Legislation
- Federal Law No. 190-FZ dated July 27, 2010 “On Heat Supply” regulates relations in the field of heating residential buildings.
- Federal Law of December 7, 2011 No. 416-FZ “On Water Supply and Sanitation” in Article 7 of Chapter 3 contains general rules for heat supply of apartment buildings.
- Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011 No. 354 “On the provision of utility services to owners and users of residential premises in apartment buildings” in Appendix 1 establishes requirements for the quality of heat provision (permissible breaks, conditions and procedure for changing fees, air temperature standards).
- GOST R 51617-2000 “Housing and communal services. General technical conditions" regulates the provision of standard levels of air heat.
- SP 60.13330 SNiP 41-01-2003 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”.
When heat depends on batteries
The heat supply is regulated by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 354 of May 6, 2011. According to this document, the start and end of heating is tied to the ambient temperature. The central heating radiators are turned on when the daily average drops 8 degrees above zero and lasts for five days. On the main territory of Russia this occurs by mid-October.
Battery under the window
Water leaves radiators when the average outdoor temperature reaches +8 degrees Celsius. And it remains so for five days. Battery shutdown times vary according to regulations.
In warm years this occurs at the end of April.
If the temperature is low, then according to the standards, heating of residential and industrial premises is maintained until mid-May. Only during this period of time should we talk about temperature standards for water in radiators. The rest of the time, fighting the cold is the job of the residents.
Heating season duration
Only residents of houses with an autonomous heating system can decide independently when to turn on the batteries. All others connected to a centralized heating system must rely on the decision of local authorities.
Of course, they cannot set this up as precisely as the residents of one house - it’s not for nothing that every spring and autumn all news sites are filled with articles “When will the heating finally be turned on/off?”
The specific timing in each region depends on weather conditions: according to standards, during the 2018-2019 heating season, the average daily street temperature must be below 8°C for 5 days in a row. The heating can be turned off again if the temperature remains above 8°C for 5 days.
In addition, there is also a small “emergency reserve” for heating shutdown standards in winter. It can be turned off, remaining within the current standards, for a period of no more than 24 hours in total, within one month. The heating can be turned off at a time for a period of 4 to 16 hours, depending on the air temperature in the living quarters - if the apartment is +12°C, for no more than 16 hours, and if +8 - up to 4 hours.
Normal water temperature
It was once believed that water for central heating should be heated to 100 degrees on the outlet and 60 degrees on the return flow. At that time there was no good equipment to control the heating of water for central heating. This approach is not cost effective. Rising fuel costs increase utility bills for homeowners.

Standard radiators
Modern equipment allows the use of low-temperature heating of apartments according to standards. This means that the water temperature standards in heating radiators are not constant. They become attached to external factors. The following are taken into account:
- Heat loss from buildings. It is theoretically possible to build a house without heat loss. To do this, you will need to cover it with insulation of at least a meter thick. In fact, 150 mm of high-performance insulation is considered good thermal insulation. But heat loss will still occur through the walls, floor and roof. The higher these losses, the more heating the home needs to create a comfortable environment.
- Heat source indicators. If the boiler does not meet the design requirements, then more heating of water for heating is required.
- Heat transfer from the metal from which pipes and batteries are made. If the metal of the pipes has low thermal conductivity, this will prevent heat loss during transportation from the heat source. Batteries, on the contrary, must have high thermal conductivity in order to transfer heat to the maximum. Cast iron batteries have lower thermal conductivity compared to aluminum and bimetallic ones. For equal heating, the water temperature must be higher in cast iron.

When assessing the comfort of housing, the temperature in the heating system is not the main indicator.
Temperature standards refer to the state of the apartment's atmosphere.
Prevention and care of radiators in summer
After the completion of the heating season, the pipeline must be tested (pressured) with increased hydraulic pressure. This is done in order to identify weak points and repair areas where ruptures or coolant leaks have occurred. The house main is subject to periodic internal flushing by utility services. Water is supplied to the system along with compressed air under pressure. A temporary break is made on the return line (unwinding of one of the connections) to drain dirty water through a hose or hose.
Dust and dirt accumulate on the outer surface of the batteries and on their ribs, which must be washed off in the summer with a cloth moistened with soapy water. Once warm, the cleaned surfaces can be coated with fresh paint. This will make them dry faster. Make the paint layer thin, otherwise it will crack later.
To avoid damage, do not use the equipment as supports or tie clotheslines to the risers. Read about warm floors on a wooden floor on our website.
Pyrometer and how to work with it
A pyrometer is an infrared thermometer. It determines temperature by electromagnetic radiation. An accurate engineering device allows you to quickly measure the temperature of an object located at a distance not exceeding three meters from the device.
Heating standards
But even this excellent equipment is capable of producing errors, which is what negligent utility workers take advantage of. When measuring temperature, the device readings will be erroneous if:
- in a relatively small room there are many objects made from various materials;
- there is high humidity or a lot of dust in the room;
- the temperature of the device differs significantly from the room temperature;
- the distance to the measured object exceeds 3 m;
- the room is very large.
How to measure coolant temperature?
The temperature of the coolant in the heating system provides for the following standards:
- Hot water in the tap should be available all year round and its temperature should be from +50°C to +70°C;
- During the heating season, heating devices are filled with this liquid.
In order to find out the temperature of the heating radiator, you need to open the tap and place a container with a thermometer. At this time, the temperature may rise by 4°C.
When a problem arises in this matter, it is tedious to file a complaint with the Housing Office, but if the batteries are airy, the complaint is written to the DEZ. A specialist should come within a week to fix everything.
There are several more ways to measure the temperature of heating radiators in an apartment building:
- Using a thermometer, the temperature of the heating pipes or the radiators themselves is measured; 1 -2°C must be added to the result obtained;
- To measure data more accurately, you need to buy a thermometer-pyrometer that can measure temperature with an accuracy of 0.5°C;
- You need to take an alcohol thermometer and place it on a certain place on the radiator, then wrap it with tape and wrap it with any thermal insulator (foam rubber, flywheel). Now it will play the role of a permanent temperature meter of the heating system;
- In the case when you have an electronic measuring device at hand, for example, a multimeter, with a temperature measurement function, a wire with a thermocouple is wound to the radiator, and the temperature of the coolant is measured.
If you are not satisfied with the temperature of your heating devices or any other parameters of the coolant, then after filing a complaint a commission will come to you whose task will be to measure the temperature of the circulating fluid in the heating system.
They must strictly act in accordance with paragraph 4, which is specified in the “Control Methods” of GOST 30494−96, and the device must have registration, as well as verification and quality certificates. The measurement range should range from +5 to +40°C, the permissible error should be within 0.1°C.
Key methods to combat leaks
If it is not possible to immediately call an emergency team, you can use the following techniques:
- self-tapping bolt,
- plaster-cement bandage,
- sealant,
- rubber gasket and clamp,
- fabric with water- and heat-resistant adhesive impregnation,
- welding

The easiest way to eliminate a leak in a cast iron battery is to fasten a self-tapping screw in an identified hole. Next, you need to take care of installing a new radiator as quickly as possible.
Hermetic seal
You can purchase polymer or powder based sealant at a hardware store. In air, this composition polymerizes, with its help you can gain time to organize a full repair. Two-component variations harden after mixing all components.
Cold weld is a two-part sealant sold in compact tubes, usually containing epoxy resin and metal powder. Before using cold welding, the area must be thoroughly cleaned and degreased. It is necessary to remove paint and rust, preferably with allowances to increase the accessible contact area. Sharpening is easiest done using a stone, which is usually used for sharpening knives. The instructions on the tube describe in detail the method of use recommended by the manufacturer; please note that some varieties cannot be used in wet conditions - water can become an obstacle to full polymerization.
Manufacturers offer liquid welding and thick welding, with a consistency reminiscent of plasticine. Before use, you need to knead both components in your hands so that the polymer acquires a uniform color without inclusions, then it is applied in a thick layer to the defective area. It is advisable not to introduce water into the system until the composition is completely polymerized. When properly applied, after a few hours a durable coating is formed that prevents the release of moisture.
Clamp and gasket
This technique is applicable to repair damage at the junction of the heating device and the main pipe. You can use a piece of a bicycle inner tube as a rubber band; it is secured with a clamp or wire.
What does temperature depend on?
There are several other factors that influence indoor temperature:
- If the air temperature outside is low, it will be lower indoors;
- Wind speed also has an impact on temperature. The stronger the wind loads, the greater the heat loss will be through windows and entrance doors;
- Tightness of sealing joints in the walls of the house. For example, metal-plastic windows and insulation of facade walls can significantly affect the temperature inside the home.
Everything described above is undoubtedly important. But the main factor that greatly influences the temperature in the rooms is the temperature of the heating radiators themselves. Typically, heating batteries powered from a central system have a temperature of 70 - 90°C.
It is known that the required temperature inside the room cannot be achieved by this factor alone, taking into account the fact that different rooms should have different temperature conditions due to their different purposes.
The temperature inside the room is also influenced by how intense the movement of people inside it is. Temperatures will be higher where people move the least.
This is the basis of heat distribution. As evidence, in sports facilities where people are constantly moving, the temperature is maintained at 18°C, since maintaining a higher temperature is not advisable.
Factors influencing the temperature of radiators:
- Outside temperature;
- Type of heating system. Standard for a one-pipe system: +105 °C, for a two-pipe system: +95 °C. The difference between supply and return should not be more than 105 - 70 °C and 95-70 °C, respectively;
- Directions for the flow of coolant into the batteries. In the case where the wiring is from above, the difference will be: + 20 °C, from below - +30 °C;
- Type of heating device. Radiators and convectors differ in heat transfer, which means that the temperature regime is also different. Convectors have lower heat transfer than radiators.
It is naturally clear to everyone that, regardless of whether it is a convector or a radiator, heat transfer will directly depend on the temperature outside. At zero street temperature, the heat transfer rate of radiators should vary within 40-45 °C supply and 30-35 °C return. For convectors, these characteristics are as follows: 41-49 °C supply and 36-40 °C return.
When the thermometer drops to -20 °C, these characteristics will be as follows: for radiators - supply 67-77 °C, return 53-55 °C, for convectors - supply 68-79 °C and return 55-57 °C. But when the thermometer reaches -40 °C, both radiators and convectors will have the same characteristics: supply 95-105 °C, return temperature 70 °C.
Battery sounds like clicking sounds
What else causes batteries to make noise, making clicking sounds and how to remove them at home? Usually the problem manifests itself when heating radiators warm up or cool down. The reason is uneven heating/cooling, as the metal expands and contracts accordingly.
To eliminate clicks and get rid of the causes of noise, try placing something between the brackets and batteries - rubber spacers up to 2-3 mm thick are enough. In the case of inexpensive bimetallic radiators, similar sounds arise due to their internal design. Their structure differs from other batteries, since two types of metals are used at once. When they do not fit well together, the expansion causes clicking and knocking noises.
If the problem cannot be fixed on your own, it is better to turn to professionals to avoid trouble. San Remo company technicians will find out and eliminate the cause of noise in batteries inexpensively and in a short time. And if necessary, they will install a heating radiator with high quality.
By clicking the “We’ll call you back” button, I accept the terms of the Personal Data Privacy Policy and give my consent to the processing of my personal data.
How are standards calculated?
As described above, the temperature graph is directly affected by the outside air temperature. Accordingly, the lower the temperature outside, the greater the heat loss. The question arises, what indicators should be used for the calculation?
This indicator can be found in regulatory documents. It is based on the average temperature of the five coldest days of the year. A period of 50 years is taken into account and the 8 coldest winters are selected. For what reasons is the average daily temperature calculated in this way?
Firstly, thanks to this, it is possible to be prepared in winter for low temperatures, which occur once every few years. In addition, taking these indicators into account, you can significantly save on costs during the creation of heating systems. In the case of mass construction, this amount will be very significant.
Accordingly, the temperature of the coolant will directly affect the temperature of the heated room.
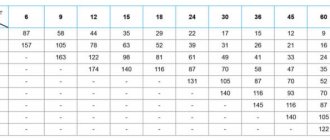
Based on the street temperature indicators, the coolant temperature is calculated and has the following values:
Using the data from the table, you can easily determine the temperature of the coolant in the heating system of a panel house. You just need to use a thermometer to measure the temperature of the coolant during drainage from the batteries. The data in the 5th and 6th columns are the supply indicators, the 7th column is the return indicator. Please note that the first three columns indicate the temperature of the coolant at the inlet, i.e. excluding losses on heating mains.
The basis for recalculation of heating costs may be a discrepancy between the standard and actual coolant temperatures. In addition, you can install a meter, but all apartments in your house must be connected to central heating. These devices must be checked every year.
Thus, comfortable living in a high-rise apartment, in a country house or in a cottage directly depends on the arrangement of the heating system in the room. To do this, you need to know the most favorable temperature of the coolant in order to create as much comfort as possible in your home.
All special parameters are in various regulatory documents; if, for some reason, they are violated or not met, the Housing Office must consider the complaint or application and carry out appropriate control of all work to correct this misunderstanding.
Reasons for interruption of heat transfer
It is worth noting that at the very beginning of the heating season, the temperature standards in the heating radiators are constantly observed and the heating works all the time. There is a heating system temperature schedule that is usually followed. In some cases, boiler houses may interrupt the heat supply to apartments.
By law, interruptions in the operation of the heating system cannot exceed the following values:
- 24 hours – if the minimum temperature in the apartment is 12 ℃;
- 8 hours – provided that the temperature in the apartment fluctuates between 10 ℃ and 12 ℃;
- 4 hours – if the room temperature drops to 8 ℃ or even lower.

All intervals given are based on a monthly basis. If these numbers are exceeded, residents have the right to file a complaint with the appropriate authorities.
Adjustment features
The parameters of heating routes are the responsibility of the management of thermal power plants and heating networks. At the same time, housing office employees are responsible for the network parameters inside the building. Mostly, residents' complaints about the cold concern deviations to the lower side. Much less common are situations where measurements inside thermal units indicate an increased return temperature.
There are several ways to normalize system parameters that you can implement yourself:
- Reaming the nozzle. The problem of lowering the temperature of the liquid in the return can be solved by expanding the elevator nozzle. To do this, you need to close all the gates and valves on the elevator. After this, the module is removed, its nozzle is pulled out and drilled out 0.5-1 mm. After assembling the elevator, it is started to bleed air in the reverse order. It is recommended to replace the paronite seals on the flanges with rubber ones: they are made to the size of the flange from a car inner tube.
- Silence the suction. In extreme cases (during the onset of extremely low frosts), the nozzle can be completely removed. In this case, there is a danger that the suction will begin to act as a jumper: to prevent this, it is turned off. For this, a steel pancake with a thickness of 1 mm is used. This method is emergency, because this can cause a jump in battery temperature to +130 degrees.
- Difference control. A temporary way to solve the problem of temperature rise is to adjust the differential with an elevator valve. To do this, it is necessary to redirect the DHW to the supply pipe: the return pipe is equipped with a pressure gauge. The inlet valve of the return pipeline is completely closed. Next, you need to open the valve little by little, constantly checking your actions with the readings of the pressure gauge.
A simply closed valve can cause the circuit to stop and defrost. A reduction in the difference is achieved due to an increase in return pressure (0.2 atm/day). The temperature in the system must be checked every day: it must correspond to the heating temperature schedule.
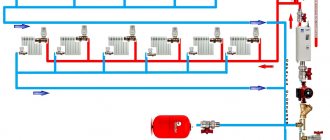
How does a heating regulator work?
A regulator is a device that provides automatic control and adjustment of the temperature parameters of the coolant circulating in the heating system.
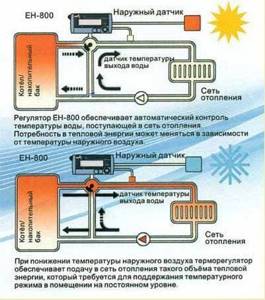
It consists of the following nodes and elements:
- Computing and switching unit;
- Actuator on the coolant supply line;
- An actuator for mixing water from the return line (sometimes a three-way valve is used and then they are combined);
- Boost pump on the “cold bypass” line (not always);
- Booster pump on the supply line;
- Shut-off fittings and valves;
- Coolant supply sensor;
- Return sensor;
- Outside air temperature sensor;
- Sensor (sensors in several places) room temperature;
The last two positions can be used either together or instead of each other, depending on how the heating schedule is set.
Now let's figure out how the control processes actually occur, how the regulator works.
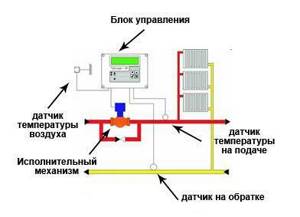
Main elements of the temperature control system
The coolant temperature at the outlet of the heating system (return) depends on the volume of water passing through it, since the load is relatively constant. Therefore, the regulator, covering the water supply, increases the difference between the supply and return to the required value (sensors are embedded in these pipelines), to the required value.
If, on the contrary, it is necessary to increase the flow, then a booster pump is installed into the heating system, which is also controlled by the regulator. To lower the temperature of the incoming flow, the so-called “cold bypass” is used - part of the water circulated through the system is again sent to the inlet.
Thus, by redistributing flows depending on the data collected by the sensors, the regulator ensures a strict temperature schedule for the heating system.

One of the Vailant regulator block models
Often the heating controller is combined with a DHW controller using one computing unit. The hot water regulator is much simpler in terms of control and actuators. Using a sensor on the hot water supply line, the passage of coolant through the boiler is adjusted, and the stable 50 degrees required by the standard is ensured.
Temperature graph of coolant supply to the heating system
Any autonomous heating system has the same operating principle - the carrier is supplied through pipes to heat exchangers (radiators, heated floors), and after heat is transferred through batteries, branches of heated floors, the cooled water is sent through the return line to the heating equipment (boiler using various types of fuel), where after heating returns to the circuit again.
When heating buildings, a slightly different principle is used - the cooled carrier from the return flow enters the elevator unit, where it is mixed with hot water (steam) of the thermal power plant, after which the liquid at an average temperature is sent to the heating circuit.
To ensure that when heating residential buildings there is no discrepancy between the external ambient temperature and the internal one, leading to too cold or hot an atmosphere in the apartments, the heating networks provide a function for regulating the parameters of the coolant. This can be done in three ways:
- Quantitative, where heat transfer is regulated by changing the volume of water passing through the pipes per unit time; with this method, the supply is controlled by an electric pump built into the heat pipe.
- Qualitative - with this option, the maximum temperature of the coolant is regulated at thermal power plants and in boiler rooms, as well as in electric transformer substations and central heating substations.
- Combined - simultaneous change in the volume and temperature characteristics of the coolant.
Typically, several buildings are connected to one heat supply line; for high-quality weather-dependent automation control, the following methods are used:
- Pressure regulators are installed in the main line, setting them to the required pressure value.
- Automatic balancing valves with nipples for changing pressure are used in the heat pipeline.
- The pressure is adjusted manually using balancing valves while monitoring the return temperatures.
- The supply volume is controlled using a special type of shut-off valves (valves).
- It uses adjustment by washer - throttle diaphragms on the supply and return heat pipelines, in which the flow area of the channel is changed.
Maximum battery heating level
But the maximum standard water temperature in central heating radiators is prescribed in SNiP 41-01-2003 “Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”.
According to this document, the standards are as follows:
- the temperature maximum for water in apartment radiators is 95 ℃ with a two-pipe heating distribution;
- for single-pipe wiring, the maximum temperature is 115 ℃;
- The recommended heating value for the coolant is in the range of 85-90 ℃, since when it reaches 100 ℃, water boils, and to prevent this, special substances are added to it.

It is worth noting that at the maximum threshold of the normal water temperature in the heating battery of 115 ℃, they work with increased load and fail quite quickly. Therefore, operating the equipment in this mode is not recommended.
Devices
The most convenient and reliable is a portable infrared pyrometer with an accuracy class of 0.5. It takes readings remotely. That is, it is enough to point the bell at the surface to measure and record the value.
It is important that all measuring instruments, the readings of which will be used for complaints to government authorities and legal proceedings, must be operational and accurate. This can be confirmed by having them verified once a year by an accredited organization.
Thermometer
Without a pyrometer, you can check the heat transfer with a regular thermometer. To do this, you need to attach it with a flask to the battery, secure it with tape, and wrap it with heat-insulating material.
Calculation of the optimal temperature of the heating device
The most important thing is that the most comfortable temperature for human existence is +37°C.
When choosing a radiator, you need to calculate whether the thermal power of the device is enough to heat the room. There is a special formula for this:
S*h*41:42,
- where S is the area of the room;
- h – room height;
- 41 – minimum power per 1 cubic m S;
- 42 – nominal thermal conductivity of one section according to the passport.
Please note that a radiator placed under a window in a deep niche will produce almost 10% less heat. A decorative box will take 15-20%.
When you use a radiator to maintain the desired temperature in a room, you have two options: you can use small radiators and increase the water temperature in them (high temperature heating) or install a large radiator, but the surface temperature will not be as high (low temperature heating) .
With high temperature heating, radiators are very hot and can cause burns if you touch them. In addition, at a high temperature of the radiator, the decomposition of dust settled on it may begin, which will then be inhaled by people.
When using low temperature heating, the appliances are slightly warm, but the room is still warm. In addition, this method is more economical and safe.
Cast iron radiators

The average heat output of a separate section of a radiator made of this material ranges from 130 to 170 W, due to the thick walls and large mass of the device. Therefore, it takes a lot of time to warm up the room. Although this also has the opposite advantage - high inertia ensures long-term retention of heat in the radiator after the boiler is turned off.
The coolant temperature in it is 85-90 °C
Aluminum radiators

This material is lightweight, easily heats up and has good heat dissipation from 170 to 210 watts/section. However, it is susceptible to the negative effects of other metals and may not be installed in every system.
The operating temperature of the coolant in the heating system with this radiator is 70°C
Steel radiators

The material has even lower thermal conductivity. But due to the increase in surface area with partitions and ribs, it still heats well. Heat output from 270 W is 6.7 kW. However, this is the power of the entire radiator, and not of its individual segment. The final temperature depends on the dimensions of the heater and the number of fins and plates in its design.
The operating temperature of the coolant in the heating system with this radiator is also 70°C
So which one is better?
It will probably be more profitable to install equipment with a combination of the properties of an aluminum and steel battery - a bimetallic radiator. It will cost you more, but it will also last longer.
The advantage of such devices is obvious: if aluminum can withstand the temperature of the coolant in the heating system only up to 110°C, then bimetal can withstand up to 130°C.
Heat transfer, on the contrary, is worse than that of aluminum, but better than that of other radiators: from 150 to 190 W.
Warm floor

Another way to create a comfortable temperature environment in the room. What are its advantages and disadvantages over conventional radiators?
From a school physics course we know about the phenomenon of convection. Cold air tends to fall, and when it warms up, it rises. That’s why, by the way, my feet get cold. A warm floor changes everything - the heated air below is forced to rise upward.
This coating has a high heat output (depending on the area of the heating element).
The floor temperature is also specified in SNiP-e (“Building Norms and Rules”).
In a permanent home it should not be more than +26°C.
In rooms for temporary stay of people up to +31°C.
In institutions where children are taught, the temperature should not exceed +24°C.
The operating temperature of the coolant in the underfloor heating system is 45-50 °C. Surface temperature averages 26-28°C