Carrying out thermal insulation work for the internal structures of a house allows you to extend the life of floors (attic, staircase, basement, interfloor), preserve heat and a good microclimate, and save money on electricity due to the use of alternative heaters.
Floors can be insulated with different insulation materials, depending on the type of construction, the recommendations of construction specialists and your own funds.
How to perform thermal insulation of floors, what is needed for this, what are the regulatory requirements, how to carry out calculations, what material is better to choose, what are the prices for them and other nuances, read more in this article.
Feasibility of implementation
Heat conservation in residential and industrial buildings largely depends on the measures taken during the construction process when constructing any type of floor. The space between rooms, especially in multi-story buildings, can separate a warm and unheated room at the same time.

Therefore, in order to avoid heat loss in the main room, it is advisable to use insulating materials at the construction stage:
- floors;
- interfloor spaces;
- attics, balconies;
- surfaces above basements.
Such measures will help save up to 15-25% of heat, which is very important for regions with cold climates and harsh winters.
Thermal insulation makes it possible not only to retain heat, but also to increase the layer of ceiling (interfloor, staircase) space. It also prevents drafts and additionally protects against unnecessary noise and sounds.
In addition, the layers of insulation that are installed under the finishing additionally protect the floors from wear and destruction, which helps to increase their service life.
There is no need to insulate the floors:
- in a favorable climate zone with above-zero average temperatures (southern regions);
- in underground basements not combined with residential apartments (cool temperatures are preferable there);
- in houses that are subject to demolition and complete modernization.
In all other cases, thermal insulation will be an appropriate solution. Thermal insulation begins only after the main construction is completed (walls are erected, roofing and windows are installed), and the ceiling is laid and fully prepared for finishing.
You can perform thermal insulation:
- in private and panel residential buildings;
- industrial and office buildings.
Thermal insulation will be especially effective for apartments on the first (above basements) and last floors (under the roof) , as well as in multi-storey buildings that are not well heated during the cold season.
Insulation of floors is carried out strictly according to technical standards and rules that regulate the sequential creation of layers of the cake.
Insulation of the attic floor with mineral wool
Mineral wool is an insulation material whose fibers are arranged in a certain way. It is this randomness that leads to the formation of an air cushion between the fibers, which imparts its properties to the insulation. However, this same feature of cotton wool increases its ability to absorb moisture. To avoid this, you need to know how to install mineral wool correctly.
Advantages of mineral wool:
- high density;
- long service life;
- Fire safety;
- ease of installation;
- the use of mineral wool for insulation of horizontal surfaces does not lead to caking, sliding and, as a result, the formation of cold bridges.
Among the disadvantages: the ability to absorb moisture.
Technology for insulating attic floors with mineral wool
There are three main ways to lay cotton wool: completely, in grooves or in cells (see photo). The choice of method depends on what load will subsequently fall on the floor. The most stable frame is obtained in the latter case.

Insulation of the attic floor with mineral wool
First stage
It starts with laying a vapor barrier film. The film will allow you to remove steam that rises from a warm living space into a cold attic. To lay the film correctly, you need to carefully read the markings on it. It is imperative to maintain an overlap of 100 mm.
Technology for insulating attic floors with mineral wool If insulation is carried out along wooden beams, then the film should go around all protruding elements. Otherwise, the beams may rot.
At the junction of the film and walls or other protruding surfaces, you need to raise it to a height equal to the thickness of the insulation plus 50 mm. and glue it with tape or wrap it on an insulation board.
Second phase
The insulation (cotton wool) is being laid. It's a pretty simple process. Plates or strips are easily cut with a construction knife to the required sizes.
When laying the sheet, you need to make sure that there are no gaps or the mineral wool material is not too compressed. Both will lead to a decrease in the quality of insulation. Typical mistakes in photos.
Technical requirements
Floors, which are horizontal structural elements, are:
- monolithic;
- wooden;
- reinforced concrete.
But the technical and regulatory requirements for arranging insulation are common for them, regardless of the material used or type of surface.
Materials that will interact with each other during the installation process must adhere well and comply with the following documentation:

GOST 16381-77-1992;- GOST 16381-77;
- GOST R 52953-2008;
- GOST 30643-2020;
- GOST 31913-2011;
- GOST 31309-2005;
- SNiP 3.04.01-87;
- SNiP 02/23/2003.
There are many additional regulatory documents that relate to:
- carrying out tests with thermal insulation materials;
- installation;
- calculation;
- selection of insulation materials for specific floors;
- product characteristics;
- layering technologies.
But the listed standards are basic. In their initial sections, these standards always offer references to other provisions on which they rely and recommend.
Important requirements for thermal insulation in residential and industrial buildings concern:
- The sequence of laying layers of the pie, and the correct calculation of materials.
- Use only high-quality certified products in work.
- Protection of floors from mechanical (shocks, deformations) and atmospheric factors (waterlogging, condensation, ice).
- Ventilation (air permeability) of the layers of the cake.
- Compliance with sanitary standards in work, and additional treatment of surfaces with antiseptic solutions.
- Purchase of consumables and tools that comply with GOST standards.
- Fire safety (selecting group “NG” - non-combustible types).
- Durability, density and strength corresponding to the indicators declared by the manufacturer in the accompanying documentation.
- Compliance with appearance and markings.
- Reliable fit and high-quality fastening to the surface, adhesion with adhesives and other building materials.
- Installation according to the plan and technical standards of construction documents.
- Using environmentally friendly industrial products that are safe for human health.
- Compliance with the slope of the material, no more than 2%.
- The use of different types of insulation (soft, hard, semi-solid, liquid).

And the thermal insulation material itself, produced in a factory, must be properly stored at acceptable temperatures, in dry rooms, excluding contact with water.
The requirements also concern the water-repellent properties of insulation and preventing the formation of mold and mildew.
Particular attention in the regulatory requirements is paid to the appearance of the products, since after installation they must form a flat surface that can be further finished, as well as sealing the joints between parts of the insulation.
Thermal insulation of all types of floors at the completion stages of construction can be done throughout the year, without focusing on seasonality.
How to properly insulate an attic in a private house with your own hands
When building a private house with an attic room, you need to properly insulate it.
Insulating the attic floor in cold and unused areas will prevent condensation from forming deep inside the house. Several reasons why the attic floor is insulated:
- High-quality thermal insulation allows you to maintain a temperature in a residential building that approximately corresponds to the dew point.
- Different temperatures at the junction of the ceilings and walls lead to the formation of mold and harmful flora, which contribute to the appearance of allergies.
How to insulate?
Insulation of floors is carried out using various types of heat insulators. These include roll, slab, bulk and foam materials. Each of them has its own advantages, which help to reliably retain heat in buildings, with certain technical characteristics.
It is most convenient to work with slab products, since they are easily transported, and installation with them is as fast as possible.
Popular materials for thermal insulation are represented by the following varieties.
Bulk solids
They are among the most affordable universal insulation materials that are easy to apply in bulk, forming a layer of at least 5 (cm).
This group of heat insulators includes expanded clay, vermiculite, slag - everything that belongs to a special breed of environmentally friendly crushed and specially processed stone, useful for construction and retaining heat.
Bulk materials are most suitable for arranging floors in rooms with a ground floor above basements, as well as for attics of private houses.
An important feature of installation with bulk materials is the use of vapor barrier and waterproofing , after uniform compaction and filling with cement mortar.
Mineral wool

It has a completely environmentally friendly composition (basalt base), is considered a universal and inexpensive heat insulator, as it is suitable for all types of surfaces, and can be laid in several layers.
The insulation is made in such a way that it completely stops cold bridges, retains heat for a long time, but due to its structure it requires protection from moisture (waterproofing) and storage in a dry room .
When forming layers of mineral wool, an overlap of up to 20 (mm) is required at the edges, which saves costs on sealants.
The only drawback of mineral wool products is the need to ventilate the room for 1-2 weeks, immediately after installation, due to the specific aroma.
Styrofoam
Refers to light and warm thermal insulation materials from the budget group , which is easy to work with. But its main disadvantages are the fragility of the base, so it requires careful handling during transportation and storage, as well as “special love” for it on the part of rodents.
They eat it, chew it and live in it, which is why polystyrene foam is not used for private homes. The insulation is not prone to the formation of mold and fungi, but when arranging layers for floors it requires mandatory vapor and waterproofing.
Penoizol, polyurethane foam (PPU)
This group of materials belongs to liquid heat insulators , which are sprayed onto the surface from ready-made factory cylinders, through a special device gun or spray gun.
Hardened foam not only retains heat well, blocking cold bridges, but also performs a protective function - it seals all existing surface imperfections (cracks, chips, unevenness).
also considered a universal product and is suitable for all surfaces on which, according to technical rules, it is applied with a layer of 15-22 (mm). The only drawback of these heat insulators is their high cost.
Glass wool
This type of insulation is considered one of the varieties of mineral wool.
The presented material is suitable for any floors and is available in slabs. It is easy to work with, as it is lightweight and adheres well to glue during installation.
Using this heat insulator, you can reliably protect the surface from drafts and cold temperatures, since it has a dense structure and can be used in several layers.

its important disadvantages are :
- need for waterproofing;
- creating sheathing;
- ventilation equipment, due to the strong absorbent surface;
- Observe precautions when working with it (gloves, protective mask).
Expanded polystyrene, Penoplex
Representatives of this class of insulation are considered among the best not only in the price segment, but primarily due to their quality characteristics.
Made from extruded polystyrene foam, an environmentally friendly material produced using improved technology that is not afraid of water and fire, the materials are able to quickly equip any floor surfaces and last for quite a long time, as they are not afraid of shrinkage and are well stored at any temperature.
Manufacturers produce insulators in slabs that are easy to transport. Some products, for example, penoplex, have a rough surface and a special edge, which adheres the products well to each other and to the ceiling.
Cardboard
Corrugated cardboard, which has a layered structure with an air gap, is used as insulation.
Corrugated cardboard can be laid in several layers , which in total must be at least 10 (cm). Cutting and fastening with such insulation is best done for waterproofing, since the paper base of the cardboard is prone to getting wet.
Of course, this method cannot be called practical and durable, but it can be used as a rough foundation in multi-story panel buildings. Moreover, it is easily attached with a stapler and cut with a stationery knife, and it can be made from unnecessary packaging boxes.
Sawdust, shavings
This method of thermal insulation also has its place, as it is considered cheap . Sawdust and shavings are used by backfilling and filling (alternating with any construction glue, clay or plaster).

Sawdust is also found in the form of glued slabs, pre-mixed with lime, in order to repel beetles and rodents.
If the sawdust is bulk, then they are filled in, carefully compacted. Several layers will be required. Since the material cakes strongly and becomes compacted over time, sawdust will need to be added every 3 years.
This is their disadvantage, since it is not entirely advisable to constantly disassemble the layer with waterproofing and finishing.
Insulation materials
For thermal insulation, four groups of insulation are used:
- Bulk. This group includes: ecowool, sawdust, expanded clay.

- Rolled. Represented by mineral wool or Isover type insulation.
- Sprayable. Penoizol belongs to this group.
- Slab. Sheets of polystyrene foam or compacted mineral wool.

In addition to the direct function of thermal insulation, they have sound insulation properties. In summer they protect the house from high ambient temperatures. Among the main properties of heat-insulating agents that are important for ceiling insulation are:
- Thermal conductivity. It will be better if this parameter is smaller.
- Moisture resistance. For any design, high resistance to moisture is important.
- Flammability. The heat insulator is laid on wooden beams, so flammable insulation cannot be used.

The process of laying thermal insulation on wooden ceiling beams
- Lifetime. This property will allow the insulation to be used for a long time without replacement.
- Environmentally friendly. Purity, absence of harmful impurities.
Before making the final choice of thermal insulation product, it is also important to analyze:
- Climatic conditions. The colder it is outside in winter, the thicker the insulation layer should be.
- Budget. Quite often the choice depends only on the availability of money.
- Additional work. What else needs to be done to insulate the ceiling?

Perhaps this is replacing structural elements, finishing materials, applying an additional layer of waterproofing or treating with fire-resistant preparations.
Sawdust
Sawdust can be used to thermally insulate the ceiling. This is due to its low price, availability, and low cost of work. The main disadvantage of sawdust is flammability and low moisture resistance. This leads to easy fire, rotting, and the appearance of fungus. Therefore, the sawdust is processed before laying.

The process of filling sawdust into the cavity between the beams under the flooring sheets
To reduce the moisture content and prevent mold, sawdust is dried in a special chamber for a year. Later they are treated with antiseptic substances and fungicides.
Slaked lime will help reduce the risk of rodent infestation. To reduce flammability, they are mixed with fire retardants.
Thermal insulation using sawdust is carried out in two ways. Sawdust is simply poured onto the prepared surface.

This method is not in demand. Since the material begins to shrink quite quickly, which requires regular replenishment. For the second method, sawdust is mixed with cement mortar.
Styrofoam
The slab is breathable, has a low price, does not accumulate moisture, and does not rot. Mold, fungi, and microorganisms do not grow on polystyrene foam. It has high thermal conductivity, resistance to high temperatures, and good sound insulation. Conducts moisture well. Light weight allows it to be installed on thin floors. Durable.

Installation of foam sheets to the ceiling
- Flammability. This is the main drawback of the material. It is not installed where there is free access to air. When used for floors, they must be treated with plaster or fire-resistant preparations.
- Rodents. Mice love to make their nests in polystyrene foam.
To prevent the penetration of rodents, use a fine-mesh metal mesh.
Expanded clay
Bulk material is the second most popular insulation material. It has high thermal insulation properties, is always on sale, and is easy to install yourself.

It's inexpensive. Disadvantages of expanded clay:
- Weight. A 20 cm layer of expanded clay has significant weight. It is used on concrete floors. Its use on thin wooden floors is not recommended.
- Moisture resistance. Expanded clay is not moisture resistant. The first layer of thermal insulation is the vapor barrier of wooden structures.
- Thermal insulation. In areas with a temperate climate, a layer with a thickness of 20 mm is laid, in cold climates - 50.
Large and small particles are mixed for installation. This combination will fill the empty space. To protect against moisture, cement mortar is poured. Its thickness should be no more than 20 mm.
Mineral wool
It is produced in the form of a roll, rolled out over the surface, and cut. The material is inexpensive, has good thermal insulation, and is quick to install. Among its disadvantages are:
- Shrinkage. The cotton wool shrinks by 15–20%.
- Moisture resistance. Cotton wool has low moisture resistance and quickly absorbs water. Therefore, when installing it, waterproofing is first laid.

- Impermeability of thermal barrier. This property depends on the air contained between the wool fibers.
The thermal barrier decreases when the cotton wool is compressed, so you should not step on it; the flooring is made immediately after installation.
Penoizol and polyurethane foam
Insulation of this type is poured or sprayed. This material cannot be laid on your own, because... its application requires special equipment, protective suits, and professional skills.

Foam products fill all the smallest cracks and cracks. They do not attract insects, do not burn, and are safe for humans. The substance contains a large number of air bubbles that help insulate a private home. Flaws:
- High price.
- Fragility. The material does not restore its original shape after damage.
- Shrinkage. Penoizol has slight shrinkage.
After complete hardening, it is necessary to replenish the settled material.
Which option is better to choose?
In addition to the above materials, slag wool, chipboard, foam glass, ecowool, and polyester fibers can also be used for arranging interfloor ceilings.
The selection of thermal insulation is based on the characteristics and type of building (wooden, brick, monolithic, prefabricated slab).
The top universal materials that are suitable for all types of buildings are presented in the table:
| № p/p | Materials | Manufacturers | Cost (RUB) for 1 piece. |
| 1. | Penoplex | "PENOPLEX SPb" | 102-319 (1 piece) |
| 2. | Penoizol | "NPP Logrus" | 383-540 (1 bottle 730 ml |
| 3. | Expanded clay | CJSC "Keramzit" | 1 400-2 200 (1m3) |
Vapor barrier
For any type of floor, vapor barrier is an integral stage of roof insulation. A thin and durable film is attached to the ceiling itself, since this helps prevent vapor condensation in the heat insulator when heat enters from the heated room.
Modern vapor barrier materials can be installed under any finishing materials. They have additional functions such as protection from wind, water, and dust. Therefore, the space under the roof will be reliably protected not only from the harmful effects of condensation, but also from atmospheric influences with maximum effect.
To install a vapor barrier, it is enough to evenly distribute the film over the surface of the attic floor and secure it with metal staples, while the joints should be taped with foil tape.
Calculation and basic formulas
For floors to be insulated, thermal engineering calculations are used. Calculations are carried out on the basis of SNiP standards 02/23/2003.

Thermal calculations are carried out by engineers, but you can do them yourself, using an online calculator that is offered by construction company websites, for example, on this site.
Depending on what indicators need to be determined, calculations require values that characterize:
- structural type of construction;
- average indoor temperature;
- humidity coefficient inside the building;
- thermal energy consumption;
- dew point;
- thermal homogeneity (coefficient);
- vapor permeability resistance;
- quantitative heat loss.
Heat losses during the installation of floors for each type of building Q are determined by the formula:
Q = (A / R) x dT , where:
- A – total surface area (m2);
- R – heat transfer resistance;
- dT – temperature difference inside and outside the building over the last 5 days.
The amount of energy to replenish heat loss W is determined using the formula:
W = ({Q + Qb} x 24 x N) / 1000 where:
N – number of days of the heating period.
Determination of the most comfortable temperature Q is calculated using the formula:
Q = S x 100 (150) W , where:
S – indicator of area with available heating (m2)
100, 150 are the specific values used that are needed to heat 1 m2 of surface area.
Calculation example:
Given an area of 240 m2, with a heat transfer resistance index of 4.375 m2C/W. The temperature difference is 23-25 °C. Determine the heat loss of the surface.
Solution: Using the formula Q = (A / R) x dT, we substitute the values and get:
Q = (240 / 4.375) x (23 – (-25)) = 2633 (W).
Answer: heat loss for an area of 240 m2 is 2633 (W).
If, based on this example with the received answer (the required values), climate calculations are carried out, then the required insulation thickness for the entire surface can be determined.
There are a large number of different thermal engineering calculations in which heat losses through ventilation and sewage systems are determined, and the total loss of energy consumption is assessed, as well as heat transfer resistance.
Installing a floor in the attic
In most cases, attics in private homes are used as utility rooms for storing unnecessary rubbish. But it is also often used to make a living room or attic. In any case, this room must have a reliable, safe floor.
The type of thermal insulation material used in a particular case will help you choose the right material for creating a subfloor in the attic. So, for example, if the attic floor is insulated with mineral wool over wooden beams or polystyrene foam is used as insulation, then the floor covering must be rigid. Thick plywood, edged boards or OSB sheets are most often used as rough material.
Expanded clay insulation is covered with thick plywood. Cement screed is sometimes used as a rough floor covering when arranging a living space in the attic, if the load-bearing characteristics of the building allow.
Sawdust-cement or sawdust-clay insulation after drying becomes rigid and resembles a reinforced concrete rough coating, so finishing can be done directly on it.
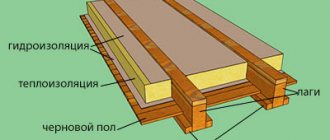
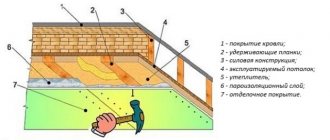
Pie layer diagram
The pie diagram, with the arrangement of thermal insulation of the floors, includes the following layers:
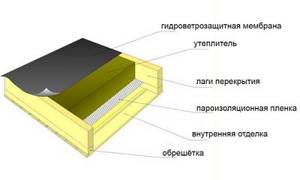
main surface (monolith, screed, any subfloor, including wooden planks), with a standard thickness of 220 (mm);- timber (beams) with logs and frame (metal, wood);
- vapor barrier (membrane or other material, especially for cold surfaces);
- waterproofing (roofing felt with mastic);
- ventilation (20 mm) gap;
- wood lathing;
- selected insulation (1-2 layers), with seams sealed using sealant;
- reinforced mesh;
- layer of finishing material (starting, then finishing);
- finishing coating (laminate, linoleum).
In some cases, the cake is supplemented with a second layer of vapor barrier and waterproofing. A layer of soil material or liquid waterproofing may also be added.
The laid insulating materials should be equal to 14-45 (cm), depending on the type of surface that is insulated.
We insulate the slab floor
If the attic floor is a concrete slab, then it can be insulated in the following ways:
- along beams;
- without using lag;
- use of solid insulation.
Insulation on beams
Wooden blocks called joists are attached to the concrete slab using self-tapping screws or dowels. Then the work is carried out using the same technology as for the construction of wooden floors. You can use any type of insulation.
Video: Insulating the attic floor
We insulate the slab floor without using logs
With this option, backfill is used - expanded clay, slag, sawdust. First, you need to stick a vapor barrier on the slab, then cover everything with the selected insulation. For a house with an attic, you will have to make a screed on top; for a cold attic, a screed is not necessary.
Insulate with solid insulation
In this case, foam concrete is used. The thickness of the foam concrete layer must be at least 40 mm. You can also use foam glass, it is much more effective, but also more expensive. No screed is required for this type of insulation.

Basic consumables and tools
In the process of insulating floors, a craftsman may need the following consumables and tools :
- The selected type of heat insulator, the adhesive composition for it. For loose materials - everything necessary for further filling the layer with M500 cement mortar.
- Vapor barrier membrane, waterproofing (roofing felt) + mastic.
- Liquid sealants, primer, brushes, antiseptic solutions for impregnating surfaces.
- Beams, logs, boards of different sizes, fasteners (corners, anchors, screws, nails, etc.).
- Laser rangefinder, tape measure, construction cord, stapler, staples, pliers, special knife, beacons.
- Reinforced mesh, drill, screwdriver, hammer.
- Grinder, grinding, hacksaw.
- Plaster, putty (starting and finishing), levelers, spatulas.
- Finish floor covering (laminate, linoleum, tiles, PVC products).
- Construction vacuum cleaner, rags, work containers, work clothes, safety glasses.
The presented list is compiled on an individual basis.
When ordering work from a construction company, it can provide consumables according to the price list itself, and this will be more profitable, since companies often work directly with manufacturers and purchase in bulk. The hired team always has tools in stock.
What materials does the market offer?
The insulation technology itself is not complicated, the right choice of material is much more important, so first we will talk about how to insulate the attic floor in a private house.
Cotton insulation
Insulating the ceiling with various types of wool is considered one of the best ways of arrangement. This thermal insulation material can have different densities; the main advantage of wool is its vapor permeability.

When choosing mineral wool, it is better to give preference to dense slabs
- Mineral wool can be made from basalt fibers or blast furnace slag. The thermal insulation characteristics of both options are approximately the same, plus this material does not burn, but basalt wool is better from an environmental point of view, and slag wool has a more affordable price.
Advice! On the market, mineral wool is represented by dense slabs and soft mats; for covering beams, it is better to take slabs, because soft mats lose volume over time (caking).
- Glass wool. As the name suggests, the material is made of fiberglass. Glass wool is significantly cheaper than its mineral counterpart; it also does not burn, but tends to lose volume. You should not take the cheapest models, as they produce a lot of harmful glass dust. The best option would be “Izover”.

Glass wool from the Isover brand is of high quality
- Ecowool appeared on the market relatively recently. It is a crumbly mass of cellulose and paper fibers. The material does not burn, but may smolder. Ecowool is blown into the walls and roofing pie using special equipment, and the insulation of the floors can be done manually; the mass is simply poured between the beams.
Bulk insulation materials
Expanded clay, perlite and vermiculite are used to insulate the attic space. The materials do not burn, have low thermal conductivity and an affordable price, but compared to cotton models, the thickness of the thermal insulation layer here should be 2 times greater.
A significant advantage is the mechanical strength of bulk insulation:
- Expanded clay. The material is obtained by firing clay. Expanded clay is durable, porous, round cylinders of different sizes and shapes; it can absorb moisture, but unlike cotton wool, the balls do not lose volume and dry quickly.
- Perlite and vermiculite are calcined volcanic rocks. They cost a little more than expanded clay, but the materials absorb moisture less, although in a dry attic this characteristic is not of great importance.

Although expanded clay is classified as a budget material, the quality of this insulation is quite high
Polystyrene
In this niche we have polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam. Such plates are made from the same material (polystyrene), only using different technologies.
- On the one hand, these materials are not afraid of moisture; their water absorption tends to zero.
- On the other hand, both polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) do not allow vapor to pass through; more precisely, foam plastic has some tiny percentage of vapor permeability, and EPS is considered an absolute waterproofer.
These materials are excellent for insulating reinforced concrete floor slabs; even screed can be poured over extruded polystyrene foam, but it is strictly forbidden to insulate a wooden floor over beams with such slabs.
If you put waterproofing in the ceiling of a cold attic, then after a couple of years the wood will begin to rot. The thing is that steam trapped from below will be absorbed into the wood, which will lead to the appearance of colonies of fungus and mold.
Some craftsmen recommend installing forced ventilation under the EPS, but as practice has shown, this approach does not solve the problem.
With active ventilation, the wood will rot less, but it will still rot, you will only extend the life of the beams a little, but the result will be the same.
The video below in this article shows what happens when insulating an EPS beam floor.
Instructions: how to install insulation correctly?
The general stages of insulation for all floors are absolutely identical. The nuances concern only some points.
For example, for the ends of slabs and plinth surfaces, the waterproofing is laid with an overlap, as if hanging down . This is necessary so that condensation from temperature changes does not linger in the layers of the cake and does not penetrate inside.
Be sure to wrap the ends of the beams, and, if possible, the entire beam with waterproofing. This method performs a protective function: it prevents the development of mold and fungi on the surface and prolongs the operation of the products.

In bathhouse ceilings, do not forget about vapor barrier. Here, many builders use foil materials to retain heat and eliminate moisture in the layers.
For example, some types of mineral wool slabs are foil-coated on one side (they are ideal for baths).
The general steps for installing floor insulation for all types of buildings are as follows:
- Thoroughly clean the surface from dust and dirt.
- Priming the floor, possibly applying liquid waterproofing.
- Reliable fastening of vapor barrier.
- Filling with bulk substances (between the timber and the joists), thoroughly priming them, filling with cement mortar. If without loose ones, form the sheathing.
- Laying waterproofing material on mastic, wrapping the beams and ends in joists.
- Fastening the insulation in 1-2 layers. After the glued insulator has dried, seal the joints between the slabs or rolls with sealants.
- Reliable fastening of reinforced mesh.
- Plastering the surface with two main layers (base and finishing).
- If necessary, additional installation of a vapor-tight membrane.
- Formation of the finished floor with prepared material.
During the work process, only dry insulation is used. Each layer of the cake that is arranged must be thoroughly dried before and after thermal insulation.
Beams with logs must be installed strictly according to the markings, with reliable fastening. If a rough or plastered surface requires sanding, they are sanded. This ensures the geometric evenness of the ceiling.
It is best to glue any heat insulator with an overlap, so that when it dries there is not a large gap between the seams and less sealant is required.
Application for floor insulation
Mineral wool slabs are used as floor insulation in a house in the following cases:
- in the floor structure of the first floor in the presence of a cold basement or underground;
- in the design of interfloor ceilings to increase sound insulation;
- in the design of the attic floor in the presence of a cold attic.
For an individual house, when installing, in all cases it is necessary that the technology be strictly followed, otherwise the insulation will not perform its function.
Difficulties and errors
Possible difficulties and errors in the process of installing thermal insulation may be associated with violation of installation technology (sequence and construction requirements), as well as the use of consumables of dubious quality.
It is advisable to purchase heat insulators and everything necessary to create a floor pie from trusted companies that provide their customers with quality certificates and guarantees.

The main mistakes, in addition to the use of low-quality insulation and violation of installation technologies, are also considered:
- Refusal of vapor barrier, waterproofing and ventilation.
This will lead to rapid deterioration of the heat insulator. It will become matted, its shape will deteriorate, and then the entire surface will deteriorate. An unpleasant smell of mold and mildew will appear from under the finishing coating. - Insufficient number of insulating layers.
The minimum standard requirements for floor layers (45 cm) will ensure heat retention and reliably protect from drafts. In the northern regions, this layer can be increased to 60 (cm), with careful sealing of the joints with sealants. - Lack of waterproofing and thermal insulation of beams with logs.
A wooden beam will fail faster (in practice, beams are most often made from it), constant cold air flows will enter the layers, which will cause the insulation to peel off from the glued surface. - The surface is not level enough for thermal insulation.
It can lead to a violation of the surface geometry, which will be very difficult to hide.
By paying attention to the examples of possible errors presented, you can always prevent the consequences.
Working under a contract with a proven and reliable company will help complete the work, according to the price list, in a fairly short time.
Insulating the attic floor with foam plastic
The installation technology process is similar to insulating an attic floor with polystyrene foam.
The advantages of these materials:
- low cost;
- ease of operation;
- waterproof.
Among the disadvantages: flammability.
Technology for insulating attic floors with polystyrene foam or polystyrene foam
The process of installing rigid foam-based insulation is more than simple and can be done with your own hands. The work can be divided into two stages:
- surface leveling. To ensure high-quality insulation, there should be no significant unevenness on the base floor. Such differences can be eliminated by screeding with sand-cement mortar.
- The slabs are laid end-to-end or between beams. The presence of timber increases the strength of the floor.
Insulation of the attic floor with polystyrene foam Rough coating
Polystyrene foam must be protected from destruction with film in an uninhabited attic. In a frequently used or residential attic, you need to move somehow, so it is better to install an OSB subfloor on top of polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene or use a sand-cement screed.
Average cost of services and work
Russian companies on their official websites in a special section indicate the cost of work on installing insulation.
Approximately, average prices by region with the provision of our own materials for clients can be presented in the table as follows:
| № p/p | Regional district (city) | Cost (rub.), 1 m2 from… | |||
| average price | Expanded clay | Mineral wool | Penoplex | ||
| 1. | Ekaterinburg | 160 | 90 | 112 | 110 |
| 2. | Krasnodar | 173 | 100 | 117 | 115 |
| 3. | Kazan | 177 | 102 | 122 | 120 |
| 4. | Novosibirsk | 243 | 120 | 143 | 135 |
| 5. | Moscow | 269 | 125 | 155 | 150 |
The indicated prices for services are approximate and may change. The cost is influenced by the professionalism of specialists, the season (in summer, services may be higher), the increasing market cost of materials, the total volume of work and the region (in the north, in Moscow Region and St. Petersburg the highest prices).
Most companies are interested in continuous operation, so they often provide their clients with discounts on services and materials.
Commonly used insulation materials
Due to the high functional properties of mineral wool, it can be used to insulate all surfaces, even uneven ones. Insulation is produced in rolls or soft slabs. Preference is given to material with a shielded heat-reflecting coating. You need to lay it tightly, but without jamming. This option has the best price/quality ratio. At low cost, good efficiency and durability. When installing insulation, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment. A protective material is placed on top of the wool that does not allow steam and water to pass through. The insulation on the floor is overlapped and glued to avoid displacement.

TechnoNIKOL attic insulation
A more environmentally friendly insulation material is stone wool. At the same time, having an excellent thermal conductivity indicator for its class, it effectively smoothes out temperature changes and maintains a comfortable microclimate.
Waterproofing
When the interfloor pie is ready, it is necessary to waterproof the cold attic space. It will help prevent the appearance of leaks and condensation. Most often, the role of waterproofing is performed by foiled polyethylene foam.
It is fastened using a stapler with the metalized side facing outward, leaving ends 15-20 cm long wrapped on the walls. The joints, as in other cases, are taped with foil tape.
A sheathing is installed over the entire surface of the resulting structure, which will subsequently serve as the basis for the final coating of the ceiling. Moreover, this is necessary to create an air-thermal floor cushion.
Using sawdust to insulate an attic
For those who don’t know, shredded wood is called sawdust. We are talking about this material now because it also has significant advantages, including:
- availability;
- naturalness;
- light weight;
- absence of any harmful or toxic substances.
The disadvantage is the same as that of polystyrene foam - flammability.
The procedure for insulation using sawdust
Step 1. First prepare the sawdust, that is, mix it with water and cement in a ratio of 10-1-1.
Step 2. Fill the attic floor with the resulting mixture, then carefully level it. Note that it is possible to insulate an attic with sawdust without a frame only if it (the attic) is non-residential. Otherwise, the sawdust will be compressed while walking, and the screed will, accordingly, collapse.
Step 3. Using timber, build a honeycomb structure. Next, fill each cell with the mixture described above. The main advantage of this technology is that a subfloor can be laid on top of the timber, and the room itself can be actively used.
Installation of a floor made of waterproof tongue-and-groove chipboard
For this type of work you will need:
- chipboards;
- insulation;
- timber for logs;
- waterproofing material;
- roulette;
- mounting adhesive for chipboard;
- waterproof PVA glue;
- construction level;
- screwdriver, hammer drill;
- self-tapping screws;
Step 1. Chipboards are brought and placed in the room where they will then be laid. They are left here for 48 hours in order to adapt to the microclimate of the room.
This is especially important if the material was transported in winter
Plates must adapt to operating conditions
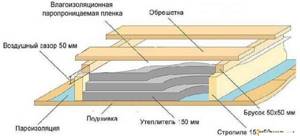
Step 2. A layer of waterproofing film is laid on the rough base, cleared of debris, overlapping the walls. Then log beams are installed in increments of no more than 30-40 cm, provided that slabs with a thickness of 16 mm are used. For thicker material, you can install logs in increments of 60 cm.
The joists are laid on top of the waterproofing
Step 3. If the pitch between the joists is larger, a sheathing of boards is installed perpendicular to the joists.
Lathing example
Step 4. The distance between the logs is filled with insulation. For example, mineral wool. In this case, the insulation layer should be 3 cm lower than the expected level of the subfloor.
Laying insulation
Step 5. Installation adhesive is applied to the edge of the joist. And the tongue of each slab is treated with waterproof PVA D-3. The latter procedure will protect the slabs from water.
Applying glue to joists
Treatment of tongue and groove with waterproof PVA D-3
Step 6. The slab is laid on the joists and pressed so that the previously applied glue is distributed over the entire surface of the joists. The slab is mounted with its long side perpendicular to the joists. Along the perimeter of the room it is secured with self-tapping screws on the joists. Step – 20 cm.
Laying the slab
Fastening the plate with self-tapping screws
Step 7. Next, the next slab is laid. The individual elements are connected using a tongue-and-groove system.
Plate connection
Step 8. Remains of PVA protruding at the junction of two slabs are removed with a soft cloth. All slab joints must be located on joists. If the joint is located between the lags, then an additional supporting jumper is made. It is installed perpendicular to the joists.
Removing excess glue
Support jumper installation diagram
The jumper is installed perpendicular to the joists
Step 9. The joints between the slabs are additionally hidden using sealants or wood coating mastic.
Sealing joints with sealant
To reduce the amount of waste, sufficiently large pieces of slabs can be used to begin the installation of any row. The main thing is that the piece of slab rests on at least three logs, that is, covers two spans. You can move on such a floor after 24 hours - this is exactly how long it takes for the glue to harden.
Video - Installation of tongue and groove slabs
Moisture-resistant chipboard can be an excellent rough (and in certain cases, finishing) base for laying the finishing floor. Its installation is not complicated, but on the contrary, it is quick and easy, and does not place any special demands on the master. Therefore, after studying the instructions, almost anyone can install such a floor.