Concrete floors
Concrete floors on the ground do not provide a basement or space under the floor for ventilation.
Appearance of concrete floor
A classic floor on any soil consists of 10 layers:
Layers that protect against groundwater and distribute the load
- Compacted clay pillow. It is necessary to stop the rise of groundwater. If, after removing a layer of soil, you reach clay, then it must be properly prepared. The clay layer cuts off the upward penetration of groundwater.
- Sand pillow. Its purpose is also to prevent the ingress of groundwater and equalize the load on the ground. Sand weakens the capillary rise of water and evenly distributes the pressure of the underlying floor layers onto the ground. Any sand will do.
- Large crushed stone. This is a kind of drainage, its purpose is to make the base strong and distribute the load. It does not allow water to flow upward due to capillary properties. Crushed stone is used in fractions of 40–60 mm.
The first three layers should be arranged in exactly this order, each with a thickness of 10 cm in a compacted state. The layers must be compacted.

Layers of concrete floor
- Waterproofing layer (roofing felt or polyethylene film). It is placed directly on the crushed stone, and it serves both to protect the crushed stone from the concrete solution flowing into it from above, and as an obstacle to the penetration of water vapor into the concrete layer from below. The film is laid over a whole sleeve (without cutting) and placed on the walls, gluing the overlaps with tape.
- Rough screed 80 mm and thicker. For it you should take washed sand and small crushed stone (10–20 mm). Steel fiber is added to the solution or reinforcement is used. In order for the screed to be ready for the next stages of work, it must be kept for a certain time.
- Waterproofing layer (coating waterproofing, roll or film). If the first layers are laid correctly and efficiently, for waterproofing you can use roofing felt without powder in 1-2 layers or a film with a thickness of at least 120 microns. The waterproofing layer must be monolithic. If roofing felt is used, the overlaps are coated with bitumen mastic, and the overlaps of polyethylene film are taped.
- Insulation. The floor can be insulated with expanded clay, extruded polystyrene foam, or polystyrene foam. The thickness of polystyrene slabs and foam sheets depends on climatic conditions, but not less than 5 cm. Expanded clay is covered with a layer of 15 cm.
- Waterproofing. It is recommended to lay waterproofing over expanded clay or other insulation. This will protect the insulation from moisture from the upper layers and improve its thermal insulation properties. At this stage, a thick polyethylene film is used, which is laid in a continuous layer.
- The screed is clean. It can accommodate underfloor heating heaters (water heating circuits, cable mats or heating cable). A layer of finishing screed is poured 50 mm or more. It is reinforced using composite or steel reinforcement, and fiber is added to the solution.
- Finish coating. If all layers are completed in the specified order, any coating can be laid.
Use of water and electric heated floors
You can also insulate an earthen floor in a house with your own hands using water or electric heated floors. For water heated floors, thermal insulation slabs are laid on the ground in the basement of the house. Next, a masonry mesh is laid to strengthen the concrete pour, and pipes for the water-heated floor are laid. A concrete screed of at least 4 cm is poured and leveled on top.
In the case of an electric floor, it is worth taking care of high-quality waterproofing. To do this, any rolled waterproofing material, for example, roofing felt, is laid on the ground. Then slabs of thermal insulation material are laid, and a rough screed is made to level the surface. After this, a reinforced mesh is placed to strengthen the concrete screed and distribute heat evenly.
After installing a warm electric floor, the system is checked for functionality before screeding the floor. You can turn on the warm electric floor only after a month has passed from the day the concrete was poured - this is necessary so that the concrete sets evenly. The main advantage of electric and water underfloor heating systems is to constantly maintain the same comfortable temperature.
How to insulate a basement from excess moisture
The basement should be dry. If moisture seeps through the walls, all insulation efforts will not bring results. Another problem is condensation. Moisture, unable to find a way out of the basement, condenses on the walls and ceiling. Mold or mildew may appear.
In a humid environment, many insulating materials lose their characteristics and become useless. For example, wet mineral wool does not prevent cool air from entering the room.
How to properly insulate the foundation and basement to avoid excess moisture? It is very important to provide ventilation holes in the basement. When there is an influx of fresh air, moisture will be able to leave the basement
If there is high humidity in the basement, you can insulate its walls with insulation that does not react to moisture. You can use special equipment to cover the entire basement with a thin layer of insulating foam. This material instantly swells and forms a smooth surface that does not allow moisture to pass through.
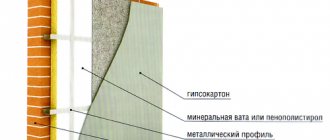
Mineral wool
Floor insulation using mineral wool
This fibrous, non-flammable material, along with the general advantages of thermal insulation materials, also has excellent sound insulation characteristics.
It effectively dampens vibrations from the ground to the floor and from the floor to the walls, which is especially important in technical and utility rooms. For thermal insulation, pressed mineral wool (mineral wool boards) is used.
They are durable and do not deform under the weight of building structures and pressure on the floor. The dimensions of the mineral wool slabs are 50 x 100 centimeters; one package is enough for a single-layer covering of 1-4 m2 of floor.
The main disadvantage of mineral wool is that it quickly absorbs moisture and releases it for a long time, so mineral wool slabs must be treated with a special composition that reduces their hygroscopicity.
Before finishing the screed, 1-2 layers of moisture-proof coating are additionally laid on the mineral wool slabs.
Technology of floor insulation on the ground
Thermal insulation of floors on the ground will be a completely pointless exercise in the case when the flooring itself is not carried out using technology. The design should be multi-layered:
The starting layer is the so-called “mother soil”. Its peculiarity is that the entire volume is concentrated inside the building structure and cannot be removed during construction. It only needs to be properly leveled and compacted using a special installation (vibrating plate).

- The layers of soil built by the embankment are up to 20 centimeters thick and are necessary in order to raise the height of the floors to the required level. Each subsequent layer requires compaction, hence the requirements for the maximum layer level - so as not to reduce the quality of compaction.
- A layer of coarse crushed stone (50 millimeters or more in size). The thickness of its backfill does not exceed 10-20 centimeters, then compaction is carried out. This layer is designed to make the soil as dense as possible, since when crushed stone is compacted, the soil experiences significant point loads.
- Leveling is carried out using a sand layer or a weak solution of cement and sand. In this way, the crushed stone surface is leveled, which allows you to create a fairly level base for laying insulation from moisture. When using sand, it must be moistened generously with water and compacted thoroughly.
- Steam and waterproofing layer. Its installation is designed to prevent an increase in humidity in the floor area and all living areas due to steam escaping from the ground. The importance of vapor and waterproofing in this design cannot be overestimated. Film coatings significantly extend the service life of the most important structural elements of a building - not only the floor, but also the walls.
- To insulate from water and steam, it is recommended to purchase special materials and only high quality ones. This can be a two-layer roofing felt coating or a modern membrane with a long service life. During installation, be sure to overlap the material on the walls and adjacent sheets by approximately 30 centimeters.
- The insulating layer will be discussed in detail below. A polyethylene film is most often laid on top of it, which serves as protection against the penetration of concrete mortar into the gaps between the insulation elements. If necessary, the heat insulation layer can be removed from under the screed with virtually no damage.

- The screed itself is one of the main components of the entire floor structure laid on the ground. It is mandatory to reinforce it, which allows you to correctly redistribute the loads exerted on the floor surface. The screed layer must be covered on top with a layer of lightweight concrete or a mortar based on cement and sand, at least five centimeters thick.
- The reinforcement element is most often a mesh with a cell side of five to seven centimeters and a rod thickness of two to three centimeters. If you plan to install a heated floor, the screed is made using a special method. The mesh is laid on top of the plastic film and the heat source tubes, laid in a special way, are attached to it. Special fibers are mixed into the screed solution, providing a greater degree of elasticity and strength properties when exposed to heat. The screed is divided into sections whose width does not exceed two centimeters. This technique allows you to avoid critical indicators of tension and cracking of the screed in the future.

Floor covering. Any type of finishing floor covering can be installed on top of ground-mounted floors. When installing a heated floor system, the range of choices narrows noticeably.
Choosing insulation that does not absorb moisture
You should study in detail the nuances of choosing insulating material for the floor on the ground. At first glance, the range of heat insulators suitable for installation under screed covering is quite large. But the variety of brands often hides the same type of insulation. According to the principle of operation, all heat insulators can be divided into two large groups. The first will contain those that are impenetrable to water and steam. In the second - materials that are able to absorb moisture and do not prevent the penetration of its vapor.

Insulation of a wooden floor
To find out which layer of the selected thermal insulation material needs to be laid for high-quality floor insulation, you can refer to SNiP number 02/23/2003, which contains all the necessary tables and thermal calculations.
For those who do not want to dive into the world of numbers and tables, I will give calculations on the thermal insulation material that I chose:
- for my son’s country house, located in central Russia, 12 cm of insulation is sufficient;
- for the northern regions of our vast country it is better to equip a layer 20 cm thick;
- Southerners are the luckiest; a house in Krasnodar or the surrounding area can be insulated with basalt mats 8 cm thick.
The thickness of the insulation layer depends on the climatic conditions of the area.
In fact, I can say that insulating a wooden house is quite simple, since its floors and interfloor ceilings are a system of support beams, which are covered with boards at the top and bottom. That is, you get these kind of containers that just need to be filled with insulating material.
However, as they say, the essence is in the details, so I’ll tell you in more detail and detail how to properly insulate the floor in a private house made of timber.
Thermal insulation of the floor in a house without a basement
When I designed and built the house, I decided against building a basement for several reasons that are not necessary to give here. This determines the technology that I will use.
So that you can gain more benefit from my story, I will outline the sequence of actions for the case when insulation occurs in a fairly old house that has been in use for a long time and the flooring has partially become unusable.
So, the instructions are as follows:
- First, I dismantle the baseboards and floorboards. If you plan to cover them again (the condition allows you to do this), I advise you to number the parts so that you can later assemble them in the same order.
Before insulation, you need to dismantle the floor boards.
- I inspect the support joists. If partial damage to the support beam is found, this area can be cut out and a new part can be installed. It can be screwed on the sides with additional boards and galvanized screws (to protect the fittings from corrosion).
The floor joists need to be inspected and damaged areas repaired.
- If the floor is not built on the ground, then a board is screwed to the bottom of the log, which will serve as the bottom of an improvised box for insulation. For this, I recommend using inexpensive edged boards, since no one will ever see them after finishing the work.
What about a wooden house?
Most often, the foundations for wooden houses are insulated with expanded clay or polystyrene foam. We pour expanded clay into a special formwork, mixing it with concrete. Foam boards can simply be glued to the foundation walls, providing waterproofing.
The simplest and most effective method of insulating the foundation of a wooden house is to spray polyurethane foam. No additional work or separate waterproofing is required. Using a special gun, we spray insulation onto all surfaces. Polyurethane foam dries instantly. It forms a smooth surface impenetrable to cold and moisture.
If polyurethane foam was applied to the outside of the building, it should be covered with other materials. The insulation is afraid of direct sunlight. We glue a mounting mesh onto the layer of polyurethane foam, onto which leveling plaster can be applied.
Types of insulation, their properties and working with them

Laying insulation on waterproofing
A wide variety of materials are used for floor insulation, but they all must meet certain technical conditions. The insulation should:
- It is good to keep warm and not lose its properties for many years;
- Absorb moisture as little as possible;
- Be durable, not sag, crack or break under the weight of the building and floor loads (this is especially important for technical premises - garages, hangars, warehouses, etc.);
- Have a low cost;
- Be comfortable to style;
- Be environmentally friendly, non-toxic and non-flammable.
The most common floor insulation materials today are polystyrene foam, extruded polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, mineral wool, foam glass, expanded clay and slag. The choice of insulation depends on the characteristics of the building and/or room, its purpose and material capabilities. Also, to insulate the floor on the ground, the “warm water floor” system is often used.
Let's briefly look at the insulating materials mentioned above.
Options for thermal insulation materials
The result of the work depends, first of all, on the quality of the materials. When assessing the positive qualities of thermal insulation and the thermal conductivity coefficient of different materials, one should not forget that natural and synthetic materials have different technical characteristics, on which the quality of work and the quality of the thermal insulation itself depend. Among the most popular materials today, it is worth highlighting insulation made from natural materials - mineral wool, expanded clay, glass wool. And artificial materials - polystyrene foam, extruded polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam. These insulation materials are quite widely represented on the market, however, in order to select the right material you need to know the basic characteristics of the material.
Expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene or polystyrene foam consists of granules bonded together during the manufacturing process. Density is a qualitative indicator of a material. The higher the density of expanded polystyrene, the higher its thermal insulation qualities. Expanded polystyrene is produced in slabs with a thickness of 20 to 50 mm. The main application is thermal insulation of buildings and communications. The material is lightweight and does not absorb water. However, among the disadvantages it is worth noting that mice often settle in the thickness of the foam. It is flammable, so you need to be careful when installing. To insulate the floor on the ground, material with a high density is used, low density is used for installation on walls and ceilings. For the floor, slabs with locking joints at the ends are used.
The attraction is low cost and availability. Most often used to fill voids under wooden floors.
Extruded polystyrene foam
This relatively new material is most often used to insulate the most critical areas, including the floor along an earthen embankment. Penoplex, unlike polystyrene foam, does not have a cellular structure consisting of individual granules. This is a material that is monolithic in structure and has a higher density compared to other materials. It is able to withstand large mechanical loads. The second important point is that it is chemically neutral, does not react with other materials and does not absorb water. This type of insulation is capable of withstanding 50 or even more freeze-thaw cycles and does not lose its characteristics and shape.
The cost of this material is higher than that of conventional polystyrene foam, but its service life is almost twice as long.
Polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is not yet used very often in thermal insulation of floors on the ground. Used as a sheet material, it has little mechanical strength, bends easily, and over time is prone to sagging under pressure. But the more modern sprayed polyurethane foam has every chance of becoming one of the most popular types of thermal insulation.
When installed, it forms a monolithic sheet of the required thickness that does not allow water to pass through. Over time, the material acquires good mechanical density and even somewhat resembles extruded polystyrene foam. Another advantage of sprayed polyurethane foam is its high adhesion; it literally fills all the cracks and adheres tightly to all surfaces.
Mineral slabs
Traditional natural materials such as basalt wool and glass wool can also be used in floor insulation. Both stone wool and glass wool are suitable for insulation work under a concrete screed. True, only of high density and subject to excellent waterproofing. The fact is that both materials tend to accumulate moisture over time. There will be nothing wrong with the mineral slabs themselves, they do not rot or deteriorate, but for concrete such a “wet” layer will create big problems.
Expanded clay
It has established itself as a reliable and popular insulation material. It can be used both for concrete pie and for insulation over a sand bed. The peculiarity of the application is to use expanded clay of the desired fraction and density. The second point is the need to lay a layer of waterproofing under the expanded clay, and it is advisable to pour a reinforced concrete screed on top.
Penoizol
Liquid foam plastic, also called penoizol, has been used for insulation in European countries for almost 80 years. Like other sprayed materials, it has excellent adhesion, so it fits perfectly on any surface. In terms of its thermal insulation properties, it can be compared with penoplex and expanded polystyrene.

Penoizol - floor insulation on the ground
A distinctive feature of this material is its excellent vapor permeability, therefore, when insulating a private house, it must be installed on reliable waterproofing.
Characteristics of foam plastics and expanded polystyrene
Despite the fact that thermal insulation made from polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene are very similar visually, the performance characteristics of the materials are different. In comparison with the main competitors - Ecowool and mineral wool, they look like this:
| Material | Expanded polystyrene | Styrofoam | Ecowool | Minvata |
| Density (kg/m 3 ) | 25 – 45 | 50 | 35 – 65 | |
| Hygroscopicity |
(group)
(%)
(W/m*S)
(Mg/m*h*Pa)
(Class)
These materials do not have the same structure, which also affects the scope of application:
- ecowool is a free-flowing product, so it cannot be used inside a wet screed, but it is easy to pour it into a wooden floor on your own without the involvement of professionals;
- mineral wool - ideal for ceilings on beams, additionally protects structures from fire, partially absorbs moisture, reducing the load on lumber;
- polystyrene foam - not suitable for floors in principle;
- expanded polystyrene is the best insulation for floors on the ground.
Important! Ecowool completely fills the volume provided to it, does not shrink, and is not tolerated by insects and rodents. Mineral wool has elasticity and adheres tightly to surfaces. Polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene do not have such properties; seams and joints must be additionally filled with polyurethane foam with similar properties. Which increases the labor intensity of the work.
Lumber Compatibility
With overlapping wooden beams, everything is exactly the opposite:
- extruded polystyrene foams and polystyrene foams are harmful here, as they interfere with the natural regulation of humidity by wooden structures;
- mineral wool and cellulose chips - Ecowool, on the contrary, help wood in this process, partially absorbing moisture, then evaporating it.

For flooring on beams, insulation with basalt or ecowool is more suitable.
Important! The practice of operating frame cottages, in which foam plastic was used inside the walls and floors, shows that repairs of the floor along the beams and other elements of the building’s load-bearing frame are required after 3 to 5 years.
Therefore, it is better to immediately include in the project construction materials and thermal insulation that are compatible, according to building physics.
Concrete compatibility
There is no loss of thermal resistance when placed in a humid environment (wetness without the possibility of evaporation) only with foamed polystyrenes and glass. The remaining materials, poured with concrete and absorbing moisture from it, lose at least 30% of their thermal resistance with an increase in humidity by 10%.
Polystyrene foam does not have sufficient strength under load-bearing structures, therefore it is also excluded from insulation for concrete structures. Among the remaining thermal insulators, extruded high-density polystyrene foam is cheaper than foam glass.

For flooring on the ground, you should choose high-density EPS.
Therefore, for slab foundations, screeds and ground floors, XPS or EPS is used in 90% of cases. Mineral wool will reduce the operating budget and make the floor covering on the ground vulnerable to excess moisture.
Thus, polystyrene foam should not even be considered for the floors of a wooden house. For floors on the ground, it is better to use high-density extruded polystyrene foam. And in the ceilings along the beams, use Ecowool, basalt or fiberglass slabs, and roll insulation.
Advice! If you need repairmen, there is a very convenient service for selecting them. Just send in the form below a detailed description of the work that needs to be performed and you will receive proposals with prices from construction teams and companies by email. You can see reviews about each of them and photographs with examples of work. It's FREE and there's no obligation.
Simply put, a ground floor is a concrete or reinforced concrete slab laid on the ground, not connected to the foundation of the building and its external walls. It can be cast separately or made by making a concrete screed.
Reinforced floor screed
No matter how hard the foam is, it will still sag a little under the load. So the screed must be reinforced.
Reinforcement can be done with ordinary reinforcing mesh made of BP II wire 3-4 mm with a cell of 100x100 or 150x150 mm. This is quite enough.
The thickness of the screed should be within 40-50 mm. If the screed is smaller, it will crack, and a larger thickness will lead to waste of materials.
Here, when pouring, beacons are definitely needed. And you need to very carefully level the screed and smooth it over them. It is on this surface that the finishing coating will be laid. Of course, the jambs can be fixed with a self-leveling screed, but why spend the extra money?
Mechanized semi-dry screed is also an excellent option for residential premises. Its strength is good for a home, but for a garage where a car will drive into it, I wouldn’t lay it down.
The surface of such a screed is very smooth, but the holes and bumps depend on the hands of those who lay it. You can’t trust it by eye, you need to check it with the two-meter rule
However, I wrote about how best to make a garage floor in another article.
This is how you can make floors on the ground with your own hands.
Insulation of earthen floors for higher ceilings
Practically, everything is the same as described above. But if the height of the ceiling allows, you can pour a concrete screed with a thickness of 5...7 cm. As you know, under the screed you also need to pour and compact a “cushion” of sand or crushed stone, or ASG, or screenings... The thickness of the cushion - 5...10 cm - is also taken into account , subtracting from the height of the room.
It will be easier and more reliable to attach sheet wood materials (OSB or plywood) to the concrete screed for the floor “pie” (see above). The mentioned materials will be fastened with dowels and nails, directly through the waterproofing, which, like on ground floors, must be laid over the screed and also in at least two layers. However, now we can say that the floor is not earthen, but concrete, and you can refer to the article Insulation of a concrete floor.
Expanded clay floor insulation technology
Expanded clay, despite its low cost, can provide effective floor insulation in an apartment. For work, it is better to use expanded clay of different sizes (from 5 to 22 mm). This will ensure good adhesion to the concrete and help avoid shrinkage of the floor. The material is light in weight, but together with the concrete screed, it still puts a load on the concrete base. Therefore, when starting work, it is necessary to evaluate the design features of the concrete slab and its condition. It is better to cover a floor insulated with expanded clay with wood.
- Before filling in the insulation, waterproofing is carried out. This stage of work cannot be ignored, since expanded clay absorbs moisture well, while losing its properties. A durable polyethylene film can act as a waterproofing layer. It is laid in such a way that its edges extend onto the walls and are higher than the pouring level. The joints are taped with construction tape. The result should be a solid, sealed canvas.
- We install beacons. Their goal is to help make the floor as level as possible and the job to be done quickly. It is recommended to make guides from a resistant and durable material, for example, from metal pipes. The first pipe is laid along the wall with some retreat. The next one runs parallel to it at the opposite wall. Everything is checked by level. A rail placed on the pipes will show the slope, if any. Between these two beacons, others are installed, taking into account the width of the rule (tool for leveling the screed). Lighthouses are fastened using cement, gypsum or alabaster mortar.
- Next, expanded clay is poured. The thickness and evenness of the layer are checked using beacons. The height of the insulation must be at least 10 cm. The strength of the finished structure depends on this. To keep the expanded clay grains immobile during further work, the poured layer of insulation is poured with a liquid solution consisting of water and cement (it is also called cement laitance). A reinforcing metal mesh is placed on top, which helps prevent deformation of the structure under heavy loads.
- The concrete screed is poured starting from the far corner of the room, gradually moving towards the exit.
- Within a week after completion of work, the structure is moistened with water. This is done to avoid the appearance of cracks. After this, a wooden or artificial covering is installed.
An insulated floor in an apartment is unlikely to disappoint anyone. It will only add an atmosphere of comfort to your home and allow you to spend time at home with the greatest comfort. The work done will help save on heating costs and give pleasure to all family members.
Instructions for laying insulation on the ground
The first stage of the work is removing construction waste and leveling the site. To obtain a high-quality result, it is recommended not only to level, but also to compact the soil on the floor. 10-15 cm of sand and a layer of gravel or fine crushed stone are poured on top of the soil.
The next step is pouring a layer of clay. Clay will play the role of waterproofing. It does not shrink and retains moisture perfectly. A polyethylene film with a density of at least 200 microns is laid on top of the clay layer.
A layer of insulation is laid on top of the film; it can be polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam, or, even better, extruded polystyrene foam. The slabs are laid in a lock; the joints, if the surface of the slabs allows, are secured with mounting tape.
Next comes the laying of plastic film. The second layer of waterproofing is laid so that the edges extend onto the wall by at least 15 cm.
The final stage is pouring the concrete screed. The filling layer must be at least 4 cm and have a reinforced frame. A standard welded mesh is suitable for it. The wire frame is installed at a height of 1-2 cm from the waterproofing. When pouring, the concrete is compacted so that the wire is in the middle of the layer. At the end of pouring, when the concrete has gained sufficient strength, the protruding polyethylene is trimmed.
Mineral insulation
These include mineral wool, expanded clay, and cement-based mixtures.
Mineral wool is considered one of the most popular materials for floor insulation. Most often it is used to insulate floors on the first floors or attics. The material is durable and will be worth the money spent on it. Cotton wool contains rocks, slag or glass. Depending on the raw material, it is divided into glass wool, basalt (stone) and slag.
Mineral wool is available in the form:
- Slabs
- Rolls
- Matov
These forms of material greatly simplify the work of insulating floors. The insulation is placed on a concrete base and covered with a layer of vapor barrier material. A wooden or artificial floor is installed on top.
Among the advantages of mineral wool is its non-flammability. It prevents the spread of fire, thereby increasing the fire safety of the entire room. Mineral wool has high thermal insulation properties and excellent sound insulation. It does not freeze or deform due to temperature changes, is not susceptible to mold and mildew, and is vapor-tight.
The disadvantages of a heat insulator are considered to be the impressive layer height and the need for additional waterproofing, since not all types of wool are moisture resistant. Glass wool is most resistant to moisture, but it is not very convenient for installation due to the flowability of small glass fragments. The presence of formaldehyde in cotton wool raises doubts among those who strive to create an environmentally friendly space in their home. However, you can avoid contact with unwanted chemical elements by working with the material correctly.
Expanded clay is a granular insulation material based on clay. In terms of cost, it is considered one of the most affordable. Expanded clay bedding for thermal insulation increases the height of the subfloor by at least 12-15 cm, so it is carried out during construction work or major repairs.
Expanded clay has good thermal insulation and strength. It is environmentally friendly, resistant to low and high temperatures. The material is considered an excellent sound insulator. Among the disadvantages of insulation are its fragility and high moisture permeability, which in some cases is absolutely undesirable.
Expanded clay can be used with cement mortar. In this case, the floor is filled with a mixture consisting of 1 bag of cement, 2 bags of sand and 3 bags of expanded clay. This expanded clay cement screed is quite durable and provides good thermal insulation of the floor in the apartment.
Thermal insulators used
The modern construction market offers a huge number of heat-insulating materials that can be used to insulate concrete and wooden floors. To make it easier for you to choose the appropriate option, I will list the main requirements that I consider important:
- light weight - this parameter is especially important in a log house, where I would advise minimizing the load on the enclosing and supporting structures;
- hydrophobicity – water often gets on the floor, not to mention air humidity, so it is desirable that the technical characteristics of the insulation do not deteriorate when wet;
- long service life - after all, you don’t want to carry out floor insulation measures every 2-3 years, especially after retirement, when you just want to babysit your grandchildren;
- environmental safety - I certainly don’t want my descendants to breathe the chemicals emitted by cheap or low-quality heat insulators.
Sawdust is one of the most environmentally friendly insulation materials.
If the price of the material is very important to you, then to choose, you can use the table in which I have summarized the cheapest, but quite effective options.
| Insulation | Description |
| Dry sawdust | They have a minimal price, but their performance properties deteriorate greatly when wet. Therefore, I highly recommend taking care of high-quality waterproofing on both sides, especially since the material has a high water absorption coefficient. But environmental friendliness is at its best. |
| Sawdust granules | A more advanced version of the previous insulation. Granules are made from sawdust, to which water-repellent substances, antiseptics and fire retardants are added. All this makes them more practical to use, but reduces their environmental friendliness. |
| Slag | A good material that attracts builders with its low cost and low thermal conductivity. However, due to its weight, I would advise using it only for insulating floors installed on the ground (without a basement). |
| Expanded clay | Mineral granules, which are quite environmentally friendly, are light in weight and inexpensive. But in order to properly insulate the floors, you will have to pour a considerable layer of material (in some cases up to 30 cm), which is not always acceptable due to the height of the ceilings. |
| Mineral wool | Only the simplest varieties, devoid of heat-reflecting additives and other modifiers that improve performance properties, are inexpensive. But the material is non-flammable and environmentally friendly, as it is made from basalt. |
| Glass wool | This material is currently practically not used for residential premises, as it requires careful waterproofing and is harmful to health. I highly recommend choosing something more suitable, especially since there are many options. |
| Styrofoam | Lightweight, porous and cheap material with low thermal conductivity. Personally, I consider the disadvantages to be low fire-fighting properties and the fact that mice like to chew foam plastic. And one more point - low strength, therefore, for example, it cannot be used under a screed. |
The floor can also be insulated with foam plastic.
In principle, there are many options, so you can choose something suitable.
All these materials are inexpensive, but to install them you will have to buy additional materials and expend considerable effort. Take this into account when choosing insulation. It is possible that the entire insulation operation will be much more expensive than you expect.
However, I will be insulating the house for my own children and grandchildren, so I am not going to save money. If you share the same opinion, then I advise you to pay attention to the following thermal insulator options:
- Vermiculite . A material for which the raw materials are processed hydrated micas, characterized by a very low thermal conductivity coefficient and a long guaranteed service life.
Vermiculite is a loose floor insulation material.
- Penoplex. This is extruded polystyrene foam, which is a distant relative of polystyrene foam. Like the latter, it consists of small closed cells filled with air, but is distinguished by its highest strength, high hydrophobic properties and non-flammability.
Penoplex is an insulating material with excellent performance properties.
- Fiber insulation with additives. We are talking about mineral wool from such manufacturers as Ursa, Isovent, Penofol and so on. They are treated with various additives and modifiers, which give the material water-repellent properties and increase wear resistance.
Ursa is a fiber insulation with improved performance properties.
Some materials have a protective heat-reflecting layer of metal foil, which increases the effectiveness of basalt wool.
For myself, I chose basalt mats, which are sold already cut into pieces. They are easier to install between joists. In my case, Izover KL37 or KT37 (one in rolls, pipe mats) came up.
Construction Features
Typically, technology allows you to install floors on the ground in a strip foundation. The method is not applicable for complex types of supporting structures that combine two or several types of foundation, for example, pile-strip.

Strip foundation in a private house Source betonbase.ru
There are several types of subfloors. Among them, concrete screed. Rely on: the structure can:
- on load-bearing walls;
- a cushion of soil backfill.
As a base, you can use plank flooring on wooden beams (joists). For each type of structure, a floor pie of a certain composition is constructed. Concrete cannot be poured directly onto the ground or clay.

Clay floors in outbuildings. Source 9ban.ru
It is necessary to prepare an intermediate base layer that provides:
- rigidity;
- thermal insulation;
- waterproofing;
- stability;
- ability to withstand loads.
The decision to lay floors on the ground is made based on the results of a soil study
It is important to know whether there is water lying close to the surface under the building. . Wooden floor on the groundSource prd.ru

Wooden floor on the groundSource prd.ru
Insulation of earthen floors
to write an article about insulating an earthen floor when I was asked this question.
Moreover, I apologize, I will write a “gag”, that is, I have not read about this anywhere. I just had the opportunity to see the earthen floor in my grandmother’s adobe hut and how she coped with this task. Further, perhaps my experience of insulating an “almost earthen” floor will be useful to someone. What does "almost" mean? One of the extensions of my house has a reinforced concrete slab foundation lying directly on the ground. Well, in the sense that there is no space between the slab and the ground...
In general, let everyone take what suits him and leave the rest for others. Go.
Thermal insulation of floors: methods and features

Laying polystyrene foam on a sand cushion for insulation
Expanded polystyrene, polystyrene foam. Insulation of an earthen floor requires laying 30 cm of gravel in the base, covered with a concrete screed (100 mm). The foam slabs are laid on waterproofing, on top of which a 4 cm thick screed reinforced with a steel/polymer mesh is applied. The installation is completed with a finished floor. You can lay waterproofing on top of the slab so that the screed is covered with foam. This method prevents the solution from getting between the plates of material and, accordingly, prevents the formation of cold bridges.
- Extruded polystyrene foam. The hardness of the slabs allows the material to withstand significant loads, so it can be laid directly on gravel. The feature of not absorbing moisture ensures ideal technical characteristics of the material when working on soil where the water level is quite high. But to create heat in a private home, the thickness of the layer of material must be at least 8 cm.
- Polyurethane foam. Work is carried out only with the hardest slabs. Low vapor permeability and high thermal insulation properties provide a good insulation layer on any soil. Moreover, when working with an earthen floor, you can choose thinner slabs.
- Minvata. Just as when working with expanded polystyrene, you need to choose dense, rigid boards that are resistant to deformation. Laying over the subfloor is carried out in 1-2 layers. To reduce the level of moisture absorption, you need to treat the slabs with a waterproofing agent. Laying thickness 10 cm.
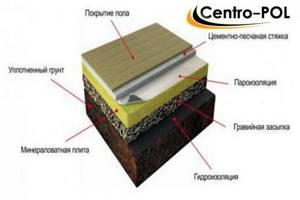
Scheme of floor insulation on the ground with mineral wool
Insulation under the finished floor can be done quickly and easily using expanded clay. Light weight, porous structure of the base will provide high thermal characteristics with low moisture absorption. When doing work with your own hands in a private mansion, you need to choose fractions of no more than 8-16 mm, while additional waterproofing is not required when backfilling a thick layer. There is also no need to lay/fill layers of gravel, screed and heat-insulating material. It is enough to pour expanded clay layer by layer to a thickness of 15 cm and compact it. To strengthen the base and simplify work with the finished floor, the expanded clay layer must be filled with a layer of lean concrete. After 24 hours, the surface hardens into a crust, on top of which the waterproofing is installed.
Features of the technology
This type of thermal insulation is considered one of the most effective, but at the same time very labor-intensive. This is due to the preliminary preparation of the soil under the building. The specificity of installing the insulating layer is that it is not rigidly attached to the walls of the building. Therefore, in addition to thermal insulation, special attention should be paid to minimal shrinkage of the entire structure during further operation.

In the vast majority of cases, this type of insulation is used for strip foundations. It should only be carried out after the building’s supporting structure has completely hardened. There is a certain scheme for performing work, which consists of the following stages:
- Soil preparation. It consists of treating the soil layer by thoroughly compacting the surface.
- Backfill made of gravel and sand. This layer is necessary for minimal shrinkage of the structure, and will also partially perform waterproofing functions.
- Concrete pad. The base on which the insulation will be installed.
- Installation of the first layer of moisture insulation. Required for high groundwater levels.
- Thermal insulation layer. It can consist of various types of insulation, ranging from available natural materials to modern polymer structures.
- Secondary waterproofing layer. Installed only for thermal insulation materials with hydrophobic properties: basalt wool, expanded clay, a mixture of clay and wood shavings.
- Concrete screed with reinforcing mesh. It is the basis for installing a finished floor.
Compared to other insulation methods, this technique is characterized by increased labor intensity and strict requirements for all layers. As a result, they should form an effective and reliable floor insulation cake. Therefore, the order of its arrangement should be considered in detail.
Types of insulation
All insulation materials can be divided into two categories: technological and those using heat-insulating materials. Technological types are divided into electric floors and water heating. Electric floors include infrared film, heating mats and heating copper cables, and water heating includes a piping system with water coolant.
Insulation materials, which use heat-insulating materials, also come in several varieties:
Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
It contains natural ingredients (wood). Produced by pressing using wood chips (sawdust) and adhesive ingredients.

There are four varieties:
- OSB-1. The moisture resistance of this modification is quite low - less than 20%. This brand is intended for interior work and contains a minimum amount of harmful substances in the adhesive;
- OSB-2. It has a more durable design and is used for covering elements of a dry room, because in a wet structure such material will be harmful to the human body;
- OSB-3 and OSB-4. They are distinguished by the greatest resistance to humidity and increased loads, but are the most toxic materials in this line.

But, despite the danger of such material, its use is quite often practiced not only in Russia, but also abroad.
Advantages of using this material:
- Saving money. The cost of such products is quite low;
- Easy to install. This material is very easy to cut and attach. It is lightweight, so there will be no special problems with its transportation;
- Long service life;
- Widespread use. This material has found application in wall cladding, roofing and flooring;
- Correct installation is a guarantee of resistance to a variety of hazards: corrosion, moisture, the appearance of microorganisms.

Mineral wool
According to regulatory documents, this material includes glass wool, slag wool and stone wool.
Glass wool fibers are tiny: the thickness is from 5 to 15 microns, and the length reaches only 50 mm. This structure allows it to be quite strong and elastic. When working with this material you need to be extremely careful - various dangerous situations may arise. For example, inhaling glass dust can damage your lungs, and if glass filaments break, there is a high probability of getting them on your skin and eyes.

Fibers produced from slag, or slag wool, have the quality of residual acidity. This has a negative effect on metal surfaces in damp areas. The material absorbs moisture well and is quite fragile. Not suitable for insulation of plastic and metal water pipes.
Stone wool differs from slag wool in that it is not prickly, so working with such material is much safer. Its most common variety is basalt wool, which has the best characteristics and does not contain any mineral or binding components. It can be formed into rolls or sheets, or stuffed into mats. When heated above the permissible temperature, it does not burn, but only melts.

Pros of using mineral wool:
- Excellent sound insulation;
- Low cost;
- Long service life;
- The ability to achieve maximum effect when waterproofing the base material;
- Used for major repairs and construction of buildings.

Expanded polystyrene
This material is produced using natural or carbon dioxide, as well as polystyrene and styrene copolymers. Most of this material is used for insulation and is the most popular in this area.
This product is divided into several types: pressless, pressed and extruded. Pressless is characterized by many heterogeneous structures. Absorbs moisture well. Marking: PSB S-X, where X is the designation of the density of the product.

Pressed has sealed pores, due to which it is considered a reliable and high-quality thermal insulation material. It becomes dense and quite durable. Marked with the letters PS.

Extruded, or penoplex, is similar in structure to pressed polystyrene foam, but its pores are much smaller. Marking – EPPS (XPS-X). The second letter X indicates its density.

The following positions can be distinguished from the distinctive qualities of this material:
- Thermal conductivity. Penoplex has the best thermal conductivity indicators. The denser the material, the higher this indicator. Therefore, the lion's share of consumers choose penoplex insulation.
- Vapor permeability. This characteristic varies in the range of 0.019-0.015 kg/ (m*h*Pa), whereas in polystyrene foam it is practically zero.
- Moisture permeability. When a pressless insulation is completely immersed in water, absorption occurs in an amount of 4% of the volume of the material, and for the extruded version - 0.4%.
- A product with medium or high density also has high strength characteristics.
- Expanded polystyrene does not collapse when exposed to substances such as soap, soda, fertilizers, lime, and cement. Damage can be caused using turpentine, acetone, drying oil, some alcohols, varnishes, and petroleum refining substances.
Perlite insulation
Insulating the floor with perlite over the ground is an effective method of thermal insulation of the bottom of the house. According to Wikipedia, perlite is a rock of volcanic origin. In its structure, this material is small, pearl-like granules, which contain silicon (65%), potassium, sodium, aluminum and other substances. Perlite is actively used in agriculture (which indicates its environmental safety), as well as in construction as a material for dry floor screed and thermal insulation.
Expanded perlite is usually used as a thermal insulation material. This material is perlite heated to a temperature of 1100°C, as a result of which an individual granule of this material increases in volume up to 15 times. Perlite has a high density (from 75 kg/m³) and a low thermal conductivity coefficient and in this characteristic is significantly superior to foam plastic and expanded clay. The technology for laying insulation is the same as for expanded clay - by pouring it between the longitudinal joists. The only disadvantage of this material is its high cost, which starts at 1,200 rubles per cubic meter. meter. In addition, perlite is not sold in all construction stores, especially in large quantities.
Peculiarities
Often in a wooden or brick house with thick ceilings you feel cold coming from somewhere below. High-quality thermal insulation will not only cost the home owner cheap, but will also allow you to achieve maximum comfort in your home.
Advantages of using floor insulation systems in a private home:
- Coolant losses will be significantly reduced, therefore, money savings will be noticeable;
- If you insulate the floor, the area of the premises will be heated evenly;
- Increased comfort in previously cold rooms;

- The lower part of the room will become much warmer;
- There will be no dryness in the air. The latest technologies will delay heat flow in the apartment;
- There will be more free space, since the use of heating systems minimizes the number of radiators;
- The heating process occurs faster, heat transfer increases;
- Such systems have a long service life.