Various materials are used to insulate roof structures. One of the most commonly used materials are polymer-based heat insulators. Insulating a roof with polystyrene foam is quite simple and quick; you can carry out this operation on your own, without the involvement of specialists. After reading this article, you will learn the technological process of roof insulation using polystyrene foam, as well as all the priority points that should be taken into account before carrying out work.
What is hidden under the name “foam plastic”?
Foam plastic is the popular name for expanded polystyrene. But it is worth distinguishing between simply expanded polystyrene and extruded polystyrene foam.
Polystyrene is a product of the polymerization of styrene, which is quite clear from the name alone. In appearance, polystyrene is hard, elastic and colorless. It does not have high mechanical bending or tensile strength, and low density. Even lenses are made from this substance, not to mention dishes and other household items.
Expanded polystyrene is foamed polystyrene, which is produced in the form of sheets up to 20 cm thick and can vary in density. It costs much less than extruded polystyrene foam, is more friable and has a more limited scope of application.
The name of extruded polystyrene foam comes from its production method - extrusion, when the raw material is squeezed out through certain holes of the same size. Even more precisely: extruded polystyrene foam is a gas-saturated melt of polyethylene. It is produced in the form of sheets with a thickness of 30 to 70 mm, and varies not only in density, but also in color. Much more durable than conventional foam, it has a tongue-and-groove system along the edges and is easy to install - there is no need to fill the joints. In addition, its thermal conductivity is even lower - in fact, the lowest of all existing insulation materials.
Extruded polystyrene foam is made by extrusion, due to which it has a uniform, closed-porous structure. Each cell has a diameter of no more than 0.1-0.2 mm.
Extruded polystyrene foam in English is called XPS, in Russian - EPPS. They are also insulated with polystyrene as a sandwich panel, when the top of this insulation is covered with an OSB board or a metal sheet:
Moreover, working with this material is quite simple:

But one of the most popular XPS products on the Russian market is the light blue Primaplex slabs. This is a fairly durable material with extremely low water absorption, dimensional stability and high frost resistance.
Laying a waterproofing layer.
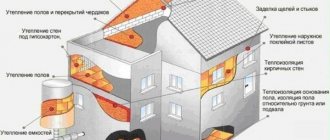
Roof insulation with foam plastic begins with laying a waterproofing layer.

There are a large number of waterproofing materials on the market, but they all have almost the same membrane structure and allow moisture to pass in one direction outward.
The waterproofing material is laid on the rafter structure without exerting tension; it is allowed to sag. The material is laid along the roof along its entire length during installation.
It is necessary to monitor the correct installation of the waterproofing layer outward.
Subsequent strips of material are overlapped by at least 10 centimeters. Next, a sheathing is made on the waterproofing material.
To create a ventilated gap between the sheathing and the film, bars 40-50 millimeters thick are nailed to the rafters, to which the sheathing is attached. Next is the roofing.
Why is foam plastic better than other thermal insulation?
Now let's look at the popular myths about polystyrene foam.
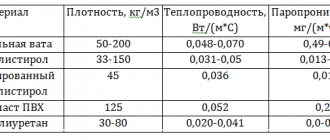
So, the first and most important quality for which this insulation is valued is its high thermal insulation. This coefficient is 0.035-0.048 W/mK at 25C, and 0.20 W/mK for its individual types, according to manufacturers. But absolutely all foamed plastics are afraid of water and quickly absorb it. And expanded polystyrene, which is made using the non-press method, has a water absorption of up to 350% of its mass. And even this is not the limit! And the more moisture in the insulation, the lower its thermal insulation properties.
But in practice, ordinary polystyrene foam lasts only 10-15 years as roof insulation, after which its heat-protective qualities sharply decrease. But extruded polystyrene foam, abbreviated as EPS, is more durable.
But polystyrene foam has the lowest thermal conductivity among all existing roof insulation materials. Even in severe frost, the temperature of 50 mm thick foam and EPS sheets will be +5°C. Plus the following advantages over other heat insulators:
- Soundproof.
- Stable dimensions throughout the entire period.
- Easy to install and cut to required sizes.
- No need for wind protection.
- Resistance to various types of chemicals.
And quite interestingly, in factory conditions they test the strength of extruded polystyrene foam: they lower it into water, heat it to +40°C and cool it to -40°C. Each such cycle is equivalent to one year of operation. Therefore, manufacturers confidently declare that extruded polystyrene foam can serve as under-roof insulation for 50 to 80 years.
And the most important advantage of extruded polystyrene foam is that it does not reduce its thermal insulation properties even when in contact with water. Whereas conventional insulation works properly for only a few years, and then, if mistakes were made in roof insulation, they gradually reduce their thermal insulation qualities and the house has to be heated more and more. This is not to mention other related problems.
But in a roofing pie, polystyrene foam can be damaged by rodents: they will not live in it, but they will make passages. Unless you hide these sheets outside:

Advantages and disadvantages of roof insulation with mineral wool
Installing an insulated roof using mineral wool may seem a little cheaper at first glance. If we talk about the obvious advantages of this roofing material, it should be noted that the low cost of mineral wool really wins over other insulation materials.
Here are the disadvantages of mineral wool:
- Great water absorption capacity;
- A high percentage of deformation from the initial dimensions (I advise you to use mineral wool not on fiberglass, but on basalt - then this disadvantage will be less pronounced);
- Significant loss of properties when wet;
- Release of microparticles into the air;
- Often an allergen;
- Requires hydro, wind protection and vapor barrier.
Is polystyrene foam safe as insulation?
Officially, this material is classified as environmentally friendly, i.e. those that do not pollute the environment and are not dangerous to humans. But let’s initially determine what influence on the human body can be considered dangerous, and what can be considered prejudice and unnecessary anxiety. You will be very surprised!
Such different concepts
Thus, in the world it is customary to refer to two main concepts for assessing the harm to the human body of certain substances: threshold and linear.
The threshold concept states that all harmful substances in a residential building must be reduced to a certain level for each of them, a threshold, which is fixed by the MPC value (maximum permissible concentration). Those. This is the amount of a harmful substance in the air that can already harm a person. Exceeding this threshold always leads to negative consequences such as illness or even death. Let's give an example: the cheapest foam plastic was chosen as insulation, it was installed incorrectly, there is no normal ventilation in the home. Result: sick liver in the household. But in a well-ventilated house, no one feels harm for a long time. Those. we are talking about the fact that the concentration of a harmful substance below the established threshold does not have a dangerous effect on a person, and a healthy body can easily cope with small toxins. It's like inhaling cigarette smoke from your interlocutor once.
In all countries of the former USSR and modern Russia, building codes are based on the threshold concept. But in Japan, Canada, Germany, the USA and Belgium, the linear concept is at the forefront, the essence of which is that the harmful effect on the human body linearly depends on the total absorption of a certain substance. Those. At one time, cigarette smoke really will not have a significant negative effect on the body, but constant smoking will. The same applies to polystyrene foam: if such insulation is used both on the roof and on the walls, then every day a person absorbs the permissible amount of styrene through the lungs, which is not so little in a year. In a word, small concentrations of poison with long-term use are also harmful. This is easy to show using the example of modern megacities: all transport exhausts and factory emissions do not individually exceed the sanitary threshold, but still life is not sweet for the city residents.
If, when insulating, we adhere not to the first concept, but to the second, then the value of the maximum permissibility of styrene in a residential area will have to be reduced by 594 times!
Of course, polystyrene is used both in the food industry of our country and in medicine. But remember that its toxicity is calculated according to the same concept - threshold. Just note that polystyrene foam and polystyrene are already being phased out in many countries, and in some even banned.
A substance that is not excreted from the body
Now let us recall that styrene is a condensed aromatic compound that contains benzene in its molecule and is bad because it is not excreted from the human body. And, according to modern scientists, in residential construction the threshold for the presence of styrene in the air should be reduced to such minimum values that any polymerization products (including polystyrene foam) should be prohibited.
Therefore, we conclude: styrene is toxic to humans primarily because it accumulates in the liver. After all, the problem is that the human body can actually cope with an ordinary toxin by simply processing it with the help of the liver and throwing it away naturally, but styrene is not removed from the body - it only accumulates. Therefore, a threshold concept cannot be applied to foam insulation - only a linear one.
In addition, according to modern SNiPs, toxicity indicators of combustion products must be determined for combustible materials. And for high-quality expanded polystyrene this value is T2, which means “moderately dangerous”.
99% polymerization
There is one more point that not everyone knows about. The fact is that 100% polymerization of EPS is only a theory, but in practice it does not even reach 98%. In addition, even the polymerization process itself is reversible, because polymers are easily destroyed by ultraviolet rays, ozone, water, oxygen, heat and mechanical stress. Then free styrene begins to separate from the EPS and penetrates into the living room, albeit in a small concentration, but it affects the heart and women’s health quite a bit. And the most common problems from this element are toxic hepatitis, and all because of the cumulative properties of styrene, it accumulates in the liver, but is not excreted.
And finally, special studies of the Russian Academy of Sciences have shown that during its period of operation, polystyrene foam decomposes up to 10-15%, and 65% of the decomposed part consists of styrene.
The solution is ventilation!
But how can the foam used to insulate the roof harm it? If this is insulation from the outside, then, of course, no way. If from the inside, but the attic is not used, then it is necessary to carefully consider ventilation. But if we are talking about a residential attic with such insulation, then things are bad. At least we don't advise you to do this.
Or it’s good to cover the foam in front with other insulation, as in this project:

The best alternative to polystyrene foam is polyurethane foam

PPU is easily applied to roofs, walls, floors, ceilings, partitions and creates an optimal layer of protection against precipitation
Polyurethane foam is also an excellent option for roof insulation. The material allows you to save heat as much as possible. This type of insulation, in compliance with all standards during the work, optimal sealing of roof seams, window, doorways and walls, creates a warm atmosphere in the house and heating costs will be minimal.
In European countries and the United States, roof insulation using polyurethane foam has been relevant for at least the last 25 years. Practical Europeans and Americans have long found out how beneficial this type of insulation is. And the work process does not raise any doubts at all. The material is easily applied to roofs, walls, floors, ceilings, partitions and creates an optimal layer of protection against precipitation and high humidity. Also, spraying has:
- the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient;
- thickness effectively saves energy consumption;
- During the work process, unique equipment is used that eliminates defects during application;
- the process takes 5-7 times less time than with other types of insulation;
- minimum weight;
- compactness during transportation;
- integrity of the applied layer, excluding cold bridges;
- no by-product waste;
- environmental safety;
- moisture resistance;
- service life of 50 years or more. Withstands temperature changes from 100 to -180 degrees.

The use of sprayed insulation helps solve the problem of mismatch between the dimensions of the span and the insulation
The process of applying a layer of polyurethane foam requires high-quality equipment. And it’s quite difficult to take action on your own, without experience and skills. To get a positive result in the end, you should contact experienced craftsmen with the necessary tools.
The Ecotermix company is a team of experienced specialists with skill and dexterity. Spraying polyurethane foam can be done in a matter of hours. Unique equipment available. High-quality and professional execution will guarantee long-term operation of the thermal insulation system.
We recommend watching a video about roof insulation with polyurethane foam from Ecotermix:
How to insulate a roof with foam plastic inside and outside?
But to answer this question, we have prepared for you a series of detailed master classes.
Basic methods of attaching foam to a surface:

But mainly two methods of fastening are popular. Adhesive:

On screws:

This is how to properly insulate an attic roof:

As insulation for a concrete roof:

Is it possible to insulate an attic with polystyrene foam?
To insulate an attic with your own hands, the choice of building materials is based on the environmental component. Expanded polystyrene is a product of synthetic origin. When the plates are heated (+25-+30 degrees Celsius), phenol, acetophenone, and methyl alcohol are released. Inspecting authorities claim that the amount of substances complies with acceptable standards. Today, manufacturers are using new technologies for the production of synthetic insulation aimed at reducing the content of residual harmful products. To simplify the choice of polystyrene foam for the buyer, finished products are divided into 2 groups:
- Technical expanded polystyrene is used for work on facades, non-residential buildings, and in road construction.
- Household insulation can be installed with your own hands inside a residential or social facility.
However, there are restrictions on the use of polystyrene foam regarding the type of structure. The addition of fire retardants reduces the melting and combustion temperatures, but it is impossible to completely eliminate this property of the thermal insulation material. When using polystyrene foam to insulate an attic roof, experts recommend using non-combustible roofing and decorative finishing. And the electrical wiring must additionally be insulated with a corrugated plastic pipe or hidden wiring should be eliminated altogether.
What difficulties may arise during insulation?
But there are many such difficulties, so get ready to study all the nuances of such insulation.
Point 1. Expansion joints
Here is the first stumbling block that may frustrate you when insulating your roof with foam plastic. This is the concept of expansion joints. Seams form over time between thermal insulation materials due to temperature changes, as well as along the perimeter and in places where beams pass. You can notice such problem areas in winter - by a thin strip of ice or snow that does not roll off. And there is a limit for deviations from the norm for these seams, and for pitched roofs it is one, but for flat roofs it is completely different.
Although some home craftsmen simply cut out the foam to the size of the rafters and insert it without any seams:

Point 2. Weathering
But the most alarming thing is that polystyrene foam undergoes weathering, during which gas-containing mixtures are formed. And weathering in an ordinary attic with its ventilation through opposite dormer windows is inevitable. It is not advisable to decorate even a residential attic with polystyrene foam, so that in the heat you simply do not inhale so-called persistent organic pollutants, which, by the way, are strictly prohibited in Western countries by the Stockholm Convention.
Point 3. Preliminary plan
Unlike the installation of conventional insulation, before installing foam sheets, you should carefully consider the plan and make sketches. There are other difficulties: for example, such panels cannot be cut and processed mechanically, they cannot be secured with screws - only inserted into the finished structure. Moreover, if you need to carry out certain communications under the roof (electricity, for example), then you will have to organize another mounting layer under the panels, at least 50 mm thick.
Technology ↑
Pitched roof ↑
External polystyrene foam insulation
External thermal insulation is carried out parallel to the roof structure. Here, as a rule, insulation is used with extruded polystyrene foam or high-density polystyrene foam.
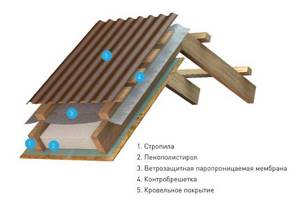
The process of insulation with polystyrene foam is performed in the following sequence:
- install a rafter system; Next, a counter-lattice is installed. To do this, wooden slats are placed on the rafter legs from below; penoplex is laid on them, placing the sheets between the rafters, flush with their upper edge; then comes the turn of the windproof vapor barrier film; install roofing material.
Insulation of the attic with extruded polystyrene foam ↑

- Penoplex sheets are laid in the space between the rafters and fixed with staples or corners. Additionally, the insulation can be supported with thin slats, placing them across the rafters. The laid and secured sheets of thermal insulation material together with the mounting rails must form a flat surface. It is necessary to provide a gap of approximately 200–500 mm between the waterproofing layer and the thermal insulation material. It is necessary for ventilation of the roofing pie. Penoplex sheets should be cut slightly wider than the pitch of the rafters so that there are no gaps between them. If there is still a gap between the rafter beams and the insulation, it is filled with either pieces of EPS or polyurethane foam, preferably polyurethane. Its excess can be cut off with a sharp knife immediately after hardening.
- Then a vapor barrier film is installed. It is fixed to the rafters with staplers. The canvases are laid with an overlap of 100-150 mm and taped with a special tape. The final stage is finishing. A counter-lattice is placed on top of the vapor barrier layer, which will become the frame for the attic cladding.