Heating systems for a private home are distinguished by their diversity. They consist of various combinations of supply and removal of coolant. The choice of heating scheme for a private house depends on the size and design of the premises, dependence on electricity, and the number of heating elements (radiators). Each option has different installation options, advantages and disadvantages. In one private house, several closed circuits can be installed to heat different rooms.
Heating a private house without radiators

When the construction of private buildings is at the design stage, selecting the optimal heat supply method is much easier. The area of construction, number of floors, and planned insulation are taken into account. No less significant are other characteristics and factors that are beneficial after the calculation of heat loss is completed. Many people today want to make heating without radiators. And today there are many alternatives. Let's take a look at them.
If you decide to avoid installing radiators inside the building, there are several alternative heating methods:
- air systems;
- water heating,
- use of convectors;
- heating using a pipeline device.
Better heating if there is no gas
If there is no gas on your street (and this happens quite often), then you will have to select an alternative source of heat.
A solid fuel boiler would be a good option. To this day, coal is a fairly affordable energy source, but it has a number of disadvantages:
- Requires constant interaction. Coal needs to be constantly added (if you do not have a bunker boiler)
- Difficult to regulate temperature
- Additional sources of safety are required, such as a heat accumulator. And this entails additional costs.
There are often problems with electricity due to the lack of necessary power, especially if you are the owner of a large house. We would suggest that you install both boilers. In mild cold, use electric heating, and when there is not enough heat, use a coal boiler.
Hello, dear Reader!
I want to tell you about what heating systems I have encountered.
Some he operated, some he assembled himself, including heating systems for private houses.
I learned a lot about their pros and cons, although probably not everything. As a result, for my home I made:
- firstly, your own scheme;
- secondly, it is quite reliable;
- thirdly, allowing modernization.
Air systems
The above type of heating may appear:
- single heater,
- the whole complex.
The complex provides the availability of heat sources and air ducts.
This is due to the maintenance and prompt provision of an increase in temperature, which can be ensured by this technique.
The presented type of heat supply is widespread:
- household sector (residential apartments, dachas, mansions),
- industry (warehouses, factory buildings).
The direct heat distributor is a pump with an internal hydraulic unit or a gas generator.
The device produces a specific amount of warm air required to heat the building, as a result of which it is distributed through a network of air ducts. It is supplied to the territory through air distribution devices. Thus, thermal saturation of the space occurs.
The following positive characteristics of the method can be identified:
- Convenient indoor temperature regulator.
- Lack of necessary installation near the windows of heating devices (as a result, heating will be without batteries) . The room looks harmonious from an aesthetic point of view. In addition, there is wide scope for implementing all kinds of designer solutions.
- Such a system supplies heat to the rooms in winter; In the summer it works like an air conditioner - for cooling.
But this principle of heat supply has a number of flaws:
- If the source of heat is a gas generator, then a significant minus is the cost of the energy resource . This fact guarantees an increase in operating costs of the system.
- The need to heat a home will require a significant amount of air. This entails the need to install large-sized air ducts that are sewn into the space under the ceiling. The situation turns out to be that the ceiling level has to be lowered to a certain height.
- Classic heat supply is considered the most optimal, when it is cool at the top and warm at the bottom. The air heating system is designed in the opposite way - the space above is perfectly warmed up, while the space below is in cold conditions. The way out of the situation is to organize a supply of warm air from the floor. Proper implementation of the system’s activities achieves the required climatic conditions.
- Reduced inertia leading to rapid cooling of the space. The reason is the instantaneous shutdown of devices.
It is rational to use air heating inside residential premises, where the heat source is a pump. It is irrational to use it as the main heat transferr, since it provides heating as a backup source.
Classification of single-pipe heating systems
There are two different types of single-pipe heating systems:
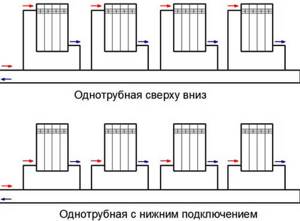
- Vertical . This type of system is used in two-story buildings. In this case, the devices are located under each other (only a slight displacement is allowed) and are connected by a common riser. Structurally, this circuit is more similar to a combined one, since the difference between the supply and return lines is very clearly visible in it. A pump is not required in this system, but it can always be installed for reliability.
- Horizontal with bottom wiring. This single-pipe heating scheme is used in one-story houses with a small area. Natural circulation in this case is quite sufficient, although there are also systems with an installed pump.
You can connect heating devices in three ways:
- Bottom;
- Side;
- Diagonally.
The most widespread is the bottom connection of radiators, which is valued for its almost invisible pipes, which improves the interior of the premises. However, from the point of view of efficiency, this option is far from ideal - the heat transfer of the batteries in this case is noticeably reduced.
The best option is a diagonal pipe supply scheme, in which the heating devices warm up properly and demonstrate maximum efficiency. In any case, before making a one-pipe heating system, you need to develop a project that shows the smallest details of the future design.
Heating via underfloor heating

It is worth noting that the heating scheme is very relevant today and is quite in demand. Although it became widely used relatively recently. Often you can do without radiators. Before installation, you need to decide whether it is justified. Since heating boilers are used quite often, it is rational to use the heating method by installing a heated floor.
This diagram is a pipe layout hidden under the floor covering. The room is heated by the heat carrier spreading through the pipes. They can be installed in several ways that affect the efficiency of the system under certain operating conditions.
Installation of a heated floor involves pipeline contours:
- snake configuration (zigzag arrangement);
- snail configuration (this installation involves a spiral arrangement of pipes).
Professionals in this matter consider the latest installation scheme to provide optimal, high-quality floor heating. When laying pipes, it is important to maintain a gap between them. It is usually calculated from power calculation considerations. It is recommended to reduce the gap as you approach the windows, and increase it when you reach the center.
Warming up buildings with a “warm floor” scheme requires a reasonable temperature distribution. The floor is heated identically over the entire surface area. The maximum value is 26°C, thereby providing a comfortable feeling to the legs. Under the ceiling, the temperature drops significantly, reaching approximately 22°C at human height.
Communications are located under the finished floor covering, and therefore designers do not have to rack their brains over interior design.
Heated floors are a winning option when it comes to saving energy consumption, as a result of which you can save your budget from financial waste. In most cases, if the heat loss at home is not great, you can do without installing radiators.
Advantages and disadvantages of Leningradka
In Soviet times, these space heating systems were widespread. During the period of mass construction, an economical and simple solution was required to provide heat to both residential and industrial facilities. And it was found.
Leningrad engineers developed single-pipe heating schemes that were progressive at that time, hence the popular name “Leningradka”. Moreover, there are now quite a lot of adherents of this system; it is especially popular in the private sector.
Pros of Leningrad:
- low consumption of materials;
- high-speed installation with a small number of welds;
- simple maintenance.
For normal operation of the system, expensive equipment is not required, which significantly reduces the cost of installation and subsequent heating operation.
Disadvantages of single-pipe wiring:
- strong temperature variation between the initial and final sections;
- You cannot integrate a heated towel rail or heated floors into the system, since the coolant will cool even faster;
- inability to regulate the temperature of radiators without additional upgrades.
Despite the disadvantages, the Leningrad system has been successfully operating for many years, both in low-rise buildings and in multi-apartment high-rises. There is only a limitation in area. It is not recommended to install Leningradka if the room is less than 36 sq.m. When turned on frequently, the boiler wears out faster than when operating in normal mode.
In the old buildings, large diameter pipes (80-100 mm) were used, which were laid around the perimeter of the house. But bulky communications in the interior do not look very attractive, take up a lot of space, and their productivity is low.

With the advent of lightweight, technologically advanced radiators that produce much more thermal power, older systems began to be gradually phased out.
Electric heating options
Electric convectors are considered the most popular device for this method of heating rooms. The main advantage is fast heating.

- they have an easy installation system,
- they are comfortable to use.
The principle of operation is quite simple: the heat exchanger heats water and supplies it to the system using a pump.
A convector, at its core, is nothing more than a simple classic heater. It is worth paying attention - it provides heat only to the space within which it is located. Therefore, it is important to calculate the power of the device for each individual room.
Other characteristics of the device, in addition to power, are no less important. For example, the size of the case. It affects the speed of air flow entering the room. A height of about 50 cm is considered optimal.
Also, such convectors are completely safe, since their body does not heat up above the norm of 45-65 ° C. They can also be supplemented with other useful devices - such as an ionizer or antifreeze.
Heating installation requirements
When building a Leningradka with your own hands, you must follow the rules:

- A boiler operating on flammable or explosive fuel is installed in a special room with a separate exit and a window to the street. The requirements for the boiler room are described in the instructions MDS 41.2-2000 and building regulations.
- The start of installation of the heating system is preceded by power calculations and project development in accordance with SP 60.13330.2016.
- The pipeline must contain a minimum number of bends and turns. It is also recommended to use taps, fittings, and pipe narrowings to a minimum, which increase hydraulic losses.
- The slope of the liner is 5-10 mm per 1 meter, except for areas up to 50 cm long, where it is not provided.
Heating with gas convectors
The devices mentioned above are powered by gas supply. Their positive features:
Gas convectors are an ideal choice for installation in an apartment or country house. The device serves not only as the main one, but also as a backup temperature controller (the temperature can rise to 38 °C).
The system is powered by natural as well as liquefied hydrocarbon gas. The fuel change occurs due to the settings of the gas valve.
The device is usually mounted on a window sill. The kit includes pipe routing and temperature sensors. This device significantly minimizes heat loss, which is an important advantage.
A flaw in the system is manifested in the construction of holes in the walls to provide chimney channels.
Pipes made of iron or polypropylene
When selecting the best heating for a private home, the issue of choosing pipes does not go unnoticed. In fact, many “advanced” countries have long abandoned the use of iron pipes because:
- Iron pipes are quite difficult to work with. This is a fairly messy process involving welding. All this takes a lot of time.
- Iron pipes cannot be hidden in walls. Although many houses are already designed taking into account the fact that no pipes will be visible.
- The material is weakly affected. It is impossible to bend, quickly cut, etc.
- Requires constant care
It would seem an obvious fact to praise polypropylene pipes. But “advanced” countries also refuse them because:
- Polypropylene pipes have a large linear expansion. This greatly affects the quality of the welds.
- Polypropylene has a large number of joints. Many joints are hidden in the screed or walls. And every joint has the potential for sudden leakage.
- Not intended for high temperatures. In fact, polypropylene pipes can cope with high temperatures, but for a fairly short time.
Heating with pipes
When arranging heating systems for country cottages, pipes are rarely used. It is required that their length be impressive, and their diameter reach 60-100 mm (sometimes even more). This will provide the necessary heat transfer flow. Now this system looks very absurd, but there is heating without radiators.
If you decide to lay a pipeline instead of radiators, you must:
- heating boiler;
- pipes;
- expansion tank;
- jumper.
The pipes are installed horizontally. The jumper serves as a connecting element. Its diameter should be less than the diameter of the pipe.
How can you regulate the temperature in Leningrad?
Adjusting the batteries allows you to create the most favorable conditions in the room. For example, a nursery requires more heat than a kitchen or living room. temperature. Is it possible to do something similar in a one-pipe system?
Method 1
It is quite possible to regulate Leningrad. To do this, a needle tap is built into the bypass running under the batteries. It is designed for smooth regulation of coolant flow. By turning the valve you can increase or decrease its passage through the battery.
When you open the tap, water will flow along the path of least resistance, that is, through the bypass. Accordingly, the radiator will heat up less. And vice versa, when the tap is turned off, the flow of coolant through the battery will be maximum.
Method 2
There is another option for regulating the temperature in the rooms, but, unfortunately, it does not provide a 100% guarantee. To increase the heat transfer of the latest radiators, additional sections are attached to them. Moreover, the temperature of the coolant may even decrease slightly. But sometimes extending the battery remains the only possible way to correct the situation without drastic changes to the entire heating system.
Method 3
In cases where the length of the branch is very large, it can be divided into 2 separate single-pipe circuits. This should lead to a smoothing of temperatures on the first and last radiator along the flow of the coolant.
Despite the simplicity of this solution, there are several pitfalls. If the pipes are connected in the wrong place, one of the lines will heat ineffectively or not work at all.
Single-pipe heating in the house
The idea of creating a one-pipe heating system in a private house may seem tempting at first glance. It is likely that one pipe instead of two is much cheaper. It’s probably easier to install such a system... A single pipe can even be placed under the baseboard - it’s not difficult to hide, it’s not two pipes...
Let's figure it out one by one: is it really cheaper? Is it easier to do? But the most important thing is how will a single-pipe system behave in operation? Will the heating in the house simply be of poor quality? Will the system's shortcomings be too significant? And therefore the single-pipe (Leningrad) will not be applicable at all...
How many radiators and how to connect them
How many radiators are there in a house? Today, an ordinary house would be a building with an attic floor and a heated area of 200 square meters. At the same time, there are about a dozen radiators downstairs and 5 in the attic. If you consider a one-story house of 100 square meters, you will need at least 8 heating devices.
If they are connected with one pipe in series one after the other, then the latter will turn out to be cold, under normal heating network parameters.
If they are connected in parallel to one pipe, the same thing will happen: the latter will be “icy” if the heating characteristics are normal... But what is meant by the word “ordinary”?
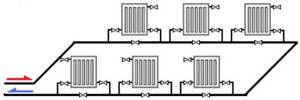
Normal Specifications
When creating heating, everything tends to be minimized, simplified, and made cheaper.
To move the coolant, circulation pumps are used, silent and low-power. The maximum engine power is usually up to 100 W. The latest computer-controlled models are able to select the most economical operating mode themselves, and users are happy when the display shows power consumption of 12 W with a house area of 150 square meters.

Pipes are used with an internal diameter of 16 mm for one or two radiators and 20 mm for a group of up to 6 pieces; 25 mm can already be the main line from the boiler for the whole house. What will happen to a single-tube if all this is applied to it?
Savings during creation and operation
If a single-pipe system is created with progressive (economical) heating parameters, then it will not work on a house scale (5 or more radiators in a ring) because the last radiators will be cold.
A conventional circulation pump will not provide the heat transfer rate (supply the necessary energy for sequential activation). And the usual pipe diameter will create too much hydraulic resistance when trying to increase fluid flow.
To heat the last device in the ring, you need a powerful pump and a large-diameter ring pipe.

What is the temperature of the radiators in Leningrad
When connected in series to one pipe, the radiators will take part of the energy and gradually cool the coolant. If the supply temperature is +60 degrees, then on each radiator the loss during normal coolant circulation (up to 30 W per pump) will be approximately 7% or 4 degrees. Then the output from the 4th radiator will be plus 48 degrees C. But the 5th in the ring will no longer be suitable for heating. And for example, on the eighth radiator in the ring it will be 32 degrees, just cold.
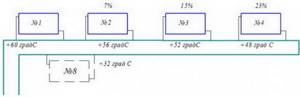
Equalizing the temperature between supply and return is only possible with a large pipe diameter and a powerful pump that creates sufficient coolant flow.
Wasteful single-pipe for large houses
In large houses, with several dozen radiators, where operational losses are not too great, you can consider the option of a single-pipe heating system.
- A large diameter steel pipe (from 50 mm) is used according to the design calculation, with a special pump that creates a significant speed of fluid movement, up to the limit of noise in the pipe. The pipe is placed along the ring of the outer wall in the internal floor space.
- Pairs of outlets for radiators or in-floor convectors under high windows are connected to the pipe. The pressure difference is created not only due to the cooling of the liquid in the devices, but mainly due to the installation of a sail in the pipe on the supply pipe.
- Significant construction costs and operational losses are offset by the high heating power, and are not significant when considering the entire costly part of building such a house. With a decrease in the heating area, the role of these costs will increase and they will turn out to be unacceptable.
Why so wasteful
Is it possible to waste resources and create such an uneconomical heating system during creation and especially during operation? Where it is possible to use 20 W for circulation, 200 W will be spent. (?), Exactly how much - only calculations for a specific hydraulic network will show, but in any case - many times more.
It remains unclear why the expensive operation is necessary, because in just one day the difference is a kilowatt or two of energy, and over the years of operation there is a decent amount of money thrown away.
Other methods of temperature equalization - deep balancing of the first radiators - makes the entire system even more expensive and unstable in operation. The recommended solution is to increase the area of the radiators to compensate for the temperature loss. But then the 8th one in the ring should have twice the area of the first one - too wasteful a heating method.
When the pipe diameter doubles, its cost increases faster. The cost of its fittings and taps increases several times. Any installer will say that a functional one-pipe with a diameter of 32 mm for 10 radiators will cost more than a two-pipe laid with a pipe of 20 and 16 mm (two dead ends of 5 pieces each).

In addition, the installer will (most likely) add that such large fittings and pipes are more difficult to install. A single-pipe with a large diameter pipe will cost more to create.
Where and how are single-tubes used?
In production, it happens that large areas need to be heated. Then it turns out that the local boiler house will be more efficient with a one-pipe system a kilometer long, with hundreds of connected heating devices and a powerful pump.
Single-pipe systems can be found everywhere in centralized networks of multi-storey buildings, because the heating riser is this system with a high circulation rate.
When Leningrad is more rational in private farming
A single-pipe system will clearly be rational when creating heating in a small room, up to 4 radiators in one ring at most, but up to 3 is better. They can even be connected in series one after the other with a polypropylene pipe with an outer diameter of 25 mm, so as not to overload the circulation pump of a minimum size of 25/40.

How to create a one-pipe heating system
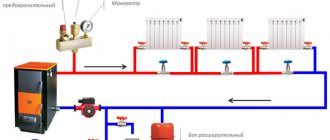
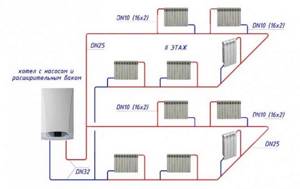
One of the options for creating a one-pipe heating system in a small private house is to create 2 or 3 rings with 2 - 3 radiators in each. Theoretically, this is possible if the boiler is located in the central part of the building and heating rings can be laid from its piping in different directions. For example, there are 4 radiators in one wing of the house, 3 in the other, and 3 in the attic floor. An approximate diagram of a two-pipe for one heating ring for 3 devices.
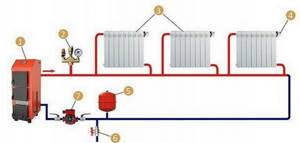
The house will have a single-pipe heating system of acceptable quality for uniform heating 10 pcs. radiators, simpler, more economical, and cheaper than if these devices were connected by two pipes.
Single-pipe wiring method
Single-pipe water heating wiring is the following main line wiring system: water heating devices are installed sequentially one after another and thus form a long pipe - the diagram will help you understand what it looks like.
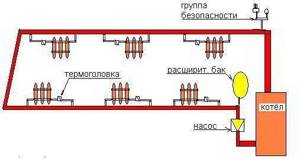
The coolant in such a system is antifreeze or water - the liquid alternately enters the radiators, which are the final link in the chain, and gives off its heat, which is then used for water heating of the house.
Thus, the system scheme consists of supplying water from the boiler to the radiator using pipes.
The disadvantage of this device is that the water reaches the closing radiator already cold.
With such a device, the single-pipe option is quite effective.
A single-pipe water heating circuit is best suited for a two-story house, because... in a house with one floor, problems may arise with the placement of the accelerating manifold, which is necessary for the quality operation of the structure.
An accelerating manifold is necessary to speed up the flow of heat from the pipes to the radiators, as well as to maintain the desired temperature and reduce noise during system operation.
Video:
At the same time, the efficiency of work depends on how high the collector will be located - which is why its installation for a two-story house will be much more efficient.
For a two-story house, all these problems disappear: the collector will work quietly and effectively maintain heat in the rooms.
The manifold of a single-pipe heating system looks like a continuation of the pipes, but at the very top of the heating system an expansion tank is connected to it.
Single-pipe wiring is inexpensive, and this is one of the main advantages in its favor. The low price is maintained due to the fact that single-pipe wiring does not require a large number of pipes.
Another advantage of this design is that it can be laid even in difficult places, for example, under doorways.
However, single-pipe water heating wiring also has disadvantages: in order to replace failed elements, you will have to completely turn it off, and uneven heating - the quality of heating depends on the distance of the battery to the boiler.
However, as has already been written, if the design is somewhat modernized and installed correctly, it will be free from such shortcomings.
Installation of the system can be done in several stages, they differ depending on the scheme.
The most profitable option is to install all elements of the system (boiler, distribution, heating main) completely inside the house, when it starts at the supply point and ends at the boiler.
Pipe connections in a single-pipe system can be of two types: diagonal and lower through.
The first type of connection is chosen most often, because it is as effective as possible.
In addition, an expansion tank must be installed in the house (most often it is placed in the attic of a two-story house), which must be connected to the wiring, water supply and sewerage systems.
The diagram will help you do everything right.
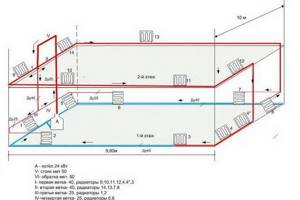
A two-story building has its own installation features.
In this case, a single-pipe circuit should include radiators on each floor, and the number of sections in them and their total number should be approximately the same so that the temperature is comfortable in all rooms of a two-story house.
This option is not very beautiful, but it is easy to implement and quite effective.
Study the diagrams of how to install single-pipe wiring for a two-story house, then it will be easier for you to decide which option is suitable for your building.
Types of structures
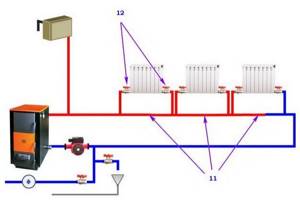
Heating circuit - elements used as a heating system by transferring thermal energy into the air. The most popular systems are those that use boilers or boilers connected to a water supply as a heating source. The liquid, crossing the heating elements, reaches the set temperature, heading into the heating circuit.
Coolant movement is ensured by two methods:
- natural;
- forced.

With forced circulation through pipes
Systems with natural movement of coolant are simple and reliable. Efficiency depends on the proper design of the heating circuit. In the latter case, a pump is introduced that creates pressure. The coolant moves through the pipeline.
Heat sources for heating liquids are boiler rooms and boiler equipment. The operating mechanism is based on the conversion of one type of energy into heat. Depending on the raw material and heating source, boilers operate on gas, solid fuel, electricity, or fuel oil.
All types of boiler units can be used to heat a private home. Gas and solid fuel devices are popular.
Depending on the connection of heating devices in the heating circuit, there are: single-pipe and two-pipe systems. Single-pipe system - when the batteries are connected in series, the water, crossing each element, returns to the boiler.
Design features
For a gravity system to work effectively, the following requirements must be met:
- the heat source is any non-volatile heat generator with outlet pipes with a diameter of 40-50 mm;
- at the outlet of a boiler or stove with a water circuit, an accelerating riser is immediately installed - a vertical pipe through which the heated coolant rises;
- the riser ends with an open-type expansion tank installed in the attic or under the ceiling of the upper floor (depending on the type of wiring and the design of the private house);
- tank capacity – 10% of the coolant volume;
- by gravity, it is advisable to choose heating devices with large internal channels - cast iron, aluminum, bimetallic;
- for better heat transfer, heating radiators are connected according to a versatile pattern - bottom or diagonal;
- special full-bore valves with thermal heads (supply) and balancing valves (return) are installed on the radiator connections;
- It is better to equip batteries with manual air vents - Mayevsky taps;
- replenishment of the heating network is organized at the lowest point - near the boiler;
- all horizontal sections of pipes are laid with slopes, the minimum is 2 mm per linear meter, the average is 5 mm/1 m.

On the left in the photo is the coolant supply riser from a floor-standing boiler with a pump on the bypass, on the right is the return line connection
Note. Slopes perform 2 functions - they help the coolant flow in the desired direction, and the air rises through the pipelines and leaves through the open expansion tank. A caveat regarding the radiators used: if the system is built correctly, steel panels also heat well.
Gravity heating systems are made open and operated at atmospheric pressure. But will gravity flow work in a closed circuit with a membrane tank? We answer: yes, natural circulation will continue, but the speed of the coolant will decrease and efficiency will drop.
Heating without pump
Previously, the design of water heating systems was carried out without circulation pumps. Difficulties arose when purchasing and installing devices that caused forced circulation of water in the circuit. When foreign manufacturers appeared on the market, the situation changed dramatically. Schemes with forced circulation of the coolant are more often used.
Disruptions in the supply of electrical energy have not been eliminated everywhere.
As soon as the power goes out, the water circulation stops. The room is cooling down. The batteries become cold. The heating system is not working efficiently. The water in the circuit freezes. The thermal energy source needs to be started.
Advantages and disadvantages
From a technical point of view, natural circulation of water is effective in tall buildings. The reason is the properties of the fluid in transferring pressure from the surface to the circuit to the lower node.
The advantage of gravitational circulation of water is the saving of building materials. There is no need for expensive pumps or electrical connections to the circuit. Any man can design, install, and operate the system. There is no need to pay for the services of a specialist. If built correctly, the system will heat the house effectively for a long time. Major repairs will not be required for more than 30 years.
The pattern of natural water circulation involves a process of self-regulation. The heating system is characterized by high thermal stability.
- high level of inertia;
- maintaining regulated pipe slopes during installation;
- use of large cross-section pipes;
- high probability of freezing due to poor water pressure;
- airing of heating devices.
To eliminate the problem of air in batteries, air bleed devices will be required. An expansion tank is installed in the system, which controls the water level in the boiler.
Natural circulation of coolant in pipes:
Operating principle
Law of physics: after heating, thermal energy increases in volume, losing its previous density. The unit in which heat is exchanged between the source and the carrier is a heat exchanger.
A heated liquid is lighter than a cooled one; the heat generator is placed at the bottom of the heating circuit. The slightly heated coolant moves upward. In its place, cold water is lowered through pipes. In the case of natural circulation in the system, three physical laws are considered: friction, expansion of bodies with increasing temperature, continuity of the jet.
The water heating circuit with natural coolant circulation includes:
- Thermal generator - boiler. The heat exchanger heats the water.
- Pipes. Form the direction of water movement. The pipeline is connected to boiler equipment and radiators.
- Heating devices - radiators in different designs (differ in shape, material).
- Expansion tank. Protects at the stage of compensating for the increase in liquid volume due to thermal expansion. Installed at the top point of the heating circuit.
The simplest scheme without a pump - the heated coolant moving through the pipes leaves the boiler, cooled water flows back. Vicious circle.
Having entered the top of the system, water begins distribution to the radiators. Processes opposite to circulation in boiler equipment are observed. Displacing the cooled liquid, the coolant fills the radiator. The water gives off heat to the battery. Thermal energy enters the air, warming the room. The liquid cools and circulates towards the boiler. The process is cyclical.
Single-pipe heating
The difference between single-pipe schemes is their efficiency. The systems are rarely used. The heated coolant, rising through the pipes, sequentially passes the batteries located on the second floor. Heading down the pipes, there are radiators located on the lower floor. Returns to the boiler.
The temperature on the upper floors of the house is higher than in the ground floor apartments. For sufficient circulation of liquid through the pipes, a high-performance heating element is required. For private homes, the scheme is suitable in terms of efficiency and quality of heating of the premises.
The system can be made more efficient by additionally introducing a bypass line. A short circuit section is made from the pipe. The diameter of the material must not exceed the dimensions of the pipeline. The bypass connects the input and output of the radiator. It is connected to the tee at the top point of the heating circuit, in front of the expansion tank. Divides the diagram into two parts.
The correct operating mechanism of the heating circuit depends on the expansion tank. Dimensions - depending on the number of batteries. Should not be filled more than three-quarters of the total volume.
In a private house, it is better to make vertical pipe connections. Two risers are being installed: a lifting riser and a lowering riser. Installation of an expansion tank will not be required if you make a system for each battery to automatically bleed the air that accumulates at the top of the convector.
Two-pipe heating circuit
The two-pipe design eliminates the problem of uneven heat distribution. Two circuits are introduced at once. The first is responsible for circulating hot water from the source to the radiator. The second is for the outflow of remaining fluid.
Methods of connecting pipes: with associated circulation, dead-end. Concurrent movement is characterized by the creation of battery taps of the same length. Uniform heating is maintained. The scheme did not gain popularity due to the high consumption of building materials (pipes).
Preference is given to a connecting circuit with circulation of cold and hot water in different directions. Batteries located closer to the heating device warm up faster.
The heating circuit is divided according to the type of pipe routing. Heated water is supplied from the ground floor, basement. The return line is located just below the supply unit.
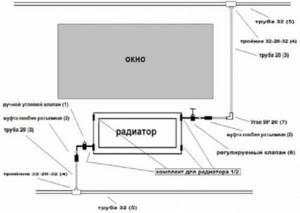
Scheme with upper piping of heating pipes
How to make a heating system with natural circulation

In the event of a power outage, the circulation pump stops, and the flow of water through the pipes of the heating network of a private house stops. The problem can be solved in 3 ways: installing an uninterruptible power supply unit, starting an electric generator, or organizing gravity flow. This means a heating system with natural circulation - convection movement of the coolant without the help of a pump. We'll tell you how to develop and make such a circuit with your own hands.
System installation
When designing a water-type heating circuit without a pump, you need to correctly position the boiler and lower radiator. The higher the battery is in relation to the boiler equipment, the worse the outflow. It is better to install heating devices in the basement. The coolant circulation rate is affected by:
- pipe section. As the diameter of the pipeline decreases, the resistance provided to the coolant increases;
- pipe material. It is better to use polyurethane products;
- number of bends. With a decrease in quantity, the efficiency of the heating circuit increases. Productivity depends on the number of shut-off valves.

Installation work
To calculate the power of boiler equipment, you need to apply the recommendations of SNiP. For one square meter of heated space, a heating element with a power of 0.1 kW is needed. When installing a heating unit, it is necessary to insulate the hot water riser and the room with the expansion tank.
Installation work: install the main riser. An expansion tank is mounted on top. Connect the wiring at 1/3 of the height of the room from the floor. The pipes are led to the radiators. Single-pipe wiring involves connecting pipes to the boiler from the last radiator. Two-pipe - parallel connection of batteries, insertion of branches into a common pipeline.
Do-it-yourself installation recommendations
To lay the main natural circulation lines, it is better to use polypropylene or steel pipes. The reason is the large diameter, polyethylene Ø40 mm and more is too expensive. We make radiator hoses from any convenient material.
Advice. When assembling a gravity heating network made of metal-plastic, do not install compression fittings - they greatly reduce the internal passage.
How to make the layout correctly and withstand all the slopes:
- Start with markings. Mark the locations for installing batteries, connection points for connections, and routes for highways.
- Mark the routes on the walls with a pencil, starting from the distant batteries. Adjust the amount of inclination using a long building level.
- Move from the outer radiators to the boiler room. When you draw all the routes, you will understand at what level to install the heat generator. The inlet pipe of the unit (for cooled coolant) must be located at the same level or below the return line.
- If the firebox floor level is too high, try moving all the heaters up. Horizontal pipelines will rise next. As a last resort, make a recess under the boiler.

After marking, punch holes in the partitions and cut grooves for a hidden gasket. Then check the routes again, make adjustments and proceed with installation. Follow the same order: first secure the batteries, then lay the pipes towards the combustion chamber. Install an expansion tank with a drain pipe.
The gravity pipeline network is filled without problems; Mayevsky’s taps do not need to be touched. Just slowly pump water through the fill valve at the lowest point, all the air will go into the open tank. If any radiator remains cold after warming up, use a manual air vent.
Using steam
The coolant can be water or steam. Steam generators are installed to convert water into steam and supply it through pipes.
Mechanism: hot air is lighter than cooled air. The heated steam quickly moves up the heating unit. Artificial heating is not required. Entering the batteries, the gas is cooled. It turns into a liquid state. Returns to the cauldron again.
Liquid-type heating systems without a pump are popular. This applies to projects of private, country houses. It is important to make calculations. This will protect you from freezing in the cold winter.
Fuel price and its characteristics
To heat a room, the design itself is not important, be it the largest pipeline or a minimized installation in which heating can be carried out without boilers, radiators and pipes; different types of fuel will change: gaseous, solid or liquid.
And it is worth noting that the choice of traditional fuel materials will not always be cost-effective and user-friendly.
- Electricity is the easiest to use, but this method is the most expensive.
- If we talk about gas consumption, it will cost several times less, but do not forget that gas supplied from the main line and liquefied gas in cylinders are fundamentally different. Methane is consumed in the common gas line, and the cylinders are filled with a mixture of propane and butane, which costs 5 times more.
- Using diesel fuel as fuel also cannot be called a cheap pleasure. In addition, this type of fuel smells unpleasant when burned, so it is not suitable for everyone, although according to its characteristics it is quite capable of replacing centrally supplied types of fuel.
- Stove heating using coal can heat a room without pipes, radiators or boilers, and it costs 3 times less than diesel fuel.
- Peat is also an ideal solution for stove heating, but compressed peat briquettes cost one and a half times more than coal and are not an economically viable choice.
- The cheapest fuel choice for a furnace system is wood. Although they are not expensive, you need to take into account that firewood burns out quite quickly (faster than coal) and it is not always possible to maintain a fire. Therefore, it is recommended to start igniting with wood and then add coal. This combined heating method is inexpensive and very effective.
- Another effective method is (which is ideal for boilers with automatic fuel loading and supply as needed) - pellets. These are compressed pellets consisting of wood waste.
Video - do-it-yourself autonomous heating. Step-by-step video instructions.
Do-it-yourself autonomous heating - step-by-step video instructions for assembling the ERA+ electric battery
Calculations
Each type of heated floors has its own calculation subtleties and design features, but the main task is to calculate the power of the heat source. This value determines the parameters of the heating system, as well as the type and quantity of materials required. The power is calculated taking into account such data as the area, shape and height of the heated room, the optimal temperature, and also depends on the design and operation of the heating system.
Calculating water heating parameters is a rather complex task that is best left to specialists. It includes the choice of the boiler, the diameter and length of the pipes, the choice of the number and types of control and distribution devices, as well as the calculation of hydro- and thermal insulation. A correctly performed calculation allows you to organize reliable and efficient operation of a warm water floor as the main heating system.
Determining the required power is the main task when designing electric floors, since the efficiency of the system and energy costs depend on its accuracy. The total power of the heating element will depend on operating conditions.
If an electric floor is used as independent heating (main heating), then the specific power should be in the range of 150-180 W/m2. If it is used as an additional heat source (comfort heating), then this value will be less (100-150 W/m2).
Read more about calculations of water and electrical transformer substations in our article.