In words, drawing up and discussing a heating system is a simple matter. However, in order for it to function correctly, be effective and economical, each element and node must be planned and calculated in detail. Heating distribution from a boiler in a private house is laid not only with beauty and comfort in mind. It is important to consider the type of system, the characteristics of the materials that will be used, and adhere to general requirements.
Primary requirements
The main task is to connect the boiler and all radiators in the most efficient way. It is important to take into account a number of requirements:
- The routing should be laid along the route with the shortest length.
- The hydraulic resistance of pipes, valves and fittings should be reduced whenever possible.
- It is necessary to think through and arrange all functional units on the line with a minimum number of bends, tees and valves. This refers to the safety group, expansion tank, circulation pump, fittings for draining and filling the system, etc.
- Pipes are selected based on the performance characteristics of the material and the heating system.
- The diameter of the pipes is calculated to minimize pressure losses on the one hand and reduce the volume of the pipeline on the other.
Pipe diameter

Theoretically, calculating the optimal pipe diameter for a heating system in a house is quite difficult. The required pressure, static and dynamic pressure, pipeline resistance are taken into account, taking into account the laying route, the roughness of the inner surface of the pipes and many additional parameters. In practice, you will still have to choose from a fairly limited list of pipe diameters from one material or another. The standard sizes and main characteristics of the pipes have long been standardized, as well as all the additional elements necessary to assemble the heating circuit from the boiler to the radiators.
The main idea is to provide:
- the speed of movement of the coolant in the pipes is at the level of 0.4-0.6 m/s;
- the resistance of the entire heating circuit is lower than the pressure created by the pump or gravity in a system with natural circulation;
- minimum volume of coolant in the pipes. Not to be confused with the total volume, including the boiler and, if necessary, storage tank.
Video instruction with advice from a specialist
Hello! I have the following problems with heat: 1) In the corner apartment in the children's room there are two supply and return pipes. The supply pipe is fiery and the return pipe is several times colder. The radiators are connected to the return line, is this correct or not? Can I connect radiators in addition to the supply and run them along a cold street wall? 2) There is no radiator or pipe in the toilet at all, although the wall is also cold (outdoor). 3) In the bedroom there is only a pipe (return) with a radiator battery connected to it, and through the wall in our kitchen there is a supply. Is it possible to somehow combine two rooms and install them in two rooms with a supply pipe?
In our 9-story building, the heating system is built like this: one supply pipe goes from bottom to top. Radiators are connected to it on all floors in parallel with jumpers. The coolant enters the radiator from below, and the upper outlet from the radiator is connected to the same pipe. Only part of the radiator warms up. How to properly connect a radiator so that it warms up completely?
Good afternoon. The nine-story building has a two-pipe heating system in every room. In one room, the heating supply pipe runs upstairs past all the radiators. Accordingly, all the radiators from the ninth floor are connected to the return line, and my battery on the second floor is generally almost cold. Tell me whether this connection is natural, or is it just a mistake made by the mechanics?
Hello! Please tell me how correct your data is in determining an effective method for connecting a radiator? And what sources can you refer to to obtain the above data? Thanks in advance everyone!
Embed the valve into the jumper (which is not entirely legal if there are valves on the radiator) or reconnect the radiator in a diagonal pattern. On propylene it is simple and fast, compact and quite aesthetically pleasing. The top insert (outlet) is transferred instead of the top plug opposite. Do not forget that the thread direction of the plugs is mutually opposite.
Obviously, you have a single-pipe heating system in your house, in which some rooms are connected to the pressure line, and other rooms are on the return line. This is a moronic Soviet system - the return water is already cooled and cannot heat the room. But you may be fined for installing additional batteries, because... such alteration of the project is not permitted
Reducing the resistance of pipes and circuits
For systems with natural circulation:
- Any turns and bends along the route are carried out taking into account the minimum permissible turning radius for the type of pipe used.
- Transitions between pipes with different diameters, insertion of risers into the distribution manifold are carried out without narrowing the smaller diameter and, if possible, with a gradual expansion/constriction of the channel.
- In front of shut-off, control valves, radiators or other equipment, a smooth section of pipe should be formed at least 5-6 pipe diameters in order to eliminate unnecessary turbulence and turbulence in the liquid flow.
For a system with forced circulation, the previous tips are not mandatory; it is important that the circuit resistance is less than the pressure generated by the pump. However, if all requirements are met, the load on the pump will decrease and its operating life will accordingly increase. Due to the forced pumping of the coolant, you can use metal-plastic pipes with a small cross-section, a lower two-pipe or one-pipe connection scheme, including packing the pipes into a screed or walls.
Wiring diagrams
In practice, a large number of possible connection types are used. You can single out four main ones, and on their basis you can choose either a ready-made solution or a combined one.
- Single-pipe wiring with or without accelerating manifold. From the boiler the pipe goes to the first radiator. The radiators are connected in series, and from the last one in the heat exchanger circuit there is a return pipe to the cold inlet of the boiler. By way of wiring orientation:
- Horizontal - an option for one-story houses with pipes laid around the perimeter of the heated building.
- Vertical - sequential connection of radiators to risers on all floors with separation of the coolant in a common distribution manifold.
Single-pipe wiring diagram with accelerating manifold
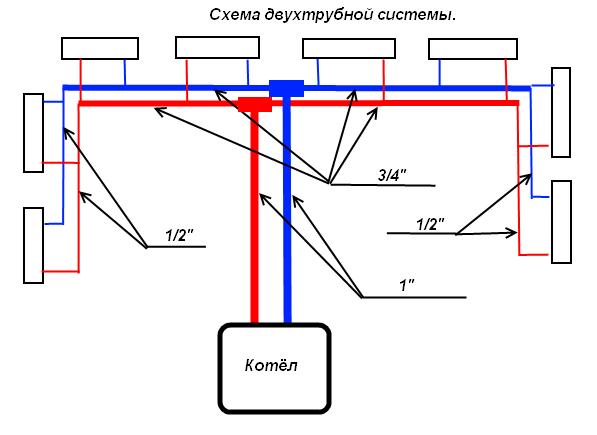
- Two-pipe distribution with top distribution. The pipe from the boiler rises to the ceiling or attic level and each radiator is connected in parallel from it. A return line is laid along the floor or basement level, connecting each radiator using tees.
Two-pipe wiring diagram with top distribution - Two-pipe distribution with bottom distribution. Only for forced circulation of coolant. Both lines from the boiler, supply and return, are laid along the floor level and along the perimeter of the heated building.
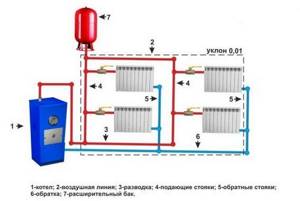
Scheme of two-pipe wiring with bottom distribution - The collector group is installed at one point, preferably in the center of the house. From it, pipes are routed to each radiator in the house or to several circuits for each room, where the radiators are connected in series or the heated floor circuit is turned on. The pipes are mounted on a rough screed and filled with concrete. The only option for pumping coolant is forced circulation.
For any switching method, a set of control equipment from the safety and diagnostics group must be selected. The composition of the equipment varies depending on the presence of a pump or the use of a gravity system.
For natural circulation everything is extremely simple:
- You need a line from the boiler to the expansion tank, located as high as possible.
- A pipe for connecting radiators is led from the expansion tank or from the manifold directly next to the tank. In the case of an accelerating manifold and a lower single-pipe distribution, the pipe descends with a gradual slope towards the first radiator.
- Next, the wiring to the radiators is carried out according to the selected connection method, with a mandatory slope of at least 2-3 degrees.
- From the last radiator there is a return line to the boiler with a connection to the lower cold inlet. On the return line, directly next to the boiler, a tee with a shut-off valve and a fitting for draining the coolant is inserted.
It is more important to correctly route the pipes. Connection points and fittings should not narrow the channel cross-section. The pipe turn or elbow is selected with a turning radius of at least 1.5 times the pipe diameter. If the pipe descends to the radiator from above or rises, then an elbow is formed first, and then the bypass and radiator are cut in.
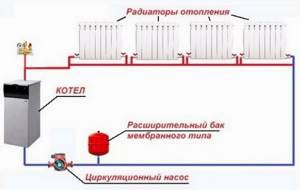
For forced circulation, the composition of the equipment has been significantly expanded:
- Expansion tank , membrane type. Installation is allowed at the hot and cold outlet of the boiler, the main thing is as close as possible to the heat exchanger or heat accumulator. For solid fuel (SF) boilers, due to the impossibility of accurately regulating the outlet water temperature, first a direct outlet with a length of at least a meter is installed with a steel pipe, and only after that the equipment is connected. The expansion tank for TT boilers is installed on the return, cold line.
- Safety group (air vent, safety valve, pressure gauge). The safety group is located at the hot outlet of the boiler. From the boiler safety group there must be a short section of pipe with the maximum permissible diameter and without any shut-off valves that can narrow the channel (ball valves are allowed). The safety group is installed at the top point of the circuit.
- Coarse filter . A mandatory element, even taking into account the preparation of the coolant. Installed in front of the circulation pump on the return line.
- Circulation pump . By default it is installed on the return line, where the coolant temperature is lower. If the system wiring is at least theoretically suitable for natural circulation, then the pump is connected in parallel to a common pipe with a bypass. Shut-off valves are installed on both sides of the pump and on the bypass. In other cases, the pump can be installed in direct flow into the return gap with shut-off valves on both sides.
- Additional pressure gauges for diagnostics. To diagnose and check the performance of the heating, it is important to know the pressure on both boiler outlets, on both sides of the circulation pump and the coarse filter, in addition to the pressure gauge installed with the safety group. Depending on the equipment connection sequence, the points may overlap and you will ultimately need to install 2-3 pressure gauges using three-way valves or tees.
- Three-way valve for bypass to the boiler.
- Tee outlet with shut-off valves for filling the system with coolant and draining.
How to set up, adjust, balance the heating system
A common situation is that one radiator is hotter than the other, which should not be the case. Or it’s cool in one part of the house and hot in another. This means that the heating system needs to be somehow adjusted, as experts say – balanced. It is possible that for this you do not need to call a plumber at all, and you can adjust the heating yourself.
To do this, control taps and/or balancing valves must be installed on each radiator or between the arms of the system.
But in some cases the system needs to be redone. Read more about possible heating problems and balancing rules below.
If there is not enough radiator power
It also happens that it is difficult to balance the heating system, since the distribution of radiator power does not at all correspond to the heat loss of the rooms.
Recommendations for the selection of radiators are as follows: for 10 sq. m. area - 1 kW, but this value is multiplied by 1.2 if the room has one window, 1.3 if the window is large, 1.4 if there are two windows and the room is corner, 1.5 if there are already 3 windows or a large glazing area.
In addition, the radiator power is indicated for a temperature of 90 degrees, but we are going to heat it at a maximum of 70 degrees, aren’t we? This means we multiply the heat loss by another 1.3. And if low-temperature heating is used - no more than 50 degrees, then multiply by 1.3 again. Why is low-temperature heating the most comfortable and economical? Read more about economical condensing boilers
The power of one section of an aluminum, bimetallic radiator (approximately 80 mm thick and wide), or cast iron radiator (old MS-140 type) is approximately 170 - 180 W. A set of 7 sections is considered to be no less than a kilowatt.
In addition, radiators must be installed in characteristic places to create a thermal curtain to the cold source. Typically - under the windows, near the door.
It is better to distribute the number of battery sections (sizes) in accordance with heat loss and the characteristics of the heating system than to balance and cover the flow of liquid.

Simple causes of heating system problems
It is possible that there is air in the heating system and for this reason the coolant does not flow well to one or more heating devices.
In the highest places in the pipeline, air valves (Mayevsky valves) are installed that can be opened manually. Or automatic air vents. Mayevsky taps are usually installed on each radiator. Walk through the system, open the taps, bleed the air.
Another reason for poor performance is clogging, first of all, of the filter element. Unscrew the filter and clean it. Before any balancing of the heating system, clean the filter.
In improperly assembled systems, in addition, there may be clogging at the lower points at differences in the pipeline level, and airing at the upper points, for example, the pipeline is wrapped around a door without an air vent.
Balancing the system using valve regulators
It is possible that the very design of the system requires balancing. For example, one long arm is used and the other is short.
Or the arm length of the dead-end pattern is too long. Or a beam scheme is used, which requires initial configuration. And it happens that they make archaic one-pipe systems with shortcomings. In either case, the result is significant uneven heating.
So, balancing valves are installed on the radiators; all that remains is to ensure that the temperature of all radiators is approximately the same.
Price for 1m2 of work
It is difficult to independently take into account all the nuances and correctly install the heating network around the house. It is much better to entrust this work to specialists who will offer the best option and a set of additional equipment. Based on experience, designers and installers are able to correctly place emphasis depending on the customer’s wishes: to provide heating with maximum efficiency and ease of use, or to strive to save money on work and installation.
The cost of the work includes separate installation of the boiler, connection of additional equipment, pipe routing and installation of radiators. Each item has its own price list, according to which the cost of all work on equipping the heating system in the house is calculated.
| Type of work | units | Cost, rub. |
| Installation of a heating boiler with a power of up to 50 kW | PC. | 12000-20000 |
| Installation of a boiler with a power of over 50 kW | PC. | 25000-50000 |
| Security group installation | PC. | from 1500 |
| Expansion tank | PC. | from 2000 |
| Circulation pump | PC. | from 2000 |
| Installation and connection of the comb (collector) | PC. | from 1500 |
| Pipe routing D16-25 | linear meters | 60-85 |
| Pipe routing D32-40 | linear meters | 75-90 |
| Pipe routing D55-63 | linear meters | 90-120 |
| Pipe routing D75-110 | linear meters | 100-150 |
| Installation and connection of the radiator | PC. | 2000-5000 |
| Installing a thermostat | PC. | 500 |
| Pressure testing according to the requirements of the boiler equipment manufacturer | from 4500 | |
| Commissioning works | from 3500 |
Routing pipes from the boiler to the radiators can average 300-500 rubles per linear meter, taking into account laying, connection, passage and wall grooves. Prices are indicative for Moscow and the region.
When solving the problem of heating a home, there are many combinations of constructing a coolant supply and removal system. Each heating installation in a private house can be classified according to several criteria.
We suggest understanding the nuances of the arrangement and operation of possible options. Understanding the design principles, pros and cons of each type of wiring will help you plan the geometry of the system and its design, taking into account the individual characteristics of the room.
The nuances of cleaning the heating system. Reminder for the homeowner
According to the All-Russian Center for the Study of Public Opinion, two-thirds of Russians dream of living in their own cottages. But some people are deterred from buying or building suburban real estate by the complexity of its maintenance. Potential homeowners are especially frightened by the maintenance of their heating system: there is a misconception that servicing equipment takes a lot of time, effort and money. Practice shows that by taking care of everything in advance, you can make your life much easier. Thus, regular inspections of the heating system and periodic cleaning of equipment will prevent any problems and save homeowners from possible problems.
Why do you need to flush your heating system?
Many homeowners carefully select engineering equipment, choosing the most modern, energy-efficient models that do not require complex maintenance and allow them to use resources wisely. But several years pass, and the effect is lost. After much investigation into the reasons, it turns out that the equipment was not properly maintained. Many people simply do not realize the need for preventive cleaning of heating boilers, circulation pumps, pipes and radiators.
“Most heating systems use water as a coolant. In a private home, it is rarely taken from a centralized system, more often from wells and wells. Such water contains oxygen, carbon dioxide and hardness salts in dissolved form, which lead to corrosion of equipment and the formation of scale on the walls,” explains Inessa Shulgina, shift supervisor of the chemical workshop of Krasnoyarsk CHPP-1 JSC.
It is believed that scale 1–2 mm thick reduces heat transfer efficiency by 10–15%. Clogged batteries do not heat, a dirty boiler heat exchanger is unproductive, and a pump with deposits does not cope with its task. As a result, in order to maintain a comfortable temperature, it is necessary to increase the coolant consumption; the equipment does not operate in optimal mode, wears out faster and requires maximum attention.
“Any heating system needs to be serviced regularly, only then will it work smoothly and for a long time. After all, for us, vehicle inspection is a mandatory procedure that does not raise any questions. It’s the same with equipment: for example, a boiler should be inspected by a specialist once a year. He will check the current settings, optimize the coolant supply and, if necessary, carry out preventive maintenance,” says Alexey Nenashev, a specialist in technical support and after-sales service for boilers at FRISQUET, the leader in the French heating equipment market.
Some heating system maintenance work can be done yourself, but there are also procedures that are best left to professionals. Let's take a closer look at each type of equipment and consider the best approach to cleaning it.
Modeling the optimal contour geometry
For one private house, several closed water circuits can be designed that will heat different rooms. They can differ significantly from each other in the type of wiring.
When designing, first of all, they take into account the operability of the system, as well as optimal geometry from the point of view of minimizing costs, ease of installation and the ability to fit heating elements into the design of the premises.
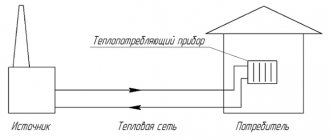
Natural and forced water circulation
Heating of the coolant for heating the house occurs in one or more devices located indoors. These can be stoves, fireplaces, as well as gas, electric or solid fuel boilers.
Water pressure in the circuit is ensured either through the use of circulation pumps or by arranging the geometry of the system to create conditions for natural circulation.
Also, the source of hot water can be a centralized heating system for several houses. In case of low pressure, it is possible to connect circulation pumps to create additional pressure and increase the speed of fluid movement through the pipes.
When choosing an option with natural circulation of coolant or low pressure in pipes with centralized heating, you must carefully consider the possibility of maximizing the use of physical laws that allow you to start and maintain fluid movement.
A mandatory element of the wiring in this case is the acceleration manifold. It is a vertical pipe through which hot water rises, then is distributed among heating appliances and, having lost its initial temperature, flows down.
Due to different densities, a difference in hydrostatic pressure between the hot and cold columns of liquid occurs, which is the driving force for water circulation.
Vertical and horizontal wiring
Hot water can be supplied to radiators in different ways. The wiring is conventionally divided into vertical and horizontal, according to the position of the pipes (risers) supplying water directly to the heating radiators.
Vertical circuits with top supply of hot water make maximum use of the difference in hydrostatic pressure between the warm and cold segments of the circuit, so they are almost always used with natural circulation, as well as with low pressure in the system.
In addition, such circuits are operational in case of emergency shutdown of the pump, which may occur due to its breakdown or lack of electricity.
Bottom supply wiring is practically not used for heating with natural circulation. If there is good pressure in the system, its use is justified, since such a scheme has two significant advantages relative to the alternative option.
- smaller total length of pipes used;
- there is no need to run the pipe through the attic or technological niches under the ceiling of the second floor.
The horizontal heating distribution scheme is used for one-story private houses. If the building has two or more floors, then it is often used in cases where vertical risers are undesirable from a design standpoint.
Horizontal pipes supplying and discharging water can be organically integrated into the interior of the premises, as well as hidden under the floor or in niches located at floor level.
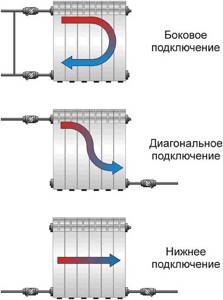
Features of connecting a radiator diagonally
Thanks to the connection of supply pipes on both sides, the heated coolant is evenly distributed across all sections. The most effective scheme is considered to be when the supply is connected at the top and the outflow at the bottom. After all, according to the laws of physics, hot liquid is always located above cold liquid. However, there is a diagonal connection of heating radiators with a lower coolant supply. The efficiency of such a system is less. This is due to the fact that, according to the same laws of physics, it is more difficult for the cooling coolant in the lower part of the sections to flow upward to the outlet pipeline.
A system in which the supply pipe is connected to the upper manifold of the heating device has greater efficiency.
An increased number of pipe lines spoils the appearance, but in a private house aesthetics fade into the background. Connecting heating devices diagonally with top supply has high efficiency, and this is the main thing for the consumer.
The layout of the heating device with a diagonal connection method is also different. The battery must be equipped with a Mayevsky crane. Install it on the upper manifold, free from the pipeline. The tap helps to bleed the air, otherwise, when aired, some of the sections will not warm up.
Regardless of whether the diagonal connection of radiators has a supply from below or from above, the outlet pipe is always suitable. If necessary, it is impossible to remove the battery without cutting the pipeline. To avoid such inconveniences, connections are made using detachable couplings. Previously, so-called threaded fittings were used. Their disadvantage is that the metal quickly corrodes. In a couple of years, it will be difficult to promote such a drive. Modern heating systems use “American” ones. The coupling consists of two parts, between which there is an o-ring. “American” is easily unscrewed with keys, after which you can freely dismantle the heating device.
Together with the “American” ones, shut-off valves are installed on each pipe. If the radiator leaks in winter, it is turned off with taps and dismantled for repairs. The rest of the system continues to function.
Choice of one- or two-pipe option
The supply of hot water and the removal of cooled water for the heating system of a private house can be done using one or two pipes. Each option has positive and negative sides, as well as features of use depending on the type of wiring.
Using a one-pipe connection diagram
A water heating scheme for a private house using one pipe for supplying hot water and discharging cooled water is called single-pipe. The main advantage of such a system is to minimize the length of the pipes.
Incorporating a distribution manifold into the system
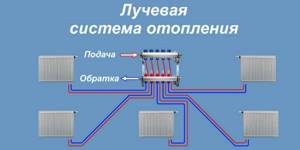
A recently popular method of organizing water heating is the so-called “radiation scheme” using a distribution manifold.
This wiring method works reliably only with good water pressure in the system, so it is not used with natural circulation.
Radial radiator connection system
The most uniform and controlled division of the coolant flow among heating devices can be achieved using a distribution manifold.
The device includes two combs, one of which receives hot water from the boiler and distributes it to the radiators, and the other returns cooled water and sends it back to the boiler.
The radiators are connected through the distribution manifold in parallel, therefore, with this wiring, a minimum difference in the temperature of the coolant supplied to the heating devices is achieved.
The main principle of heating operation
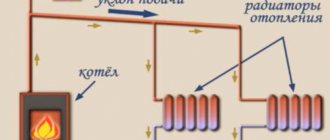
Any type of heating system is closed. In a simple version, any wiring diagram can be considered as a ring consisting of pipes. It circulates hot liquid from the heating boiler to the heating devices, remaining in them for some time. The coolant releases thermal energy during circulation and is again directed inside the boiler for heating. The cycle repeats periodically.
Any heating scheme includes:
- Heating boiler
- Connecting system pipes
- Radiators or similar heating devices
- Armature
- Expansion tank
- Circulation pump
Balancing
The horizontal two-pipe scheme in its original form is ineffective: the coolant circulates only through the heating devices closest to the boiler or pump. The problem is solved by balancing - throttling each battery to obtain the same temperature.
Please note: due to the inertia of the system, stabilization of the coolant temperature takes several hours. Hence the obvious instructions: when performing self-balancing, the position of each throttle changes to the minimum value with repeated temperature control after 2-4 hours.
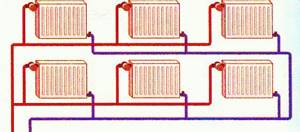
If you close the throttles on the radiators closest to the boiler, water will flow through the ones further away.
Basic types of heating schemes
All types of schemes can be divided into 4 subtypes: open and closed, pump and gravity.
In the gravity system of a private house (system with natural circulation), the movement of coolant occurs through natural circulation. By following simple laws of physics, the system is installed in such a way that it does not require an additional pump. Well suited for small one-story houses
In the forced water heating scheme of a private house, liquid occurs due to the action of the circulation pump. When using such a system, pipes can be mounted in walls, in the floor, along the ceiling, and hidden from human eyes. With the correct selection of the pump, water heating will work successfully. Such wiring schemes are great for two-story houses.
An open system differs from a closed system by an expansion tank. A closed system uses a membrane tank. It allows you to maintain the required pressure in the system and compensates for the expansion of the coolant.
Now let's look at each scheme in more detail.
How to repair a heating circulation pump
Pumps for circulating water in the heating system circuit are durable and practically not subject to breakdown. If a malfunction does occur, you can repair the equipment yourself. The equipment has a simple design; kits of parts for it are widely available for sale. What makes the situation easier is the fact that almost every circulation pump, regardless of model and manufacturer, is susceptible to the same types of breakdowns.
Features of application
Pumps are used in home heating systems to ensure forced movement of coolant along the circuit. This makes it possible to heat large areas when the pipes are so long that the natural flow of liquid is difficult.

Sometimes the water moves so slowly that it has time to cool before entering the boiler to be reheated. A circulation pump was developed specifically to solve such problems.
Recommendations for the user
To avoid breakdowns, you must adhere to the following rules:

- do not turn on the equipment idle when there is no coolant in the system circuit;
- do not use the pump at zero flow;
- do not allow excessively low or high fluid supply;
- heat the coolant in the system circuit to a temperature of no more than 65°C, otherwise salts will precipitate. Even better is to fill the boiler and circuit with softened water;
- avoid long downtime of the pump, and even in the summer season you need to turn it on for 10-15 minutes at least once a month to avoid blocking the shaft as a result of oxidation;
- flush the heating system before use;
- monitor the quality of the power supply: faults are possible in the network, including power surges.
Differences in faults between “dry” and “wet” pumps
“Dry” pumps, the rotor of which does not interact with water, suffer from a common problem for all models - damage to the sealing rings. This leads to a violation of the tightness of the working part of the rotor, and liquid enters the motor. Then repairing the unit with your own hands becomes impossible, since almost all of its electrical elements will fail due to a short circuit.

The cause of destruction of the sealing rings is suspensions in the coolant and various particles in the air surrounding the boiler and pump. Rings can also be damaged by natural wear and tear: their maximum service life is 2-3 years.
“Wet” pumps are more convenient to maintain - they are designed on a modular basis. However, this equipment quickly deteriorates due to startup with zero supply or lack of coolant in the system.
“Dry” pumps are more durable; they can withstand such loads, although they wear out faster in unusual situations.
Diagnostics and prevention of breakdowns
You can determine whether the circulation pump requires repair based on a number of signs. The easiest way is to turn on the equipment and check if it makes noise. Sometimes extraneous sounds are accompanied by noticeable vibration. It is recommended to ensure that the pump motor does not overheat.

Check whether the water pressure in the pipe corresponds to the parameters in the technical data sheet of the device. The features of coolant circulation do not depend on the characteristics of the heating boiler and are completely determined by the operational properties of the pump.
Visually inspect the pump housing to ensure there are no leaks. The most vulnerable point is considered to be the connection between the pipe and the unit. Check the condition of the gaskets and fastening of the bolts, as well as the presence of grease on the threaded flanges.

Pay special attention to the electrical circuit: check the fixation of the wires, get rid of moisture in the electrical wiring and, if necessary, attach the housing ground to the appropriate terminal.
Mechanical damage
Although if the circulation pump breaks down, you need to contact a specialized service, some problems can be fixed yourself. For example, if the equipment makes noise and vibrates during operation, it means that one of the bearings is worn out. You can replace it yourself: these parts are sold in any city, and you can find out the required standard sizes of the part by looking at the technical data sheet of the unit.
If a sharp noise is heard when the device is turned on, this indicates the presence of air in the flow part of the pipeline. If the coolant level is minimal, the pump may be damaged, especially if the unit is equipped with a “wet” rotor. The solution to the problem is to bleed air from the heating circuit and install an air vent at the highest point of the piping assembly.

Sometimes the noise when turned on is accompanied by strong vibration, which indicates low pressure in the suction pipe. In this case, you just need to increase the pressure on this section of the pipeline.
Additional options
If the repair does not help and the pressure remains weak, it means that the pump is installed incorrectly, so that the impeller rotates in the opposite direction. It is also possible that the circulation ring has high hydraulic resistance. Then the pump filter must be cleaned, and then the diameters of the pipelines and control valves must be checked.
A long-used pump may start without noise or vibration, but stop working after a while. The reason for this is the presence of lime deposits between the stator “jacket” and the rotor, which are formed due to increased water hardness. The best way to get rid of the problem is to disassemble the pump and clean all parts. At the same time, inspect the water heating boiler: liquid with a high salt content could also cause damage.

Often the pump turns on, but its shaft cannot rotate. This means that the part is blocked by a foreign object or has oxidized due to prolonged inactivity. In the first case, it is enough to dismantle the electric motor block of the circulation pump and remove the object. In the second, everything is also simple: to perform repairs, you need to turn the wheel by hand or with a screwdriver.
Remember: before removing the engine, you must disconnect the motor from the power supply and drain the water from the unit.
Solving power problems
There is another reason why the pump shaft does not rotate - problems in the electrical circuit. In such a situation, it is necessary to check the supply voltage, which must correspond to the passport data, the presence of all phases and the correct connection of the terminals.
Checking the phases is also necessary to eliminate such a problem as the activation of external motor protection immediately after starting the unit. Sometimes the cause of blocking is the lack of phase grounding. If not, it is recommended to inspect the fuse contacts: they may be dirty or open.
Due to the modular design of the pumps, faulty parts of the electrical circuit can be easily replaced. The required characteristics of the components are indicated in the technical data sheet of the device.
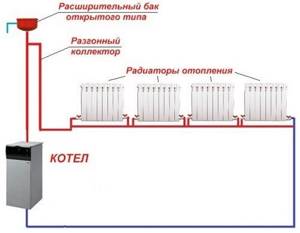
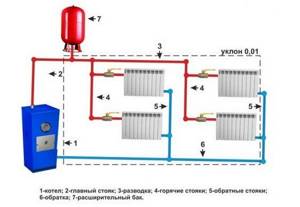
Gravity heating system, advantages and disadvantages
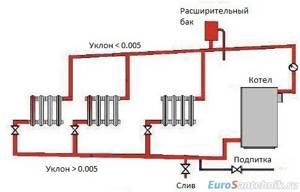
In this type of heating system for a private house, hot water, heated inside the boiler (usually solid fuel), moves upward, after which it ends up in the heating radiators. From them, heat goes into the room and is again sent to the return pipeline. From it it already goes into the heating boiler. The constant movement of heated water is ensured by the necessary inclination of the supply (direct) pipeline and return, as well as the use of pipes of different diameters. For the supply from the boiler, pipes of a smaller diameter are used, and for the return, the pipeline in which water is directed to the boiler, a larger one.
The gravity-flow wiring diagram for the water heating system of a private house has a specific device in the form of an open expansion tank connected to the outside space, mounted at the top of the pipeline. The tank is intended to take part of the water when it is heated, since this process is accompanied by an increase in the volume of coolant. An expansion tank filled with water creates the hydraulic pressure in the heating system necessary for fluid movement.
As water cools, its volume decreases. Some of the liquid from the open tank again enters the pipeline system. This ensures the necessary continuity of water flow circulation.
A gravity heating system has the following advantages:
- Uniform distribution of thermal energy
- Sustained action
- Autonomy from power grids
A gravity heating system also has disadvantages:
- Difficult installation. The slope angle of the pipelines must be observed
- Significant length of pipes
- The need to use pipes of different sizes
- Inertial system. It reduces the degree of control of the heating process
- The need to heat water to a relatively high temperature, which limits the use of polypropylene materials for pipes
- Significant volume of pipeline
- Inability to connect “warm floors”
Options for schemes with a boiler
When the standard power of the device of 9-13 liters is not enough to meet the needs of the residents (example: there is a bath in the bathroom), the system is supplemented with a boiler. If an indirect heating boiler is selected, then it is impossible to simulate the flow with an additional circulation pump, which is turned on and stopped by a thermostat signal.
An incorrect circuit leads to a problem in the form of prolonged heating of the boiler. During this time (up to 2 hours), the house is not heated and the rooms cool down. Plus, the boiler life is reduced due to the “clocking” effect and hot water entering the second circuit rather than cold. Bacteria multiply in the boiler itself.
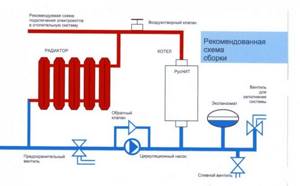
The correct scheme is to connect an indirect boiler to the heating circuit. The thermostat is connected to the boiler automation. The DHW outlet pipes are simply plugged
In this scheme, heating between the circuits is provided by a three-way valve. The boiler loads in 20-25 minutes. The plugs do not affect the life of the heat generator.
More practical options are installing a layer-by-layer heating boiler (there are models for dual-circuit systems) or an electric storage tank. The first does not have a heat exchanger, which reduces the cost of the system. The second significantly improves the comfort of using hot water.
In a circuit with an electric boiler, check valves and safety valves are mounted on the supply pipe. The latter sometimes leaks water that needs to be disposed of. The safety valve requires manual inspection 2 times a month
In the case of an electric boiler, it is recommended to additionally install an expansion tank. And if the pressure in the system is more than 6-8 bar, you will need a pressure relief valve to reduce it.
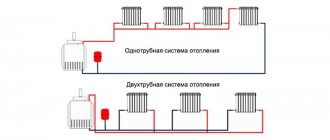
Single-pipe heating circuit
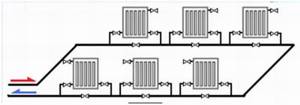
As a rule, this system wiring diagram is used in private one-story houses and is characterized by easy installation, low labor costs and low cost. Radiators are connected to the heating pipe in series. There is no provision for waste coolant removal. This water heating scheme has many disadvantages when heating a private house:
- loss of thermal energy - each subsequent heating device will heat up less than the previous one;
- the inability to regulate the heating intensity in one room without similar consequences for the rest. By reducing the temperature in one of the radiators, all subsequent radiators will inevitably cool down;
- the need to additionally equip the heating system with a pump to maintain operating pressure in it.
There are technological methods that can be used to partially get rid of these problems. You can improve the operation of a single-pipe wiring diagram using special equipment: thermostatic valves, radiator regulators, air vents, balancing valves. Their use will slightly increase the cost of installation, but will allow the temperature in one of the radiators to be lowered or lowered without undesirable temperature changes in the remaining heating devices.
What kind of piping can be made from polypropylene pipes
The piping for a home heating system can be very different. The thing is that the consumer is always trying to reduce the amount of consumables, while simultaneously trying to install radiators in all heated rooms.
It should be said right away that these are relics of the past. Unlike expensive metal pipes, polypropylene consumables are much cheaper and easier to install. therefore, it is not worth saving on the length of the pipeline. Choose the type of harness that will bring maximum benefit in your case. The only reasons that may influence the choice of type of harness are the following factors:
- what heating circuit is used (one-pipe system or two-pipe);
- what type of radiator connection you have chosen (diagonal, side or bottom).
As a rule, when using any heating scheme: single-pipe or two-pipe, you can use any type of heating radiator connection.
According to experts, pipeline laying must minimize the number of bends. A smooth highway remains resistant to hydrodynamic loads. The number of zones in which air can accumulate will be reduced in the pipeline.
There are specific features for piping a single-circuit and double-circuit heating system using polypropylene pipes.
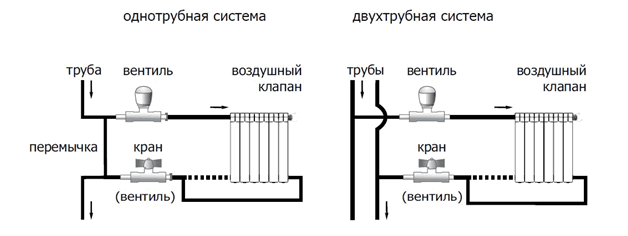
- Typically, such a system uses a series connection of radiators;
- A bypass is always installed in front of the battery, connecting the supply pipe and return pipe. During normal operation of the heating system, the bypass is not activated. When carrying out maintenance work or in the event of an emergency, the water supply to the radiator is stopped. The coolant circulates freely through the bypass.
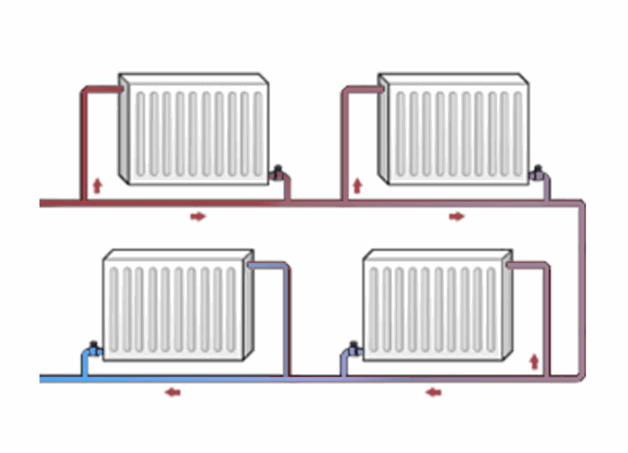
- Both parallel and serial connections of batteries are used;
- Both radiator hoses are connected to different pipes. The upper one is connected to the supply pipe, the lower pipe is connected to the return pipe. Typically, radiators are connected in parallel in two pipe systems, so installing bypasses is not required.
Tying polypropylene pipes with radiators is done in two ways: soldering and using fittings. Radiators are installed and connected using a soldering iron and American-style plumbing wrenches.
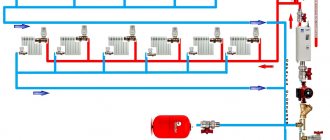
Two-pipe heating circuit
This water heating system is widely used in houses of any number of floors. Its peculiarity is that water is supplied to the radiator through one pipe, and drained through another. The heat exchangers are connected to the heating system not in series, but in parallel.
- coolant with the same temperature is supplied to each radiator;
- it becomes possible to install a thermostat on radiators to set the desired temperature in each individual room;
- disconnection or malfunction of one of the batteries will not affect the operation of the others.
The system has a number of disadvantages. Its installation requires a large number of pipes and connecting elements, which leads to an increased degree of complexity of installation work and a higher cost of the entire water heating system.
What is the advantage of horizontal wiring of the heating system?
Having considered all types of horizontal wiring of the heating system, we can conclude that the horizontal layout has a number of valuable advantages:
- The wiring makes it possible to provide precise control of heat consumption and, if necessary, it is easy to install a heat meter on it;
- The horizontal two-pipe distribution system allows for adjustment of the heating mode in each area;
- The system is more adapted to modern heating devices, since it provides the possibility of hidden connection;
- The presence of a large number of control and shut-off valves has a positive effect on the reliability of the system - this is one of the most reliable heating systems for multi-storey buildings.
Thus, horizontal heating distribution can be successfully used for installation in multi-storey apartment buildings.
Heating scheme with heated floors

Heated floors provide horizontal thermal radiation, maintaining a higher temperature at foot level and reducing it to a comfortable level at higher altitudes. In areas with warm climates, the circuit can be used as the only source of heat. In northern latitudes it must be combined with the installation of a radiator heating system.
Structurally, the underfloor heating system is a network of pipelines. Heating can be done from any heat sources.
System advantages:
- uniform distribution of heat throughout the entire volume of the room;
- improving the aesthetic appearance of the room due to the absence of pipes and radiators.
Gravity system "Spider"
The vertical heating circuit of a private house with a top spill without the use of a circulation pump is called “Spider”. The main advantage is complete autonomy from gas or electricity, which is especially in demand in rural areas or in holiday villages. In the circuit, the coolant moves due to the temperature difference at the inlet and outlet of the heating device. In the absence of gas and electricity, it is best to use a solid fuel boiler.
The operating principle of the “Spider” is based on the laws of physics - hot water rushes upward, displacing cold water downward. As a result of heating, the water rises from the boiler along the riser to the radiator, gives it part of its thermal energy and moves to the next one until it returns back to the boiler. The functioning of the system depends on the accurate selection of pipes and compliance with slopes. Water intake must be carried out above the level of the heat exchangers. The boiler should be located lower. The main disadvantage of the scheme can be considered quite complex installation work .
Scheme "Leningradka"
“Leningradka” is one of the simplest, but nevertheless quite effective and economical heating schemes for wiring a private house. It is similar to a single-pipe scheme, that is, the coolant sequentially passes through all the radiators of the room, gradually losing its heating temperature. The main pipe is placed along the floor and loops the circuit from the heating device. It is best to use Leningradka in one-story houses so that all batteries are on the same level. In this case, the system can operate with natural circulation, but when installing it in two-story houses, it is necessary to use a forced supply of coolant.
The advantages of this scheme are:
- economical consumption of materials;
- easy installation;
- long-term reliable operation;
- the ability to hide the main pipe under the floor covering to improve the aesthetics of the interior.
Leningradka" is not without significant drawbacks:
- inability to maintain the same temperature in all rooms;
- horizontal wiring does not allow connecting heated floors or heated towel rails;
- a large area of the room requires the use of a circulation pump to ensure operating pressure in the system.
Which scheme should you choose?
Let's decide right away about single-pipe and gravity-flow systems. If you live in a modern metropolis or close to it, if everything is in order with energy resources (with light in the first place), if you do not need to save much, then do not consider these schemes.
They appeared at a time when electricity was poor, and various types of pipes were also absent. We had to use metal. Now everything has changed and these systems have become obsolete.
Gravity flow schemes can be implemented in houses remote from civilization. For example, at your dacha.
If you want to use a radiator system in a private house, then the best choice would be a two-pipe dead-end heating circuit or a radiant one. Both systems operate almost identically. They differ only in implementation.
Before using a water heated floor, you should calculate the heat loss at home. They will help you understand whether it will be enough as the main heating or whether you will have to use radiators as well.
For heating individual residential buildings, single-pipe and two-pipe systems with natural or forced circulation of coolant are widely used. Each of them has its own area of application and certain advantages and disadvantages - if single-pipe decoupling schemes work well with radiator heat exchangers, then a collector heating system is indispensable when installing multi-circuit heated floors.
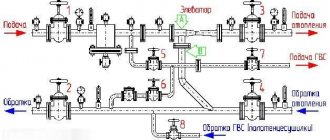
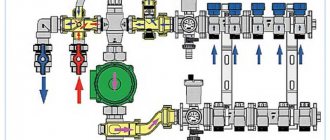
The collector (parallel) junction is widely used in heating schemes of individual houses for heating rooms and is the most expensive, its cost is comparable to a two-pipe distribution system. However, every house cannot do without such a scheme, in which a large number of heat exchange radiator circuits and heated floors are used to supply heat to the premises.

Rice. 1 Collector heating system for a private house - installation example
Radiant heating scheme
The radial water heating wiring diagram is newfangled. When using it, hot water is evenly distributed throughout the room through the collector. The degree of heating of the home is regulated by changing the heating of the water and the speed of its movement through the pipes.
It is an improved version of the two-pipe circuit. To distribute the coolant, the same collector is used as in a warm field.
The main advantages of the beam wiring scheme include:
- Jointlessness. There are no joints inside the screed. The likelihood of leakage is significantly reduced
- The ability to turn off each device individually on the collector without harming the entire system
The only drawback is the price. Due to the use of a collector and an additional number of pipes, the price of the system also increases.
Collector - a system for everyone
This system is also called beam system. The essence of the scheme is this. In a heated room, usually closer to the center, there is a collector, from which two pipes go to each radiator - supply and return.
Pipes in it are usually used from metal-plastic or cross-linked polyethylene. They are most often laid in the floor structure (in a screed), less often along the ceiling of the lower floor. The beams approaching the radiators are of different lengths, so careful balancing is necessary for proper operation. The advantages of such a system are the absence of pipe connections located in the screed, since the beams are made from single pieces and the speed of installation. Moreover, the second advantage is quite controversial. The main disadvantage of such a system is its high cost - a large number of pipes and collectors cost money.