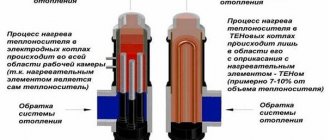
How to reduce gas consumption?
If suddenly your gas costs do not suit you, then the following recommendations will help you optimize them:
- Start insulating your home. The better you insulate your house, the less heat you will lose to the street.
- Check windows and doors for possible cracks. A lot of heat is lost through such structures
- If you use an open heating system with a tank on the roof, then convert the heating system to a closed one. A significant amount of heat is also lost through the roof.
- If you have a simple floor-standing boiler, then replace it with a wall-mounted one. Costs can also be reduced by 10-30%.
- Have your heating system serviced. Sometimes this can also have a positive effect on gas consumption. This is especially true for the boiler itself.
What determines the boiler's appetite?
Firstly, from its power. The larger it is, the higher the consumption of gas boilers will be. Moreover, you will not be able to reduce the appetite of a heat-generating device by using it. If you purchased a 20 kW gas fireplace, then even at minimum it will consume more than a 10 kW device at maximum. Therefore, be careful when choosing the power of heat-generating devices.
Secondly, from the temperature “overboard”. In this case, the already mentioned power regulator comes into play. After all, at a low temperature in the house, we will try to squeeze the maximum number of calories out of the heating by turning the regulator knob to the maximum. And if in relatively warm (for winter) weather the regulator is set to “one” or “two”, then in 30- or 40-degree frosts it is switched to “five” or even “seven”. And the number of cubic meters of gas passing through the nozzles into the combustion chamber doubles.
Gas consumption by a boiler depends on many factors
Thirdly, on the calorie content of the gas. This value is not controlled by the consumer. Therefore, gas distribution companies sometimes play around with the composition of “blue” fuel. After all, the same compressed nitrogen pumped into the central pipeline costs 2.5-3 times less than natural gas. Now, fortunately, such fraud schemes are no longer practiced, but gas workers can easily supply “undrained” gas with a high content of water vapor and other impurities into the pipes. And if your kettle boils not in 2-3 minutes, but in 5-7, then what can you ask from the heating system? You approach the boiler and turn the power regulator to maximum, closing your eyes to the accelerated rotation of the gas meter disk.
Fourthly, on the technical condition of the heat exchanger. Heating of water or coolant in gas appliances occurs in a heat exchanger - a special copper pipeline located either in the combustion chamber or behind its walls. And if the heat exchanger becomes clogged with scale or scale residues from the batteries, then you will have to add power, compensating for the decreased heat transfer. Moreover, a clogged heat exchanger steals cubic meters much more actively than real or mythical tricksters from a gas distribution company.
Fifthly, on the number of heating circuits. Almost all modern gas boilers have more than one heating circuit. After all, such heat-generating devices serve not only the wiring of the heating system, but also the home hot water supply line. To do this, a second circuit is installed into the structure of the gas hearth and the throughput of the nozzles is increased, increasing the power. And the more power, the higher the consumption.
How to calculate correctly?
You can find out the consumption of blue fuel for heating a house by calorie indicators on the basis of the management company. If this option does not work out, then you can put a conditional figure in the calculations, but it is best to take it with some margin - 8 kW/m³. But there is also often a situation when sellers provide information regarding the specific heat of combustion expressed in other units, that is, kcal/h. Don't worry, these numbers can be converted to Watts by simply multiplying the data by a factor of 1.163.
Another indicator that directly affects fuel consumption is the possible thermal load on the heating system, which consists of heat loss due to additional building structures of the building, as well as possible losses spent on warming up the ventilation air. The most suitable calculation option is to conduct or order detailed and accurate calculations of all existing heat losses. If you do not have the opportunity to use such methods, and a fairly approximate result will satisfy you, then there is an option to recalculate using the “enlarged” method.
- With a ceiling height of up to three meters, you can count on heat of 0.1 kW per 1 sq. m of heated area. As a result, a building of no more than 100 m² requires 10 kW of heat, 150 m2 - 15 kW, 200 m2 - 20 kW, 400 m2 - 40 kW of heat energy.
- If calculations are carried out in other units of measurement, then per 1 m³ of volume of a heated building there is 40-45 W of heat. Its load is checked by multiplying the indicated indicator by the volume of all available heated rooms in the building.

The efficiency of the heat generator, which affects the most efficient fuel consumption, is most often noted in the special technical data sheet of the equipment.
If you have not yet purchased a heating unit, you can take into account the efficiency data of gas boilers of different types from the following list:
- gas convector - 85 percent;
- boiler with an open combustion chamber - 87 percent;
- heat generator with a closed combustion chamber—91 percent;
- condensing boiler - 95 percent.
The initial calculation of the use of liquefied gas for heating can be calculated using the following formulas:
V = Q / (q x efficiency / 100), where:
- q is the level of caloric content of fuel (if it was not possible to find out the data from the manufacturer, it is recommended to set the generally accepted norm at 8 kW/m³);
- V is the consumption of the main gas that needs to be found, m³/h;
- Efficiency is the efficiency of fuel use by the currently available heat source, written as a percentage;
- Q is the possible heating load for a private house, kW.

By calculating gas consumption for 1 hour in the coldest times, we can get the following answer:
15 / (8 x 92 / 100) = 2.04 m³/h.
Working for 24 hours without a break, the heat generator will consume the following amount of gas: 2.04 x 24 = 48.96 m³ (for ease of measurement, it is advisable to round to 49 cubic meters). Of course, during the heating season the temperature tends to change, so there are very cold days, and there are also warm ones. Because of this, the average daily gas consumption that we found above will need to be divided by 2, where we get: 49/2 = 25 cubic meters.
Having the data that has already been determined above, you can calculate the gas consumption of a turbocharged boiler for 1 month in a house of 150 m², which is located somewhere in central Russia. To do this, we multiply the daily consumption by the number of days in the month: 25 x 30 = 750 m³. Using the same calculations, you can find the gas consumption of larger and smaller buildings
It is important to know that it would be very good to carry out such calculations even before the building is completely constructed. This will give you the opportunity to carry out activities that could help improve the operating conditions of the premises, while saving on heat consumption

Review of imported and Russian manufacturers of propane boilers
To begin with, let’s make a reservation that before purchasing you should find out about the parameters (technical characteristics) by which boilers of this type are usually selected.
- Power. It depends on it whether the equipment will heat the entire area of the building and whether it will provide the required amount of hot water.
- Boiler type. According to the method of installation, there are wall-mounted and floor-standing boilers, according to the type of combustion chamber - open and closed, and if it is possible to provide hot water - single-circuit and double-circuit.
- Gas pressure. The passport of the heating unit must indicate the minimum value of gas pressure in the range of 3-4 mbar. After all, the lower the indicator, the greater the volume of gas will be released from the cylinders.
- Gas consumption. To generate 1 kW of heat, a cylinder boiler consumes about 0.12 kg/h. It turns out that for a heat generator with a power of 15 kW, fuel consumption will be about 1.7 kg/h. These figures are conditional, because the intensity of liquefied gas consumption depends on many nuances (equipment efficiency, power, level of automation, outside air, required temperature in the house, heat loss of the building, need for hot water).
- Efficiency The operation of the equipment will be more economical and efficient if the efficiency is higher. On the market you can choose gas boilers with an efficiency of 90 to 94%.
Before purchasing liquefied gas boilers, calculations are carried out that show the profitability of the installation, as well as the features of maintenance and operation of the heating system.
The average monthly consumption of liquefied gas for heating a house of 150 m² is about 841.5 liters per month.
Boilers operating on liquefied gas, Russian-made and foreign-made, differ in prices. Many companies offer heating devices that can be switched to run on liquefied gas.
Brands of gas heating boilers:
- Italian brand "Baxi";
- Protherm (Slovakia);
- Zhukovsky Machine-Building Plant (ZhMZ) produces two types of gas boilers - AKGV and AOGV;
- Factory Conord.
| Manufacturer and model | Efficiency, % | Maximum thermal power, kW | Overall dimensions (HxWxD), mm | Description and differences |
| Baxi ECO Four 1.24 | 90,9 | 24 | 730x400x299 | Single-circuit wall model. Atmospheric burner. Copper heat exchanger. When the pressure drops to 4 mbar it works stably. Electronic ignition. Built-in pump. |
| Baxi MAIN 5 14 F | 92,9 | 14 | 730x400x299 | Wall-mounted boiler with DHW circuit. Electronic atmospheric burner. Bithermic heat exchanger. When the pressure decreases it works up to 4 mbar. Electronic anti-scale fuse. |
| Protherm Cheetah 11 MOV | 88,4 | 11,0 | 742x410x311 | Double-circuit wall model. Heat exchanger "pipe in pipe". Natural cravings. Built-in microprocessor. Winter-summer function. |
| Protherm Panther 25 KTV | 92,8 | 24,6 | 742x410x311 | Double-circuit boiler. The combustion chamber is closed. Information display. Minimum pressure 5 mbar. Anti-freeze function. |
| ZhMZ Comfort AOGV-11.6-3 | 86,0 | 11,6 | 850x310x412 | Floor. The combustion chamber is open. Built-in piezo ignition. German automatic equipment Mertik Maxitrol. Steel heat exchanger. |
| ZhMZ Universal AKGV-17.4-3 | 88,0 | 17,4 | 1050x420x480 | Double-circuit floor-mounted equipment. SIT automation. Heat exchanger made of stainless steel. |
| Concord DON KS-TG-16/20S | 90 | 20 | 775x405x1070 | Combination boiler: can operate on both gas and solid fuels. Honeywell - American draft regulator. Adaptation to hard water. |
Thus, heating a private house, cottage or bathhouse using a boiler running on liquefied gas is a good alternative to other heating options. Moreover, this type of fuel is widespread almost everywhere.
Which gas to choose, which is more profitable
To connect to the main gas pipeline, the user will have to pay for the project and installation work. And these expenses cannot be called insignificant. The growing appetites of gas services make gasification of homes a very expensive undertaking. However, all these expenses pay off during operation. As of March 2021, the cost of a cubic meter of gas, depending on the region of the Russian Federation, ranges from 4.44 to 8.66 rubles. The average price is 6.55 rubles. As a result, heating a house with natural gas of 150 or two hundred square meters, taking into account the estimated consumption rate for the season, will cost 29,825 and 39,038 rubles.
Liquefied fuel does not require insertion into the main line, but to store it it is necessary to build a gas tank - a container that accepts the required volume of fuel. In addition, this container will have to be periodically filled with gas, which is delivered to the site using special transport, and this service is not cheap. And the gas tank will have to be repaired and maintained. After all, the safety of all residents of a house heated by liquefied gas depends on its condition.

Liquefied fuel storage
At the beginning of spring 2021, a liter of liquefied gas at gas stations cost from 11 to 20 rubles, depending on the region of the Russian Federation. The average cost of this fuel was 15.5 rubles. Therefore, heating a 150-square-meter house with liquefied gas will cost 98,394 rubles. For housing with an area of two hundred square meters you will have to pay even more - 131,192 rubles. As you can see, liquefied fuel has surpassed natural gas in cost by 3.3 times. Therefore, conclusions regarding whether it is profitable or unprofitable suggest themselves - natural (main) gas, with all the bureaucracy and complexity of the connection process, will be much more profitable than liquefied fuel.
Where to buy a gas boiler using liquefied gas
In Moscow and Moscow Region
- MirCli (mircli.ru/kotly-otopleniya/nastennye-gazovye-kotly/odnokoturnye-kotly) – Leningradsky Ave., 80, building G, tel. +7 (863) 303–35–06, +7 (800) 775–29–90.
- IM “Gas Boilers” (https://msk.kotel-gazoviy.ru/na-szhizhennom-gaze/) – Moscow, st. Podolskikh Kursantov, 22, tel..
In St. Petersburg
- ProTeplo (https://www.proteplo-spb.ru/products/kotly-na-szhizhennom-gaze) – st. Chugunnaya, 14, lit. K (entrance from Mendeleevskaya 5), tel. +7 (812) 241–12–06.
- TechnoDOM (https://www.teh-dom.ru/gazovye_kotly_na_sgigennom_gaze#0) – Marshal Govorova Ave., 35, BC Yellow Corner, p. 119, tel. +7 (812) 671–00–88.
In conclusion, I would like to remind you that, despite all its advantages, liquefied fuel is not a competitor to natural gas. However, if connection to the pipeline is not available, then it can be argued that an LPG boiler is the most profitable and convenient option for organizing heating of a country house.
Gas boilersBoilers
The cost of heating services per 1 sq. m in Gcal in 2021 in an apartment building
Heating charges vary from region to region. The maximum indicators (which, of course, are in demand) are set by the regional administration, as a rule, for every six months. Plus, the formulation “heating price per 1 kW per m²” is not correct - government authorities limit the cost of the gigacalorie itself consumed by a utility unit.
After all, a gigacalorie is an analogue of a unit of work (the same Joule or kilowatt-hour), simply having a larger scale for convenience. For example:
- 1 gigacalorie corresponds to 4,184,000,000.00 Joules (4.184 gJ);
- 1 gigacalorie corresponds to 1,162.22 kilowatt-hours (kWh).
It is convenient to account for heat in gigacalories due to the large scale of thermal energy consumption (heat has an extremely high energy density compared, for example, with the same mechanical work).
These standards vary greatly among different regions due to the fact that temperature climatic regimes also differ significantly between them (winter in the Stavropol region is one thing and quite another in Anadyr). In addition, even within the same region (subject of the Federation) there may be several types of standards, depending on the quality of the house for which this standard is applied.
If this is a wooden barracks built in the 50s of the last century, then it will require more energy to maintain a comfortable temperature environment than in more modern multi-story buildings.
The standard is set specifically for 1 m² of living space, that is, there is a link: the larger your apartment, the more you will have to pay for heat if standard coefficients apply, regardless of how effective the thermal insulation is in your home.
Understanding this, the state administration seeks to create conditions and stimulate the process of equipping all consumers with individual heat meters, that is, at a minimum, to install communal heat meters.
However, there are a number of limitations:
- Now an individual metering device for an apartment (in houses built before 2012) is installed if there is a centralized supply from a single riser. If there are several pipes, then the installation of an IPU is considered physically impossible at this stage due to the need to install a large number of meters (for each battery), the high cost of the process and the complexity of accounting. Apartment buildings put into operation after 01/01/2012 (as a new building or after a major overhaul) are required by law to be equipped with individual and communal heat meters.
- Also, sometimes technical difficulties arise that make it impossible to install a common house metering device (CDMU).
In these cases, accounting is carried out in accordance with the standards. But if it is technically possible to install IPU and ODPU, and consumers still prefer to remain on the standard system of charging for heat supply, then penal increasing coefficients already begin to apply (you can learn how to decipher KPU, IPU and other abbreviations in the receipt for housing and communal services find out here).From 01/01/2017, this increasing coefficient is equal to 1.1 to the fee set by the heat supply organization. The very cost of 1 Gcal per 1 square meter in each region, of course, will be different.
Questions about meters
The reasons for such calculations are related to the choice of type and modification of the meter. Even a modest error here can cause negative consequences. Most often there are problems with the functioning of the meter. It is replaced and then the gas pipes are redone.
The type of this device must correspond to the equipment installed in the house.
The meters are marked G. It reflects their power qualities. In fact, it informs you what total gas consumption should occur in the house so that the meter accurately and without failures reflects it.
Example: the apartment has a gas stove. Gas consumption within one hour is in the range of 0.03 - 1.2 cubic meters. It is necessary to install the simplest device in the apartment. Installing a meter with an impressive volume is not reasonable.
If your home has both a gas stove and a boiler or water heater, the picture changes dramatically. And these devices produce completely different indicators. Even if the boiler or boiler consumes natural gas minimally, this parameter will still exceed the maximum value for gas consumption in liters for a stove with 4 burners. Here you will need to install a complex meter designed to work in such conditions.
In homes where complex gas appliances are installed, the minimum gas consumption data is calculated based on the technical properties of the stove. The maximums are calculated in aggregate. The abundance of gas appliances can cause another serious problem: a huge range will appear between the extreme points of consumption.
Example: there is a stove in the house. It operates on natural gas. The heater and boiler operate on the same fuel. Minimum data for calculation (cost per hour) – technical data of the furnace. This is 0.3 cu. m., maximum figures will reach 7.1 cubic meters. Often even greater values are obtained. And there is simply no device to cover such a range.
In such a situation, several devices are installed. A meter with indexes G1.6 is placed on the stove (the power of the meter is 1.6, the stove has 4 burners) or G2.5. Its version G4 (minimum) is mounted on equipment that consumes significant gas. There is a legal subtlety in this situation. When two counters are working, the same number of personal accounts are opened. There are separate payments for them. At the same time, the cost of installing these devices doubles.
The principle of calculations changes in the presence of a boiler with two circuits. The minimum data is determined on the basis of the technical figures of the stove and this apparatus. The difference between the extreme flow rates is more modest. And choosing the right meter is much easier.
Benefits for labor veterans and disabled people
Benefits for payment of thermal energy are provided at 2 levels:
- On the federal:
- heroes of the USSR and social labor;
- veterans and disabled people of the Great Patriotic War;
- persons affected by the Chernobyl accident;
- disabled people of all three groups;
- citizens raising a disabled child.
- At the regional:
- low-income and large families;
- pensioners;
- labor veterans;
- Home front workers during the Second World War and residents of besieged Leningrad;
- public sector workers.
The benefits themselves are provided either in the form of compensation (then part of the funds for the consumed resource is returned to the subject in the next month) or in the form of subsidies (which is less common).
The only way to get the modernization of housing and communal services in the country off the ground is to create a system of incentives for owners to optimize their costs for consumed utilities. To do this, it is necessary that there is a direct and strict correlation between the amount of payment and the volume of consumption. And this can only be achieved through the mass introduction of individual metering devices (in our case, heat).
To resolve your issue, seek help from a lawyer. We will select a specialist for you. Call
Badly
Healthy! 1
Questions about meters
The reasons for such calculations are related to the choice of type and modification of the meter. Even a modest error here can cause negative consequences. Most often there are problems with the functioning of the meter. It is replaced and then the gas pipes are redone.
The type of this device must correspond to the equipment installed in the house.
The meters are marked G. It reflects their power qualities. In fact, it informs you what total gas consumption should occur in the house so that the meter accurately and without failures reflects it.
Example: the apartment has a gas stove. Gas consumption within one hour is in the range of 0.03 - 1.2 cubic meters. It is necessary to install the simplest device in the apartment. Installing a meter with an impressive volume is not reasonable.
If your home has both a gas stove and a boiler or water heater, the picture changes dramatically. And these devices produce completely different indicators. Even if the boiler or boiler consumes natural gas minimally, this parameter will still exceed the maximum value for gas consumption in liters for a stove with 4 burners. Here you will need to install a complex meter designed to work in such conditions.
In homes where complex gas appliances are installed, the minimum gas consumption data is calculated based on the technical properties of the stove. The maximums are calculated in aggregate. The abundance of gas appliances can cause another serious problem: a huge range will appear between the extreme points of consumption.
Example: there is a stove in the house. It operates on natural gas. The heater and boiler operate on the same fuel. Minimum data for calculation (cost per hour) – technical data of the furnace. This is 0.3 cu. m., maximum figures will reach 7.1 cubic meters. Often even greater values are obtained. And there is simply no device to cover such a range.
In such a situation, several devices are installed. A meter with indexes G1.6 is placed on the stove (the power of the meter is 1.6, the stove has 4 burners) or G2.5. Its version G4 (minimum) is mounted on equipment that consumes significant gas. There is a legal subtlety in this situation. When two counters are working, the same number of personal accounts are opened. There are separate payments for them. At the same time, the cost of installing these devices doubles.
The principle of calculations changes in the presence of a boiler with two circuits. The minimum data is determined on the basis of the technical figures of the stove and this apparatus. The difference between the extreme flow rates is more modest. And choosing the right meter is much easier.
Consumption of liquefied propane-butane mixture
Not all owners of country houses have the opportunity to connect to a centralized gas pipeline. Then they get out of the situation using liquefied gas. It is stored in gas holders installed in pits, and replenished using the services of certified companies that supply fuel.
If liquefied gas is used to heat a country house, the calculation formula is taken as the basis. The only thing you need to take into account is that the bottled gas is a G30 mixture. In addition, the fuel is in an aggregate state. Therefore, its consumption is calculated in liters or kilograms.
Formula for calculating fuel mixture consumption
A simple calculation will help you estimate the cost of a liquefied propane-butane mixture. The initial construction data is the same: a cottage with an area of 100 square meters, and the efficiency of the installed boiler is 95%.

When calculating, it should be taken into account that fifty-liter propane-butane cylinders, for safety reasons, are filled to no more than 85%, which is about 42.5 liters
When performing calculations, we focus on two significant physical characteristics of the liquefied mixture:
- The density of bottled gas is 0.524 kg/l;
- The heat released during the combustion of one kilogram of such a mixture is equal to 45.2 MJ/kg.
To facilitate calculations, the values of heat released, measured in kilograms, are converted into another unit of measurement - liters: 45.2 x 0.524 = 23.68 MJ/l.
After which joules are converted to kilowatts: 23.68/3.6 = 6.58 kW/l. To obtain correct calculations, the same 50% of the recommended power of the unit is taken as a basis, which is 5 kW.
The obtained values are substituted into the formula: V = 5/(6.58 x 0.95). It turns out that the consumption of the G 30 fuel mixture is 0.8 l/h.
An example of calculating liquefied gas consumption
Knowing that on average 0.8 liters of fuel are consumed per one hour of operation of a boiler generator, it will not be difficult to calculate that one standard cylinder with a 42-liter refill will be enough for approximately 52 hours. This is a little more than two days.
For the entire heating period, the consumption of the combustible mixture will be:
- For a day 0.8 x 24 = 19.2 liters;
- For a month 19.2 x 30 = 576 liters;
- For a heating season lasting 7 months, 576 x 7 = 4032 liters.
To heat a cottage with an area of 100 square meters you will need: 576/42.5 = 13 or 14 cylinders. For the entire seven-month heating season, you will need 4032/42.5 = from 95 to 100 cylinders.

To accurately calculate the number of propane-butane cylinders needed to heat a cottage for a month, you need to divide the consumed monthly volume of 576 liters by the capacity of one such cylinder
A large volume of fuel, taking into account transportation costs and the creation of conditions for its storage, will not be cheap. But still, in comparison with the same electric heating, such a solution to the issue will still be more economical, and therefore preferable.
How much does heating cost?
The amount of heating depends on the amount of gas consumed and the price per 1 m3 in a given region. By simply multiplying two numbers, you can determine costs per day, per month or for the entire heating season.
In terms of absolute price per m3 (kg), main methane is 3-4 times cheaper than propane-butane mixture. However, when comparing the heating consumption of a building of 100 m2, methane requires an average of about 3000 m3, and only 1000 m3 of liquefied mixture. Therefore, it can be argued that how much liquefied gas costs for heating a house is the same price for main gas, due to higher consumption.
How to find out gas consumption for heating a house
How to determine the gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m2, 150 m2, 200 m2? When designing a heating system, you need to know how much it will cost during operation.
That is, determine the upcoming fuel costs for heating. Otherwise, this type of heating may subsequently prove unprofitable.
How to reduce gas consumption
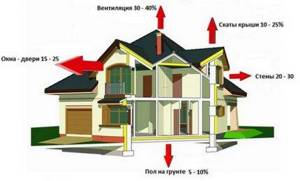
A well-known rule: the better the house is insulated, the less fuel is used to heat the street. Therefore, before starting the installation of the heating system, you should perform high-quality thermal insulation of the house - roof/attic, floors, walls, replacement of windows, airtight sealing loop on the doors.
You can also save fuel due to the heating system itself. By using heated floors instead of radiators, you will get more efficient heating: since heat spreads by convection currents from bottom to top, the lower the heating device is located, the better.
In addition, the standard temperature of floors is 50 degrees, and radiators are on average 90. Obviously, floors are more economical.
Finally, you can save gas by adjusting the heating according to time. There is no point in actively heating a house when it is empty. It is enough to maintain a low positive temperature so that the pipes do not freeze.
Modern boiler automation (types of automation for gas heating boilers) allows remote control: you can give a command to change the mode through a mobile provider before returning home (what are Gsm modules for heating boilers). At night, the comfortable temperature is slightly lower than during the day, etc.
How to calculate main gas consumption
The calculation of gas consumption for heating a private home depends on the power of the equipment (which determines the gas consumption in gas heating boilers). Power calculation is performed when choosing a boiler. Based on the size of the heated area. They calculate for each room separately, focusing on the lowest average annual temperature outside.
To determine energy consumption, the resulting figure is divided approximately in half: because throughout the season, the temperature fluctuates from severe minus to plus, gas consumption varies in the same proportions.
When calculating power, the ratio is based on the ratio of kilowatts per ten square meters of heated area. Based on the above, we take half of this value - 50 watts per meter per hour. At 100 meters – 5 kilowatts.
Fuel is calculated using the formula A = Q / q * B, where:
- A – the required amount of gas, cubic meter per hour;
- Q – power required for heating (in our case 5 kilowatts);
- q – minimum specific heat (depending on the type of gas) in kilowatts. For G20 – 34.02 MJ per cubic meter = 9.45 kilowatts;
- B is the efficiency of our boiler. Let's say 95%. The required figure is 0.95.
We substitute numbers into the formula, and for 100 m2 we get 0.557 cubic meters per hour. Accordingly, gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m2 (7.5 kilowatts) will be 0.836 cubic meters, gas consumption for heating a house of 200 m2 (10 kilowatts) will be 1.114, etc. It remains to multiply the resulting figure by 24 - you get the average daily consumption, then by 30 - the average monthly.
Calculation for liquefied gas
The above formula is also suitable for other types of fuel. Including for liquefied gas in cylinders for a gas boiler. Its calorific value, of course, is different. We accept this figure as 46 MJ per kilogram, i.e. 12.8 kilowatts per kilogram. Let's say the boiler efficiency is 92%. We substitute the numbers into the formula, we get 0.42 kilograms per hour.
Liquefied gas is counted in kilograms, which are then converted to liters. To calculate the gas consumption for heating a 100 m2 house from a gas holder, the figure obtained from the formula is divided by 0.54 (the weight of one liter of gas).
Next, as above: multiply by 24 and 30 days. To calculate fuel for the entire season, we multiply the average monthly figure by the number of months.
Average monthly consumption, approximately:
- liquefied gas consumption for heating a house of 100 m2 is about 561 liters;
- liquefied gas consumption for heating a house of 150 m 2 - approximately 841.5;
- 200 squares – 1122 liters;
- 250 – 1402.5, etc.
A standard cylinder contains about 42 liters. We divide the amount of gas needed for the season by 42, find the number of cylinders. Next, we multiply by the price of the cylinder, we get the amount needed for heating for the entire season.
Quick estimate
It is quite simple to estimate by eye how much gas will be consumed by your gas boiler.
We will start from either the volume of the heated room or its area:
- in the first case, we use the standard 30-40 W/cubic meter. m;
- in the second case - 100 W/sq. m.
The standards are taken taking into account the ceiling height in the room up to 3 meters. If you live in the southern regions, the numbers can be reduced by 20-25%, and for the north, on the contrary, they can be increased by one and a half times or doubled. Those. take in the second case, for example, 75-80 W/sq.m or 200 W/sq.m.
By multiplying the corresponding standard by the volume or area, we get how many watts of boiler power are needed to heat the room. Next, we proceed from the standard statement that modern gas equipment consumes 0.112 cubic meters of gas to generate 1 kW of thermal power.
We multiply again - this time the gas consumption standard (number 0.112) by the boiler power obtained in the previous multiplication (do not forget to convert watts to kW). We get the approximate gas consumption per hour.
The boiler usually works 15-16 hours a day. We calculate the daily gas consumption. Well, when the daily consumption is already known, we can easily determine the gas consumption for the month and for the entire heating season. The calculations are approximate, but quite sufficient to understand both the principle of calculation and the expected gas consumption.

A regular calculating machine is sufficient to calculate gas consumption. If you don’t want to delve into calculation formulas, use online calculator programs online. Enter the initial data and immediately get the result
Example.
Let's say the area of the room is 100 m².
Let's calculate the boiler power: 100 W/sq. m * 100 m² = 10000 W (or 10 kW).
Let's calculate the gas consumption per hour: 0.112 cubic meters. m * 10 kW = 1.12 cubic meters. m/hour.
Let's calculate gas consumption per day (16 hours of operation), per month (30 days), for the entire heating season (7 months):
1.12 cu. m * 16 = 17.92 cubic meters m 17.92 cu.m. m * 30 = 537.6 cubic meters. m 537.6 cubic meters m * 7 = 3763.2 cubic meters. m
Note: you can immediately determine the monthly and seasonal power consumption of the boiler in kW/hour, and then convert it into gas consumption.
10 kW * 24/3*2 * 30 = 4800 kW/hour - per month 0.112 cubic meters * 4800 kW/hour = 537.6 cubic meters. m 4800 kW/hour * 7 = 33600 kW/hour - per season 0.112 cubic meters * 33600 kW/hour = 3763.2 cubic meters. m
All that remains is to take the current gas tariff and convert the total into money. And if the project involves installing a double-circuit system that will not only heat the house, but also heat water for domestic needs, add another 25% to the power of the equipment and, accordingly, to the gas consumption of floor-standing gas heating boilers.

The simplest thermal imagers cost at least $300, and the price of professional ones starts from several thousand, but these devices show all the places through which cold air enters the house and heat escapes out
The boiler works and does not turn off
The next reason for the high gas consumption is the fact that the boiler simply does not turn off, or turns off, but extremely rarely. The most common reason for this phenomenon is that the gas boiler simply does not understand that it needs to be turned off somehow. Why is this happening?
Gas boilers are configured in such a way that they respond to shutdown based on return temperature. When the return temperature (the sensor most often stands on the supply, but due to circulation, until the temperature is reached, it will not turn off) reaches the required degrees, the boiler turns off. In other cases, it continues to work, and it does not matter what your supply temperature is set to. Until the boiler reaches the desired temperature, which is set in its software, it will continue to operate continuously. Continuous operation is associated with increased gas consumption and most likely at some point you will feel stuffy. Most often, this problem is due to the fact that boilers are installed in old heating systems, which, as a rule:
- unregulated;
- made on metal;
- Cast iron batteries with a large volume of water are installed.
Consequently, the boiler completely distills the coolant through a large circle, and the coolant has time to cool down during this time. In any case, the boiler copes with its task, but due to problems with circulation, the speed of movement of the coolant, as well as high heat removal, the return temperature is low.
At some point, the household really gets hot because the boiler is working non-stop. The boiler consumption at this moment is prohibitive.
Only installing a room thermostat will help cope with this problem. When you install a room thermostat, the boiler will be forced to turn off, no matter what the return temperature is. For example, if the thermostat is set to 20°C and the room temperature reaches the same level, the boiler is forced to turn off.
If you have high gas consumption, check whether the gas boiler turns off at all. If this does not happen, installing a room thermostat will solve the problem.
Low supply temperature

Another problem associated with a constantly running gas boiler is setting the boiler to a low temperature. Because of this, the boiler also constantly works and does not turn off.
It is a mistake to believe that if you are hot and you set the temperature to 40°C, but there are cast iron radiators or aluminum or other radiators in the house, then the boiler will work normally and turn off normally. Usually, under such conditions, on the contrary, a problem arises from the fact that the return flow has cooled down. The fact is that this kind of radiators does not accumulate heat, the heat transfer process occurs quickly, and the return also cools down quickly.
When you set a higher operating temperature for such radiators (It’s not for nothing that it is indicated in the passports when purchasing such radiators. The operating temperature range ranges from 60°C and above), the problem is leveled out, and the boiler returns to normal operation. Therefore, when you set a low temperature in the boiler in the hope that it will save money, this is not always the case. If the house has ordinary radiators, then the boiler, on the contrary, is required to operate at a higher temperature. And if at some point you feel hot and you want to lower the temperature, but the boiler won’t turn off, then the solution is simple - install a room thermostat.
Safety Recommendations
Converting the boiler and reconfiguring it to consume liquefied gas dictates the need to “reconfigure” your attitude towards the device for supplying and storing blue fuel.
You must remember that:
- Cylinders or gas tanks, which are gas storage tanks that supply fuel to household appliances as needed, need to be refilled periodically.
- To fill a group of cylinders or a gas holder with gas, you need to contact certified organizations that have equipment to record the weight of the gas in the cylinder and its actual volume in the gas holder.
- Filling closed gas tanks is carried out to 85% of the useful volume of the vessel. This reserve is necessary in case of thermal expansion of the fuel to avoid an explosion.
A non-hazardous situation that requires special attention when replenishing liquefied blue fuel reserves is the filling of liquid with a density different from the density of the previous liquid. Because of this difference, the remaining liquefied gas may not mix with the newly filled portion.
In the tank, due to the difference in density, a kind of two non-connecting sectors are formed, in each of which liquefied gas circulates. However, convective heat exchange will occur at the sector boundary after a short period. After the temperatures are equalized, the densities will be equal and the liquids will be able to mix.

Liquefied gas, like main gas, is a highly flammable, combustible liquid with a high flame propagation speed. To avoid catastrophic situations, you should strictly follow the operating rules and fill the cylinders no more than 85%
Usually this process, meaning direct mixing, is accompanied by intense evaporation of liquefied gas. To avoid associated losses, mixing devices should be used during the filling process. But it is better to choose a method that eliminates the above-described phenomenon.
Replenishing cylinders and gas tanks with blue fuel in general is a process that requires increased attention, otherwise problems can be very serious and even catastrophic. The rapid spread and evaporation of the liquefied gas mixture is recognized as a significant problem.
If the rules for the safe operation of gas-consuming equipment are not violated, main methane rarely explodes. This only happens with significant leaks, if the technical state of the gas in the surrounding space changes dramatically. For example, in a kitchen with obvious signs of a leak, instead of mandatory ventilation, they turn on the light.
When liquefied gas expands in a closed container due to external heating, it will necessarily explode if there is not enough space left in the container for its expansion. Blue fuel burns extremely intensely. Since the gas is quickly absorbed by the atmosphere, the combustion zone expands at high speed.
Calculation method for natural gas
The approximate gas consumption for heating is calculated based on half the power of the installed boiler. The thing is that when determining the power of a gas boiler, the lowest temperature is set. This is understandable - even when it is very cold outside, the house should be warm.
You can calculate gas consumption for heating yourself
But calculating gas consumption for heating using this maximum figure is completely incorrect - after all, the temperature is generally much higher, which means much less fuel is burned. That’s why it is generally accepted that the average fuel consumption for heating is about 50% of the heat loss or boiler power.
We calculate gas consumption by heat loss
If you don’t have a boiler yet, and you estimate the cost of heating in different ways, you can calculate it from the total heat loss of the building. They are most likely known to you. The technique here is this: they take 50% of the total heat loss, add 10% to provide hot water supply and 10% to remove heat during ventilation. As a result, we obtain the average consumption in kilowatts per hour.
Next, you can find out the fuel consumption per day (multiply by 24 hours), per month (by 30 days), and, if desired, for the entire heating season (multiply by the number of months during which the heating operates). All these figures can be converted into cubic meters (knowing the specific heat of combustion of gas), and then multiply the cubic meters by the price of gas and, thus, find out the heating costs.
| Crowd name | Unit | Specific heat of combustion in kcal | Specific heat of combustion in kW | Specific heat of combustion in MJ |
| Natural gas | 1 m 3 | 8000 kcal | 9.2 kW | 33.5 MJ |
| Liquefied gas | 1 kg | 10800 kcal | 12.5 kW | 45.2 MJ |
| Coal (W=10%) | 1 kg | 6450 kcal | 7.5 kW | 27 MJ |
| Wood pellets | 1 kg | 4100 kcal | 4.7 kW | 17.17 MJ |
| Dried wood (W=20%) | 1 kg | 3400 kcal | 3.9 kW | 14.24 MJ |
Example of heat loss calculation
Let the heat loss of the house be 16 kW/hour. Let's start counting:
- average heat demand per hour - 8 kW/h + 1.6 kW/h + 1.6 kW/h = 11.2 kW/h;
- per day - 11.2 kW * 24 hours = 268.8 kW;
- per month - 268.8 kW * 30 days = 8064 kW.
Convert to cubic meters. If we use natural gas, we divide the gas consumption for heating per hour: 11.2 kW/h / 9.3 kW = 1.2 m3/h. In calculations, the figure 9.3 kW is the specific heat capacity of natural gas combustion (available in the table).
Since the boiler has not 100% efficiency, but 88-92%, you will have to make further adjustments for this - add about 10% of the obtained figure. In total, we get gas consumption for heating per hour - 1.32 cubic meters per hour. Next you can calculate:
- consumption per day: 1.32 m3 * 24 hours = 28.8 m3/day
- monthly demand: 28.8 m3/day * 30 days = 864 m3/month.
The average consumption for the heating season depends on its duration - multiply by the number of months while the heating season lasts.
This calculation is approximate. In some months, gas consumption will be much less, in the coldest month - more, but on average the figure will be about the same.
Boiler power calculation
The calculations will be a little simpler if you have the calculated boiler power - all the necessary reserves (for hot water supply and ventilation) have already been taken into account. Therefore, we simply take 50% of the calculated capacity and then calculate the consumption per day, month, per season.
For example, the design power of the boiler is 24 kW. To calculate gas consumption for heating, we take half: 12 k/W. This will be the average heat demand per hour. To determine fuel consumption per hour, we divide by the calorific value, we get 12 kW/hour / 9.3 k/W = 1.3 m3. Then everything is calculated as in the example above:
- per day: 12 kW/h * 24 hours = 288 kW in terms of the amount of gas - 1.3 m3 * 24 = 31.2 m3
- per month: 288 kW * 30 days = 8640 m3, consumption in cubic meters 31.2 m3 * 30 = 936 m3.
Next, add 10% for the imperfection of the boiler, we find that for this case the consumption will be slightly more than 1000 cubic meters per month (1029.3 cubic meters). As you can see, in this case everything is even simpler - fewer numbers, but the principle is the same.
By quadrature
Even more approximate calculations can be obtained based on the square footage of the house. There are two ways:
- You can calculate according to SNiP standards - on average, heating one square meter in Central Russia requires 80 W/m2. This figure can be used if your house is built according to all requirements and has good insulation.
- You can estimate based on average statistical data: with good insulation of the house, 2.5-3 cubic meters/m2 is required;
- with average insulation, gas consumption is 4-5 cubic meters/m2.
Each owner can assess the degree of insulation of his home; accordingly, one can estimate what gas consumption will be in this case. For example, for a house of 100 sq. m. with average insulation, 400-500 cubic meters of gas will be required for heating, for a house of 150 square meters it will take 600-750 cubic meters per month, for heating a house with an area of 200 m2 - 800-100 cubic meters of blue fuel. All this is very approximate, but the figures are derived based on many factual data.
Gas boiler power calculation
The main share of fuel consumption is heating. An important parameter of any house or apartment that affects the amount of gas spent on heating is the heat loss indicator. The task of heating is precisely to correctly compensate for these losses, creating conditions for comfortable living.
In order to calculate the need for liquefied gas, it is necessary to determine the amount of heat loss at home or the thermal power required for full heating. The rated power of the heating system - gas boiler - depends on this indicator
As a standard for calculations, we will take a house located in an area with an average climate, in satisfactory condition and insulated in accordance with technology. The area of the house is 80 m2.
The average values of heat loss and boiler power can be determined by the quadrature of the area.
The formula looks like:
Q = S × Рр /10, where
Q—calculated heat losses (kW);
S is the area of the premises that are heated (m2);
Рр - specific power of a gas boiler (kW/m2) - power for every 10 m2.
The specific power for heating an area of 10 m2 has already been approximately established, taking into account adjustments for regions with different climates. For our reference house, located, for example, in the Moscow region, Рр = 1.2 - 1.5 kW.
Taking into account a house area of 80 m2, the optimal power of the heating system will have the following value:
Q = 80 × 1.2 / 10 = 9.6 kW.
Although simplified, this formula reflects the most accurate results.
Often, for convenience in carrying out calculations, unit is taken as the value of specific power. Based on this, the power of the heating system is taken at the rate of 10 kW per 100 m2 of heating area.
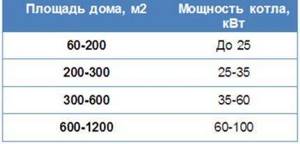
Since the gas supply system of your home includes not only heating, but also water heating and other equipment, the boiler power is determined by adding 20-25% of the reserve to the calculated heat losses
The second option, but accepted with a greater degree of error, is to calculate the cost of thermal energy for the heat loss of a building by cubic capacity - the volume of heated premises. Depending on the climate zone, 30 - 40 W are allocated for heating one cubic meter of a room with a ceiling height of up to 3 m.
Factors affecting gas consumption
The gas holder has the form of a volumetric tank that is filled with liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). This is a mixture of two gases - propane and butane.
Storing gas in such tanks, with its further use for heating the house, may be due to the following factors:
- the inability to tie into the main gas pipe or the high cost of such a connection;
- constant and unresolved by gas services problems with gas pressure in the central pipeline.
For normal operation of most gas boilers, the gas pressure in the pipeline must be at least 35 mbar. This standard is often not maintained in main gas pipelines and ranges only from 8 to 22 mbar.
To determine the volume of liquefied gas in a tank, there are mechanical level gauges or more modern remote telemetry systems. Such equipment can be supplied complete with the tank or purchased separately. The average daily gas consumption can also be determined by the difference in gas meter readings, if available.
But a more accurate answer to the question of how much gas in a gas holder is enough to heat a home, what its consumption is and how to minimize costs for it, mathematical calculations will help. And this despite the fact that objectively such a calculation will be of an average nature.
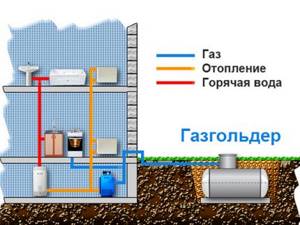
Fuel in an independent gas supply from a gas holder is consumed not only for heating. Although in much smaller volumes, it is also spent on heating water, operating a gas stove and other household needs.
It should be taken into account that gas consumption is influenced by the following factors:
- climate of the region and wind rose;
- square footage of the house, number and degree of thermal insulation of windows and doors;
- material of walls, roof, foundation and the degree of their insulation;
- number of residents and mode of their stay (permanently or periodically);
- technical characteristics of the boiler, the use of additional gas appliances and auxiliary equipment;
- number of heating radiators, presence of heated floors.
These and other conditions make the calculation of fuel consumption from a gas tank a relative value, which is based on average accepted indicators.
Pay attention to heat losses
The following calculation method assumes that the level of heat loss of the building is known - and this statement is true in most cases.
The calculation process is simple:
- The total heat loss is divided in half, and 10% is added to the resulting value for hot water supply and ventilation heat outflow;
- The result of the previous action (measured in kilowatts per hour) allows you to find out the gas consumption for a day, a month or the entire heating period;
- The total gas consumption is converted into cubic meters (for this you will need to find out the specific heat of combustion of the gas) and multiplied by the cost of one cubic meter, as a result of which you can get the cost of heating for the desired period of time.

Using a similar method, you can calculate the consumption of any fuel - you just need to know the heat capacity of a particular energy resource. In addition, it is worth remembering the efficiency of heating equipment, which in the case of gas boilers fluctuates around 90%, i.e. It is worth adding another 10% to the total expense.
Of course, the described technique cannot give an exact answer to the question of how much a gas boiler consumes per month. On cold days, consumption will increase, and on warm days it will decrease, and this is completely logical. However, even a rough calculation allows you to understand how much gas a gas boiler consumes per month and how profitable its installation will be.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
Thermal conductivity and resistance to heat transfer of materials. Calculation rules for walls, roof and floor:
The most difficult part of the calculations for determining the volume of gas required for heating is finding the heat loss of the heated object. Here, first of all, you need to carefully consider geometric calculations.
If the financial costs of heating seem excessive, then you should think about additional insulation of the house. Moreover, heat loss calculations clearly show the freezing structure.
Please leave comments in the block below, ask questions about unclear or interesting points, and post photos related to the topic of the article. Share your own experience in carrying out calculations to determine heating costs. It is possible that your advice will be very helpful to site visitors.