An alternative to the usual sectional, panel and tubular models is the so-called plate radiator. Its design ensures effective heat transfer over a significant length of pipelines, which allows the effective use of such products not only in residential buildings, but also in public buildings and industrial facilities.
In our article we will talk about the features of plate models, and also describe their main advantages and disadvantages.
Installing heat exchangers on pipes can significantly increase heating efficiency
Radiator design
Depending on the design features, radiators can be divided into several subtypes:
- Sectional heating radiators - these batteries have several sections, so you can assemble a radiator of the desired size and power. The sizes and shapes of sections may vary.
- Tubular radiators are a solid metal structure that has an upper and lower horizontal collector and vertical tubes welded to it. Such batteries are the prerogative of centralized heating, for which they were designed.
- Panel batteries can be either steel or concrete. Concrete ones are built inside walls; they can only transfer heat by radiation.
- Plate batteries - have convective heat exchange, consist of a core and ribs made of thin metal plates mounted on it.
Separately, there are corner heating radiators. They can be made in any given design option. However, corner radiators are designed for installation in the corners of rooms.
Corner radiators
Which heating battery to choose for your home
Shopping list? Don't like the look of the batteries in your home? Do you think that their sharp corners and elevated surface temperatures are dangerous for your little child? Buy a screen for the radiator and install it - it will not take much time and will not require serious financial investments. Meanwhile, such a product can provide:.
Plate heating radiators: characteristics, photos. Heating radiators Plate heating radiator: features of old ones.
With the onset of the warm season, it's time to think about the efficiency of your heating system. If it requires replacement, summer is the best time for installation work. At the height of the heating season, it will not be possible to replace radiators.
Thin metal plates are mounted on the tubes. They are designed to increase the level of heat exchange between the heating element and the air in the room. Plate batteries are used in public spaces and industrial buildings, industrial workshops. In frequency housing construction, they have not received proper distribution for a number of reasons. However, they are widely used for heating multi-apartment buildings, where centralized heat supply dominates. With good insulation of the building, a plate heating device is able to maintain the air temperature at the proper level with minimal thermal energy consumption.
Important: there is an opinion that the cast iron radiator now is worse than in Soviet times.
Radiators are an integral attribute of heating systems, unless heated floors are used instead. It is not always easy to combine their appearance with the interior. This can be done easier if you use radiator screens. The screens have an attractive design and shape, so there is always something to choose from. What materials are screens made of and which one is better to choose? This will be discussed in the article. The screen for a heating radiator has several purposes.
Modern heating radiators come in several types. Depending on the material from which they are made, these devices have different characteristics. This is why problems often arise with how to choose the right heating battery.
To decide which heating battery to choose, you need to pay attention not only to the size and appearance of the radiators, but also to their features
VIDEO ON THE TOPIC: Choosing a heating radiator // FORUMHOUSE
Kinds
Taking into account the arrangement of sections in the structure, tubular radiators are of the following types:
- horizontal;
- vertical.
Based on the shape of the heating structure, the following radiators are distinguished:
- radius;
- flat;
- corner;
- designer
The radial device follows the bends of the arc; in a flat radiator, the sections are arranged in a row. Corner devices are divided into two sections, which are located opposite each other at an angle, and as for designer radiators, such models are notable for their originality; in such models, the pipes can be curved in different ways, for example, repeating the shape of a wave or being round.

Taking into account the method of installation of tubular radiators, they can be of the following types:
- wall;
- floor;
- corner.
The first type of radiator is purchased most often; however, the height of the product has limitations. Floor heating devices are installed on metal fasteners - legs, corner models are produced to order, they are mounted to the wall, the number of turns is selected individually, in each specific case. As a rule, a complex device configuration implies a higher cost of the finished radiator.
You will learn more about the types of radiators by watching the following video.
Choosing which heating radiators for a private home is best

The main component of the heating system is, of course, the heating radiators. Their choice must be approached with particular seriousness, because the strength, durability and reliability of your heating system depend on it. Let's consider the main advantages of the heating system of a private house:
- Its operation is carried out at low pressure, which has a beneficial effect on operation;
- There are no large water shocks in this system, which provides a wide selection of radiators;
- By observing the necessary technical conditions for the acid balance of water, the choice of radiators is very wide.
Taking into account the above, the choice of radiators should be made taking into account the maximum heat transfer coefficient and a good price-quality ratio. Without going into details, any type of radiator can be used in a private home. But knowing the advantages of one or another still won’t hurt.
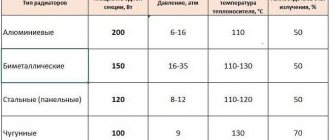
The following types of materials are used for the manufacture of radiators: cast iron, aluminum, metal (steel), bimetal.
Precautionary measures
Like working with any other tool, operations with an extractor require compliance with certain rules. For safe and fruitful work, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- To protect your eyes from damage, you must use safety glasses. Flying chips or metal fragments pose a serious hazard to your eyesight.
- Using a larger extractor will destroy the walls of the fragment, making them difficult to remove.
- The tool is made of hard but brittle metal. To avoid breakage, distortions must be avoided.
- The body of the bolt remaining inside the surface must not have radial cracks. Otherwise, it will not be possible to drill a hole without compromising the integrity of the walls.
- It is not allowed to use non-standard objects to rotate the extractor: pliers, pliers, etc., or to extend the crank handles with tubes. This may cause the rod to fail.
- It is necessary to correctly distribute the applied forces so as not to break the thread of the spiral extractor.
It is clear that it is more effective to carry out operations to unscrew broken fasteners using a special device. To do this, it must be of good quality and made of high-alloy tool steel or chrome vanadium alloy.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=C1J7z64mjJM
Plate heating batteries
Along with sectional, tubular and panel heating devices, plate heating radiators have also become widespread. In terms of heat output, they are second only to panel-type heating devices. But in comparison with them they have a much lower price, can operate at a system pressure of more than 10 Atm (up to 17-20 Atm) and allow hidden installation in in-floor niches.

Outdated finned heating device.
A significant difference between plate heating batteries and other types is the method of heating the room. In all other designs, up to 70-80% of the power is spent on radiating heat and heating the walls and objects in the room, which then heats the air. In plate-type ones, this power serves to heat the air directly and enable its convection (mixing) in the middle of the room. Hence the second name for these heating systems – convector heaters.
Air heating is at the same time both a positive quality and a minus, which determine the area of use of these devices. But the thing is that heating the premises to the required temperature using heat radiation, although it takes more time, the effect of it lasts longer, and the conditions created are better suited for people to stay in from the point of view of comfort.

Behind the heat supply device there is a heat-reflecting aluminum plate.
Ribbed ones, on the contrary, can quickly heat large volumes of air to the required temperature, but at the same time they create significant air flows, which cause discomfort for people present in a stationary position. This is actually the reason for their use in the corridors of public buildings, stairwells, gyms, warehouses, etc. In other words, where there are large volumes of premises and there is constant movement of people (or does not happen, as in warehouses).

An outdated plate heating device in the entrance of a residential building
Design and types
The design of a plate heating radiator is based on one or more straight, U or W-shaped tubes, to which many metal heat exchange plates are perpendicularly welded or otherwise secured. The coolant moving through the tubes heats these plates, and they then release the resulting heat into the room.
In most cases, the finished device is placed in the middle of a thin-walled housing, which serves to protect against burns and cuts from the sharp edges of the plates. The housing or casing also protects the heater plates from dust and damage from mechanical factors. However, there are models, mainly steel radiators with increased fin thickness and trimmed edges, which are intended for operation without a casing, “as is”.

Old finned battery.
Along with the shape and size, the following main types of plate heating batteries are distinguished.
- According to the material of the device: steel; copper; bimetallic in combinations: steel - copper, steel - aluminum, less often copper - aluminum.
- By the number of pipes: single-pipe and multi-pipe with a manifold.
- By connection method to the main line: with side and bottom connections.
- According to the installation option, there are suspended heating devices and built-in type in a floor niche. The latter are placed either directly on the ceiling or on insulating material.

Outdated plate heating radiator.
If we talk about the pros and cons, then obvious positive qualities include low cost, high heat transfer and air heating speed. And also reliability due to the small number of connecting nodes. The most serious disadvantages: uneven temperature distribution across room levels and high requirements for cleanliness. Although, it would be more correct to call the latter a secret positive quality of steel plate heating radiators.

A ribbed heating device behind which is an aluminum heat-reflecting plate.
Summarizing. The vast majority of manufactured heating devices operate on the principle of convective air circulation. However, there are models with a built-in fan. This, therefore, raises the price and overall energy consumption of the device, but also by increasing the intensity of air mixing partly solves the problem of a sharp difference in temperature across the height of the room.
Of steel

Steel panel radiators - as a rule, such radiators are installed in private houses, cottages, or low-rise buildings. Thermal indicators are the most highly efficient.
If you put such a radiator in a high-rise building, you will not receive the required amount of heat, and use in central heating systems can lead to radiator malfunction (due to high pressure and possible water hammer).
Flaws:
- In open heating systems (with access to oxygen), steel radiators rust. Because of this, they are not recommended for open heating systems.
- Without coolant, steel begins to rust.
How to connect a radiator correctly
To connect the battery to the heating system, follow these recommendations:
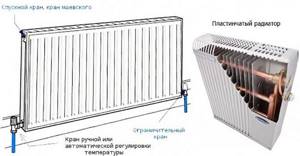
- Determine the type of device you are using. Plate devices are produced together with a tap and a valve insert with a thermostat. Using these parts, you can automatically regulate the temperature of the water in the system, as well as the heating of the air in the room.
- Some versions of radiators are produced with mechanisms for connecting to the system under the floor surface or installed in the walls of the home.
- Connect the equipment according to the appropriate diagram. There are two main connection options - side or bottom. In the first case, it is more convenient to connect the device to a vertical riser, whereas in the case of horizontal wiring, you will have to use special fittings. The lower location of the fittings suggests the reverse connection method - to a horizontal riser or to a vertical one through fittings.
- Since steel has high inertia, there must be forced circulation of water in the system using a pump. Thus, heat transfer will occur more efficiently and quickly.
- It is not advisable to install steel heating devices in open systems due to the saturation of water with oxygen. Such installation can lead to the development of corrosion processes, which will lead to rapid wear of the equipment. The increased acidity of the coolant gradually destroys the coil, so unscheduled repairs of the device may be required.
- If there are no alternatives for installing the circuit in an open system, it is necessary to protect the elements with an anti-diffusion barrier. It will prevent air from entering the pipes, therefore, the acidity of the water will remain low.
Steel radiators: technical characteristics, advantages and disadvantages
When arranging their own home, many homeowners are faced with the problem of choosing radiators for heating structures. A fairly good option are steel radiators whose technical characteristics are impressive.
Information regarding the technical characteristics of heating devices, and more specifically:
- working and testing pressure;
- coolant temperature;
- other parameters that influence the efficiency of a particular model.
This information is completely understandable for every consumer. This article talks about the technical characteristics of steel heating radiators.
Heating batteries made of steel come in two types:
General disadvantage of steel radiators
The “weak link” common to all steel radiators is their susceptibility to oxygen. Well, that is, they rust, as everyone well knows. Moreover, they rust not so much on the outside as on the inside, when the coolant is drained from them.
This does not mean that you should completely disown steel batteries. You just need to understand in which heating systems they should be installed. Steel batteries are suitable for closed systems. As a rule, this is in private homes.
That's all about steel radiators, I hope now you can decide exactly which heating radiator to choose.
When arranging a home with a heating system, it is necessary to pay special attention to heating devices, in particular radiators. The level of heating of the room largely depends on them
Among the variety of such elements, I would like to mention thin radiators. They are much lighter in weight than cast iron heat exchangers, which makes their installation process easier and more convenient.
Characteristics of flat radiators and their design
Flat steel radiator with a smooth surface Steel products are included in the category of thin heating radiators. To make them, metal sheets are taken and passed through stamping. Using welding, iron blanks are connected into an appropriate structure, which ensures the reliability and strength of the connection. To connect to the general system, pipes are used. The coolant moves through a special channel located between two plates.
The design is:
- single-row and multi-row;
- with a smooth surface;
- with a profiled surface on one or both sides;
- flat;
- with or without ribs;
- with thermostat.
A small depth is characteristic of each stamped sheet, which is associated with other design features:
- Two panels welded together have high heat transfer.
- A small internal cavity for coolant movement. This is not only a plus, but also a minus. On the one hand, saving on coolant saves the budget, on the other hand, it is necessary to constantly monitor the level of supplied temperature.
With thermostat With ribbed surface
Dimensions
The depth of the product depends on the number of ribs inside
- Type 10. This group includes products with a depth of 46 mm.
- Type 11. The thickness of these products is slightly increased, corresponding to 59 mm. This is due to the addition of convection fins to one side of the battery.
- Type 12. The thickness of such radiators is 64 mm, due to the arrangement of convection fins between two panels.
- Type 22. Product made of two panels equipped with fins. The depth of the product reaches 102 mm.
- Type 33. The widest radiators, their thickness is 157 mm due to the arrangement of three plates with three parts of fins.
Power depends on product type, height and length.
The lowest heat transfer is characteristic of products of types 10 and 11 with a height of 300 mm and a length of 400 mm. It is 265 W. If we compare a radiator with the same parameters of class 21, the heat transfer will be 370 W.
Basically, flat heating radiators are produced with a height from 300 mm to 600 mm, and radiator lengths from 400 mm to 3000 mm.
Design and purpose of plate radiators
You can select, buy and install any radiator, but it will be useless if the room or building is not insulated - only in combination with thermal insulation work will a plate radiator prove to be most effective. In addition, the efficiency of a radiator is not the high temperature of the coolant, which is released into the air through tubes and plates, but the maintenance of a constant and comfortable temperature in the room throughout the entire time. Therefore, if you correctly decide on the surface of such heating batteries, you cannot get burned - firstly, the temperature will not be critical, and secondly, the plates are covered with a metal casing.
If we approach the issue fundamentally, then plate heating radiators are a design variant of convectors with a difference in the number of tubes and plates (fewer tubes, more plates).
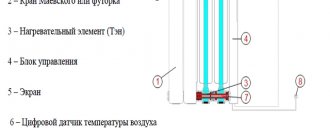
Internal structure of a plate radiator
Similar to panel-type radiators, in plate-type devices there is a classification according to the number of heat exchange tubes and panels (plates), which are manufactured by hot stamping and spot welding. Due to the tight connection, heat is transferred not only from the surface of the plates, but also from other areas of the device - from tubes and even connecting seams and joints. The marking of devices occurs in this way: if the radiator has one panel (plate on the body) and one heat exchanger, then it is marked as class “11”. Three plates and two tubes - “32” class, etc.
If you want to buy and install a new radiator in a store or replace an old one, then complete with the new model you will receive an installation kit and instructions for assembly and fastening. Depending on the design of the device, its connection can be threaded or welded, which depends on the coolant input/output device. In addition, you will need to connect the Mayevsky tap and thermostat or two separate devices - the Mayevsky tap itself and a separate thermostat. It is not at all necessary to install a thermostatic valve, but it will allow you to automatically regulate the temperature in a separate room by limiting the flow of coolant into the radiator coil. The latest models of plate batteries are often equipped with built-in thermostats and taps.

Plate heating radiators with thermostat
Tubular steel heating radiators
Steel heating radiators of this type are installed much less frequently than panel appliances. The reason for less popularity is the high cost of tubular devices. The structural solution of such heating radiators is a series of vertical or horizontal steel pipes that are connected to collectors. As a result, the heater quickly heats up and cools down, and its operation is controlled using an automatic controller.
The design of tubular radiators can be very attractive; they are often made in the form of interior items, as in the photo. They have the following parameters: height 190 – 3000 millimeters, depth – no more than 225 millimeters, length has no limit. Experts recommend: if tubular steel heating radiators are installed under a window, make sure that their length is at least 75% of the width of the window opening.
These devices have the following parameters:
- working pressure not higher than 12 atmospheres;
- crimping pressure up to 25 atmospheres;
- maximum coolant temperature 120 °C.
Since tubular devices can withstand strong water hammer, they are considered an ideal solution for installation in apartments of multi-story buildings.
Battery materials
Plate radiators can be made of various materials, which affects the rate of heat transfer and other performance characteristics. Modern devices are most often made on the basis of:
- Become. The plates and pipes of the device are made from this material. The radiator turns out to be very durable, it can easily withstand even strong water hammer. The disadvantage is the slow rate of heat exchange.

Steel radiator Source utepleniedoma.com
- Copper. The all-copper accordion battery has good power and heat transfer rate. Excellent characteristics are overshadowed by the high price of the finished product, so a combination of materials is most often used. Copper tubes are equipped with cheaper steel or other metal plates. As a result, the final cost of the device can be significantly reduced.
- Aluminum. This is a relatively cheap solution that has a high heat transfer rate. The disadvantage of this option is insufficient strength, so it is not used in central heating systems. It makes sense to combine aluminum plates with copper pipes to obtain stable equipment.

Accordion radiators of different generations differ in the number of working circuits and panels for convection. If there is a single circuit and a set of plates, the battery is designated class 11. There is also a class 22, which indicates double the number of these parts. If two sets of plates are combined with a common coil, such a product will belong to class 21.
The dimensions of plate batteries can vary significantly, which makes it easy to select a device for a specific room. The appliances come in a variety of designs in the market, so users can purchase a suitable option for each style.
What are radiator screens made of?
Grids and boxes are made from almost any material. The main condition is their resistance to high temperatures. The exception is plastic products, since to increase strength the box will have to be made too wide. As a result, the radiator will dissipate heat worse and its efficiency will decrease. Other types of materials are quite suitable for making screens. The most common among them:
- Wood. Its appearance and environmental friendliness make wood products one of the best options for casings.

Wooden screen Source bykdyb.ru
- MDF boards. They are resistant to temperature fluctuations and tolerate changes in humidity levels in the house.

Battery screen made of MDF board Source craftsman.in.ua
- Glass. Heat passes through it well, and the product also gets a beautiful exterior that fits perfectly into almost any room style.

Glass screen Source otoplenie-expert.com
- Metal. Its high thermal conductivity promotes better distribution of air flows and increases the working surface of the device. Steel and copper casings can be used for a long time; they do not deform or deteriorate under the influence of temperature changes. For this reason, such materials are especially often used in combination with cast iron radiators.
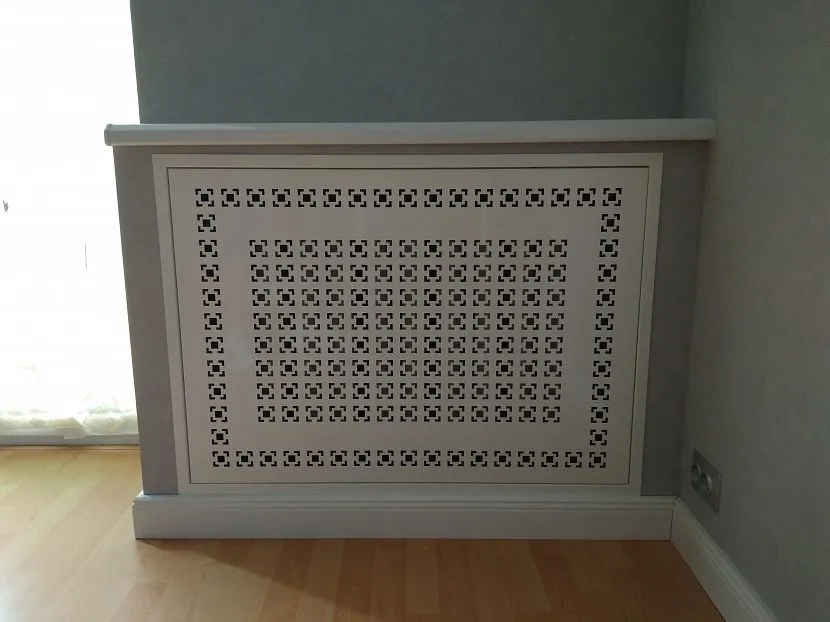

Metal screen Source craftsman.in.ua
Steel plate batteries
During the Soviet Union, cast iron radiators were common, which had the appearance of an accordion. Many people confuse such devices with the plate type, which was made primarily of steel. It can still be found in the hallways of old houses and in old government buildings.
The basis of the devices is a tube with plates located on it. The latter perform the function of heat exchange due to the large total surface area. Modern products have increased efficiency due to improved design.
The advantage that distinguishes the steel accordion battery from other types is its ability to withstand pressure of 20 atmospheres. The coolant is passed through the pipes under high pressure, which causes their surface to quickly heat up and transfer thermal energy to the plates. The surface of the latter comes into contact with the air, as a result of which it also becomes warmer.
Such devices have become popular due to their low cost. A modest exterior and rapid surface contamination are considered disadvantages that can be eliminated with the help of special screens. When open, such products are often installed in public places and enterprises, and in residential buildings protective covers are installed on them.
Steel radiator: accordion or plate does not go out of use in our country, since its advantages outweigh its disadvantages. There are many options for such devices, some of them are quite suitable even for use in central heating systems. If necessary, you can purchase exactly the variety that is most effective in a particular room.
Determination of thermal power of plate heating devices
The formula for determining the thermal power that a steel plate heating radiator can produce, and a real example of calculating this parameter, are given below. To calculate the power of the device, it is enough to know the heat loss coefficient of the heated room, the area of the room and its total volume. The passport of any radiator indicates its calculated power at a hot water temperature in the system of 60 0 C. Also, the attached documentation indicates recommendations for the heated area for a specific radiator model.
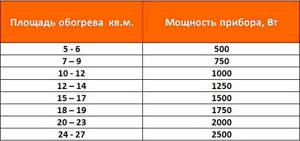
The thermal output (power) of heating devices depends on the length of the body and the number of plates. The standard height of radiators is 200 mm, the number of plates varies. For example, heat transfer for a radiator with one tube and a body length of 600 mm will be equal to ≈ 347 W. When the length is increased to 3000 mm, the heat transfer will increase to 1730 W. But with the same body length (3000 mm) and an increase in pipes to 4, heat transfer there will already be 4179 W, and with a body length of 1000 mm, four tubes with coolant will give 1393 W of power. Therefore, which radiator is best to buy for a specific room is determined based on the following requirements:
- To heat 1 m2 of a room with a ceiling height of 3 m, you need to spend 100 W;
- For a room with an area of 16 m2, the radiator must have a thermal power of 1600 W, provided that the room has no more than one window, the room is not corner and the ceiling has a height of no more than 3 m. For other initial conditions, correction factors Kp are introduced:
- For two windows Kp = 1.8 / 1600 x 1.8 = 2880 W;
- For a corner room Kp = 1.8 / 2880 x 1.8 = 5184 W;
- For a ceiling 2.65 meters high Kp = 2.65 / 3.0 = 0.88 / 5148 W x 0.88 = 4547 W;
- For PVC windows Kp = 0.8 / 4547 W x 3637 W.
Convector radiators

Convector-type radiators are connected to a conventional heating system. A distinctive feature is a completely different way of functioning.
Panel, sectional or tubular radiators release heat into the environment from their hot surface, which allows them to heat the room.
Convectors work differently. Their design provides for the presence of many thin air channels located between the ribs of the plates.
The air in the room passes through them, at the same time it heats up, becomes lighter and rises, which ensures continuous movement and mixing of air, i.e. constant heating
This allows you to evenly warm the room, which is important, even the presence of many interior items and partitions will not interfere
- They are light, compact and reliable, because... made from copper, steel and aluminum - corrosion-resistant materials
- Requires a relatively small volume of water in the system.
- Heats up quite quickly and cools down just as quickly
- Such radiators allow you to heat rooms with high ceilings
- A heating system with convector radiators allows you to save money when purchasing equipment. Those. In such a system, pipes of small diameter are used, the power of the circulation pump is quite low, and the coolant itself has a small volume.
- Very simple installation, which can be carried out without any special skills.
- There is a huge selection of appearance options for the convector housing. What can be a beautiful addition to your interior. Replacing the housing is very simple and only takes a few minutes.
- Increased security, i.e. The heat exchanger is completely closed by the housing.
All batteries have their drawbacks, which are functional in nature. The convector radiator is durable, economical, safe and quite beautiful. The only negative is the high price, because they are made from high-quality and expensive materials.
Such a characteristic as power will help to correctly give preference to one or another type of radiator. It is easy to calculate it: in a room with a ceiling height of 300 cm and one window, 100 W will be needed to heat one square meter. When the room has two external walls, add another 20%. If there are two external walls and two windows, add 30%. When the window faces north, you should add 10%. An important factor will be the installation of radiators, because no matter how good the batteries you purchase, if they are installed incorrectly, it will still be of zero use.
There are certain rules for installing radiators:
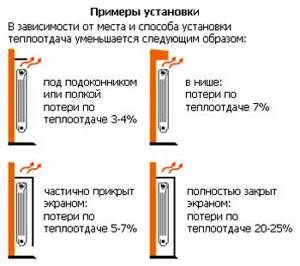
- batteries must be placed under windows
- their length must correspond to the length of the window, or at least half the length
- in the corner room you can install an additional pair of radiators along the outer wall
- It is better to install heating risers in corners. This will ensure they warm up and avoid blackening of the wall and the formation of mold.
- they must always be available.
When choosing heating radiators, you should rely on the technical characteristics of the radiators and the heating system itself, as well as your budget. With proper study, you can always find a middle ground for yourself.
You might be interested in reading:
- Installation of sandwich chimneys through the wall of the house. Step-by-step technology
- How to heat a country frame house. Options and profitable ideas
- Do-it-yourself stove installation for a home with a water circuit for heating
- Do-it-yourself chimney cap and installation in the house
Radiators made of Corado steel
The Czech company Corado is already well known on the domestic market. This is due to the design features of its products.
Corado steel radiators (technical characteristics in the product data sheet confirm this) are made from pressed sheet cold-rolled steel:
- The material from which Czech panels are made is chemically inert, so it is not affected by low or high pH values of water.
- A large model range allows you to choose a heater of the required power, color and size (table of steel heating radiators from this issue).
- They contain less coolant, which reduces energy consumption for heating it.
As experts note, Corado radiators offer unsurpassed quality at an affordable price.
To summarize, we can say that steel panel radiators are an opportunity to choose an effective model from a wide range of products with the required level of heat transfer, which will create pleasant warmth and microclimate in any room.
Steel panel radiators
These radiators are rectangular panels:

The panel radiator is made of two steel sheets welded together. Vertical grooves are pressed into the sheets through which the coolant circulates.
Steel panel radiators are made of one, two or three panels. Vertical pipes are welded to the back sides of these panels to enhance convection:

Pipes to enhance convection for panel radiators
Panel radiators are produced in heights of 300...900 mm, lengths up to 3 m, depths of 60...165 mm.
The advantage of panel radiators is their low weight, thanks to which they can be mounted alone, powerful brackets are not needed, and the wall material can be not only concrete or brick, but also wood and some kind of frame cladding (as you probably guessed, comparison carried out with cast iron radiators).
In panel radiators it is easy to control the coolant temperature due to the low thermal inertia of these heating devices.
Disadvantages of steel panel radiators:
- panel heating radiators are designed for low pressure (6-8 atm - working and up to 13 atm. test), hence their sensitivity to water hammer;
- the inner surface of the panels is susceptible to corrosion;
- poor hygiene, because dust and cobwebs accumulate between the panels, and getting to this nasty stuff is very difficult.
From all of the above, we draw conclusions: it is more correct to install panel radiators in private homes and take care of the quality of the coolant.
Of steel
This category includes heat devices with high efficiency and a working pressure of 9 atm, withstanding 13 atm. crimping. Such batteries are in demand in individual construction, or if multi-storey buildings have their own heating unit.
Radiators are made of steel sheets with stamped recesses for coolant. Protruding fins are welded on the back side to increase thermal output: they enhance the conventional air flow. Heating devices are made of low-carbon steel with high anti-corrosion properties. Coating – powder enamel.
They are divided into two categories: panel and tubular. Panel ones represent a continuous heat-conducting surface, tubular ones consist of sections in the form of vertical pipes and can be different in design, as a result of which their cost is slightly higher.
Product Description
Device design
Dilapidated plate heating radiators in the USSR were used virtually on a par with the usual cast-iron batteries. They were installed in schools, clinics, government institutions - i.e. where it was necessary to heat a large amount of air.

Today, the design of similar devices has been improved a couple (mostly through the use of modern materials), but the non-specialized scheme has remained unchanged:
- The base of the system is formed by a U-shaped curved tube through which the coolant moves . Taps are installed at the inlet and outlet, allowing the radiator to be disconnected from the system.
Note! Simple ball valves are used much more often, because adjustment of the coolant flow is not necessary, but greater reliability is needed.
- Heat exchange plates are placed on the tube . They can be made of the same material as the pipe itself, or they can be made of a different metal.

- Much more often, this entire system is housed in a thin-walled iron casing, the main function of which is to protect the heat exchangers from dust and protect people from scratches and burns when interacting with the heater . To allow warm air to escape, holes are made in the upper part of the housing.

Operating principle
This system functions quite simply:

- The coolant (warm water or high-temperature steam) moves through pipes under pressure of up to 20 atmospheres. Along with this, the high speed of movement leads to the fact that when moving along the circuit, the temperature of the coolant decreases slightly.
- When passing through the area with heat exchangers, water transfers some of its energy to the plates. Those, for their part, quickly heat up to a high temperature.

- Cold air enters the radiator housing through holes in the bottom.
- The large area of the plates facilitates heat transfer, because their entire surface is in contact with air.
- Once the ambient temperature increases, it rises up and exits the housing through the holes in the lid.
Note! There are also open-frame models, but their operating efficiency is lower due to a certain percentage of heat loss.
The process of vertical movement of air during heat exchange occurs continuously and is called convection. The heating devices themselves are quite often called convectors. It is necessary to emphasize that the natural rise of air is not always sufficient. In this case, a fan is mounted in the lower part of the case, which supplies the movement of air masses. On the one hand, the price of heating also increases due to the use of additional electricity, but otherwise the efficiency also increases significantly.
Main varieties
Today, the market offers a couple of varieties of plate-type batteries. They can be roughly divided according to a number of indicators:

Old finned battery.

Selecting a radiator type
The choice of model depends on the needs and technical characteristics of the heating system. Any type of radiator is suitable for private houses with an autonomous heating system.

If you are purchasing a device for an apartment located in a multi-story building, you should think about purchasing a panel model, since the operating pressure in such buildings is quite high.
In addition, in multi-apartment high-rise buildings, the heating system “suffers” from pressure surges. Tubular and plate batteries may not withstand water hammer, become deformed or lose their tightness.
When choosing a heater, you should also take into account the interior of the room. There are decorative models, the height of which is only 20 cm. They are installed near the floor and serve not only as heating devices, but also as interior elements.
Cast iron sectional radiators
The first development of cast iron batteries was carried out almost 150 years ago by our compatriot.
A few years later, the Americans received the patent and finalized the design. Radiators gained popularity after the advent of the central heating system, and their mass production began during the Industrial Revolution. The batteries that were used in the USSR and now remain in many homes are branded MC 140. The value “140” is the power supplied by one section. The operating and test pressure of the battery is 9 and 18 atmospheres, respectively. Number of sections – from 4 to 10.

Today, cast iron radiators are again gaining popularity, thanks to improvements in their design and design.
The advantages and disadvantages of batteries of this type are approximately the same.
- Long service life (more than 50 years);
- Affordable price;
- Resistance to mechanical damage;
- Corrosion resistance;
- High abrasive wear. Pebbles and sand in water do not cause much damage to the battery from the inside;
- Heating efficiency with the maximum number of sections.

- Heavy weight and bulkiness;
- Possibility of depressurization of joints;
- Accumulation of rust inside during long-term use;
- Unpresentable appearance;
- Difficulty in integrating radiators into autonomous heating systems, the impossibility of saving on coolant;
- Difficulty in cleaning.
What types of low heat exchangers are there?
Devices are distinguished based on the following criteria: the type of material from which they are made, the design features of the main components - sections, plates and height. They are produced in heights from 200 to 450 mm, lengths from 500 to 6,000 and depths from 10 to 230. The following types are distinguished:
1. Cast iron sectional, ribbed. The advantages are good thermal inertia and corrosion resistance. Disadvantages: low operating pressure up to 10 atmospheres, fragility, susceptibility to the accumulation of dirt and plaque inside the channels, which reduces heat transfer over time. Compact batteries made of cast iron are models MC 140M-300 (height 388 mm).
2. Steel panel radiators consist of one or more heating plates enclosed in a ribbed shell. They have excellent thermal conductivity and low inertia, and consume a minimal amount of coolant. For example, a steel radiator measuring 100 mm deep, 300 mm high and 1,000 long can create an effective thermal curtain near a window with a glazing area of up to 4 m2.
Disadvantages: not resistant to water hammer; when water is drained, corrosion can form on the walls of the panels; the convection method of heat transfer contributes to the formation of small dust particles in the room. Of all compact heating devices they have the highest cost. For example, the price of a Kermi radiator with a height of 300 mm, depending on the length and depth, is 1,260 - 5,100 rubles.
3. Aluminum casting and extrusion sections are characterized by light weight, good heat dissipation and elegant design. The technical characteristics of a low aluminum radiator allow it to withstand operating pressures of up to 16 atmospheres. Disadvantages: low convection, service life (10-15 years), instability to water hammer and, as a result, possible leaks between sections. You can buy a 200 mm battery made of aluminum for 340 - 1,250 rubles.
4. Bimetallic ones consist of 2 parts: a core made of steel or copper pipes and an aluminum shell. The advantages are: the ability to withstand high (up to 100 atmospheres) pressure, small volume of water consumed and good corrosion resistance. The sectional low bimetallic radiator Rifar Base 200 has a closed rear surface, which allows it to be mounted in close proximity to glass surfaces. Some models are equipped with legs for installation on the floor. However, in terms of heat transfer, bimetallic batteries are inferior to aluminum products, and their cost is 10-15% higher.
5. The lowest are plate batteries of the convector type. Such linear or plinth radiators have a height of 200 to 400 mm and can be attached to the wall and floor, and, if necessary, covered with decorative grilles. They are characterized by good heat transfer and the ability to withstand operating pressures of up to 20 atmospheres. Produced in the form of solid products of a certain length. If there is a leak, they require a complete replacement, which causes some inconvenience.
What to consider when purchasing
The modern market for heating appliances is saturated with products from Russian and global brands that differ in technical characteristics, quality, and price. In order to avoid unnecessary costs and not make mistakes with quality, experts recommend taking into account the following factors:
1. For centralized heating systems that are installed in residential multi-storey buildings, cast iron radiators are suitable. For buildings with panoramic windows, it is better to use bimetallic or aluminum ones.
A clever meter that saves electricity. Pays for itself in 2 months! Everyone needs to know this in order to save!
For closed heating systems that are installed in private homes, batteries made of steel or aluminum are recommended.
2. The length of the radiator must correspond to the size of the window opening or be 10-20 cm longer. Otherwise, it will not be possible to create an effective thermal curtain, which will lead to uneven heating of the air in the room.
Technical characteristics and cost of the most popular models
Connecting convectors
Two types of convectors are sold by connection. You need to pay attention to this when purchasing. The first type is a convector with a side connection. The second type is a convector with a bottom connection0. It is equipped with a valve insert.
Disadvantages of convectors:
- the powerful vertical flow of heated air created by the convector is not only a plus, but also a minus of this heating device, since the room is heated unevenly in height;
- the heat transfer of the convector may decrease over time due to dust settling on it, and it is difficult to clean the plates;
- the presence of copper in the convector (in some models) can cause electrochemical corrosion of system elements if this is not taken into account;
- the somewhat “shabby” look of the old models (however, modern models do not have this drawback).
In addition to the wall convectors shown in the photo above, there are also linear and baseboard convectors. They are attached to the floor or the bottom of the wall:
Skirting convectors are produced with a height of 200 mm, and their length can be quite significant. The appearance of the convector is enhanced by decorative panels.
Technical characteristics of converters:
- working pressure - 15-16 atm.;
- test pressure - 22.5-24 atm.
(other models can withstand even more: 25 and 37.5 atm, respectively)
Where to install heating convectors?
It is best to install convectors near large stained glass windows, in rooms with high ceilings, in swimming pools, on loggias, in service or utility rooms, in corridors.
But in bedrooms, children's rooms, etc., it is better to install radiators of other types.
That's all about steel radiators, I hope now you can decide exactly which heating radiator to choose.
Aluminum
Aluminum heating radiators are made not from pure aluminum, but from an alloy based on it. This metal was not chosen by chance, as it has one of the highest heat transfer coefficients - 4-4.5 times better than cast iron and 5 times better than steel.
Table with thermal conductivity coefficients of different metals
That is why aluminum radiators are distinguished by their high power (180-190 W per section), no less high heating rate and low inertia. They work very effectively in tandem with thermostats, allowing you to maintain a stable temperature with an accuracy of one degree. The advantages of aluminum radiators include their low weight (one section weighs 1.5-2 kilograms), which makes delivery and installation easier. Another positive point is that the shape is designed so that it has a large cross-section of channels for the coolant (slightly smaller than that of cast iron “accordions”). This is good, since there is a low probability that these channels will become clogged and the radiator will stop heating.
Now about the disadvantages of aluminum radiators. They are related to the properties of aluminum. As you know, it is a chemically active metal. It actively interacts with most of the chemical table, and reacts especially violently with copper. And in modern heating systems, copper parts are often found. Such a proximity threatens the rapid release of copper parts of the system and system, as well as increased gas formation. They have learned to deal with gases - they install automatic gas vents (valves) in systems, and they save copper by not placing it close to aluminum appliances. The process, of course, is still going on, but not with such intensity.
Aluminum radiators look modern
The chemical activity of aluminum also manifests itself in demands on the quality of the coolant. Not in the sense of its contamination, but in the sense of its acidity. Aluminum radiators work normally in systems with coolant acidity no higher than 7 (Ph 7).
The softness of aluminum is also not very good for the operation of the heating system. The alloy from which heating radiators are made contains additives that increase its hardness, but still, they do not work in high-pressure networks. Typical operating pressure is 8-16 atm depending on the type and manufacturer.
Based on all of the above, there appears to be an area in which aluminum radiators will be the best. These are individual heating systems with boilers controlled by automation. They also do well in apartments, but only in small buildings (up to 10 floors), in which coolant with Ph 7-8 circulates.
Design and principle of operation of flat batteries
For the manufacture of steel flat heating radiators, stamped metal sheets connected to each other are used. High-tech welding contributes to the formation of reliable, durable joints.
Two connected panel planes exhibit a high degree of heat transfer; a small internal cavity is formed in them, through which the coolant circulates. In order to use the equipment as rationally as possible, you need to adhere to the recommended temperature regime. To optimize fuel consumption, fins were added to the planes, resulting in the formation of a new class of technology - convection finned batteries. Additional elements are attached to the surface using spot welding; in cross-section, the equipment has the shape of a trapezoid.
Flat batteries in the upper part are equipped with perforations - these are zones for the exit of heated air. The casing contains metal pipes with radiator plates. The working fluid, circulating through the tubes, releases part of the heated air; the flow path also passes through the upper zone with metal perforations. In the process of heating the front part, a little more thermal energy is released.
Flat radiators are optimal for closed-type heating systems; they are not advisable to install in centralized networks. These devices work with coolants exhibiting low pressure levels.
Main characteristics of a typical radiator
Regardless of the complexity of the heating system, the main task is to maintain the set temperature in the house or apartment. The heating radiator plays a key role in this, carrying out heat exchange between the air in the room and the coolant.
Uniform heating, efficient heat transfer, microclimate maintenance, stable operation - these are the basic requirements for a heating battery.
In residential premises, single, panel or sectional twin radiators are installed that do not emit toxins when heated
The main parameters influencing the choice of a specific model:
- System operating pressure. Depends on whether the device is connected to an autonomous or centralized network. It is arranged on a gravity or forced principle. On average it varies from 3 to 10 bar or in a similar atmosphere range.
- Thermal power. A characteristic required to calculate the thermal power required to heat a room. It is also needed for selecting individual components of sectional batteries. Approximately 1 kW is required to process 10 m².
- Modularity. The quality inherent in prefabricated radiators, which makes it possible to assemble and disassemble the device to suit individual requirements.
- Speed of reaction to tº. More precisely, the ability to respond to changes in coolant temperature. period of time for cooling and warming up.
- Possibility of equipping with automation. Devices that monitor weather conditions and independently eliminate air jams.
The devices now presented for sale ensure free circulation of the coolant liquid throughout the system. They are characterized by corrosion resistance and attractive appearance.
Sectional radiators differ in the shape and size of the sections, ensuring the supply of the required amount of thermal energy
The thermal efficiency of a radiator depends on the energy dissipation surface area. A flat metal convector has a much smaller area compared to a sectional aluminum convector of the same geometric size. Because the latter radiates heat over the entire area of the fins.
Main types of heating devices
The following types of batteries are most often used in everyday life:
- Sectional. They are made from aluminum or several different metals. These structures consist of parts connected to each other using steel nipples. They look attractive and provide good air circulation. Such devices may include several sections in one battery.

Sectional battery Source eurosantehnik.ru
- Tubular. These designs are not widely used. Among their advantages are a long heat transfer time and an aesthetic appearance of the device.

Tubular battery Source stroy-podskazka.ru
- Panel. One of the most effective devices for home use. Pros: large working area, good level of convection, varied design and wide range of equipment. Such a battery can be selected for almost any room; the sizes of radiators differ markedly from each other. Among the disadvantages are high prices for products, as well as low operating pressure.

Panel battery Source gopb.ru
- Lamellar. They are characterized by a high level of pressure, have good heat transfer and provide effective air circulation. These devices can be used as in-floor convectors; they are available in a variety of shapes and designs.

Plate battery Source gidroguru.com
Plate heating radiators, their characteristics, selection and installation
Radiators are devices for transferring heat from a medium circulating through pipes into a room. Their efficient operation is achieved not only due to the large area of the heated surface, but also due to the thermal conductivity of the material.
The choice of the fundamental principle and type of convector lies on the analysis of the pricing policy and the physical characteristics of each of them. Since savings when purchasing can “result” in harsh months both in insufficient heat transfer and in violation of the integrity of the entire heating system.
Let's sum it up
In conclusion, we can say that by focusing on the varieties, materials and operating process of a particular type, you are guaranteed to select the heating radiators that best suit your expectations and the heat supply system. Follow simple rules that will help you slowly choose a decent option without extra costs: 1. Determine the characteristics of your home: area, ceiling height, number of window and door openings. Also consider the heating device and coolant. The criterion of individual or mainline system is also important. 2. Having studied the properties of the types of radiators, select the one that, in your opinion, will complete the task without causing negative incidents or causing damage. Do not be tempted by the low price, pay attention to the brand and reputation of the manufacturer. 3. Look for real user reviews about products of a certain brand on the Internet. It is better to do this on specialized forums. It would be a good idea to look at photo and video reviews. 4. To install the purchased radiator, contact a specialist. Do not attempt it without experience in this field. This is fraught with disruption of the functionality of the entire system and dire consequences, including battery failure. 5. When choosing a design, do not forget about the style direction of the rest of the room. Do not make the radiator a foreign object. Choosing the right attractive and functional heating element is not an easy task, but a persistent search will certainly provide a positive result.
A plate steel radiator is a fairly simple, but effective design. It should not be used everywhere, but where you need to quickly and efficiently heat a large area, it will definitely be appropriate. You can study the features of such batteries in more detail if you take the time to watch the video in this article.

Design characteristics
Thin heating radiators have an unusual body. They are made from rolled steel sheets, and in order to increase their thermal power, special ribs are used, which are mounted inside the thermal block. The use of special reinforced fiber in the design of the heating device makes it possible to make invisible those areas through which the connection to the heating system pipeline is made.
Narrow radiators are equipped with two plate parts, made by stamping and welded to each other. Between these structural elements there is a thermal channel, which is provided for coolant circulation. To connect such plate heating batteries to a centralized main, special outlets are provided. And through certain types of connecting elements, it is possible to form plate heating radiators from several plates in order to heat large areas.
Some models of narrow radiators are equipped with plates with convection fins, thanks to which the heat transfer rate increases several times. It is for this reason that the power of the heating unit, which has fins, will be almost half that of traditional heat exchangers. But at the same time, this design causes an increase in the amount of dust that will collect on the ribs.
Plate heat exchangers with convective fins are best placed in rooms that have high sanitary requirements. This will avoid the formation of large amounts of dust and increase heating efficiency.
Marking
Slim radiators are manufactured in accordance with standards, and each type is classified according to a specific characteristic. As a rule, almost all manufacturers of such heating devices adhere to this classification and label their products accordingly. So, the first number indicates the number of partitions in the thermal device, and the second – the number of plates that are equipped with convective fins.
The modification of plate heating batteries is as follows:
- 10 – single-plate heater without convection fins;
- 11 – single-plate heater with one convection rib partition;
- 21 – two-plate heater with one convection rib partition;
- 33 – three-plate heater with crown convection rib partitions.
Is it possible to install thin radiators in an apartment?
The question can be roughly divided into 2 types of apartments - in an apartment building with centralized heating and apartments with individual heating. Unfortunately, even manufacturers confirm that it is not recommended to install steel panel radiators in houses with central heating. The problem is not high pressure, it is precisely thin batteries that are designed for such operating pressure (up to 10 atmospheres), but the risk of clogging pipes and convectors.
For various reasons, a large amount of air circulates in a centralized system, which greatly accelerates the process of corrosion of the internal surface of the convector. Since 90% of steel panel radiators are supplied without anti-corrosion protection of the internal fabric, the maximum service life of such products does not exceed 3 years.
Types of radiators
In modern construction supermarkets and markets, various types of radiators are presented. They are divided according to the material from which they are made, shape and design features. According to the material:
- cast iron
- aluminum
- steel
- bimetallic
- sectional
- lamellar
- tubular
Each type is distinguished by its heat transfer characteristics, resistance to corrosion processes, durability, ability to withstand hydraulic shocks and aggressive coolant environments, and, of course, aesthetics. Radiator models also vary in cost:
- Economy class. These include inexpensive cast iron and aluminum batteries, which have a number of disadvantages.
- The average price category is presented in the widest range. These are steel and bimetallic models of heating devices.
- The premium class is represented by radiators made of stainless steel and artistic cast iron, as well as more expensive and high-quality bimetallic models. This also includes steel tubular radiators.
Cast iron radiators
Although batteries made of cast iron do not meet modern requirements, they continue to be produced to this day. Manufacturers have slightly diversified and improved their appearance, made the radiators more stylish and added decorative screens to them. With the advent of the new generation of heating devices, cast iron has not lost its position, so it is unlikely that these batteries will disappear from our apartments in the near future. The cast iron radiator, familiar to many, remains out of competition due to its unpretentiousness. It is not afraid of rusty and contaminated water, aggressive additives present in the coolant of a centralized heating system, and the presence of bacteria. The appearance of radiators is universal and allows them to be installed in residential, public, utility and industrial premises. The main disadvantage of cast iron is its low thermal conductivity. The temperature of the coolant inside the battery is much higher than on its surface. Therefore, in winter, cast iron radiators are rarely very hot. In addition, despite sufficient strength, old batteries in Soviet-built houses begin to gradually fail, requiring replacement. The appearance of cast iron batteries and their aesthetics leave much to be desired, despite all the efforts of manufacturers and designers. Another disadvantage that you should pay attention to is the brittleness of cast iron. If a heavy metal object accidentally falls on the radiator, the cast iron may crack.
Aluminum radiators

Important! Aluminum radiators cannot withstand excess pressure and water hammer - they can simply burst. Therefore, it is recommended to use such batteries in private homes, where the pressure in the heating system is not too high and can be easily adjusted independently.
Cheap aluminum radiators are the most susceptible to corrosion and have a short service life. When choosing, you need to remember this.
Steel radiators
There are two types of steel radiators:
- Panel ones are quite unpretentious in operation and relatively inexpensive.
- Tubular - can become a design element of any room. They belong to the premium class.
The design of panel heating devices is quite simple. They are made of two plates, in the recesses of which collectors are formed through which water circulates. The plates are connected to each other by welding. They are compact, although their height can reach up to 0.9 meters and length up to 3 meters. The batteries are ideal for offices, shopping and entertainment centers, public buildings and warehouses. Steel tubular heating batteries, in addition to high heat transfer, are characterized by a long service life. Manufacturers of the products claim that they can be used for at least 25 years. The unusual design allows you to install such radiators in residential areas. Their only drawback is their high cost, so tubular radiators can only be found in expensive private cottages.
Bimetallic radiators

Bimetallic radiator Viertex 70 mm They are made of two types of metal:
- steel, characterized by its unpretentiousness to the quality of the coolant
- aluminum from which the fins are made
The cost of bimetallic radiators is higher than cast iron or aluminum, but their quality is much better. They combine the best properties of aluminum and steel, as well as the design features of sectional and tubular radiators.
Note! Bimetallic heating devices can withstand operating pressures of up to 40 atmospheres and hydraulic shocks. In addition, they are resistant to oxidation and corrosion.
Due to the small diameter of the steel channels, the volume of coolant inside is reduced, which makes bimetallic radiators more economical. Plus, they quickly respond to changes in heating mode.