Home > Document
| Document information |
| Date added: |
| Size: |
| Available download formats: |
Acting Director of AF JSC TPP A.M. Kamshekin
ON HYDROPNEUMATIC FLUSHING OF CENTRAL HEATING SYSTEMS OF BUILDINGS FOR ALL PURPOSE
Flushing the system is necessary after repairs, installation, and also after the end of the heating season to remove sludge and dirt.
The most effective is the hydropneumatic method of flushing - bubbling water with compressed air to create a violent movement of the environment in the system.
To eliminate the possibility of contamination of an already washed area, washing is carried out in the following sequence.
To flush heating systems, the following fittings must be installed at the inlet (see Appendix 1):
for connecting the compressed air pipeline from the compressor DN 32mm (18),
for connecting a cold water pipeline DN 50mm (19),
for drainage of drained water DN 50mm (20).
To ensure the possibility of removing large contaminants from pipes, the diameter of the drain pipes should be taken from the following ratios:
If there is a drainage device in the chamber, flushing water is discharged directly into the drain, and if there is no drainage, into the nearest storm drain or into the chamber, from where it is pumped out.
When flushing heating networks, mobile compressor stations with a capacity of 5-6 m3/min, pressure up to 6 atm, or another type of diesel compressor can be used.
Depending on the throughput of the drainage device, compressor power and possible water consumption, several flushing modes are used.
The normal washing mode is considered to be the movement of the mixture, accompanied by shocks and slippages of alternately water and air.
When introducing compressed air into the area being washed, it is necessary to ensure that water cannot enter the compressor receiver, for which the valve on the water supply line should open only after the pressure in the receiver becomes greater than the pressure of the water supply system.
Taking the reduced speed of movement of flushing water equal to 1 m/sec, the approximate water consumption during flushing for various pipe diameters will be:
Pipe diameter, mm
Water consumption, m 3 / h
Tap water pressure is selected in the range from 1.5-3.0 atm. At a pressure of more than 3.5 atm. Stressful operating conditions for the compressor are created under which it cannot provide normal network flushing.
At a pressure of 1 atm. compressed air from the compressor can block the access of water to the pipeline and at the end of the section only air will escape. In this case, you should alternate the operation of the compressor with stopping it for 10-15 minutes with a continuous supply of water.
Keep the air pressure in the flushed pipeline at 3-3.5 atm.
In addition, it is necessary to comply with the requirements for the premises and placement of input nodes in accordance with the ITP room must comply with the requirements of SNiP 2.04.07-86 and “SNiP 31-01-200 and each input node must contain (see Fig. 1.):
-water jet elevator (16),
- installed design restriction device (nozzle) (17),
- mud traps on the supply and return lines (14,15)
-four valves (1,2,3,4)
- inserts for pressure gauges (5,6,7,8,9)
- inserts for thermometers (10,11,12,13).
If there are no connections for flushing the internal heating system and, as a result, no flushing is carried out, the consumer will not be connected during the heating season, as it clogs the heat distribution networks.
And also, the absence of inserts for pressure gauges and thermometers does not make it possible to carry out adjustment work, therefore, consumer claims for unsatisfactory heat supply will not be accepted and all responsibility falls on the utility service provider (MC, HOA, etc.).
Hydropneumatic flushing of heating systems - instructions
- Flushing of the heating system is carried out in the presence of a representative of the energy supply organization.
- The foreman of the district's heating unit is invited to begin flushing, and in his presence, flushing work begins.
- During flushing, the heating system is disconnected from the district heating network by valves 1, 2, 3, 4. If the valves do not have a sufficient closing density, additional blinds (plugs) made of 3mm sheet steel must be installed.
- By the beginning of the new heating season, these valves must undergo an inspection.
Preparatory work
Rubber hoses are connected to the fittings used for flushing. Hoses (rubber sleeves) are connected using half-nuts “ROT” (according to GOST 2217-76). It is necessary to install check valves on the air and water inlets that will be used for flushing.
Before washing, remove the nozzle from the elevator.
- The system is filled with cold water through valve 19 with open valve 21 of the air collector and open valves 22 and 24, as well as closed valves 1; 2; 3; 4; 18; 20 and 23. After water appears in valve 21, this valve and valve 19 must be closed.
- Blow air through each riser of the heating system.
- To do this, close all taps 24 on the risers. Open air valve 18. By sequentially opening valves 22 on the heating risers, the risers are purged with air from the bottom up.
- To drain waste water into the storm drainage sewer system, you need to put a flexible rubber hose on fitting 20.
- Starting from the far riser, hydropneumatic flushing of all risers is carried out sequentially.
- To do this, you need to open sequentially valves 22 and 24 on the risers with air valve 21 open. Next, open water valve 19 and air valve 18.
Why do pipes get clogged and when do you need to flush your heating system?
During operation, any heating system experiences pipe contamination in one way or another. This may be a fairly small sedimentary layer, the accumulation limit of which is limited by the volume of coolant in the isolated network. But in municipal distribution pipeline systems, the amount of dirt can become so large that the water stops flowing completely. There are several reasons for this phenomenon:
- dirty coolant, soil getting into the heating network during pipeline repairs;
- accumulation of bacterial waste products;
- the formation of a sedimentary layer of mineral salts, the concentration of which in the public heating structure is quite stable due to the constant addition of water to the boilers;
- consequences of destruction of steel pipes, remains of oxidized metal.

Advice! Determining that the heating system needs to be purged with a compressor or another cleaning procedure is quite simple. The first sign of a clogged radiator is uneven surface temperature. The second manifestation that indicates clogged pipes is differences in the heating of radiators in different rooms.
Do not think that owners of modern individual systems will never need a compressor for flushing heating. An isolated structure, where a limited volume of coolant circulates, is generally stable without adding new portions of water with mineral impurities. However, the speed of fluid passage, the so-called volumetric pumping of the working fluid per unit time, plays an important role in it.

Warm floors are especially critical to changes in circulation patterns. The effective cross-section of its thin tubes drops significantly even when a modest coating appears on their walls. In addition, even a thin layer of deposits that does not have a significant effect on the fluid flow greatly reduces heat transfer in any system with steel, cast iron, aluminum or bimetallic radiators. Therefore, a compressor for flushing heating can be useful not only to service companies providing relevant services, but also to individuals.
Hydropneumatic flushing of heating systems with bottom wiring
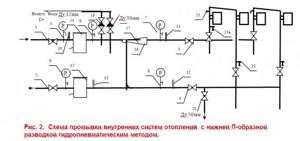
In heating systems with a bottom heating circuit, flushing is carried out in a similar way. The system is filled with water through valves 19; 24 and 22, while valve 21 is open.
Next, air is purged, starting from the last, of each heating riser. When flushing along the risers, water can be discharged from each riser through tap 23a.
To divert the air-water mixture from several risers at once, the mixture is discharged into the storm drain through drainage 20 (see Fig. 2).
Hydropneumatic flushing of heating systems is carried out until the discharged water is completely clarified.
- After finishing washing, you need to dump the residual water.
- Fill the heating system and perform a one-time reset.
- Next, fill the system with water and take a sample for analysis.
Flushing heating systems is necessary for efficient heating of premises. This procedure is recommended to be carried out once a year, before hydraulic tests. As a last resort, you need to flush the heating system at least once every few years - this will help increase the heating efficiency. Owners of private houses will also be able to reduce resource costs for heating and extend the service life of pipelines.

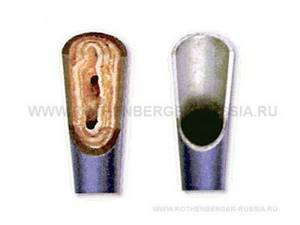
As a result of hydroflushing, various deposits are removed from pipes and radiators: scale, rust, scale, etc. Sometimes they occupy more than 2/3 of the pipeline diameter. The thicker the layer of deposits, the more the amount of thermal energy transferred to the room decreases. You can see what pipes with deposits look like in the photo.
Housing office employees must flush heating systems every year. But in practice this is not always done. As a result, hydropneumatic flushing of heating systems is carried out by specialized companies that house residents contact.
Flushing heating systems using compressors

Every company involved in pipeline maintenance is faced with the need to carry out routine maintenance work on flushing heating systems. Rust, scale salts and solid foreign bodies accumulating at the bottom and on the internal surfaces of pipes and heat exchangers significantly reduce heat transfer and impede hydrodynamics. According to statistics, heating systems with a 10-year service life are more than 50% clogged with various contaminants. Considering that every millimeter in the thickness of deposits increases fuel consumption by approximately 20-25%, it becomes obvious that it is advisable to carry out regular flushing of pipelines. In the Russian Federation, the frequency of flushing heating systems is regulated by SNiP 3.05.01-85.

Until recently, there were two ways to deal with deposits in heating systems: flushing with water or chemical reagents. Hydraulic flushing of the system is effective in the presence of minor contamination. This method requires the least cost and time. The main advantage of the hydraulic method is its safety for the environment. However, if heating systems are seriously contaminated, this method is not effective enough.
Chemical flushing of heating systems is carried out when pipelines are significantly contaminated with organic compounds or hardness salts that require dissolution. Depending on the nature of the contamination, acidic or alkaline reagents are used, which are subsequently neutralized and discharged into the sewer network. This washing method is most successfully used to remove lime and calcium deposits. In this case, flushing is carried out using reagents based on various acids (hydrochloric, orthophosphoric, etc.). Thus, chemical flushing is more effective than flushing the heating system with water, however, due to the use of active chemicals, it is more aggressive to materials from which the heating system is manufactured, as well as to the environment.
Traditionally, flushing heating systems with these methods is carried out using special pumps that pump water and chemicals through the system. The pump is connected to the inlet and outlet of the system, forming a loop through which the liquid circulates continuously. The direction of water flow can be adjusted manually or automatically. If chemical flushing is necessary, the pump tank is filled with a reagent, which then enters the system. According to existing standards, hydraulic flushing of heating systems is recommended to be carried out once a year, chemical flushing - once every 5-6 years.
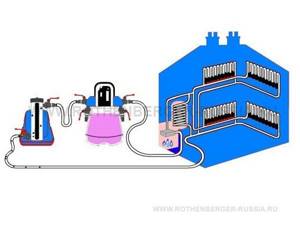
However, today there is an alternative to pumps and traditional flushing methods: it has become possible to clean heating systems using a pneumatic-hydraulic pulse method using special compressors. The principle of flushing heating systems using compressors is quite simple: compressed air is pulsed into a system filled with water. At the same time, the speed of water movement in the system increases, which creates an additional cleaning effect, and the resulting water-air mixture effectively loosens scale and rust deposits on the walls of pipelines. The main advantage of this flushing method is that, while being very effective in removing even complex contaminants, it is absolutely safe for both the environment and the heating system itself. With regular use of this method (at least once every 4 years), it is possible to maintain the high quality of pipelines without resorting to aggressive flushing methods.

Initially, flushing compressors were designed to clean underfloor heating systems from silt deposits. However, due to the efficiency of the water-air mixture, which is superior to water in terms of cleaning characteristics, compressors have also begun to be successfully used for flushing heat exchangers and heating systems.
The next step in the development of flushing compressors was the ability to carry out chemical flushing with their help. Thanks to this function, it became possible to use compressors for washing and disinfecting drinking water systems. In accordance with European standards DIN 1988-2/EN 806-4, drinking water pipelines require flushing before commissioning. These standards also regulate the sanitation of drinking water systems in the event of pipeline contamination with Legionella and the need for disinfection. All these tasks are easily solved with the help of a flushing compressor. Chemical washing is carried out using additional devices (injectors, gearboxes, containers) that are compactly and conveniently attached to the compressor. Thus, modern flushing compressors are multifunctional devices with electronic control and are capable of working with any chemical reagents intended for flushing heating systems or disinfecting drinking water systems.
A new stage in the development of technology for flushing heating systems using compressors was marked by the release of a new product from ROTHENBERGER (Rothenberger, Germany) - the ROPULS eDM compressor. Using a special free application, this model allows you to record all washing cycles. Thanks to the built-in Bluetooth transmitter, real-time washing information is sent to the receiving device and can be saved in pdf format. The possibility of logging allows you to document the entire washing process and generate a ready-made report on the work performed.

The technology for flushing heating and water supply systems using compressors has a number of features that must be taken into account when working with these devices. So, unlike pumps that flush through a loop circuit, the compressor is connected only to the inlet of the system using hoses supplied with the device. Thus, a water-air mixture or chemical reagent is supplied to the system and then discharged into the sewer network. This feature imposes certain requirements on the washing process. In this regard, when using the chemical flushing mode, it is recommended to shut off the system after filling it with a chemical reagent, leave the system shut off for the period necessary to dissolve the deposits, and then drain the reagent and flush the system with water in a pulse mode. When working with a compressor, it is recommended to use a fine filter. Cold and hot water pipes must be flushed separately. Pipeline systems are washed in sectors. Typically, each upstream pipeline is considered a flushing section. The flushing duration should not be less than 15 seconds per linear meter of pipe. In addition, each rinsing point must be rinsed for at least 2 minutes.
What are the advantages of compressors over traditional flushing pumps? First of all, the pneumatic-hydropulse method is a more effective method compared to flushing the system with water and a less aggressive method compared to chemical flushing. Also, unlike pumps, compressors do not have strict restrictions on the volume of the flushed system. The relative limitations of the operating range when using a flushing compressor are determined by the height of the water supply, which, however, are removed if the compressor can be connected to the highest point of the system. Another advantage of flushing compressors is its wide functionality: as a rule, these devices can be used as standard compressors for working with pneumatic tools.
Flushing heating systems is an integral part of the operation of internal communications. Their thermal conductivity properties directly depend on the state of the systems. Devices traditionally used for these purposes (flushing pumps) allow heating systems to be flushed only with water or chemicals. The use of compressors allows, along with the above cleaning methods, to flush heating systems with a water-air mixture. Thus, flushing compressors are reliable and efficient devices that are a worthy alternative to flushing pumps and allow you to cope with serious contamination of pipeline systems in a gentle, environmentally friendly way.
What is hydroflushing

For hydropneumatic flushing of pipelines to be successful, it is necessary to calculate a number of parameters and find out:
- length of flushed pipes;
- speed of water movement;
- air flow and pressure (determined based on the diameter of the pipes).
To obtain the required speed of movement of the water-air mixture, the communications should be flushed in separate sections - by risers or their groups.
Preparation for hydropneumatic flushing of the heating system

Before you start cleaning, you should do the following:
- examine communications;
- identify sections of the pipeline that need to be flushed separately and break the procedures into stages;
- if necessary, install shut-off valves to block sections of pipes and remove washed out deposits;
- make the required calculations to obtain a good washing result;
- determine whether a hydraulic test of the heating structure is necessary.
After completing the preparatory activities, wash the communications until the mixture of water and air becomes lighter. After cleaning, repeat hydraulic tests are carried out (about











