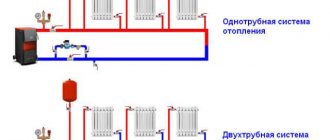
Increase in pressure in the heating circuit
Now you know how to increase the pressure in the heating system, after first getting rid of the causes of the drop.
Next we will deal with its increase. If it constantly jumps, it means that the equipment is not operating in the correct mode. There may be other problems that will be discussed in this review. Sometimes the pressure indicator jumps just like that - this happens when some heating boilers operate with faulty sensors. But you still shouldn’t count on their incorrect operation, since inaction can lead to damage to the heating equipment. Most often, boilers suffer due to hydraulic overloads - heat exchangers and other internal components cannot withstand and burst.
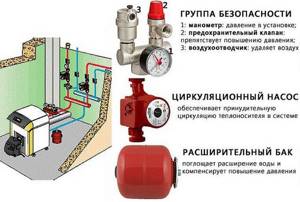
A safety team will help prevent damage to the heating system due to high hydrodynamic loads. It is a mandatory element of every closed circuit. The group consists of the following parts:
The maximum pressure for most boilers is 3 atmospheres. Therefore, it is necessary to create conditions for their safe operation. The safety valve is responsible for this. Having opened, it will release part of the coolant and immediately close.
- Pressure gauge (or thermomanometer) – used to obtain control information.
- Air vent – removes air from the circuit.
- Safety valve – protects the circuit from hydraulic overloads.
The most important link here is the safety valve. It will automatically release pressure if it goes beyond dangerous limits. Typically, users do not pay any attention to pressure gauges. After all, you won’t monitor the indicators every hour for fear of an emergency. This is why a safety valve is a must – it is a simple and effective safety feature.
Eliminating the causes of growth
The presence of air pockets can cause a gradual increase in pressure in the heating circuit. They must be removed promptly. The simplest option is to use a manual air bleeder, which is installed next to the safety group. Mayevsky taps located on radiators are also used for this. Sometimes, to completely remove air, the coolant is changed and the system is refilled.
Too high a temperature is another reason for increased pressure. Typically, the temperature of the coolant in heating systems varies between +70-80 degrees, sometimes a little more, sometimes a little less. If for some reason it rises to higher levels, this will provoke expansion of the coolant. It will begin to put pressure on the pipes and radiators, causing the needle on the pressure gauge to creep up. To prevent an accident, it is necessary to allow the coolant to cool. After this, we understand the initial reasons for the rise in temperature.
A clogged heating circuit can also cause increased pressure in the system. The heating does not clog very often, but this cannot be ruled out. The cause of blockages is most often contaminated coolant - this is typical for systems with metal pipes that are subject to corrosion.

One of the reasons for the breakdown may be scale in the pipes. Usually, sections of pipes after blockages are colder - this is how we calculate the contaminated section.
Other reasons for increased pressure in the heating system:
- Users have messed with valves and valves - this is causing cold radiators.
- Constant replenishment of the circuit with water - this is necessary for the initial filling of the system or when the pressure drops; the rest of the time the water supply must be shut off.
- A breakdown of the circulation pump or its incorrect setting - excessive pressure is created along with an increase in pressure.
- Clogging of one or another circuit - blockages in individual “directions” can provoke a rise in pressure in the entire heating system.
All this knowledge is more than enough to maintain the correct coolant pressure in the heating system.
Possible faults and corrective actions
Significant pressure drops in the heating system when the boiler operating temperature changes can be caused by incorrect calculation of the volume of the expansion tank and the pressure in its air chamber.
Leaks are usually found at threaded connections and are due to insufficient sealant. It will be easier for a beginner to achieve the tightness of such a connection using the Tang it Unilock sealing thread. In case of some “overdose”, unlike tow, it does not cause destruction of the screwed-on part.

In polypropylene pipelines, leaks often occur due to improper welding technology.
For example, some users weld pipes without a coupling - just butt welding.
Such a connection is very short-lived and breaks down very quickly under pressure.
Incorrectly made or defective connections must be cut off and replaced with high-quality ones.
If the water used as a coolant has not been desalted, the heat exchanger will have to be descaled over time. To do this, the boiler is disconnected from the heating circuit and washed with special reagents, for example, Antiscale. The entire heating system can be subjected to such flushing, but due to its complexity, this task should be entrusted to professionals.
Spring safety valves can stick, so they must be opened periodically using a special lever.
In the USSR, the issue of reducing the cost of construction, including the organization of the heating system, was especially relevant. It was at that time that the Leningradka heating system for private and apartment buildings was invented. Let's consider whether it is relevant today.
In what cases is a hydraulic arrow needed for heating and how it functions, read this article.
Why does blood pressure drop?
A decrease in pressure in a heating structure is observed very often. The most common causes of deviations are considered to be: the release of excess air, air escaping from the expansion tank, coolant leakage.
There is air in the system
Air has entered the heating circuit or there are air pockets in the batteries. Reasons for the appearance of air gaps:
- non-compliance with technical standards when filling the structure;
- excess air is not forcibly removed from the water supplied to the heating circuit;
- enrichment of the coolant with air due to leaky connections;
- malfunction of the air bleed valve.
If there are air cushions in the coolant, noise appears. This phenomenon causes damage to the components of the heating mechanism. In addition, the presence of air in the heating circuit units entails more serious consequences:
- vibration of the pipeline contributes to weakening of welds and displacement of threaded connections;
- the heating circuit is not ventilated, which leads to stagnation in isolated areas;
- The efficiency of the heating system decreases;
- there is a risk of “unfreezing”;
- There is a risk of damage to the pump impeller if air gets into it.

To eliminate the possibility of air entering the heating circuit, it is necessary to correctly put the circuit into operation, checking all elements for functionality.
Initially, testing is carried out with increased pressure. When performing pressure testing, the pressure in the system should not drop for 20 minutes.
For the first time, the circuit is filled with cold water, with the taps open to drain the water and the valves open to vent. The network pump is turned on at the very end. After removing the air, the amount of coolant required for operation is added to the circuit.
During operation, air may appear in the pipes; to get rid of it you need to:
- find an area with an air gap (in this place the pipe or battery is much colder);
- Having previously turned on the structure’s replenishment, open the valve or tap further downstream of the water and get rid of the air.
Air comes out of the expansion tank
The causes of problems with the expansion tank are as follows:
- installation error;
- incorrectly selected volume;
- nipple damage;
- membrane rupture.
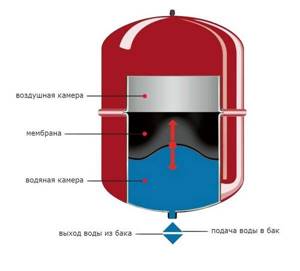
Photo 3. Diagram of the expansion tank. The device may release air, causing the pressure in the heating system to drop.
All manipulations with the tank are carried out after disconnecting from the circuit. For repairs, it is necessary to completely remove water from the tank. Next, you should pump it up and bleed the air a little. Then, using a pump with a pressure gauge, bring the pressure level in the expansion tank to the required level, check for leaks and install it back on the circuit.
If the heating equipment is incorrectly configured, the following will be observed:
- increased pressure in the heating circuit and expansion tank;
- reducing the pressure to a critical level at which the boiler does not start;
- emergency releases of coolant with a constant need for replenishment.
Important! There are samples of expansion tanks on sale that do not have devices for adjusting pressure. It is better to avoid purchasing such models.
Flow
A leak in the heating circuit leads to a decrease in pressure and the need for constant replenishment. Liquid leakage from the heating circuit most often occurs from connecting joints and places affected by rust. It is not uncommon for liquid to escape through a torn expansion tank membrane.
You can determine the leak by pressing the nipple, which should allow only air to pass through. If a coolant loss location is detected, the problem must be corrected as soon as possible in order to avoid serious accidents.

Photo 4. Leak in the heating system pipes. This problem may cause your blood pressure to drop.
We are losing it, or why the pressure drops
There can be two main reasons for a gradual or sudden decrease in pressure in an autonomous system:
- heat exchanger malfunction,
- one or more leaks in the circuit.
Any damage to the boiler must be diagnosed and promptly repaired. Causes of pressure loss may include contamination, microcracks, high wear, manufacturer defects and, again, defects in the expansion tank. Any damage is corrected accordingly.
Leaks are often the cause of pressure drops. There are many weak points - these are poor-quality soldering of plastic or metal pipes of the circuit, and loose connections with radiators, and breaks in worn pipes, and cracks in the rubber membrane of the expansion tank when the coolant enters and remains in the air chamber.
In the latter case, you can detect the leak yourself: just press the spool, with the help of which air is pumped into the chamber. Water dripping or flowing from inside will confirm your guess.

Finding a leak in a pipeline, which is often hidden inside the floor or walls, is quite difficult. First, you should inspect the visible areas. Pay attention to the floor, even if it is dry, spots of dried water may remain in places of leakage. Salt or rust deposits at the joints may also indicate a loss of tightness.
If the design of the circuit allows, you can turn off individual sections of the network one by one, so it will be easier to find the breakdown.
In cases where the pipeline is hidden or visual inspection is unsuccessful, pressure testing will be required. It is quite difficult to do it yourself, since it requires both skill and special equipment. First, the coolant is drained from the system, the boiler and radiators are insulated, and air is forced into the circuit with a compressor under pressure. The end result is that the network pressure should be 20 percent higher than the operating norm. The system is left in this state for several hours and the pressure is measured again. If it falls, you need to look for places where there is depressurization. To do this, visible seams can be lubricated with soapy water; the escaping air will appear as bubbles. It will tell you where the leaks are and the characteristic hissing sound.
The breakdown areas are further sealed or the failed section is replaced with a new one.
How to control the pressure in the system?
To control, pressure gauges are installed at various points of the heating system, and (as mentioned above) they record excess pressure. As a rule, these are deformation devices with a Bredan tube. If you need to take into account the fact that the pressure meter must work not only for visual control, but also in the automation system, electric contact or other types of sensors are used.
The insertion points are determined by regulatory documents, but even if you have installed a small boiler for heating a private house, which is not controlled by GosTechnadzor, it is still advisable to use these rules, since they highlight the most important points of the heating system for pressure control.
Pressure gauges must be installed through three-way valves, which ensure their purging, reset to zero and replacement without stopping the entire heating.
Control points are:
- Before and after the heating boiler;
- Before the entrance and after the circulation pumps;
- Output of heating networks from a heat generating unit (boiler house);
- Input of heating into the building;
- If a heating regulator is used, then pressure gauges are embedded before and after it;
- If there are mud traps or filters, it is advisable to install pressure gauges before and after them. Thus, it is easy to control their contamination, taking into account the fact that a working element creates almost no difference.
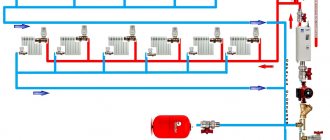
System with installed pressure gauges
A symptom of malfunctions or improper operation of the heating system is pressure surges. What do they mean?
How to deal with pressure changes?
Possible solutions to problems when reducing the load inside communications:
- When a leak is detected, the system is repaired. If necessary, the sealing gasket and section of the pipeline are replaced, and couplings are installed.
- The equipment is being adjusted, which is necessary in cases where the coolant parameters were initially set that do not correspond to environmental conditions.
- If the clearance of communications has decreased, the system is flushed from scale. In this case, the boiler is first dismantled.
- When the heating system circuit has been changed, the area of the facility has increased, a more suitable pipe diameter is determined, and then the communications are replaced.
If the question of why differences occur and how to deal with them is being resolved, it is necessary to inspect the entire circuit for leaks and check the operation of the equipment.
Why is pressure needed?
Pressure in a heating system is the process of the coolant acting on the walls of the boiler, pipes, and radiators. Before water fills the pipeline, it is equal to atmospheric pressure (1 bar). This indicator changes as soon as the liquid begins to be poured into the pipeline and warms up. The coolant expands, the pressure increases to normal levels.
Reliable and efficient operation of a heating structure depends on pressure values. It provides it with extremely high performance and ensures that energy reaches the pipeline of all apartments in a multi-story building. This parameter determines the speed of water flow and, accordingly, the intensity of the heat exchange process between the structural components of the heating system. Therefore, the higher its performance, the greater the efficiency of the heating system.
How is pressure in pipes measured?
This indicator is measured in pascals and atmospheres. The second scale is most often used. Individual approaches are used to heat objects of various purposes and heights.

So, the norm is:
- autonomous boiler - 1.5-2 atmospheres;
- houses 3-5 floors - 2-4 atmospheres;
- nine-story buildings - 5-7 atmospheres;
- high-rise buildings - 10 atmospheres;
- underground supply lines - 12 atmospheres.
Pressure adjustment is carried out using automatic and manual valves, expansion tanks, regulators and safety membranes. The condition of the heating system is monitored by pressure gauges installed on the pipes at certain intervals.
As a rule, control devices are mounted at the entrance to the building and at its highest point.
Reasons for increasing power
An uncontrolled increase in pressure is an emergency.
May occur due to:
- the automatic control of the fuel supply process is faulty;
- the boiler operates in manual high-burning mode and is not switched to medium or low-burning;
- malfunction of the storage tank;
- malfunction of the fill valve.
The main reason is overheating of the coolant. What can be done?
- The operation of the boiler and automation should be checked. In manual mode, reduce the fuel supply.
- If the pressure gauge readings are critically high, drain some of the water until the readings drop into the work area. Next, check the readings.
- If no boiler malfunctions are identified, check the condition of the storage tank. It accepts a volume of water that increases when heated. If the damping rubber cuff of the tank is damaged, or there is no air in the air chamber, it will fill completely with water. When heated, the coolant will have nowhere to be displaced, and the increase in water pressure will be significant.
Checking the tank is easy. You need to press the nipple in the valve to fill the tank with air. If there is no air hissing, then the reason is a loss of air pressure. If water appears, the membrane is damaged.
A dangerous increase in power can lead to the following consequences:
- damage to heating elements, up to rupture;
- overheating of water, when a crack appears in the boiler structure, instantaneous vaporization will occur, releasing energy equal in power to an explosion;
- irreversible deformation of boiler and heating elements and rendering them unusable.
The most dangerous thing is a boiler explosion. At high pressure, water can heat up to a temperature of 140 C without boiling. When the slightest crack appears in the jacket of the boiler heat exchanger or even in the heating system next to the boiler, the pressure drops sharply.
Superheated water, with a sharp decrease in pressure, instantly boils with the formation of steam throughout the entire volume. The pressure instantly increases from steam formation, and this can lead to an explosion.

At high pressure and water temperature above 100 C, you cannot suddenly reduce power near the boiler. Do not fill the firebox with water: strong temperature changes may cause cracks.
It is necessary to take measures to lower the temperature and smoothly lower the pressure by draining the coolant in small portions at a point far from the boiler.
If the water temperature is below 95 C, adjusted for the thermometer error, then the pressure is reduced by releasing part of the water from the system. In this case, steam formation will not occur.
Causes of pressure surge when starting the heating system
Pressure readings may decrease after starting the heating system, up to the automatic shutdown of the wall-mounted boiler in a private house for the following reasons:
- Residual air comes out of the pipelines and channels of heating devices. The pressure gauge registers a pressure drop of 1–1.3 bar. The coil failed and the air chamber of the tank was emptied. The membrane works in the opposite direction, and the container is filled with water. When the heating system heats up, the pressure rises to a critical level. The coolant is drained through the safety valve and the pressure drops to a minimum.
- Small leaks occurred at pipeline connection points.
How to create and add pressure to a heating system
To create or add pressure in a heating system, several methods are used.
Crimping
Pressure testing is the process of initially filling the heating system with coolant, temporarily creating a pressure that exceeds the operating pressure.
Attention! For new systems, during commissioning, the pressure should be 2-3 times higher than normal, and during routine checks, an increase of 20-40% is sufficient. This operation can be performed in two ways:
This operation can be performed in two ways:
- Connecting the heating circuit to the water supply pipeline and gradually filling the system to the required values, controlled by a pressure gauge. This method will not work if the pressure in the water supply is not high enough.
- Use of manual or electric pumps. When there is already coolant in the circuit, but there is not enough pressure, special pressure testing pumps are used. Liquid is poured into the pump reservoir, and the pressure is brought to the required level.

Photo 1. The process of crimping the heating system. In this case, a manual pressure test pump is used.
Checking the heating main for tightness and leaks
The main purpose of pressure testing is to identify faulty elements of the heating system in the maximum operating mode in order to avoid accidents during further operation. Therefore, the next step after this procedure is to check all elements for leaks. Tightness control is carried out by the pressure drop over a certain time after pressure testing. The operation consists of two stages:
- Cold test, during which the circuit is filled with cold water. Within half an hour, the pressure level should not drop by more than 0.06 MPa. In 120 minutes the drop should be no more than 0.02 MPa.
- Hot check, the same procedure is carried out, only with hot water.
Based on the results of the fall, a conclusion is made about the tightness of the heating system. If the test is passed, the pressure level in the pipeline is reset to operating values by removing excess coolant.
Jumps in a working heating system and how to deal with them
If, even a few weeks after the start of the regular heating season, the pressure in the system “dances”, it is worth rechecking all problem areas and making sure that each of the elements of the heat exchanger safe operation unit is working:
- pressure gauge,
- an air vent through which air leaves the coolant,
- a safety valve that releases part of the water in the event of a pressure surge or boiling (by the way, it is better to connect the valve to the sewer, otherwise hot water will end up on the floor),
- For large houses, expensive but very “smart” automatic machines are relevant, capable of monitoring the situation around the clock.
In any case, it is worth remembering that problems with the heating system are not only a loss of a comfortable microclimate in the home and material costs, but also a threat to the safety of both the entire building and its inhabitants. This means that inattention is unacceptable here.
Leak test
To ensure that the heating is reliable, after installation it is checked for leaks (pressure tested).
This can be done immediately on the entire structure or its individual elements. If a partial pressure test is carried out, then after its completion the entire system must be checked for leaks. Regardless of which heating system is installed (open or closed), the sequence of work will be almost the same.
Preparation
A test pressure is considered to be 1.5 times the working pressure. But this is not enough to completely detect a coolant leak. Pipes and couplings can withstand up to 25 atmospheres, so it is better to check the heating system under this pressure.
The corresponding indicators are created using a hand pump. There should be no air in the pipes: even a small amount of it will distort the tightness of the pipeline.
The highest pressure will be in the lowest place of the system; a monometer is installed there (reading accuracy 0.01 MPa).
Stage 1 - cold test
Over the course of half an hour, the pressure in the water-filled system is increased to the initial values. Do this twice, every 10-15 minutes. The fall will continue for another half hour, but without exceeding 0.06 MPa, and after two hours - 0.02 MPa.
At the end of the inspection, the pipeline is inspected for leaks.
Stage 2 - hot check
The first stage has been successfully completed, you can begin hot leak testing. To do this, connect a heating device, most often a boiler. Maximum performance indicators are established; they should not be greater than the calculated values.
Houses are preheated for at least 72 hours. The test is passed if no water leakage is detected.
Plastic pipeline
The plastic heating system is checked at the same temperature of the coolant in the pipeline and the environment. Changing these values will increase the pressure, but in fact there is a water leak in the system. For half an hour the pressure is maintained at a value one and a half times higher than the standard value. If necessary, pump it up slightly.
After 30 minutes, the pressure is sharply reduced to a reading equal to half the working one, and held for an hour and a half. If the indicators begin to increase, it means that the pipes are expanding and the structure is sealed.
Often, when checking a system, technicians perform a pressure drop several times, either increasing or decreasing it, so that it resembles normal, everyday working conditions. This method will help identify leaky connections.
Air test
Multi-storey buildings undergo airtightness testing in the fall. Instead of liquid in such cases, air can be used. The test results are slightly inaccurate due to the fact that the air is first heated during compression, then cooled, which contributes to a drop in pressure. Compressors will help increase this parameter.
The sequence for checking the heating system is as follows:
- The structure is filled with air (test values - 1.5 atmospheres).
- If a hiss is heard, it means there are defects, the pressure is reduced to atmospheric pressure and the defects are eliminated (for this, a foaming substance is used, it is applied to the joints).
- The pipeline is again filled with air (pressure - 1 atmosphere), held for 5 minutes.
What does pressure in pipes affect?
Not everyone realizes how important it is to maintain the required pressure in the pipeline through which the coolant moves.
The pressure created in the system determines the following indicators:
- Room temperature. If the liquid moves slowly along the line, it does not enter the heat exchangers. In addition, before reaching the turning section of the circuit, it has time to cool down significantly.
- Presence of air pockets. If the pressure is insufficient, air bubbles form, preventing circulation. As a result, the flow of water throughout the riser stops.
- Pipeline integrity. With excessive pressure, gaskets rupture, threads on fittings break and batteries are destroyed. Watching the video will help you visualize the consequences of violating the heating technology of buildings and structures.
When the coolant flow rate decreases, energy consumption for heating increases, which leads to an increase in material costs.
Determining factors: expansion tank capacity, system type, etc.
The pressure in the heating system depends on several factors:
- Equipment power. Static is set by the height of a multi-story building or the rise of the expansion tank. The dynamic component is determined to a greater extent by the power of the circulation pump and, to a lesser extent, by the power of the heating boiler.

When ensuring the required pressure in the system, the appearance of obstacles to the movement of coolant in pipes and radiators is taken into account. During long-term use, scale, oxides and sediment accumulate in them. This leads to a decrease in diameter, which means an increase in resistance to fluid movement. This is especially noticeable with increased water hardness (mineralization). To eliminate the problem, periodically thoroughly flush the entire heating structure. In regions where water is hard, hot water purification filters are installed.
Normalization of working pressure in apartment buildings
Multi-storey buildings are connected to central heating, where the coolant is supplied from a thermal power plant, or to house boiler rooms. In modern heating systems, indicators are maintained in accordance with GOST and SNiP 41-01-2003. Normal pressure ensures a room temperature of 20–22 °C with a humidity of 30–45%.
Depending on the number of storeys of the building, the following standards are established:
- in houses up to 5 floors high 2-4 atm;
- in buildings up to 10 floors 4-7 atm;
- in buildings above 10 floors 8-12 atm.

It is important to ensure uniform heating of apartments located on different floors. The condition is considered normal when the difference between the operating pressures on the first and last floor of a multi-story building is no more than 8-10%
The condition is considered normal when the difference between the operating pressures on the first and last floor of a multi-story building is no more than 8-10%.
During periods when heating is not needed, the system maintains minimum levels. It is determined by the formula 0.1(Hx3+5+3), where N is the number of floors.
In addition to the number of floors of the building, the value depends on the temperature of the incoming coolant. Minimum values have been established: at 130 °C - 1.7-1.9 atm, at 140 °C - 2.6-2.8 atm. and at 150 °C - 3.8 atm.
Attention! Periodic performance checks play an important role in heating efficiency. They are controlled during the heating season and in the off-season
During operation, control is carried out using pressure gauges installed at the inlet and outlet of the heating circuit. At the inlet, the amount of incoming coolant must comply with established standards.
Check the pressure difference at the inlet and outlet. Normally, the difference is 0.1-0.2 atm. The absence of a drop indicates that there is no movement of water to the upper floors. An increase in the difference indicates the presence of coolant leaks.
In the warm season, the heating system is checked using pressure tests. Typically testing is provided by cold water pumped through. Depressurization of the system is detected when the indicators drop within 25-30 minutes by more than 0.07 MPa. The norm is a drop of 0.02 MPa within 1.5-2 hours.

Photo 1. The process of crimping the heating system. An electric pump is used, which is connected to the radiator.
What is the optimal pressure in a closed heating system?
The heating of “high-rise buildings”, which is provided according to a closed circuit, is discussed above. When arranging a closed system in private homes, there are nuances. Typically, circulation pumps are used that maintain the desired parameters. The main condition for their installation is that the pressure created should not exceed the values for which the heating boiler is designed (indicated in the equipment instructions).
At the same time, it must ensure the movement of coolant throughout the system, while the difference in water temperature at the outlet of the boiler and at the return point should not exceed 25-30 ° C.
For private, one-story buildings, the pressure in a closed heating system is considered to be within the range of 1.5-3 atm. The length of the pipeline during gravity flow is limited to 30 m, and when using a pump, the restriction is removed.
Types of pressure
There are:
- static pressure is a constant value, depends on the height of the column, is not affected by temperature changes and arises only due to the influence of gravity (water of any temperature presses on the walls of the pipes), the value of this parameter increases by 1 atm for every 10 m rise;
- dynamic - subject to decrease/increase, which is a consequence of changes in the properties of hot water during heating, and additionally this value is affected by the operation of pumps that ensure forced movement of the coolant through the pipes.
Dynamic pressure depends not only on the temperature of the liquid and the parameters of the pumping equipment, but also on the regulator, thanks to which hot water is distributed in the system. Considering that all of these factors are constantly changing, the pressure periodically decreases and increases. This parameter must be controlled, because if there is a significant drop, the speed of liquid movement through the pipes will decrease, which will lead to cooling of communications, and at the same time stopping the pumps. As pressure increases, the risk of equipment failure increases.
There is another variety. The working pressure is combined from the listed loads (static and dynamic). This ensures normal operation of the heating system and reduces the risk of an emergency.
Reasons for deviation from the norm
The need for heating occurs throughout the entire cold period of the year, which means 6 months of continuous heat supply (for mid-latitudes). During such a period of time, the system must uninterruptedly produce the required thermal power, and the pressure in the line must have a constant value. In practice it doesn't always happen this way. The influence of external and other factors causes interruptions in the operation of heating equipment. Let's consider the reasons that affect the parameters of autonomous systems.
Why do pressure readings drop?
The first and main reason for a decrease in the operating parameter is a coolant leak at the junctions of pipelines with heating equipment. To temporarily eliminate this deficiency, use a boost valve. If not, refill the line with coolant as the pressure drops, from the water supply network or well. Such measures will temporarily normalize the pressure force.
To completely eliminate the deficiency, you must:
- detect a leak;
- turn off the heat source;
- drain the coolant in the main section, having previously shut off the flow of water;
- repair the required unit;
- pump water, turn on the boiler.
IMPORTANT! If it is not possible to drain the coolant in a separate area, in autonomous systems the line is emptied, and after the malfunction is eliminated, it is refilled!
Leak detection is possible if there is a wet spot or droplets on the pipe connections. In cases where it is not possible to see a leak, first increase the pressure to 3 atmospheres and turn on the circulation pump. If this does not help, then drain the water and pump in air. The location of the air leak is determined by sound, and verified using soapy water, which will indicate the exact location of the defect.
The reason for the decrease in pressure may be wear and tear of heating equipment, the appearance of scale in the heat exchanger and system pipes. Another little-known reason for a decrease in operating parameters is a decrease in temperature. When an unheated house cools down in the cold season, and the coolant cools accordingly, the parameter value drops by 0.5 atm or more. In such a situation, maintain the lower limit of the value at 0.9-1.0 atm and prevent the coolant from freezing during periodic heating operation.
Why does blood pressure increase sharply?
A malfunction of the automation system that ensures automatic filling of the main line is often the reason for a rapid change in parameters. In addition, slowing down the circulation of coolant through the pipes leads to overheating, and accordingly to an increase in pressure. The reason may be air locks, as well as the presence of dirt in the filter or other system components.
To identify the reasons for the growth of the controlled parameter, all emerging factors are compared, and then conclusions are drawn. A simple method of eliminating a sudden increase in pressure is to bleed off excess coolant, forcefully turn on the pump, then pump up water, if necessary, to the set value. Repeating the procedure with a smaller amplitude of jumps and gradual leveling of the controlled parameter indicates the elimination of the air lock.
The inability to eliminate the cause using this method indicates the presence of “impenetrable” dirt that interferes with the normal operation of the boiler. To eliminate this reason, first clean the filter, and if that doesn’t help, clean the heat exchanger. Cleaning methods are used both mechanical and hydraulic. It is important not to damage the internal cavity and connecting pipes.
REFERENCE! When operating solid fuel boilers, especially during ignition, the pressure surge can change the value by 1-1.2 atm! It is important to compare the change in the controlled parameter with the increase in temperature. The direct dependence of the compared values indicates the need to slow down the ignition of the unit.
How to find a leak in a heating system
The first step is to try to identify the leak yourself.
- It is necessary to walk along the visible part of the pipeline in heated rooms (radiators, connecting fittings to the pipeline, the integrity of the pipes themselves).
- If laminate is laid, inspect it for swelling in the joints, especially near radiators, and discoloration (darkening).
- Check the condition of all pipes and connections in the boiler room; it is advisable to take a flashlight, then dried smudges will be visible.
- Look for water on the floor, rust, and inspect the shut-off equipment.
- Inspect the boiler itself, boiler, expansion tank.
- If there are suspicious places (dry smudges, dried puddles), place a sheet of paper; a leak will be detected if traces of moisture are found on this piece of paper.
If a leak is not detected, you should contact a special heating service. Technicians will look for leaks in inaccessible areas.
The inspection is carried out as follows:
— Liquid is being drained from the heating system.
— Next, specialists connect the compressor, unscrewing the tap or fittings and check the overall heating circuit or cut off part of the circuit and check it.
“ Then they walk along the circuit being tested and perceive by ear where the air leak occurs. If detected, it is necessary to dismantle the floor covering in the leak areas.
— And finally, part of the heating system pipeline is repaired or replaced and the floor covering is repaired.
What should normal blood pressure be?
The term “normal” means an indicator at which optimal coolant circulation is formed and there is no threat of an emergency. Each element of the heating system has a design strength and resistance to a certain temperature.
There are the following criteria for normal pressure (in atmospheres):
- seamless steel pipes - 20;
- steel pipes with seam -16;
- polypropylene reinforced products - 5;
- aluminum radiators - 6;
- panel batteries - 9;
- cast iron sections - 15.
In all cases, before making a decision to replace radiators, piping and risers in an apartment, you must consult with specialists.
It is advisable to purchase products designed for double dynamic pressure. This is necessary because hydrodynamic shocks in the system are not uncommon when pumping equipment malfunctions.
Dependence of pressure on coolant temperature
The pressure in the heating pipes is directly dependent on the temperature of the coolant supplied to the heating circuit.
It is known from the laws of physics that as temperature increases, a liquid tends to increase in volume. Accordingly, excess coolant appears in the heating system.
The reverse process occurs when the coolant temperature decreases. The pressure in the heating circuit will drop as the liquid decreases in volume.
To stabilize the situation, an expansion tank is used, which allows you to take part of the liquid when the temperature increases, and when the temperature decreases, return it back to the system.
As you can see, this process is automated using the elementary laws of physics; constant manual adjustment is not required.
Ways to deal with unstable blood pressure
Sometimes, despite struggling with constant interruptions for several days, it is not possible to achieve a positive result. Then it’s worth checking additionally:
- serviceability of the pressure gauge;
- is the air vented through a special air vent;
- Is the safety valve for releasing liquid when it boils or reaches a critical temperature working?
In order to combat unstable pressure, expensive systems are sometimes used that allow automated monitoring and adjustment of pressure in the heating system.
Read more: How to measure gas pressure and Which pressure sensor to choose?
In conclusion, it is worth noting that it is extremely important to immediately respond to changes in normal pressure. If it is exceeded or decreased, you should immediately find out the cause of the malfunction. This will help save money and time in the future, and eliminate the cost of expensive repairs.
Reasons for the fall
Along with the increase in pressure, another cause for concern arises - a drop in pressure of water or other coolant in the heating circuit. There are reasons such as:
- Leaks in radiators or piping.
- Airiness (presence of so-called air pockets). There are special air bleeders on heating radiators.
- Malfunction of the expansion tank (the most common is damage to the membrane).
- The expansion tank is not adjusted.
- The boiler heat exchanger is not working.
- Circulation pump malfunction (low power, complete stop). Since the circulation pump plays an important role in the heating system, you should not skimp on it, especially considering the many offers on the market from unknown brands with an attractive price but extremely low reliability.