Duration of commissioning work when starting heating in microdistricts
- adjustment tests under operating conditions, balance experiments (setting optimal modes, testing valve control in manual and automatic modes, checking automation settings, identifying deficiencies and developing proposals for eliminating them), the result is an individual test report;
- comprehensive testing (72 hours of continuous operation for all major equipment, 24 hours for heating networks), its beginning is considered to be the time when all systems are started at maximum load.
Some companies document all activities directly related to the preparation and testing of devices in a separate document - the Commissioning Methodology, which comes as an addition to the Program.
In the Program they include more general things of an organizational nature. That is, there is an actual division of the entire complex of work into organizational, legal and technical components.
According to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 23, 2006 No. 307 “On the procedure for providing utility services to citizens,” the requirement for utility heating services is uninterrupted round-the-clock heating during the heating season. The permissible duration of a heating break is a total of no more than 24 hours within one month.
In case of failure to provide utility services or provision of utility services of inadequate quality, the consumer notifies the contractor's emergency dispatch service or other service specified by the contractor. A notification about the failure to provide utility services or the provision of utility services of inadequate quality can be made by the consumer in writing or orally (including by telephone) and is subject to mandatory registration with the emergency dispatch service.
The technical report is usually issued by an involved specialized organization within one month. proektoved.com Commissioning of heating systems Before putting the heating system into operation, it is necessary to perform a number of preparatory work, conduct tests and establish the interaction of various units with each other. All this is included in the commissioning of the heating system, the purpose of which is to identify and eliminate shortcomings and errors made during installation, as well as to bring the entire system into compliance with the standards established for it.
As a result of this work, the client receives a reliable, productive and efficient system. The cost of heating commissioning is fully paid for by subsequent trouble-free operation and safety of the equipment. Composition of commissioning works
Commissioning work is carried out after installation.
As part of the commissioning and commissioning of refrigeration supply, the following types of test work are performed:
- checking the correct assembly of all components and components of refrigeration equipment;
- filling the cooling system with all necessary working media (freon, nitrogen and oil);
- checking the functioning of protection and control equipment;
- starting the system and bringing it to the required operating mode;
- briefing (and, if necessary, training) of service personnel.
Important! The last point can be included in the commissioning program only by agreement with the customer. The procedure for commissioning heating and heat supply systems The term “heat supply” is usually associated with the organization that supplies the coolant, while the concept of “heating” is associated with its consumption and is applicable to organizations involved in the operation heated rooms
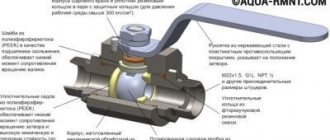
Heating adjustment work using shut-off valves
Throughout the entire process, the water entering the system must have a constant temperature. Adjustment is usually made according to temperature changes by changing the volume of supplied water, which depends on the type of heating system and thermal input.
Temperature changes depend on the volume of water consumed and this value is inversely proportional. Thus, in order to increase the difference to the required value, the coolant flow should be reduced. To do this, either close the valve located at the inlet or reduce the flow itself.
The more water passes through heating devices, the higher the speed of its movement and, accordingly, the coolant cools less. As a result, the average temperature in the radiator increases and the heat transfer of the device increases. After completing the adjustment in the heating unit, individual risers of the structure are subject to adjustment. If problems arise, repairs are carried out in such a way that it is possible to use control valves for the heating system on risers or balancing valves (more details: “Regulation valves for heating radiators, valve installation”).
One way to adjust the heating system is shown in the video:
When there are only taps on the heating risers, only preliminary adjustments are made. It should be taken into account that the closer the riser is to the inlet, the more the tap should be opened. This is necessary so that the heating shut-off valves on the closest riser allow a minimum volume of water to pass through.
At the same time, on the riser located farthest away, you need to open the tap, such as in the photo. First, they check the quality of heating of the furthest riser and finish with the one that is closest.
Typically, in two-pipe systems, due to pressure, devices on the upper floors overheat. If this deficiency is not present on the lower floor, then adjustment of the upper heating radiators is necessary. If there is a double adjustment valve, it is possible to reduce the flow area. In the absence of such taps, the heating radiators are adjusted by installing throttle washers.
In two-pipe heating systems, the uniformity of heating of radiators will increase with increasing water flow. The most important parameter for heating structures is operating pressure (read: “Losses and pressure drop in the heating system - solving the problem”). To lower it, use a pressure regulator in the heating system, and to increase it, use circulation pumps.
The temperature of the coolant when adjusting the device cannot exceed 50-60 °C. After completing the adjustment, the water temperature must be brought to 90 °C, and the heatability of the radiators must be checked again at this temperature. It is advisable to seek the services of specialists to adjust heating systems.
How to set up, adjust, balance the heating system
A common situation is that one radiator is hotter than the other, which should not be the case. Or it’s cool in one part of the house and hot in another. This means that the heating system needs to be somehow adjusted, as experts say – balanced. It is possible that for this you do not need to call a plumber at all, and you can adjust the heating yourself.
To do this, control taps and/or balancing valves must be installed on each radiator or between the arms of the system.
But in some cases the system needs to be redone. Read more about possible heating problems and balancing rules below.
If there is not enough radiator power
It also happens that it is difficult to balance the heating system, since the distribution of radiator power does not at all correspond to the heat loss of the rooms.
Recommendations for the selection of radiators are as follows: for 10 sq. m. area - 1 kW, but this value is multiplied by 1.2 if the room has one window, 1.3 if the window is large, 1.4 if there are two windows and the room is corner, 1.5 if there are already 3 windows or a large glazing area.
In addition, the radiator power is indicated for a temperature of 90 degrees, but we are going to heat it at a maximum of 70 degrees, aren’t we? This means we multiply the heat loss by another 1.3. And if low-temperature heating is used - no more than 50 degrees, then multiply by 1.3 again. Why is low-temperature heating the most comfortable and economical? Read more about economical condensing boilers
The power of one section of an aluminum, bimetallic radiator (approximately 80 mm thick and wide), or cast iron radiator (old MS-140 type) is approximately 170 - 180 W. A set of 7 sections is considered to be no less than a kilowatt.
In addition, radiators must be installed in characteristic places to create a thermal curtain to the cold source. Typically - under the windows, near the door.
It is better to distribute the number of battery sections (sizes) in accordance with heat loss and the characteristics of the heating system than to balance and cover the flow of liquid.
Simple causes of heating system problems
It is possible that there is air in the heating system and for this reason the coolant does not flow well to one or more heating devices.
In the highest places in the pipeline, air valves (Mayevsky valves) are installed that can be opened manually. Or automatic air vents. Mayevsky taps are usually installed on each radiator. Walk through the system, open the taps, bleed the air.
Another reason for poor performance is clogging, first of all, of the filter element. Unscrew the filter and clean it. Before any balancing of the heating system, clean the filter.
In improperly assembled systems, in addition, there may be clogging at the lower points at differences in the pipeline level, and airing at the upper points, for example, the pipeline is wrapped around a door without an air vent.
Balancing the system using valve regulators
It is possible that the very design of the system requires balancing. For example, one long arm is used and the other is short.
Or the arm length of the dead-end pattern is too long. Or a beam scheme is used, which requires initial configuration. And it happens that they make archaic one-pipe systems with shortcomings. In either case, the result is significant uneven heating.
So, balancing valves are installed on the radiators; all that remains is to ensure that the temperature of all radiators is approximately the same.
The principle of balancing is the simplest - do not close (open as much as possible) the taps on the coldest ones and “tighten” the hottest ones a little. As a result, more coolant will flow to the cold ones, less to the hot ones, and their temperature will equalize.
An example of how to adjust heating in a one-story house
A typical example is that it was not possible to make two arms of a dead-end circuit, since the pipes were being laid in the way of a door, so they made one arm and put “as many” 7 radiators on it.
As a result, the temperature of the latter in the shoulder is 9 degrees less than that closest to the boiler. You can do the following: on the last 3 radiators, leave the taps completely open. On the first, open the balancing valve from the fully closed position by 1.5 turns, on the second - by 2 turns, on 3 and 4 by 2.5 turns.
It is assumed that the balancing valve is adjustable in total by 4.5 turns, and the length of the pipelines is within the limits of a small house. But regulators come in different designs, different lengths, so in each case there is a different number of revolutions.
After balancing, you need to wait 20 minutes, then measure the temperature of the incoming radiator pipe again, you may have to additionally adjust something by a quarter turn...
Adjustment principles
Significant closures cannot be created. The basic principle of balancing is to open the path for coolant movement as much as possible. Closure is a forced measure.
Therefore, achieving the same temperature in this example is not worth it. It is correct to agree that the first one will be hotter by 3 - 4 degrees at a coolant temperature of 80 degrees and by a couple of degrees with low-temperature heating of 50 degrees.
How to measure it? Professionals would look at each radiator through a thermal imager and take a thermal photo. But you can also get by with contact thermometers - special devices for heater installers. But in everyday life, they often measure simply with their hands and judge by how they feel. The earlobe is sensitive in this regard - but is it worth rubbing your ear on the radiators...
Example for a two-story house
Another typical example is when the designers and installers managed to design the heating system in such a way that they installed approximately equal power radiators on both the first and second floors (the areas are approximately equal), and they forgot to solder the balancing of the floors relative to each other.
As a result, it is still cold on the first floor, but it is already hot on the second floor.
Again, balancers installed directly on the radiators will help out. On the second floor, we simply open the taps by 2 turns instead of the full 4.5, thus reducing the liquid flow by 30 percent. By reducing the energy output, we equalize the temperature regime, and if necessary, close more...
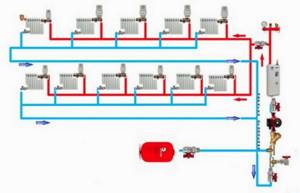
The diagram in which there is no possibility of balancing between two arms is a typical mistake in homemade systems.
Commissioning according to the project
With the usual proper installation of a modern heating system, balancing is not needed at all; the circuit is designed so that all radiators heat optimally. In addition, they are often automated with thermal heads, with which you can set the temperature in a separate room.
Designers and design data introduce a little confusion into the issues of heating adjustment. The project includes the amount of coolant passing through and the balancing of each radiator - how many revolutions each balancing valve of a certain type should be turned.
This achieves a certain accuracy in the implementation of design decisions. But for the user this practically does not matter, since adherence to design accuracy has very little effect on the final result. But large balancing values (as in the examples above) cannot be included in the project. Therefore, very precise regulation according to the design can be ignored.
Noisy radiator
Another point that needs to be addressed is too much coolant passing through the radiator. At the same time, the radiator makes noise and this is unpleasant. Reasons: incorrect heating scheme, unbalanced (closed) other radiators, too powerful pump in the system. All this needs to be eliminated.
An overly powerful pump is a problem with homemade heating systems, because home craftsmen “seem” that they can’t spoil the porridge with oil. But what happens here is something else - a lot of money wasted and noise in the radiators. How to select a pump for a heating system... A noisy radiator requires balancing the system or reworking it.
A difficult case is the closure of the pipeline passage during installation. It is difficult to identify a defective location; sometimes it is necessary to redo an entire arm of the pipeline. This is typical for polypropylene pipes, in which sagging of material is possible during soldering. More details - how to solder polypropylene and prevent defects
Recalculation for heating when setting up a heating system
The purpose of individual tests is to prepare for complex testing in the presence of a working commission.
Complex tests represent actions carried out after the acceptance of mechanisms by the working commission, and the complex testing itself. At the same time, the interconnected joint operation of all installed equipment is checked at idle, then under load, after which the technological mode envisaged by the project is reached.
Although this is not prescribed by law, in recent years the customer has increasingly required that a commissioning program be drawn up for testing work. This gives confidence that not a single nuance will be missed, and the operation of all systems will comply with approved standards and design documentation.
Methods for adjusting the heating system
It often happens that errors made during the installation of a heating system can only be detected after the equipment is put into operation. Among the reasons for failures in the heating supply of a house is incorrect determination of the required amount of coolant. When there is little liquid in the system, the room will be cold, and if there is a lot, the air overheats and does not pass to other rooms.
To adjust the operation, adjustment of the heating structure is required. If this is not done, then the service life of the equipment will be significantly reduced.
Adjustment of the heating system is carried out using one of two methods:
- in a qualitative way - by changing the temperature of the coolant;
- quantitative method - it changes the volume of liquid.
Qualitative adjustment is carried out at the heat source, and quantitative adjustment is carried out directly on the heating structure. Before starting to carry it out, determine the volume of liquid consumed and the temperature of the coolant, using special devices for this - a water meter and a flow meter.

When there are no such devices, then the actual flow rates are compared with the calculated data. Most often, two-pipe heating systems are installed, which can provide warmth and comfort in the house. You will also need shut-off and control valves for heating.
Proportional method
The method is based on the patterns of flow deviation in parallel sections of the system when regulating one of them. From the hydraulics course it is known that pipeline circuits can be connected in parallel, in series and in branches. Each section of the pipeline has a certain resistance characteristic S [Pa/(kg/h)2]. Depending on the method of connecting various pipelines, these characteristics are summarized in a certain way.
With a series connection, this dependence has the form: S = S1 + S2, G1 = G2. For parallel connection:
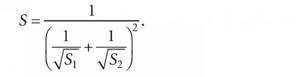
The pressure loss in the area is determined by the following equation:
Δр = SG2.
It is known that in parallel connected pipelines there will be equal pressure losses. Accordingly, for the system (Fig. 3) we obtain:
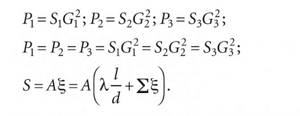
It is assumed that adjusting one of the valves in the circuit does not lead to a proportional change in the parameters in the remaining valves in the circuit.
There is a proportional relationship between water flow rates in the system circuits - a change in the resistance of one of the valves entails a redistribution of flow rates while maintaining the proportion between them (Fig. 3).
We recommend: Hydropneumatic flushing of the heating system (hydropneumatic flushing, hydropneumatic flushing), do-it-yourself repair: instructions, photo and video tutorials, price
Algorithm for adjusting the heating system using the proportional method:
1. Define circulation rings.
2. Select the main circulation ring.
3. Open the valve of the main circulation ring (while slightly closing the remaining valves of the circuit). If you are not sure which circulation ring is the main one, we leave it open.
4. We determine the existing proportion between risers or the proportion between actual and design costs in risers (circuits).
5. We find the riser or circuit relative to which we will carry out regulation (usually this is the circuit with the smallest ratio G1ph/G1pr).
6. Then, using the method of successive approximations, the flow rate in circuit 2 is set by an adjustable valve G1ph/G1pr = n = G2ph/G2pr, etc.
7. At the final stage, we adjust the main valve, setting the ratio Gph/Gpr = 1 on it, and according to the law of proportionality in the remaining circuits of the system, the ratio G1ph/G1pr = G2ph/G2pr = 1 will also be established.
This control method is used in large branched systems.
Pros: it is possible to configure complex branched systems; possibility of quick adjustments when regulating by design method in case of changes in installed systems relative to the design. Disadvantages: the presence of a large number of balancing valves and, as a result, increased pressure losses in the system; multiple measurements of coolant flow rates in circuits; the need for measuring instruments and time.
What types of heating systems are there for an apartment building?
Depending on the installation of the heat generator or the location of the boiler room:
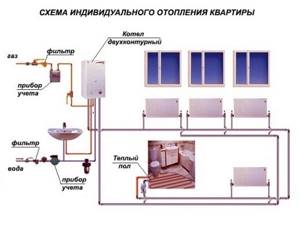
- An autonomous system in an apartment where the heating boiler is installed in a separate room or in the kitchen. The costs of purchasing a boiler, radiators and corresponding materials for piping are returned quickly, since such an autonomous system can be adjusted based on your own considerations regarding the temperature regime in the house. In addition, an individual pipeline does not lose heat, but on the contrary, it helps to heat the premises, since it is laid throughout the apartment or house. An individual boiler does not need to be adapted for the reconstruction of central heating - once drawn up and implemented, the heating scheme will work for a lifetime. And finally, the already working circuit can be supplemented with parallel or sequentially connected circuits, for example, a “warm floor”;
- An individual heating option that is designed to serve an entire apartment building or an entire residential complex is a mini-boiler room. Examples include old boiler houses serving a neighborhood, or new complexes for one or more houses using different energy sources - from gas and electricity to solar panels and thermal springs;
A centralized heating scheme in a multi-storey building is still the most common working solution to the problem.
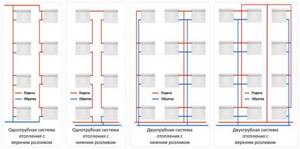
Heating schemes depending on the parameters of the working fluid:
- Heating using ordinary water, in the pipes of which the coolant does not heat above 65-70 0 C. This is a development from the field of low-potential systems, but most often old schemes work with the temperature of the working fluid reaching 80-105 0 C;
- Steam heating, where not hot water moves through the pipes, but steam under pressure. Such systems are becoming a thing of the past, and today they are practically not used in the delivery of heat and heating of any type of apartment buildings.
Based on the piping diagram:
- The most common is a single-pipe heating system for a multi-story building, where both supply and return pipes are one thread of the heating main. Such a scheme can still be found in “Khrushchev” and “Stalin” buildings, but in practice it has a big drawback: batteries or radiators connected in series to the circuit do not ensure uniform heat transfer - each subsequent heating device will be a little colder, and the last radiator will be a little colder. the pipeline will be the coldest. For at least approximately equal distribution of heat throughout the rooms, each subsequent radiator in the circuit must be equipped with a larger number of sections. In addition, in a single-pipe heating scheme in a five-story building, you cannot use radiators that do not meet the design parameters, and devices for regulating heat transfer - valves, etc. regulation;
- The Leningradka scheme is a more advanced solution, but according to the same single-pipe scheme. This scheme has a bypass (pipe jumper), which can connect or disconnect additional heating devices, thereby regulating the heat transfer in the room;
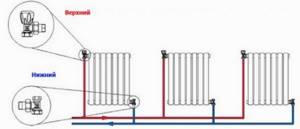
A more advanced two-pipe heating system in an apartment building began its existence with the construction of buildings according to the so-called “Brezhnevka” project - a panel house. The supply and return in such a scheme operate separately, so the temperature of the working fluid at the inlets and outlets of the apartments of a 9-story building is always the same, as in radiators or batteries. Another plus is the possibility of installing an automatic or manual control valve on each heating device; The radial (collector) scheme is the latest development for atypical housing. All heating devices are connected in parallel, and taking into account the fact that this is a closed OO system in an apartment building, the piping can be made hidden. When implementing a beam scheme, all control devices can limit or increase the heat supply in dosed quantities.
How to properly start heating in an apartment building
One of the most important problems that utilities face is starting heating. The risk of errors occurring in an apartment building is, of course, higher than in a private building. But in each case, it arises mainly due to non-compliance with the rules. To avoid unpleasant situations when connecting heating, you need to follow the sequence of necessary actions.
When the heating season begins, it often happens that the heat is distributed unevenly on the top floors. The reason for this is that the heating system starts up too quickly, which creates air pockets that prevent the uniform heating of all apartments in the house.
When the heating season ends, the system remains idle, causing its pressure to drop. That is why the question of how to properly do heating, as well as its further regulation in an apartment building, is a fairly pressing issue.
The main mistakes that are made when starting and adjusting heating in an apartment building
In order not to encounter many problems when starting the heating, as well as during its operation, you should know the main mistakes that are made in this process:
- Starting the heating via the flow line too abruptly.
- Getting rid of water or coolant in the basement. It would be correct to skip this step, because the air will not leave the system in any case - it rises up.
- There is also no need to drain water and air from all living areas in the house.
If everything is done correctly, this need will disappear on its own.
At the same time, it should be taken into account that in order for the system connection to go smoothly, the participation of 2-3 people is necessary. This is necessary so that the speed of actions and their coordination are as effective as possible.
How to start heating without making mistakes in an apartment building
So, in order for the heating system to function as efficiently as possible, it must first be started correctly. For those who do not know how to properly and safely start heating in an apartment building, the action plan is as follows:
- Slowly introduce coolant into the system. Make-up pumps must be turned on at the lowest power so that filling occurs gradually.
- To ensure that the procedure is not violated, you need to fill the system through the return line. The bottom-up starting system is suitable for all types of houses. With this type of operation, the coolant will smoothly displace the air that has accumulated during the entire period of inactivity of the system. These steps can be used to adjust the launch in such a way as to avoid the occurrence of air locks.
- The next step is to get rid of any remaining air in the system. This is necessary to ensure that the heating works correctly and that there are no complaints about its malfunction throughout the next season. This should be done in the attics of a multi-story building, where the air collectors are located. You need to lower the start valve on them, waiting until the characteristic sound, which signals the absence of air, stops.
- While continuing to connect the system, you need to remove water from the system, finally getting rid of any remaining air. This must be done extremely carefully, using any container, so as not to flood the residents of the upper floors.
- If the house does not have an attic, the water must be drained on the top floor using a Mayevsky tap. The system starts only after this action.
Ways to correctly connect the necessary heating radiators in an apartment building
If heating is carried out correctly, the house is warm and comfortable. To achieve this, you need to properly connect the radiators. There are many schemes for this action:
- parallel connection;
- diagonal;
- single-pipe;
- single-pipe with jumper;
- single-pipe bottom;
- single-pipe bottom with a jumper or tap;
- two-pipe;
- two-pipe bottom;
- two-pipe diagonally.
Despite the abundance of radiator connection schemes, in practice one-pipe and two-pipe connections are used. In order to know how to set up and then start heating in an apartment building, you need to know the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
The first connection method has a number of disadvantages, although it requires less costs. The main one is the loss of heat as you travel. In this case, water is supplied vertically from the basement to all floors, enters each of the apartment’s radiators, and, when cooled, enters the same pipe.
Ultimately, almost cold water reaches the top floor, causing dissatisfaction among the residents in the house.
As for the two-pipe heating system, it can be open or closed. However, in any case, the level of heat conservation is an order of magnitude higher than with a single-pipe scheme. This effect is achieved by the fact that the cooled water no longer enters the pipe, but leaves through the return channel. This keeps the order of supplying a constant temperature.
How to adjust the heating level in an apartment building
To ensure that the heating system is adjusted properly, pipes of different diameters are installed in an apartment building. The speed and pressure of the liquid together with steam, and accordingly the level of heat, is directly related to the size of the pipe opening. That is why, in order to ensure that the adjustment is carried out correctly, pipes of different diameters are used.
The maximum size of 100 mm is located in basements. This is where the connection of the heating system begins. As for the entrances, for uniform distribution of heat, pipes are installed there, the diameter of which does not exceed 50-76 mm. However, such adjustment does not always give the desired heating effect. Residents of the top floors of the house suffer from this, where the temperature drops noticeably.
To regulate this process, use the launch of the hydraulic heating system. This is the connection of circulation vacuum pumps, which ensures the launch of an automatic pressure control system. Installation, as well as subsequent startup, is carried out in the collector of a separate building. Accordingly, the order of heating distribution along the entrances and floors in the house changes.
If the number of floors is more than two, then it is mandatory to start the system along with pumping for water circulation.
PNR heat supply
According to the importance of the procedure, the heat supply installation can be compared with the installation of equipment or design. At the moment of launch, all its components are monitored, as well as the readiness of the equipment, its effectiveness and productivity
Pressure testing as a fundamental stage in preparing a heating system
When the main phases of the installation process are completed, it is necessary to do commissioning work - check the efficiency of the heating, its serviceability, and also bring the equipment to operating parameters. Pressure testing is considered one of the initial stages of the heat supply system. This procedure ensures comfortable living in the room, in which the heating system functions correctly.
Crimping consists of the following sequential actions:
- Checking communications using extra pressure;
- Pump testing;
- Checking the reliability of pipelines is a fundamental stage of heat supply installations, which is considered mandatory;
- Monitoring the tightness of pipe coils;
- Hydraulic checks.
Pressurized communications are left under pressure for a day
It is necessary to pay attention that during a temperature change, the load in them will decrease slightly - you should not be afraid of this. This is a traditional physical process when, when a substance cools, it contracts
Even a person who does not have much knowledge in this area can handle the heating supply system - the procedure is simple and does not require specific abilities.
Test run for commissioning heating systems
The heating system is tested before the heating period begins. Before filling the pipes with water, they must be washed. The process removes very small particles of metal and polymer materials that become stuck during pipe processing.
The flow of liquid during heating supply is done according to the schedule for the start of heating work. The test is performed at a temperature of 60-70 degrees, depending on the period of the year: frozen pipes must be warmed up in advance.
The duration of the test is 7 hours, and the equipment test should show good results. All equipment must withstand the test load: this means that the pipes are ready for continuous operation.
Having launched test testing, the basement floors of the building are monitored. This is where problems may arise due to differences in pressure levels. To release air during heat supply, special opening devices are used, by means of which the remaining substances that appear are removed.
The final step is to check the boiler and adjust it, after which we proceed to use the heating completely.
Commissioning of electrical equipment

Commissioning work that accompanies electrical installation work is a set of works that includes checking, adjusting and testing electrical equipment in order to ensure the electrical parameters and modes specified by the project. Qualified commissioning work carried out by electrical installation employees will not only be able to identify possible violations during electrical installation work and shortcomings in the operation of the equipment before it begins operation, but will also ensure its guaranteed operation for quite a long time.
The need for heating
The need to heat your own home has always existed, but the ways to achieve this goal were very different. For hundreds of years, classic Russian stoves were used in Russia, and a little later fireplaces appeared. Traditional heating structures have been replaced by modern devices and heat supply systems, which are superior in quality and efficiency to their predecessors.
Currently, the heating system is a structure that usually consists of the following main elements:
- heating boiler;
- pipeline;
- heating appliances.
There is a coolant inside the heating system. In most cases, water is used to heat private households, since in case of leakage it does not pose a danger to people and the environment from an environmental point of view. Of all types of liquid coolants, it is water that accumulates heat best and, when cooled, releases it.

In addition, it flows well and moves almost instantly within the elements of the system. Water is always available in the water pipes and can be added to the heating structure at any time.
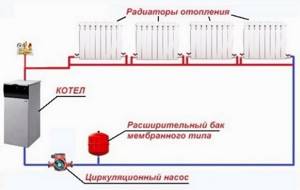
The functioning of the system consists of moving hot coolant through it using a circulation pump. The water is first heated in the boiler and then distributed through pipes from which it flows into the radiators.
How to adjust the temperature

This indicator can be adjusted using special equipment - mixers, taps and servos. Mixers are a tap with two or three working positions. The inlet riser pipe is connected to one of the inputs, and the outlet pipe is connected to the second. The third is used to regulate the temperature in a separate section of the highway. Mixing units are equipped with a temperature sensor and a control unit. The sensor sends a signal about the temperature of the water inside the riser, and the control unit regulates the valve, thereby regulating the two-pipe heating system. You can adjust the heating of water in radiators with your own hands using taps. But servo drives will eliminate the need to do this, since with their help the heating of the risers will be adjusted automatically. The design of the servo drive includes a thermostat on which the desired temperature value is set. After this, the servo drive will begin to measure the incoming coolant flow and, if necessary, reduce or increase it. Important! It is impossible to regulate the pressure using thermostats, since they limit the flow of water only in one section of the system, without affecting its general condition and the heating of the remaining risers
How to set up, adjust, balance the heating system
A common situation is that one radiator is hotter than the other, which should not be the case.
Or it’s cool in one part of the house and hot in another. This means that the heating system needs to be somehow adjusted, as experts say – balanced. It is possible that for this you do not need to call a plumber at all, and you can adjust the heating yourself. To do this, control taps and/or balancing valves must be installed on each radiator or between the arms of the system.
But in some cases the system needs to be redone. Read more about possible heating problems and balancing rules below.
If there is not enough radiator power
It also happens that it is difficult to balance the heating system, since the distribution of radiator power does not at all correspond to the heat loss of the rooms.
Recommendations for the selection of radiators are as follows: for 10 sq. m. area - 1 kW, but this value is multiplied by 1.2 if the room has one window, 1.3 if the window is large, 1.4 if there are two windows and the room is corner, 1.5 if there are already 3 windows or a large glazing area.
In addition, the radiator power is indicated for a temperature of 90 degrees, but we are going to heat it at a maximum of 70 degrees, aren’t we? This means we multiply the heat loss by another 1.3. And if low-temperature heating is used - no more than 50 degrees, then multiply by 1.3 again. Why is low-temperature heating the most comfortable and economical? Read more about economical condensing boilers
The power of one section of an aluminum, bimetallic radiator (approximately 80 mm thick and wide), or cast iron radiator (old MS-140 type) is approximately 170 - 180 W. A set of 7 sections is considered to be no less than a kilowatt.
In addition, radiators must be installed in characteristic places to create a thermal curtain to the cold source. Typically - under the windows, near the door.
It is better to distribute the number of battery sections (sizes) in accordance with heat loss and the characteristics of the heating system than to balance and cover the flow of liquid.
Simple causes of heating system problems
It is possible that there is air in the heating system and for this reason the coolant does not flow well to one or more heating devices.
In the highest places in the pipeline, air valves (Mayevsky valves) are installed that can be opened manually. Or automatic air vents. Mayevsky taps are usually installed on each radiator. Walk through the system, open the taps, bleed the air.
Another reason for poor performance is clogging, first of all, of the filter element. Unscrew the filter and clean it. Before any balancing of the heating system, clean the filter.
In improperly assembled systems, in addition, there may be clogging at the lower points at differences in the pipeline level, and airing at the upper points, for example, the pipeline is wrapped around a door without an air vent.
Balancing the system using valve regulators
It is possible that the very design of the system requires balancing. For example, one long arm is used and the other is short.
Or the arm length of the dead-end pattern is too long. Or a beam scheme is used, which requires initial configuration. And it happens that they make archaic one-pipe systems with shortcomings. In either case, the result is significant uneven heating.
So, balancing valves are installed on the radiators; all that remains is to ensure that the temperature of all radiators is approximately the same.
The principle of balancing is the simplest - do not close (open as much as possible) the taps on the coldest ones and “tighten” the hottest ones a little. As a result, more coolant will flow to the cold ones, less to the hot ones, and their temperature will equalize.
An example of how to adjust heating in a one-story house
A typical example is that it was not possible to make two arms of a dead-end circuit, since the pipes were being laid in the way of a door, so they made one arm and put “as many” 7 radiators on it.
As a result, the temperature of the latter in the shoulder is 9 degrees less than that closest to the boiler. You can do the following: on the last 3 radiators, leave the taps completely open. On the first, open the balancing valve from the fully closed position by 1.5 turns, on the second - by 2 turns, on 3 and 4 by 2.5 turns.
It is assumed that the balancing valve is adjustable in total by 4.5 turns, and the length of the pipelines is within the limits of a small house. But regulators come in different designs, different lengths, so in each case there is a different number of revolutions.
After balancing, you need to wait 20 minutes, then measure the temperature of the incoming radiator pipe again, you may have to additionally adjust something by a quarter turn...
Adjustment principles
Significant closures cannot be created. The basic principle of balancing is to open the path for coolant movement as much as possible. Closure is a forced measure.
Therefore, achieving the same temperature in this example is not worth it. It is correct to agree that the first one will be hotter by 3 - 4 degrees at a coolant temperature of 80 degrees and by a couple of degrees with low-temperature heating of 50 degrees.
How to measure it? Professionals would look at each radiator through a thermal imager and take a thermal photo. But you can also get by with contact thermometers - special devices for heater installers. But in everyday life, they often measure simply with their hands and judge by how they feel. The earlobe is sensitive in this regard - but is it worth rubbing your ear on the radiators...
Example for a two-story house
Another typical example is when the designers and installers managed to design the heating system in such a way that they installed approximately equal power radiators on both the first and second floors (the areas are approximately equal), and they forgot to solder the balancing of the floors relative to each other.
As a result, it is still cold on the first floor, but it is already hot on the second floor.
Again, balancers installed directly on the radiators will help out. On the second floor, we simply open the taps by 2 turns instead of the full 4.5, thus reducing the liquid flow by 30 percent. By reducing the energy output, we equalize the temperature regime, and if necessary, close more...
The diagram in which there is no possibility of balancing between two arms is a typical mistake in homemade systems.
Commissioning according to the project
With the usual proper installation of a modern heating system, balancing is not needed at all; the circuit is designed so that all radiators heat optimally. In addition, they are often automated with thermal heads, with which you can set the temperature in a separate room.
Designers and design data introduce a little confusion into the issues of heating adjustment. The project includes the amount of coolant passing through and the balancing of each radiator - how many revolutions each balancing valve of a certain type should be turned.
This achieves a certain accuracy in the implementation of design decisions. But for the user this practically does not matter, since adherence to design accuracy has very little effect on the final result. But large balancing values (as in the examples above) cannot be included in the project. Therefore, very precise regulation according to the design can be ignored.
Noisy radiator
Another point that needs to be addressed is too much coolant passing through the radiator. At the same time, the radiator makes noise and this is unpleasant. Reasons: incorrect heating scheme, unbalanced (closed) other radiators, too powerful pump in the system. All this needs to be eliminated.
An overly powerful pump is a problem with homemade heating systems, because home craftsmen “seem” that they can’t spoil the porridge with oil. But what happens here is something else - a lot of money wasted and noise in the radiators. How to select a pump for a heating system... A noisy radiator requires balancing the system or reworking it.
A difficult case is the closure of the pipeline passage during installation. It is difficult to identify a defective location; sometimes it is necessary to redo an entire arm of the pipeline. This is typical for polypropylene pipes, in which sagging of material is possible during soldering. More details - how to solder polypropylene and prevent defects
- Call on Skype inchin64
Adjustment methods

The balancing procedure involves adjusting the shut-off valves. This is done in two ways:
- Adjustment of each valve and temperature measurements after each adjustment of their position;
- Dividing the system into modules and adjusting them separately. In this case, each area of the room receives its share of the total heat emitted by the system.
Before balancing, the heating system is diagnosed by opening all shut-off valves and test running; In this way, it will be determined in which part of the circuit the imbalance occurred.
- Coolant flow and pressure regulators;
- Balancing and bypass valves.
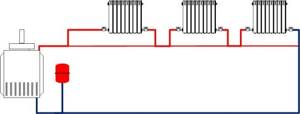
The necessary adjustment components are installed based on the type and complexity of the system. So, with a single-pipe circuit, ordinary taps will suffice. Balancing the heating system in this case is carried out by simply tightening them until the desired temperature is reached. Two-pipe circuits require balancing valves. They, firstly, provide more precise adjustment, and secondly, they allow you to connect a special device to measure the characteristics of the coolant supply - pressure, flow and temperature.
Temperature adjustment method
The temperature adjustment method is similar to the trial and error method, they can even be called analogues. However, there are a number of “buts”. This method is based on the law of conservation of energy and on instrumental measurements of the temperature of the coolant at the inlet and outlet of the heating device. The method is based on the law of conservation of energy, the equation for determining the amount of heat:
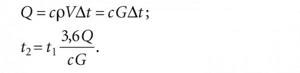
When heat Q is transferred from the coolant through a heating device to the room, the temperature of the coolant t2 decreases. We change the flow rate G - heat transfer is regulated.
This method is used in fairly simple systems where balancing valves without fittings are used.
Pros: accessibility. This method can be used in situations where other methods are not available. This method is used when the master is limited in resources (instruments, modern balancing and automatic valves, “intelligence”, etc.).
Disadvantages: this method is inaccurate, especially in situations where the coolant temperature difference is insignificant. That is, the accuracy of the method increases with increasing outdoor temperature. An overestimated area of heating devices also leads to incorrect results.
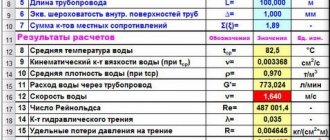
We set up the heating system of a country house ourselves

In my previous article, I wrote that one of the effective ways to modernize heating systems in private buildings is to switch from an open heating system to a closed one. The heating system of a residential building improved in this way has many advantages, which together ensure its simple operation; you just need to turn on the boiler at the beginning of the heating season and turn it off at the end. All!
However, in order for the heating system of a country house to work in this mode (turned on, “forgot” for six months, turned off), you need to correctly configure and adjust its operating parameters. This is what my article will discuss. I will make the main calculations, conclusions and calculations using the example of my heating system, but the reader can always use this information by drawing an analogy with his own specific case.
What is needed in order to properly connect the heating system.
Requirements for the start-up procedure and correct operation of the heating system are regulated by the design documentation. In order to regulate the heat supply in an apartment building correctly, it is carried out in accordance with the requirements of this documentation. All heating system radiators have thermostats, temperature meters, manual and automatic start-up and control balancing valves. Radiator adjustment does not require special tools; it is done by the residents themselves. As for the start-up and adjustment of other types, they are carried out directly by professionals in this field. At the same time, the most efficient operation of the radiators and, accordingly, the heating system itself as a whole is achieved.
Thus, in order to know exactly how to regulate the heating, as well as to ensure an even supply of heat in an apartment building, it is necessary to take into account many details.
What does the normal functioning of the heating system depend on? There are several objective factors that directly affect efficiency, reliability and maintenance of its performance. Therefore, first of all, you need to know how to properly start the heating system in the house. It is best to consider this procedure using the example of an autonomous system of a country cottage.
Pnr heating system
PRP of the company you have chosen;
- whether they have relevant experience;
- terms of service and warranty.
In this case, the following requirements must be met:
- Activities related to the commissioning of engineering systems (including commissioning and commissioning of air conditioning systems) must be carried out within the time limits established by the regulations.
- The equipment is put into operation under strict control by specialists from the contractor company.
- Upon completion of the entire complex of commissioning works, you must receive a documented guarantee of their high-quality implementation.
- The guarantee for them is provided from the moment of final commissioning of the facility.
Commissioning tests mean work performed on already installed (assembled) equipment, ready for launch and commissioning.
Attention
Home » Heating » Commissioning of heating systems Program for carrying out commissioning During the implementation of many projects, capital construction or reconstruction of buildings and structures is carried out with the installation of new equipment or specialized processes. Such work includes the installation of fire extinguishing systems, electrical supply, air conditioning, ventilation, fire alarm systems
Setup
Setup is preparation for use. Synonyms for the word adjustment: adjustment, debugging, repair, adjustment, checking, correction. Antonyms: disassembly, breakdown, accident.
So, the heating system is filled and pressurized. It's time to start adjusting, thermal testing and putting it into operation. Before adjustment, the following work must be completed:
- heating system installed;
- its compliance with the project was checked;
- the system is flushed and filled with water;
- commissioning of the main equipment was carried out.
During the commissioning process the following must be done:
- turn on the main equipment;
- listen carefully and take a closer look at what is happening around - extraneous noises, vibrations, the presence of water leaks, the smell of burning, bright flashes and much more should alert you.
Maybe it's time to run away from here? Or is it necessary to open the closed valve at the pump? Or maybe after pressing the “On” button nothing changed because they forgot to plug the plug into the socket or did not open the gas supply valve to the boiler?
Responsibilities of the customer
Implementation of general, operational and technical management of the quality of construction, installation, adjustment and testing of equipment; carrying out pre-start and start-up operations on equipment, components and units; work of acceptance committees; elimination of equipment defects, construction and installation.
Ensuring the organization and conduct of pre-installation inspection of equipment and equipment.
Providing commissioning work at all stages:
— financing of work;
— qualified operating personnel (starting with unit testing);
— working tools and materials in the required quantities;
- standard instruments, design and factory technical documentation.
Ensuring the safety of equipment and installations, experimental control systems, as well as documentation, equipment and apparatus of organizations involved in commissioning work at the power unit and a regime that excludes access by unauthorized persons.
Providing personnel of commissioning and research organizations with office and laboratory premises, housing and other household services.
Development, together with the general contractor, of measures to ensure safe working conditions, and the adoption of general measures for industrial safety and fire safety at the power unit.
Duration of commissioning work when starting heating in mkd
Important
Flushing of heat consumption systems is carried out annually after the end of the heating period, as well as installation, major repairs, routine repairs with replacement of pipes (in open systems, the systems must also be disinfected before commissioning). The systems are washed with water in quantities exceeding the calculated coolant flow rate by 3-5 times, and complete clarification of the water must be achieved
When carrying out hydropneumatic flushing, the flow rate of the air mixture should not exceed 3-5 times the calculated coolant flow rate. Tap or process water is used for washing.
Connecting systems that have not been flushed, and in open systems, flushed and disinfected, is not allowed. Diaphragms and nozzles of hydraulic elevators must be removed when flushing the heating system.
After flushing, the system must be immediately filled with coolant.
Rules for starting heating
When starting the heating system in the summer, it is necessary to close the valves first on the return pipe and then on the supply pipe.
Then the heating system is inspected and the coolant is circulated in the external network. If there are no leaks, the valves are opened - first on the return pipeline, and then on the forward pipeline. Next, the circulation of coolant in heating devices is monitored and air pockets are removed from them, if necessary. Air removal is carried out periodically, at intervals of 2-3 hours, until airing is completely eliminated. Compliance with all norms and rules for putting the heating system into operation will ensure high efficiency and trouble-free operation of the heat supply system during the harsh winter period.
Use of materials is permitted only if there is an indexed link to the page with the material.
Commissioning of heating systems
Before putting the heating system into operation, you need to do a number of preparatory works, carry out checks and establish the mutual action of a variety of units with each other. All this is included in the commissioning of the heating system, the purpose of which is to detect and remove disadvantages and errors made during installation work, as well as to bring the entire system in accordance with the standards established for it. As a result of these works, the customer receives a good, productive and effective system. The cost of work on setting up and starting up the heat supply is fully reimbursed by the subsequent trouble-free operation and safety of the equipment.
Scope of commissioning and commissioning work
- Commissioning work is done after installation work has been completed. These include:
- Connecting the boiler to the gas main (if a gas boiler is used);
- Setting up security systems;
- Installing an electrical voltage stabilizer and connecting the boiler to it;
- Coordination of the operation of the boiler and indirect (if used);
- Connection of thermal converters and their adjustment;
- Testing and pressure testing of heating systems;
- Filling the system with coolant;
- Bleeding air from the system and balancing it;
- putting the system into operation;
Upon completion, a report on the commissioning work of the heating system is drawn up, which lists the scope of work performed and draws conclusions regarding subsequent operation and improvement of the operation of the equipment.
The essence of the system check processes and its start-up
As you can see, commissioning work consists of a huge number of operations, the most important of which are related to testing the heating system. Let's take a closer look at one of the main stages of commissioning - pressure testing of the system. It should be performed to detect all suspected areas of leakage. The essence of the procedure is to pump water or air into the system under pressure a couple of times higher than the working pressure. During crimping, all connections must be checked very carefully. If air is used during testing, the pipe connections must be coated with a soap-based solution.
Another stage of verification is thermal testing of the system. Its goal is to warm up all radiators with water at a temperature of 60-70 0C for 7 hours. At the same time, monitoring is carried out to monitor the degree of heating of the radiators, the temperature of the coolant at the outlet and inlet to the boiler, and the air temperature. If all indicators are as close as possible to the design ones, the system has successfully passed thermal testing. If not, then further adjustment is made. Before filling the system with water for testing, it should be flushed to remove equipment preservatives and other debris from the pipes.
To start the system, you need to fill it with a coolant, bleed the air and put the boiler into operation. To fill the system with coolant, the make-up tap is opened, the location of which can be found in the documentation for the boiler room equipment. When the system pressure can reach the required value, the valve is closed and the boiler is started for the first time. After turning on the circulation pump, you should bleed the air from it by slightly unscrewing the screw in the very center. When water flows from under the screw, it must be turned all the way. Then the electronics will put all boiler systems into operation, and for some time air will be removed from the system, which will be indicated by gurgling sounds. When the system is working properly, you need to check the pressure, and if necessary, bring it up to normal by replenishing the amount of coolant.
After the first start-up of the heat supply, you can adjust the system using taps for adjusting heating devices. It is necessary to ensure that the energy of the coolant is sufficient to warm up the last heating device in the chain. Such adjustment may take a couple of days and is carried out during operation. There is no need to worry about this, because in general the system is already debugged and does not stop working in normal mode.
Connecting the boiler to the water supply and heating circuit
To connect the heating device to the water supply and heating circuit, you will need to remove the protective casing from the boiler itself. But before this, the supply fitting of the heating device is connected to the input fitting of the heating circuit, and the return fitting is connected to the output fitting. The inlet connection for water supply is connected to the water main, and the outlet connection of the heating device is connected to hot water consumers.
After these manipulations, an important stage of commissioning will be the release of excess air from the circulation pump of the gas boiler. To do this you need:
- Unscrew the central nut on the body of the pump itself with a regular flat-head screwdriver;
- turn the pump shaft several turns with a screwdriver;
- screw the central nut into its original place.
After this procedure, the heating circuit is filled with water. To do this, you need to open the supply and return taps, as well as the taps on the water supply from the main and at the outlet to the DHW consumers. After opening these taps, you need to open the heating circuit feed tap, which is located at the bottom of the heating device. This valve turns approximately half a turn, counterclockwise.
While filling the system with water, you need to constantly monitor the pressure using the built-in pressure gauge. This device is located on the front of any heating device. After the system is filled with water and the pressure on the pressure gauge has reached 1.2 atmospheres, the make-up valve can be closed by rotating it clockwise until it stops. After filling the heating system with coolant, the protective casing of the heating device can be installed in its normal place.
Responsibilities of the head commissioning organization
3.2.1. Ensuring that the scope of commissioning work on equipment is completed in accordance with the agreed distribution of volumes between the involved commissioning organizations.
3.2.2. In addition to performing your scope of commissioning work:
— distribution of volumes of adjustment work (when drawing up a coordination plan);
— coordination of the actions of all participants in commissioning work: development of engineering support for commissioning work, participation in the development and coordination of a combined schedule of construction, installation and commissioning work, development or coordination of work and technical programs for commissioning work in accordance with the instructions of Appendix 3, participation in the formation of consolidated commissioning unit teams, including separating a number of unit foremen from its composition;
— monitoring the results of commissioning work by all participants, participation in the work of acceptance committees;
— ensuring round-the-clock duty of leading specialists to provide operational technical assistance during the period of startup operations on the equipment;
— submitting for consideration by the launch headquarters questions and proposals regarding the organization and progress of construction, installation and commissioning work;
— generalization, together with co-executing organizations, of the results of commissioning work and, on their basis, prompt issuance to the customer, design organizations and manufacturing plants (in a copy - to the relevant departments) of proposals for improving technology, circuits, modes and designs of equipment and monitoring their implementation;
— summarizing operating experience of similar equipment and issuing proposals for implementation to the customer;
— development, together with the customer, of instructional and technical documentation.
The main commissioning organization, together with the customer, bears the main responsibility for the timing and quality of commissioning and commissioning of equipment.
3.2.3. The instructions of the head commissioning organization regarding the technology and timing of commissioning work are mandatory for all organizations involved in the supply of equipment.
3.2.4. The main form of activity of the head commissioning organization is the conclusion of a single contract agreement for the implementation of the entire complex of commissioning works with the involvement of other commissioning organizations on a subcontract basis.
3.2.5. Additional performance by the commissioning organization of the “head” functions is paid in accordance with the “Regulations on the relationship of general contractor organizations with subcontractors”, approved by the Decree of the USSR State Construction Committee and the USSR State Planning Committee dated 07/03/87, No. 132/109 and an agreement with the customer.
3.2.6. In the absence of a head commissioning organization, its functions in terms of distribution, control and coordination of work are performed by the customer or, when the project is delivered on a turnkey basis, by the general contractor.