Why insulate the foundation
Thermal losses of the building through the foundation are small - from 5% to 15%. Its position and the peculiarities of the “physics” of heat transfer affect it.
About 15% of losses remain on the foundation and floor, but how much this is in absolute value depends only on the owner of the house Source ps-b.ru
There are only three ways to transfer thermal energy: radiation, convection (for gas and liquid media) and thermal conductivity.
Radiation is clearly not “about the foundation”, but about the heating system devices. They have a higher temperature compared to air and surrounding objects and serve as sources rather than “receivers”. But the walls of a heated room during the cold season emit energy in the infrared spectrum to the street. To see this background, just look at them through a thermal imager. It is especially bright in uninsulated areas and “cold bridges”.
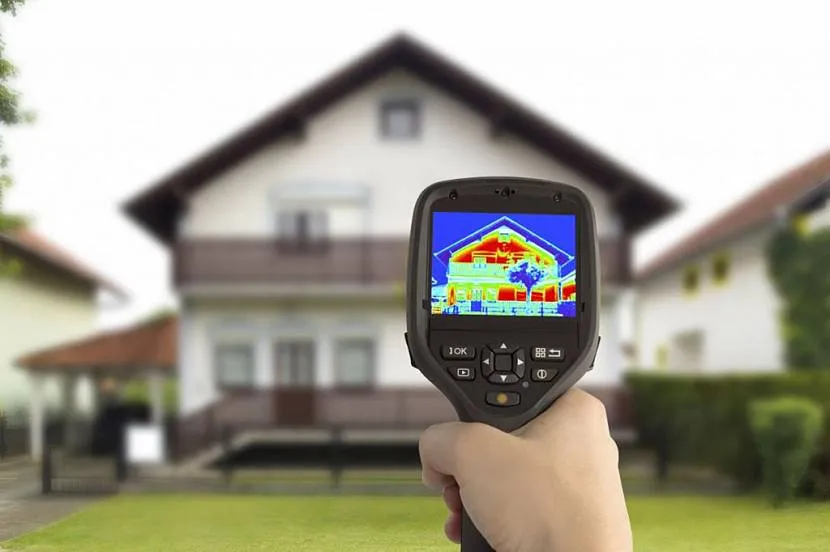

It’s so easy to see how heat escapes through uninsulated walls Source rte-france.com
Natural convection is characterized by an upward flow of warm air and a downward flow of cold air. Of course, the temperature of the foundation cannot affect this process. It is important here to insulate the roof and ceiling so that they do not quickly “cool” the warm air.
Of the above three methods of transferring thermal energy, it is “thanks to” the thermal conductivity of structural materials that a cold foundation affects heat loss and heating costs of the house. And the thermal conductivity of reinforced concrete, from which the foundation is usually made, is quite high, so its low temperature is transferred to the walls and load-bearing partitions.
The air in the room cools due to the enclosing structures, which release heat to the environment. For the underground part of the foundation it is soil, for the base and walls it is air. Insulating the foundation reduces these losses.
Warming sequence

Insulation of strip foundations
The technology for attaching heat-insulating material depends on the season of work and the design of the base.

When working with a strip foundation located underground, it is necessary to provide access to the walls of the base of the building. If the house is just being built, then this is easy to do
The insulation is attached to the surface immediately after dismantling the formwork panels , before backfilling the trench.
For already used houses, a trench from 50 cm wide and deep to the level of soil freezing is prepared along the perimeter. The insulation is attached to the slab foundation only before it is poured.
Mistakes made at any stage will cause a violation of the integrity of the heat-insulating layer and lead to freezing of the foundation. Sometimes it is not possible to install external thermal insulation.
If the house has been in use for a long time, then opening the foundation is a risky process; it is recommended to carefully prepare for the work in advance. There is a risk of subsidence of part of the horizontal foundation of the building and destruction of supporting structures.
To avoid this problem, it is better to insulate the foundation from the inside, and then use the surfaces for decorative finishing. Although protecting the inside of the foundation does not insulate the foundation itself, but the underground rooms.
Video description
The heat loss of a building and the purposes of insulating the foundation are described in detail in the video:
But there is also another function of thermal insulation of the foundation of a house - increasing the service life of the foundation. Building materials have such a criterion as frost resistance. Its numerical expression means how many freezing cycles (assuming water saturation) must pass before signs of destruction appear. Therefore, for regions with cold and long winters, insulation and waterproofing of the foundation is a prerequisite to ensure the strength and durability of the structure.
How to insulate a foundation with your own hands
It is impossible to choose the right material for insulating the foundation of a house without taking into account the type of foundation. In temperate latitudes, strip foundations are most often installed under load-bearing walls. In recent years, Swedish USP technology has been used for prefabricated buildings; concrete is insulated during the construction process.
When installing foundation insulation with your own hands, it is advisable to follow the sequence of operations.
Tape
There are two methods of insulation: expanded clay and sheet materials.
Technologies and materials
There are only two types of foundations that need to be insulated: slab and strip. For columnar and pile foundations, we can only talk about thermal insulation of the floor of the first floor and the insulation (basement) - a kind of screen that protects the subfloor. But piles and pillars do not directly insulate.
Plate
The technology for insulating a slab foundation is no different from the thermal insulation of concrete floors on the ground:
- a solid base of compacted soil;
- geomembrane as protection against capillary rise of groundwater;
- crushed stone-sand cushion to improve the bearing capacity of the soil and proper load distribution;
- roll waterproofing;
- sheet insulation (expanded polystyrene or EPS);
- plate.

See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in foundation repair and design.
The Swedes have slightly improved the technology and already at the stage of pouring the base they install a “warm floor” into the slab. In our country it is often done the old fashioned way - in a screed or under the finishing floor covering. Scandinavians are “boring” people and already know in advance where not only the partitions will be located, but also how the furniture will stand (one of the conditions for the correct operation of the “warm floor”). Our people have a different character - they are not only furniture, but also interior walls are often moved from place to place.
Strip foundation
Insulation of this type of base has a wider selection of materials and technologies:
- permanent formwork;
- fastening sheets of foam plastic or extruded polystyrene foam;
- spraying liquid polyurethane foam;
- filling of expanded clay.
Among foundation insulation materials, only one popular thermal insulation material is missing - mineral wool. When saturated with water, any type of water loses its thermal insulation properties. And although it not only easily absorbs, but also easily releases moisture, it is impossible to create conditions for its weathering for the foundation.
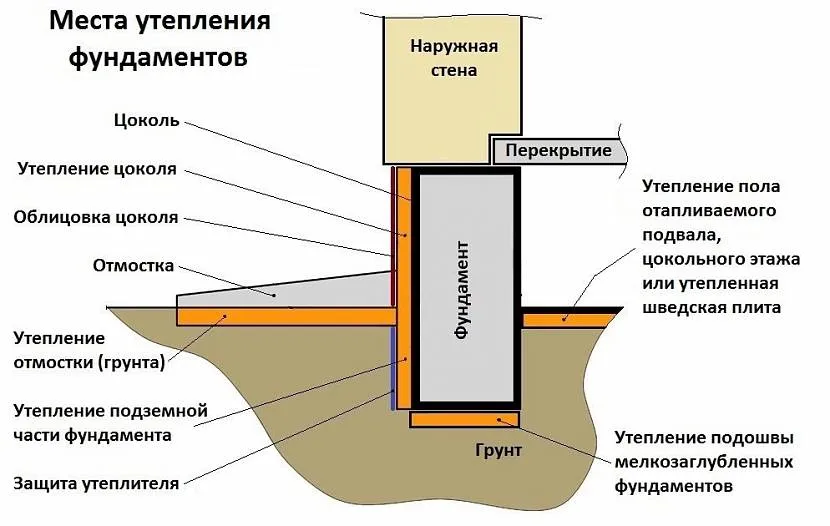
Places for foundation insulation Source anticafe-sandbox.ru
The advantage of external insulation
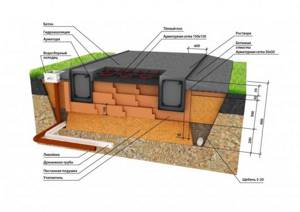
Insulating the foundation of a house
With external insulation, you protect concrete from temperature changes. It does not suffer from cold and microcracks do not appear in it. With internal insulation of basement rooms, only the basement is protected from the cold, and the concrete is exposed to the destructive effects of temperature changes.
Protecting a building with internal insulation helps prevent condensation, which often forms in any basement conditions. But do not forget that the outer side of the foundation in this case will freeze, it will be affected by groundwater - which will negatively affect the ability to withstand loads, durability and strength of the foundation - cracks may form.

Insulation of the foundation outside a wooden house
In addition, during prolonged frosts, deformation of the base may occur. Most often, this drawback is almost unnoticeable, but with frequent temperature changes, the base may collapse. After installing the internal thermal insulation, it is covered with plaster or decorative panels.
It is imperative to insulate the house; this affects not only the level of heat loss, but also the service life of the residential building. Insulating the foundation from the outside with your own hands can significantly increase comfort in living quarters and protect the lower part of the house and walls from damage caused by freezing moisture.
The most important thing in this case is to follow the sequence and rules of work, try to reduce possible disadvantages of the material and use only high-quality products.
VIDEO: All about insulating the foundation of a private house. The cheapest and easiest insulation option
Technologies for insulating strip foundations
Each type of insulation has its own characteristics, which dictate the methods of its application.
Permanent formwork
This is the only method of insulation that is possible only at the stage of construction of a monolithic strip foundation. In fact, this technology can be called “two in one”, when the formwork made of thermal insulating materials remains as part of the structure upon completion of construction. Moreover, permanent formwork solves two problems - how to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside and from the inside.
Structurally, there are two types: block and panel. When pouring a strip foundation, shields are used. The blocks have walls and wide transverse bridges, which reduces the strength of the reinforced concrete base.

Ready-made kits have a set of polymer jumpers that can be used to adjust the width of the foundation Source visualizepicture.com
Requirements for thermal insulating material for the foundation

Insulation of strip foundations
Any base during the warm season is affected by low temperatures and moisture. To protect it, a suitable insulation is selected, which must have the following properties:
- efficiency;
- resistance to temperature changes ranging from -40 to +30 degrees;
- resistance to moisture;
- durable material structure that can withstand pressure;
- high thermal insulation qualities;
- unattractive to insects and rodents.
The ability of the material to withstand open fire does not matter : since it will be located under the surface of the soil, the possibility of such exposure is minimal. Vapor permeability is also not important.
Video description
You can get acquainted with the features of polystyrene foam insulation technology in the video:
Insulation with sprayed polyurethane foam
Among all polymer insulation, sprayed polyurethane foam is the most expensive type. Its advantage is that the thermal insulation layer has no seams, and foamed polyurethane has very good adhesion to all types of building materials.
Application of polyurethane foam to a surface cleared of dirt is very quick. There are two types of materials: two-component and one-component.
In the first case, professional equipment is needed, the work of which is to supply both components under pressure to the working head, where they are mixed and foamed.
Single-component polyurethane foam is produced in liter aerosol cans, and even an untrained beginner can handle them correctly. But this technology is good for a small area of work, or when it is necessary to apply a small layer up to 2 cm thick.

Spraying polyurethane foam is similar to painting with a spray gun, so it is better to cover the cladding of the house. Source ppuspb.ru
If the soils are dry, the water level is low and proper drainage work has been carried out, then waterproofing of the foundation and base need not be carried out - there are no seams, and the water absorption of hardened polyurethane foam is small (no more than 2%). When finishing the base with plaster, reinforcement is not necessary - there are no joints, like with foam plastic slabs, and, therefore, there are no prerequisites for cracks to occur.
In addition to the price, polyurethane foam has one more small drawback, which is a consequence of its advantage - good adhesion. When carrying out work on insulating the basement, it is necessary to protect walls that already have finishing (or do not require it) - this is easier than cleaning off hardened foam.
Insulation with expanded clay
Recently, this bulk material is rarely used for foundation insulation. Its use is limited by two factors: quite high, compared to polymer insulation, water absorption and thermal conductivity.

The thickness of bulk thermal insulation can reach 60 cm Source obustroeno.com
The first indicator lies in the range of 8-20% of the volume. Moreover, such water absorption is typical for “fresh” expanded clay - over time it becomes even higher. For comparison, for ordinary polystyrene it is no more than 4%. Therefore, waterproofing of both the foundation and the entire insulation layer is necessary.
It is impossible to ensure complete “tightness” of expanded clay, and it will take a long time to dry underground, wrapped in film - its use is not recommended in conditions of high seasonal rise of groundwater.
Thermal conductivity also does not meet modern requirements for thermal protection of buildings - 0.07–0.18 (W/m*°C) versus 0.02–0.04 for polyurethane foam, 0.03–0.04 for EPS/EPS. Therefore, the recommended thickness of bulk thermal insulation for our middle latitudes lies in the range of 40–60 cm.
The insulation scheme looks like this:
- dig a trench of the estimated width (or clear the cavity of the pit) to the heel of the foundation;
- lay a waterproofing film over the entire area of the trench - foundation-bottom-wall;
- fill and level expanded clay;
- cover with film on top;
- pour a layer of sand;
- make a blind area.
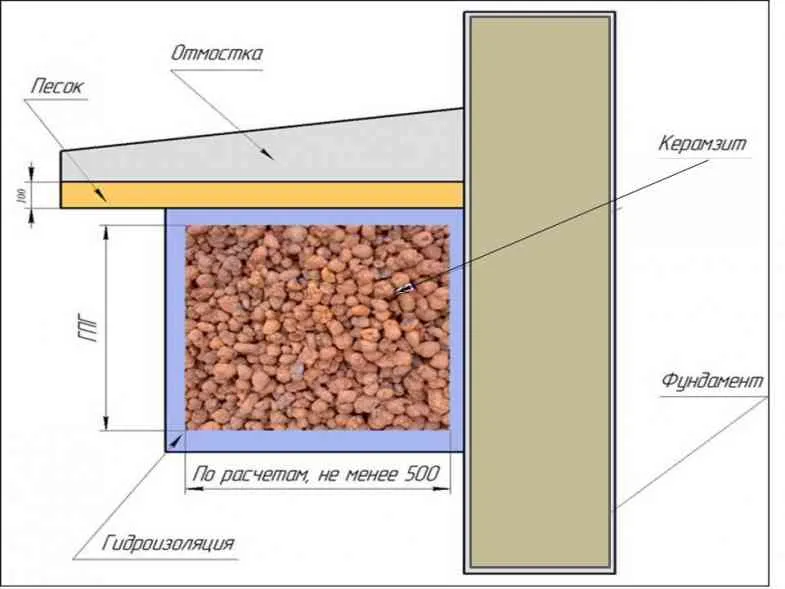
The advantage of expanded clay is its environmental friendliness and low price. Although, taking into account waterproofing and a large volume of materials, the cost of work in the end will not be so low. In addition, the base will have to be insulated using one of the above methods.
What is foamed polyurethane foam, how is it used to insulate the foundation
Do-it-yourself insulation of the foundation of an already built house has recently become popular with the help of foamed polyurethane foam, which is characterized by excellent consumer qualities. The only disadvantage is the need to use a special installation during application, in which the polyol and isocyanate are mixed under pressure, after which the synthesis of the polymer begins. During the reaction, carbon dioxide is formed, which creates bubbles that are separate from each other. Spraying is carried out in a thin layer on a previously cleaned and prepared base.
Before insulating the foundation, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the positive and negative qualities of the material:

Foamed polyurethane foam is used for insulation of already constructed buildings
- Excellent thermal insulation properties, which are improved due to the presence of carbon dioxide bubbles, because the thermal conductivity coefficient of polyurethane foam is slightly lower than that of air.
- Resistant to mold and fungal growth.
- Continuity of the applied layer without gaps, joints, cracks or seams.
- Light weight, which allows the solution to be used on houses with any type of foundation. At the same time, high strength, rigidity and elasticity.
- Easy repair. If a certain area is damaged, it can be easily cleaned and filled with a new portion of polymer.
- Quick application. Spray insulation takes no longer than one day to complete.
In addition to the need to use special means for application, the disadvantages include the high cost of the material and the inability to carry out the work independently.
Foundation preparation: cleaning, leveling, waterproofing
There are two concepts in construction: how to
to do, and how
to
do it. This does not apply to multi-storey construction, and to private buildings either, but when finishing, especially those parts that will be hidden from view, you can save a lot of money without compromising quality and functionality.
Substrate preparation - cleaning. Cleaning can be done at any time, but the best tool for this is a brush with coarse synthetic bristles.
We clean the entire surface with a brush, trying to remove as much dust, sand from cracks and cracks, and adhering dirt as possible. Once you consider the surface to be sufficiently clean, it is a good idea to rinse the concrete with water, ideally from a hose.
We will start from the fact that when installing or pouring a foundation, vertical angles and ideal planes are not always obtained, or rather, they are never obtained. In order to correct the error, it is necessary to level the foundation with cement mortar - plastering.
How to do it:
- We install plaster beacons along the foundation according to the marked planes and angles. This is where the tricks begin - the deep foundation will be filled up, so maintaining vertical angles is impractical (permissible deviations from the vertical are up to 2 cm);
- Prepare cement mortar in a ratio of 1:3 (1 part cement and 3 parts sand) and apply it to the concrete. Depending on the thickness of the layer, we carry out this operation the required number of times;
- Using an even lath (rule), we level the solution along the beacons.
- Leave the foundation until completely dry - at least a week in dry weather.
Note! In order for the insulation to perform its function as best as possible, the foam boards are glued to a flat, even surface, but not necessarily a vertical one. The adhesive mixture should be evenly distributed between the concrete and the foam.

Waterproofing the foundation using the coating method
Our next action will be waterproofing the foundation. The mastics used to protect the base differ in composition and performance characteristics. There are three main types of mastic: bitumen, polymer and combined. Their working qualities are divided into cold and hot.
Hot mastics, mainly bitumen-based, must be heated before use until the required consistency is achieved. Cold - ready to eat straight from the original packaging.
In foundation waterproofing, they mainly use:
- fast-hardening bitumen-emulsion mastic;
- hot or cold rubber bitumen, with the addition of crumb rubber;
- polymer, neutrally reacting to penoplex;
- bitumen-polymer mastic with a large tension reserve.
Waterproofing mastics are applied with a roller, brush or spray. At home, for small volumes, I advise you to apply mastic with a brush. A brush, unlike a roller, creates a layer almost a millimeter thick, so you don’t need to do the second approach.
On a note! The basic rule is that mastic must be applied continuously: one approach – one wall.

Penoplex panel
What and how should you isolate?
The main types of insulation that are used for the walls of a house are not always suitable for the foundation, this is due to the increased humid operating environment.
Some manufacturers specifically produce insulation materials modified for insulating foundations. The most suitable materials for this purpose are:
- Penoplex.
- Polyurethane foam.
- Minvata.
When using the latter, it is necessary to install an additional layer of vapor-proof membrane and ventilation slots.
Penoplex

This is a new insulating material that replaced polystyrene foam, but does not have most of its disadvantages.
Technical characteristics of Penoplex “Foundation”:
- low moisture absorption, less than 0.4% by volume;
- high strength to compressive loads - 0.13 MPa;
- thermal conductivity - not higher than 0.034 W/(m*°K);
- operates in the range - 70 to +75 C;
- sound barrier - 41dB;
- vapor permeability - 0.006 mg/(m.h.Pa);
- material density - 25 kg/m³;
- elasticity - 15 MPa;
- slab dimensions - 585 x 1185 mm;
- thickness from 20 to 100 mm;
- The price of packaging with a thickness of 50 mm is 2035 rubles.
- The price of packaging with a thickness of 100 mm is 2960 rubles.
Penoplex is glued to the surface of the foundation using adhesives that should not contain solvents; it is possible to install the slabs mechanically with the subsequent installation of a facing layer. They are placed on a flat outer waterproof surface.
Laying begins from the bottom, the slabs are laid horizontally, the next row comes with offset seams in a checkerboard pattern. If during installation seams of more than 5 mm are formed, they are filled with polyurethane foam.
For these purposes, experts recommend purchasing slabs with L-shaped edges that tightly overlap each other, preventing the formation of “cold bridges.” Below the soil level, glue is applied at various points around the perimeter and in the center, so that the condensate that will collect between the surface of the foundation and the Penoplex flows down unhindered.
Note! It is prohibited to install insulation on wet waterproofing; it must dry for at least seven days.
Polyurethane foam

Polyurethane foam insulation is the most effective thermal insulator on the market. It is suitable for insulating basements of any type. This material has excellent waterproofing and thermal insulation properties:
- moisture absorption, less than 4% by volume;
- thermal conductivity - not higher than 0.025 W/(m*°K);
- operates in the range -50 to +50 C;
- vapor permeability coefficient 0.015 mg/(m.h.Pa);
- density 20-80 kg/m³;
- flammability class G1 - non-flammable;
- environmentally friendly;
- thickness from 100 mm;
- service life of at least 30 years;
- price 750 rub./m².
Advantages of polyurethane foam for internal thermal protection:
- continuous laying surface, no “cold bridges”;
- high protective properties against heat loss and moisture penetration;
- good adhesion to the foundation surface;
- antibacterial resistance to mold;
- quick application of material to foundation walls;
- self-extinguishing material.
The disadvantages of this material include high cost , the need to have expensive equipment for spraying and experienced performers.
The technology for internal thermal protection of the foundation with polyurethane foam is simple. Using special balloon equipment, a protective substance is sprayed onto the walls under high pressure, resulting in a layer of insulator firmly adhered to the base.
How the process of spraying polyurethane foam (PPU) occurs is shown in the video below:
Expanded clay
Using expanded clay is the most cost-effective option for thermal protection of the base of a house from the inside. The material has exceptional water-repellent characteristics, it removes water, while creating an air cushion that qualitatively protects the floor from cooling, average thermal conductivity from 0.34 W/m³ C.

Thermal insulation of the foundation with expanded clay is carried out on the entire surface or on the formwork installed on the inside of the base. Technology of internal thermal protection of the base with expanded clay:
- Prepare formwork with a height of up to the 1st floor.
- Formwork boards are treated with special antifungal compounds.
- The formwork is strengthened.
- The bottom is covered with a waterproofing film.
- Cover with expanded clay over the entire height of the formwork structure.
On a note . Expanded clay insulation is the most budget-friendly and affordable option. It can be purchased with fractions from 5 to 10 mm, in bags of 0.05 m³ - from 108 rub./bag, in big bags of 1 m³ - from 2100 rub./m³ and in bulk - from 1900 rub./m³.
Styrofoam
This material is also a budget material, but it is very flammable and releases toxic substances when burned. Therefore, it is not recommended for installation in residential premises. If the basement is used for domestic purposes or utility rooms, for example, laundries, it is better not to install this material there.

Technical characteristics of polystyrene foam:
- low moisture absorption, less than 0.1% by volume;
- high compressive strength - from 0.07 to 0.35 MPa;
- thermal conductivity - not higher than 0.04 W/(m*°K);
- vapor permeability coefficient - 0.005 mg/(m.h.Pa);
- density from 15 to 50 kg/m³;
- elasticity - 15 MPa;
- dimensions - 1200 x 1200mm;
- thickness from 30 to 100mm;
- price 50 mm thick, 250 rub. for 1 sheet;
- price 100 mm thick, 500 rub. for 1 sheet.
Minvata

Mineral wool is the most preferred material for internal insulation , since it is absolutely non-flammable, is a cheap insulator and has high thermal resistance.
The disadvantages of the material include its high hygroscopicity and loose structure, due to which its installation requires an additional special vapor-proof layer and lathing to fix the slabs and create ventilation gaps so that moisture can be easily removed without entering the insulator. If it gets wet, it can no longer be dried, the work will have to be redone from “0”.

Characteristics of mineral wool:
- thermal conductivity - not higher than 0.06 W/(m*°K);
- strength from 0.08-0.6 kg/cm²;
- density from 35 to 100 kg/m³;
- water absorption up to 30%;
- dimensions 0.6 m²;
- thickness from 30 to 100 mm;
- vapor permeability 1;
- sound absorption - 0.7;
- fire resistance - non-flammable material;
- service life over 50 years;
- price Knauf TeploKnauf 100 mm, 3 m² - 720 rubles;
- price Rockwool Standard 100 mm, 2.4 m² - 650 rubles;
- price Isover Slab 100 mm, 2.88 m 2 - 670 rub.;
- price TechnoNIKOL 100 mm, 4.32 m 2 - 890 rub.
Features of the use of thermal insulation for foundations
Insulation is performed only for two types of foundations - strip and slab. Speaking about thermal insulation of pile and columnar structures, we mean installing insulation on the lower surface of the slab, which is the floor of the first floor, and insulating the foundation base from the outside.
There is simply no point in insulating support pillars and piles. In these places there is practically no temperature difference between the surface of the building structure and the environment.
Application of polyurethane foam
For professional performance of thermal insulation work, a two-component polyurethane foam composition and special equipment for mixing and spraying the finished mixture are used.

Before starting work, the surface must be cleaned of old plaster layers and large contaminants. There should be no grease stains or loosely held layers of building materials on it. Thorough cleaning and priming are not required if the surface is dense and durable.

Expanded polystyrene boards
Speaking about the installation of polystyrene foam boards, first of all you need to study:
- the need to install a waterproofing layer;
- method of fastening slabs to the vertical surface of the foundation;
- protection of the polymer from negative environmental influences.
Rolled materials impregnated with bitumen are used as hydraulic insulation. They paste over the surface using hot bitumen.
The use of primers or other liquid materials is not recommended, since they will not be able to ensure the normal fastening of the heat-insulating material to the surface.
Initially, PPS boards are fixed to the surface using special glue. When installing adjacent elements, it is necessary to provide locking connections to seal the seams. The final fastening of the slabs is carried out using special plastic nails with large round heads (fungi).
Slabs made of ordinary EPS, which is manufactured using a thermal method, are subject to protection from negative influences. This is due to the presence of open pores on the surface of the material. The treatment can be done with a cement or stable adhesive solution, which is applied after installation of the slabs.
Expanded clay backfill
The foundation wall must be covered with a waterproofing layer of rolled materials. To insulate the strip foundation with expanded clay, a trench 40-60 cm wide is dug along the perimeter of the building to the depth of soil freezing.
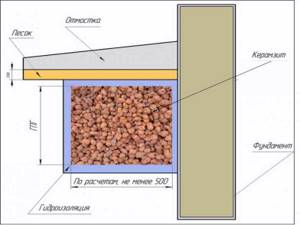
A sand cushion 5-7 cm thick is poured onto its bottom. After this, the trench is completely covered with expanded clay granules to the level of the blind area and compacted well. The blind area is poured directly onto the expanded clay layer.
For slab foundations, a layer of expanded clay can be used as a support cushion instead of sand. The granules are poured into an even layer 70-100 mm thick, slabs of the main heat insulator are laid on them, onto which concrete is then poured.

Features of insulation of wooden houses
Owners of wooden houses often complain that the floor freezes in winter. A frozen foundation transmits its low temperature to the entire house, greatly cooling it. Not only can the floor freeze, but heating, sewer and water supply pipes can also be damaged. Wood, no matter how reliable it may seem, is susceptible to all sorts of natural factors. It needs protection no less than other materials.
Wooden houses are usually lighter than stone ones. They are erected on shallow foundations, and sometimes on poles or on piles, which, at first glance, greatly simplifies the work of insulating them.
However, when insulating such houses, it is also important to take into account the depth of soil freezing in a specific geographic area. The insulation circuit and insulation must be made at a depth greater than the freezing depth. Only in this case will there be an effect from the work done.
Decorative finishing of the foundation
After gluing the penoplex, its surface is reinforced with a mesh - fiberglass (more often) or metal (less often). This technology prevents cracking and improves the adhesion of the finishing layer to the insulation.
- We apply a layer of glue on the insulation, the area equal to the mesh sections, 2-3 mm thick.
- We embed the mesh in the glue and remove the excess with a spatula - the mesh should be completely covered with glue.
- Apply glue to the adjacent area, catching the previous one, and glue the mesh in the same way. The edge of the strip should overlap the previous piece.
- After drying, we clean the surface with sandpaper or a coarse mesh for grouting the putty.
After drying, apply a couple of leveling layers. After about a day (depending on weather conditions), the foundation can be improved: plastering, puttying or gluing ceramic tiles.
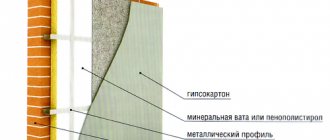
Metal profile installation technology
- secure the base profile with dowels or with an adhesive solution;
- on the corner sections of the building, install a special profile (support), leaving a small gap of three millimeters. Secure the parts with connecting elements;
- use pads to level the structure - this advice is relevant for significant uneven walls;
- Fill the gap between the guides and the wall surface with mounting foam.
Recommendations
- fasten the metal rail “conscientiously”, the quality of the work performed and the durability of the structure depend on this. If you fix the guide at only two points, then over time, under the influence of temperature, it will begin to deform, and corrosion of the material will occur;
- The slats must be fixed using special dowels. Spacer fasteners are installed in the longitudinal holes of the guide;
- control the horizontalness of the installed rail using a building level;
- When installing corner slats, the material is cut at a certain angle so that a gap remains at the joints. The gap will eliminate the possibility of deformation of the rack structure.
Having installed a reliable metal structure, you can proceed directly to insulating the base.
First of all, the insulated surface is cleaned of construction dust and dirt, and then it is disinfected. The walls should not have significant differences, otherwise it will affect the quality of the work performed. To improve adhesion, the surface is treated with a primer. When the walls are dry, you can begin laying foam boards.
When choosing an adhesive for fixing insulation, pay attention to the instructions - the instructions should indicate what materials it is intended for. The work is simplified by the fact that you have already installed the metal profile and now you do not have to adjust the slabs and align them horizontally
Laying the insulation accordingly begins from the bottom batten
The work is simplified by the fact that you have already installed the metal profile and now you do not have to adjust the slabs and align them horizontally. The installation of insulation accordingly begins from the bottom batten.
For extra reliability, it is recommended to use additional fasteners in conjunction with the polymer adhesive. They, in turn, are fixed directly to the wall surface through insulating material. The material is fixed at five points - in the corners and in the center. Plastic fasteners are inserted into pre-drilled holes with a hammer drill. At the same stage, reinforcement of the layer is performed. For these purposes, you can use a mesh made of metal, plastic, or fiberglass. The first option, according to builders, is preferable. The mesh is buried in an adhesive solution previously applied to the penoplex.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=tbLUX4OCRq0
Before proceeding to the next step, you need to make sure that the glue has dried well and strengthened. Then the wall surface is primed. The composition will ensure better adhesion of subsequent materials.
The next layer is plaster. Before facing work, the insulated wall is re-primed.
Which insulation to choose: inside or outside?
Definitely, it is better to insulate the foundation from the outside. In this matter, builders show enviable solidarity and give weighty arguments in defense of this method.
The outside is most exposed to weather conditions. When moisture gets into the micropores of the foundation material, it freezes, expands and leads to the formation of microcracks.
Repeated processes of freezing and freezing, temperature changes gradually lead to destruction of concrete, and a threat to house construction arises.
External insulation can reduce heat loss to a greater extent than internal insulation, the cost of heating the house is reduced, and it also improves the waterproofing of the basement and foundation.
Method selection criteria
There are quite a lot of offers on the construction market for building materials for thermal insulation of foundations, but none of them are universal. The contractor will need to carefully calculate and select a thermal insulation material for a specific foundation in order to achieve the desired effect.
Fundamental criteria for selecting heat-insulating material for the foundation of a house:

Show the stability of the material, since it will work throughout the year in conditions with changing soil pressure, both compressive and tensile forces.- Have high hydraulic resistance so as not to absorb moisture from the air.
- Have low thermal permeability.
- Have low vapor permeability.
- Have high reliability.
- Have high durability.
- Have a low price.
- Be available on the building materials market.
Advice . When choosing an option for insulating a basement from the inside, you will also need to take into account the structure of the house, the material of the walls and foundation, the presence of external insulation of the walls and base, the presence of ventilation and heating systems in the basement, and the need for external finishing.
Choosing insulation for the base
Among the wide variety of modern insulation materials, only slab and sprayed polymer-based materials fully meet the above requirements. Let's take a closer look at their characteristics.
Expanded polystyrene foam

Expanded polystyrene foam

Insulation with polystyrene foam
Foamed polystyrene (foam plastic) has been used as insulation for a long time, and still does not lose its position. It retains heat excellently, does not accumulate moisture, is easy to cut and is lightweight, which allows installation without much effort. In addition, polystyrene foam has the lowest cost among other polymer insulation materials, and this is a strong argument in its favor when thermally insulating large areas or on a limited budget.

Base insulation with polystyrene foam
To insulate the base, it is necessary to choose foam plastic of the PSB-S 25 or PSB-S 35 brand, which is characterized by increased density and resistance to mechanical loads. The thickness of the slabs varies between 20-100 mm, and depending on climatic conditions, the insulation can be laid in 1 or 2 layers. The material can withstand temperature changes from -60°C to +80°C without changing its characteristics, so it is not afraid of the most severe frosts and summer heat. The service life, on average, is 25 years, and with high-quality arrangement of the thermal insulation cake, it is 10 years more.
Characteristics of foam plastic
Despite all the advantages, foam plastic also has disadvantages: it has low bending strength, that is, it is quite fragile and is often damaged by rodents.

Mice gnawed through the insulation
In addition, in the absence of waterproofing, moisture penetrates into the upper layers of the material and, freezing, causes the slabs to crumble.
Extruded polystyrene foam

Extruded polystyrene foam
EPPS has a denser structure than polystyrene foam, and its cell size does not exceed 1 mm. This results in almost zero water absorption and greater mechanical strength. Extruded polystyrene foam is also more resistant to chemical attack, microorganisms, and shrinkage deformations. Due to low vapor permeability, this insulation is not recommended for use on wooden surfaces, but it is ideal for thermal insulation of plinths.

Penoplex
EPPS is in high demand; the most popular are insulation brands Penoplex, TechnoNIKOL XPS, Styrofoam, TEPLEX, URSA XPS. They are produced in slabs of various thicknesses and densities, standard sizes are 1200x600 mm and 2400x600 mm. The material can withstand temperatures from -50 to +75°C without loss of characteristics, is easy to install and lasts for about 50 years, provided the installation technology is followed.

TechnoNIKOL extruded polystyrene foam

Thermal insulation Ursa XPS
The disadvantages include the flammability of the insulation - almost all brands of EPS have flammability classes G3 and G4. When melted, the material releases toxic substances.

Combustion of penoplex
Another disadvantage is the high cost. However, properly executed thermal insulation quickly pays for all costs when the heating season begins.
Using penoplex
Penoplex material is more advanced than polystyrene foam. Insulating the foundation with penoplex prevents its deformation, the building will last longer.
Penoplex has a closed-cell structure, so it is not susceptible to the destructive effects of water. Other important advantages of the material are its strength and low thermal conductivity.
How is installation carried out?
Penoplex can be installed only a week after waterproofing, the methods of which were described above.
Penoplex is produced in the form of slabs with grooves of a certain configuration. These grooves ensure a very tight fit of the plates to each other without gaps.
Fastening is carried out with special adhesives. You need to choose only those compounds that are not capable of destroying the insulation. The glue is applied pointwise, gradually treating small surface areas. The slab is applied to the foundation and pressed for 40 seconds. After gluing the slabs, proceed to the next section. The process continues until the entire surface of the base of the building is insulated.
The slabs must be glued so that they protrude 35–50 cm upward. After installation is completed, the resulting voids are filled with non-heaving materials. At the end, thermal insulation of the soil is carried out around the perimeter.