Why is ceiling vapor barrier necessary?
Rockwool ceiling vapor barrier is an excellent way to protect and extend the life of a wooden floor, which:
- significantly extends its service life, eliminating rotting from the inside and deformation of building materials;
- increases the percentage of heat retained by the ceiling in the room;
- makes the attic an inaccessible place for mold and mildew to form.
In addition, it is worth paying attention to the absolute absence of the need for further additional maintenance of vapor barrier materials, given their composition and the design of the entire floor. Therefore, by installing a vapor barrier on the steam room ceiling during the initial construction or during repairs, you don’t have to worry about possible problems in the future
How to lay film correctly
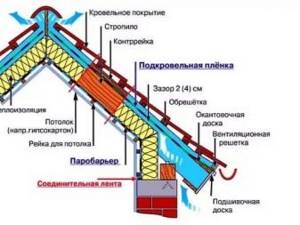
The waterproofing film is mounted from bottom to top with an overlap of panels of at least 15 cm. The fastening is carried out to the rafters. The film should sag between the rafters, but no more than 2 cm. Additionally, a sealing tape is glued on top, and then a counter-lattice block is nailed.
If it is necessary to increase the length of the canvas, then the joint should be on the rafter leg. Extensions are also done with an overlap of 15 cm.
The superdiffusion film is laid on the ridge without tearing. When installing other types of waterproofing materials in the ridge area, it is necessary to leave a “gap” of about 5 cm on each side.
Vapor barrier for attic pie
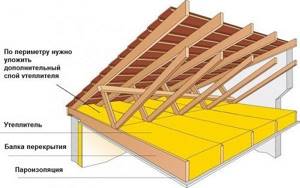
- Attic floor (ladders) - necessary for maintenance, repair of the roof and attic space. In order to get to the attic, provide an attic ladder with an insulated hatch (Thermo). To exit from the attic to the roof, we recommend installing blind or glazed exit hatches (Velux, Vilpe, etc.) on the roof.
- Para- or super-diffusion moisture-proof membrane - for effective removal of steam from insulation.
- Insulation - mineral wool slabs. Recommended thickness for the Moscow and Leningrad region is 300mm. 200 mm are laid in the space between the beams, the remaining 100 mm are laid perpendicular to the laid layers - counter-insulation. For comparison, building codes in Finland determine the thickness of insulation from 400 to 500 mm. It is recommended to delay the installation of insulation as much as possible - no earlier than 6 months after the completion of the construction of the house frame. Because For the construction of floors, timber with natural moisture is mainly used. The timber must dry thoroughly, otherwise there is a high probability of wood being damaged by fungi and mold, which entails additional costs for dismantling/installation work and treating the wood with bleaches and antiseptics.
- Counter grille and ventilated gap. For effective ventilation and removal of steam from the surface of the moisture-proof membrane.
- Floor beams. As a rule, in private housing construction a 50x200mm board or 100x200mm natural moisture timber is used.
- Lathing is the basis for laying insulation. It is recommended to use a 100x20 (25) mm board as lathing and lay it in increments of 70-80 mm. The resulting cracks will form an additional air thermal layer under the insulation. That. The insulation slabs (mats) will not lie on a vapor barrier film, but on a rigid base, already under which there will be a vapor barrier. This solution eliminates the possibility of accidental damage to the vapor barrier or its pushing through when laying insulation, during maintenance and repair work of the roof and attic. In this case, you can begin interior decoration of the premises, and postpone the installation of insulation as much as possible (see above).
- Vapor barrier of the attic floor on wooden beams
- is attached using a construction stapler from below to the rough ceiling (lathing), which allows you to cut off vapors from the entire floor structure. It is necessary to overlap the vapor barrier rolls by at least 15-20 cm and carefully glue them with aluminum adhesive tape. It is necessary to form overlaps on the walls of 15-20 cm and carefully glue them (place them under plaster and other wall finishing). Carefully seal the places where chimneys, ventilation pipes and other utilities pass through the attic floor using special hoses. The best material for vapor barrier is high-density polyethylene film of 200 g/m² and above. - We close the attic - the finished ceiling is attached to the vapor barrier
. The finished ceiling (OSB, gypsum board, etc.) is installed along the sheathing and guides. For the best fire protection, it is recommended to “sew up” the ceiling with 2 layers of plasterboard sheets.
Styrofoam
Insulating an attic space with polystyrene foam is a good option for converting it into an attic, suitable for year-round use. This material has low thermal conductivity, as it is produced in the form of foamed air granules pressed into slabs.
During installation, the foam must be cut so that the plates fit tightly between the attic floors. Any gaps and cracks become “bridges” for the penetration of cold, and thereby significantly worsen the quality of insulation.
In this case, it is necessary to maintain a distance between the foam board and the waterproofing film of at least 2-3 cm. It is recommended to use it as insulation with a thickness of 70 mm, and in regions with a harsh climate - 100 mm.
Attention! When installing a vapor barrier film, you need to pay attention to the fact that it faces the insulation with the required layer, according to the instructions. Otherwise, the opposite effect will be produced: all the steam will be directed towards the insulating material.

Advantages of a cold attic
The advantages of choosing a cold attic are that:
- Waterproofing is much more reliable. The fact is that when creating a warm attic structure, the integrity of the rolled waterproofing is in any case interrupted by superstructures, which significantly reduces its reliability. In the design of a cold attic, add-ons should be done to a minimum.
- Maintenance becomes as simple as possible. An attic is an attic and often something needs to be corrected or replaced, which is as easy as shelling pears with this design. There is a lot of space, repairing a cold attic is convenient and practical.
- The heat-transfer surface area is minimal. With this design, there is only minimal heat loss from those rooms that are located directly under the attic.
- Possibility of operation. As mentioned above, such an attic can be easily adapted both for storage and for other needs of the owners. Depending on the method of entry into the attic, whether it is a ceiling hatch from the living room, or a door from the street, even feed supplies can be stored in it, if we are talking about a rural house.
Is it possible to use roofing felt?
Sometimes roofing felt and its analogues are used as waterproofing for pitched roofs. But these materials are intended for waterproofing flat roofs over a continuous floor.
The technological map of the TechnoNikol company for the installation of bitumen roll materials indicates that the roofing material is attached to the base using mastics or by fusing.
Mechanical fasteners at large roof slope angles are used as additional “point” fixation to prevent bitumen waterproofing from slipping in hot weather. And this limits the scope of use of roofing felt on pitched roofs.
On those roofs where the slope angles are large and the technology for laying the roof is continuous, lathing is not needed, it is not economically profitable to install it, even though roofing felt is cheaper than waterproofing films. But only mechanical fastening along a row sheathing does not provide sufficient reliability of fixation due to the low tensile strength of roofing material.
What kind of film to put under the insulation in the attic All about insulation and energy efficiency
When ensuring insulation of a private house and insulation of the roof along the rafters, one must not forget that special attention should be paid to such a place as the attic. Development of attic floor insulation with mineral wool
Development of attic floor insulation with mineral wool
Warm air tends to rise to the top, and therefore, in a temporarily unheated room, heat can escape through the cold attic space. Therefore, the issue of insulating the attic must be resolved without delay.
1 Why do you need attic floor insulation?
Insulating a cold attic floor with stone or mineral wool is generally necessary in lightly used rooms that are properly equipped with special roof ventilation.
The attic, or rather its ceilings, serves as a kind of boundary between heat and cold. In such places, the attic floors are exposed to intense moisture due to the formation of condensation.
However, you can properly insulate the floors in the attic of a house with mineral wool with your own hands. The very process of insulating the floor in the attic with mineral wool is the creation of a durable thermal insulation coating, which will have a low degree of thermal conductivity.
The technology itself for insulating mineral wool floors in the attic, as well as Energoflex thermal insulation for pipes, implies strict adherence to its stages and requirements.
The technology itself is quite simple and understandable. Good attic floor insulation using mineral wool helps close unwanted gaps.
To do this, the insulation must be laid tightly. In most cases, mineral wool is used to insulate the attic of a house.
The presented insulation is the most suitable for this type of work; it can also be used to insulate the floor surface in the living areas of the house.
Schematic insulation of the attic floor with mineral wool
By organizing good insulation with mineral wool, the most optimal temperature will be maintained in residential premises.
If the procedure is performed incorrectly, moisture rising from the floor of the house will lead to the formation of condensation.
It will accumulate on the ceiling and then seep through the ceilings. The resulting temperature difference in those areas where the attic floors adjoin the walls of the house initiates the formation of mold and microscopic fungi, which can be causative agents of allergic diseases.
1.1 Requirements for attic insulation
The process of insulating the attic floor and insulating the roof of a house with your own hands, or rather the level of its quality, has a direct impact not only on the size of heat loss, but also on the service life of the entire truss structure and roof covering.
The fact is that water vapor located inside the heated room diffuses to the attic of the house. In order for the insulation used to provide a high degree of calculated efficiency of the thermal insulation layer, it must always be dry.
Based on this, the insulation must be protected from excessive humidification by vapors of rising heated air using a special vapor-proof material.
Sawdust
Sawdust is a product of lumber processing in the woodworking industry. This is the cheapest insulation for attic floors, since you can buy sawdust at any sawmill for free. Thus, sawdust is still an option as a reliable heat insulator in attic spaces.
On a note! Sawdust is of organic origin, therefore, it is completely harmless to human health. Since ancient times in Rus', sawdust mixed with clay has been used as insulation in attics.
Sawdust has the following advantages:
- Low cost of thermal insulation. Probably, the popularity of such insulation lies precisely because of this factor: its cost is almost equal to the cost of transportation.
- Safety for human health. Wood shavings and sawdust do not cause skin irritation, allergies, or poisoning, which cannot be said with complete confidence about modern insulation materials.
- Low thermal conductivity coefficient. Unlike wood, chips have a porous structure, so they have low heat conductivity.
- Easy installation. To form a heat-insulating layer in the attic floors, no special skills are required. You just need to mix sawdust with clay or lime, and then pour it into the space between the attic floors.
The only significant drawback is the fire hazard of the material, despite the mixture with other non-flammable substances.

Recently, two types of insulating materials have become popular for insulating attic floors: blown-in wool and ecowool. The latter material consists of 80% cellulose fibers made from waste paper, and 20% from additives, which are fire-fighting and antiseptic components.
This material has low thermal conductivity, it is very light, and looks like regular polyurethane foam. Both types of insulation are usually sprayed onto the boards between wooden beams, but sometimes ecowool is used in granules in a crumbly state. In this case, this mixture, as an option, is simply poured between the floor beams and compacted.

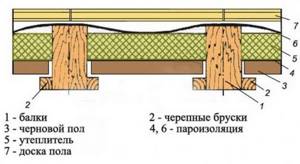
Steam and thermal insulation of a cold attic
For a roof with a cold attic, it is most important to minimize heat loss through the attic floor. Vapor barrier is mandatory for both wooden and reinforced concrete floors
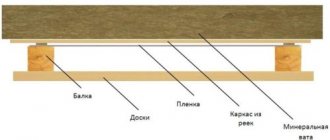
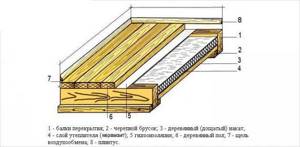
It is laid on the ceiling itself and protects the insulation from vapors that can condense in the heat insulator after passing through the ceiling of the living room. Slab and bulk materials can be used as insulation. The ceiling pie consists of a vapor barrier, floor beams and insulation.
The following types of heat insulators are often used in ceiling coverings:
:
- expanded polystyrene and foam boards;
- mineral wool slabs or mats;
- expanded clay granules;
- fuel or granulated slag;
- sawdust with lime or clay;
- pumice.
The thickness of the required insulation layer is selected depending on the estimated winter temperature using the table below.
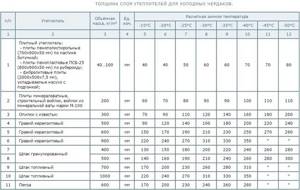
Winter temperatures are calculated according to SNiP 2.01.01-82 (building climatology and geophysics) or selected by regions of the Russian Federation from the corresponding climate maps.
The insulation is laid between the joists or ceiling beams, and a boardwalk is made on top for the attic passages. Joists are usually 50 mm thick, and decking boards are 25-35 mm thick.
Attic waterproofing device
Waterproofing roofs with a cold attic, according to many experts, is a controversial issue. Some say that waterproofing must be present under the roofing material, while others categorically recommend that it be abandoned. Here, a lot depends on the type of roofing material and the angle of inclination of the roof slopes.
Metal roofs are most susceptible to corrosion, which occurs due to possible small leaks or condensation
Therefore, we once again draw your attention to the fact that ventilation plays one of the main roles in the fight against condensation.
For flat metal roofs, experts recommend installing superdiffusion membranes. It will prevent moisture from entering the outside of the roof when snow or rain blows in. No matter how well the roof is laid, there is always the possibility of minimal leaks. That is why, by paying a little extra, you will receive additional protection from moisture getting on the insulation in the ceiling of a cold attic.

If, for example, slate is used as a roofing material, then waterproofing can be abandoned. There is also corrugated sheeting with an anti-condensation coating on the market, which can hold up to 1 liter of water per 1 m2. For our part, we recommend always using waterproofing membranes, because this is the cheapest and easiest additional way to protect your roof from possible leaks
.
When installing waterproofing membranes, a counter-lattice is used. It serves as a fixing strip and, due to its height, provides the necessary clearance for ventilation of the under-roof space. The installation of lathing in a cold attic is no different from insulated roofs. The dimensions of the sheathing and its pitch determine the type of roofing being installed.
Cold attic temperature
To prevent ice and icicles from forming on the roof, it is necessary to maintain the correct temperature and humidity conditions in the attic. If the thickness of the thermal insulation material is insufficient, significant heat losses occur through the ceiling. Warm air, heating the roof covering, causes snow to melt and ice dams to form. By choosing the right insulation layer, this can be avoided.
The effectiveness of a heat insulator can be assessed by measuring the temperature of the top layer of insulation. The electronic thermometer is immersed in insulation by 10-20 mm. The temperature readings taken should correspond to the values in the table below.
As you can see, the design of a cold attic pie is not particularly complex in design. The main task is to ensure the necessary intensity of ventilation and the thickness of the thermal insulation layer in the ceiling.
We will install copper roofing quickly and efficiently
What waterproofing materials can be used
There are three types of modern materials:
Superdiffusion membranes. They have good waterproofing properties and high vapor permeability. They are rarely used in cold roofs due to their high cost and excessive “breathing” properties. The main purpose is to protect the insulated roof. It is installed on non-insulated roofs if there are plans for further insulation and conversion into an attic or used attic.
Diffusion membranes. Good waterproofing properties and average vapor permeability. The optimal choice for slate, ondulin, ceramic and cement-sand tiles.
Water vapor barrier films with anti-condensation surface. This is a universal material that is characterized by high waterproofing properties and limited vapor permeability. Such materials can also be used as a vapor barrier. Recommended as waterproofing for cold roofs with metal roofing. They block most of the water vapor in the warm air, which is then ventilated through the eaves and ridge vents of the attic ventilation and through the dormer window.
Peculiarities
Most of the warm air masses escape through the roof. Therefore, when building a house with an uninsulated attic, you need to carefully approach the topic of insulating the attic floor with wooden beams. After all, it creates a certain barrier between warm rooms and a cold attic.
Let's consider the special criteria for attic insulation that affect the maintenance of temperature in the house:
- Purpose of the room.
The attic is a kind of buffer between the environment and the living rooms. Its task is to regulate the temperature difference between the external environment and the house. - Temperature regime.
In any season and on any day, the temperature of the air masses in the attic will always be higher than outside the window. This is why the attic is very cold in winter, and unbearably hot and stuffy in summer. - Heat loss in winter.
The more a substance heats up, the less dense it becomes. This is a physical phenomenon. This is why in residential premises with a heating system, warm air from household appliances is concentrated in the ceiling area. That is, if you do not insulate the ceiling, then in winter all the warm air will warm the attic.
- Excessive heat in summer.
In summer, the reverse process can be observed. The roof, heated by the rays of the sun, will warm up the attic air, which, in turn, will penetrate into the room through the attic floors. - Reverse circulation of air masses.
In contact with the ceiling without thermal insulation, warm air becomes cold, more dense and, as a result, sinks to the floor. This is reflected in the living space in the form of circulating drafts that cause harm to human health.

- The appearance of excess moisture.
When it comes into contact with an uninsulated attic, hot, humid air turns into condensation. The overall level of humidity in the house increases, which leads to mold growth in the corners. - Saving
. The heat lost through the roof without insulation is about 30%. This means that with proper insulation of the attic floor, you can save 30% of the fuel used. Using air conditioning in the summer will also cost less.

The entry of warm air masses into a technical attic (non-residential) leads to negative consequences:
- Due to the mixing of warm and cold masses, condensation may appear in the attic. Water falling on the surface can lead to rotting of wood on load-bearing beams.
- If the attic is warm, the snow collected on the roof will begin to melt. The water dripping at the same time will begin to turn into icicles. Ice forms on the drainage system.

Vapor barrier membranes
Diffuse (breathable) membranes are classified as the most effective and expensive vapor barriers. This group of products contains both single-sided and double-sided materials
The former allow steam to pass through only in one direction, so during installation it is extremely important not to confuse which side to lay the fabric towards the insulation and which to the load-bearing surface. Double-sided ones work in both directions, so there are no problems with them

Vapor barrier membranes can be single-layer or multi-layer. The first ones have an affordable price. Multilayer ones have the function of accumulating moisture inside the canvas and gradually releasing it.
A special group of products in this category are “smart” membranes. They are able not only to absorb vapors, but also to regulate the level of humidity of surrounding materials, while simultaneously acting as a water barrier. These membranes are the best choice. But their cost is beyond the means of most private home owners.
Vapor barrier membranes "TechnoNIKOL"
The undoubted leader in this category of materials is TechnoNikol membranes. For vapor barrier of wooden ceilings, the “Optima” brand is recommended for use. This hydrophobic polypropylene membrane consists of three layers:
- upper and lower polypropylene;
- medium – high-tech functional vapor-permeable film.
- weight 80 g/m2;
- thickness 0.3 mm;
- vapor permeability 5 g/m2x24 hours.
The TechnoNIKOL Optima membrane is produced in rolls. The width of the canvas (roll height) is 1.5 m. The length is 50 m. This material is optimal for vapor barrier of any type of ceiling, intended for installation indoors and on external surfaces of buildings.
Superdiffuse reinforced membrane

Diffusion membrane films "TechnoNikol"
Rules for installing a vapor barrier for a wooden ceiling
Step 1. The membrane is laid directly on the insulation so that the smooth side is directed inside the room.
Step 2. It is possible to lay the strips in different directions: parallel or perpendicular to each other.
Step 3. During installation, an overlap of at least 10 cm must be observed.
Step 4. To attach the membrane to a wooden floor without insulation, use galvanized screws with wide heads or staples with an anti-corrosion coating.
Step 5. The joints of the canvases are sealed using self-adhesive mounting tape.

Use foil tape, width 50 mm, length 30 lm.
Step 6. When laying on a floor with insulation, it is necessary to bring the edges of the panels onto the wall by 15-20 cm and secure them with suitable materials (slats or metal profiles).
Step 7. Mounting tape is glued along the perimeter of the vapor barrier layer.
Step 8. Between the membrane and the material with which the wooden floor will be lined, leave a ventilation gap 3-4 cm wide.
Step 9. Particular attention is required to the places where the vapor barrier comes into contact with the structural elements of the floor and the building: beams, chimneys, ventilation ducts.

Ceiling vapor barrier in wooden floors
During installation of the vapor barrier, it is necessary to ensure that the film is laid evenly, without folds or sagging. A guideline for correct installation can be a colored stripe, which is the center line along the entire length of the canvas.
Video - Ceiling vapor barrier
An equally good choice are multilayer vapor barrier membranes of other brands: Dorken Delta REFLEX/REFLEX PLUS and Dorken Delta LUXX. The first is a four-layer material, is particularly durable and can provide 100% waterproofing of a wooden floor. The second has limited vapor permeability, ensuring gradual and uniform removal of moisture from the living space.
Insulation technology
To apply the insulation correctly, follow the step-by-step instructions:
Step #1 . Carry out an inspection and, if defects are found, eliminate them. Treat boards and timber with antiseptics and fungicides.

Step No. 2. Lay out the vapor barrier material, seal all gaps with mounting tape.

Step No. 3. Lay (pour) insulation into the openings of the wooden floors on the floor.

Step No. 4. Pay special attention to the joints between the slabs of insulating material. If necessary, apply additional insulation.
Step No. 5. Lay the waterproofing film overlapping, and fasten the joints with mounting tape.
Step No. 6. Separately install insulation on the ventilation duct, chimney pipes in the form of basalt wool, perlite, and it is advisable to install a special corrugation on top.

Floor design
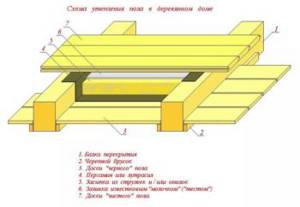
Before proceeding to a detailed description of creating the correct “pie” for the first floor, it is worth noting the constituent elements and technical rules.
- Priming. The ceiling of the first floor separates the room from the underground space, the surface of which is soil. The soil becomes a source of moisture entering wood structures, which can negatively affect their technical properties. Therefore, this surface must be waterproofed. There is no need to waterproof the second floor.
- Ventilation must be provided in the underground space so that moisture penetrating from the ground is evaporated and does not enter the floor ceiling.
- Brick pillars on which wooden floor beams lie.
- Wooden beams. The beams serve as a supporting element for the floor joists. Depending on the step at which the beams are laid, the choice of the thickness of the boards for the supports depends. The structure should easily tolerate possible loads without deforming the floor.
- Logs are transverse boards lying on the end sides. They serve as the basis for laying the finished floor in the form of floor boards or using plywood or other tile backing.
- Insulation material is filled between the bars. In this case, it is necessary to take into account that there is a gap between the insulation and the finished floor for ventilation.
- Vapor barrier and waterproofing, allowing you to protect the insulating material from moisture entering it.
- Finish floor with or without sheet and tile backing. When using boards, they are laid on bars, and finishing coatings such as laminate, parquet, tiles are placed on a leveling layer of tile material.
When using an insulated coating, it is necessary to take care of damping gaps for ventilation under the floor.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay for the attic of a house is a traditional method of thermal insulation of a technical floor. This material is poured between wooden floors with a layer thickness of at least 150 mm. This mass is a universal means that can insulate floor structures, and it can also be used as thermal insulation together with other bulk materials.
Attention! Expanded clay is a fairly light insulation material, but when a thick layer is applied, the load-bearing surface of the ceiling will bear a large load.
Thermal insulation is best carried out at the construction stage of the building, since it is easy to waterproof the ceilings of the rooms under the attic and provide for an exhaust hood.
To do this, cover the ceiling with a vapor barrier film to protect the expanded clay layer from getting wet. It is not recommended to pour it directly onto the floorboards for another reason: during operation and operation of the room, a lot of dust is released, which penetrates into the living rooms.

Choice of insulation
The methods of insulating the ceiling of the upper floor of the ceiling along beams in a private house are very diverse. When doing the work yourself, the insulation is placed between the joists and provides reliable thermal insulation and noise protection. There are many options for insulating a structure, the most common of which are:
- insulation with mineral wool;
- laying expanded polystyrene (foam plastic or penoplex) on wooden beams;
- filling with expanded clay;
- insulation with sawdust;
- filling the ceiling space with foam.
Each of these options has its own characteristics and advantages.
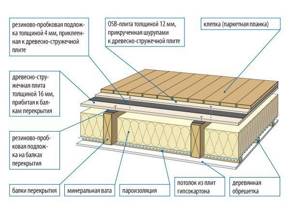
Mineral wool insulation
The material is available in two versions: plates and rolls. Insulating the attic floor with mineral wool has the following advantages:
Styrofoam
Foam plastic has become one of the most common materials for thermal insulation. It has earned its place in the top three thanks to its very attractive price. Using this insulation in an individual home provides the following advantages:
- high degree of protection;
- resistance to rotting and mold and mildew;
- low degree of water absorption;
- ease of installation and no need for complex tools and protective equipment;
- the light weight of the material prevents excessive load on the structure and allows for insulation from below.
Extruded polystyrene foam

Being the closest relative of foam plastic, penoplex is devoid of most of its disadvantages. In the process of improving performance characteristics, the cost has increased. The material is produced fireproof, it has sufficient strength for use as a base for flooring and is light in weight for use in ceiling construction. Do-it-yourself installation is quite simple. This issue is discussed in detail in the article. The text discusses options for using both penoplex and polystyrene foam for different types of floor construction.
For people who decide to build their own wooden house, the naturalness of the materials is usually important. Here penoplex, like foam plastic, loses to other types of insulation due to its artificial origin.
Expanded clay or sawdust
If you decide to use completely natural materials in your home, these two types of insulation will become indispensable helpers. They do not have high heat-protective characteristics, like previous types, but provide reliable protection from the cold with a sufficient layer thickness. Sawdust can be obtained almost free of charge; expanded clay is also an inexpensive material.
Insulation of the attic floor can be carried out by non-professionals and does not require special skills. The application is limited by the physical characteristics of these materials: they cannot be used for thermal protection from below.
Heat protection foam

Polyurethane foam insulation is a fairly new material in construction. When constructing a building yourself, this method can provide high speed work and reliable protection from the cold. You can read about insulating a building, including attic floors, with foam in the article.
This provides a large selection of materials for insulation and significant savings on construction.
A large percentage of heat losses occur precisely through the ceiling of the upper floor, which is why it is so important to choose the right insulation and follow the installation technology. Are you insulating your house for winter and don’t know how to insulate the attic floor using wooden load-bearing beams? Having gained experience in this matter, I will accurately convey the technical aspects of thermal insulation, and also describe step by step the procedure for carrying out the work
Are you insulating your house for winter and don’t know how to insulate the attic floor using wooden load-bearing beams? Having gained experience in this matter, I will accurately convey the technical aspects of thermal insulation, and also describe step by step the procedure for carrying out the work.
Extruded polystyrene foam
When insulating the ceiling of a living space over attic floors, this material is considered the best option for many builders. This insulation does not cause any difficulties during installation; it can be laid under any beam ceiling.
It also saves space, since you can get by with two to three times less thickness than using the same mineral wool. Extruded polystyrene foam comes in different types, as it is produced by different manufacturers. To insulate attic floors, the density of such material should be about 32-34 kg/m, and its thickness should be from 40 to 100 mm.
Manufacturers also produce shaped elements from expanded polystyrene, which are used to lay out complex fragments in the attic ceiling. It is convenient to install this insulation in two layers: the first layer is laid between the attic floors, and the second layer is applied end-to-end along the bottom row, covering the wooden beams as well.