- home
- Services
- Residential insulation
- What is the best way to insulate a floor under a screed? We understand the choice of optimal material
—
—
—
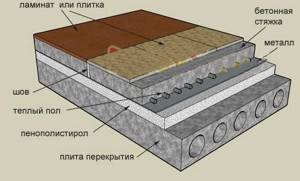
Since about 30% of all heat loss occurs through the floor, it needs insulation in the same way as other structural elements of the room - walls and ceiling. The main method of thermal insulation is insulating the floor under the screed.
When insulating under a screed, it is very important to choose the right thermal insulator. Insulation materials such as expanded clay, polystyrene foam, mineral wool, penoplex and polyurethane foam are most often used as insulation for installing a heat-insulating layer under screed. You can also install a floor heating system, which can be infrared, electric or water.
What is Penoplex, types, scope of application
Penoplex - under this brand back in 1998, extruded polystyrene foam boards - EPS - began to be produced in the Leningrad region. A little later, factories appeared in Perm and Novosibirsk, then in Taganrog, two factories in Kazakhstan, in the Tula region. So the geography of production sites is wide.
Penoplex insulation boards are orange in color
Brands for private construction
Currently, two types of Penoplex slabs are produced - for private and professional construction. For private there are three types: Comfort, Foundation and Wall. The names reflect the scope of application of the materials. They differ in density and compressive strength.
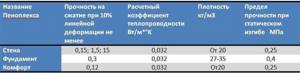
Penoplex Comfort and foundation are used for walls. What is the difference? Strength and density
The remaining characteristics are the same - they are produced from the same raw materials, using the same equipment. But their purpose is different: Comfort - sound and heat insulation, Foundation and Wall are more aimed specifically at thermal insulation. Although, according to the manufacturer, their noise reduction indices are the same. It’s just that in the Comfort category there is a larger selection of plate thicknesses: 20 mm, 30 mm, 40 mm, 50 mm and 100 mm. The rest have only two thicknesses - 50 mm and 100 mm.
Which Penoplex for flooring under the screed can be placed from this line? Penoplex Foundation. It fits all the criteria. Recommended for laying floors on the ground and on a concrete slab, above a ventilated underground, on a loggia or balcony. The only thing I'm not happy about is the thickness - there are only two options - 50 mm and 100 mm. This is inconvenient since the required/desired thickness is often different. This limits the use of this type of material in screed.
For professionals
Line for professionals - Base, Facade, Roof, Slope, GEO and 45. There are also blocks and shaped products. The blocks are used in heavy construction and private owners have not yet adapted them. Shaped products are a useful thing for insulating wells and solving other similar problems.
Of all the above, it is recommended to use GEO and Slope for floor screeding. The difference between them is in shape: GEO has a standard type of slabs, Slope - slabs with a longitudinal difference in height. They will come in handy if you need to create a floor slope. Their density and strength are higher than those of the materials of the previous category.
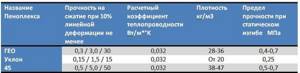
Characteristics of PENOPLEX, which can be placed under a screed
Penoplex GEO is convenient to use under screed because there are slabs of this category of different thicknesses - 40 mm, 50 mm, 60 mm, 80 mm and 100 mm. It is easy to dial the desired thickness.
Sometimes they think of using Penoplex 45 for the floor under a screed, but this strength is clearly excessive. This type of material is used in road construction. In any house there will not be even close to such a load. So this type of EPS should not be used.
Types of insulation, main performance characteristics
Thermal insulation materials are used in various options for insulating floors under reinforced screed, based on their performance characteristics and the requirements for insulation.
Popular and widely used materials from Russian and foreign manufacturers:
- polystyrene foam (expanded polystyrene);
- extruded polystyrene foam;
- mineral wool;
- expanded clay;
- perlite;
- vermiculite;
- isover;
- other innovative materials.
The project provides for thermal engineering calculations and working drawings of the floors. If the project is drawn up independently, it is recommended to do the thermal engineering calculations using an online calculator. The calculator algorithm is based on the formulas and requirements of SNiP II-3-79.
For insulation, a product is purchased that is most suitable in terms of its technical and economic indicators for floors of a particular design. The main indicators by which insulation is selected:
- Geometric dimensions: width, length, sheet thickness.
- Density or weight of 1 m^3 of insulation. The higher the density, the higher the strength of the material, but the lower the thermal conductivity, vapor permeability, and water resistance.
- Compressive strength, which determines how much pressure the material will withstand before the height decreases by 10% of the original. This indicator affects the permissible load on the floors during operation.
- Water absorption. An indicator of how much water the insulation absorbs as a percentage of its volume per day or 30 days.
- Vapor permeability. The amount of water vapor in grams allowed by standards to pass through the material by 1 m^2 in 1 hour at a pressure of 1 Pascal.
- Thermal conductivity coefficient is a tabular value for a specific insulation indicated by the manufacturer (k). Allows you to calculate the thickness of the insulation using the empirical formula: h=R*k. R is the normalized value of thermal resistance, tied to the climatic region in Russia.

Indicators of the normalized value of thermal resistance are determined according to the climatic regions of Russia GOST 30494
*
Extruded polystyrene foam
This is foamed polystyrene, produced by passing under pressure through an extruder. The feedstock in the form of small polystyrene granules is placed in a special chamber called a reactor. Here, at high pressure and temperature, the granules are saturated with air purified from water vapor and mixed with adhesive synthetic resins.

Penoplex is one of the best modern insulation materials
Then the pressure is sharply released, the mass of gas-saturated particles increases in volume, and a foamy structure is formed. After passing through the extruder, excess gas is removed and remains only in the cells of the feedstock - closed particles 0.1-0.2 mm in size. On the molding line, sheets of the required size are obtained from a homogeneous mass.
Extruded polystyrene foam occupies a leading position in the insulation market. This reliable and practical material is produced in accordance with GOST 32310-2012. Extruded polystyrene from large manufacturers of such brands as:
- Penoplex,
- Ursa,
- TEPLEX,
- FLOORMATE 200
- TechnoNikol,
- Penostex.
| Name of product | Dimensions mm | Density kg/m^3 | Strength kPa | Coeff. Thermal conductivity | Water absorption % | Degree flammability |
| Technoplex | 1180* 580* 50 | 26 | 0.2/0.4 | 0.034 | 0.4 | G4 |
| TechnoNikol CARBON ECO | 1180* 580* 10/100 | 26 | 0.2/0.4 | 0.034 | 0.4 | G4/G3 |
| TEPLEX 35/45 | 1200* 600* 20/110 | 31/45 | 0.3/0.5 | 0.028/0.03 | 0.4 | G1/G4 |
| Penoplex 35/45 | 2400* 600* 40/100 | 38/47 | 0.4/0.7 | 0.028/0.03 | 0.4 | G1/G4 |
*
Advantages and disadvantages of application:
- Light weight and good workability make it possible to use extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) for floor insulation; even one worker can handle the job.
- The low coefficient of thermal conductivity allows, with a slab thickness of 10 centimeters, to achieve a sufficient level of thermal insulation of the concrete floor to maintain the standard temperature.
- Low water absorption and vapor permeability determine its use in floors on the ground, floors of the first floor where there is a basement.
- The high compressive strength of the material allows the use of EPS in floors with high loads and traffic intensity.
- High chemical resistance to acids, cements, bleach, hydrocarbons.
- The material is environmentally friendly and does not harm human health.
- Manufacturers guarantee the service life of extruded polystyrene foam to be 25-50 years; it is not subject to rotting and can withstand sudden temperature changes.
Extruded polystyrene foam deserves only positive recommendations; it is non-toxic during installation and during operation.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool insulation includes:
- slag,
- glass wool,
- mineral wool,
- BTV,
- isover,
- pure flax slabs,
- isophas,
- other slabs produced abroad.

Glass wool is made from a molten mixture of sand, glass, soda, and limestone. Fibers are drawn out and mats are formed by pressing these fibers. The mats have different thicknesses, sizes, and are available with foil coating.
Glass wool has fairly high thermal insulation properties, does not burn, does not rot, and is resistant to chemicals. When installing mineral wool, the fibers break, forming an air mixture that penetrates clothing, the human body, and eyes. This causes irritation to the skin and other organs.
Important! You cannot work with glass wool without safety glasses, a respirator or gauze bandage, gloves, and special clothing.
Another important drawback is that glass wool has high moisture permeability and the ability to absorb water, while losing its thermal insulation properties.
This disadvantage is completely absent in mats based on basalt wool. This material is made from a molten mass of basalt rocks. The drawn fibers, up to 80 mm long, are stronger than glass wool fibers. Working with basalt wool mats is much easier and safer.
Mineral wool boards are used to insulate floors in wooden houses, laying them between joists or to insulate ceilings. Dense mats BTV, BSTV are used as insulation for floors on the ground or for continuous monolithic foundation slabs.
| Name of product | Dimensions fibers mm | Compressibility % | Coeff. Thermal conductivity | Application temperature С0 | Degree flammability |
| Slag | 16 | No data | 0.46-0.48 | <250 | NG |
| Glass wool | 15/50 | No data | 0.039-0.046 | -60/+450 | NG |
| Mineral wool | 16/80 | 40 | 0.077-0.12 | +300/+600 | NG |
| BTV | 700/1000 | 40 | 0.039-0.046 | -190/+700 | NG |
Penoplex thickness for screed
The question often arises not only about the density or brand of Penoplex under the screed, but also about the thickness. To say for sure, it is necessary to carry out thermal calculations. After all, the thickness of the insulation depends on the heat loss that goes through the floor. If it is a floor on the ground, it is one thing; if it is a screed on a concrete slab in a high-rise building, it is quite another, even if they are in the same climatic zone.
And the thickness of Penoplex depends on where you are going to make the screed and how you will use it. In the case of laying a heated floor, the layer is made to the maximum - there will be less heat loss, lower heating costs.

What thickness of Penoplex should be placed under the screed - table of recommendations for the first floor and unheated rooms below
However, calculations are done very rarely; usually the principle “like everyone else” is used. Here are the average thickness values of Penoplex for floor screed:
- Screed on a concrete floor with a heated room from below - 20-40 mm. If you want to achieve a soundproofing effect, it is better to lay 50 mm thick.
- For concrete preparation (on the ground) and a slab with an unheated room below - from 100 mm and more - depends on the region. The table shows the manufacturer's recommendations for the thickness of Penoplex for the first floors or higher, but with an unheated room below.
If you plan to make a heated floor (water or electric), then add another 10-20 mm to the thickness.
Material characteristics
It’s worth starting with the fact that, depending on the scope of application, a material of one density or another is chosen. Insulation of the floor structure is carried out using penoplex grade 35 or 45. There is also material of grade 31, 31C and 45C.
Characteristics of penoplex grades 35 and 45
Penoplex insulation grade 35 is a universal insulation material and can be used not only for floors, but also for walls with a foundation.
Table 1. Excellent performance qualities of grade 35
| Indicator name | Units | Meaning | Explanation |
| Density | Kg/m3 | From 28 to 38 | The material can withstand significant loads. |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | W/m×°С | 0.03 | This is a fairly low figure that guarantees the energy efficiency of the floor structure. |
| Hygroscopicity | % | 0.4 | When testing was carried out during the day, the material absorbed moisture in the specified volume only in the first 10 hours. |
| Flammability | Category | G1 | When combined with a concrete screed, which is not subject to combustion, such insulation, which already belongs to a high category of fire resistance, is completely fireproof. |
| Noise absorption | db | 41 | Relevant for apartments and multi-storey buildings |
| Tensile strength | MPa | 0.4 – 0.7 | The material allows you to create a reliable, solid base. |
| Temperature range of application | °C | -50 to +75 | It will be an ideal material for insulating screeds on cold concrete floors. |
Penoplex insulation grade 45 has a higher density, therefore it is more often used for insulating screeds on a soil base. This heavy-duty material is even used in road construction.
Application of penoplex in road construction
Table 2. Excellent performance qualities of grade 45
| Indicator name | Units | Meaning |
| Density | Kg/m3 | From 40.1 to 47 |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | W/m×°С | 0.03 |
| Hygroscopicity (tested during 24 hours) | % | 0.2 |
| Flammability | Category | G4 (together with a heat-resistant coating does not play a role) |
| Noise absorption | db | 41 |
| Tensile strength | MPa | 0.4 – 0.7 |
| Temperature range of application | °C | -50 to +75 |
Standard marking on the packaging of Penoplex insulation
On the packaging of penoplex you can see the following types of markings:
Characteristics of the main types of insulation
To summarize, we can distinguish several types of penoplex that are used to insulate floor screeds:
- "Penoplex" grades 35 and 45, suitable for roofs, floors above warm and cold basements, in garages and storerooms.
- “Penoplex Foundation”, which has high moisture resistance, heat and sound insulation properties and can be used not only for insulating foundations, but also for ground screeds.
- "Penoplex Comfort" is a common type of insulation for interior work and is not afraid of high humidity. Placed on a rigid base (concrete floor slabs).
Insulating the floor under the screed
Any screed (concrete, CFRP, self-leveling compounds) on top of Penoplex is done in the same way. The presence of reinforcement also does not affect the technology of laying slabs. Let's start with the fact that the slabs have formed projections, that is, a locking connection. This eliminates the appearance of through cold bridges.
It is cut, like any EPS, with a fine-tooth hacksaw (for plastic or metal). A more serious tool is not required. You can straighten the cut or trim it a little with a sharp knife (regular or construction knife). The rules for laying on the floor are very simple:
- For better heat retention, it is better to lay two layers. Their total thickness should match or be slightly larger than the selected one.
- Before laying Penoplex on the floor under the screed, roll out the damper tape around the perimeter.
- We lay the first layer so that the seams in the rows shift and there are no intersections in the form of a cross. That is, we start the first row, for example, with a whole slab. The second is from the segment that remained after trimming the last one in the first row. If it is too narrow, it is better to cut the new one in half.
- You can glue the joints of the first layer slabs with tape, but this is not necessary, since the edges in the form of locks are sufficient fixation. But for those who like it “more reliable”, you can glue it.

It is necessary to lay penoplex under the screed with the seams offset so that they do not coincide
- The slabs of the second layer are laid so that the seams do not coincide. That is, to lay the first row in the second layer, halves are needed. To do this, the slab is cut lengthwise. That is, the junction of two rows will be above the middle of the bottom sheet. And so that it does not completely coincide, you need to start the first row in the second with a quarter. In the second row it is very advisable to glue the joints. Firstly, because they will be walked on - there is no escape from this. Secondly, because it is necessary to protect the joints from leakage of the solution.
Should polystyrene foam be attached to the base? For what? Loaded with a screed and everything on it, it won't go anywhere. If this installation method seems very unreliable to you (but this is what the manufacturer recommends), you can fasten it. The first layer is a dowel-nail with a large plastic head. The second one is usually not attached, but you can attach it with glue (PVA, for example). You can secure the first one with glue or some kind of mastic, but you will have to wait until the adhesive composition dries.
Insulation of concrete floors with roll insulation
In my opinion, this is the easiest way to insulate the floor. Roll insulation is used. This may be a more expensive cork insulation:
Or cheaper foamed polyethylene, the names of which are full with and without foil:
For insulation with roll insulation, the main requirement is a smooth and clean floor surface. Clean does not mean that the concrete slab needs to be washed and shampooed. It is enough to sweep it thoroughly so that there are no stones on it that could tear the insulation.
That's all. There is no additional hydro- or vapor barrier, because foamed polyethylene does not allow water or steam to pass through.
Next, we roll out our penoizol or whatever you chose. Most likely it will be in strips that need to be laid with the known overlap of 15 cm.
Further steps depend on the planned final coating. Under the tile you will have to put a layer of moisture-resistant plywood or OSB-3 on top of the roll insulation. Between the sheets of these materials we must leave gaps of 5...10 mm, which can be filled with sealant. We fasten the plywood (OSB) with dowels and nails to the slab, thus simultaneously fixing the penoizol. At this point, the insulation of the concrete floor with rolled material is completed; all that remains is to lay the finishing coating.
There is no need to put additional plywood under the laminate. And do not use penoizol that is too thick, otherwise in places where there are overlaps you will get too high “steps”...
If the final covering is a floorboard, then a gap is needed between it and the rolled insulation. If you've read about insulating a roof or wooden floor, you can already guess how to get this gap. If not, don’t worry, I’ll tell you here. We fasten the counter-lattice to the floor with the same dowel-nails, which again will help the insulation to be fixed. What a counter-lattice is can be understood from the figure, although it shows the insulation of a wooden floor:
The distance between the slats of the counter-lattice is 50...60 cm. The slats are perfectly obtained from a board with a cross-section of 25x100 mm (usually sold in 3 m lengths), if you spread it lengthwise, but you can also buy slats of 25x50 mm (for some reason they are already called a picket fence in the store , although they still need some work before the picket fence).
This is interesting: Insulation of the concrete floor of the first floor: we analyze it in detail
Penoplex screed: technology
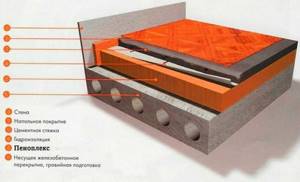
Let's consider the simplest case - Penoplex for a floor under a screed on a concrete base. This can be concrete preparation in a floor structure on the ground, or a concrete floor in a high-rise building or private house. The procedure is as follows:
Local irregularities larger than 5 mm are leveled. The manufacturer does not specify the alignment principle. That is, it can be a leveling screed (if there are too many irregularities) or local filling of potholes and cracks with a solution. In the second option, it is necessary to trim/cut/knock down the strongly protruding fragments. Sometimes they even level it with sand. This method is also not excluded.
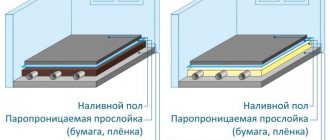
Standard scheme for using Penoplex under screed

? Actually, the whole technology. All clear. Only questions may arise regarding the minimum thickness of the Penoplex screed. The manufacturer recommends at least 40 mm. When laying floors in wet rooms, it is advisable to cover the slab with waterproofing. Choose the type of waterproofing material yourself. The rest of the technology is the same.
Insulation on floor slabs
You will need to acquire the following tools and materials:
- building level;
- polymer putty;
- primer;
- moisture-repellent film;
- insulation;
- polyurethane glue;
- self-leveling composition.

The sequence of work is as follows:
- First of all, the floor slabs are checked for flaws. Any protrusions, cracks, or depressions must be eliminated. The protrusions can be knocked down using a hammer drill, and the cracks and holes can be covered with polymer putty. If there are a lot of flaws, the base will have to be leveled with a self-leveling mixture. If the slabs are in normal condition and free from damage, you can limit yourself to removing debris and removing dust.
- If a floor no lower than the second floor is subject to insulation, then the penoplex is spread directly onto the floor, which has been pre-treated with a primer mixture. If the ceiling is part of the basement or first floor, then it is advisable to cover the floor with a water-repellent film. It turns out that, based on the location of the ceiling, it is either primed or covered with a protective layer of moisture insulation. In the latter case, the joints of the film must be taped.
- You need to apply a layer of glue to the underside of the insulation, then apply it to the floor and press down firmly. The position of each individual slab is checked with a building level, while simultaneously controlling the horizontality of adjacent pieces of insulation so that the surface is perfectly flat. Each subsequent row of slabs is laid with an offset of half the width of the segment so that the seams do not coincide.
- A layer of polyethylene film is laid on top of the insulation for waterproofing.
- A classic cement screed up to 5 cm thick, or a self-leveling compound can be poured onto the waterproofing layer. Once the screed is completely dry, you can begin laying the finished floor.
Laying heated floors on Penoplex
There are differences, but they only concern the laying of pipes or heating cables/mats. Preparation of the base, the first layers, including the waterproofing layer on Penoplex, were described above. A steel mesh is laid on the waterproofing film. It is needed to fix the cable or pipes in a given position. When using heating mats, they can be placed in a layer of tile adhesive - this is simpler and more effective, so this type of heating elements for the floor is rarely used at this stage (although no one prohibits it).
Which mesh should I use? Depends on the step at which you need to lay the pipe or cable. You can lay 50*50 mm, 100*100 mm or 150*150 mm. It is important that the chosen scheme can be implemented. What is the thickness of the wire in the mesh? Not less than 3 mm. In the case of a cable, perhaps 2 mm is possible. And before pouring the screed, the pipes will be filled with coolant and need to be held in place, so a mesh made of 3-4 mm wire is needed.

You can use Penoplex under a warm water floor without any problems
To prevent the mesh with coolant from moving when filled, it must be attached to the Penoplex. There are several options:
- Plastic clips that are driven into the insulation. But the thickness of the mesh rods is at least 4 mm.
- The metal tie is aimed at the insulation on both sides of the mesh cell.
- Special harpoon clamps.
- Special tires, but they are expensive.
- A mat with bosses is laid on top of the Penoplex. Then the grid is not needed. But these mats are also expensive.
After the mesh is secured, we attach the pipes or cable. The easiest way is with plastic ties, or knitting wire. But the wire can theoretically fray a pipe or cable as it increases or decreases in size (from heating and cooling) during operation. Therefore, if knitted with wire, it is in a plastic sheath. Manufacturers of pipes for heated floors have it.
Actually, that's all. Then they pour the screed, level it, and wait until the concrete gains strength.
We insulate with our own hands
Before insulating a concrete floor, you need to carefully check the condition of the base. If there are cracks, crevices and potholes on the subfloor, this will reduce the quality of the thermal insulation work, so the defects must be eliminated. In case of height differences (this can be checked using a level), the surface is leveled with leveling mixtures.
Expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene (EPS) is a type of foam material that comes in the form of individual slabs. Such products are characterized by low thermal conductivity and high strength. The service life can reach 20-30 years.
To complete the work, you will need a set of materials consisting of polystyrene foam boards, construction film, damper tape and a membrane to protect against steam. Additionally, you will need construction tape. Gypsum fiber sheets and glue are used for the top covering. To assemble the thermal insulation layer, you will need fasteners and additional tools.
Mineral wool on joists
The advantage of this material is low thermal conductivity and increased sound insulation properties. Such insulation for concrete floors can only be used in the technology of laying on joists, since the material cannot withstand loads.
The frame is created using timber and chipboard or plywood (layer thickness from 18 mm). Assembly occurs using self-tapping screws and dowels. The speed of assembly will be increased by a hammer drill and a drill, as well as a mounting knife, a level (construction level) and a tape measure.

Before making a frame, you should read the recommendations of experts:
- The film is laid overlapping on the subfloor (the joints can be 15-20 cm). The strips are attached to each other with tape.
- The bars should have dimensions of about 110*60 mm. They are laid edgewise on the base. The pitch is chosen taking into account the thickness of the coating; it is about 300 mm.
- You can secure the logs to the base using dowels and self-tapping screws. To begin with, the logs are drilled through, and you need to go a little deeper into the base. The fastening pitch is 40-50 mm.
- Mineral wool is laid between the floors. The material should tightly fill the entire space. To do this, roll out the roll and cut the cotton wool in the places where the joists pass.
- Plywood is laid on top of the joists. The sheets are placed joint-to-joint, with a distance of about 10 mm from the wall. The long side of the plywood should be perpendicular to the bars. This layer is attached to the frame using self-tapping screws.

Prices for Rockwool mineral wool
Rockwool mineral wool is in high demand due to its good performance characteristics at an affordable cost. The price of this material depends on the size and thickness of the layer. In construction stores in Moscow, packaging can be found for 470-500 rubles.
Under the screed
Insulation of a concrete floor in a private house can be done under a screed. Here you need to stock up on polystyrene foam boards.
The prepared base must first be cleaned of dirt and dust.

Immediately after this you can begin installation:
- The damper tape is glued around the perimeter so that it covers the junction of the wall and the floor.
- Glue is applied to the first polystyrene board. It needs to be distributed in the center and in the corners.
- The next slab is covered with glue according to the same scheme. The slabs must be glued tightly to each other (joint to joint).
- After the first layer has been laid, proceed with the installation of the second row. It is important to remember that the slabs are laid with a shift.
- The insulation for a concrete floor is covered with a layer of film and the joints are sealed with tape.
- A reinforced mesh is placed on top (there should be a gap of 2-3 cm from the wall to the mesh).
- Beacons are installed on the reinforced layer. You can fix them with a small amount of solution.
- The solution is poured into the recesses formed between the beacons and leveled using the rule.
- After drying, the beacons are removed, and the resulting recesses are filled with solution.
Foamed polyethylene
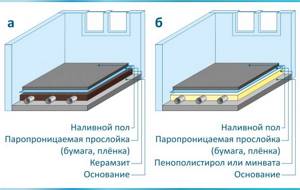
Steam- and moisture-proof polyethylene is often used as a substrate for linoleum and laminate, but complete insulation of concrete floors in a private house will not work. It is better to use it in a heated floor system or complement another thermal insulation system.
Dry screed on Penoplex
Cement-sand or concrete screed is, of course, good. And it is the best solution if you want to make a warm floor from heating. But the mass of materials amounts to tons. Raising this to any level is already a problem. You also need to wait at least 28 days for the concrete to gain strength. It's faster and easier to make a dry screed. Not in the sense that from a solution that is called dry. And using sheet materials - plywood, OSB, gypsum board. This base will be suitable for any finishing coating. Even under tiles, but with certain reservations - glue is needed for complex unstable bases.
You can make a flat floor without concrete and mortar: lay Penoplex for the floor under a screed made of gypsum plasterboard, plywood or other sheet materials
How to make a dry floor screed using Penoplex? Just:
- Level the base.
- If necessary, we lay or apply waterproofing.
- We lay out Penoplex slabs, preferably in two layers with bandaging of the seams.
- We lay one layer of sheet material. Again, we move the seams.
- The second layer of sheet material is also staggered.
- We fasten through with suitable fasteners. It depends on the material that was laid on the insulation.
- Further on the technology of laying the flooring.
The thickness of gypsum boards for laying on Penoplex on the floor is 20 mm, plywood is better to take 10-12 mm, OSB can be smaller. You can also put GVL on Penoplex. The slabs lie flat, without differences, so the base is suitable for this material. But it does not have the disadvantages of gypsum plasterboard and OSB, and the cost is approximately the same as them.
Installation Tips

To properly lay the insulation on the floor on the screed, you need to follow some simple recommendations. Every nuance can be decisive during the installation process.
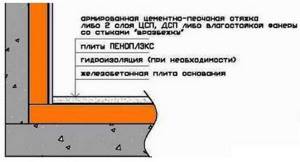
When making a screed, you should leave a gap of 1-3 cm between the wall and the floor. Without waterproofing, thermal insulation for a concrete screed is not done. It is important to follow the sequence of work when organizing thermal insulation. The floor cake must consist of at least five layers.
Upon completion of laying the thermal insulation for the concrete floor screed, professionals recommend additionally installing insulation reinforcement.
Which insulation to choose
The parameters for choosing an effective insulation under the screed must meet the following requirements:
- light weight;
- fire resistance;
- environmental friendliness;
- resistance to rotting;
- ease of installation;
- good thermal conductivity;
- affordability.
The most commonly used types of floor insulation are the following materials:
- foam plastics;
- polyurethane foams;
- mineral wool;
- expanded clay;
- sheet foam.
Using expanded clay under floor screed
Expanded clay has a number of positive properties - fire resistance, environmental friendliness, and relatively low weight. The material is quite fragile, so care and precision are required when filling it under the future screed. Destroyed granules lose their thermal insulation properties.
In rooms with low ceilings, the use of an expanded clay pillow will increase the field level by at least 15 centimeters.
A smaller thickness of expanded clay will not provide sufficient strength characteristics of the floor. In addition, expanded clay should be protected with water-repellent compounds or special materials for waterproofing - the material absorbs moisture well. It will be necessary to reinforce the layer of expanded clay insulation before laying the screed. The advantages of expanded clay include its low price.

Polystyrene foam as floor insulation
Sheet foam is used as thermal insulation under floor screed. The sheets are laid on the prepared base in a checkerboard pattern, the joints are sealed with tape or putty.
Polystyrene foam can be used for screeding and in the form of granules. To do this, parts of cement and granules are mixed in equal proportions. A solution is made which is used to fill the screed. In this case, the thickness of such a screed must be at least 20 cm. Otherwise, the strength of the coating and its thermal insulation are reduced.
Fixing the foam can be done either with adhesive mixtures or using special disc-shaped dowels.
Polystyrene foam has good thermal conductivity, is a very light material, does not allow moisture to pass through, and is affordable. It can be easily processed and cut with an ordinary construction knife.

Characteristics of thermal insulation materials for insulating concrete floors
Let us dwell in more detail on the performance properties of the most common insulation materials:
- fibrous. A typical representative of fibrous heat insulators is mineral wool;
- leafy Among the many sheet insulation materials, polystyrene foam is most often used;
- crumbly. Of the various types of crumbly materials, granulated expanded clay is popular;
- sprayed. One of the representatives is a polyurethane foam mixture, sprayed using special devices;
- polymer. They are represented by an expanded range of self-leveling mixtures.
Expanded polystyrene is most often used to insulate concrete floors
Let's start with mineral wool, which is offered in rolls or individual mats. The insulation is made not only on a mineral basis. Along with mineral wool, wool is used using dolomite, basalt or limestone raw materials. Glass production waste and slag are also used for production.
The main advantages of the material:
- ease of use;
- Fire safety;
- increased plasticity;
- reduced thermal conductivity.
However, mineral wool can absorb moisture and needs additional waterproofing.
Extruded polystyrene foam is sold in sheet form. The material is a type of polystyrene foam, but differs from it in the following properties:
- increased strength;
- long period of use;
- increased reliability;
- fire safety;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- environmental cleanliness.
Among the advantages of polystyrene foam sheets the following are also noted:
- noise insulation properties;
- moisture resistance;
- vapor permeability;
- reduced thermal conductivity;
- ease of installation.
The disadvantages include the increased cost of the material.
Granulated expanded clay is a very popular insulation material among builders.
Expanded clay is used in the form of granules made by firing clay. The main properties of expanded clay are:
- environmental friendliness;
- fire resistance;
- frost resistance;
- durability;
- reduced thermal conductivity.
Polyurethane foam is a sprayed insulation material. Distinctive features of the material:
- reduced thermal conductivity coefficient;
- resistance to open fire;
- Possibility of use in damp environments.
In addition, there are no joint areas or cold bridges in the polyurethane foam coating. If it is necessary to further thermally insulate the surface, apply the first layer, after which it has hardened and then re-sprayed. The main disadvantage of polyurethane foam is the need to use special equipment to spray insulation onto the surface.
Polymer heat insulators include:
- working mixtures supplied in liquid form, intended for pouring heated floors;
- special paint, after application of which the thermal insulation properties of concrete increase.
The durability of the floor depends on the correct choice of material.
Advantages of polymer materials:
- thermal insulation characteristics;
- integrity of the formed layer;
- reduced hygroscopicity;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- perfect flatness.
Disadvantages include increased costs for the purchase of polymer materials.
Mineral wool for thermal insulation screed
Mineral wool is used quite often as insulation. Moreover, this material has good sound insulation properties. The disadvantage and very significant is the high ability to absorb moisture. When moisture penetrates, mineral wool ceases to function as a heat insulator. Protecting mineral wool from water is the most important task. Therefore, high-quality waterproofing of the material must be performed. The technology for laying mineral wool mats is as follows:
- the base is prepared (cleaning from dirt, dust, debris);
- cracks and large gaps are sealed with mortar or other materials;
- a layer of waterproofing coating is laid;
- mineral wool mats are laid for waterproofing;
- a vapor barrier layer is laid on top of the wool;
- clamps are installed to provide a ventilation gap;
- a reinforcing layer of metal mesh (minimum 3 mm wire) is installed on the clamps;
- concrete screed is poured.
The technology takes a lot of time, but if followed, the effect of significantly reducing heat loss through the floor is achieved.

Installation of polystyrene concrete insulation
Installation of polystyrene concrete insulation is similar to the installation process of other insulation materials, but has one important difference - the screed can be made without reinforcement , depending on the load on the floor. The work is carried out as follows:
- A vapor barrier based on polyethylene is laid on the base;
- Expanded polystyrene sheets are laid, the joints can be blown out with foam;
- An additional layer of vapor barrier is laid on top of the thermal insulation;
- The walls are laid with damper tape;
- A screed made of concrete or self-leveling mixture is poured.
Subject to the installation conditions, any of the materials presented for insulation will last a long time and help protect the house from the cold . The main thing is to choose the right thickness of the material, taking into account possible heat loss and the insulating properties of the insulation.
Extruded polystyrene foam for screed
Compared to polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam has high strength and greater density. The closed structural cells of the material give expanded polystyrene foam almost complete protection from moisture. The material is difficult to burn, which makes it possible to use it when insulating wood floors.
It is advisable to apply insulation with extruded polystyrene foam on the ground. Before this, the soil level should be leveled and compacted.
A layer of crushed stone is poured and compacted. Sand bedding is made and compacted. The base should be as level as possible on a horizontal plane. Sheets of material are laid out on the prepared base at intervals. The joints are sealed with tape. A layer of waterproofing is required. A reinforcing mesh made of metal or plastic reinforcement is laid over it. The floor base prepared in this way is poured with concrete mortar.

How and with what to insulate a concrete floor in a private house with your own hands correctly
In the construction of high-rise and low-rise buildings, concrete is one of the most popular materials. Walls and floors made from it are relatively cheap and have a long service life. However, the owners of such housing are forced to think about insulation, since concrete slabs have high thermal conductivity and it is difficult to retain heat in such a building.
Application of polyurethane foam insulation
The use of liquid material - polyurethane foam - is an ideal option from the point of view of workability. Thermal insulation of the floor in this case is ensured by 100%. There are no cold bridges, there is no need to use hydro- and vapor barrier materials. The work is carried out according to the principle of spraying onto the surface of the subfloor. The thickness of the layer of such insulation, even in minimal values, makes it possible to achieve good, effective insulation of floors.
After drying (3-4 hours), a continuous hard shell is formed. You can pour screed over it without mesh reinforcement.

Methods for laying insulation
There are several ways to insulate a concrete floor in a private house.
Before settling on one option or another, you should take into account recommendations for choosing insulation and the method of attaching them:
- Laying in one layer. This thermal insulation system is considered the simplest and fastest. Any selected insulation (preferably in the form of slabs) is laid on the prepared subfloor, which can be secured with glue or dowels.
- Frame system. Installation using this technology requires more time and effort, but its advantage is the ability to use loose rolled thermal insulation (for example, mineral wool).
- Under the screed. During the work, insulation is laid on the subfloor, filled with screed and covered with any finishing material.

Use of lightweight heat-insulating screeds
Providing good thermal conductivity is achieved by using a material such as perlite in concrete screeds. Lightweight concrete with perlite is environmentally friendly, durable, and retains heat well.
The disadvantage is the fact that the perlite screed must be protected with water-repellent compounds. Perlite is a very hygroscopic material.
Choosing floor insulation is a rather complicated process. The variety of materials and their characteristics require a careful approach to the selection process. The price issue is also important. Choose the golden mean between consumer properties and price.
Recommendations for choosing thermal insulation for concrete floors
At the stage of choosing a material for floor insulation, it is necessary to pay attention to some important characteristics
Recommendations for choosing thermal insulation for concrete floors
Density. The weight of thermal insulation directly depends on it. The less dense the insulation, the more pores it contains and the greater the amount of heat will be retained inside the room.
Strength. It is better that the strength of the material is as high as possible.
Thermal conductivity. This coefficient reflects the ability of thermal insulation to transmit heat. It is better for this indicator to be as low as possible.
Moisture resistance. The higher it is, the better.
Moisture permeability. This figure should be minimal. Otherwise, the insulation will very quickly become saturated with moisture, against which its thermal insulation characteristics will noticeably deteriorate.
Durability. At this point, everything is very clear: the greater the durability, the longer the selected material will last.
Environmental friendliness
Those who plan to build an environmentally friendly building using natural and completely safe materials should pay attention to this parameter.
Popular insulation materials for concrete floors
- Basalt and mineral wool. The most popular and widely used insulation materials. Among the advantages, low density and relatively low thermal conductivity should be noted. Also, mineral wool insulation is characterized by high sound insulation properties. The main disadvantage is the low environmental friendliness of the insulation. It also absorbs moisture, which does not have the best effect on its characteristics as a heat insulator and overall durability.
- Styrofoam. Along with mineral wool insulation, it is a very popular material. The only drawback is poor environmental friendliness. Otherwise, if we consider polystyrene foam as insulation, there are no complaints about it.
- Extruded polystyrene foam. Its properties are similar to polystyrene foam, but it is noticeably ahead of it in almost all respects.
- Polyurethane foam. It withstands temperature changes, water ingress and various mechanical loads well. For many years it perfectly performs its main function without deteriorating its thermal insulation qualities. The only negative point is that it is artificial and not environmentally friendly.
- Expanded clay. Characterized by very high thermal insulation properties. It is an environmentally friendly material with low thermal conductivity. Despite all the advantages, expanded clay is also not without its disadvantages. First of all, this is a fairly large weight of the finished insulation layer. Secondly, the material absorbs and retains moisture for a long time, which somewhat worsens its properties and can lead to other problems.
- Foam glass. It has many undeniable advantages, for example, low weight, very low thermal conductivity, environmental safety, moisture resistance, durability, etc. Among the significant disadvantages, one can highlight only the relative fragility of the insulation, i.e. it is not adapted to large mechanical loads.
- Cork. A completely natural material with good thermal insulation properties. Cork works best when used in the construction of raised floors, and also as a heat insulator under the main covering.
- Perlite. According to the method of application, it has much in common with expanded clay. The only difference is that perlite is noticeably superior in quality to expanded clay, which makes its use much more preferable.
The following is a simple table in which you can consider the main characteristics of existing insulation materials. Be sure to take them into account when choosing a material in order to choose the insulation that is best suited specifically for your concrete floor.
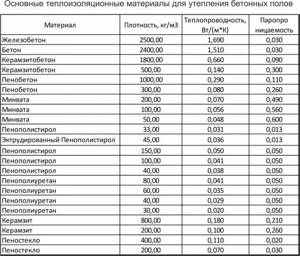
Table
Step-by-step insulation of the floor under the screed with your own hands

Protecting your home from the penetration of cold is an important part for ensuring comfort and reducing the cost of maintaining a home. City apartment owners are less concerned about this problem. Floors there are not the main source of heat loss. For some owners of housing on the ground floor, this issue is also relevant.

Owners of private houses have to solve this problem more often, especially if certain rules and regulations were not followed during construction. In this case, you need to know how to insulate the floor yourself.
How to choose floor insulation: a comparative review of 10 different options
The question “Which insulation is better for the floor?”
are asked by everyone who loves comfort. It's always nice to walk barefoot without fear that your limbs will freeze. And this is especially true in the off-season, when central heating (if any) is not yet turned on, and in winter, when the temperature outside is sub-zero. It is then that people often turn their attention to floor insulation. We will tell you how to choose the material and how to lay it correctly. After all, a well-insulated floor is one of the components of heat preservation in a living space. When choosing insulation materials, it is important to take into account the climate zone (how cold it can be in winter), the characteristics of the room and its purpose, the type of existing or planned floor covering. For example, floor insulation in an apartment and in a wooden house will differ significantly.
Materials and tools for insulating floors under screed
In most cases, the work does not require the use of special equipment. Any home craftsman or man who regularly does housework has a set of necessary equipment.
It is necessary to prepare the following mandatory set of tools:
- Level. The laser device is very convenient. If it is not there, you can use a hydraulic analogue. You can make a level yourself from a transparent elastic tube of the required length or a rubber hose by inserting glass tubes of a suitable diameter at the ends. Use a hand-held metal or plastic level with great care. At long distances it can give significant deviations.
- Measuring tool. Ruler, tape measure and square. They will help to accurately determine the area, mark out the waterproofing material and insulation.
- Cutting tool. Most of the work can be done with a construction knife, but sometimes it is convenient to use a regular hacksaw when cutting polystyrene foam.
- Equipment for mixing screed mortar. If the household has a household concrete mixer, then the work will go quickly. If you don’t have it, you can select a container of the required volume or mix the mixture directly on the concrete surface, after laying a thick film or old linoleum on it.
- Power tools - drill, hammer drill, grinder. This kit will help you quickly and efficiently install beacons on a concrete or wooden floor base, cut mesh and reinforcement to strengthen the screed.

As you can see, no special tools are required. It is much more important to have the desire and strictly follow the recommendations. Then insulating the floor with foam plastic under the screed will meet the necessary requirements. Attentiveness and accuracy will be good helpers in your work.
The following materials may be needed:
- Insulation. For the soil base, it is recommended to use a slab with a thickness of 100 mm. In all other cases, it is enough to purchase 50 mm material. It is preferable to purchase extruded floor insulation under the screed.
- Waterproofing material. The range allows you to choose the optimal option for floor insulation in a particular case. The most common materials in this category are: roofing felt, roofing felt, bitumen mixtures, specialized films and membranes. Foil waterproofing materials have a shielding effect and are laid with the metallized surface up on polystyrene foam under the floor screed.
- Fastening and guiding elements. Depending on the method of screed installation, the following products are used: self-tapping screws, anchor bolts, beacons and screed level slats.
- Sand-cement mortar. The dosage is traditional and does not depend on the quality of the heat insulators. Sometimes it is advisable to apply a finishing coating using self-leveling compounds for laying technological materials that require a particularly flat surface.

Insulated “floor pie”
To achieve a truly warm floor, you need several layers of different materials. Depending on where it is installed, the number of layers will vary. For example, for private houses it is necessary to create a powerful base, which consists of a pillow. In this case, gravel is used as the material. The thickness of the base should be approximately 25 to 30 cm.
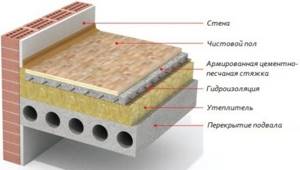
A screed (also called a rough screed) is laid on top of the gravel; its thickness should reach 50–100 mm. After the screed has completely dried, a layer of insulation is laid on it. Its thickness depends on the type, characteristics of the material, as well as the goals being pursued.
Attention! There is debate over whether it is worth strengthening the insulation or not. The most practical solution would be to symbolically tack the sheets to the screed using adhesive mixtures for rational distribution over the floor surface. After laying the waterproofing layer and finishing screed, the material will be securely fixed and will not go anywhere. Therefore, rigid fixation is a waste of time and resources.
A layer of waterproofing is laid on the insulation. It has the same structure as cement and is sold in the form of ready-made mixtures, which for use can simply be diluted with water, following the manufacturer’s recommendations, and applied to the insulation. Waterproofing is necessary to prevent finishing screed from getting into the joints, which leads to freezing of the structure.
Now you can begin laying the finishing screed. Its optimal layer is 50–80 mm. To create a strong structure, it can be reinforced with steel reinforcement or mesh. After the finishing screed has dried, finishing materials are laid: laminate, parquet, linoleum.
Insulation of the floor under the screed on the ground
Successful implementation of this type of insulation will be done if the master follows simple rules, the main one of which is high-quality surface preparation:
- ground level measurement. Beacons are placed along the perimeter and points inside it;
- the entire surface is compacted. It is better to perform this operation several times, each time generously filling the soil with water to allow it to shrink;
- After compaction, a control measurement of the soil level is made. Height differences are kept to a minimum. Ideally, the floor under the screed should not have horizontal discrepancies of more than 1 cm. In this case, the insulation boards will lie flat, and the foam screed will be of the same thickness.
Using Penoplex
The name Penoplex itself is a brand. And the material itself is a high-density polystyrene board. For screed floors this is the best option.
- It has low thermal conductivity - 0.031 W/m K.
- It has a high density - 45 kg/m³, which affects the compressive strength. And for genders this is one of the important indicators.
- Does not absorb moisture.
- Does not allow steam to pass through.
- Chemically inert.
- Absolutely environmentally friendly.
- Easy to process.

Today, manufacturers produce foam boards with a tongue-and-groove connecting lock, which makes it possible to assemble a seamless coating on the floor base.
The process of insulation with penoplex is simple. It is necessary to lay the slabs over the entire surface of the concrete floor, connecting them together with a lock, then stretch the reinforcing synthetic mesh over the top, and only then you can pour the solution.
How to insulate a floor screed in an apartment?
If directly on the screed, then - laminate, parquet board with a backing. Basically, wood flooring. If you still install the logs under the plank flooring, then it will be possible to provide more serious insulation there.
So it seems cold or not?) The easiest way is to buy insulated linoleum on a felt basis, just don’t glue it to the base. Take semi-commercial or commercial. You need to decide on the basis. Do you have high humidity in your apartment? If so, then jute and felt bases will not work. Then take a base made of foamed vinyl and polyester. It will last a long time, is durable and is not afraid of moisture, with good thermal insulation properties.
The cheapest option can be considered polystyrene foam; it can be purchased in any store from 100 rubles per sq.m., but it is fragile. Penoplex is a more durable material. Its cost is higher, but it is durable and you can find an option for slabs with grooves, which will make working with joints easier. What remains are mineral wool slabs. Expensive, the material needs to be protected from moisture, but it has excellent thermal insulation characteristics, does not emit harmful substances and is more expensive)))
Igor, is the board cold?! Are you laughing? Linoleum, even insulated, is significantly inferior in heat transfer to boards. Even if the linoleum base copes and insulates the interior of the apartment from the coolness of the screed, the surface of this floor covering itself will remain cool. In general, at the same room temperature, the board on the floor will be warmer than linoleum.
Good afternoon. To keep your apartment warm, it is best to install a heated floor: film or mats, just right for any material, tile, laminate, linoleum, etc. I recommend it to everyone
Polystyrene foam, expanded clay, penoplex, and any other roll insulation can be used for finishing the floor. The final floor covering, in terms of thermal insulation, will work well with laminate or carpet. In general, there are quite a few options for insulation for floor screed under the finishing coating. The choice is up to your wallet and taste, but I still recommend covering the floor with laminate.
1) according to the material Penoplex polystyrene foam, if you make the cake using technology so that it does not emit harmful fumes, then you can use expanded clay bedding and, accordingly, a screed. You can fill it in or make it semi-dry (if the thickness of the screed allows.
2) for the finishing coating I would recommend cork flooring (there are 2 installation methods
a) adhesive (from 1800 RUR m2) per material
b) castle, price guide (from 2500 RUR m2 is the cost of the material)
If you are heat-loving, then use an electric heated floor, which is used under laminate.
There’s nothing I can say about carpet, it’s not an amateur, the only downside is to constantly clean, wash, remove stains or debris.
Andreev Vyacheslav, I addressed my message to Ali, not to you. I have insulated linoleum on the screed (expensive, thick, it practically doesn’t even press against the sofa), with a small carpet on top. It’s warm, the floors aren’t icy or cold, you can walk and it won’t harm your health. “The screed seems to be cold. “- these words interested me, since the author himself does not seem to know whether she is cold or not. In my case, insulated linoleum is sufficient. 6th floor, panel house, neighbors are all there.
Igor, it means I misunderstood, you thought you wrote it to me about the floorboard. I'm glad for your linoleum, not everyone is so lucky.)
Yes, not everyone, so a person needs to decide). Is she cold or not? In my case, the screed was flooded due to strong changes. Linoleum was brought to order from the Czech Republic. Why? A friend works in Moscow (office renovation). They laid this linoleum, it showed itself well after a while, and the plans were for a laminate with a good backing. Everything was replayed. That's why I asked the question. How's the dampness? Maybe not everything is so critical and lags are not needed at all. It would be nice to hear from Ali to give more constructive advice.
Igor, it’s unlikely that Ali will go to the Czech Republic to buy linoleum, and there’s no point. In Moscow, you can also buy commercial insulated linoleum, or two-layer household linoleum of good quality. But its cost is comparable to the price of a good parquet board. And if you compare these two coatings, the parquet board will win with a clear advantage. Linoleum has one plus - it is easy to clean.
Laminate or carpet are also the first to come to mind as finishing options for the floor. They have good thermal insulation, materials, and are affordable for many, inexpensive in general. Well, you should not forget about waterproofing before thinking about floor insulation. Otherwise, without it, 50% of the thermal insulation effect of any material makes no sense.
Who said that I went to the Czech Republic to buy linoleum? It was delivered to order. I listened to my friend’s advice and I don’t regret it, he’s doing great. You can buy ours, no problem, I told my story. Each material has its pros and cons, so you need to look at the conditions in which a particular material is used. And for this you need a more accurate description of the place where it will be used.
Floor insulation is usually carried out (screed) with glass wool, mineral wool, expanded polystyrene, expanded clay, wood shavings, and cut polystyrene foam. And as a finishing coating for the floor, to make it warm to walk on, you can use a floor board or cork. Laminate and carpet are also good materials for this purpose. But first of all, pay attention to the options made of cork and wood.
People, tell us in more detail about expanded clay and how expensive it is. And thanks for the advice
Expanded clay is not fast and not that cheap. You need to choose a fraction, waterproofing, or choose between a dry option and a wet one. This is a very laborious process. If you are not familiar with the technological process, then it is better not to get involved. If you are really interested, I can tell you in detail about the dry version. Need to? Expanded clay is a good material, but you will have to suffer.
If you choose the dry option, then there will be no problems with insulation. Waterproofing is laid on the floor, expanded clay of different fractions is poured between the joists, it is advisable to mix it to enhance the effect. A subfloor made of chipboard, plywood or boards is laid on top. What effort is there, only the joists need to be leveled in advance or replaced if there are damaged ones. I only changed a few, the rest were in good condition. Next is processing of joints and finishing coat.
With a wet screed, expanded clay is mixed with liquid concrete and poured between the beacons. This method is suitable for surfaces with large differences; at the same time, you will level the base for further laying of the floor covering. Expanded clay screed is much lighter and this will reduce the load on the base. BUT, the thermal conductivity of such a screed increases, take this into account.
I had little choice, since the apartment was in terrible condition and had wooden floors. I've never seen anything like this, but I tore off the linoleum, fiberboard, 2 layers of boards and only then got to the joists. The floors were very cold, no one lived below. I replaced some of the joists, put polystyrene foam between the joists, covered with chipboard, underlayment and laminate. The floors are warm, inexpensive, I did it myself.
Choice
Concrete screed is far from the only way to insulate and level floors, especially in a private home. Instead, wooden logs are often used, which are easier to install, do not require long exposure, allow you to create a mini-underfloor (technical space for laying communications and storage), and, importantly, are lightweight.

Mineral wool

Spray polyurethane foam
Almost any insulation is suitable for such structures - from traditional mineral wool to ultra-modern sprayed polyurethane foam. Since the space between the joists is filled with a heat insulator, and the top is covered with OSB or plywood, it does not bear any load. The method of laying all components of the floor is dry. Consequently, neither high strength nor moisture resistance is required from the insulating material. And the consumer has much wider choice.

Expanded polystyrene

Expanded clay
Only two options are recommended for concrete screed: expanded polystyrene and expanded clay. Both work well in bending and compression, and have not only heat but also sound insulating properties. The materials are absolutely safe for health and are not affected by fungus. To make a specific choice, you need to become more familiar with each of them.
Expanded polystyrene
This type of insulation can be called improved polystyrene foam. Today it is recognized as a favorite in the construction industry. 98% of polystyrene foam consists of air enclosed in a thin polymer shell. Available in two versions: pressless (PSB) and extruded (EPS). There is also a loose variety, which is foam granules, but it is used extremely rarely.

PSB has a lower price, however, its water resistance and strength are also low. Builders prefer its analogue, which is produced at high pressure and therefore has improved characteristics. Extruded polystyrene foam is even used for runways and highways. Its compressive strength is considered the highest among existing thermal insulators.
EPPS is also characterized by:
- light weight;
- ease of assembly;
- durability;
- high moisture resistance;
- vapor permeability;
- ability to reduce noise and vibration levels;
- elasticity.
Domestic products are popular on the Russian market. Therefore, extruded polystyrene foam is known to many under the name of this brand. EPPS is produced in slabs with dimensions of 1200x600 mm, thickness from 20 to 150 mm. They can be foil-coated on one or both sides, which enhances the heat-insulating and moisture-proof properties. The one-sided covering is placed “facing” the living space.

The disadvantages of polystyrene foam of all types include flammability. Manufacturers are working to improve the fire safety of the material, experimenting with various fire retardants, but so far no effective impregnations have been found. That is why it is recommended to “hide” polystyrene foam under concrete, which reliably protects it from open fire.
A screed with an EPS layer is called a floating screed. It is permissible to install heated floors in it - this is one of the most effective solutions. In order for the structural “pie” to last as long as possible, it is necessary to take into account all the subtleties of its arrangement; there are no “extra” actions here. There are two types of installation - for floors on the ground and on the ceiling.
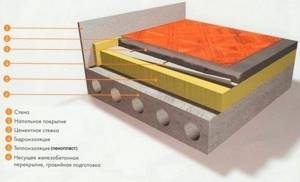
Insulation on a reinforced concrete slab
The “pie” is made as follows:
- Thoroughly clean the base from dust and construction debris.
- A primer is applied for better adhesion of the top layers and strengthening the surface of the load-bearing concrete structure.
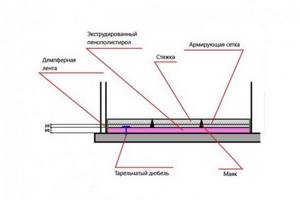
- A damper tape is laid along the perimeter - a strip of foamed polyethylene, which will help avoid concrete ruptures when drying and compressing. Depending on the height of the “pie”, the thickness of the conventional “bumper” ranges from 8 to 15 cm. It is important that the liquid concrete solution does not flow behind the tape when pouring. The extra centimeters are cut off at the end of the work.
- EPS slabs are laid (it is best if they have a locking connection). In any case, the joints are taped. The slabs themselves are attached to the base using foam adhesive.
- You can cover the insulation with a 300 micron thick polyethylene film, additionally protecting it from moisture. But this is not necessary for extruded polystyrene foam.
- A reinforcing mesh is placed on top of the insulation.
- Install “beacons” along which the screed will be aligned. At the same time, if necessary, a heated floor system is installed.
- Apply liquid or semi-dry concrete mixture, leveling it according to the rule. A day after pouring, the concrete begins to gain strength. To ensure even drying, its surface is moistened from time to time.
If you plan to lay linoleum or laminate, it is better to make another layer under them - a self-leveling layer.
In multi-storey buildings of the old housing stock, where the floor is not monolithic, but prefabricated, there are often differences between the slabs that do not allow the polystyrene foam to be laid evenly. In this case, a rough concrete floor screed is first made. It is recommended to lay any waterproofing material under it - polyethylene or rolled bitumen, placing it on the walls. This will protect the lower floors from leakage.
It should be remembered that additional layers of flooring “eat up” the living space and it becomes uncomfortable to be in it. Therefore, they choose insulation with a thickness of no more than 50 mm, and the screed is made 30 - 50 mm high.

If there is an unheated basement below, waterproofing must be done under the insulation. It is even better to use a hydro-vapor barrier membrane, such as ONDUTIS, which protects against condensation. To reduce the humidity of the basement in winter, install small ventilation holes - vents, which are constantly kept open until the frost subsides. A plastic film is laid on the earthen floor or a layer of lean concrete about 50 mm high is poured. The load-bearing walls of the first floor in the lower part are insulated.
Ground installation
In private houses on a strip foundation without a basement, the floors should be insulated more thoroughly than usual. After all, there is no additional protection between the ground that freezes in winter and the living spaces on the first floor. To enhance the strength characteristics of the floor, it is recommended to make a rough screed. Its location varies depending on the groundwater level. But it is important that the finished floor is level with the threshold of the building.
The classic “pie” diagram looks like this (from bottom to top):
- compacted soil;
- crushed stone;
- sand and gravel cushion with pouring and compaction;
- rough screed, better reinforced, especially under heavy loads;
- vapor barrier
- insulation;
- polyethylene;
- reinforced finishing screed.
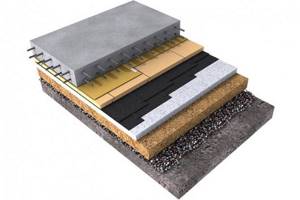
If groundwater lies below 2 m, the concrete base can be poured directly over the ground, removing the fertile soil layer and making a small sand and crushed stone backfill.
Expanded clay
The material is obtained by firing clay shales, which foam and form granules that are hollow inside. Expanded clay is the most environmentally friendly, lightest and cheapest type of insulation. It has noise-proof and anti-vibration properties, is easy to install, does not mold or be corroded by fungus. In addition, unlike expanded polystyrene, expanded clay does not burn.
But the ceramic granules themselves are fragile and absorb water well. If they are used as dry filler, falling asleep between the joists, no problems arise. But under the concrete, expanded clay must be poured with a liquid cement-sand mortar. It is better to buy a ready-made mixture that contains all the necessary proportions. And only after it has dried, make a clean concrete floor screed with reinforcement.
Expanded clay has a low heat capacity. Therefore, to ensure the proper level of insulation, it is poured in a thick layer. But this apparent minus turns into a plus in houses of old construction, when builders replace the wooden floor along the joists with a more modern and comfortable concrete screed. A high layer of expanded clay ideally compensates for the difference in height, without gaining critical mass with heavy concrete.

For floors on the ground, clay insulation is also considered a good option, more economical and functional than polystyrene foam. Another advantage is that it does not require a flat base.
Standard “pie” made of expanded clay:
- load-bearing concrete slab;
- expanded clay spilled with cement “milk”;
- reinforced concrete.
Penofol
Foamed polyethylene, covered with foil on one or both sides, is a new word in the market of thermal insulation materials. Penofol is non-toxic, moisture resistant, does not allow sound, vibration and heat to pass through. It has a small thickness, which allows you to maintain the useful height of the premises and is produced in rolls - a significant advantage that facilitates installation. The only obstacle may be the cost of penofol. But its durability compensates for this “shortcoming”.
Most often, a new generation of heat insulator is used when installing water-heated floors:
- A rough leveling layer is made from expanded clay mixed with cement.
- Lay sheets of penofol with the foil facing up. The edges are connected with a special aluminum tape.
- A water floor system is mounted on top and secured with reinforcing mesh.
- Set up a clean concrete screed.

It is highly undesirable to use penofol for electric heated floors, and the intra-apartment wiring system under the floor must be reliably insulated. Insulation is a conductive material.
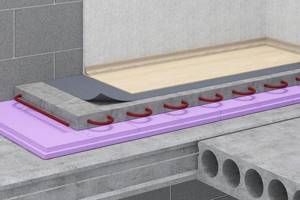
Insulation under the screed with PENOPLEX® materials
As general construction practice shows, a building loses up to 15% of heat through floors, especially if the house has a ventilated underground. This problem can be solved by installing high-quality thermal insulation under the screed. It will not only reduce heat loss through the foundation, but also extend the life of the entire building as a whole. For this, a variety of materials are used - expanded clay, polystyrene foam, liquid polyurethane foam and even mineral wool. However, extruded polystyrene foam is considered the best option for insulation under floor screed, which has a number of advantages:
- has excellent thermal insulation properties - PENOPLEX® slabs 50 mm thick retain as much heat as a 350 mm layer of expanded clay. This allows not only to properly insulate the base, but also to reduce the height of the floor;
- withstands severe loads due to its high strength - it is resistant to mechanical stress, does not break and practically does not shrink;
- is not afraid of water, has zero moisture absorption and low vapor permeability. It has absolute biostability - does not rot or become moldy;
- is not subject to shrinkage and does not change its size with changes in ambient temperature;
- It is light in weight and does not exert significant load on supporting structures;
- environmentally friendly and durable - the service life of the material is at least 50 years if the installation technology is followed.

Among other things, the insulation is produced in the form of plates and is easily cut to the required sizes. Its installation is not particularly difficult and does not require construction skills or the use of special equipment.
Material requirements
Insulation is a necessary part of the “pie” of any floor on the first floor of a private house. Especially if there is no heated basement below. In high-rise apartments, additional thermal insulation will also not be superfluous, performing not only a direct function, but also a noise-proofing function. It is also mandatory when installing heated floors, so that the system does not work in vain.
Of the many types of insulation, only a few are suitable for installation under a concrete screed. They must meet the following characteristics:
- High moisture resistance . When wet, the insulation may lose its insulating properties. Therefore, only water-resistant materials are used for pouring liquid concrete.
- Resistance to temperature changes . Floors on the ground or above an unheated basement in winter freeze on one side and are warmed up by heating devices or a “warm floor” system on the other. It is important that the material does not deform, causing cracking of the overlying layers.
- Light weight . The concrete screed itself is massive and its installation on existing floors, especially in high-rise buildings of the Stalinist and Khrushchev type, is the ultimate load. Light, but high-quality insulation will allow you to reduce the thickness of the top layer to a minimum and reduce the overall weight of the “pie”, without losing its insulating properties.
- Ecological cleanliness . Despite the fact that the owners of a house or apartment do not directly come into contact with the material, the influence of toxic substances, if any, cannot be completely excluded. It is better that every component of the floor is safe for health.
- Easy to install . This parameter is especially important for home craftsmen who fill the floor with their own hands.
- Compressive strength, elasticity, resistance to uneven loads. Insulation materials have the ability to compress under pressure. But if they start to “play,” for example, under point loads from cabinet furniture, this will lead to cracking of the concrete, as well as problems with the top coating, primarily with ceramic tiles.
- Biostability. Mold and fungus should not develop in the coating, which significantly accelerates its destruction.
- Acceptable price. Sometimes it is this factor that turns out to be decisive when choosing a heat insulator. But it is advisable to take into account the long-term perspective, because some materials can last for decades, helping to significantly save on repairs.