychrometric hygrometers are widely used.
- A psychrometric hygrometer is called a psychrometer for short.
- A homemade psychrometer can be made from two identical household thermometers. We'll call one thermometer a wet thermometer and the other a dry thermometer.
- Relative humidity can be determined using a psychrometer and a psychrometric table.
- First we measure the air temperature, and then the relative humidity.
- Relative humidity is a fractional value. It is indicated as a percentage. The numerator of the fraction is the density of the vapor present in the air; the denominator is the maximum vapor density at this temperature, i.e., the density of vapor saturated at this temperature.
- Absolute and relative air humidity are related. Knowing the air temperature and one of the humidity levels, you can determine the second humidity (you can use the absolute humidity to determine the relative humidity and vice versa). To do this, use the table of water vapor densities at different temperatures.