External facade insulation systems are special structures that protect walls from the cold. Currently, there are several approaches to solving this problem, so the wide choice often leaves users with difficult choices.
There are many different systems for insulating facades on the market, each of which requires compliance with a number of norms and rules - from the selection of materials to installation.
Advantages of external thermal insulation systems
External insulation is considered the most popular - it has repeatedly proven its effectiveness. Internal thermal insulation, of course, also plays an important role in construction, but its advantages are incomparable to external ones. An external thermal insulation system has many advantages.
Reduced environmental impact
External insulation protects walls from overheating and hypothermia in any season of the year. As a result, the durability of the building increases, cracks do not appear on the facade, the plaster does not peel off, and the seams do not depressurize.
Exposure to moisture is eliminated: with external thermal insulation, the destructive effects of snow and rain are significantly reduced. There are also no ice formations in the thickness of the wall surfaces due to capillary moisture and its condensate.
Condensation protection
In the cold season, it is not uncommon for the temperature of the façade walls to drop below the “dew point”. As a result, condensation forms on the internal surfaces. The external façade insulation system prevents its appearance.
Smoothing or eliminating cold bridges
External facade insulation technology involves heat accumulation by the walls. As a result, the temperature of the coolant in the heating system decreases and the orientation of the building ceases to play a role - the temperature dependence disappears. “Bridges of cold” either smooth out or disappear.
Creating the perfect wall surface

Due to heat insulators, the wall structures of the building look smooth, and various defects inherent in stone and concrete are hidden by insulation.
High noise absorption
Most insulation materials are considered good sound insulators. Their use reduces noise coming from the street and creates a comfortable environment in the premises.
Durability
Although heat-insulating materials are constantly exposed to the environment, their production technology has long made it possible to create products that last for decades without losing their initial performance properties. 30-50 years is the average service life for any high-quality insulation.
Classifications
To protect the thermal insulation layer from destructive and pervasive atmospheric influences, various facade insulation technologies have been developed. Today, there are several options for external insulation systems for facades: wet and ventilated, siding, thermal panels, etc. Each technology has its own characteristic features.
Thermal insulation board
The efficiency of insulation work and the durability of the system largely depend on the façade slab. Facade insulation systems are made in two ways - contact and hinged. Contact methods - wet insulation, suspended methods - insulation of a ventilated facade.

If we consider the issue from the standpoint of cost, then the most economical and at the same time effective technology for insulating facades can be defined as thermal insulation systems with “wet” protection of each subsequent layer of insulation.
Installation of a wet facade
Since the work will be carried out at a certain height, you need to prepare a stepladder or install scaffolding in advance. The arrangement of a wet façade involves a strict order of application of layers with a mandatory preparatory stage.
Taking measurements
To assess the evenness of the facade, you need to hang it using laces:
- A piece of reinforcement up to 1.5 cm thick is attached in the upper corner, and a plumb cord is tied at a distance of the thickness of the insulation plus 1 cm.
- Another piece of reinforcement is nailed from below, the cord is pulled and tied.
- The second nylon cord is fixed in the same way on the opposite side of the wall, and a horizontal cord is attached to them with paper clips.
- By moving the latter, you can measure the distance to the wall at different points.
- The measurement results are recorded and an approximate deviation map is drawn.

This method reveals blockages in walls and the presence of bumps. This data will help you decide whether it is necessary to further increase the thickness of the insulation or whether you will have to cut off some parts of the sheets. Excessively protruding areas are cut off or cut down.
Preparing the walls
The base must be clean, durable, open-pore, rough. All height differences of more than 1 cm are eliminated, sagging from the mortar is cut off, cracks are covered with cement mixture. Concave areas are also sealed, otherwise voids will form in these places under the insulation.
The crumbling areas are cleaned down to the base layer, and any remaining paint must be removed. Scrubs oil, grease, and bitumen stains. Old plaster is left only if it holds tightly.

Moss, mold, and fungus are cleaned off and the walls are treated with a special bactericidal composition. All metal elements before fixing the insulation (antenna fasteners, air conditioners, etc.) are coated with an anti-corrosion compound.
Priming the walls
Priming is carried out when the repair layer on the walls is completely dry. Apply the product with a roller or brush, not missing even small areas. Places with increased absorbency are treated especially carefully, 2-3 times. Allow the primer to dry, then proceed to the remaining steps.

Installation of the base profile
To prevent damage to the insulation from below and securely hold the first row of slabs, first attach the base profile. It is placed 40-60 cm above the base level so that the insulation fits in without a gap.
Holes are made in the wall for fastening (3 holes for every meter of profile). They lean the part, insert plastic dowels into the holes, and hammer it in with a hammer. The next profile is applied end-to-end, without overlap.

Installation of insulation boards
To install the insulation, use cement-based adhesive for exterior use, which is diluted with water (according to the instructions) using a drill with a mixer attachment. Leave the mixture for 5 minutes, knead again and get to work.
The composition is applied to the insulation in strips 3-4 cm wide, retreating 3 cm from the edge. Several large slides are placed in the center. Along the contour of the insulation board, the glue strip is broken in some places with a spatula to reduce the risk of air pockets.

Applying glue to façade insulation
Further progress of work:
- Immediately after applying the glue, a sheet of insulation is applied horizontally to the facade, and passed over it with blows of a mallet or fist through a trowel.
- Align the position of each sheet of insulation according to the level.
- Excess glue is immediately cleaned off.
- Incorrectly applied insulation is torn off, the solution is removed, a new one is applied, and only then the manipulations are repeated.
- The sheets are placed from bottom to top horizontally with staggered seams, overlapping at the corners, followed by cutting two elements along each other.
- Any seams should not be wider than 2 mm (in extreme cases, a thin strip of insulation is inserted into the gap or sealed with polyurethane foam).
- After 48 hours, all unevenness of the insulation is removed with a grater with sandpaper attached to it.

After the glue has dried, the slabs are additionally fixed with dowels with wide heads. Using a puncher, drill holes 1.5 cm longer than the dowel, install mushrooms (about 5 per sheet of insulation) and spacer tips.
Application of a base layer of reinforced plaster
Wet plaster of the facade must be reinforced with a special alkali-resistant fiberglass mesh, which is attached to the same glue. Work begins with corners and slopes and only then begin to process the main plane of the walls.

Strengthening corners
For this purpose, plastic corners with a mesh are used, which do not deteriorate from the action of cement mortar, do not suffer from rust and are easy to cut. Work begins from any corner on which a solution 2-3 mm thick is applied.
Place the parts level, carefully aligning them horizontally and vertically. The protruding glue is smoothed out with a spatula, and the corners are securely fixed.

Reinforcement of window and door openings
Using a level, check the position of the slopes again and, if necessary, go over them with a trowel. Apply a layer of mortar, apply and stretch the profile mesh, embed it in the glue and iron it. The entire perimeter of the opening is treated in this way.
Then they install the corners with fiberglass mesh and window sill profiles, controlling their position with a level. Next, additional strips of fiberglass mesh 30-40 cm long are glued onto the internal corners, the width of which is equal to the width of the slope.
Surface reinforcement
For reinforcement, choose a fiberglass mesh coated with a special polymer composition that is not afraid of alkali corrosion. The mesh density can vary between 160-220 g/m². If the indicator is lower, the material will begin to stretch and the reliability of the reinforcement will decrease.
To secure the mesh, proceed in the same way as in the case of corners. It is attached to a layer of adhesive mixture by recessing.

This stage begins only 3 days after fixing the insulation, but no later than 14 days, otherwise the heat-insulating layer will begin to deteriorate. They work in dry weather at temperatures no higher than +25 degrees.
Fastening the reinforcing mesh to the insulation
When attaching, the nets move from above, from the left corner, sideways and downwards in diagonal movements. At the bottom of the wall, near the base profile, the material is cut evenly.
The glue is scooped up with a narrow spatula, transferred to a wide tool and stretched directly over the insulation sheets. The layer thickness should not exceed 3 mm. Work with small areas (approximately 1 m²), since the cement mortar dries quickly.
The fiberglass mesh is placed so that the 10 cm wide edge rests on the insulation not covered with glue. Afterwards, iron it with a spatula towards the edges, while the glue is evenly distributed over the insulation sheet.

The seams are joined only vertically, since the mesh is sold in rolls. The edge left without glue serves as an overlap area. It is covered with the mixture, the next strip of material is placed on top and processed with a spatula so that the seam is smooth.
Decorative finishing
Most often, walls using wet facade technology are treated with decorative plaster and then painted. Methods for decorating walls after fixing insulation and reinforcement:
- Allow the wall to dry completely, then sand it with a plastic float in a circular motion.
- They brush off the dust from the wall and prime the coating.
- Start applying mineral, silicone, acrylic or silicate plaster using the chosen method (for example, bark beetle).
- After drying, paint the plaster with facade paint.

Contact method
Contact insulation is based on the use of special plates made from different raw materials. This includes mineral wool, polystyrene foam, and cellular glass. For finishing, thin-layer decorative plaster is used.
Plaster finishing simultaneously performs a protective and decorative function. Considering the quite reasonable cost of insulation, the facade becomes both beautiful and quite warm. The thermal insulation system of the facade is applicable to residential buildings, both existing ones and new buildings.

Such a facade makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the walls and increase them in terms of energy savings and noise insulation. The fire safety of the “wet facade” in question is also noted.
In addition, the “wet method” does not actually increase the load on the structure of the structure. When using this technology, there is an undeniable possibility of continuous thermal insulation, even despite the impressive area of the facade.
Types of contact systems
There are two types of contact insulation system for facades - light and heavy wet method. In the latter case, the functions of the supporting structure are performed by a metal mesh, which is connected to the wall and insulation with fasteners (braces and spacers).
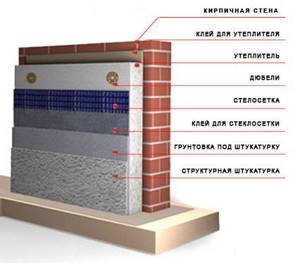
The easy wet method involves installing a heat-insulating layer consisting of facade slabs with glue to the outer part of the wall. After fastening, the insulation material is again covered with glue, on top of which a reinforced glass fiber mesh is placed. If necessary, the slabs are attached to the wall not only with glue, but also with dowels.
The load-bearing function falls on the heat-insulating facade slab. A reinforcing layer is distributed over the fiberglass mesh. As a rule, the total thickness of all layers is no more than 9 mm.
General advantages of external wall insulation
- A warm facade reduces gas and electricity consumption by one and a half to two times;
- Due to proper thermal insulation of the walls of the house and sealing of joints, the microclimate in the interior is normalized. In winter, the temperature in the house does not drop below 22 degrees Celsius. And in the summer it remains comfortably cool due to the accumulation of heat outside the insulating panels;
- If the installation of insulation and cladding is carried out according to all the rules, you can observe a noticeable increase in the sound insulation of the walls of the house;
- The cladding protects the walls of the building from the penetration of moisture and precipitation, as a result the facade does not freeze, and therefore is not at risk of premature destruction;
- The appearance of the building is noticeably improved, which increases its liquid value;
- The need for constant repair of the façade of the house and its supporting structures disappears. Proper installation of insulation and exterior finishing delays the repair period for at least twenty-five years;
- Modern insulation systems reduce the cost of excavation work and strengthening the foundation, make it possible to reduce the thickness of walls and save on the installation activities themselves.
Want more information on the topic?
Look at these articles: Using thermal panels for insulation and cladding of the facade of a house One of the most important stages in the construction and finishing of a house is ... A brick house: how to insulate it from the outside The climatic conditions in our country are really quite ... A wooden house: how to sew up a pediment At the final stage of constructing a wooden ... How to insulate the facade of your house from the outside It doesn’t matter whether you do it yourself or with...
Advantages of the easy “wet” method
The advantage of facade insulation systems made using the light wet method lies in the location of the so-called “dew point” outside the wall. Thanks to this, the problem of “cold bridges” that can reduce thermal insulation disappears.
Another plus is that the living space is not reduced, because all the necessary work is carried out outside. Insulation materials are also universal materials in terms of finishing. Based on them, you can implement an aesthetically attractive architectural project of almost any complexity - for example, decorating walls with marble chips or tiles.
Flaws
This approach has some disadvantages:
- foam has very low vapor permeability characteristics - sometimes this causes discomfort due to high humidity;
- the problem of the integrity of the external finishing of the facade during shrinkage processes is not solved if the plaster layer functions for shear;
- even with very low vapor permeability, the outer layer of the finish, as well as the adhesive composition, is saturated with moisture.
Installation of a contact system has its own characteristics. One of them is careful preparation of the base.
If the structure is installed using the light wet method, the minimum ambient temperature should be at least 5°C. The low maintainability of local areas turns replacement into a labor-intensive undertaking.
External thermal insulation value
Heat is lost from rooms for two reasons: due to cold air currents and due to heat exchange between the walls of the house and the environment. In the first case, heat is lost due to a violation of the hermetically sealed joint between the floors and the load-bearing elements of the buildings. In the second - due to insufficient insulation of the walls, roof and basement.
Carrying out thermal insulation work increases the amount of heat accumulated by the wall.
As a result, even if the heating stops, a wall insulated from the outside cools down six times slower than one insulated from the inside.
Another undeniable advantage of external thermal insulation systems is the shift of the “dew point” outward, beyond the walls, which protects building facades from freezing and rapid destruction. Lightweight thermal insulation blocks reduce the load on the foundation and the cost of strengthening it.
Mounted systems
Wall mounted facade insulation systems are considered more modern and have many advantages over the contact method:

- their use makes it possible to reduce energy costs for heating by more than 1.5 times;
- no need to prepare the base before installation;
- can be installed at any time of the year;
- service life is about 30 years.
Insulation boards in this case are attached to the surface mechanically - dowels or load-bearing elements are used. At a distance of 2-5 cm from the outer part of the heat insulator, elements of external finishing are placed, which perform two functions at once: the first is decorative, the second is protective.
The surface layer of the system is made of various materials - from stone and metal to ceramics and wood. You can decorate the facade with glass, which has become very popular in the decoration of office buildings. In this case, the insulation board is covered with white or black glass fiber canvas. An important advantage of ventilated facades is the removal of moisture accumulated in rooms without forced ventilation.
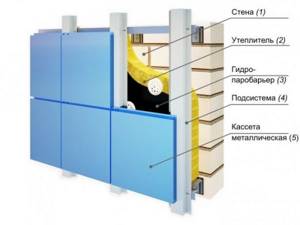
For the manufacture of curtain-type facades, sandwich panels are often used - structures consisting of a heat-insulating core and 2 steel sheets. They are suitable for finishing both new and reconstructed buildings. Products from different manufacturers differ in color, size and other features. However, high-quality sandwich panels are united by high reliability, durability and wide functionality.
Advantages of complex systems for facades
When using facade insulation systems, the color scheme of the facade can be changed at any time. Taking into account the thermal insulation system of the facade at the design stage of the building saves on expensive building materials for walls. The difference in price for a medium-sized building with and without insulation is on average about 150 thousand rubles, but if you take into account the heat savings, such finishing will pay for itself by reducing heating bills within 5-7 years.
If the structure is built from foam concrete, based on the insulation system, it is possible to use a block whose thickness is 10-15 cm thinner. When erecting a building made of brick, the fence structures are mounted in one brick and are 64 cm.
Thermal insulation materials for facade design
There are several types of materials for thermal insulation:
- stone (mineral) wool;
- glass wool;
- Styrofoam;
- EPPS;
- polyurethane foam;
- ribbon tow.

Mineral wool is suitable for buildings located in areas with high humidity, since it has low water absorption. This is a fire-resistant, environmentally friendly material, which also has good sound insulation properties and low thermal conductivity.
Glass wool is an affordable, lightweight material, but it has high water absorption and is harmful to health, which also needs to be taken into account
The cheapest material that holds heat well is polystyrene foam. Among its disadvantages is that it is flammable and therefore dangerous. And small inhabitants of the streets - rats and mice - also like to chew on it. When exposed to sunlight, foam releases substances harmful to humans.
Extruded polystyrene foam is a universal material. Many experts recommend using it not only for insulating the facade of a building, but also as a building material for flooring. The material has good sound insulation and is resistant to moisture and therefore mold does not grow on it.
With polyurethane foam, everything is generally simple - it is sprayed onto the walls. Among the advantages, one can also highlight that after it no gaps are formed and subsequently the use of sealant is not required.
Tape tow allows steam to pass through well, so it does not disrupt gas exchange with the outside world. But at the same time, it also allows water to pass through perfectly and therefore additional waterproofing is required.
Each material has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it can be quite difficult to single out any main one. Different insulation materials can be used for the same building.
Types of facade insulation systems can be divided into wet and suspended.
Standards
Everything that happens in the atmosphere, including the phenomena of natural cycles and the consequences of technogenic human activity, causes increasingly sharp temperature changes, which is strongly reflected on the surfaces of structures and buildings. Without additional protection, facades gradually deteriorate under the aggressive influence of the environment.
As a result of such exposure, the building cannot effectively conserve heat during the cold season. Today in construction it is believed that, regardless of what material the walls were built from, it is necessary to carry out auxiliary insulation with a material at least 50 mm thick.
According to Russian standards, for a brick-silicate wall built with 1.5 bricks, it is necessary to use insulation with a thickness of 100-120 mm. Such a house will fully comply with current energy efficiency requirements. Naturally, the market value of such a house with subsequent insulation using facade insulation technology increases almost 2 times, but an insulated facade will subsequently bring serious savings on repairs and heating.
Criteria for choosing insulation
When selecting facade insulation, it is necessary to take into account the type of wall material, thickness, architectural features and dimensions. Climate and weather conditions are also taken into account. The thickness of the insulation layer is determined by the building density of the area - a building that stands alone requires a larger layer of insulation than a house located in the central part of a densely populated village.

The thermal insulation layer in facade systems is made from extruded or ordinary polystyrene foam, as well as from laminated or ordinary mineral wool. Both types of material are supplied in slabs. Mineral wool is made from glass, soda, limestone and sand. Its structure is represented by glassy thin fibers. Positively distinguished by high vapor permeability.
Expanded polystyrene is a polymer that has the following positive qualities: it does not enter into chemical reactions with other substances, is resistant to moisture and is not susceptible to rotting and fungus. It is recommended for use for insulating plinth slabs. According to statistics from the last 3 years, consumers prefer systems made of polystyrene foam as the cheapest material.
Methods for insulating building facades
There are several ways to create a warm building façade. The optimal solution should be selected based on the design of the façade walls and environmental conditions. In general, building insulation systems can be divided into the following types:
- insulation under plaster (light and heavy plaster systems);
- ventilated facades;
- facade thermal panels.
"Wet" facade
This is one of the most common and inexpensive ways to insulate walls. The insulation is solid types of mineral wool and polymer blocks. Thermal insulation is attached to the walls using glue and dowels. A reinforcing mesh is stretched over it, onto which a primer and a thin layer of plaster are applied. Plaster solutions must be sufficiently vapor permeable. Thanks to fillers such as marble chips and polymer additives, the outer layer of finishing is very strong and reliable. This technology is especially in demand in low-rise construction.

The structure of the “wet” method of thermal insulation of walls
In turn, “wet” can be divided into two subspecies:
- Lightweight plastering systems . Due to its low cost, this subtype of “wet” facade is more popular. Thermal insulation is attached to the walls using glue and dowels, as well as a protective cladding coating. The structure is protected from mechanical damage by aluminum profiles, as well as elements that increase the tightness at the junction of the finishing with doors, windows and roofing;
- Heavy plastering systems . They differ from the previous type of structures by a more massive plaster layer, which protects the insulation and walls, and also increases their resistance to mechanical and weather conditions. The thickness of the plaster can reach up to 5 centimeters. Depending on the number of floors of the building, the reinforcing wall is selected, as well as the method of attaching the insulation to the walls.
Ventilated facade
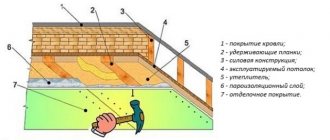
The peculiarity of this method of insulation lies in the arrangement of a special hanging system, consisting of several layers like a layer cake: sheathing, insulation, moisture-proof membrane, cladding, as well as an air gap between the insulation and the exterior finish.
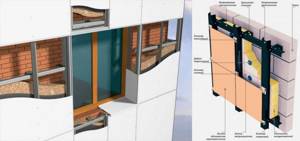
Structure of the hanging system
Polypropylene foam and mineral wool are most often used as insulation.
Curtain facades are used for finishing and insulating industrial, administrative and residential buildings of any number of floors. For the finishing layer, you can choose any cladding: plastic, wood, metal, glass, clinker tiles for brick, block house, siding, sandwich panels. Therefore, hanging systems can give the building any desired look.
Facade thermal panels
Another modern way to carry out cladding and insulation work at the same time. This method of finishing buildings is the simplest and fastest. Insulated blocks are a sheet of expanded polystyrene, the front side lined with tiles or steel sheets painted to resemble bricks. Such thermal panels are glued to the walls with a special solution and secured with dowels through special “masonry” joints.
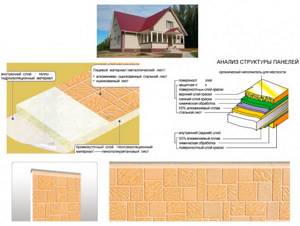
Structure of the Stenolit panel
The façade systems “Stenolit”, made on the basis of domestic materials and Japanese designs, are very popular among specialists. “Stenolit” blocks are maximally adapted to the harsh Russian climate and, along with light weight, have such qualities as ease of installation, effective thermal insulation, and affordable cost.
Stenolit blocks consist of polyurethane foam thermal insulation and a steel coating with a special resistant paint. On the outside, thermal panels can imitate brickwork and other natural materials.
Thanks to the special coating, the service life of Stenolit panels significantly exceeds the service life of its analogues.
Warm blocks for cladding buildings protect walls from external influences and deformations, extend their service life, and improve sound, moisture and thermal protection.
The main advantages of Stenolit wall panels include:
- protective function (products manufactured under the Stenolit brand effectively protect building facades from moisture, precipitation, temperature changes, and sunlight;
- excellent thermal insulation (in this indicator, warm blocks are superior to foam concrete, brick and mineral wool);
- beautiful exterior (Stenolite thermal panels significantly improve the appearance of the building, regardless of its original architectural orientation);
- a wealth of shades and textures, including imitation brickwork and wood;
- anti-vandal characteristics;
- excellent fire safety;
- color fastness and the ability to withstand direct sunlight for a long period of time without loss of original quality;
- preservation of the functional characteristics of the material in any weather and regardless of the intensity of use;
- simplicity and speed of installation;
- ease of maintenance (just wash the panels with water from a hose).
Installation
You can install a facade insulation system with your own hands, however, specialists with experience will cope with this task faster. Insulation work involves several stages, after each of which you need to check the absolute evenness of the surface, cleanliness and smoothness.

It is very important that there are no depressions or cracks on the surface of the walls - otherwise the finishing layer will not be continuous, and the thermal insulation will become ineffective.
Preparatory stage before wall insulation
In order for the insulation to adhere well to load-bearing walls, to be even and to fit well, you must first carefully prepare the surface.
Fixing the base profile
A necessary procedure used to fix insulation and decorative trim, if necessary, to protect the end. Before the glue dries, the sheets are not stable and can move. For proper fixation, markings must be made first.
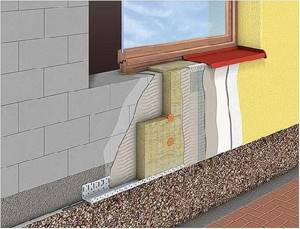
Installation of external window sills
An external window sill is also called a sill because of its main function: draining water away from the window. The window sill is an integral part of the building facade and gives the window frame a finished look. If the sills are installed correctly, water will not fall onto the wall surface. The external window sill is fixed directly to the window.
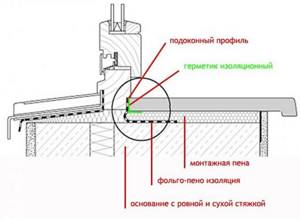
Figure 4. Installation of external window sills
Differences in materials
Weather requirements are the same for both mineral wool and expanded polystyrene. The technology in both cases is virtually identical, and only the fastening method differs. Glue is applied to polystyrene foam boards over the entire surface, around the perimeter, or in “patches”.
In the case when polymer insulation is fixed to plastered walls, in addition to glue, dowels are used, at a rate of at least 4 per 1 m2. For mineral wool slabs, mechanical fastening is mandatory. Dowels with a tip made of galvanized steel are used.
The next point that requires special attention is the hydrophobicity of mineral wool. On this basis, before applying an adhesive solution to the surface of the slab, it is first puttied with an identical solution. Next, a layer of reinforcement must be applied to the thermal insulation slabs; after setting, it is primed with plaster mixture.
The plaster backing compound of the wall protects the building for 6 months if work is suddenly suspended. The procedure for applying the plaster itself summarizes. When directly applying and drying the plaster, temperature indicators should vary in the range from +5С to +25С.