- Features of laminated veneer lumber as a building material
- Which is better: finishing the facade or installing thermal insulation inside
- Materials for insulating a house from the inside Mineral wool
- Ecowool
- Polyurethane foam
- Styrofoam
- Preparing the premises
- Preparing walls and installing sheathing
Glued laminated timber is the most expensive type of wooden beam used in construction.
The high price of the material is explained by the technology of its production, as well as the qualities it possesses. The beams are made of thin wooden lamellas, glued together and tightly pressed. This technology eliminates cracking of the material and shrinkage of the structure.
Typically, for low-rise construction, beams with a cross section of 150x150 cm are used, but in cold regions such wall thickness is not enough to ensure a sufficient level of heat in the room. The problem is solved by insulating the walls from the inside or outside.
In addition, insulating walls, in particular finishing the facade, reliably protects wood from atmospheric phenomena, increases its resistance to combustion, which has a positive effect on the durability of housing, as well as on its safety.
Another important factor that determines the importance of increasing the thermal insulation qualities of walls is saving on heating. The better the walls are treated, the lower the cost of heating it.
Wall insulation
Houses made of laminated veneer lumber with a wall thickness of 200 mm or more can withstand the most severe frosts and do not require additional insulation, even when built in the north of Russia. But for houses with thinner walls - for example, country houses - heating can become the most expensive service in the field of housing communications, because in cold weather the walls transmit 40% of the heat. Therefore, by properly insulating the walls of your country house, you will solve both thermal and financial issues.
Common insulation materials in order of decreasing thermal conductivity
The key characteristic of insulation is thermal conductivity. It shows the amount of heat that passes through a sample of material 1 m thick, with an area of 1 m2, in 1 second. The lower the thermal conductivity, the more effectively the insulation retains temperature and the less thickness you will need to thermally protect your home.
Fiberboard, 0.08 - 0.1 W/m*S
- Not susceptible to rotting, insects and rodents when dry;
- Does not deform from frost and prolonged exposure to moisture.
- Susceptible to fungus at humidity levels greater than 35%, which is why it should not be used in damp areas.
Foam plastic, 0.037 - 0.047 W/m*S
- Fungus and mold do not form on the surface of the foam;
- Easy to process and install.
- It is fragile and therefore requires additional protection from mechanical damage;
- Easily destroyed under the influence of nitro paints or paints and their vapors. This means you are limited in your choice of finishes.
Sprayed ecowool, 0.04 W/m*S
A loose material that is 81% cellulose and 19% additives.
- Creates a uniform layer without cracks and gaps;
- Does not require a frame for application;
- Protected from fungus and rodents.
- Shrinks up to 20%;
- Price.
Cork material, 0.04 W/m*S
It consists of slabs of crushed cork oak bark and binding additives of organic origin.
- Hard and durable;
- Resistant to rotting and mold formation when exposed to moisture;
- Not afraid of rodents;
- Does not change volume with humidity fluctuations.
Stone wool, 0.035 - 0.039 W/m*S
It is also mineral wool and basalt insulation. Often, buyers believe that these are different insulation materials - in fact, these are varieties of the same material.
- It fits well due to its elasticity, softness and lightness;
- Not attractive to rodents and microorganisms.
- Absorbs moisture and, as it gets wet, loses its thermal insulation properties. Therefore, it provides for the installation of vapor and moisture insulation;
- Fibers that separate from the cotton wool and enter the lungs cause irritation;
- It compacts and clumps.
Sprayed polyurethane, 0.03 W/m*S
- Creates a uniform layer without cracks and gaps;
- Does not require the creation of a frame for application;
- Not susceptible to chemicals.
- Price;
- Rapid aging.
Liquid ceramic insulation, 0.002 - 0.005 W/m*S
It is a liquid suspension in the form of microcavities formed by silicone, ceramics and a polymer binding liquid. There is a vacuum inside these microcavities.
- It is applied like paint, which means you do not need special skills;
- When dry, it forms a layer of up to 3 mm, without creating a load on the house;
- You can immediately apply paint or wallpaper to it;
- Easily restored and repaired;
- Does not form seams, which means no cold bridges;
- “Side” effect: protection against mold;
- You can add pigments of the desired shade, and thereby use them as a finishing material.
- The material is not cheap and requires high consumption: 0.5 l/m?. And you need 3 – 6 layers depending on the thickness of the walls.
What else to consider?
Other significant parameters of insulation are:
- Water absorption - the less, the better;
- Vapor permeability - the higher the better. Vapor permeability allows excess moisture to be removed both from the material itself and from the room and structure of the house;
- Flammability. There are classes from NG (non-flammable) to G4. The smaller the number after “G”, the worse the materials burn.
Our insulation materials have the following characteristics:
| Characteristics / Material | Water absorption,% by volume | Vapor permeability, mg/m*h*Pa | Flammability |
| Fibrolite | 35—45 | 0,1 | G1 |
| Styrofoam | 3 | 0,05 | G1 |
| Ecowool | 16 | 0,3 | G1 |
| Cork materials | 0,01 | 0,001 | G1 |
| Stone wool | 1,5 | 0,5 | NG |
| Polyurethane | 3 | 0,05 | G2 |
| Ceramic insulation | 1 | 0,02 | G1 |
When choosing insulation, consult your architect-designer. He will suggest the option that is most suitable in terms of the layout and location of the house.
How to insulate - from the outside or from the inside?
Outside. Experts are unanimous on this. And this is due to the disadvantages that insulation from the inside implies:
- Reducing the area of premises;
- The impossibility of insulating the junction of the ceilings and the walls. “Cold bridges” form in these zones, and heat is lost so quickly that heat loss can exceed heat loss through the entire perimeter of the wall;
- Increased formation of moisture indoors associated with the use of a vapor barrier that protects the insulation. This will require you to frequently ventilate the rooms and increase heating costs;
- Reduced service life of the house due to the fact that the wall is exposed to the cold in winter, during the year - under the influence of the environment;
- The texture and smell of natural material will not be preserved inside, which is important for a good rest.
Insulation options
When insulating houses made of laminated veneer lumber, as in most other cases, two options can be used.
Insulation of a house made of laminated timber from the outside
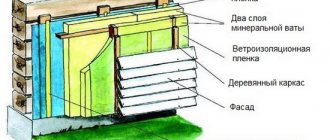
Most often, this method of insulation is used when a technology known as a “ventilated facade” is used. It has long been known and is actively used in both private and urban multi-storey construction. The structure consists of a layer of insulation (the minimum layer for central Russia is 10 cm), laid using a frame on the walls, and finishing hanging material. In this case, a gap remains between the structural elements, which is necessary for the free circulation of air and the removal of excess moisture through it. It was this gap used for ventilation that gave the name to the entire structure.
Various types of mineral wool are most often used as insulation (the characteristics of ecowool insulation are among the best), extruded polystyrene foam and other materials are less common. The outer finishing layer can be made from ordinary and inexpensive vinyl siding, imitation timber, clapboard, fiber cement board and many other materials.
Stages of work production:
- surface preparation: removal of areas with rot and mold, antiseptic treatment and treatment with fire retardants (if necessary);
- caulking of cracks between the bars, as well as around the perimeter of windows and doors;
- construction of a frame made of bars, its thickness should be equal to the thickness of the insulation used, the width between the bars is 2 cm less than the width of the insulation;
- laying insulation in 2-3 layers with overlapping joints;
- installation of a windproof membrane on tape;
- facing the facade with the selected finishing material.
The ventilated facade has only one drawback - it hides the attractive appearance of the walls made of laminated veneer lumber. On the other hand, the finishing material used for external insulation can also look no less aesthetically pleasing.
In rare cases, insulation can also be carried out by laying an external brick wall with laying insulation between the laminated veneer lumber and the newly erected wall. But this option is quite labor-intensive, and also does not have many of the advantages of a ventilated façade, namely:
- the presence of a facade will lead to an increase in the service life of walls made of maple timber, since they are much less exposed to external influences;
- the presence of a ventilation gap allows the walls to breathe, creating a favorable microclimate in the building;
- all materials necessary for insulation are available and relatively inexpensive;
- the technology of work is simple and can be done by hand;
- The ventilated façade is easy to use and quite repairable if problems arise.
Currently, another technology has become widespread that can be used both externally and internally - spraying a thermal insulating layer of polyurethane foam. The quality of insulation is superior to all analogues, but widespread use is hampered by the high cost of the work.
The long list of advantages of external insulation does not at all exclude the possibility of performing work according to the second option.
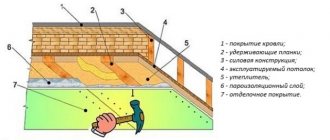
Insulation of a laminated timber house from the inside
Carrying out insulation work from inside the house also has a number of advantages. The first and most important of them is the low cost of work, since there is no need to do expensive finishing to cover the insulation. It is simpler and easier to carry out work from the inside; in addition, it can be carried out at any time of the year.
At the same time, with this method of insulation, the internal space is reduced, which is a significant disadvantage of the technology. In addition, when insulating from the inside, the dew point may be located in a wall made of laminated veneer lumber, which can also lead to negative consequences.
When insulating a house from the inside, the same materials are used as insulation as when performing work outside: various types of mineral wool, extruded and regular polystyrene foam, etc.
The stages of work are largely the same as those carried out during external insulation:
- preparation and caulking of walls. It is necessary to remove all damaged areas of the material and perform thorough treatment with a special antiseptic. The gaps between the bars are sealed with jute fiber or tow, standard in such cases;
- vapor barrier device. Any modern vapor barrier material or ordinary PVC film can be used;
- construction of a frame made of wooden blocks. The requirements for it are similar to those for external insulation;
- laying insulation;
- laying the second layer of vapor barrier. It is recommended to use foil-coated material, which allows maximum heat retention inside the room;
- installation of an outer layer of plasterboard for final finishing. It is necessary to leave a ventilated gap between the second layer of vapor barrier and the gypsum board sheets.
To improve the quality of ventilation, it is recommended to install forced exhaust in the building by combining the air ducts from the rooms into one. A small fan mounted in a convenient place with bolts, inexpensive in cost and operation, but extremely useful, is quite suitable for this.
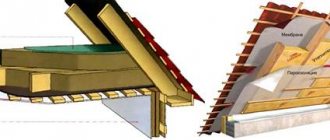
Insulation from outside
The best option for insulating a wooden house would be to create a ventilated facade system with an air gap - the rising currents themselves will remove unnecessary moisture.
This system has high heat-protective qualities and ensures dry walls. It is necessary to pay attention to the sealing of windows and doors, floors, installation of interfloor ceilings and attics. Floor insulation is carried out by laying a layer of waterproofing and heat insulation, on top of which a layer of vapor barrier is placed
Beginning of work
To begin with, the entire surface of the walls is well treated with antiseptics and fire retardants. After processing, gaps and cracks are eliminated at all joints and between the timber. Gaps are eliminated with polyurethane foam or sealants, which are used when laying a log house. More often it is flax batting, jute fiber or tape tow.
After sealing all the gaps, vertical load-bearing slats are placed on the walls. The distance between them is left slightly smaller than the width of the future insulation material. This is done for easier and tighter entry into the structure.
Laying
Between the supporting rails, starting from the underside of the wall, sealing plates are laid. The slabs are secured using anchor fasteners, with the joints located close to each other and to the edges of the sheathing.
The second frame row of beams is attached in a horizontal direction. Mineral wool slabs are installed in the gaps between them. In this case, the upper slabs must overlap the joints of the underlying layer. The second layer of heat insulation is also strengthened with anchors. In addition, the densely elastic structure of the fiber boards itself contributes to a fairly reliable installation of the material between the sheathing beams.
A diffusion membrane is fixed to the surface of the insulation, permeable from the inside to steam and air, but completely closed from the outside to wind and external moisture. This layer will perfectly protect the insulator and the wood underneath from adverse weather conditions.
Ventilation layer and finishing
The frame for exterior finishing must be fixed so that there is an air gap between the finishing layer and the heat insulator for ventilation of water vapor. After all, external moisture will inevitably condense on the surface of the insulation, which should be able to evaporate.
External facade finishing is mounted on the frame. This can be lining, siding or panels made of polymers. You can decorate the building with a block house - a polymer that imitates wood with its texture and pattern
It is important to prevent heat loss through other areas - roof, floor, foundation, windows, doors
Insulation of the external wall of a house with ecowool
Ecowool, thermofloc or uniol is a cellulose insulation consisting of 81% from newsprint processed into cellulose fiber, 12% from boric acid and 7% from borax. Boric acid is an excellent antiseptic, and the drill reduces the fire hazard of highly flammable ecowool. It also contains lignin, which, when interacting with water, easily sticks to the insulated wall.
Ecowool protected from rodents than polystyrene or mineral wool. Ecowool is an unshaped crumbly mass of gray or milky color, so it is packaged in briquettes with a density of 110 kg/m3. Before use, ecowool is poured out of briquettes, dried, increasing in volume by 3-4 times.
- high thermal insulation properties, unlike mineral wool, which already at 1% humidity significantly loses its thermal insulation properties, ecowool can withstand up to 20% humidity;
- good soundproofing properties, so it can protect the room inside the house from noise from the street;
- if water gets in, ecowool dries quickly;
- ecowool does not create a “greenhouse effect” inside the house, maintaining a natural level of air humidity;
- during operation, ecowool does not emit toxic fumes, because lignin, boric acid and borax are natural materials;
- ecowool fills the entire volume of the prepared frame, therefore it does not create “cold bridges”;
- in case of fire, ecowool does not burn, but only smolders, having a flammability group of G2 and a smoke generation group of D2;
- when installing ecowool, you can use metal profiles, because when interacting with metal it does not cause corrosion;
- When using ecowool, there is almost no waste left.
- It is impossible to lay ecowool yourself; you need special equipment and the work of a qualified specialist;
- due to the flowability of the material, a lot of dust is generated when working with it;
- Ecowool cannot be laid in places with a constantly high level of humidity; pipelines and furnaces cannot be thermally insulated with it.
Insulation methods
An external curtain façade is considered the most economical insulation option. The material for it may be different, which affects the final cost of the object. Brick, clapboard, slatted boards, porcelain siding, cinder block - the list goes on.
The insulation can also be different - jute fiber, mineral wool, and other materials. You can build a house or a bathhouse from already insulated laminated veneer lumber - wooden plates (lamellas) are sandwiched with ecowool. In any case, there must be an air gap between the insulation layer and the outer facade for more effective thermal insulation.
Regardless of what material will be used in the insulation process, it should be covered with waterproofing to protect it from the condensation process.

Spraying with polyurethane foam is a more progressive method that has many advantages:
- The material does not burn.
- Not susceptible to the growth of bacteria and rot.
- It is durable and at the same time maintains high performance qualities.
- Excellent level of sound insulation.
- There is no need to use additional fasteners.
- Environmentally friendly material.
- Quite a simple installation method.
The higher cost is paid off by the service life; moreover, this method of insulating an external wall is more practical and is suitable even for residents with allergic diseases.
Foam panels are also deservedly popular.
They themselves are an excellent thermal insulation material, are not affected by moisture, and besides, you can reduce the cost of the house by choosing a thinner beam - for example, 150x200 mm.
Video description
Caulking with rolled material: you will see how to do it correctly in the video:
The corners of the timber are caulked using the same technology:
- If the gaps are wide, a cord is formed from the insulation tape. Roll it into a ball.
- Unwind part of the cord and weave loops from it. Then each loop is pushed inside the seam.
- Hammer the loops with a spatula, first from above the joint, then from below.
- After sealing the seams, final caulking is carried out if necessary. It involves residual filling of joints and is carried out if necessary.
- The density of the caulk is checked with a kitchen knife. The knife blade should not extend into the joint more than 1.5 cm. If this condition is met, caulking is done correctly. If not, then additional caulking is required.

Checking the density of caulk Source 24aul.ru
Caulking of corners is carried out using the same technologies using roll insulation, for this they move along the seam from the bottom up. To ensure uniform laying of the material, it is constantly tensioned and straightened.
How to insulate a house made of laminated veneer lumber

Insulation of laminated timber - methods and materials
“I was told that wood is a very warm material, so why insulate it further?” — this is roughly the thought that some readers may have. Now we will explain everything. Let's start with why this is generally needed and in what ways it is carried out. We will tell you how to insulate laminated timber in the second part of the article.
Thermal insulation of walls: why and how?
Thermal insulation of walls has many advantages:
- increasing the comfort of people living in the house;
- reducing the cost of maintaining the required temperature;
- increasing the service life of the timber itself;
- acceleration of warming up of the building;
- slowing down heat dissipation.
About a third of the thermal energy leaves the room through the walls, the rest comes from windows, floors, ceilings and ventilation. By reducing the thermal conductivity of the building itself by half, you can save up to 15-17% of heating costs. If the amount seems insignificant, calculate the expenses over several decades.
There are three main types of insulation for walls made of laminated veneer lumber.

1 — An intercrown seal is laid between the rows (crowns) of timber to prevent cold air from blowing in. Additionally, the cracks are caulked. This procedure is mandatory; without it, the whole house will be blown out, and moisture will get into the space between the crowns, causing the destruction of the tree.

2 - External insulation reduces heat loss through the walls. The layer of porous material covering the outside of the house protects well from the cold, and at the same time covers the timber from the effects of atmospheric phenomena. A small drawback of this approach - hiding the texture of the wood - can be easily corrected by using planken or block house for finishing.
The house requires treatment and maintenance
You can’t build a house and forget about maintenance. Of course, you won’t have to caulk three times, deal with through cracks and renew the coating every year, but a house made of laminated veneer lumber also needs regular maintenance.
Painting
Before shipping, parts are treated with a transport antiseptic. This coating protects the tree for six months. During this time, you need to apply permanent protection and paint the walls. Paint is usually renewed every 5-10 years (depending on whether the entire house or its sides are on the sunny or shady side).

Delivery and storage are important: the house kit is folded on wooden supports in secure packaging. Only dry timber is the key to high-quality assembly.
Laying insulation
Typically, timber houses are insulated with mineral wool. So, sheathing is placed on the walls on the outside of the house. The pitch between the bars should be such that the insulation sheet fits between them. For example, when insulating a house in the Moscow region, you can use no more than two layers of mineral wool. However, to insulate a house made of timber in Novosibirsk, more material will be needed to maintain heat in the house.
Mineral wool will not only retain heat in the room, but will also protect the walls from constant temperature changes. In addition, the facade of the house will be protected from exposure to UV rays and moisture. Obviously, the timber will last much longer with insulation than without it.
Be sure to leave a gap between the wall and the finishing material. To prevent the wind from fraying the material in this area, it is covered with a protective film through which water vapor can escape, but water itself cannot.

Video description
Caulking timber: how it happens is shown in the video:
To understand how to properly caulk a house made of timber, we will consider in detail the methods of caulking with various materials.
Caulking technology with fiber insulation:
Moss or flax tow is applied to the gap with fibers across it, then, holding the material, it is pressed deep with force with a special spatula.

Caulk of towSource fasad-exp.ru
- The remaining material should be carefully rolled up into a tight roller, pushed into the gap, leaving the tip out.
- Then the next strand needs to be woven into the remaining “tail” and the same actions must be performed again. It is necessary to ensure that the formed roller is not interrupted along the length of the wall.
Technology of caulking with rolled material:
- The tape is rolled out along the wall of the log house, but not stretched. Place it on the ground. They don't cut it.
- Starting from the corner, the edge of the tape is applied to the seam with fibers across and the middle is pushed into the gap. At this stage, the edges remain hanging down by 5-6 cm. This is how the seam is initially caulked along its entire length.
- The remaining material is carefully pushed between the beams, ensuring that the seams are filled as tightly as possible.
Types of timber
First of all, it is worth noting that you should not confuse timber with timber, these are completely different concepts.
To ensure that air circulates well in the room and it is easy to breathe, pine is used for construction.
For the construction of private houses, the following lumber is used:
- solid (the cheapest of all listed types; shrinkage is long);
- glued (contains useful components; expensive);
- profiled (the wood does not crack, since there is no internal pressure due to the type of connection - “tenon and groove”).
According to the processing methods there are:
- the “face” can be either even, smooth, or convex;
- "comb" (German profiled);
- Finnish profiled (there are several spikes for connection);
- “with cups” (riflings are observed at the joints, in the corners).
Log house insulation technology
The question of how to insulate a house made of profiled timber can be solved in several ways. The simplest option is to caulk the inter-crown cracks. The technology is simple but labor-intensive. The insulation has to be repeated at certain intervals.
Another way is to insulate the walls from inside the building. The slabs are installed using a hydro- and vapor barrier layer, after which they are sheathed with plasterboard or other finishing materials. The technology is in demand on the market, but its main disadvantage is considered to be a reduction in the usable area of the interior.
External insulation avoids the loss of free space, and also gives the house a completely different appearance.
The most popular is the ventilated facade technology.
Installation is carried out in several stages:
- A sheathing of bars is assembled over the entire surface of the external walls. The dimensions of each square must correspond to the dimensions of the thermal insulation slabs.
- To install a ventilated façade, the air gap must be on both sides of the insulation. Therefore, the sheathing is made two-level.
- Thermal insulation boards are laid end-to-end. Possible gaps are additionally insulated.
- A diffuse membrane is being installed to protect the insulation from moisture and dampness.
- The last step is to install the decorative covering. The insulation under the new facade breathes and retains its characteristics throughout its entire service life.

Technology of applying polyurethane foam coating.
This thermal insulation is installed using special equipment on the surface of the wood and reliably protects the house from heat leaks, exposure to moisture and harmful microorganisms. An inexpensive way is to insulate with foam plastic, which is glued to the walls and additionally secured with dowels. In both cases, installation of cladding is assumed.
Insulating a cottage from profiled timber is a popular way to make the building warmer, save on wood and operating costs. To choose the optimal insulation option, it is better to contact qualified specialists. Installation of thermal insulation will ensure comfortable living conditions in the house.
Required materials and tools
To thermally insulate a ventilation façade at a workplace, you must have:
- insulation made from basalt fibers;
- pine or spruce slats 50x50 or 50x100 mm (the specific size is selected according to the thickness of the mat);
- rail 50x30 or 50x40 mm for counter-lattice;
- wood screws with a diameter of 4.8 mm and a length exceeding the height of the plank by 5-10 cm for sheathing;
- wood screws 4.2x75(76) mm for counter-lattice;
- hydro-vapor barrier membrane type A or AM;
- antiseptic (antifungal drug);
- special dowels with a wide head for attaching mats to the wall;
- scotch;
- scaffolding or trestles;
- screwdriver;
- spray;
- wood saw;
- level, preferably laser;
- plumb line;
- construction stapler;
- roulette;
- square;
- knife for cutting insulation.