In order to comfortably survive the cold season, you need to worry about creating a high-quality heating system in advance. If you live in a private house, you have an autonomous network, and if you live in an apartment complex, you have a centralized one. Whatever it is, it is still necessary that the temperature of the batteries during the heating season is within the limits established by SNiP. In this article we will analyze the coolant temperature for different heating systems.
The heating season begins when the average outside temperature per day drops below +8°C and stops, respectively, when it rises above this mark, but it also lasts for up to 5 days.
Standards. What temperature should be in the rooms (minimum):
- In the living room +18°C;
- In the corner room +20°C;
- In the kitchen +18°C;
- In the bathroom +25°C;
- In corridors and stairwells +16°C;
- In the elevator +5°C;
- In the basement +4°C;
- In the attic +4°C.
It should be taken into account that these temperature standards refer to the heating season and do not apply to the rest of the time. Also, it will be useful information that hot water should be from +50°C to +70°C, according to SNiP-u 2.08.01.89 “Residential buildings”.
There are several types of heating systems:
With natural circulation
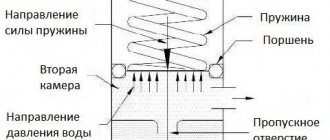
The coolant circulates without interruption. This is due to the fact that the temperature and density of the coolant changes continuously. Because of this, heat is distributed evenly across all elements of the heating system with natural circulation.
The circular water pressure directly depends on the temperature difference between hot and cooled water. Typically, in the first heating system the coolant temperature is 95°C, and in the second 70°C.
Pressure, water speed and return temperature in the heating system
Basically, the requirements for heating systems imply dividing the specifics of heating into two types:
- independent, here the source of heat energy is located directly in the room - used in an individual house or in multi-storey buildings of an elite type;
- dependent, where a network of pipelines is connected to the heating complex - used in most houses in the urban area and urban-type settlements.
Due to the specific nature of the circulation of the coolant, water is predominantly used, where the speed of water in the heating system directly affects the temperature in the radiators. Circulation is divided into natural (based on the principle of gravity) and forced (heating system using a pump). According to distribution, it is customary to distinguish between a heating system with lower and upper pipe distribution.
Temperature
Despite the wide selection of heating systems provided, the options for heat supply and return are quite limited. The maximum temperature in the heating system must also be set according to the rules in order to avoid further malfunctions.
Radiators are connected to the heating system in one of three ways: bottom, side or diagonal.
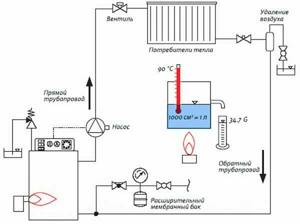
Also, the lower connection is also called differently: “Leningradka”, saddle. According to this scheme, the return and supply are installed at the bottom of the battery. In most cases, it is used when pipes are laid under the baseboard or under the floor surface. The return temperature in the heating system should not differ from the supply temperature.
Water speed
If there are few sections, heat transfer will be extremely ineffective compared to other schemes - the speed of water in the heating system decreases, which leads to heat loss.
Side heating is the most popular type of connecting radiator batteries to heating. The supply of water as a heat carrier is carried out in the upper part, and the return is connected from below, so that the return temperature in the heating system is considered equal.
With forced circulation
This system is divided into two types:
The difference between them is quite big. The layout of the pipes, their number, and the sets of shut-off, control and control valves differ.
According to SNiP 41-01-2003 (“Heating, ventilation and air conditioning”), the maximum coolant temperature in these heating systems is:
- two-pipe heating system - up to 95°C;
- single-pipe - up to 115°C;
The optimal temperature is from 85°C to 90°C (due to the fact that at 100°C, water already boils. When this value is reached, special measures must be used to stop boiling).
The amount of heat emitted by the radiator depends on the installation location and the method of connecting the pipes. Thermal output can be reduced by 32% due to poor pipe placement.
The best option is a diagonal connection, when hot water comes from the top and return flow from the bottom of the opposite side. This is how radiators are tested during testing.
The worst thing is when hot water comes from below, and cold water comes from above on the same side.
How to make radiators hot, looking for solutions
If you find that the return is too cold, you should take a number of steps to find the causes and troubleshoot problems. First of all, you need to check that the connection is correct. If the connection is not made correctly, the down pipe will be hot when it should be slightly warm. The pipes should be connected according to the diagram.

To avoid air pockets that impede the flow of coolant, it is necessary to provide for the installation of a Mayevsky valve or bleeder for air removal. Before bleeding the air, you need to turn off the supply, open the tap and let out the air. Then the tap is turned off and the heating valves open.
Often the cause of cold return is the control valve: the cross-section is narrowed. In this case, the tap must be dismantled and the cross-section increased using a special tool. But it is better to buy a new faucet and replace it.
The reason may be clogged pipes. You need to check them for passability, remove dirt and deposits, and clean them well. If passability cannot be restored, the clogged areas should be replaced with new ones.
If the coolant flow rate is insufficient, you need to check whether there is a circulation pump and whether it meets the power requirements. If it is missing, it is advisable to install it, and if there is a lack of power, replace or upgrade it.
Knowing the reasons why heating may not work efficiently, you can independently identify and eliminate malfunctions. Comfort in the house during the cold season depends on the quality of heating. If you carry out the installation work yourself, you can save on hiring third-party labor.
When autumn confidently strides across the country, snow is flying above the Arctic Circle, and in the Urals night temperatures stay below 8 degrees, then the word form “heating season” sounds appropriate. People remember past winters and try to understand the normal temperature of the coolant in the heating system.
Prudent owners of individual buildings carefully inspect the valves and nozzles of boilers. By October 1, residents of an apartment building are waiting like Santa Claus for a plumber from the management company. The Lord of valves and valves brings warmth, and with it joy, fun and confidence in the future.
Calculation of the optimal temperature of the heating device
The most important thing is that the most comfortable temperature for human existence is +37°C.
When choosing a radiator, you need to calculate whether the thermal power of the device is enough to heat the room. There is a special formula for this:
S*h*41:42,
- where S is the area of the room;
- h – room height;
- 41 – minimum power per 1 cubic m S;
- 42 – nominal thermal conductivity of one section according to the passport.
Please note that a radiator placed under a window in a deep niche will produce almost 10% less heat. A decorative box will take 15-20%.
When you use a radiator to maintain the desired temperature in a room, you have two options: you can use small radiators and increase the water temperature in them (high temperature heating) or install a large radiator, but the surface temperature will not be as high (low temperature heating) .
With high temperature heating, radiators are very hot and can cause burns if you touch them. In addition, at a high temperature of the radiator, the decomposition of dust settled on it may begin, which will then be inhaled by people.
When using low temperature heating, the appliances are slightly warm, but the room is still warm. In addition, this method is more economical and safe.
Cast iron radiators

The average heat output of a separate section of a radiator made of this material ranges from 130 to 170 W, due to the thick walls and large mass of the device. Therefore, it takes a lot of time to warm up the room. Although this also has the opposite advantage - high inertia ensures long-term retention of heat in the radiator after the boiler is turned off.
The coolant temperature in it is 85-90 °C
Aluminum radiators

This material is lightweight, easily heats up and has good heat dissipation from 170 to 210 watts/section. However, it is susceptible to the negative effects of other metals and may not be installed in every system.
The operating temperature of the coolant in the heating system with this radiator is 70°C
Steel radiators

The material has even lower thermal conductivity. But due to the increase in surface area with partitions and ribs, it still heats well. Heat output from 270 W is 6.7 kW. However, this is the power of the entire radiator, and not of its individual segment. The final temperature depends on the dimensions of the heater and the number of fins and plates in its design.
The operating temperature of the coolant in the heating system with this radiator is also 70°C
So which one is better?
It will probably be more profitable to install equipment with a combination of the properties of an aluminum and steel battery - a bimetallic radiator. It will cost you more, but it will also last longer.
The advantage of such devices is obvious: if aluminum can withstand the temperature of the coolant in the heating system only up to 110°C, then bimetal can withstand up to 130°C.
Heat transfer, on the contrary, is worse than that of aluminum, but better than that of other radiators: from 150 to 190 W.
Warm floor

Another way to create a comfortable temperature environment in the room. What are its advantages and disadvantages over conventional radiators?
From a school physics course we know about the phenomenon of convection. Cold air tends to fall, and when it warms up, it rises. That’s why, by the way, my feet get cold. A warm floor changes everything - the heated air below is forced to rise upward.
This coating has a high heat output (depending on the area of the heating element).
Calculation of heating operating temperature conditions
When calculating heat supply, it is necessary to take into account the properties of all components. This is especially true for radiators. What is the optimal temperature for heating radiators - +70°C or +95°C? It all depends on the thermal calculation, which is performed at the design stage.
An example of drawing up a heating temperature schedule
First, it is necessary to determine the heat losses in the building. Based on the data obtained, a boiler with the appropriate power is selected. Then comes the most difficult design stage - determining the parameters of the heat supply batteries.
They must have a certain level of heat transfer, which will affect the temperature chart of the water in the heating system. Manufacturers indicate this parameter, but only for a certain operating mode of the system.
If to maintain a comfortable level of air heating in a room you need to spend 2 kW of thermal energy, then the radiators must have a no less heat transfer rate.
To determine this, you need to know the following quantities:
- The maximum permissible water temperature in the heating system is t1. It depends on the power of the boiler, the temperature limit on the pipes (especially polymer ones);
- The optimal temperature that should be in the heating return pipes is t This is determined by the type of pipeline layout (one-pipe or two-pipe) and the total length of the system;
- The required degree of heating of the air in the room is t.
Having these data, you can calculate the temperature difference of the battery using the following formula:
Next, to determine the power of the radiator, use the following formula:
Where k is the heat transfer coefficient of the heating device. This parameter must be indicated in the passport; F – radiator area; Tnap – thermal pressure.
By varying various indicators of the maximum and minimum water temperatures in the heating system, you can determine the optimal operating mode of the system
It is important to correctly initially calculate the required power of the heating device. Most often, the low temperature indicator in heating radiators is associated with heating design errors
Experts recommend adding a small margin to the obtained radiator power value - about 5%. This will be needed if the outside temperature drops critically in winter.
Most manufacturers indicate the heat output of radiators according to accepted standards EN 442 for mode 75/65/20. This corresponds to the normal heating temperature in the apartment.
Temperature standards
Requirements for the temperature of the coolant are set out in documents that specify the standards that establish the design, installation and use of engineering systems of residential and public buildings. They are described in the State Construction Standards and Rules:
- DBN (V. 2.5-39 Heating networks);
- SNiP 2.04.05 “Heat supply, ventilation and air conditioning system.”
For the calculated supply water temperature, the figure that is equal to the temperature of the water leaving the boiler, according to its passport details, is accepted.
For autonomous heating, it is necessary to decide what the temperature of the coolant should be, taking into account the following factors:
- Beginning and ending of the heating season based on the daily average outdoor temperature of +8 °C for 3 days;
- The average temperature inside heated residential and public buildings should be 20 °C, and for industrial buildings 16 °C;
- The average design temperature must comply with the requirements of DBN V.2.2-10, DBN V.2.2.-4, DSanPiN 5.5.2.008, SP No. 3231-85.
According to SNiP 2.04.05 “Heat supply, ventilation and air conditioning system” (clause 3.20), the limit values of the coolant are as follows:
For a clinic - 85 °C (excluding psychiatric and drug departments, as well as administrative or home use premises);
- For residential, public, and also domestic buildings (not counting halls for sports, trade, spectators and passengers) - 90 ° C;
- For auditoriums, restaurants and premises for production of categories No and B – 105 °C;
- For catering companies (excluding restaurants) it is 115 °C;
- For production premises (categories B, D and D), where flammable dust and aerosols are emitted – 130 °C;
- For staircases, lobbies, pedestrian crossings, technical premises, residential buildings, industrial premises without the presence of flammable dust and aerosols – 150 °C.
- With an average reading outside the window of 0 °C, the supply for heating devices with different wiring is set at 40 to 45 °C, and the return temperature at 35 to 38 °C;
- At -20 °C, the supply is heated from 67 to 77 °C, and the return rate should be from 53 to 55 °C;
- At -40 °C outside the window, absolutely all heating systems are set to the maximum possible values. On the supply side it is from 95 to 105 °C, and on the return side it is 70 °C.
Depending on external factors, the water temperature in the heating system can be from 30 to 90 °C. When heated above 90 °C, dust and varnish begin to decompose. For these reasons, sanitary standards prohibit greater heating.
To calculate good indicators, specialized graphs and tables can be used, which set standards depending on the season:
Heat meters
Let us remember once again that the heat supply network of an apartment building is equipped with thermal energy metering units, which record both the gigacalories consumed and the cubic capacity of water passed through the intra-house line.
In order not to be surprised by bills containing unrealistic amounts for heat when the degrees in the apartment are below normal, before the start of the heating season, check with the management company whether the meter is in working condition and whether the verification schedule has been violated.
Many manufacturers of boiler equipment require that at the entrance to the boiler there be water at least a certain temperature, since cold return water has a bad effect on the boiler:
- boiler efficiency decreases,
- condensation on the heat exchanger increases, which leads to corrosion of the boiler,
- Due to the large temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the heat exchanger, its metal expands differently - hence the stress and possible cracking of the boiler body.
The first method is ideal, but expensive.
Esbe
offers a ready-made module for mixing into the boiler return and controlling the loading of the heat accumulator (relevant for solid fuel boilers) - the LTC 100 device is an analogue of the popular Laddomat unit.
Phase 1. Beginning of the combustion process. The mixing device allows you to quickly increase the boiler temperature, thus starting water circulation only in the boiler circuit.
Phase 2: Start loading the storage tank. The thermostat, opening the connection from the storage tank, sets the temperature, which depends on the version of the product. High, guaranteed return temperature to the boiler, maintained through the entire combustion cycle
Phase 3: Storage tank during loading. Good control ensures efficient loading of the storage tank and correct stratification within it.
Phase 4: The storage tank is fully loaded. Even at the final stage of the combustion cycle, the high quality of regulation ensures good control of the return temperature to the boiler while simultaneously fully loading the storage tank
Phase 5: End of combustion process. By completely closing the top opening, the flow is directly directed into the storage tank, using the heat in the boiler
The second method is simpler, using a high quality three-way thermomixing valve.
For example valves from ESBE or VTC300. These valves vary depending on the power of the boiler used. VTC300 is used for boiler power up to 30 kW, VTC511 and VTC531 - for more powerful boilers from 30 to 150 kW
The valve is mounted on the bypass line between the boiler flow and return.
The built-in thermostat opens input “A” when the temperature at output “AB” is equal to the thermostat setting (50, 55, 60, 65, 70 or 75°C). Input “B” closes completely when the temperature at inlet “A” exceeds the nominal opening temperature by 10°C.

When the coolant temperature at the outlet of valve “AB” is less than 61°C, inlet “A” is closed, and hot water flows through inlet “B” from the boiler supply to the return. If the temperature of the coolant at the outlet “AB” exceeds 63°C, the bypass input “B” is closed and the coolant from the system return flows through inlet “A” into the boiler return. Bypass output “B” opens again when the temperature at outlet “AB” drops to 55°C
When a coolant with a temperature of less than 61°C passes through the “AB” outlet, the “A” input from the system return is closed, and the hot coolant from the bypass “B” is supplied to the “AB” output. When the temperature at the outlet “AB” reaches more than 63°C, inlet “A” opens and water from the return is mixed with water from bypass “B”. To equalize the bypass (so that the boiler does not constantly operate in a small circulation circle), a balancing valve must be installed in front of the “B” inlet on the bypass.
Good values in a personal heating system
Individual heating helps to avoid most of the problems that arise with a centralized network, and the comfortable temperature of the coolant can change according to the season. In the case of autonomous heating, the concept of norms includes the heat output of the heating device per unit area of the room where the device is located. The heat regime in this situation is ensured by the design characteristics of the radiators.
The main thing is to ensure that the coolant in the network does not cool below 70 °C. A value of 80 °C is considered good. With a gas water heater, it is easier to control heating, since manufacturers limit the possibility of heating the coolant to 90 °C. By using sensors to regulate the gas supply, the heating of the coolant can be adjusted.
It is a little more difficult with solid fuel devices; they do not regulate the heating of the liquid, and can easily turn it into steam. And in such a situation it is unrealistic to reduce the heat from coal or wood by turning the knob. Control of heating of the coolant is quite relative with high errors and is done using rotary thermostats and mechanical dampers.
Central heating
How does an elevator unit work?
At the elevator entrance there are valves that cut it off from the heating main. Along their flanges closest to the wall of the house, there is a division of areas of responsibility between homeowners and heat suppliers. The second pair of valves cuts off the elevator from the house.
The supply pipe is always at the top, the return pipe is always at the bottom. The heart of the elevator unit is the mixing unit, in which the nozzle is located. A stream of hotter water from the supply pipe flows into the water from the return pipe, drawing it into a repeated circulation cycle through the heating circuit.
By adjusting the diameter of the hole in the nozzle, you can change the temperature of the mixture entering the.
Strictly speaking, an elevator is not a room with pipes, but this unit. In it, supply water is mixed with return water.
What is the difference between the supply and return pipelines of the route?
- In normal operation it is about 2-2.5 atmospheres. Typically, 6-7 kgf/cm2 enters the house on the supply side and 3.5-4.5 on the return side.
Please note: at the exit from the thermal power plant and boiler house the difference is greater. It is reduced both by losses due to the hydraulic resistance of the routes and by consumers, each of which is, simply put, a jumper between both pipes.
- During density tests, pumps pump at least 10 atmospheres into both pipelines. Tests are carried out with cold water with the inlet valves of all elevators connected to the route closed.
What is the difference in the heating system
The difference on the highway and the difference in the heating system are two completely different things. If the return pressure before and after the elevator does not differ, then instead of supply, a mixture is supplied to the house, the pressure of which exceeds the readings of the pressure gauge on the return by only 0.2-0.3 kgf/cm2. This corresponds to a height difference of 2-3 meters.
This difference is spent to overcome the hydraulic resistance of bottlings, risers and heating devices. Resistance is determined by the diameter of the channels through which water moves.
What diameter should be the risers, fillers and connections to radiators in an apartment building?
The exact values are determined by hydraulic calculation.
In most modern houses the following sections are used:
- Heating outlets are made from pipes DN50 - DN80.
- For risers, a pipe DN20 - DN25 is used.
- The connection to the radiator is made either equal to the diameter of the riser, or one step thinner.
A caveat: you can only underestimate the diameter of the line relative to the riser when installing heating yourself if you have a jumper in front of the radiator. Moreover, it must be embedded into a thicker pipe.
The photo shows a more sensible solution. The diameter of the liner is not underestimated.
What to do if the return temperature is too low
In such cases:
- The nozzle is drilled out
. Its new diameter is agreed with the heat supplier. An increased diameter will not only raise the temperature of the mixture, it will also increase the drop. The circulation through the heating circuit will speed up. - In the event of a catastrophic lack of heat, the elevator is disassembled, the nozzle is removed, and the suction (pipe connecting the supply to the return) is turned off. The heating system receives water directly from the supply pipe. Temperature and pressure drop increase sharply.
Please note: this is an extreme measure that can only be taken if there is a risk of heating defrosting. For normal operation of thermal power plants and boiler houses, a fixed return temperature is important; By turning off the suction and removing the nozzle, we will raise it by at least 15-20 degrees.
What to do if the return temperature is too high
- The standard measure is to weld the nozzle and re-drill it, with a smaller diameter.
- When an urgent solution is needed without stopping the heating, the difference at the entrance to the elevator is reduced with the help of shut-off valves. This can be done with an inlet valve on the return line, monitoring the process using a pressure gauge. This solution has three disadvantages:
- The pressure in the heating system will increase. After all, we limit the outflow of water; the lower pressure in the system will become closer to the supply pressure.
- The wear of the cheeks and valve stem will accelerate sharply: they will be in a turbulent flow of hot water with suspensions.
- There is always the possibility of worn cheeks falling. If they completely shut off the water, the heating (primarily the access heating) will defrost within two to three hours.
Why do you need high pressure in the line?
Indeed, in private houses with autonomous heating systems, an excess pressure of only 1.5 atmospheres is used. And, of course, more pressure means much higher costs for stronger pipes and power supply for injection pumps.
The need for greater pressure is associated with the number of floors in apartment buildings. Yes, circulation requires a minimum drop; but the water needs to be raised to the level of the jumper between the risers. Each atmosphere of excess pressure corresponds to a water column of 10 meters.
Knowing the pressure in the line, it is not difficult to calculate the maximum height of a house that can be heated without the use of additional pumps. The calculation instructions are simple: 10 meters multiplied by the return pressure. A return pipeline pressure of 4.5 kgf/cm2 corresponds to a water column of 45 meters, which, with a height of one floor of 3 meters, will give us 15 floors.
By the way, hot water supply in apartment buildings is supplied from the same elevator - from the supply (at a water temperature of no higher than 90 C) or return. If there is a lack of pressure, the upper floors will remain without water.
Coordination of coolant and boiler temperatures
Regulators help set the temperature of the coolant and boiler. These are devices that form automated control and adjustment of supply and return temperatures.
The return temperature depends on the amount of liquid passing through it. Regulators cover the liquid supply and increase the difference between supply and return to the level that is necessary, and the necessary indicators are placed on the meter.
If it is necessary to expand the flow, an increase pump can be added to the network, which is controlled by a regulator. To reduce the heating of the supply, a “cold start” is used: that part of the liquid that has passed through the network is again transported from the return to the inlet.
The regulator redistributes the supply and return flows based on the data collected by the meter, and ensures the strict temperature standards of the heating network.
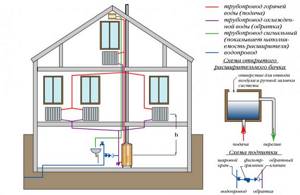
Heating system
Why do you need an expansion tank?
Accommodates excess expanded coolant when it is heated. Without an expansion tank, the pressure may exceed the tensile strength of the pipe. The tank consists of a steel barrel and a rubber membrane that separates air from water.
Air, unlike liquids, is highly compressible; with an increase in coolant volume by 5%, the pressure in the circuit due to the air tank will increase slightly.
The volume of the tank is usually taken approximately equal to 10% of the total volume of the heating system. The price of this device is low, so the purchase will not be ruinous.
The correct installation of the tank is with the hose facing up. Then excess air will not get into it.
Why does pressure decrease in a closed circuit?
Why does pressure drop in a closed heating system?
After all, the water has nowhere to go!
- If there are automatic air vents in the system, the air dissolved in the water at the time of filling will escape through them. Yes, it makes up a small part of the coolant volume; but a large change in volume is not necessary for the pressure gauge to register the change.
- Plastic and metal-plastic pipes may be slightly deformed under the influence of pressure. Combined with high water temperature, this process will speed up.
- The pressure in the heating system drops when the temperature of the coolant decreases. Thermal expansion, remember?
- Finally, minor leaks are easy to see only in centralized heating through rust marks. Water in a closed circuit is not so rich in iron, and the pipes in a private house are most often not made of steel; therefore, it is almost impossible to see traces of small leaks if the water has time to evaporate.
Why is a pressure drop in a closed circuit dangerous?
Boiler failure. In older models without thermal control - up to an explosion. Modern older models often have automatic control of not only temperature, but also pressure: when it falls below a threshold value, the boiler reports a problem.
In any case, it is better to maintain the pressure in the circuit at a level of approximately one and a half atmospheres.
How to slow down the pressure drop
In order not to recharge the heating system over and over again every day, a simple measure will help: install a second expansion tank of a larger volume.
The internal volumes of several tanks are summed up; the greater the total amount of air in them, the smaller the pressure drop will cause a decrease in the volume of coolant by, say, 10 milliliters per day.
Where to put the expansion tank
In general, there is no big difference for a membrane tank: it can be connected in any part of the circuit. Manufacturers, however, recommend connecting it where the water flow is as close to laminar as possible. If there is a tank in the system, the tank can be mounted on a straight section of pipe in front of it.
Ways to reduce heat loss
The above information will help to be used for professional calculation of the coolant temperature norm and will recommend how to determine situations when it is necessary to use a regulator.
However, it is important to remember that the temperature in the room is influenced not only by the temperature of the coolant, the air from the street and the strength of the wind. The degree of facade insulation, windows and doors in the house should also be provided for.
To reduce heat loss from your home, you need to take care of its maximum thermal insulation. Thermally insulated walls, sealed doors, and plastic windows can help reduce heat loss. This will also reduce heating costs.
It is no less important than the presentation! Heating system return: what is it?
The strength and productivity of a heating system depends on the good performance of all parts included in it.
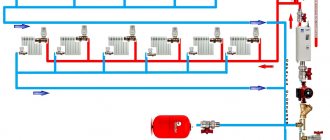
These include : a boiler for heating the coolant, heating devices connected to it and to each other in a certain way, an expansion tank, a circular pump, shut-off and control valves, pipe wire of the required diameter.
Creating very efficient heating system is possible thanks to specialized knowledge and experience in this area of life. The return pipe wire plays a very important role in the heating process of the room.
Why doesn't the return work work?
There are many problems associated with return flow in a heating system.
Squeezes feed
The water temperature in the return pipeline is determined by the design of the heating system and corresponds to the value in the temperature chart approved by the service organization.
Often apartment residents are faced with a problem when the return flow squeezes the supply.
A common reason is the transition of hot coolant from the supply line to the return circuit through various parts (for example, jumpers) of the hot water supply pipeline or ventilation. With an automatic control device, as a rule, it is enough to configure it correctly.
The coolant does not drain well
If the circulation of fluid in the heating circuit is disrupted, the water in the return pipes does not drain well. Initially, check that the power of the circulation pump meets the requirements. The reason may be hidden in a banal pipeline leak . The situation with poor circulation is typical for apartment buildings located on the final section of a heating main with insufficient pressure drop .
Types of heating schemes
For buildings with several floors, a single-pipe direct distribution system is sometimes used. It does not have a clear division of pipes into the supply of liquid to the heating devices and the return, thanks to which the complete circuit is figuratively divided into two identical parts. The riser coming out of the boiler is called the supply, and the pipes coming out of the last heating device are called the return. The advantages of this scheme:
- saving time and financial costs;
- convenience and simplicity of installation work;
- beautiful view;
- the absence of a return riser and the methodical placement of heating devices (the coolant is supplied to the 1st, after the 2nd, 3rd and so on ).
For a single pipe system, a vertical wiring design with a vertical circuit and heat supply from above is popular.
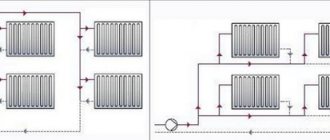
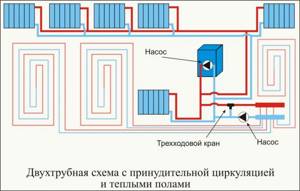
With a two-pipe wiring system, we mean the installation of two closed, parallel-connected circuits, one of them provides the function of supplying the heat carrier to the device for heating the room (heat exchanger), the second - the function of its removal (return).
Heating devices are connected in several ways:
- Lower (or saddle, crescent-shaped). Takes into account the connection of the supply and return to the lower connecting holes of the heating device. An air vent and a plug are installed on the upper holes. Used for systems in which pipes are hidden under the floor or baseboard. Suitable for multi-section heating devices; with a small number of sections, heat loss reaches up to 15%.
- The lateral method is popular. The pipes are connected to the heat exchanger on one side: the heat carrier supply is through the top, the return line is through the bottom. Not suitable for devices with a large number of sections.
Photo 2. Heating circuit with two pipes with a side connection type. The supply and return temperatures are indicated.
- The diagonal (or lateral cross ) method involves supplying hot water from above, connecting the return line from below and on the other side. Suitable for heating devices with at least 14 sections.
- The third option for organizing a heating circuit is considered a hybrid method, which is based on the simultaneous use of one-pipe and two-pipe systems. For example, the collector circuit involves supplying a heat carrier through a single riser; subsequent on-site wiring is carried out according to an individual plan.
Working principle on how to increase productivity
A single circuit does not provide equal heating of the radiators; heat transfer decreases as it moves away from the boiler (the latter heating devices receive coolant cooler than the first ones). The disadvantage of such a system is the high pressure values of the coolant.
Reference. The productivity of a single pipe system increases if there is a bypass or circulation pumps formed on each floor.
Advantages of the two-pipe heat supply option:
- heating the required number of devices in the same way, regardless of their distance to the heat source;
- adjusting the temperature regime, carrying out repair activities on an individual device does not affect the operation of others.
Minuses:
- complexity of the wiring diagram;
- complexity of installation and connection.
The most productive system of two pipes, which is also often selected for heating luxury housing, is considered an excellent choice for private construction
Return in the heating system - its purpose
The return in the heating system is the coolant that has passed through all the heating radiators, lost its primary temperature and is now cold and supplied to the boiler for the next heating. The coolant can move in both a two-pipe and an improved single-pipe heating system.
A single-pipe heating system implies a sequence of connections of heating radiators. That is, the supply pipe is connected to the first radiator, from which the next pipe goes to the second radiator, and so on.
If a one-pipe heating system is improved, its design will be something like this: along the perimeter of the entire room there is one pipe into which the supply and return pipes of each radiator can be inserted. In this case, it is possible to install a control valve on each battery, with which you can very successfully regulate the air temperature in a given room.
The big advantage of such a heating system is the minimal number of pipes in it. And the minus is the temperature difference between the first radiator from the boiler and the last. This problem can be eliminated with the help of a circulation pump, which will move all the water through the heating system much faster, and thus the coolant will not have time to reduce the temperature.
A two-pipe heating system consists of two pipes. One pipe is the supply of hot coolant, the second pipe is the return pipe in the heating system, through which already cooled water from the radiators enters the boiler. This system allows you to connect all radiators almost in parallel, which allows for flexible configuration of each radiator individually without affecting the operation of the others.
Consequences of cold return
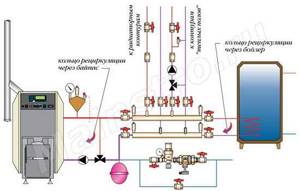
Circuit for heating return
Sometimes, with an incorrectly designed design, the return flow in the heating system is cold. As practice shows, the fact that the room does not receive enough heat with a cold return is half the trouble. The fact is that at different supply and return temperatures, condensation may form on the walls of the boiler, which, when interacting with carbon dioxide released during fuel combustion, forms acid. It can also damage the boiler much ahead of time.
To avoid this, it is necessary to carefully consider the design of the heating system; special attention must be paid to such a nuance as the return temperature in the heating system. Or include additional devices in the system, for example, a circulation pump or boiler, which will compensate for the loss of warm water.
Radiator connection options
Now we can more than confidently say that when designing a heating system, the supply and return must be perfectly thought out and configured. If the heating system is not designed correctly, more than 50% of the heat can be lost.
There are three options for inserting a radiator into the heating system:
The diagonal system gives the highest efficiency coefficient, and is therefore more practical and efficient.
The diagram shows a diagonal inset
How to regulate the temperature in the heating system?
In order to regulate the temperature of the radiator and reduce the difference between the supply and return temperatures, you can use a heating system temperature controller.
When installing this device, do not forget about the jumper, which must be located in front of the heating device. If it is absent, you will regulate the temperature of the batteries not only in your room, but throughout the riser. It is unlikely that the neighbors will be happy with such actions.
The simplest and cheapest option for a regulator is to install three valves: on the supply, on the return and on the jumper. If you cover the valves on the radiator, the jumper must be open.
There is a huge abundance of different thermostats that can be used in apartment and private buildings. Among the wide variety, each consumer can choose a regulator that will suit him in terms of physical parameters and, of course, cost.
How different should the rhythm of feed and return be?
Why “should it be 45...55”? What if I heat the house with warm walls and floors? – at 55 you can already boil the eggs (softened). What if I have small (baseboard) heating appliances? - at 45 you will freeze even today.
“45...55” are ordinary stereotypes of thinking, formed on the usual diagram of heating devices such as “1 elbow per 2 m2”.
Less is better. However, it will be completely “0” only if there is absolutely no heat transfer (heating). You can switch the pump to mode 2 or even 1.
A delta of 20 degrees is considered wonderful. However, if this mouth does not exist and the batteries are hot, then this is also good. This means that the battery power is less than the boiler power. And the uncooled water goes back to the boiler. So in your case, the boiler will turn on less often (it already receives hot water). You can reduce the flow rate. Then the delta will be higher, but the boiler will also turn on more often. Strictly speaking, if heat loss in the pipes is neglected, the efficiency of the system will not change. The amount of energy the boiler consumes will increase the temperature in the house. So what?
I have a solid fuel boiler, it does not turn off and will not turn on either)))
By hand kmk less than 20 degrees.
Well, this is when it already goes out. Although I can set the electric boiler to 65 degrees. It will warm up
And by the way, why is it not recommended what to do when it’s already completely burned out, turn off the supply to it and wait until it boils.
And below there is condensation, and it is very angry with firewood (sulfur, and ultimately sulfuric acid). Accelerated rust of the pipe coil. It's not very scary for cast iron. And steel can “eat up” in a season or two (there were posts on SOK). When it has already burned out, there are no problems - there is no more condensation. But at the kindling step - well, maybe for quite a long time - the boiler itself is cold + the return flow is cool. That is why they provide protection against cold return in the form of a controlled circular pump directly on the boiler piping. It does not stop working very simply: until the return temperature reaches +65°C, the water moves in a small circle (almost like a thermostatic valve in a car). Most manufacturers build a circular pump directly into the boiler.
Data. Solid fuel 25 kW on coal. On wood I think below.
The heated area is 100 sq.m. There is no insulation of any 15 cm timber, the floors and ceilings are actually 20 cm of cotton wool)), not caulked. There are 8 design radiators with a total power of approximately 12 kW. And an indirect heating water heater is connected. But DHW is not consumed much, so it does not play a significant role in the calculation (I turn it off altogether, when the boiler has cooled down, the indirect heating water heater will also cool down (( )
And I wouldn’t say that it’s very warm in my large rooms. You can't breathe in the bathroom or bedroom. But in the living room and kitchen room it’s so-so, 20 degrees, but I’d like 25)) But all approaches to design radiators are hot.
PS there are suspicions that this is what heats up, but in general it sucks.
In an apartment, I would throw it away))) but on a summer cottage you need 15 of them. It turns out to be expensive, but these are very cheap.
Maybe change to cast iron, or leave it as is for now.
Something practically free no matter what. I have about 1 heating device that costs 5 thousand. In the end there are 2 pieces, plus thermal and connection, etc. and TP)))
I know Denis, but what’s the point, he won’t honor the 70% discount))))
What temperature should I set on the heating boiler?
With the onset of cold weather, the question increasingly arises on thematic forums about what temperature to set on the heating boiler. After all, owners want to achieve a comfortable temperature in their home, but at the same time not pay extra for heating. Of course, there are no exact values here, but we will try to give general recommendations.
Let's say right away that the temperature regime will depend on the weather conditions outside, the quality of insulation of the house, the type and quality of windows in the house, as well as a number of other objective factors that need to be taken into account. Therefore, we cannot say that all our recommendations will suit you personally. However, we must share them.
What temperature to set in the heating boiler: low and high values
Let us share our experience regarding different temperature conditions.
- 40 degrees.
This regime often turns out to be economically unprofitable. At this temperature, a gas boiler may well underheat to half a degree. Because of this, the circulation pump and heating do not turn off. Accordingly, gas consumption only increases. In some boiler models, the flow rate may be even higher than at the set temperature of 70°C. In addition, it is better to refuse such a temperature regime in cases of unstable operation of the electrical network. The coolant will cool down in a short time, the room will become cold within a few hours. - 50 degrees.
Most tests show that gas flow is lowest when this temperature is set. However, the circulation pump runs for quite a long time, which increases electricity costs. Plus, in case of power outages, the batteries retain heat a little longer. In general calculations, this mode of system operation is less economical than the next one. - 60 degrees.
This is rightfully the most economical mode. More gas is required than in the 50-degree mode, but electricity costs are noticeably reduced. Total costs are lower. And the room is heated better. - 70 degrees.
In this mode, less electricity is consumed, but gas consumption increases. But a more important problem is that with some boiler models, in this mode of operation, fluctuations in the air temperature in the room are possible. They can be either practically invisible or quite noticeable. The fact is that radiators continue to strongly heat the rooms even after the heating in the boiler is turned off, then they cool down, then they become very hot again.
Setting the temperature even higher is not a good idea unless you live in cold northern regions. And there are several reasons for this. – the house simply doesn’t need such high temperatures.
And even if you need to heat the rooms as much as possible, it is better to set the temperature lower.
If the values are too high, an unpleasant smell of burning dust from the batteries appears, and polypropylene pipes wear out faster.
So what temperature should the heating boiler be? We recommend around 60-65 degrees if the outside temperature is not lower than -10°C. If lower, you can increase the power. If it's near zero outside, you won't need more than 50-55 degrees.
What temperature on the boiler is optimal for heating without a difference in room temperatures?
Often, the most important thing for a homeowner is not savings, but uniform heating of all rooms in the house. The boiler operates continuously, preventing the temperature from falling below the selected value. Of course, this mode requires more electricity, but you can save on gas.
40 degrees is not always enough for comfortable and uniform heating. With this mode, the house will warm up by an average of 20-20.5 degrees at an outside temperature of at least -9°C. If twenty degrees in the room is not enough for you, you can set 45-50 degrees on the boiler.
Note!
Many people say that if the boiler operating temperature is set to less than 70 degrees, this provokes the formation of condensation in the boiler, which is harmful to the system.
However, too high values can damage the equipment over time. The same polypropylene pipes that we have already talked about.
Therefore, when deciding what hot water temperature to set on the boiler, be sure to find out what the manufacturer of a particular model says about this. Perhaps they have set a clear standard.
What should the boiler heating temperature be according to current standards?
In Russia, GOST R 51617-2000 is in force, according to which the standard air temperature in residential premises during the heating season should be within 18-25 degrees Celsius. Accordingly, you can try several boiler operating modes, changing the temperature indicator to choose the most suitable one.
We recommend not allowing frequent and noticeable changes in temperature. This is bad for health and can disrupt the operation of boiler equipment.
If you want to save a little money, you can install a room thermostat with the ability to customize the operating schedule.
For example, set the maximum temperature in the room at night to not exceed 18-20 degrees, and in the morning the air warms up more. By regulating the gas supply, you can save a lot of money during the heating season without sacrificing comfort.
You can choose the optimal temperature for yourself by trial - just determine in which operating mode you are comfortable and the fuel consumption is the most rational. You can also get advice from a representative of the manufacturer.
Or from the specialists “Profteplo”. We not only sell and install boiler equipment in Kaluga and the region, but we can also give recommendations on working with different types of boilers.
To get advice, contact the Profteplo manager by phone number.
Source: https://teploknam.ru/stati/kakuyu-temperaturu-vystavlyat-na-kotle-otopleniya.html