Thermal insulation plaster
The process of plastering walls is quite labor-intensive. Often it is necessary to attract specialists who will perform the work better. Simple plastering does not retain heat in the house, which means additional installation of thermal insulation and additional investment will be required.
To get rid of two problems at once, performing only one operation, warm plaster was invented. This is possible thanks to the vermiculite or foam granules contained in the composition. They create a thermal insulation layer.
This material appeared on the construction market relatively recently and is practically unknown. In stores you can find two types of mixtures: for external and internal use.
Where is plaster used for wall insulation?
According to the scope of their use, plasters can be divided into facade (materials for external use) and mortars for internal use, although most of them are universal.
Interior work
Thermal insulating plaster is an excellent solution for insulating rooms from the inside. It is applied in a thin layer (often up to 2.5-5 cm), which will not reduce the usable area, but will prevent heat from escaping from the building. The material will also help to organize reliable sound insulation, reducing the noise level in the apartment.
When laying plaster on interior walls, it is important to consider the location of the dew point. At this point, the temperature drops in such a way that moisture from the air begins to condense. If the dew point plane is inside the main wall, the latter will gradually collapse. It is important that water vapor from the air does not turn into a liquid state and freeze. This will not happen only if the house is heated excessively or with high-quality insulation of the external walls together with the internal ones.
Thermal insulation mixture for interior work Vermix ШВ50
Insulating plaster is also suitable for other interior work:
- finishing of door and window openings, slopes;
- sealing shells, cracks, depressions;
- eliminating areas of delamination of plain plaster;
- cladding of curved architectural structures, niches, domes.
Exterior works
Warm plaster is ideal for the facade. Usually its layer does not exceed 5 cm, in rare cases it is increased to 10 cm, but it is applied in several stages and only on the reinforcing mesh. The dried material is coated with protective compounds, such as paint, to reduce the risk of impregnation with moisture from the atmosphere.
In exterior work, insulating plaster can be used for finishing plinths, sealing various cracks, covering floors, and ceilings in unheated rooms. The material is used to insulate sewer risers and water supply systems. Plaster will reduce heat loss in garages, auxiliary buildings, and other structures, and it can be used as a main or auxiliary (additional) heat-insulating layer.

Applying warm plaster to the facade
Plaster is excellent for finishing hard-to-reach areas where the use of conventional insulation is not possible or interferes with the design of architectural solutions. It is recommended for use in areas adjacent to materials with completely different technical characteristics (for example, where a wooden surface borders on a plaster layer).
Material composition
The mixture can be used for permanent plastering of walls or simple putty of formed irregularities.
The solution performs two functions at once: leveling and thermal insulation. This effect can be achieved thanks to additional substances added to the sand-cement mixture. Composition of warm plaster:
- Foamed vermiculite.

Vermiculite
- Wooden sawdust.
- Granulated expanded clay of fine fraction.
- Finely ground pumice.
- Expanded polystyrene granules.
Insulating plaster – what is it?
Let's look at what warm plaster is. Everyone has long been accustomed to the fact that the classic plaster mixture is a cement-sand mortar containing certain additives. The latter can be lime (to prevent the walls from becoming damp) or all kinds of polymer adhesives (for better adhesion) or even dyes. But what is the mixture for insulating plaster?
In fact, everything is very simple: a filler with a thermal conductivity coefficient significantly lower than that of hardened cement mortar is added to the usual cement-sand mixture (which may also include other polymer components).
Such additives may include:
- expanded vermiculite;
- expanded clay;
- volcanic pumice chips;
- sawdust;
- polystyrene foam granules.
In essence, warm plaster is the same classic plaster mixture that has long been used for finishing buildings and structures, only with additional inexpensive “insulating” components.

Manufacturers and prices
Despite the fact that warm plaster has appeared recently, it has managed to gain its place in the market, and competition has arisen among the emerging companies. Popular brands:
- Umka. Popular among other types of heat-insulating plaster. Used for interior finishing work. The base includes granulated silicon beads, which increase the strength of the material. The solution is used as a vapor barrier, moisture-repellent, sound and thermal insulation material. The price of warm plaster per 1 kg is from 100 rubles.

Umka
- Varmix (may also be called “Mishka” due to the characteristic emblem on the product packaging). The solution has good adhesive properties; reinforcing mesh and surface priming are not required. The predominant use of the mixture is for exterior finishing work. The composition costs from 120 rubles/kg.

Varmix
- Knauf. A universal product that can be used indoors and outdoors. Finishing is carried out on any type of coating, even for insulation of floor slabs.

Knauf Grünband
Application technology
If you decide to apply insulating plaster yourself for interior work and want the result to be good, follow the technology:
- Prepare the wall. Remove the finish and old plaster, followed by dust. Prime so that the mixture adheres better to the wall. If there are large cracks, fill in reinforced mesh.

Preparing the wall for application
- Prepare the solution. Pour into the container as much water as written on the package. Pour in the material and stir with a mixer. To make sure the mixture is properly thick, scoop it up with a trowel and turn it over. If the mixture does not fall off, then the thickness is normal.

Preparing the solution Note: The solution must be prepared within 2 hours. Afterwards it loses its properties.
- Apply the solution. To do this, use plastering tools: spatula, trowel, grater, rule. Before applying, wet the wall generously with water. The layer thickness should not be more than 2 cm - otherwise the plaster will fall off. Apply the next layer after 4 hours.

Application of the solution
- Check the result. The next day, when the mixture has hardened, apply a two-meter rule to the wall. If gaps appear more than three millimeters per meter, it means that the surface is not smooth - level it. Wait another 3-4 weeks for the mixture to fully harden and see if the plaster is cracking or peeling. If everything is in order, finish with finishing material.

Checking the result
Types of warm plaster
The high technological qualities of the material are due to the addition of insulating materials to the base. There are three types of warm plaster:
- Contains vermiculite. The filler is extracted from rock and undergoes heat treatment. It is added as an antiseptic, which protects the walls from the accumulation of fungal formations. It can be used equally, both indoors and for finishing facades.
- With polystyrene foam filling. The additive helps to cope with the thermal insulation of walls. Can be used for interior and exterior finishing works.
- Filled with sawdust. The composition contains clay and paper, which adds heat-insulating properties to the material. The downside of the mixture is its instability to precipitation.
Interior finishing with plaster with the addition of sawdust requires good ventilation of the room. Otherwise, the formation of mold cannot be avoided, which will lead to complete destruction of the surface.
Economical plaster thermal insulation.
Polymer plasters can only be purchased; you cannot make them yourself. But it is more economical to mix solutions with mineral binders yourself.
Hiring hired workers is expensive. But, if you make the mixture yourself, the overall price will drop slightly. Many developers save in this way: they hire plasterers and do the “dirty” work for them. Considering that the help of a helper is paid not per m2, but per day, the savings may not be significant. Approximately 800-1200 rubles/day.
Even cheaper is preparing the wall yourself, placing beacons and rough plastering. The “specialists” will only have to level the coating and apply a decorative solution.
Thermal insulating cheap plaster for exterior use.
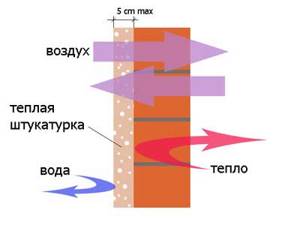
Insulating mixtures are more expensive than regular ones because they are more complex. Moreover, not everything can be done with your own hands.
However, the production of cement-based mortar is within the capabilities of any novice builder and can significantly reduce the cost of funds. As a filler, you can use both moisture-resistant bulk materials (foam glass, expanded clay sands) and non-moisture-resistant ones (sawdust, perlite, vermiculite). The latter are only protected with a layer of dense concrete.
For external heat-insulating plaster it is possible to use polystyrene fillers. The most economical filler is crushed polystyrene foam. Its cost is zero, it is free. If you use foam packaging for grinding.
This type of concrete is widely used in Russia and abroad. It is not dense and is not applicable in structures requiring high strength. But it is quite suitable for external insulating plasters.
Do-it-yourself thermal insulation plaster for interior work.
Developers pay less for a square meter of finishing without filler than for a mixture with filler. Therefore, some, especially “enterprising” builders, are trying to add insulating bedding to ready-made mixtures. This is prohibited: such manipulations greatly weaken the solution, reducing its strength and durability.
To reduce the cost per sq.
It’s easier to make the batch yourself using inexpensive fillers and binders. Thus, clay-sawdust mortar is practically free, although it is not inferior in strength to gypsum. data-matched-content-ui-type=”image_stacked” data-matched-content-rows-num=”2″ data-matched-content-columns-num=”3″ data-ad-format=”autorelaxed”>
Cement heat-insulating plaster Knauf Grünband
Let's take a separate look at the Knauf thermal insulation mixture. The product line includes many well-known products that are used in interior decoration, but in this case, we will give a brief overview of warm plaster.
The solution contains fine-grained, about 1.5 mm in diameter, heat-insulating components. Application of the finished mixture can be done either manually or using electrical equipment.
In addition to the main task, plaster:
- It is used as a waterproofing layer when finishing facades, basements, bathrooms, and other rooms with a high degree of humidity.
- Strengthens the surface of the building facade. The surface covered with Knauf Grünband plaster mixture is protected from mechanical damage and natural shrinkage processes of the soil. With this finishing, the surface remains intact and does not become cracked after the building shrinks.
- Knauf is often used as a finishing decorative coating. The advantage allows you not to use additional finishing compounds.
The composition is sold in construction stores, in packages of 25 kg.
Advantages and disadvantages of cement plaster
Like any finishing material, DSP has a sufficient number of pros and cons. The main advantage is the availability of the mixture and the ability to make it yourself. By changing the proportions of the active substance, you can adjust the density, strength and purpose of the finished solution for plastering walls.
Advantages of cement mixture:
- Durability of the coating. The service life of plaster on the facade of a building in an unchanged condition reaches 20 years, and indoors 50 years or more.
- Resistance to mechanical damage. The cement mixture is not subject to chips and scratches. After application, cracks may appear, the appearance of which can be prevented by adding plasticizers to the composition or covering them with putty.
- Resistance to precipitation, temperature changes and ultraviolet radiation.
- Long-term retention of plasticity after kneading for 1-5 hours. Also, application does not require special plastering skills; the solution easily applies to block, brick and concrete. Also suitable for wooden bases.
- Good vapor permeability and antibacterial properties of cement create a healthy microclimate indoors.
The coating is safe to use and does not burn; universal, suitable for finishing the whole house. By adding additional components to the solution, you can set the desired characteristics of the coating - noise and heat insulation, smoothness after drying and decorative qualities.

Cement plaster has decorative properties
Disadvantages of cement-sand mortar:
- Heavy mixing requires effort or the use of mixers and concrete mixers, depending on the required volume of the mixture.
- Incompatible with gypsum bases, and on smooth concrete walls the surface must be scored to improve adhesion.
- Susceptibility to cracks when buildings dry out and shrink, which necessitates the use of plasticizers.
- A long drying time can delay finishing work. At normal humidity of 65-75% and a temperature of 18-20 degrees, the layer of plaster will be ready for further processing in 14 days. If conditions change, this period is extended to a month.

Typically drying times range from two weeks to one month.
Specifications
The properties of the mixture are determined by the composition, which can be made from different grades of cement, sand fractions and additional components that improve the quality of the coating.
Density
The main characteristic that determines the strength of the layer on the base. When applying plaster to the surface, the average value is 1500-1800 kg/m3. Density depends on the filler fraction; the finer the sand, the higher the figure.
Thermal conductivity
Applying DSP to walls can reduce losses from heating devices. Depending on the application layer, the thermal conductivity inside the room changes. With an average coating thickness of 3-4 cm, the coefficient is 0.3 W. Plaster can be applied in a layer of up to 10 cm, but not more than 2 cm, without the use of reinforcing mesh, in one stage of work. In this case, intermediate drying of the surface for 72 hours is necessary.
Vapor permeability
Determines the comfort of living in a room. If the walls strongly absorb moisture and do not release it well into the air, the humidity in the house increases, which will lead to the appearance of mold. The vapor permeability of cement mortar is 0.09 mg/mhPa, this is a normal indicator for creating a good indoor microclimate.

Cement-sand mortar prevents the formation of fungus and mold on the walls
Drying time
Depends on the density of the solution and the thickness of the application layer. When covering the base 2 cm, it is recommended to dry for 48-72 hours. If the surface is prepared for facing with ceramic tiles, then the time frame is doubled. The coating gains full strength in 20-30 days, depending on humidity and ambient temperature.
When choosing plaster for a facade, such a characteristic as frost resistance is also taken into account, which for a normal mixture is at least 50 cycles.
Work progress
For thermal insulation plaster to be effective, a number of rules must be followed:
- Carry out high-quality surface preparation.
- The consistency of the water in the mixture must correspond to the proportions described in the instructions.
- Dry plaster is poured into poured water and stirred thoroughly for 5 minutes.
- Mixes are made in small portions, which can be completed in a short period of time.
- Finishing work is carried out in the following temperature range – from +5 to +30°C. Wind, raindrops, and direct sunlight are not allowed when plastering the surface.
- Make sure that all electrical points in the finishing area are de-energized.
- All work is carried out in protective clothing and glasses.
- If plastering was carried out on beacons, they must be removed after completion of the work.
- The thermal insulation layer should not exceed 25 mm. If you need to increase the thickness of the applied plaster, do it in stages - layer by layer, until the required dimensions are reached.

Applying a warm layer
Thermal conductivity coefficient of plaster.
- Cement-sand mixture. It has the highest ability to transmit heat through itself. The thermal conductivity of cement-sand plaster is 0.93 W/(m•°C).
- Lime-cement-sand - 87 W.
- Lime-sand – 81.
- Clay-sand coating - 69.
- Gypsum plaster is considered the “warmest”. But this is not entirely true: the thermal conductivity of gypsum plaster is 35.
- Cement-perlite mixture - 3.
- Clay-sawdust coating - 29.
- Gypsum-perlite - 23.

Thus, gypsum-perlite heat-insulating plaster thickness. 2.5 cm will protect a wall with the same effectiveness as a cement-sand wall with a thickness of 10 cm.
However, in general this is not significant. For example, heat-insulating plaster on a brick wall (thickness 51cm and thermal conductivity 0.9). Its contribution to heat savings will be only 3.3%.
Before you buy a mixture, you should pay attention to the thermal conductivity coefficient of the material. But you shouldn’t count on “over-insulation” with plasters - their volume in the total mass of the structure is not significant.
Reinforcing layer
After preparation, you can proceed to plastering the reinforcing layer. Often, plaster alone is not enough to level out detected differences; then a reinforcing mesh is required. It strengthens and fastens the plastered surface, significantly increasing the permissible dimensions of the layer thickness. Although manufacturers claim that plaster does not need to be reinforced with reinforcing mesh, it is better to consult with knowledgeable people before making a final decision.

With reinforcement
Types of liquid insulation for walls
Modern heat insulators can be divided into groups according to different indicators. We will give the most common classification.
Liquid foam
Today the construction market offers several types of such insulation materials.
Polyurethane foam (PPU)
The material is developed on the basis of liquefied urethanes, which, under the influence of a chemical reaction, form a foamy substance, increasing in size by almost 50 times. After 24 hours, the mixture finally hardens, forming a durable, finely porous layer, reminiscent in structure of polyurethane foam. Polyurethane insulation is applied using a special spraying unit, which delivers the contents to the surface under high pressure.

Polyurethane insulation is applied using a special spraying installation
Penoizol
Penoizol differs from the previous thermal insulator in its lower price, lower density and poor thermal conductivity. This budget option is made by urethanes, which belong to the urea-formaldehyde group. In terms of efficiency, it can be compared with traditional insulation (foam or mineral wool). The material is also applied under high pressure using a spray gun. The finished volume, as a rule, does not exceed more than 30 times the original mixture.
Polynor
Another heat insulator based on heterochain polymers. Available in small cylinders. One container is enough to finish 1 square. m when applying a layer thickness of about 60 mm. Compared to other materials, Polinor is much more expensive, and therefore it is not profitable to use it for large rooms. A convenient container with a nozzle allows you to apply insulation without preliminary preparation of the material.
Warm paints
They contain ready-made additives that do not require pre-foaming.
"Corundum"
The Russian brand that produces this insulation provides a guarantee for its products for up to 15 years. The material has a uniform viscous texture with high adhesion to various surfaces. Corundum is applied with a spatula or paint brush. It can also be sprayed, but must first be diluted with water.
The manufacturer offers several variations of thermal insulation:
- "Facade";
- "Winter";
- "Anticor";
- "Fire protection";
- "Lotus";
- "Classic";
- "Waterproofing";
- "Sanitary";
- "Foundation".
"Armor"
This thermal insulation is produced by a Vologda company that has copyrights to the insulation composition. The paint has a fairly thick consistency, allowing it to adhere well to any surface. It has water-repellent properties and can also be used as a waterproofing coating. Like the previous mixture, “Bronya” is available in several versions:
- "Classic";
- "Light";
- "Standard";
- "Universal";
- "Facade";
- "Metal";
- "Wall";
- "Fire protection";
- "Volcano";
- "North";
- "Winter";
- "Anticor".
"Akterm"
The country of origin of this thermal insulator is Russia. The company produces paints intended for two types of work: insulation and waterproofing. The Akterm product line is represented by 13 formulations with different technical characteristics:
- "Concrete";
- "Metal";
- "Anticor";
- "Facade";
- "Standard";
- "North";
- "Volcano";
- "Akterm - NG paint";
- "Anti-condensation";
- "Fire protection";
- "Hydrophobizer";
- "Zinc";
- "Plast".
When using Akterm thermal paints for walls or facades, you can add different colors to them.
"Astratek"
Another Russian brand that ranks first among manufacturers of modern liquid insulation. The paint has a uniform texture, the consistency resembles a suspension. This liquefied structure allows it to be applied not only with a paint brush, but also with a sprayer. The manufacturer produces several variations of formulations:
- "Facade";
- "Metal";
- "Universal";
- "Anti-condensation".

"Corundum" "Armor"

"Akterm"

"Astratek"
Ecowool
The composition of this environmental material includes several components:
- recycled cellulose;
- minerals;
- boric acid;
- wood;
- waste paper
The thermal insulator is well suited for insulating floors, as well as areas of walls where condensation often forms. The ecowool market is represented by several brands:
- Greenfiber – has thermal and waterproofing properties, absorbs noise;
- Ekovilla is a heat insulator with high technical performance and a long service life;
- Termex – is characterized by increased environmental friendliness;
- “Ecowool Extra” - used mainly for residential buildings or apartments;
- “Equator” is made using European technologies, observing international standards.

Ecowool is well suited for wall insulation
Advantages and disadvantages of warm plasters
Warm plaster has its pros and cons.
Advantages:
- Over time, the material does not change. Remains in its original form.
- Has high strength.
- Does not contain substances harmful to health.
- Resistant to low air temperatures.
- Good adhesive properties.
- Can be applied to any surface.
- Often does not require reinforcement with reinforcing mesh.
Minuses:
- When compared with classic types of insulating materials, plaster is inferior in performance. To achieve the result, it is necessary to create a layer 2 times thicker than conventional insulation.
- Cannot be used as a topcoat. After drying, it has a rough surface and requires additional processing.
Characteristics of plaster
Thanks to warm plasters, you can quickly and effectively insulate homes and other buildings. Heat-saving plaster allows you to replace a layer of more expensive insulation, reduce the thickness of the brickwork, and reduce the overall load on the walls. The average technical characteristics of insulating solutions are as follows:
- specific gravity - 200-300 kg/cubic. m (3-4 times lighter than conventional plasters);
- fire safety group - NG-G1;
- high plasticity;
- solidity of the layer, absence of delamination and shedding;
- Suitable for surfaces made of brick, stone, concrete, plasterboard, cellular concrete, etc.

Mixture consumption
To avoid unnecessary material costs, it is necessary to carry out calculations.
For 1 sq. per meter of working surface, on average, 10-18 kg of plaster is consumed. If work is carried out from the outside, costs may increase to 25 kg. The outer side is subject to influence, which means it needs reinforcement and a greater thickness of the working layer.
The products differ in composition - the reason for the different consumption of the plaster mixture. Overspending may be affected by uneven walls and inexperienced workers.
Varieties by composition
There are 2 types of heat-insulating plaster mixtures:
- Warm cement plaster. This includes all of the above cement-containing mixtures with the specified additives.
- Foamed plaster. A component is added to the cement-containing mixture that causes the formation of foam when interacting with water. The structure of the solution in this case will be similar to foam concrete in both its raw and hardened form. This type of plaster has significantly higher thermal insulation properties, but it requires mandatory subsequent processing - painting, since the porous structure, like a sponge, can effectively absorb moisture.

How to make warm plaster with your own hands
It is not always possible to buy a ready-made plaster mixture, especially if you need to carry out a large volume of work. Some craftsmen make warm plaster themselves. The components included in the mixture can be purchased at any hardware store.
Preparation:
- The main binder is cement, 1 part.
- Thermal filler - polystyrene granules, 1 part.
- Antiseptic – perlite, 3 parts.
- Polypropylene fiber – 50 grams.
- Using the manufacturer's instructions, we purchase a plasticizer.
Manufacturers
By purchasing the most popular warm Knauf plaster, you get a smooth, high-quality wall surface and save on energy resources: the thermal conductivity of this mixture is 0.55 W/m°C, the minimum layer thickness is 10 mm, the maximum is 30 mm.

Affordable, Unis Teplon is a mixture intended for interior surfaces, made on the basis of gypsum and perlite. Maximum maximum layer without reinforcement: 50 mm, with mesh: 70 mm. Thermal conductivity: 0.23 W/m°C.

Using Paladium Palaplaster-207 material, you will receive a high level of sound insulation of walls; it is made of cement and foam glass. This mixture is used for rough surfaces under wallpaper or continuous painting.
Reviews
I am very pleased with the purchase; after completing the finishing work, in the first winter I discovered that the heat-insulating properties of the walls had increased noticeably. I noticed that I could hear the children less when they were playing on the street. Of course, this is not enough for complete sound insulation, but I think that in the spring I will start replacing the double-glazed windows.
Alexander. Belgorod
I was satisfied with the heat-insulating properties, but I expected the plaster to be the finishing coat. It’s a pity that I had to additionally buy putty for exterior work and level the surface. I lost time and spent more money than I planned.
Vladimir. Rostov-on-Don
Rating of the best
Let's consider several main brands of mixtures for warm plasters:
UMKA® UB-21 TM
Here, ceramic silicon balls are used as a heat-insulating filler. Thanks to the porous structure of this filler, Umka warm plaster provides not only reduced thermal conductivity and a high level of heat conservation, but also high-quality sound insulation. In addition, an array of such plaster has a low specific gravity, due to which it is firmly held on the surface of the capital structure even without a reinforcing mesh.

PALADIUM Palaplaster-207
The sand-cement mixture here contains a special component as a heat-insulating filler - foam glass - a porous but durable filler in the form of granules. It does not contribute to the absorption of moisture vapor from the air, is absolutely “indifferent” to fire, and most importantly, it provides increased heat and sound insulation of the surface of the capital structure.

De Luxe "TEPLOLUX"
The plaster mixture is intended for laying on a concrete base or on foam concrete blocks - it is to these surfaces that the composition demonstrates the maximum degree of adhesion. The mixture contains plaster insulation - 3 mm granules of the same foam concrete (so this property of this plaster mixture is quite understandable).

UNIS TEPLON
This is a variant of gypsum plaster. Gypsum itself is significantly less thermally conductive than solid cement. However, to enhance the thermal insulation properties, perlite (or volcanic glass) granules are added to this mixture.

HAGAst AuBenputzPerlit FS-402
This plaster mixture is based on cement, but also contains perlite, which makes it possible to achieve high sound and heat insulation properties. The mixture is specially intended, mainly for finishing surfaces made of gas and foam concrete.

Knauf Grinband
This thermal plaster contains polystyrene foam granules as an insulating filler, with a fraction of no more than one and a half millimeters. In addition, the mixture contains polymer components that reduce the dispersion of the dried mass and prevent contact of polystyrene granules with moist vapor contained in the atmosphere.

Useful tips and tricks
When applying the plaster mixture, it is extremely important to observe the temperature regime. The composition of warm plaster, due to the presence of a significant amount of filler in it, is less adhesive than classic plaster.

And you need to pay attention:
- on the atmospheric temperature at which work is carried out;
- on the wall temperature;
- on the temperature of the plaster mixture itself.
The ideal option would be if the surface temperature of the wall being finished and the ambient air temperature coincide, and the temperature of the mixture exceeds them by no more than 10°C.
The mixture for warm plaster has a lower specific gravity than the composition of traditional plaster. Therefore, it is necessary to use reinforcing mesh only if a relatively thick layer of this finishing coating is laid (more than 40 mm). And if the wall is plastered without a mesh, the applied mixture should be leveled relative to the pre-set beacons.
Types of facade plaster
Plaster mixtures are used both for leveling walls and for decorative finishing. They can have different compositions and differ in their characteristics:

- Mineral plaster is sold in the form of a dry mixture and is one of the most inexpensive types. The basis of the mixture is cement, to which various substances can be added that reduce water absorption, the development of fungi, and improve adhesion. The solution is easy to apply and has high vapor permeability. When the house shrinks, such a coating may become cracked due to lack of elasticity.
- Silicate plaster is durable, elastic, vapor-permeable, protects walls from moisture, and does not attract dust.
- Acrylic plaster is more durable (up to 25 years) and elastic. It forms a layer that does not allow moisture to pass through, so it is not compatible with all materials. Can be applied to a foam insulation layer. It is not recommended to apply it near busy highways, as it is prone to dust contamination.
- Silicone plaster is a modern coating with high elasticity, vapor permeability and antistatic properties. It has a long service life, is resistant to atmospheric influences, precipitation, and aggressive environments. Sold ready for use.