Properties
The exact physical characteristics of modern polystyrene greatly depend on how it was produced, but in general, when they talk about simple polystyrene without any specifications, they mean a material with very specific parameters. Its density is not the highest (1060 kg/m3), but the material does not have a specific melting point - already at 60 degrees above zero it begins to lose its shape, at 105 it can spontaneously ignite, and when heated to 200 degrees, the destruction of its chemical structure begins.
The molecular weight of the substance is also by no means specific and strongly depends on the method of producing polystyrene - it usually ranges from 50 thousand to 300 thousand, although emulsion options sometimes demonstrate significantly higher values. The solubility of polystyrene is significant in a number of substances, including its own monomer, as well as acetone, aromatic hydrocarbons and esters.

Polystyrene has pronounced dielectric properties that do not change regardless of the environment. This material is also practically indifferent to the destructive effects of acids and alkalis, salts, and alcohols. We have already listed above the substances that can still dissolve it, and it also oxidizes, halogenates, nitrates and sulfates.

In its original form, without additional coloring, polystyrene (at least its block variety) is not only colorless, but also transparent. The structure practically does not retain visible light, transmitting 90% of its amount, and this allows the use of such material in the manufacture of optical glasses. At the same time, ultraviolet and infrared radiation do not pass through polystyrene surfaces so reliably.

If we consider the properties of polystyrene as the advantages that make it so popular in various fields, first of all it is worth highlighting the following important points.
- Combination of low cost and ease of processing. At its price, polystyrene can be considered one of the main engines of modern civilization, given its properties. It is not for nothing that today so many products are produced with the direct participation of this material - there is simply no alternative to it.
- Good chemical resistance. Most substances that can get on a polystyrene surface in everyday life do not pose any danger to it - this is great news for manufacturers who want to produce products that are durable. Moreover, in a chemical laboratory, having an impressive set of reagents at hand, dissolving polystyrene is not difficult.
- Toxicity is within relatively safe limits. Polystyrene emits relatively few harmful fumes and from an environmental point of view, with certain reservations, is considered harmless. At least, experts do not put forward any restrictions regarding the use of polystyrene materials inside residential premises, and even dishes can be made from polystyrene.
- Wide range of applications. Due to its qualities, ease of processing and coloring, polystyrene can be used as a raw material for the production of anything.
With all the advantages of polystyrene, it also has disadvantages, and although there are not many of them, sometimes they play a very significant role.
Advantages of polystyrene foam
In a number of situations, foam plastic has no alternatives , which is due to its unique properties.
- Little weight . The manufacturing technology of expanded polystyrene involves subsequent cooling of polystyrene, which accounts for only 2% of the structure of the finished product, and the rest is occupied by air bubbles. This feature makes polystyrene foam boards so light: their weight is so small that even a child can hold them in their hands. It is a well-known fact that the weight of polystyrene foam is more than comparable to water. For this reason, if you throw him into water, he will not drown. This feature ensured its distribution as buoys, giving hints about places where the depth reaches its maximum levels.
- Other advantages of expanded polystyrene include the absence of problems in processing and installation. But at the same time, it is necessary to gain an understanding of the technology for gluing slabs to a specific surface and strictly follow the requirements of the instructions.
- A significant advantage of polystyrene foam is its high resistance to external factors. This material is neutral to the effects of sunlight, sudden temperature fluctuations, is frost-resistant, and is also resistant to high atmospheric pressure. It was these qualities that ensured its distribution as a building material used in the construction of residential buildings and finishing work.
- It is also worth mentioning such a parameter as heat capacity. It is no coincidence that it is widely believed that polystyrene foam is able to provide the best level of thermal protection. This material also has a low coefficient of thermal expansion: foam boards remain stable at operating temperatures in the range from - 180 to + 80 degrees. When working with large-format blocks, they are most often laid on the walls of buildings, which significantly increases the heat-saving characteristics of the house.
- The ability to effectively withstand external impact noise and create structures of complex configuration, which is practically realized through the use of solutions based on cement, gypsum and mastic.
- Foam boards are safe to use in construction in terms of fire safety. Therefore, for buildings where such a threat is particularly high, this material seems to be the best choice. Although he cannot eliminate the fire, he will still prevent its spread and even be able to reduce it.
- Plates of this material have a significant service life.
- In addition, they demonstrate neutrality to many chemicals. This material is absolutely environmentally friendly, does not generate dust and has no unpleasant odor. The material is absolutely safe for health, since the main components used for its production are gases and substances that do not harm the environment and humans. The boards do not contain freon compounds that can have a destructive effect on the ozone shell.
Properties of expanded polystyrene
Water absorption
The correct technology for insulating walls with penoplex outside the house and how thick should the insulation be?
Colony of bacteria on EPS
Expanded polystyrene is able to absorb water upon direct contact. The penetration of water directly into plastic is less than 0.25 mm per year, so the water absorption of polystyrene foam depends on its structural features, density, manufacturing technology and the duration of the period of water saturation. The water absorption of extruded polystyrene foam, even after 10 days in water, does not exceed 0.4% (by volume), which determines its widespread use as insulation for underground and buried structures (roads, foundations).
Vapor permeability
Expanded polystyrene is a low vapor permeable material.
A feature of the vapor permeability of expanded polystyrene is that it does not depend on its degree of foaming and the density of expanded polystyrene and is always equal to 0.05 mg/(m*h*Pa) [ source not specified 2606 days
], which is not equivalent to the vapor permeability of mineral wool (0.55 mg/(m*h*Pa)).
Biological resistance
Despite the fact that polystyrene foam is not susceptible to the action of fungi, microorganisms and mosses, in some cases they are able to form colonies on its surface.
Mealworms can eat and digest polystyrene.
Insects can settle in polystyrene foam, birds and rodents can make nests. The problem of damage to polystyrene foam structures by rodents has been the subject of numerous studies. Based on the results of tests of polystyrene foam on gray rats, house mice and voles, the following was established:
- Expanded polystyrene, as a material consisting of hydrocarbons, does not contain nutrients and is not a breeding ground for rodents (and other living organisms).
- In forced conditions, rodents act on extruded and granulated polystyrene foam just like any other material, in cases where it is a barrier (impediment) to access to food and water or to satisfy other physiological needs of the animal.
- Under free choice conditions, rodents interact with polystyrene foam to a lesser extent than under forced conditions, and only if they need bedding material or there is a need to grind down their incisors.
- If there is a choice of nesting material (burlap, paper), polystyrene foam attracts rodents last.
The results of experiments with rats and mice also showed a dependence on the modification of polystyrene foam; in particular, extruded polystyrene foam is damaged by rodents to a lesser extent.
Durability
One way to determine the durability of expanded polystyrene is to alternate heating to +40 °C, cooling to −40 °C and aging in water. Each such cycle is taken to be equal to 1 conventional year of operation. It is stated that the durability of polystyrene foam products according to this test method is at least 60 years, 80 years.
Solvent resistance
Expanded polystyrene has little resistance to solvents. It is easily soluble in the original styrene, aromatic hydrocarbons (benzene, toluene, xylene), chlorinated hydrocarbons (1,2-dichloroethane, carbon tetrachloride), esters, acetone, carbon disulfide. At the same time, it is insoluble in alcohols, aliphatic hydrocarbons and ethers.
What foam sizes should you choose?
It all depends on your needs.
For example, if you decide to insulate the walls of your house with polystyrene foam, then sheets measuring 1000×1000 mm and 1000×500 mm are suitable for solving this problem. The optimal thickness is mm.
Usually they buy sheets of 1000x1000 mm. And to fill the remaining areas, the existing sheets are cut into two parts:
You can also buy the required number of sheets measuring 1000x500 mm for these purposes. But this is in cases where the walls are smooth, without numerous elements that will prevent the laying of entire sheets. Otherwise, you will still have to frequently adjust the width of the sheets.
That is why many people buy polystyrene foam with dimensions of 1000×1000 mm to insulate the walls of their houses. And during the installation process, they are adjusted to the required dimensions (the sheets are cut into pieces). This material is easy to cut, so everything is simple here.
Also, when choosing, consider the cost of the sheets. For example, it may turn out that buying 1 sheet of 1000x1000 mm in size will be more profitable than two sheets of 1000x500 mm.
If you decide to buy expanded polystyrene 2000×1000 mm, then keep in mind that such sheets may be more difficult to install. It is often easier to install two 1000x1000mm sheets than one 2000x1000mm sheet. Of course, a lot depends on what purposes you need this material for.
In general, now you know what sizes of foam there are. We hope that you have already made your choice.
Application area
Extruded gray polystyrene foam has a wide range of applications. Mainly used for insulation work. The scope of use is limited only by temperature indicators (not higher than 75°C). The material can be laid in damp places, in the ground.

Typically, the scope of use is limited only by financial capabilities. The high cost makes it impractical for use in many places. In places where there is no need for high technical characteristics, ordinary polystyrene foam is used instead of PPS, reviews of which are also positive, in order to save money.
Used for insulation:
- concrete or wooden floors;
- walls indoors or outside the building. Compatible with any material;
- wells. Often concrete rings are coated with material for additional protection;
- blind areas;
- surface of the earth. To prevent destruction of the structure, paint is applied. Even a thin layer will not allow the composition to deteriorate.
In addition to the listed areas, the material is used in road construction. Included in many refrigeration units as extruded insulation. Used in agriculture. Roofs and underground floors are insulated with expanded polystyrene. One of the promising areas is the production of sandwich panels.
Technical characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam
The material has some of the highest technical characteristics on the market of insulation products. Any gas has a much lower thermal conductivity than solids. For air, the figure is 0.026 W/m*oC. Extruded polystyrene foam is an air mixture of approximately 90%. It has a thermal conductivity of 0.03 W/m*oC. Almost like air, which means heat is retained perfectly.
The material is produced with different densities. Manufacturers offer from 25 to 47 kg/m3. The higher the number, the greater the strength. As the density increases, the strength increases from 20,000 to 50,000 kg/m2.

Water is poorly absorbed by polystyrene foam. In about a month, one tile can absorb about 0.4% of its own volume if it is completely immersed in water. Further, the percentage of absorbed liquid does not increase, but stops. Vapor permeability is minimal. It is 0.0128 Mg/(m*h*Pa). Often companies specializing in repair work suggest not using vapor barriers, limiting themselves to using only polystyrene.
The insulation is able to withstand temperatures ranging from -50 to +75°C. Its use is possible in almost any climate. The flammability is high, the class varies depending on the addition of additional substances, from G1 to G4.
Some models have a special recess along the edges. Made to increase the tightness of the slabs by insulating the seams. This innovation prevents cold layers from forming between the elements, ensuring complete heat retention.
Adhesive for polystyrene foam
What is the best way to insulate the walls of a house from the outside?
Today, the market for adhesive compositions is represented by such manufacturers as Ceresit, Knauf, Technonikol and others. The glue must have the following properties:
- water resistance;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- high adhesion force;
- no runoff from the surface;
- no toxicity.
A distinctive feature of PPS is its poor resistance to some chemicals, therefore the adhesive should not include:
Fastening slabs to walls can be done using:
- polyurethane glue;
- dry mixtures.
Polyurethane adhesive has a high level of adhesion between the insulation and the base and is easy to use.
Glue made from a dry polymer-cement mixture is flexible and hardens quickly. It has a high level of adhesion to the surface. The mixture is diluted with water in a ratio of 1 kg of mixture per 0.24 liters of water.
Fastening polystyrene foam sheets only with dowels is less effective than first fastening them with glue, and then fixing already glued polystyrene foam sheets with dowels.
By using glue for PPS, greater efficiency can be achieved during insulation than with the mechanical method of fixing the slabs.
The “wet facade” insulation technology with polystyrene foam is identical to the “wet facade” insulation technology with polystyrene foam. You can read more about this in the article “Insulation of facades with polystyrene foam technology.”
In conclusion, we can say that expanded polystyrene is the best material option for insulating buildings. It is not susceptible to precipitation and aging and lasts up to 50 years.
For instructions on using TechnoNIKOL adhesive foam for polystyrene foam boards, watch the video:
Technical characteristics overview
There are different brands of polystyrene foam, each of which has its own set of properties and parameters. Based on this information, a choice should be made.
Thermal conductivity index
Closed cells represent the structure of the foam plastic, due to which this type of insulation acquires the ability to retain heat in the room. The thermal conductivity coefficient is: from 0.033 to 0.037 W/(m*K).
Due to the low thermal conductivity of the insulation, a high degree of energy saving is ensured.
Insulation is considered effective if the value of this parameter is no more than 0.05 W/(m*K). There are more effective materials, however, the average characteristics of polystyrene foam allow it to be successfully used to this day.
Soundproofing qualities, wind protection
The best material for protection against extraneous noise is a material that has the following technical characteristics: low thermal conductivity and at the same time the ability to allow air to pass through. Porous foam fits these criteria. This means that this type of insulation does an excellent job of protecting the object from noise.
Moreover, the greater the thickness of the sheet, the better the soundproofing qualities of the material. If you need to protect an object from the wind, then foam plastic will successfully solve this problem, since it consists of many closed cells.
Moisture absorption
The ability of this type of insulation to absorb water is quite low, which allows it to be considered non-hygroscopic. The moisture absorption rate with constant contact with water throughout the day corresponds to 1%.

The material is indifferent to moisture and practically does not absorb it.
This is slightly more than that of penoplex (0.4%), but also less than that of most of some other analogues, for example, mineral wool. Due to its low hygroscopicity, the service life of the foam is significantly extended, as the risk of mold or mildew formation is reduced.
Temperature
The insulation in question does not change its properties with a significant increase in temperature (up to 90 degrees). Low values also do not have a detrimental effect on this type of material, so it is used, in particular, for thermal insulation of external walls. But during installation using adhesive, it is recommended to observe the temperature regime: not lower than +5 and not more than +30 degrees.
Influence of external factors
These include: temperature changes, wind load, rain, snow and any mechanical source of pressure. The strength of the foam sheet is low under the influence of the last of the factors considered.
Due to its thermal insulation characteristics, polystyrene foam is widely used for insulating walls, roofs, ceilings, and balconies.
This is due to its low weight and large-cell structure. Moreover, the thickness of the material practically does not change the situation. If we compare it with penoplex, this option has high strength characteristics.
Degree of resistance to chemicals and microorganisms
When in contact with a number of substances, the properties of the foam do not change, these include: salt solutions, alkali, acid, gypsum, lime, bitumen, cement mortar, some types of paints and varnishes (silicon-based and water-soluble compositions). It is necessary to avoid contact of polystyrene-based insulation with the following substances: solvents, acetone, turpentine, gasoline, kerosene, fuel oil.
Given the low hygroscopicity and closed structure of the material, foam plastic does not provide suitable conditions for the proliferation of harmful microorganisms.
Fire safety
The insulation belongs to highly flammable materials (flammability categories G3 and G4), however, its burning time, provided that the ignition source is eliminated, does not exceed 3 seconds.

If you choose polystyrene foam insulation, be aware that it does not resist fire well.
It would be a misconception to consider such a material completely safe, but it is still often used, due to the release of less energy during combustion, as well as spontaneous attenuation.
We carry out the preparation
Which foundation is better for a frame house?
First you must carefully prepare the walls
This is recommended in warm weather, however, more importantly, the walls must be dry and not damp! If it rained, wait at least a week, after which you can start
First stage. External walls
Start by clearing the exterior walls of anything that is crumbling or peeling. If the walls were painted, then remove the paint; if they are covered with lime, clean it off. Swollen areas of plaster/tiles must be beaten off - let only what is held strong enough remain. This way the polystyrene foam boards will be fixed as efficiently as possible!

After this, level the walls (differences should be no more than 1 centimeter per square meter). If there are larger pits/protrusions, smooth them out or level them with plaster mortar. The smoother the walls are, the easier it will be for you to work with them.
Second phase. Primer
Is it necessary to prime the walls at all? No, if after running your palm over them it remains clean. In all other cases, a primer is required so that the glue adheres better to the surface. It will take a little time, and the procedure itself is not complicated, but the benefits are really noticeable!

As for the choice of composition, in this case any primer for facade work will do. For example, “Ekomis”, “Ceresit”, “Tokan”. The mixture can be diluted or not diluted - it depends on the specific manufacturer and form of release. To apply, use a sprayer or brush. In the second case, the application will be of better quality.
Third stage. Preparing insulation
Make sure that the surface of the polystyrene foam boards is not so smooth. If you use ordinary polystyrene foam, the structure of which is looser, then the material does not need preliminary preparation. Make scratches on the EPS boards, otherwise they will simply fall off from the adhesive.

Take a spiked drywall roller and carefully roll it in all directions. Another option is to use a wire brush to create grooves. As for softer methods, they simply do not work in this case. The procedure is easy, but requires a lot of time. It is advisable to prepare the surface of the slabs before installation on the walls. And if the heat insulator is laid in two layers, then the slabs must be processed for both layers.
Fourth stage. Ebbs, slopes, window sills
All these elements must be installed before installing the insulation material. In this case, the thickness of the heat insulator and finishing coating must be taken into account. And if window sills and everything else are already there, they should be replaced.

Main construction areas where polystyrene foam is used
Expanded polystyrene can be used for external and internal work, in the construction of panel houses and in monolithic construction, for insulating load-bearing structures, etc. Its scope of application is simply enormous, so let’s look at individual areas in more detail.
Foundation thermal insulation
The foundation is the basis of the building, and the durability of the building and thermal comfort depend on it. Therefore, the issue of foundation insulation should be raised first. Most often, foam plastic is used as permanent formwork, which allows saving on reinforcement and concrete mix. Also, with the help of expanded polystyrene, reliable protection of the foundation is provided from freezing, which can adversely affect the integrity of the structure. In combination with waterproofing, foam creates a very reliable barrier against the cold.
Floor insulation
In this case, polystyrene foam is used not only to provide thermal insulation, but also to reliably dampen impact noise. 50mm thick foam plastic slabs are laid on the waterproofing layer. After this, the seams are sealed and the flooring is laid.
Thermal insulation of walls
As a rule, walls are insulated from the outside. If it was decided to insulate from the inside, then the foam plastic should be glued to the slats so that there is a minimum layer of air between it and the wall. This will prevent condensation from appearing on the walls. When polystyrene foam is exposed to ultraviolet rays, the material is destroyed. Therefore, when insulating the outside, a layer of glue, for example CM11, is applied to the foam plastic. Thus, when insulating one should take into account not only the price of polystyrene foam
, but also for additional finishing materials.
So, it is clear that it is not in vain that such a request as buy polystyrene foam Moscow
so popular in search engines. After all, this material can be used at almost any stage of building construction.
Penoplex "Roof" - properties and characteristics
Penoplex insulation of the “Roofing” series is a renamed material “Penoplex 35”, which is recommended for use in insulating pitched and flat roofs of any design. The use of the “Roof” series makes the further operation of the roof as simplified as possible, since the reliability and long service life of the insulation minimize the possibility of repairing the roof surface. The popularity of this innovative insulating material is also due to the fact that greenhouses and summer gardens can be built on such a surface - such trends are now in fashion. Penoplex can withstand such high loads that it doesn’t care about soil loads of up to several tons. Characteristics of the foam insulation brand “Roof” are in the table below:
“Comfort” is a universal brand of heat insulator
Scope of application
Expanded polystyrene is used as an element for insulating various objects. This could be, for example, water pipes.
It is used to work with:
- window and door slopes;
- roofing;
- floor;
- walls.
High-density polystyrene foam is required where high demands are placed on the quality of structures. The use for pipe insulation is economically justified. They take block polystyrene foam so that in case of damage the pipe can be easily accessed. To do this, remove a certain area of the protective coating.

Expanded polystyrene is actively used for pipe insulation
Expanded polystyrene is actively used in the construction of transport routes. It is used because it reduces the vertical load on the road surface during the construction of structures. It is also used in the production of SIP panels. We can say that its scope of use is almost unlimited. It has a low density and is therefore not sufficiently resistant to mechanical damage. This must be taken into account when choosing it as a material for work.
Release forms
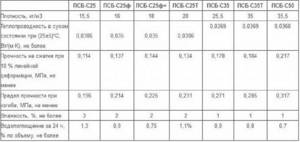
The density of the material is the determining factor when dividing foam into grades. It directly affects strength and thermal conductivity. The technical characteristics of individual brands will help determine the scope of use of the material:
- The PSB-S 15 marking belongs to slabs with the lowest density, which is 15 kg per m3. Such expanded polystyrene boards are extremely lightweight and are used for insulating cabins and construction trailers, i.e. in places of temporary residence of people.
- The most popular brand is PSB-S 25, where the density, accordingly, is 25 kg/m3. Scope of application: insulation of building facades, floors, and as roof insulation.
- Polystyrene foam PSB-S 35 has a density of 35 kg per cubic meter. The high technical characteristics of expanded polystyrene with marking 35 are in demand in the production of reinforced concrete structures and sandwich panels.
- Polystyrene foam 50 has an extremely dense structure. Due to this, the slabs are actively used in arranging flooring in refrigerated warehouses and road construction.
Analyzing the tables with technical characteristics, we can conclude that it is advisable to purchase polystyrene foam boards for the purpose of insulating walls with a density of 25 and 35 kg/m3. Moreover, for internal insulation a density of 25 will be sufficient, and for finishing the outside it is better to use foam plastic 35.
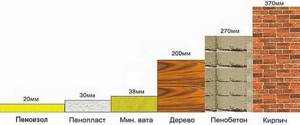
When choosing a material for wall insulation, the thickness of the foam matters. It is impossible to give exact recommendations. The choice depends on a number of related factors, which include:
- Climatic conditions of the region where the building is located.
- Material used to construct walls. Often the walls of a building consist of several layers, differing in their technical characteristics. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the total indicator.
- The density of the polystyrene foam board, which is determined by the marking.
Usually, due to a combination of factors, if it is necessary to insulate internal walls, 50 mm foam plastic is used; the use of 100 mm foam plastic is more in demand for external work.

Basic properties of polystyrene plastics
| Properties of polystyrene | PS | OOPS | ABS | MSN |
| Density, kgm3 | 1050 | 1060 | 1040 | 1040 |
| Melting point, C | 190-230 | 190-230 | 210-240 | 205-220 |
| Breaking stress, MPa, at: | ||||
| Stretching | 35-40 | 27-56 | 36-60 | 90-100 |
| Bend | 55-70 | 55-60 | 50-87 | — |
| Compression | 80-100 | — | 46-80 | — |
| Elongation at break, % | 1,0-1,5 | 1,0-2,0 | 1,0-3,0 | — |
| Impact strength, kJm2 | 12-20 | 40-50 | 80-100 | 11-18 |
| Brinell hardness, MPa | 150 | 110 | 100 | 170 |
| Heat resistance according to Martens, C | 60-70 | 65 | 86-98 | 70-72 |
| Dielectric constant at 106 Hz | 2,5 | 2,7 | 2,4-5,0 | 2,9 |
| Tangent of dielectric loss angle at 106 Hz, x104 | 2-4 | 4-8 | 300 | 1,8 |
| Specific volumetric electrical resistance, Ohm∙m | 1015 | 5∙1013 | 5∙1013 | 4∙1014 |
| Electric power, MWm | 25-40 | — | 12-15 | 24 |
ABS plastic is a product of graft copolymerization of three monomers - acrylonitrile, butadiene and styrene, and the static copolymer of styrene and acrylonitrile forms a rigid matrix in which rubber particles up to 1 micron in size are distributed. An increase in impact strength is accompanied by maintaining at a high level the basic physical-mechanical and thermophysical properties (Table 1). ABS is opaque. Available in stabilized form as powder and granules. Used for the manufacture of technical products. In the ABS brand, the first two digits indicate the Izod impact strength value, the next two indicate the MFR (melt flow rate), the letter at the end of the brand indicates the processing method or special properties. For example, ABS-0809T is characterized by impact strength - 8 kJ/m2, MTR - 9g/10 min, and increased heat resistance (T). Copolymers of stinol with acrylonitrile (SAN), stinol with methyl methacrylate (MS) and stinol with methimethacrylate and acrylonitrile (MSN) are used in industry. Polystyrene is processed by all known methods.
Preparatory work
Insulating the facade with foam plastic begins with preparing the walls. Let's immediately say when it is better to start work - in the warm period of time. But the most important indicator is the humidity of the walls. They must be dry. After the rain, it is advisable to wait a week for dry, preferably windy, weather. After that you can start.
Preparation of external walls
Preparation for insulating the facade with polystyrene foam begins with cleaning everything that flakes and falls off. If the walls were covered with paint, it is removed, the lime is cleaned off. If there are swollen areas of plaster or tiles, they will be resurfaced. Only what holds tightly should remain.

Then it’s time to level the walls. It is very good if the insulation boards lie on the wall with their entire surface, without voids. But such walls are the exception rather than the rule, therefore unevenness of about 1 cm per square meter is acceptable. Protrusions and holes that are large in depth/height must be leveled - filled with plaster mortar (pre-primed) or cut off. The smoother the surface, the easier the work will be.
To prime or not
There is no need to prime only those walls; running your hand over them will leave your palm clean. If there are white marks, pieces of plaster, sand, etc., it is better to prime it. This will ensure better contact of the glue with the wall. The operation takes little time, is simple, requires little money, and has great benefits. So if you are doing the insulation of the facade with foam plastic or EPS “for yourself”, it is better to prime it.

Any primer is suitable for facade work. Normal companies are Ceresit, Master, Stolit, Kreisel, Tokan, Ekomix. The primer is diluted or not, depending on the release form and instructions, applied with a brush or spray. Spraying is faster and easier, but using a brush is better.
Preparation of EPPS
If you decide to insulate the walls outside with expanded polystyrene (EPS), its surface must be made not so smooth. Polystyrene foam has a looser structure and does not require preliminary preparation. You need to make scratches on the surface of the EPS, otherwise it will fall off from the glue.

Take a spiked roller, which is used to process drywall, and roll it well in all directions. The second way is to take a brush with metal bristles and make grooves with it. Softer methods don't work. The work is not hard, but it takes a lot of time. This must be done before you begin installing polystyrene foam on the walls. If the insulation is laid in two layers, it is necessary to process the sheets for both layers.
Finishing window sills, slopes, ebb
It is better to install all elements - window sills, slopes and ebb (drip) before installing the insulation on the walls. When installing, you need to remember that you will still have a significant thickness of insulation + finishing. If window sills and slopes have already been installed, they will have to be replaced - they will be too short. In order for everything to look organic and fit easily into the insulating pie, the elements must have the following dimensions:
- The window sill should protrude beyond the plane of the wall by 3-4 cm (more or less is not necessary). If the insulation thickness is 60mm, you will need a window sill 100-110mm deep (60mm insulation, 10mm finish, 30-40mm overhang). When installing a window sill, all voids must be filled. You can lay thermal insulation plates, fill the gaps with polyurethane foam and lay a window sill on top of it all, load it with something heavy and leave it for 3-4 hours.
- When separating the slopes, they should protrude beyond the plane of the existing wall (without insulation) by 1 cm. This will make it easier to connect it with the insulation. They sit it on glue (the same one that will be used when insulating the facade with foam plastic). There is another subtlety here: finishing the slopes requires insulation of a smaller thickness - 20-30 mm maximum. The thicker one will simply “climb” onto the glass (don’t forget about the presence of finishing layers, leave about 10 mm on them).
- Between the base and the insulation, a drip line is installed (also called a “drip cap”). This is a strip of galvanized steel with powder paint. It is mounted on the base with self-tapping screws or dowels (depending on the material of the base) in increments of 20 cm. Sold in pieces of two meters, during installation one piece overlaps the other by 10-15 cm. The ebb is necessary so that water flowing down the wall does not flow into the house, and merged into the street.
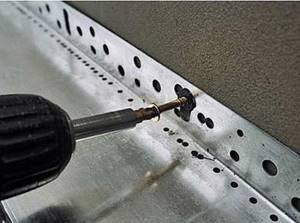
As you can see, the preparatory work before insulating the facade with foam plastic (polystyrene) also takes time. They are not complicated, but have a significant impact on the overall result.
Fire hazard of polystyrene foam
Fire hazard of untreated polystyrene foam
Unmodified polystyrene foam (flammability class G4) is a flammable material, ignition of which can occur from the flame of matches, a blowtorch, or from autogenous welding sparks. Expanded polystyrene does not ignite from a calcined iron wire, a burning cigarette or from sparks arising from a point of steel. Expanded polystyrene is a synthetic material characterized by increased flammability. It is capable of storing energy from an external heat source in the surface layers, spreading the fire and initiating fire intensification.
The ignition temperature of polystyrene foam ranges from 210 °C to 440 °C depending on the additives used by manufacturers. The ignition temperature of a specific modification of polystyrene foam is determined according to the certification class.
When ordinary polystyrene foam (flammability class G4) is ignited, a temperature of 1200 °C develops in a short time; when using special additives (fire retardants), the combustion temperature can be reduced according to the combustion class (flammability class G3). Combustion of expanded polystyrene produces toxic smoke of varying degrees and intensity, depending on the impurities added to the expanded polystyrene to reduce smoke formation. The smoke emission of toxic substances is 36 times greater in volume than wood.
The combustion of ordinary polystyrene foam (flammability class G4) is accompanied by the formation of toxic products: hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen bromide, etc.
For these reasons, products made from untreated polystyrene foam (flammability class G4) do not have approval certificates for use in construction work.
Manufacturers use expanded polystyrene modified with special additives (fire retardants), thanks to which the material has different classes of ignition, flammability and smoke generation.
Thus, with correct installation, in accordance with GOST 15588-2014 “Heat-insulating polystyrene foam boards. Technical conditions", polystyrene foam does not pose a threat to the fire safety of buildings. “Wet facade” technology (WDVS, EIFS, ETICS), which involves the use of expanded polystyrene as insulation in the building envelope, is widely used in construction.
Modified polystyrene foam for fire safety
To reduce the fire hazard of polystyrene foam during its production, fire retardants are added to it. The resulting material is called self-extinguishing polystyrene foam (flammability class G3) and is designated by a number of Russian manufacturers with an additional letter “C” at the end (for example, PSB-S).
On May 1, 2009, the new federal law FZ-123 “Technical Regulations on Fire Safety Requirements” came into force. The methodology for determining the flammability group of combustible building materials has changed. Namely, in Article 13, paragraph 6, a requirement appeared that excludes the formation of melt drops in materials with group G1-G2
Considering that the melting point of polystyrene is about 220°C, all insulation based on this polymer (including extruded polystyrene foam) from 05/01/2009 will be classified with a flammability group no higher than G3.
Before Federal Law 123 came into force, the flammability group of brands with the addition of fire retardants was characterized as G1.
Reducing the flammability of polystyrene foam in most cases is achieved by replacing the flammable gas for “inflating” the granules with carbon dioxide.
Composition and structure of the material
The main component of polystyrene foam is foamed polystyrene, and the finished product contains only about 2% of the polymer itself (by volume). The rest of the space is occupied by gas (natural or carbon dioxide), enclosed in closed polystyrene capsules or cells. The macrostructure of the material consists of granules with a diameter of several millimeters, compressed and then cut into conglomerates of various shapes.
The walls of the polymer capsules have minimal porosity, so almost no moisture gets into the gas cells. This keeps the density of the foam low and preserves its thermal insulation properties. To reduce flammability, a number of additives are introduced into the material to reduce the spontaneous combustion time (without an external flame source). This increases fire safety under short-term exposure to fire.