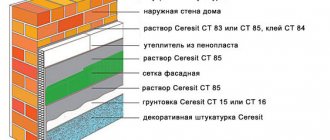
Mulwatt
4994 0 0
Mullvatt September 7, 2016Specialization: Capital construction work (laying a foundation, erecting walls, constructing a roof, etc.). Internal construction work (laying internal communications, rough and fine finishing). Hobbies: mobile communications, high technology, computer equipment, programming.
To choose insulation, you need to know its technical characteristics.
In my professional activities, I have used many different insulation materials for thermal insulation of buildings and structures. They have different characteristics that make them suitable for performing certain tasks.
For a novice craftsman who is building a house or doing repairs with his own hands, it is necessary to know the important operational properties of the material, which affect the correct choice of thermal insulation.
Today I will talk about several completely different materials and describe in detail all their important parameters. This instruction, as well as the table of thermal conductivity of insulation given below, will help you navigate when going to a construction supermarket.
Review of hygroscopicity of thermal insulation
High hygroscopicity is a disadvantage that needs to be eliminated.
Hygroscopicity is the ability of a material to absorb moisture, measured as a percentage of its own weight of insulation. Hygroscopicity can be called the weak side of thermal insulation and the higher this value, the more serious measures will be required to neutralize it. The fact is that water, getting into the structure of the material, reduces the effectiveness of the insulation. Comparison of hygroscopicity of the most common thermal insulation materials in civil engineering:
| Name of material | Moisture absorption,% by weight |
| Minvata | 1,5 |
| Styrofoam | 3 |
| PPU | 2 |
| Penoizol | 18 |
| Ecowool | 1 |
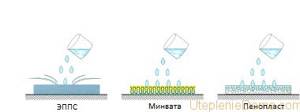
A comparison of the hygroscopicity of home insulation showed the high moisture absorption of foam insulation, while this thermal insulation has the ability to distribute and remove moisture. Thanks to this, even when wet by 30%, the thermal conductivity coefficient does not decrease. Despite the fact that mineral wool has a low percentage of moisture absorption, it especially needs protection. Having absorbed the water, it holds it, preventing it from leaving. At the same time, the ability to prevent heat loss is catastrophically reduced.
To prevent moisture from entering the mineral wool, vapor barrier films and diffusion membranes are used. Basically, polymers are resistant to prolonged exposure to moisture, with the exception of ordinary polystyrene foam, which quickly deteriorates
In any case, water does not benefit any thermal insulation material, so it is extremely important to exclude or minimize their contact
Statistics
Many people believe that it is enough to buy insulation and install it on the wall and it will function normally. You need to select the right material and, most importantly, it should be enough. The thickness of different insulation materials varies greatly, so you need to familiarize yourself in advance with the thermal conductivity of which material you will be working with.
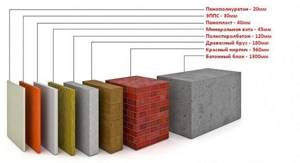
Not everyone will want to shell out large sums of money for insulation for a wall made of aerated concrete, which suddenly won’t work. Much depends on the thickness of the wall and the insulation itself; 10 cm will be enough for the use of wool to be correct. Which cotton wool is best for insulation? To begin with, it is worth comparing the characteristics of different types of thermal insulation.
Additional properties of thermal insulation materials:
Density. The ratio of mass to volume occupied by a material.
Moisture absorption. Determines the amount of moisture contained in the insulator
It is important to consider the total moisture content of the material at various temperature changes, relative to the importance in the air. Hydrophobization significantly reduces the properties of mineral wool to absorb moisture
For this purpose, special additives are specially introduced that protect the material from water.
Biosecurity. The ability to counteract the dominance of microorganisms, as well as the development of fungal formations and some types of insects. For the most part, all living creatures are attracted to dampness, so the moisture-protective properties closely interact with thermal insulation.
Fire resistance. Structures can withstand high temperatures for a long period without collapsing.
Fire safety.
Strength. If the strength is high, then the material is used to insulate load-bearing fencing structures. There is also a separate parameter - bending strength. This applies to those insulation materials that are installed on pipelines and other similar objects. Tensile strength is necessary in order to determine the possible level of safety during storage, transportation and installation.
Endurance. A material can lose all its properties and features when the temperature increases or decreases.
Heat capacity. In conditions of frequent thermal changes, this characteristic is extremely important.
Frost resistance. The ability of the material to withstand repeated temperature changes at any stage of freezing. Relevant in winter with severe frosts. The main thing is that no visible signs of destruction of the insulation structure are noticed.
Insulation for the walls of a house is not the only function that can be limited. The home owner should give preference to external insulation, as well as thermal insulation of pipelines.
from different sides of the house with equal efficiency.
Thermal insulation properties can be leveled due to a number of mistakes. For example, inappropriate fasteners. When insulating with foam plastic, dowels and cheap, low-quality glue are used.
If you have forgotten the parameters of moisture resistance, density or other insulation characteristics, then it is worth looking at the ratings of various thermal insulators. The table will help you quickly navigate and find the best material based on one of its properties.
The basement deserves just as much attention as the rest of the house.
It takes an important part in the heat losses of the building, its role is key. Especially when it comes to facade insulation

This instructional text will help home owners who decide to install thermal insulation themselves, without the help of specialists. Let's start with filling, the technology of which turned out to be unsophisticated and simple.
- We drill holes on the outside wall in a staggered pattern.
- We stretch the tubes from the special installation and insert them into these holes.
- After this, we supply the foam material.

The whole process happens so quickly. That two people are enough to insulate three floors of a cottage. Insulating the outside with slabs will be much more expensive than the above insulation option. The price of many companies increases with each centimeter of cavity width.
Table of thermal conductivity of thermal insulation materials
To make it easier to keep your house warm in winter and cool in summer, the thermal conductivity of walls, floors and roofs must be at least a certain figure, which is calculated for each region. The composition of the “pie” of walls, floor and ceiling, the thickness of the materials are taken into account so that the total figure is no less (or better yet, at least a little more) recommended for your region.
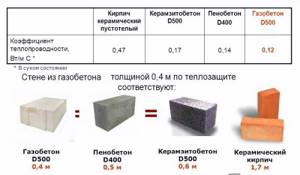
Heat transfer coefficient of modern building materials for enclosing structures
When choosing materials, it is necessary to take into account that some of them (not all) conduct heat much better in conditions of high humidity. If such a situation may occur for a long period of time during operation, the thermal conductivity for this condition is used in the calculations. The thermal conductivity coefficients of the main materials used for insulation are given in the table.
| Name of material | Thermal conductivity coefficient W/(m °C) | ||
| Dry | At normal humidity | At high humidity | |
| Woolen felt | 0,036-0,041 | 0,038-0,044 | 0,044-0,050 |
| Stone mineral wool 25-50 kg/m3 | 0,036 | 0,042 | 0,,045 |
| Stone mineral wool 40-60 kg/m3 | 0,035 | 0,041 | 0,044 |
| Stone mineral wool 80-125 kg/m3 | 0,036 | 0,042 | 0,045 |
| Stone mineral wool 140-175 kg/m3 | 0,037 | 0,043 | 0,0456 |
| Stone mineral wool 180 kg/m3 | 0,038 | 0,045 | 0,048 |
| Glass wool 15 kg/m3 | 0,046 | 0,049 | 0,055 |
| Glass wool 17 kg/m3 | 0,044 | 0,047 | 0,053 |
| Glass wool 20 kg/m3 | 0,04 | 0,043 | 0,048 |
| Glass wool 30 kg/m3 | 0,04 | 0,042 | 0,046 |
| Glass wool 35 kg/m3 | 0,039 | 0,041 | 0,046 |
| Glass wool 45 kg/m3 | 0,039 | 0,041 | 0,045 |
| Glass wool 60 kg/m3 | 0,038 | 0,040 | 0,045 |
| Glass wool 75 kg/m3 | 0,04 | 0,042 | 0,047 |
| Glass wool 85 kg/m3 | 0,044 | 0,046 | 0,050 |
| Expanded polystyrene (foam plastic, EPS) | 0,036-0,041 | 0,038-0,044 | 0,044-0,050 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS, XPS) | 0,029 | 0,030 | 0,031 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete with cement mortar, 600 kg/m3 | 0,14 | 0,22 | 0,26 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete with cement mortar, 400 kg/m3 | 0,11 | 0,14 | 0,15 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete with lime mortar, 600 kg/m3 | 0,15 | 0,28 | 0,34 |
| Foam concrete, aerated concrete with lime mortar, 400 kg/m3 | 0,13 | 0,22 | 0,28 |
| Foam glass, crumbs, 100 - 150 kg/m3 | 0,043-0,06 | ||
| Foam glass, crumbs, 151 - 200 kg/m3 | 0,06-0,063 | ||
| Foam glass, crumbs, 201 - 250 kg/m3 | 0,066-0,073 | ||
| Foam glass, crumbs, 251 - 400 kg/m3 | 0,085-0,1 | ||
| Foam block 100 - 120 kg/m3 | 0,043-0,045 | ||
| Foam block 121-170 kg/m3 | 0,05-0,062 | ||
| Foam block 171 - 220 kg/m3 | 0,057-0,063 | ||
| Foam block 221 - 270 kg/m3 | 0,073 | ||
| Ecowool | 0,037-0,042 | ||
| Polyurethane foam (PPU) 40 kg/m3 | 0,029 | 0,031 | 0,05 |
| Polyurethane foam (PPU) 60 kg/m3 | 0,035 | 0,036 | 0,041 |
| Polyurethane foam (PPU) 80 kg/m3 | 0,041 | 0,042 | 0,04 |
| Cross-linked polyethylene foam | 0,031-0,038 | ||
| Vacuum | |||
| Air +27°C. 1 atm | 0,026 | ||
| Xenon | 0,0057 | ||
| Argon | 0,0177 | ||
| Airgel (Aspen aerogels) | 0,014-0,021 | ||
| Slag | 0,05 | ||
| Vermiculite | 0,064-0,074 | ||
| Foam rubber | 0,033 | ||
| Cork sheets 220 kg/m3 | 0,035 | ||
| Cork sheets 260 kg/m3 | 0,05 | ||
| Basalt mats, canvases | 0,03-0,04 | ||
| Tow | 0,05 | ||
| Perlite, 200 kg/m3 | 0,05 | ||
| Expanded perlite, 100 kg/m3 | 0,06 | ||
| Linen insulating boards, 250 kg/m3 | 0,054 | ||
| Polystyrene concrete, 150-500 kg/m3 | 0,052-0,145 | ||
| Granulated cork, 45 kg/m3 | 0,038 | ||
| Mineral cork on a bitumen basis, 270-350 kg/m3 | 0,076-0,096 | ||
| Cork flooring, 540 kg/m3 | 0,078 | ||
| Technical cork, 50 kg/m3 | 0,037 |
Some of the information is taken from standards that prescribe the characteristics of certain materials (SNiP 23-02-2003, SP 50.13330.2012, SNiP II-3-79* (Appendix 2)). Those materials that are not specified in the standards are found on the manufacturers’ websites
Since there are no standards, they can differ significantly from different manufacturers, so when purchasing, pay attention to the characteristics of each material purchased
Which insulation is better
It is important to note that the type of insulation should be selected in accordance with the type of construction of the residential building and the type of its cladding (“Exterior decoration of the house”). When choosing insulation for the walls of a house, it is important to pay attention to:
- fire hazard - the material should not be flammable;
- the ability of the insulation material to “breathe”;
- sound insulation;
- the material from which the house is built;
- type of foundation;
- insulation thickness;
- climate of the area;
- resistance of the insulation material to rotting, etc.
Important! You can insulate the walls of your house yourself, but during the work you must follow certain rules and observe safety precautions.
Therefore, it is advisable to entrust this work to professionals who will correctly select the right type of insulation and perform the necessary work efficiently.
Types and characteristics
The range of mineral wool is quite diverse and can satisfy the needs of even the most demanding consumer.

"Rocklight"
This type is characterized by low weight and standard dimensions of minislabs, as well as a low content of formaldehyde and phenol. Due to its durability, the material is widely used for insulating country houses and cottages, allowing for a long time without worrying about repairing thermal insulation.
The slabs are suitable for finishing vertical and inclined surfaces and can be used to insulate attics and attics. The material has excellent vibration resistance and is neutral to alkalis. The slabs are not of interest to rodents and insects and are not prone to fungus.

“Rocklight” is distinguished by high thermal resistance: a 12 cm thick layer of mini-slab is equivalent to a thick brick wall 70 cm wide. The insulation is not subject to deformation and wrinkles, and during the freezing-thawing process it does not settle or swell.
"Technoblock"
Medium-density basalt material used for installation on layered masonry and frame walls. Recommended for use as the inner layer of a ventilated facade as part of two-layer thermal insulation. The density of the material is from 40 to 50 kg/m3, which guarantees excellent sound and heat insulation properties of this type of slabs.

"Technoruf"
High-density mineral wool designed for insulation of reinforced concrete floors and metal roofing. Sometimes used to insulate floors that are not equipped with a concrete screed. The slabs have a slight slope, necessary to drain moisture to the drainage areas, and are covered with fiberglass.

"Technovent"
A non-shrinking board of increased rigidity, used for insulation of ventilated external systems, and also used as an intermediate layer in plastered facades.

"Technoflor"
The material is intended for insulation of floors subject to severe weight and vibration loads. Indispensable for arranging gyms, production workshops and warehouses. The cement screed is poured over the mineral slabs. The material has low moisture absorption and is often used in combination with a “warm floor” system.

Mineral wool used for external heat and sound insulation of brick and concrete walls under plaster.

"Technoacoustic"
A distinctive feature of the material is the chaotic weave of fibers, which gives it excellent soundproofing characteristics. Basalt slabs cope well with airborne, impact and structural noise, absorbing sound and providing reliable acoustic protection of the room up to 60 dB. The material has a density of 38 to 45 kg/m3 and is used for interior decoration.

"Heat roll"
Rolled material with high sound insulation properties and having a width from 50 to 120 cm, a thickness from 4 to 20 cm and a density of 35 kg/m3. It is used in the construction of private houses as a thermal insulator for pitched roofs and ceilings.

"Techno T"
The material has a narrow specialization and is used for thermal insulation of technological equipment. The slabs have increased hardness and high heat resistance, allowing the mineral wool to easily withstand temperatures from minus 180 to plus 750 degrees. This allows you to isolate gas ducts, electric precipitators and other engineering systems.

Reminder to the buyer
- there is no universal insulation;
- each element of the building needs a thermal insulation material that has specific properties;
- for thermal insulation of pitched roofs, fiberglass and basalt mats and slabs are suitable;
- the ideal insulation for a flat roof and foundation is extruded polystyrene foam, a material with mechanical and moisture resistance;
- for external thermal insulation of walls in wet-type systems, polystyrene foam, extruded polystyrene foam or stone wool are recommended;
- Fiberglass boards are suitable for suspended ventilated facades.
Conclusions:
What properties of Penoplex determine the high level of consumer demand?
When choosing a material, its unique low thermal conductivity, light weight, simple installation and long service life are taken into account.
- New generation extruded polystyrene foam thermal insulation differs from polystyrene foam in its perfectly homogeneous structure, resistance to compression loads and other adverse external influences.
- For all its advantages, mineral wool has strict weight restrictions. Therefore, to insulate devices that do not have a sufficient safety margin, lightweight materials based on polystyrene foam are used.

The disadvantages of Penoplex Facade, which you can buy from our company at any time of the year - zero vapor permeability and fairly low heat resistance, are partially or fully compensated by the use of façade systems with slot ventilation and the installation of heat-resistant protective and decorative coatings.
As for the insulation of underground structures, including foundation ones, in this case moisture- and frost-resistant polystyrene foam does not have a worthy alternative.
The strength of the foundation lining is sufficient to protect the waterproofing from damage by seasonal movements of heaving soils. The range of polystyrene foam insulation includes panels of different sizes: from 30 to 100 mm thick. In most central regions, panels with a thickness of 50-60 mm are in high demand. You can buy Penoplex 50 mm in Moscow with significant discounts at promotional and seasonal sales of building materials.
Conclusion and video
Rolled thermal insulation is in many cases preferable because it is characterized by flexibility. In addition, the material of this group has low thermal conductivity, which allows it to be used to insulate an object. However, it should be borne in mind that fiber roll coatings do not tolerate contact with liquids well, so they must be carefully protected with waterproofing.
If you plan to use foam insulation, it is important to remember that they do not allow steam to pass through, which means the microclimate in the room may worsen. To avoid negative consequences when installing this type of insulation, it is recommended to install supply and exhaust ventilation or increase the efficiency of natural air circulation in the room.
Sources
- https://stroy-podskazka.ru/uteplenie/materialy/rulonnye/
- https://uteplix.com/materialy/rulonnyj-uteplitel.html
- https://dolgostroi.pro/drugoe/kakoy-uteplitel-luchshe-rulonniy-ili-plitniy.html
- https://teplo.guru/uteplenie/utepliteli/rulonnyiy.html
Density and thermal conductivity of thermal insulation in the form of plates and segments
The table shows the density values and temperature dependence of the thermal conductivity of thermal insulation molded in the form of slabs, segments, etc., as well as their maximum operating temperature.
Thermal insulation density, thermal conductivity and temperature are indicated for such thermal insulation as: diatom segments, sovelite segments and shells, newel shells, asbestos cement segments, vulcanite slabs, vermiculite shells, foam concrete segments, foam glass slabs, cork segments, peat segments, mineral wool segments, alfol smooth sheets (segments), corrugated aluminum foil (segments), ball insulation backfilled into segments, rod thermal insulation backfilled into segments (porcelain rods with a diameter of 0.5 mm).
The lightest thermal insulation is alfol; according to the table, it has a density of 200 kg/m3 and a maximum operating temperature of up to 500°C. High-temperature thermal insulation (up to 2000°C) includes ball and rod insulation. However, such thermal insulation has a high density and low thermal conductivity, equal to 0.23...0.39 W/(m deg). The thermal conductivity of thermal insulation depends on temperature. The table presents formulas for the temperature dependence of thermal conductivity of thermal insulation and its maximum operating temperature.
Note: to calculate the thermal conductivity coefficient from the dependencies in the table, it is necessary to enter the temperature in degrees Celsius.
What is the most important characteristic of insulation?
The main characteristic of insulation is thermal conductivity. The smaller it is, the better the material and the more efficiently it will cope with retaining heat in the house. The average thermal conductivity range of insulation ranges from 0.029-0.21 W/ (m/°C). The standard is the thermal conductivity of air - 0.025 W/(m/°C), therefore the thermal conductivity of the most effective insulation should be as close as possible to this parameter. The thermal conductivity of water is tens of times greater than the thermal conductivity of air, so the thermal insulation material should always remain dry.
Advantages and disadvantages
When choosing thermal insulation, you need to take into account not only its physical properties, but also parameters such as ease of installation, the need for additional maintenance, durability and cost.
Comparison of the most modern options
As practice shows, the easiest way to install polyurethane foam and penoizol, which are applied to the surface to be treated in the form of foam. These materials are plastic; they easily fill cavities inside the walls of a building. The disadvantage of foaming substances is the need to use special equipment to spray them.
As the table above shows, extruded polystyrene foam is a worthy competitor to polyurethane foam. This material is supplied in the form of solid blocks, but with the help of a regular carpenter's knife it can be cut into any shape. Comparing the characteristics of foam and solid polymers, it is worth noting that foam does not form seams, and this is its main advantage compared to blocks.
Comparison of cotton materials
Mineral wool is similar in properties to foam plastics and expanded polystyrene, but it “breathes” and does not burn. It also has better resistance to moisture and practically does not change its qualities during operation. If you have a choice between solid polymers and mineral wool, it is better to give preference to the latter.
Stone wool has the same comparative characteristics as mineral wool, but the cost is higher. Ecowool has a reasonable price and is easy to install, but it has low compressive strength and sags over time. Fiberglass also sags and, in addition, crumbles.
Bulk and organic materials
Bulk materials such as perlite and paper granules are sometimes used to insulate a house. They repel water and are resistant to pathogenic factors. Perlite is environmentally friendly, it does not burn and does not settle. However, bulk materials are rarely used to insulate walls; it is better to use them to equip floors and ceilings.
Among organic materials, it is necessary to highlight flax, wood fiber and cork. They are safe for the environment, but are susceptible to burning if not impregnated with special substances. In addition, wood fiber is susceptible to biological factors.
In general, if we take into account the cost, practicality, thermal conductivity and durability of insulation, the best materials for finishing walls and ceilings are polyurethane foam, penoizol and mineral wool. Other types of insulation have specific properties, since they are designed for non-standard situations, and the use of such insulation is recommended only if there are no other options.
Manufacturers and selection criteria
One of the leading companies producing roll insulation is the German company Knauf . A distinctive feature of the product is the absence of formaldehyde. In addition, the materials are characterized by ease of use. This company provides installation instructions for almost every roll, which will allow novice builders to do their insulation work better. Due to the composition, insects (beetles, ants) and rodents (rats) will not be able to settle in such thermal insulation.

No less famous is the French brand Isover . This company has a huge selection of roll-type insulation. Foil rolls are also available. The products of this company are used for insulating interior spaces, as well as outside buildings.
Due to its composition, it is fire-resistant; in the event of a fire or brief ignition, it does not support combustion and goes out on its own.

The most widespread in the European part of Russia is the Spanish company URSA . Its products are somewhat cheaper than the French brand, the range is in no way inferior to it, which makes the materials in demand among buyers. The company provides a very long warranty on its products; it is better to check the exact warranty figures immediately before purchasing.
How to choose materials for thermal insulation at home
Note that there is no universal best insulation. For each individual case, you need to select the appropriate material.
To figure out how to choose thermal insulation for your home, consider its types:
Mineral wool. Easy to install and insulates well. But it cannot withstand pressure and is not suitable for wet areas. Depending on the type of raw material from which it is produced, there are stone (basalt), glass and slag. Basalt-based home insulation is completely non-flammable and does not chip. Glass wool has two main advantages: it is non-flammable and very cheap. But working with it is not at all comfortable, since the material is itchy and causes allergies. Slag wool is only suitable for attics and non-residential buildings as it is not environmentally friendly.
- Foam glass
. Available in blocks, durable. This is a new and expensive material. - Styrofoam
. Its popularity is determined by its low price. Does not absorb moisture, is partially vapor permeable, does not rot, does not mold. Durable. But it has low strength. Rodents love to build nests in polystyrene foam. The optimal density is 25 kg/m2. - Expanded polystyrene
. This insulation is made from the same material as foam, but it is modern and more durable. Used for walls, foundations, flat roofs. At the same time it provides moisture insulation. Currently, polystyrene foam is the leader in the thermal insulation rating. - Sheet polyurethane foam
. Its properties are similar to expanded polystyrene, but it is breathable and easily absorbs water. - Foam
. It is made on the basis of polyurethane foam or penoizol. Good for insulating walls outside. Covers the surface completely, without cold bridges, due to which the walls after treatment have minimal thermal conductivity. But insulation in this way is expensive - the technology requires the use of special equipment and qualified personnel. - Foamed polyethylene foam
. There is PPE or NPE. Take only PPE - it is more durable. It is used for insulating pipes, internal walls, and floors. There are options with reflective foil film.
Important characteristics:
- Thermal conductivity
. Shows how much heat in watts the material will lose. The lower the coefficient, the better. The average value is 0.038–0.046 W/mK. - Vapor permeability
. The ability of the material to breathe, allowing moisture vapor to pass through. Quality required for timber structures. - Shrinkage
. It is desirable that it be minimal or absent. Otherwise, over time, under the influence of its own mass, the thermal insulation will decrease in volume and deteriorate its properties. - Hygroscopicity
. Determines the ability of a material to absorb water vapor. Materials with high hygroscopicity are less effective because liquid increases thermal conductivity. Also, such insulation cannot be used in damp places.
- Operating temperature
. Correctly selected insulation for this parameter will serve with high quality and for a long time. For example, in the northern regions frosts can reach -40 and -50 °C. In summer, metal roofs heat up to 80–90 °C. - Flammability
. Insulation materials are flammable and non-flammable. Indoors it is better to use non-flammable or low-flammable ones. Also, non-combustible insulation materials should be used in fire hazardous areas. - Environmental friendliness
. Important for use in residential areas. Environmentally friendly materials do not emit harmful substances. - Firms
. There are a lot of manufacturers of high-quality thermal insulation. Among the brands that have proven their effectiveness are the following: Rockwool, Isoroc, Energoflex, Penoplex, Akterm Nord, TechnoNIKOL, URSA, Hotrock, KNAUF, Isover, Ecostroy.
Important selection options
The efficiency of insulation is most influenced by its thermal conductivity coefficient, that is, the ability of the material to retain thermal energy indoors. However, this is not the only parameter that should be considered when purchasing.

Insulation should be assessed according to several criteria that are important for its further operation.
I have compiled a small table in which I indicated the characteristics that I consider important.
| Characteristic | Description |
| Thermal conductivity | The lower the thermal conductivity of the insulation used in the work, the better they work and the smaller the thermal insulation layer needs to be used. But it is important to pay attention to the fact that this parameter does not change depending on external natural factors. |
| Vapor permeability | The ability of the material to allow air to pass through can be considered both an advantage and a disadvantage. The choice largely depends on the material of the enclosing structures (for example, wood or reinforced concrete). I personally prefer insulation with high vapor permeability, as they allow you to create a comfortable microclimate indoors with a normal level of humidity. |
| Water absorption | The water absorption coefficient of the heat-insulating material should be minimal, since moisture entering inside, firstly, reduces its operating efficiency, and secondly, reduces its service life. In addition, material with low water absorption usually does not require the installation of additional waterproofing layers. |
| Strength | In relation to thermal insulation, strength refers to the ability of a material to withstand external mechanical stress. Strength is directly dependent on density. What does density affect? For thermal conductivity. Therefore, the most durable insulation materials retain heat worse and you need to choose the “golden mean”. |
| Sound absorption | Noise protection is not the main function of insulation, however, the high absorption coefficient of sound waves will allow you to avoid installing additional layers of other materials, which reduces construction costs and time for installing the insulating layer. |
| Chemical resistance | The material must withstand contact with aggressive chemicals. Usually it is enough for the insulation not to be destroyed during surface finishing with various building solutions (alkaline environment) and to withstand the effects of contaminated precipitation (acidic environment). |
| Biological resistance | Taking into account the characteristics of the operation of insulating layers (especially external ones), it is necessary to check that the material you choose is not susceptible to biocorrosion - the destructive effects of mold, mildew and microorganisms. |
| Flammability | When choosing one or another insulation material, you should find out its behavior during a fire. The best choice is to purchase non-flammable and flame-retardant insulation. As a last resort, it is necessary to use materials with fire retardants that limit the further spread of the flame. |
| Environmental friendliness | Materials for insulation (especially internal) should not cause harm to human health. It is better if the emission level of hazardous chemical compounds is zero. As a last resort, comply with established standards. It is also advisable to select a material that can be installed without the use of personal protective equipment (respirators, goggles, overalls, and so on). |
| Life time | The ideal option is when the service life of the heat-insulating material is equal to the same parameter for insulated structures. But here it is important that throughout this time the material you choose retains its original performance properties. |
Below are comparative characteristics of several types of insulation according to these ten parameters.
Efficiency of multilayer structures
Density and thermal conductivity
Currently, there is no building material whose high load-bearing capacity would be combined with low thermal conductivity. The construction of buildings based on the principle of multilayer structures allows:
- comply with design standards for construction and energy conservation;
- keep the dimensions of enclosing structures within reason;
- reduce material costs for the construction of the facility and its maintenance;
- achieve durability and maintainability (for example, when replacing one sheet of mineral wool).
The combination of structural and thermal insulation materials ensures strength and reduces thermal energy loss to an optimal level. Therefore, when designing walls, calculations take into account each layer of the future enclosing structure.
It is also important to take into account the density when building a house and when insulating it. The density of a substance is a factor influencing its thermal conductivity and ability to retain the main heat insulator - air
The density of a substance is a factor that affects its thermal conductivity and ability to retain the main heat insulator - air.
Calculation of wall thickness and insulation
Calculation of wall thickness depends on the following indicators:
- density;
- calculated thermal conductivity;
- heat transfer resistance coefficient.
According to established standards, the value of the heat transfer resistance index of external walls must be at least 3.2λ W/m •°C.
Calculation of the thickness of walls made of reinforced concrete and other structural materials is presented in Table 2. Such building materials have high load-bearing characteristics, they are durable, but they are ineffective as thermal protection and require an irrational wall thickness.
table 2
| Index | Concrete, mortar-concrete mixtures | |||
| Reinforced concrete | Cement-sand mortar | Complex mortar (cement-lime-sand) | Lime-sand mortar | |
| density, kg/cub.m | 2500 | 1800 | 1700 | 1600 |
| thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m•°С) | 2,04 | 0,93 | 0,87 | 0,81 |
| wall thickness, m | 6,53 | 2,98 | 2,78 | 2,59 |
Structural and thermal insulation materials are capable of being subjected to fairly high loads, while significantly increasing the thermal and acoustic properties of buildings in wall enclosing structures (Table 3.1, 3.2).
Table 3.1
| Index | Structural and thermal insulation materials | |||||
| Pumice concrete | Expanded clay concrete | Polystyrene concrete | Foam and aerated concrete (foam and gas silicate) | Clay brick | Sand-lime brick | |
| density, kg/cub.m | 800 | 800 | 600 | 400 | 1800 | 1800 |
| thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m•°С) | 0,68 | 0,326 | 0,2 | 0,11 | 0,81 | 0,87 |
| wall thickness, m | 2,176 | 1,04 | 0,64 | 0,35 | 2,59 | 2,78 |
Table 3.2
| Index | Structural and thermal insulation materials | |||||
| Slag brick | Sand-lime brick 11-hollow | 14-hollow silicate brick | Pine (cross grain) | Pine (longitudinal grain) | Plywood | |
| density, kg/cub.m | 1500 | 1500 | 1400 | 500 | 500 | 600 |
| thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m•°С) | 0,7 | 0,81 | 0,76 | 0,18 | 0,35 | 0,18 |
| wall thickness, m | 2,24 | 2,59 | 2,43 | 0,58 | 1,12 | 0,58 |
Thermal insulation building materials can significantly increase the thermal protection of buildings and structures. The data in Table 4 shows that the lowest values of the thermal conductivity coefficient are found in polymers, mineral wool, and slabs made from natural organic and inorganic materials.
Table 4
| Index | Thermal insulation materials | ||||||
| PPT | PT polystyrene concrete | Mineral wool mats | Thermal insulation boards (PT) made of mineral wool | Fibreboard (chipboard) | Tow | Gypsum sheets (dry plaster) | |
| density, kg/cub.m | 35 | 300 | 1000 | 190 | 200 | 150 | 1050 |
| thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m•°С) | 0,39 | 0,1 | 0,29 | 0,045 | 0,07 | 0,192 | 1,088 |
| wall thickness, m | 0,12 | 0,32 | 0,928 | 0,14 | 0,224 | 0,224 | 1,152 |
The values of the tables of thermal conductivity of building materials are used in calculations:
- thermal insulation of facades;
- general building insulation;
- insulating materials for roofing;
- technical insulation.
The task of choosing optimal materials for construction, of course, implies a more comprehensive approach. However, even such simple calculations already at the first stages of design make it possible to determine the most suitable materials and their quantities.
Features of three-layer wall construction
This type of wall construction is similar to a sandwich. Two walls, and between them a heat-insulating material. Walls made of foam block and brick are often insulated in this way.
Option for wall insulation using sandwich technology.
This insulation option is used in almost all new buildings. Rough brick wall, insulation and facing layer.
Extruded polystyrene foam boards are best suited for this type of insulation. Despite the good thermal insulation properties, this type of wall insulation also has a drawback. It is not as durable as other insulation options.
Inorganic options
Along with organic TIMs, inorganic insulators are also widely used. They are based on various mineral components - glass, slag, rocks, asbestos and others. As a result of processing these elements, various heat insulators are obtained. The leader in the field of inorganic insulation is, of course, mineral wool.
Mineral wool
This material is available in two varieties. Slag mineral wool is made from various wastes of ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy. Stone wool is based on various rocks - limestone, basalt, etc. Phenols or ureas are used to bind elements. Mineral wool is produced in the form of rolls or blocks.
The positive properties of this insulator include:
- low density with excellent thermal insulation characteristics;
- zero flammability;
- high level of noise absorption;
- long service life.
The disadvantages of this material include high vapor permeability. Therefore, it must be laid in conjunction with a high-quality vapor barrier layer.
Glass wool
The raw material for glass wool is glass and glass production waste. Thanks to its thick and long fibers, glass wool is stronger and more resilient than mineral wool.
When heated, glass wool does not emit harmful substances, has good noise absorption and thermal conductivity characteristics, and is also resistant to aggressive substances. Available in rolls.
Ceramic wool
Aluminum, silicon or zirconium oxide gave the consumer an excellent thermal insulation material called ceramic wool. It is produced using a centrifuge. At high speeds, the starting materials are inflated, which, after cooling, are shaped into rolls.
Ceramic wool is not afraid of high temperatures, so it can be placed on roofs or in rooms with large temperature differences. It does not deform, does not burn and is not afraid of chemically active influences. The density of this TIM is about 350 kg/m3, thermal conductivity is up to 0.16 W/m per Kelvin.
Industrial insulation
Industrial thermal insulation will cost much more, since it will be necessary to purchase materials for thermal insulation in large quantities. The smaller the room, the simpler the insulation methods. How to choose insulation so that the characteristics of thermal insulation materials are as effective as possible?
To avoid the formation of barriers during internal insulation, they try to reduce the humidity in the wall layer behind the insulation. A vapor barrier, as well as heat-protective materials with the lowest vapor permeability value, cope with this task. The material should not breathe, then moisture will not penetrate inside, but if this happens, then only forced ventilation will help.

At first it only seems that industrial insulation is no different from the insulation of private houses or apartments. To choose the right materials for thermal insulation, you need to study large amounts of information. For example, the classification of thermal insulation materials, the exact volumetric weight of the insulation, and also consider all types of thermal insulation.
Fire safety indicators:
- Flammability.
- Flammability.
- Smoke generation.
- Degree of toxicity during combustion
- Flame propagation speed.
When dry, this material does not expand, which means it will not move the walls. The good thing about hygroscopic material is that it absorbs moisture well and also releases it well. A good vapor barrier, just like regular foam, prevents any living creatures from appearing inside. Effective for thermal insulation of baths, saunas and industrial buildings.
In industrial buildings, a completely different insulation technology was used than it is now. If they wanted to make the building beautiful and warm, they built a brick box, then made an air gap and built another circle (external wall). Such a gap between bricks is most often observed in rural areas, where many residents still have old houses inherited from their grandparents. After a while, someone thought of increasing the thermal insulation performance of their home by filling this air gap. Initially it was polystyrene foam, but then they switched to penoizol.
Area of application of mineral wool
Cotton wool for insulation has a low thermal conductivity coefficient, so it is used in various construction and industrial fields
It is important to emphasize that it is an almost irreplaceable heat insulator when it comes to working with hot enclosing elements, because it has a low level of flammability
In addition, it is now actively used in insulating building facades, as well as for creating internal insulation in concrete and reinforced concrete buildings. Mineral wool is used for arranging drainage and heating systems. In the last few years, due to its availability, this material has also begun to be used for the construction of small baths. Comparative characteristics of insulation materials
Vapor permeability
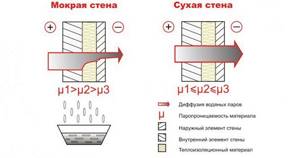
Vapor permeability is the ability of a material to retain or transmit steam. Denoted by the Greek letter mu (μ). The unit of measurement for the vapor permeability coefficient is mg/(m·h·Pa). If the insulation has high vapor permeability, then it is called “breathable” insulation.
The vapor permeability of the insulation allows moisture to be removed from the structure. At the same time, there will be no problems in the operation of such a design if the dew point is in the insulation and normal air exchange is ensured in the room. Failure to comply with these requirements may result in mold growth and accelerated deterioration of the house structure.
Made from organic materials
The main component is made from natural raw materials, mainly slag, but it can also be sawdust or shavings.

There are also variations with cement additions to organic raw materials. This insulation is very resistant to fire, more moisture resistant, and also weakly reacts with chemical and biologically active substances. The maximum temperature threshold of such insulation is 140 degrees.

There are several types of such insulation:
- arbolite (wood - sawdust, straw, shavings with chemical components)
- PPVC (foam type, main raw material – special resins)
- Chipboard (the same wood chips, but with synthetic resins and additional sandics)
- DVIP (similar to chipboard, only the base is made up of wood waste from paper and straw. Chemical reagents like septic tanks are also added)
- foam insulation (the second name is mipora, it consists of an aqueous emulsion of a certain resin, glycerin, as well as petroleum products)
- EPS (foam plastic, the main component is polystyrene (a petroleum product), the sheets themselves consist of only 2-3% of it, the rest is air)
- ecowool (recycled paper, cardboard and other waste paper). The release form can be either in the form of mats or in the form of sprayed insulation.

Review of manufacturers, or what does the Russian market offer?
Let's look at which manufacturers today supply stone wool to the domestic market of insulating materials:
Knauf: recognized world leader
The most famous manufacturer of stone wool in the whole world is the German concern Knauf. He began producing products in 1932, and in the field of thermal insulation he mainly specializes in basalt fiber, although he sometimes produces fiberglass materials.
Knauf has a fairly well thought out choice of insulation for different house structures, for which they produce as many as five series for roofs, walls, ceilings and partitions. Knauf also has universal mineral wool, which is suitable for any task:
Today Knauf produces stone wool literally for the whole world. But, unfortunately, buyers often complain about the increased rigidity of the slabs, which prick.
Of course, it’s not like glass wool; it’s more likely that there’s just an unpleasant sensation when working with bare hands. On the other hand, no one abroad would even think of working with cotton insulation without gloves.
Rockwool: high quality
No less famous is Rockwool - a Danish company that has been operating since 1909. All its factories use only European equipment, which the company is especially proud of. Stone wool is supplied in the following forms:

By the way, Rockwool also has factories in Russia. Among other advantages of this basalt insulation, users usually note that it does not crumble or shrink, and also pleases with a wide selection of sizes and packaging. Those. It’s quite easy to choose the right option for building your favorite home.
Ursa: expensive equipment
But Ursa have developed a new line of mineral wools. In fact, these are three entire production sites operating as the Ursa Eurasia association. Their main trump card is high-tech equipment. Previously, they worked more with fiberglass boards, but today they use more natural basalt raw materials with acrylic-containing components.
Urs also has factories in Russia, namely in the city of Chudnovo. According to the manufacturer, new high-tech equipment from Europe was also imported there, and therefore you don’t have to worry about quality.
And Russia especially liked the Pureone series. By the way, this manufacturer’s basalt insulation is considered one of the best in terms of sound and heat insulation, although it has insufficient vapor permeability, as some complain.
TechnoNIKOL: for special loads
TechnoNIKOL is one of the most famous manufacturers of basalt insulation in Russia, producing its products under the Rocklight brand:

What’s interesting is that each TechnoNIKOL enterprise has its own laboratory. Thanks to this, multi-stage control is constantly carried out over the products. As a result, TechnoNIKOL received a European level certificate for its products.
And at one time, TechnoNIKOL modernized its production lines and was able to achieve a rather unique property of mineral wool - increased rigidity, thanks to which each basalt tile can withstand a load of up to 7 tons. The manufacturer is also trying to make the insulation unattractive to small rodents, but they love such materials so much.