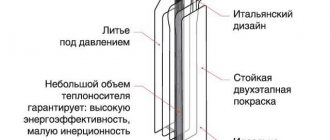
Steel heating radiators
This type of product in question is less popular than aluminum radiators, but experts believe that this is incorrect.
There are a lot of advantages that elevate steel heating radiators to the highest levels of the rating. Advantages of steel heating radiators:
- It is possible to purchase tubular steel radiators or panel radiators. The latter option is very budget-friendly, it is often used in the installation of heating systems in private homes and is popularly called convectors. But tubular steel radiators will be much more expensive - this is due to the original production technology of the product in question.
- Both types of steel heating radiators have a high level of heat transfer - experts classify this indicator as excellent. At the same time, extremely low inertia is noted.
- Such products are absolutely harmless and environmentally friendly - they are used to equip heating systems literally everywhere: schools, kindergartens, hospitals, and so on.
- The volume of coolant required for the normal functioning of a system of steel heating radiators is extremely small.
- The cost of the product in question is low; such heating radiators are available to absolutely everyone.
Disadvantages of steel heating radiators:
- It often becomes necessary to drain the water from the entire heating system - in this case, the walls of the radiators come into contact with oxygen, and this provokes the development of corrosive processes.
- It is strictly forbidden to use steel radiators for arranging a heating system in multi-storey buildings - they are susceptible to water hammer like no other.
- Since the type of product in question has good convection, this can provoke the appearance of drafts and the rise of dust particles into the air.
Aluminum heating radiators: battery design and properties
Modern aluminum heating radiators are very popular. Such equipment can be seen both in city apartments and in offices. They are especially often installed by owners of private and country houses. The technical parameters of the batteries make them an excellent option for one-, two- and three-story buildings. The article discusses the device, characteristics, advantages and disadvantages, the main models of aluminum batteries, and also describes how to disassemble, assemble and wash an aluminum radiator.
Advantages and disadvantages
Today, panel batteries can be found on the market in various countries, as they are the most traditional device that provides high-quality heating and meets energy saving requirements.
The main advantages of such radiators include:
- Stylish design. The product has a simple and neat appearance. Manufacturers produce devices in various designs, from classic to modern.
- Convenient adjustment. The degree of heating can be easily controlled using mechanical and electronic devices.
- High heat dissipation. Thanks to the special convection principle, the device has increased efficiency.
- Affordable price. Compared to other types of heating devices, panel radiators are cheaper because steel is used for their manufacture.
- Saving energy resources. The device has a small capacity, so much less electricity is consumed to heat it.
- Multifunctionality. The product can be used both as a radiator and a convector.
- Light weight. The design is lightweight, so it is quite possible to install it yourself.
- Large selection of models. Radiators of any power and size are available on the market.
Panel batteries have the following disadvantages:
- Instability to water hammer. Because of this, radiators cannot be connected to central heating systems.
- High sensitivity to acidic environment. To protect the steel surface of a product from corrosion, it is necessary to constantly maintain its pH level in the range from 8.3 to 9.5.
- According to the operating instructions, it is prohibited to drain water from the system for a long time. If this is not done, the inner walls of the panels will come into contact with oxygen, which will lead to their corrosion.
How to choose the right radiator
Before choosing a heating source, you need to know exactly what functions it will perform. For example, heating elements for different areas will be different. Steel panel heating radiators are installed only in a private (autonomous) manner, and the pressure should not exceed 10 atmospheres.
To determine which convector to choose, you can make an approximate calculation. For example, for a standard house with a ceiling height of up to 3 meters, the thermal power should be 100-150 watts per square meter.
Next, we multiply the indicator by the area of the room or the entire house and find out the total thermal power. The total number is divided by the number of spaces expected for batteries. The result is the thermal power for one battery. The number of heating points for the entire home is calculated in a similar way.
Aluminum radiators are suitable for heating different rooms: from residential to domestic. Due to the fact that the devices heat up quickly, they have a high heat transfer coefficient.
In addition to significant advantages, they also have a number of disadvantages. Among them are rapid cooling after turning off the heating and a short service life. Over time, deposits of minerals and salts form in the sections, which reduces heat transfer.
For multi-storey buildings with a large number of apartments, a radiator such as a bimetallic one is suitable. Why he? Because it is able to withstand high internal pressure or sudden temperature changes (water hammer).
Everyone knows that many residential complexes have outdated heating systems, and they do not operate according to standards. A bimetallic radiator is protection against leaks and floods.
Criteria for choosing radiators for an apartment
The decision to purchase a certain type of radiator is influenced not only by its technical parameters and the operating conditions of the central heating system. There is a certain procedure for choosing the right heating batteries.
It is imperative to pay attention to the following nuances:
Operating pressure. Each product has a passport, where this parameter must be indicated by the manufacturer. Its value should be at least 1.5 times the actual pressure in the heating structure. It is precisely its differences that most often cause the breakdown of modern devices.
Possibility to prevent water hammer. This has a strong impact on the battery life. In apartments where there is central heating, it is impossible to protect yourself from them. Therefore, preference should be given to those units that have a high degree of resistance to water hammer.
Number of sections. Some batteries can be expanded during use
When it is difficult to decide on the size of the structure, you need to pay attention to such radiators.
Device power. Not all batteries are able to cope with creating a comfortable microclimate in the house in regions where the outdoor temperature drops below - 40 degrees
Therefore, information about which batteries are the warmest is so important. Some foreign products are designed for 80-90 degrees, and for areas with severe winters it is advisable to select models with a heating temperature of up to 120-130 degrees.
Coolant quality. Domestic central heating systems circulate water whose quality is so poor that it damages the internal surfaces of radiators. Therefore, it is better to purchase batteries with thick walls.
Appearance and product design. When choosing batteries for rooms that have undergone modern renovations, it is unlikely that anyone will want to install bulky structures. From the rich assortment on the market, you can always choose an original model.
Length of service life. Replacing heating appliances in an apartment is an expensive undertaking, so new products must last at least 20 years.
Easy to install. This criterion is only relevant when the heating equipment is installed independently. It is impossible to install a heavy cast-iron structure alone, but there will be no problems with lightweight panel radiators.
Information about what kind of heating radiators there are for an apartment will not be superfluous for those who want to purchase new appliances. Experts do not advise saving much on their purchase, since cheap products can cause an accident in the house and cause a lot of trouble for residents of an apartment building.
Batteries made of various metals and their properties
When purchasing batteries, homeowners should not make mistakes and limit themselves to just a few types of options considered. With a huge number of innovative and traditional radiators on the market, buyers have dozens of battery models made from various metals that differ in shape, color, size and purpose. Therefore, it is important to choose an option that optimally complements the heating system, taking into account the ergonomics of the battery, which affects the distribution of air masses and its performance.
Criteria such as maximum pressure in the system, type of coolant and the possibility of installing an individual thermostat directly depend on the material from which the radiator is made. Therefore, all these aspects should be taken into account by buyers who want to buy heating batteries for their home.
Cast iron is a traditional material for batteries
If, when choosing heating devices, we proceed from the aspect of financial benefit, then the most affordable option on today’s market is a cast iron battery, the price of which is significantly lower than the cost of analogues made of bimetal or copper. On the one hand, cast iron batteries take a long time to heat up and are not as sensitive to changes in thermostat settings as their aluminum counterparts, but on the other hand, they take much longer to cool down.
This feature is due to the high density and large mass of cast iron, which is the optimal metal for the manufacture of radiators that provide soft, wave-like heating even after the boiler is turned off. The affordable cost of cast iron radiators makes them an acceptable option for most homeowners. However, before buying water heating radiators made of cast iron, home owners should choose reliable walls designed to accommodate radiators.
Metal has a large mass and a heavy cast-iron radiator should be mounted only on reliable load-bearing walls, avoiding installation on fragile internal partitions between rooms. The design of cast iron batteries is quite monotonous and in order to fit it into a modern, sophisticated interior, homeowners will need to spend money on purchasing decorative grilles or boxes to transform the appearance of the batteries.
Aluminum is a light and beautiful metal for radiators
The owner can buy heating batteries, the price of which is slightly higher than their cast iron counterparts, made of aluminum.
The radiators instantly heat up and within a few moments after the heating system is started directly, they begin to transfer heat into the room.
But at the same time, aluminum radiators cool down just as quickly. To solve this problem, owners install thermostats that regulate the temperature of the coolant and help heat the house more evenly. In a heating system, aluminum radiators, the price of which depends on the number of sections, are quite effective, but you need to know about some nuances.
In addition to the high price, aluminum heating batteries also have a number of other pitfalls, which are important to know about before purchasing. Since aluminum is a sensitive metal, inhibitors must be used in the heating system. These are substances added to the composition of the coolant and prevent scaling, scale formation, corrosion, foaming, swelling and dissolution of rubber seals of heating systems, etc.
Having selected the optimal inhibitor for the coolant, you can install aluminum batteries in your home heating system and not worry about the radiator rotting or rusting over time. In addition, both residents of apartments and owners of private houses can buy aluminum heating batteries, the price of which depends on the reputation of the manufacturer, because such radiators are distinguished by their universal scope of application.
Steel – metal for panel and tubular batteries
Homeowners who are interested in selling heating batteries from modern manufacturers can pay attention to innovative panel and tubular radiators made of steel. Such products have a glossy, smooth surface that provides an attractive appearance, and are the choice of many architects, developers and property owners who, in addition to their aesthetic design, value steel radiators for their high performance, affordable price and environmental properties.
Steel quickly releases heat and ensures a uniform increase in temperature and a high level of comfort in the home.
Another benefit of steel radiators is their ability to provide significant energy savings and cost savings on your annual heating bills. The energy efficiency of steel batteries is complemented by their long service life and productive operation in heating systems with standard coolant pressure, so homeowners can buy both new and used heating batteries and install them in their home.
The disadvantage of steel batteries that do not have anti-corrosion treatment is similar to the disadvantage of aluminum analogues - the devices are sensitive to the quality of the coolant and, when used in central heating systems, can quickly lose their quality. To avoid such phenomena, it is worth installing radiators in autonomous heating systems and using recommended inhibitors for the coolant. Before installing a heating battery, the price of which is indicated on the contractor’s website, it is important to make sure that the thermal power calculations are made correctly.
Bimetal - an innovative solution for battery production
Many homeowners are interested in installing heating batteries in an apartment; the cost of the work is of secondary importance, since the choice of the most efficient and economical batteries comes first. Such devices are bimetallic Italian heating batteries, presented on the market by leading manufacturers. They are currently sold in many hardware stores, so finding the answer to the question: where to buy bimetal heating batteries will not be difficult. At the same time, the rather high price of a bimetal heating battery is fully justified by decent performance indicators.
Bimetallic radiators combine the positive features of aluminum and steel appliances. At the same time, manufacturers made sure that the batteries were free from critical shortcomings of their prototypes. As a result, consumers have the opportunity to purchase energy-efficient, reliable and sensitive batteries for their heating system, which are protected from the ravages of corrosion through a unique design.
Design features also lead to a number of other advantages. In particular, the batteries are resistant to pressure surges and can function effectively in central heating systems, where pressure is pumped up to 35-40 atmospheres using circulation pumps. At the same time, batteries should not be used in heating systems with natural coolant circulation, since this may reduce their declared functionality.
Copper radiators
sales leader
Copper radiators work according to the principle:
- Radiation—in this case, the darker the color of the battery itself, the more intense the radiation.
- Convection—heat exchange.
- Thermal conductivity - transfers heat from heated to less heated areas of the battery.
Advantages of copper radiators:
- The best indicator for thermal conductivity is on average 5 times more effective than other types of radiators.
- Copper is an environmentally friendly material; it prevents harmful bacteria from multiplying.
- Strength and durability. The service life of a copper radiator is 50 years (subject to the necessary operating rules).
- Full resistance to any chemical reactions, no corrosion.
Radiators are partly made of copper and aluminum alloy; they are also effective, but are more vulnerable due to which their service life is reduced. The price of batteries made of copper and aluminum is much lower.
- Lateral connection - if installed incorrectly, there may be a risk of reducing heat transfer efficiency by an average of 5%.
- Bottom connection.
- Diagonal connection.
- Serial and parallel connection.
Cast iron radiators [ edit | edit code ]
Cast iron sectional heating radiators are designed for central heating systems in residential, public and industrial buildings with a large number of floors. They are distinguished by significant thermal power per unit length of the device and, accordingly, compactness. Cast iron radiators are also less susceptible to poor quality coolant and are resistant to corrosion.
Cast iron radiators are strong and quite durable. Their large mass, on the one hand, provides them with high heat capacity and, accordingly, thermal inertia, allowing them to smooth out sudden changes in temperature in the room; however, it is also a disadvantage, creating difficulties during installation or maintenance. Disadvantages also include the tendency of intersection gaskets to degrade; During long-term use (over 40 years), the radiator nipples may be destroyed. Cast iron radiators require periodic painting; in addition, the walls of the internal channels are rough and porous, which over time leads to the formation of plaque and a decrease in heat transfer. The working pressure of the cast iron section is no more than 6-10 atm.
Bimetallic batteries
When answering the question about which heating radiator is best for a private home, you should think about purchasing a model of this particular type first. Bimetallic batteries are currently perhaps the most popular type of such equipment. The design of radiators of this type includes elements made of two types of metal - aluminum and steel (or copper). Hence their name. The advantages of bimetallic radiators, among other things, include:
ability to withstand very high coolant pressure (up to 35 atm) and water hammer;
attractive appearance;
durability (can last up to 25 years).
In general, bimetallic heating radiators are best suited for a private home. Reviews of models of this type available on the Internet clearly indicate this. Country property owners consider such equipment to be of very high quality, easy to install and operate. In appearance, such radiators resemble aluminum ones, but at the same time they are much more reliable. Their design is such that they look like a monolithic product. Since the performance characteristics of such batteries are better than aluminum ones, they cost a little more (about 25%).

How to assemble a radiator?
Aluminum heating radiators are assembled according to the following algorithm:
- place the battery on a flat surface;
- Inspect each threaded connection for chips, cracks and thoroughly clean with sandpaper. Degrease the ends using gasoline. Gaskets can be washed in soapy water;
- connect the sections. To do this, you need to put the seals on the nipple nut and place them on both sides of the device section. Make a couple of turns with the key in the upper and lower holes. When the key stops turning, you can pull it out using the lever;
- A plug should be placed on the unused hole. And on the other side, attach a Mayevsky valve to remove excess air from the system. Now the radiator can be connected to the system according to the selected scheme.
We check which radiators are suitable for residential heating
Batteries made of steel - fell, attacked by high pressure
Steel radiators are lightweight and thin. Good heat transfer and small volume of water make them economical and efficient. Yes, and they are inexpensive. But in terms of pressure they “let us down” - they can withstand only 6-8 atmospheres. They are not suitable for apartments, period.

Aluminum radiators - are eaten by corrosion, burst from water hammer
These radiators look nice, and 190 watts of thermal power pleases the consumer. However, wait, apartment dwellers – it’s too early to rejoice. Hot water with chemical impurities and high acidity quickly “eats” batteries from the inside. After all, aluminum is too active. And he can't cope with a lot of pressure. Average operating pressure is up to 16 atmospheres. And water hammer can destroy even a brand new aluminum radiator.
Bimetallic batteries are good for everyone, just expensive
This is one of the newest developments in heating devices. Such radiators are called bimetallic - after all, they contain two metals. This can be, in particular, aluminum and steel, or aluminum and copper.

Manufacturers guarantee that such batteries will work for at least forty years. They are suitable for an apartment in all respects, as you can see.
- They can withstand temperatures even up to 130 degrees.
- Their operating pressure is stated to be up to 30 - 50 atmospheres, depending on the manufacturer and model. With them you can stop being afraid of water hammer.
- Anti-corrosion external and internal primer makes the batteries durable and resistant to destruction.
- Light weight makes installation, carrying and transportation of such batteries easy.

Alas, not everyone can buy such an expensive device. And if they offer you something similar at an affordable price, don’t believe it. They will slip a fake. If you really buy, then buy products from trusted brands - the Russian company Rifar, Italian - Sira or Global. There are also good Chinese manufacturers. They, like Russian ones, have a slightly lower price than radiators from Europe.
Good old cast iron gets a second life
Fifty years, no less, is the life span of such a battery. In vain do some manufacturers of new products claim that it is high time to forget about this “old stuff”. Thinking for a long time about which heating radiators to choose for an apartment, many settle on cast iron radiators. They certainly won’t “play tricks” when they come into contact with dirty domestic water in the heating system. This metal is chemically passive, and it is not afraid of either high acidity or the presence of chemical additives in the coolant. And no abrasive will harm thick walls. So cast iron for an apartment (especially in an old house) is very good.
- Radiators made of cast iron are distinguished by the fact that they retain heat for a very long time - the residual value of its retention is 30 percent. And for all other types of batteries this figure is half as much
- Heat transfer due to the radiant heating method is much more effective than when using convection (as in bimetallic and aluminum products. Cast iron radiators heat not only the air, but also nearby objects.
- When draining water from the system in the summer, cast iron batteries will not rust - this is a significant plus.
- The large heat transfer area is another plus.
- Cast iron usually withstands pressure drops that central heating suffers from well. The operating pressure can reach up to nine to twelve atmospheres. But it doesn’t always withstand high-power water hammers - the fragility of this metal lets it down.
- The cost of these devices is usually lower than bimetallic radiators. Sometimes this is the determining factor.
These radiators are, of course, heavy, which causes some inconvenience during their installation. Well, yes, cast iron a priori cannot be light. But this weight results in large wall thicknesses, which give the radiators the required strength. Having installed cast iron radiators once (and this will be done by specially trained people - plumbers), you can forget about replacing them for many years.
The appearance of cast iron radiators today is no longer as poor as in Soviet times. Very attractive externally, figured cast batteries have appeared, made in a “retro” style, which harmonize very well with sophisticated rooms. For example, you can mention products from Roca and Konner.
True, the cost of such miracle batteries is quite high. Ukrainian, Russian and Belarusian models are more budget-friendly, many of which must be painted before use. But they also look quite decent, their design fits into the interiors of modern apartments.
Which ones are better to choose?
So, for central heating, which tests the strength of radiators with poor water quality, pressure surges, etc., the best option is cast iron radiators. They are the most resilient of all.
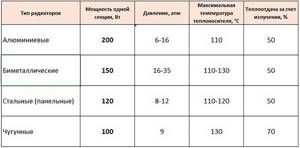
Comparative table of characteristics of radiators made of different materials
If funds allow, you can install bimetallic radiators (the pressure that can destroy such a device is 170 atm! Even the most obstinate heating plant is not capable of this).
In private homes, any batteries are suitable. There are no water hammers, the pressure is less than 3 atm, high-quality water is poured and heated to 900C. Only cast iron batteries are not so convenient due to their bulkiness and large amount of water in the system.
Well, if you are going to fill the system with antifreeze, opt for steel panel or bimetallic radiators.
The decision on what size the battery will be will be determined by the windows. They should be 60% or more of the window width.
In the case where water is supplied from one side, it is not recommended to install more than 10 sections - the distant ones will still not warm up enough.
The passport data of the radiator must state that the manufacturer recommends it for central heating and provides a guarantee.
Battery technical parameters
Each radiator is characterized by technical and design features that allow some models to warm up the room faster, while others, for example, consume less coolant. The ratio of these product characteristics required by the buyer often determines his choice:
Power
The larger the device and the higher the number of sections in it, the greater the power. This characteristic determines the quality of heat transfer of the battery. But high power means high energy consumption, so efficient heating will cost you to use more electricity.
Pressure
The operating pressure level varies greatly among radiator models: from 6 to 100 atmospheres. The higher this indicator, the better the product withstands water hammer. In addition, a device that can withstand 16 atmospheres or more can be installed in a central heating network.
Temperature
It depends on how hot the coolant inside the work area is (according to SNIPs, this value cannot exceed 95 °C). For example, in oil radiators the surface temperature reaches 150 °C, while in most centralized and autonomous heating systems the coolant temperature does not exceed 100 °C.
Heat dissipation
This is one of the most important characteristics of any radiator, since it determines how quickly and efficiently the device will warm the air in the room.
The highest levels of heat transfer are found in products with convectors and wide heat-dissipating plate casings.
Room heating
There is a direct dependence on the first and fourth characteristics. The more powerful the battery and the higher the level of heat transfer, the faster it will warm the entire room to the temperature required by the homeowner.
Important! It is practically useless to heat a room with poor insulation - even the most powerful heating systems will not help. Before installing a radiator in a house, garage, apartment or any other room, it is important to ensure that hot air will not escape from cracks in the walls or windows
Radiator compatibility with heating system
Heating systems come in two types:
- Open – in apartment buildings;
- Closed - in private homes.
If the system is closed, a person is his own boss in choosing a radiator. And if the heating is centralized, you need to collect information about it. What is the pressure in the pipes, water quality, maximum temperature.
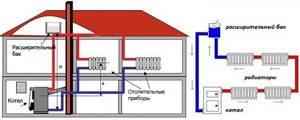
Layout of an open heating system
The official calculated indicators for an open single-pipe system may be the same, but when heating is started, after the summer period, sometimes these data go off scale, and hydraulic shocks occur. Imported radiators may not be designed for this.
The passport data of the radiator must state that the manufacturer recommends it for central heating and provides a guarantee.
Principles for classifying radiators for apartments
Water heated to 95 °C is usually used as a coolant in centralized heating systems. Moreover, it is not purified distilled, but technical grade with dissolved salts and additives.
As a result, the material from which the battery in the apartment is made must easily withstand the effects of temperature changes, moisture, and impurities contained in the coolant for a long time.
To last for many years, an apartment heating battery must:
- withstand operating pressure up to 9 atm (ideally up to 12–15 atm);
- made of metals resistant to chemical and electrochemical corrosion;
- have high heat transfer.
The pressure in apartment radiators fluctuates around 4–7 atm. Much here depends on the number of floors of an apartment building, the temperature outside the window and the operating conditions of the heating network. But during pressure testing and water hammer, the pressure can briefly rise to 15 atm and higher.
Also, the heating device in question must be easy to install, have a presentable appearance and low cost. But, most importantly, it must have excellent heat transfer characteristics.
The main task of the radiator is to transfer heat to the room that came through the water pipes. The more effectively he does this, the better it is for the owner of the apartment.
There are two main criteria for classifying heating batteries:
- Material of manufacture.
- Design.
All other parameters are technical characteristics of a specific radiator model.
Types of radiators by design

The heating capacity of batteries depends on the exchange area, so the design is important.
The choice of form is influenced by factors:
- ceiling height and room area;
- maximum pressure in the heating line;
- duration of operation (long-term or periodic);
- boiler power, pipe material, characteristics of other devices in the system;
- chemical composition and physical properties of the energy carrier.
Radiators are selected in the form of sections, panels, plate and tubular types. The climate in the region and the required heating conditions, the presence of aggressive factors, and the cost of batteries influence.
Sectional radiators
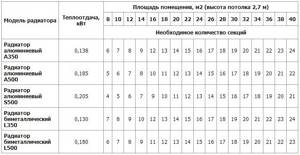
Heat exchangers connect sections of the same type, which inside have 2–4 channels for water movement. Prefabricated elements are made of aluminum, steel, cast iron of various shapes and lengths. Heating of the room is coordinated by the number and size of sections.
Prefabricated batteries transfer heat by convection and radiation, operate economically, and are equipped with manual and automatic temperature controllers, taps, and valves. The products are inexpensive, and the ability to choose the center distance makes them popular for different buildings.
Disadvantages include the risk of leaks due to a sudden surge in pressure, difficulties with cleaning internal channels and external cleaning of the intersection space.
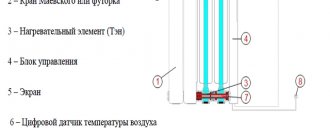
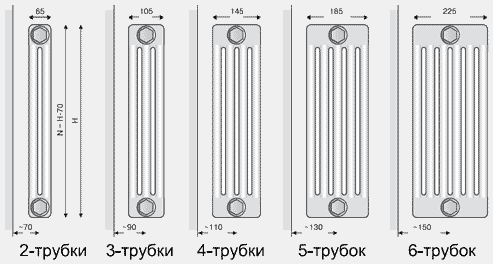
Tubular batteries
Design of tubular batteries.
The power depends on the diameter of the pipes. The cross-sectional design of the radiator includes 1 – 6 vertical collectors, which are connected by an upper and lower pipe; the coolant circulates unhindered. Heat transfer depends on the diameter of the pipes and the dimensions of the heat exchanger (0.3 - 3.0 m). The units can withstand pressures up to 20 atm.
Tubular batteries withstand pressure changes and hydraulic shocks. Smooth interior contours resist the accumulation of dirt and deposits. Welded joints do not leak. The appearance fits into various interiors. Radiators are available in all sizes and differ in body shape. The disadvantage is the high cost.
Panel models

A panel radiator looks like two metal panels welded together. Inside the plates there are vertical channels for circulation of the energy carrier, and ribs are attached to the outside, which increase the heat transfer surface. The panels are arranged in 2 or 3 rows, the material is steel.
Advantages of the models:
- low inertia makes it possible to quickly respond to changes in external temperature;
- due to its lightness, massive fastenings are not required;
- compact devices can be placed in any part of the room;
- low price.
To heat the model, you need half as much water as a sectional battery. The disadvantage is that panel installations cannot withstand high pressure in the main line; purified energy carriers without dirt and impurities must be poured into the system. Poor quality painting of joints leads to corrosion and leaks.
Lamellar

The operating principle of the radiator is convection exchange. The heat exchanger is a core with fixed fins made of thin metal. Inner tubes serve to transfer water. This type of radiator is installed in industrial and public buildings, multi-apartment buildings with a centralized main line.
The degree of heating is regulated by increasing the number of plates. Radiators effectively heat the room, but when the boiler is turned off, cooling occurs quickly. The coolant must be heated to a high temperature and pass under pressure.
What is the difference between bimetallic and semi-bimetallic radiators?
In real bimetallic heating devices, only the outer part is made of aluminum. Radiators are produced like this: steel core pipes are welded and then filled with aluminum under pressure. As a result, the coolant comes into contact only with steel, without touching aluminum surfaces. This saves the radiator from corrosion and gives it increased strength. Well, the shaped body increases heat transfer performance.
They also make radiators whose core is made not of steel, but of copper. This is a real salvation for those autonomous heating systems where antifreeze is added to the water. After all, such a coolant will quickly destroy steel pipes.
Semi-bimetal
A semi-bimetallic radiator has a core consisting of two metals. The vertical channels in it are reinforced with steel elements, but the horizontal ones are reinforced with aluminum. Due to the increase in the amount of aluminum in the product, the heat transfer of the radiator increases. However, hot water with a high alkaline content (in central heating) coming into contact with this aluminum causes corrosion. And one more thing: different thermal expansion of aluminum and steel core parts can cause their displacement, leading to instability of the radiator.
As a rule, bimetallic radiators are installed in apartments with a central heating system. There are 2 big problems in such systems - high pressure with periodic surges and poor-quality coolant. Both will have a fairly large negative impact on semi-bimetallic radiators.
Radiator design features

The battery is a separate heating device that contains elements with internal channels for the movement of energy carriers. Heat is removed by convection, radiation and heat transfer.
Sectional types allow you to increase the heating area by adding elements. Panel installations cannot be changed in shape, which is taken into account when calculating and installing the system. The accompanying passport indicates the temperature criteria for the operation of the device, operating pressure parameters, and heat transfer.
Radiator section
The cross-sectional structure of a heating battery consists of a metal pipeline in the form of combined horizontal collectors through which water passes. The channels are connected using small-diameter vertical tubes, and the entire system is housed in a housing made of cast iron, steel or aluminum. The separate sections are screwed together.
Radiators serve to heat the room, so the design of the devices affects the quality of heat exchange. The material of the heat exchanger and housing plays a role, so bimetallic options are used, including 2 types of materials.
Radiators must be able to be cleaned periodically, because... scale deposits on the inner surface reduce heat transfer.
Manufacturers
Among the many brands, the following brands have proven themselves well:
Lideya (Russia). This manufacturer has received many positive reviews, as all of its products are of high quality finish. The radiator panels are coated with a unique two-layer varnish, and the devices can operate in one-pipe or two-pipe heating systems.
- Biasi S.p. A. (Italy). The radiators of this company are created using the latest technologies, so their heat transfer is high and the rooms are heated instantly. The devices can also operate at low temperatures; their operating pressure limit is 9 bar.
- Korado (Czech Republic). Batteries have either one, two or three panels. The main features of the products are their wide range of colors, small volume of coolant, and convenient brackets. The pressure limit reaches 8.7 bar, and the water heats up to +110 C.
Connecting the radiator yourself
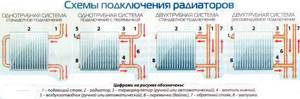
In the multi-apartment sector, the batteries are mounted on one side of the room. The radiator is connected using several methods depending on the pipe layout.
Diagonal or cross connection is used. The underwater pipe is connected to one side of the battery at the top, and the outlet pipe is connected to the other side at the bottom. This scheme is relevant for installations with a large number of sections of considerable length.
The bottom connection involves connecting the inlet and outlet from the radiator from below to two pipes on both sides of the heat exchanger. The scheme is characterized by low efficiency, but this option cannot be avoided if the heat supply system is located in the floor.
Aluminum radiators [ edit | edit code ]
Aluminum radiators today are considered the most efficient due to the high thermal conductivity of aluminum and the increased surface area of the radiator due to the protrusions and ribs. Almost all modern radiators designed for operation in central heating systems have an operating pressure of more than 12 atm, and a pressure test pressure of more than 18 atm.
The advantages of aluminum radiators include lightness, small size, high operating pressure, maximum level of heat transfer [ source not specified 2672 days
], large cross-sectional area of the intercollector tubes.
A significant disadvantage of aluminum radiators is the corrosion of aluminum in an aqueous environment, which is especially accelerated by contact of two dissimilar metals or the presence of stray currents in the heating network [ source not specified 2672 days
] .
Aluminum is an active metal, and if the oxide film covering its surface is damaged, then upon contact with water the latter decomposes with the release of hydrogen. If the heating device is hermetically sealed, the increasing gas pressure can cause the radiator to rupture. This phenomenon is combated by applying a polymer coating to surfaces in contact with water, which also improves anti-corrosion properties, allowing the use of coolants with a pH level from 5 to 10; reduces hydrodynamic resistance, prevents blockages and sticking. If the radiator does not have an internal polymer coating, turning off the taps on the supply pipes is prohibited [ source not specified 2672 days
] .
Aluminum radiators are most often divided into three main types: cast with solid sections, extruded with a mechanically connected set of sections, and combined, combining the qualities of both of these types. For work in conditions of high [ what?
] operating pressure, bimetallic radiators made of aluminum and steel are used.
Solid aluminum radiators [ edit | edit code ]
These radiators are structurally composed of profiles made by extrusion and connected to each other by welding. The aluminum used in them does not require any additives and therefore retains its ductility; Accordingly, external shock impacts and internal water hammer do not cause chipping of the ribs and cracking of such radiators. The absence of intersectional gaskets in such radiators gives them strength and reliability, and with an internal polymer coating, their durability can exceed that of cast iron radiators [ source not specified 2672 days
] . However, since their design is non-demountable, they cannot be expanded during operation.
Sectional aluminum radiators [ edit | edit code ]
Such radiators structurally consist of sections made by injection molding, which are connected to each other using threaded connecting elements (nipples); the intersection joint is sealed using gaskets made of paronite, high-temperature silicone or other materials. Sectionalization provides the opportunity to expand the radiator during operation or replace a damaged section, however, the presence of intersectional connections has a negative impact on reliability; In addition, the inner surface of the sections is characterized by greater roughness.
Oil radiators [ edit | edit code ]
The oil radiator consists of a sealed housing filled with mineral oil, in which an electric heater is located. The heat from the latter is transferred to the oil, then to the housing, the temperature of which does not exceed 60-70 °C, and from it to the surrounding air. Using oil as a coolant eliminates the possibility of rust. In heating systems where water is used for heat transfer and corrosion of metal parts may occur after the end of the heating season, moisture is removed by blowing with dry compressed air.
Baseboard heating
The shape of baseboard heating resembles old-style plate radiators - these are two pipes with a large number of thin plates. The difference is that these thin pipes, usually copper, have such a small height and width that they are hidden behind a high plinth of a special shape (open at the top). Due to the high heat transfer coefficient of copper, the power of these small radiators is high, and it is gained thanks to the length - even along the entire perimeter of the room.
In addition to invisibility, baseboard heating has another advantage - most of the heat is transferred not by convection, but in the infrared range - from heated walls. A flow of warm air rises along the walls, warming them up. When walls heat up, they begin to emit heat, which our body perceives as more comfortable. Disadvantages of this system
Baseboard heating is almost invisible

The disadvantages of baseboard heating are its demands on the coolant and thermal conditions (it cannot be overheated), low operating pressure (up to 10 atm). All this suggests that such systems can only work in individual heating, and with boilers controlled by automation.
Cast iron radiators.
If we talk about cast iron radiators, they are the oldest type of heating devices based on water circulation. And, speaking frankly, this type of radiator has not yet surpassed others in terms of characteristics. Modern cast iron radiators, thanks to new technologies and design, have a very attractive appearance. The reduced volume of sections, and in connection with this, a decrease in the volume of coolant, makes it possible to control the heat transfer of modern cast iron radiators.

This type of radiator is the most durable and corrosion resistant, with a service life of 50 years or more. They also tolerate coolant of any quality well. Thanks to the radiation of the heat flow of cast iron radiators, the room is evenly heated throughout its entire height, which has a positive effect on human health.
The working pressure of cast iron radiators is 9 atm, and the test pressure is 15 atm. Due to their low hydraulic resistance, radiators of this type are ideal for heating systems with natural circulation.
Thus, the positive characteristics of cast iron radiators include the following:
- high thermal conductivity;
- portability of all types of coolants;
- resistance to high pressure in the heating system;
- low price;
- operability even with contaminated coolant or increased aggressiveness.
Disadvantages of cast iron radiators
- heavy weight;
- good thermal inertia (long heating and long cooling), which eliminates and complicates the use of automation;
- difficulties when cleaning the radiator from dust;
- rough surface (this disadvantage is absent in modern radiators);
- requires pulling of intersection connections before installation;
- due to the large volume, more coolant is required;
- expensive and labor-intensive installation;
- high thermal inertia.
Aluminum
Aluminum heating radiators are made not from pure aluminum, but from an alloy based on it. This metal was not chosen by chance, as it has one of the highest heat transfer coefficients - 4-4.5 times better than cast iron and 5 times better than steel.
Table with thermal conductivity coefficients of different metals
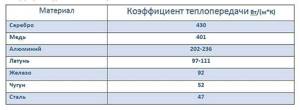
That is why aluminum radiators are distinguished by their high power (180-190 W per section), no less high heating rate and low inertia. They work very effectively in tandem with thermostats, allowing you to maintain a stable temperature with an accuracy of one degree. The advantages of aluminum radiators include their low weight (one section weighs 1.5-2 kilograms), which makes delivery and installation easier. Another positive point is that the shape is designed so that it has a large cross-section of channels for the coolant (slightly smaller than that of cast iron “accordions”). This is good, since there is a low probability that these channels will become clogged and the radiator will stop heating.
Now about the disadvantages of aluminum radiators. They are related to the properties of aluminum. As you know, it is a chemically active metal. It actively interacts with most of the chemical table, and reacts especially violently with copper. And in modern heating systems, copper parts are often found. Such a proximity threatens the rapid release of copper parts of the system and system, as well as increased gas formation. They have learned to deal with gases - they install automatic gas vents (valves) in systems, and they save copper by not placing it close to aluminum appliances. The process, of course, is still going on, but not with such intensity.
Aluminum radiators look modern

The chemical activity of aluminum also manifests itself in demands on the quality of the coolant. Not in the sense of its contamination, but in the sense of its acidity. Aluminum radiators work normally in systems with coolant acidity no higher than 7 (Ph 7).
The softness of aluminum is also not very good for the operation of the heating system. The alloy from which heating radiators are made contains additives that increase its hardness, but still, they do not work in high-pressure networks. Typical operating pressure is 8-16 atm depending on the type and manufacturer.
Based on all of the above, there appears to be an area in which aluminum radiators will be the best. These are individual heating systems with boilers controlled by automation. They also do well in apartments, but only in small buildings (up to 10 floors), in which coolant with Ph 7-8 circulates.