What modern pumps offer
Anyone who wants to choose a pump needs to know the difference between modern robotic models and the old options that are familiar to everyone. You can find out more about this…. But now, for those interested in the process, let’s look at the graphs.
It is known that GRUNDFOS is a trendsetter in this matter. The latest models of this company, the ALPHA2 and ALPHA3 series, are computer controlled and they are able to work not only with fixed speeds, but also select the speeds and power consumption optimally - with the best energy savings, i.e. adapt to the network every time it changes.
In the previous example, on a conventional pump, when the radiators were closed, the pressure increased and the power increased accordingly. But with the automated option, on the contrary, when part of the radiators (circuits) is closed, both the flow and pressure of the pump decrease, and, accordingly, the power - see the graph - the pump changes speed and moves to a point on another graph. The pressure, unlike the first example, did not increase, but decreased by the amount H2.
Selection by pressure
Some owners of heating networks will want to calculate the required coolant flow rate, hydraulic resistance at different flow rates, in order to build a graph... to select a pump on a scientific basis... But most understand that this is unnecessary, and nothing good will come of this idea, and read on...
Indeed, everything has already been calculated a long time ago, and it turns out that there are simply no unsuitable circulation pumps on sale.
Each such unit belongs to a certain standard size. These are the following values - 25/40, 25/50, 25/60, 25/80... The first number simply means the diameter of the connection thread, most often it is 25mm - “inch”, less often 32 or 20 mm. The second figure characterizes the pump completely - this is the created pressure in kilopascals - for the first example it is 40 kPa, which is approximately 4 m of water column.
The coolant flow rate at such a pump pressure in conventional heating networks will be normal - energy transfer will be ensured if the pump, of course, is selected for its heated area. For which, in fact, it was designed.
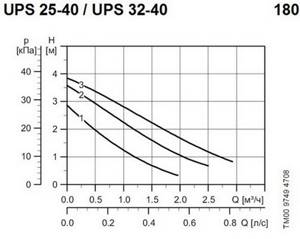
Let's take a close look at the graphs of the now outdated Grundfos UPS 25-40 pump, which has only 3 fixed speeds. At 2.5 meters of pressure, it will give more than 1.0 m3/hour of flow - just what you need for a small house.
How to properly deal with old pump designs
Pumps with 3 fixed speeds are cheap and very common. These old, time-tested samples, although they consume excess electricity, are not on a cosmic scale, since their own power is not great, ranging from 10 to 100 W. And they are completely incapable of emptying the home owner’s pocket no matter how they are used.
Nevertheless, it is advisable to select the rotation speed of the pump rotor in accordance with the current heating power. The off-season will require a minimum of energy transfer. And in cold weather you need to set (probably) the highest speed of the pump so that it takes enough coolant from the boiler operating at full power….

If the newest pump is selected
If we use the latest electronically controlled pump, type ALPHA2 from GRUNDFOS, then the electronic control will decide everything for us and select the speed so that energy consumption is minimal.
GRUNDFOS, in fact, to work on the radiator, asks the user to turn on the AUTOADAPT mode and not worry about anything else.
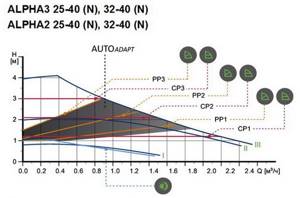
On the graphs, the point of operation on the heating network will fall somewhere in the shaded area. Now, when the thermal heads on the radiators are automatically closed, the pump will reduce its energy and will produce adequately lower pressure and lower coolant consumption. The entire system will be balanced in terms of flow and pressure.
Operating modes of “single pressure”, “proportional pressure”, etc. are also possible. You can get acquainted with this in a little more detail - how to set the optimal mode on electronically controlled heating pumps
How to choose a pump for a heating system
Let's return to the main question - choosing a circulation pump for a private home - what to do if you need to buy a circulator, but it is not clear which one is suitable...
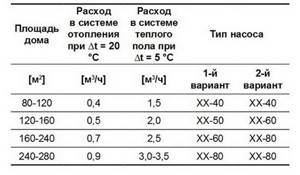
It was noted above that you can find mainly three standard sizes of circulation pumps on sale - for 40 kPa, 60 kPa and 80 kPa pressure (for example, 25/40 - for 4 m of water). It turns out that each standard size is suitable in terms of power (pressure and flow coolant) for a certain heated area. So a 25/40 pump is quite applicable up to a house area of 120 sq. m. in our climate. And in heat-saving houses, it can handle 160 square meters. And 25/60 should not be used for an area of less than 160 sq. m., but it will cope with the delivery of coolant to an area of 240 sq. m. But it is better to refer to the recommendations from the manufacturer. This is what GRUNDFOS recommends for its products (the first option is a product with fixed speeds, conventional pumps)
What are the most common mistakes when choosing
When choosing a pump, users often proceed from the principle “you can’t spoil the porridge with oil.” After consulting with a salesperson in a store, who is happy to sell everything that is not needed and that is more expensive, they often decide to take a more powerful pump, just in case...
As a result, in an ordinary house of 120 square meters, with 7 radiators, an expensive, powerful pump of 25\80, or even 32-120, is installed. Which, to the horror of the underground rodents, begins to drive water through the scanty heating system with an eerie noise. And also consume electricity to overcome significant hydraulic resistance (the diameter of the pipes in small systems is not large) in double or triple the amount required.
It is recommended to select a circulation pump of the required size. Preferably from a reputable manufacturer.
- Adjusting the pumping speed will help establish a suitable thermal regime. This is necessary so that in the off-season the pump does not work the same way as in the frosty winter and uses energy more economically. Some pumps need to change speeds manually, others (for example, some Grundfos models) do this automatically.
Summer mode is needed to protect the pump and check valves from damage during the warm season. The system will automatically turn on for a couple of minutes every 24 hours to avoid souring.
If the house has both a heating boiler and a water-heated floor, not only a circulation pump is installed, but also a comb. Its task is to control the temperature of the entire system and distribute heat evenly across the circuits.
The fact is that the temperature of the water from the boiler is 60-70°C. It is suitable for radiators, but is too hot for underfloor heating. To reduce the temperature, water from the boiler is mixed with cooled water from the return flow of the heating circuit in the comb. You can insist and maintain a comfortable floor temperature using a thermostat.
Thanks to the comb, circulation pump and thermostat, the warm floor will not burn your feet and will not overheat the room.
Pump selection based on calculation results
Having carried out the previous calculations, it is necessary to determine the operating point of the heating system. To do this, draw a diagram with coordinates P and J, on which you need to find the point at which the data from the previous calculations intersect. Knowing how to select a circulation pump for heating according to the table, you don’t have to worry about other steps - all you have to do is look through the manufacturers’ catalogs and find the unit that best suits the intersection point.

Of course, you can always choose a more efficient pump model, but a device that is too powerful is not cost-effective. There are two reasons for this, and they are very simple: firstly, increasing productivity always leads to an increase in the cost of the pump, and secondly, a powerful unit will consume much more electricity during operation.
However, the last factor can be mitigated by choosing a pump with automatic speed control. Such a device can independently regulate its operating mode, thereby reducing electricity consumption. When choosing, you should also pay attention to the noise level produced by the pump, especially if it will be installed in a residential area. The best option, well suited to this condition, are pumps with a wet rotor - they operate almost silently.
Types of models
The company offers many variations, which are divided into several classes. This significantly complicates pump selection. The Danish company specializes in the production of:
- pump for the heating system;
- Grundfos well pumps;
- devices for high pressure cold water;
- sewer models.
Each class has an individual purpose, as well as a different design and operating scheme. Therefore, before choosing a device, you should decide for what purpose it is needed.
The smallest circulation pump for heating
Compact units designed for an operating voltage of 12V are widely used due to the following advantages:
- Minimum power consumption;
- Soft start;
- Electronic control of turbine speed;
- Long service life;
- Versatility and ease of installation;
- No vibrations during operation;
- Built-in overheating protection.

The use of such devices can significantly reduce electricity costs without loss of efficiency.
Selecting a pump for a home heating system.
The selection of a circulation pump for the boiler room of a private house, cottage or cottage must be taken very responsibly. It would be better, of course, to entrust this to professionals, although if you have a little basic knowledge and not too serious requirements for the heating system, you can do the calculation yourself, based on our recommendations.
The circulation pump is selected according to the water flow in the heating system in m3 per hour and the developed pressure in M, based on the size of the house and the materials used in the construction of the house. An experienced designer will select a pump specifically for the heating system in your home. If you are ready to take responsibility when choosing, we recommend choosing a pump with automatic control or at least several operating speeds. It is of course more expensive, but it will allow you to correct errors in installing a heating system or choosing a circulation pump. Pumps with a so-called wet rotor have an adjustable rotation speed, and therefore it is possible to adjust the coolant circulation within certain limits and correct a mistake with the selection of a pump.
And so, to select a circulation pump for a private home, you need:
UPS pump with threaded or coupling connection
1. Know the height from the pump installation point to the top point of the topmost heating device.
2. Heated area of the room.
3. Determine the approximate resistance of your heating system. For example, let's start with it.
The so-called plastic pipes (Pilsa or PPR PN10, 20.25) are not specifically focused on the material - the properties are approximately the same. Diameter DN40 with cast iron batteries, heating system resistance 1m. DN 32 with aluminum heating radiators - 1.2 - 1.5 m. DN25 with bimetallic heating devices – 2m.
Select the pressure developed by the pump. For example, the height from the pump to the top point of the topmost heating device is 4 meters (the house has two floors, the pipes are thin, the heating devices are bimetallic), the pump must develop a pressure of 4+2 = 6 meters.
Now, to find m3/hour, we convert the heated power into the required heat. 10 m of heated area is 1 kW, if the walls are warm and thick we take 0.8 kW, thin and cold 1.2 kW.
The house is warm with an area of 200 m2, the walls are thick. 200/10x0.8=16 kW or 16x0.86=13.76 kcal
Now decide what temperature difference you need in the heating system, we recommend 8-10 degrees, no more and no less. More is bad for the boiler and comfort; less, you will have to purchase a more powerful and expensive pump, which also consumes more electricity. We choose 10 degrees.
Therefore, for a warm two-story house with an area of 200 m2, with plastic pipes hidden in the walls and bimetallic radiators, you need a circulation pump with a capacity of 1.4 m3/hour at a pressure of 6 meters. To avoid errors, the circulation pump should have these characteristics at second speed , and the pump itself should be selected as three-speed.
The wet rotor circulation pump UPS 25-70 from GRUNDFOS meets these conditions. The price of a branded pump is 140 Euros, a Chinese one is 70-80 Euros. It consumes 150 W of electricity per hour .
If we used thicker pipes and aluminum radiators, then a UPS 25-60 180 circulation pump would be suitable, but it already costs 110 Euros. This pump consumes less electricity - 110 W per hour.
As you can see, it is better to design a heating system and select a circulation pump before starting work, so you can still save on materials and operating costs.
Read the following article to learn how to properly install a circulation pump for a heating system.
Paramonov Yu.O. Enterprise Energostrom LLC, 2013.
How much energy do pumps consume?
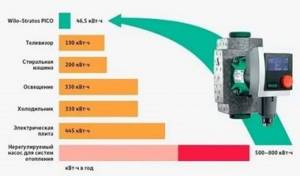
The pump is the main element of the heating system. The purpose of the device is to ensure forced circulation of water in a closed circuit. The operation of the pump allows you to speed up the movement of the coolant in the system and make the process of circulating the liquid medium more productive. There are different types of equipment, regardless of their type, the efficiency of the process is achieved. But the question arises: what is the power consumption of the pump, how to calculate it, what to do to ensure that electricity consumption is moderate.
Consumption
Pumps
The energy intensity of a pumping station is determined based on its power. Manufacturers offer pumps of different power: from six hundred watts to one and a half kilowatts. These are devices for domestic use, more powerful systems are intended for industrial use. Pump performance depends on the volume of pumped water and pressure.
Different types of pumping equipment have their own characteristics and technical characteristics. Let's look at the types of devices in more detail.
The issue of energy saving is becoming increasingly relevant. It is possible to save and reduce costs not only with the help of energy-saving lamps, but also through the use of energy-saving appliances and devices. A circulation pump belongs to this category. It is used for forced circulation of media in a closed system. Thanks to the continuous movement, the temperature of the media remains high and a large amount of energy is not wasted on reheating. This leads to resource savings.
Types of heating pumps
A circulation pump is the best choice as it provides efficient and fast heating of your home. Circulation pumps are divided into 2 types: wet and dry. You need to contact professionals, they will select a pump.
Dry circulation pumps are rarely used today. This type of equipment has a special design, here the rotor is completely isolated, it has no contact with water, while rotating, it creates air turbulence, which ensures pumping of coolant. Pumps are relatively reliable and efficient, but due to the principles of their operation, they can break down quite often and require constant maintenance.
O-rings are used inside, which wear out due to temperature and difficult operating conditions. Such pumps produce a loud sound during operation, so they are installed in a separate room. Most often, such pumps are used in private homes or industrial facilities.
Wet pumps have a more correct and advantageous design. The impeller and rotor are immersed directly in the coolant. The impeller rotates in a certain direction and thereby creates the necessary coolant pressure in the system. The liquid itself acts as a lubricant and at the same time cools the pump rotor. As a result, the service life of such equipment is much longer than that of dry type pumps.
During operation, the wet type pump does not make noise, so it can be safely installed even in a small apartment; it will not interfere in any way.
How to calculate a heating pump
If you want your house to be heated efficiently, you need to choose the right pump power for your heating system. The performance of the pump will determine how quickly the room is heated, how efficiently the coolant energy is used, and how long the pump will operate without maintenance.
If you make the correct calculations and know exactly what power of the heating pump in a private home is needed, you can save significant money and extend the service life of all heating equipment.
It is necessary to understand that calculating the power of heat pumps is very difficult; for this you need to have certain knowledge and skills. If you have never encountered such a task before, then you should entrust the work to professionals. The specialists are experienced, they have already done similar work many times, they understand exactly what kind of circular pump you need and how to calculate its power.
Circulation pump power for heating
In order to understand how to calculate a heating pump, you need to turn to specialized formulas.
The formula for calculating the required thermal power is:
where V is the volume of the heated room (the product of width times length times height) in m3
ΔT – difference between the air temperature outside the room and the required temperature inside the house, °C
K – heat dissipation coefficient, dimensionless K = 3 ÷ 4 – for wooden structures without insulation. K = 2 ÷ 2.9 - for brick structures with little thermal insulation. K = 1 ÷ 1.9 - for standard brick structures (double brickwork) with average thermal insulation. K = 0.6 ÷ 0.9 - structures with good thermal insulation - double brick walls with thermal insulation, double or more double-glazed windows, thermally insulated roof.
For example, let’s calculate the required thermal power for a house with a heated area of 120 m3, the air temperature outside in winter is -10 °C, the required temperature inside the house is 23 °C, therefore ΔT = 33 °C. Standard brick building K = 1.
Then P=V*ΔT*K = 120 * 33 * 1 = 3960 kcal / h
This value is then converted to kW
This is a classic option for calculating the thermal power for heating a room in a domestic case; in order to find out the power of the circulation pump for heating, it is assumed that heating 10 square meters of a room requires 1 kW of thermal energy.
Therefore, if the area (and not the volume as in the previous formula) of the room is 100 square meters, a pump with a power of at least 10 kW is required.
The formula for calculating pump performance (flow) looks like this:
Q - flow rate in volumetric value, cubic meters. m./h;
R is the amount of heat required for a certain room (required thermal power), kW;
TF—inlet temperature, degrees Celsius;
TR—outlet temperature, degrees Celsius.
a special calculator for you that will help you choose a pump of the required power in the article on how to choose a heating pump.
It is necessary to understand that this is a universal formula that is suitable for all types of heating systems. But you also need to be aware that changes may be made to the formula; you need to clearly understand that everything depends on the features and unique design of your heating system. Experienced professionals can pay attention to all the details, they can change the formula depending on certain circumstances.
It is also necessary to understand the fact that your heating system may have more than one circuit, so it will be necessary to use several pumps. It will be necessary to calculate the power of the heating system pump for each individual circuit; it will be necessary to calculate the efficiency of the pump in certain conditions.
In any case, you should pay attention to many details. Therefore, if you have not carried out calculations before, then they should be entrusted to the best professionals.
Pump power for heated floors

Warm floors are in very high demand on the market. This is understandable; such an addition to the heating system makes your life in a house or apartment more comfortable. Warm can independently increase the temperature inside a small room, it can make your life more comfortable and practical, you will simply get great pleasure from walking on a warm and pleasant surface. It is safe for the health of both adults and children.
The power of the pump for a heated floor is determined using the same formulas.
If the underfloor heating system is water-based, then it uses a circulation pump of a certain power. By choosing the optimal pump power for a heated floor, you can determine the efficiency of the pump and achieve the most optimal result.
Heated floor systems do not use very powerful pumps; the system uses a small amount of coolant and should not operate under very high pressure. However, the power must be sufficient to ensure optimal circulation of the coolant through the underfloor heating system.
Video calculation of pump power for heating
When asked how to calculate the power of a heating pump, the first thing that comes to mind is that you need to turn to professionals, the best specialists in their field. Experienced professionals can do everything necessary to select the optimal performance of the future pump. This will lead to the fact that the pump will work throughout its entire period, will perform all the functions assigned to it, and will create the necessary pressure of the heating system.
The article above and the section about heating pumps on our website provide all the necessary information, but if it is difficult to choose the equipment yourself, then it is better to entrust this work to professionals; they will cope with the task.
The main thing about gas and electric power
All energy-dependent boiler models constantly consume electricity during operation. Without it they simply won't work. In regions where there are power outages, it is necessary to either install non-volatile boilers or use uninterruptible power supplies.
If the voltage in the network is not constant, a stabilizer can solve the problem. It will protect expensive equipment from power surges and avoid breakdowns.
Today, the minimum electrical power of gas boilers is 65 kW. If the productivity is higher, then the kW consumption will be higher. For example, double-circuit heating boilers consume significantly more electricity, but they solve the issue of hot water supply.
If it is important to you how much electricity a gas boiler consumes per month, and you do not want to overpay, pay attention to energy-dependent boilers with high heating output. You can find relatively inexpensive 35 kW models. But non-volatile boilers of the same power cost on average twice as much.
For private houses, the following boiler characteristics are recommended:
- heating capacity – from 10 to 30 kW;
- power – from 65 kW and above;
- presence of an expansion tank of 10 liters. and more;
- ability to work at low gas and water pressure.
Today, many models from Beretta, Baxi, Ferolli, and Aton have these characteristics.

What is electrical power and how to calculate how much electricity a gas boiler consumes per month?
It is based on your power consumption that you pay your electricity bills. It is measured in watts and kilowatts. You can calculate how much electricity a double-circuit gas boiler consumes yourself. Manufacturers indicate the electrical power value in the technical documentation. Please note that they indicate exactly the maximum value, which is an order of magnitude higher than the average.
Important!
Thermal performance and electrical performance are different values. The first is usually indicated in kilowatts, the second in watts.
To calculate how much electricity a wall-mounted gas boiler consumes per day, it is enough to multiply its electrical power by the operating hours per day. For example, 120 W x 24 hours = 2880 Wh. To find out the value in kilowatts, divide it by 1000. We get 2.88 kWh. Next, just multiply the resulting value by the number of days in a month: 2.88 x 31 = 89.28 kWh per month.
If you have a single-circuit boiler, then the calculation of consumption is done only for the heating season - 5-7 months. But for dual-circuit models, electricity consumption in the warm season must also be taken into account. After all, you will use hot water regularly.

The most active consumers of electricity in the heating system
There are three main components that determine how much electricity a gas boiler consumes per day:
- Circulation pump. Depending on the model, coolant volume and other parameters, it can consume up to 200 watts of electricity per hour of operation. At the same time, it requires compliance with good voltage parameters. If the voltage “jumps” or is weak, this leads to failures. The pump may start to make noise or even break down.
- Protective automation. It needs little electricity - no more than 30 W. However, if there are frequent fluctuations in the electrical network, the automation may also break down. In particular, the controller breaks down, causing the boiler to simply turn off.
- Burners. They require ignition for normal operation. Burners also require electricity. And if there are any violations of the power grid parameters, this leads to unstable operation of the system.
Selection criteria for circular pumps
Taking into account the features described above, the consumer should pay attention when choosing the equipment he needs:
Performance
This indicator is calculated at a minimum level of system load and is directly related to several parameters that can be combined in a single calculation formula: Performance = Q: (1.16 x DT)
measured in kg/h.
Each indicator needs explanation:
- Q – heat consumed by the room. Counted in watts (W). For each type of premises, SNiPs define their own standards for such consumption. The indicator depends on the region of location and the type of building. For example, in Europe, 100 W are allocated for heating 1 m² of a private house, and 70 W for an apartment building. For the countries of the former CIS, the standards established in 1986 apply, which are: - 173 - 177 W per square meter. m. in buildings up to three floors; - 97 - 101 W per sq. m. in buildings with more than 3 floors.
- 1.16 is an indicator of the heat capacity of water. For other liquids this number is different.
- DT – difference in temperature values of the return and supply branches of the pipeline.
Pump selection by power:
Pressure
This characteristic shows the device’s ability to overcome resistance:
- pipeline;
- locking system;
- fittings;
- devices;
- height changes.
To calculate the indicator, use the formula:
Head = (R x l + Z)/p x g
In it: R – resistance value of a straight pipe, measured in Pa/m; I – length of the entire system, shown in meters; Z – resistance of fittings, indicated in Pa P – density of the coolant, given in kg. per cubic meter; g is the acceleration of gravity, which is indicated in m/sq. With.
The final pump head number is measured in meters. Heating systems installed in specific buildings cannot be accurately measured for the specified values, therefore, when calculating, average values are taken: R = 100 - 150 PA per meter; Z = 30% of the R value. The last indicator can be increased due to the presence in the system:
- thermostatic valve, which will increase the number by 70%;
- three-way mixer, giving an increase of up to 20%.
When calculating the pressure, it is recommended to use another formula in which the pressure is equal to:
R x l x ZF The last two letters (ZF) determine the safety factor of the circuit, which is not equipped with additional devices.
- The basic circuit safety factor is 1.3.
- If there is a thermostatic valve, then the ZF value is 2.2.
- When adding a three-way mixer, the figure is 2.6.
This indicator greatly simplifies the calculations.
Video instructions for calculating the required pressure and volumetric flow:
Calculation formulas
Without carrying out the calculations below, it is not possible to select the right pump, so this point is simply indispensable.
Productivity
This parameter in calculations is usually denoted by the letter Q and shows how much heat can be moved by the pump per unit time.
The formula looks like this:
Where:
- Q —volume flow, m 3 /h;
- R — required power for the room, kW;
- TF is the value of the liquid temperature at the system inlet, ᵒС;
- TR is the temperature of the liquid at the outlet of the system, ᵒС.
The value of R in European countries is usually taken:
- 100 kW/m 3 – for a private house with no more than two apartments.
- 80 kW/m 3 – for large apartment buildings.
Napor
The value of pressure (pressure) does not depend on the height of the building, but on its hydraulic resistance, so this is what needs to be calculated.
Formula:
Where:
- Nn – pressure value, m.
- I – total pipeline length, m.
- R – friction resistance of a straight pipe, Pa/m.
- ZF – safety factors, which is equal to:
- 1,2 – for the mixer and natural circulation device;
- 1.3 – for fittings and fittings;
- 1.7 – for TV;
Tips for choosing

- Previously it was said that pumps can be with “dry” and “wet” rotor types , as well as using manual or automatic speed control systems. Experts recommend using circulation devices whose rotor is immersed in liquid. This design is not only quieter, but also handles the load better.
- When choosing a circulation pump, you should pay attention to the housing material. Stainless steel, brass or bronze are best, but cast iron products are best avoided - they will not last long under such conditions.
- The efficiency of the device will depend not only on the factory parameters, but also on correctly performed calculations, so do them twice.
Best manufacturers and cost
Unitherm circulation pump
Nowadays, quite a lot of manufacturers are engaged in the manufacture of circulation pumps. Among them: Italian companies General Hydraulic, Dab, Speroni, as well as German ones - Unitherm, Wilo and Grundfos. The last two brands provide a wide range of their products, so among them you can easily select the necessary product of any parameters.
The cost of such products directly depends on technical characteristics, such as power and pressure, as well as on the factory equipment and additional services (control panel, speed switching, material and types of seals).
Also, the reputation of the manufacturer is considered an important fact. As mentioned earlier, the best companies produce guaranteed reliable products, but they also cost more.
As an option, let’s consider the cost of two popular models with approximately the same parameters: one is cheap, and the second is a popular model among the best companies.
This will make it possible to determine the price range:
- Vortex HZ 401 – DN25 – 3430 rub.
- Grundfos ALPHA2 25-40 – 9560 rub.