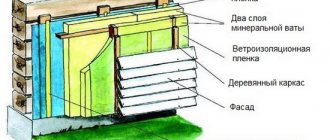
Careful insulation of inter-crown joints and sealing of seams can increase the thermal resistance of log walls made of rectangular or profiled timber by 10% - 12% and by 15% - 20% - walls made of cylindrical logs. However, not only thermal insulation is important, but also a number of other functions that the insulation must perform. How various materials presented on the construction market cope with the task, as well as a special approach to insulating wooden baths, is discussed in this review.
Requirements for an ideal interventional heat insulator for a log bathhouse
In addition to the maximum possible coefficient of thermal resistance, inter-crown insulation for a bathhouse must:
- Have moderate vapor permeability. The temperature and humidity in the steam room fluctuate intensely. The ability of a heat insulator to accumulate and evaporate moisture should be comparable to that of wood. Only then will it be possible to avoid condensation of liquid between the crowns, which contributes to the development of bacterial and fungal flora.
- Demonstrate volume recovery after removal of the load. For a log house in which a steam room is installed, it is doubly important to compensate for the cyclic change in the gaps between the beams. Indeed, here, in addition to natural shrinkage and the change of seasons, the wood is affected by extreme changes in humidity, which contribute to the expansion and contraction of logs. Only inter-crown insulation with good residual elasticity is capable of filling gaps of varying sizes.
- Contain antiseptics and/or other substances that resist the formation of mold and rot.
- Be distinguished by biological resistance and stability of properties. That is, to be “uninteresting” for birds and insects, and also not to become brittle and lose integrity under the influence of temperature, humidity and solar radiation.
- Be moderate in price and easy to use. You don’t expect to spend 30% or 40% of the budget of the entire building on purchasing insulation for inter-crown joints, do you?
- Harmonize with the aesthetics of the log house.
- Be an environmentally friendly material.
Insulation and sealing
The material that is laid between beams or logs during the construction of a log house works to reduce heat transfer.
The individual elements that are used to seal the joints from the outside after construction are not so much thermal insulators as sealants. They perform the function of wind and moisture protection, reduce convection heat transfer and, if possible, decorate the exterior and interior. Sometimes it makes sense to use different materials for insulation and sealing.
The main thermal insulators used: pros and cons
The origin of the word “caulk” is associated with hemp, from which hemp and twine for sealing cracks were made hundreds of years ago. Products based on this plant are still produced in separate nonwoven fabric factories. But sphagnum moss and “cuckoo flax”, which were once the most popular sealants in Russian wooden architecture, are now perceived as exotic. We will limit ourselves to considering what is present on the shelves of construction supermarkets and specialty stores.
Rolled flax insulation
Inter-crown linen seal
This inter-crown insulation is made from flax fibers using needle-punched technology. We can order any strip width from 3 to 40 cm in 0.5 cm increments. The thickness at a density of 700 g/m² is 8 - 10 mm.
Linen wool (as this thermal insulator is also called) is one of the best means for residual elasticity, heat conservation, environmental friendliness, and aesthetic properties. In addition, flax fiber tape is currently the most inexpensive way to efficiently caulk a chopped bathhouse. Rolled flax is easy to use. The strip is laid in the groove of the crown and adjusted with staples. The log can then be mounted. Wind is not a hindrance to installation.
Among the disadvantages of flax, it is not the best biostability. Birds happily take it out of the cracks to build nests. Some insects also live in this material.
Rolled jute insulation and jute-linen materials
Jute inter-crown seal
Thermal insulation made from jute is a coarse, homogeneous non-woven fabric produced using the same technology as the insulation made from flax. Jute inter-crown insulation is a durable and relatively rigid tape, which, in addition to good heat-shielding and hydrophobic properties, is distinguished by the presence of 20% lignin in its composition. Lignin is a resin similar in properties to the resins of coniferous trees. Thanks to its presence, jute exhibits both positive and negative qualities.
Inter-crown insulation made of jute has pronounced antiseptic properties. Birds are indifferent to it, and insects are repelled by the smell of lignin. The only thing in which jute is inferior to its flax counterparts is residual elasticity. This material cakes and forms layers under high pressure that are close in density to natural wood.
Jute roll fabric is produced in strips with a width of 10 to 20 cm. With a density of 700 g/m², its thickness is 4 - 6 mm, and the cost is approximately the same as the price of linen fabric.
Trying to combine the advantages of two types of plant fibers and compensate for their disadvantages, manufacturers of non-woven fabrics began to produce combined materials. It is assumed that the jute component provides them with strength, antiseptic action and biological resistance, and the flax component provides elasticity.
Rolled insulation made from artificial fibers
Synthetic inter-crown insulation
The Scandinavians have developed and are promoting several types of inter-crown non-woven tapes based on synthetics - polyester, padding polyester and other fibers. According to experts, these materials can displace natural linen and jute insulation from the wooden construction sector, which uses well-dried raw materials. This includes, for example, laminated veneer lumber produced in Norway and Sweden.
Wood with natural (medium) and high levels of humidity reacts to contact with synthetics quite capriciously: with the formation of non-evaporating internal condensate films and the formation of mold.
Ropes and ropes made from natural fibers
The wall sealed with rope looks elegant
Ropes for sealing joints, made of jute or flax, have all the advantages and disadvantages of these materials. On the street side, preference should be given to jute seals. Linen cords are sometimes used for aesthetic reasons, when light gray is more suitable for an interior or exterior ensemble than brownish-gray jute.
Wool felt
Felt made from sheep wool undergoes special processing and is used to produce thermal insulating plates for wooden construction. In almost all respects, processed wool is superior to inter-crown insulation materials of plant origin. Except for one indicator - price. The price tag for special wool felt is quite impressive. For this reason, the material is practically not used in the construction of baths.
Sealing pastes
Sealing pastes
Many types of acrylic, silicone, latex and rubber compounds are produced under the general hyperbrand “warm seam”. Some of these sealants are intended for thermal insulation of crowns over sample areas. Others are made to make sealing joints. And all of them are characterized by increased adhesion to wood.
Sealants are not suitable for chopped baths due to their zero vapor permeability. But for residential log houses they are used with great success.
How to insulate a log house
A log house is a constantly changing structure. The greatest changes occur in the first year after construction - the wall shrinks by about 8%. But in the future, uneven drying or periodic expansion of the wood leads to the formation of gaps between the logs, changes in the height and other dimensions of the wall. Such a structure must be insulated reliably, for a long time. How to do it?
How to remove cracks and eliminate air permeability
If there are through gaps in the wall, which is typical for a log house, then there is no point in talking about heat preservation in a wooden house. Air permeability should not exceed standard values. You can reduce it in two ways:
- Caulk the cracks. Sealing material is placed between the logs, both during construction and after cracks appear.
- By placing a continuous air barrier made of insulating material on the wall. We will consider how best to insulate further.
Materials for caulking a log house
To eliminate cracks in a wooden frame and seal the crowns, natural materials are usually used. They go well with wood and have been known to builders for a long time.
- Jute.
- Linen.
- Hemp (Industrial hemp).
What usually grows in areas where wooden houses are built is also not outdated:
- sphangum moss;
- cuckoo flax;
The shape of insulating sealing materials for a log house can vary as follows:
- Fibrous - for caulking cracks that appear over time.
- Tape - for laying between logs during construction.

How crowns are compacted, caulking
When building a log house, strips of sealant are laid on top of an already installed log along its entire length. Moreover, the width of the material should be such that it protrudes slightly on both sides of the log. Then the edges of the material are wrapped and hammered between the logs both outside and inside, thereby achieving better compaction of all irregularities.
During subsequent caulking, the fibrous material should be evenly distributed along the area intended for compaction. Local packing of a large amount of material can lead to distortion of the structure and the appearance of cracks in other places. A special tool is used - a caulk. The material is driven in on both sides of the wall.

Protection of log seams
But it is better to protect the natural sealant from atmospheric influences - rain, snow and wind. In addition, biodestruction is also affected - insects and birds. Now, to seal the sealing material from the outside, you can use modern compounds - special sealants for wood. It is important that they retain some elasticity for a long time, therefore they cover the cracks from through blowing and after movements characteristic of a log house.
Rational combinations of insulation
The combination of linen insulation with jute rope seals has proven itself well. In this option, it is possible to compensate for the low biostability of flax, while maintaining its elasticity. In some cases (in the steam room there is no covering of logs with clapboard and other materials), it is permissible to seal the seams on the street side with rubber or latex paste, using jute tape as an inter-crown heat insulator.

External interventional sealing of the bath
Jute sealing material

This insulation is made from the natural jute plant; it grows in India, Bangladesh and Kazakhstan. Despite the fact that it is brought from other countries, it has a low cost. Insulation is made in various forms: tow, rope, rope and tape. It is recommended to use a jute tape seal for laying between the crowns of the log house. It is made in various sizes, so you can easily select this insulation to fit the size of your logs or beams. The jute tape is easy to install; it is simply laid out over the log, secured with a stapler and covered with another crown on top. Even with a strong desire, birds will not remove such insulation from the inter-crown seam to build their nests.

Jute has properties similar to wood, only they differ in their density. It is natural, natural, and rotting processes will occur in it. Jute tape breathes even under strong compression, is not afraid of moisture, it absorbs and, if necessary, releases it. You can use it to insulate both residential buildings and bathhouses made of various types of wood (rounded and chopped logs, natural and laminated veneer lumber, etc.) This insulation has a pleasant golden hue, also similar to wood, which explains the attractive, non-obtrusive eyes inter-crown seam insulated with jute.
Summary
And yet, is there a universal solution for most chopped baths? interventional insulation for timber: which one to choose without going into the analysis of details? If you trust the experience of builders specializing in the construction of wooden spa areas, then in functional terms it makes sense to limit yourself to jute tape, and use sealing ropes more as a decoration. The selected option works well for profiled and rectangular timber, regardless of the structure of the building and the initial moisture content of the material.
However, it is necessary to identify exceptions to the general rule: a universal solution is not suitable for log houses with increased pressure on the inter-crown contact area. These include bathhouses made of rounded logs of small diameter, as well as two-story buildings.
conclusions

That is why it is recommended to seek professional help or advice. The fact is that experienced craftsmen will arrange your bathhouse and the insulation pie in it in the shortest possible time and without harm to their health and yours. But if you decide to take on the task of insulating a timber bathhouse from the outside with your own hands, then it is extremely important to study the basic materials on this topic outlined above.