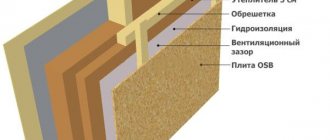
Vapor permeability
High vapor permeability is another disadvantage of insulation. It’s not bad when the house “breathes” and water vapor leaves it. But only 30% of the steam escapes through the walls, and the rest through the ventilation. And the high vapor permeability of insulation is more of a minus than a plus.
Vapor-permeable materials allow heat to be “blown” out of the house, and most of them are hygroscopic, i.e. perfectly absorb moisture. This figure is especially high when insulated with penoizol, which absorbs 23 times more liquid than ordinary cotton wool.
But if penoizol easily not only takes up, but also gives off moisture, then insulating wool “clings” tightly to it. Therefore, insulation with mineral wool or ecowool is a dubious step, requiring numerous additional protective measures that increase the cost of the procedure. At the same time, there is no certainty that the walls will not be constantly wet, and in the cold season, the absorbed water freezes, turning into destructive ice crystals.
Anyone who has decided to insulate themselves should familiarize themselves with the vapor permeability coefficients of the materials used.
| Name | Coefficient mg/m*h*Pa |
| PPU | 0,02 |
| Foamed polyethylene | 0,02 |
| Styrofoam | 0,03 |
| Penoizol | 0,2 |
| Ecowool | 0,3 |
| Minvata | 0,4-0,6 |
| Glass wool | 0,6 |
| Fibrolite | 0,11-0,16 |
Low vapor permeability is another advantage of polyurethane foam. It does not allow moisture to enter the wall material, and it is discharged into the exhaust system. Therefore, mold and mildew will not spread on the walls.
Analysis of technical characteristics of polyurethane foam
This article will look at rigid polyurethane foam. It is increasingly being used on construction sites. It has low thermal conductivity and hydrophobicity. PU foam does not allow water vapor to pass through and does not rot. Fungus and mold do not form on its surface. It does not react with most reagents.
For a comprehensive study of this thermal insulation material, its main properties are considered:
- Thermal insulating properties.
- Soundproofing properties.
- Moisture resistance.
- Vapor permeability.
- Behavior in various chemical environments.
- Resistance to open fire.
- Density.
- Lifetime.
- Environmentally friendly.
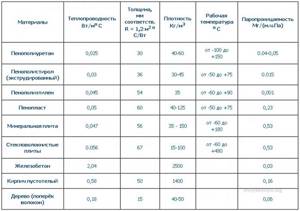
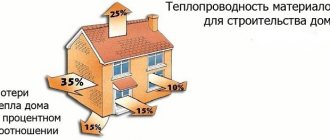
Summary table of average parameters of the main thermal insulation and finishing materials
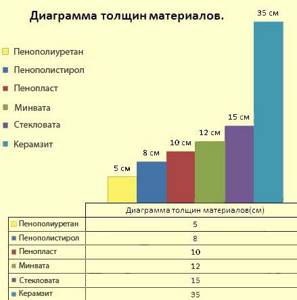
Thermal conductivity coefficient, EFFICIENT service life and layer thickness
| Name | Coefficient of thermal conductivity | Life time | Layer thickness |
| Polyurethane foam | 0,025 | 50 years | 5 cm |
| Expanded polystyrene | 0,035 | 15 years | 8 cm |
| Styrofoam | 0,04 | 10 years | 10 cm |
| Mineral wool, basalt fiber | 0,045 | 8 years | 12 cm |
| Glass wool | 0,05 | 5 years | 15 cm |
| Expanded clay | 0,15 | 40 years | 35 cm |
Examples of calculating the thickness of insulation
FOR THOSE WHO BUILD
In order to achieve the required minimum value of thermal resistance R=3.0, we give four examples.
The walls of the house are made of sand-lime brick, wall thickness is 0.38 m. R = 0.44.
Required R value - R_walls = 3.0 - 0.44 = 2.56. Now we multiply 2.56 by the thermal conductivity coefficient of polyurethane foam = 0.025. We get:
2.56 x 0.025 = 6 cm polyurethane foam.
(expanded polystyrene - 9 cm, polystyrene foam - 12 cm, mineral wool, etc. - 15 cm, glass wool - 20 cm, expanded clay - 35-40 cm)
All materials except polyurethane foam still need to be attached to the surface. Expanded clay needs to be filled in. PPU is applied immediately in finished form.
The walls of the house are made of 150 mm wooden beams. R=1.07.
1.93 x 0.025 = 5 cm PU foam.
The walls of the house are made of foam aerated concrete block 40 cm. R= 1.1
1.9 x 0.025 = 5 cm PU foam.
Insulation of roofs made of sheet metal (corrugated sheets, metal tiles) or hangars. R=0.1
2.9 x 0.025 = 7 cm PU foam.
Thus, a metal structure insulated with a 7 cm layer of polyurethane foam acquires the required thermal resistance value R = 3.0 and is suitable for year-round use.
Now compare this with what we see around us. Almost nowhere else is there such a level of thermal insulation of buildings, but R=3.0 is the required minimum!
Using polyurethane foam as insulation, you can significantly reduce construction costs by constructing thinner walls, a less massive foundation, etc.
A light frame house on a columnar foundation, sheathed on the outside with DSP or siding and insulated with a 7 cm layer of polyurethane foam, which is TWICE WARMER than a cottage with walls two bricks thick. And the cost of these houses is incomparable. An insulated PPU frame house measuring 12 x 9 will cost 800-900 thousand rubles, and an insulated house of the same size made of brick or blocks will cost 2 - 2.5 million rubles.
If you build such a house with your own hands (the technology is available to everyone, if there is a desire), then its cost will not exceed 600 thousand rubles. The main material is timber 150x50 or 200x50. There is hardly a more advantageous offer: for relatively little money you can get a warm house for year-round living, without worrying about the quality of the insulation, and save a round sum on heating every year.
In such a warm house, there is absolutely no need for bulky and expensive water heating systems in the form of electric or gas boilers, pipes and radiators. For heating 80 sq.m. A few heaters with a total power consumption of 3 kW are sufficient. and a 5 kW petrol generator for emergencies.
If the funds allow you to build a brick house, then PPU can significantly reduce the initial costs of the foundation and brick, and then significantly reduce heating costs.
For example. In Samara there is a house insulated with a 15 cm layer of rigid polyurethane foam. The wall material is sand-lime brick. The total area of the house is 365 sq.m., 1st floor and attic.
Heating - electric infrared heaters, no boiler or radiators.
Total power consumption in winter, including heating and all household appliances - 3,500 kW/month. or 4.9 kW/hour.
At electricity prices in 2015, home expenses in winter amount to no more than 5,000 rubles/month.
The house has a stable temperature of +23 - +24.
Comparison of polyurethane foam with other insulation materials ↑
What are the differences between polyurethane foam (PPU) and other insulation materials? They can be clearly seen in the following table, which shows the figures for density, porosity, temperature range and service life.
| Type of thermal insulation | Density, kg/cub.m | Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/m*K | Porosity | Service life, years | Operating temperature range |
| Polyurethane foam ( PPU ) | 8 — 100 | 0,019 — 0,028 | closed | 25-50 | -180С +150С |
| Mineral wool | 55 — 150 | 0,052 — 0,058 | open | 5 | -40С +700С |
| Cork board | 220 — 240 | 0,040 — 0,060 | closed | 8 | -30С +90С |
| Foam concrete | 250 — 400 | 0,145 — 0,160 | open | 10 | -30С +120С |
| Expanded polystyrene | 40 — 150 | 0,040 — 0,060 | closed | 7-12 | -100С +80С |
| Penoizol | 8 — 15 | 0,040 – 0,047 | open | 10 | -50С +120С |

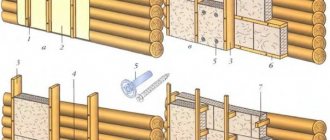
| 1 | brick. masonry | 860mm |
| 2 | foam concrete | 360mm |
| 3 | tree | 140mm |
| 4 | fiber | 65mm |
| 5 | cork | 50mm |
| 6 | mineral wool | 60mm |
| 7 | polystyrene | 40mm |
| 8 | polyurethane foam | 25mm |
The numbers speak for themselves, and by analyzing them, you understand what the choice of polyurethane foam technology is based on on the part of those people who gave it preference. We tried to figure this out in more detail.
The fact is that despite the development of this industry, spraying with polyurethane foam technology has not yet entered our lives to such an extent as to displace traditional types of insulation, which have already gained a strong position. If we compare, we can say that PPU is taking its first steps.
And yet, progress does not stand still and polyurethane foam technologies have been chosen more and more recently. One of the main obstacles to this seems to be price. It's clear that people are looking for cheaper options. But polyurethane foam, perhaps, cannot be classified as a cheap option.
Advantages
But there are advantages that seem almost indisputable:
- Environmental friendliness of the material;
- High thermal insulation (from cold, moisture and noise);
- Immunity to chemical solutions and compounds;
- Lightness (low weight).
If we look in more detail and comprehensively, it turns out that, in fact, none of the other insulation materials known today are as effective as polyurethane foam.
Judge for yourself.
Thermal properties (0.019 - 0.028 W/m*K) are ensured by a special closed-porous structure, as well as the solidity of the mass;
Ease of installation: polyurethane foam fits onto any surface configuration without additional fasteners, while providing very reliable thermal insulation. Polyurethane foam and applied quickly (up to 400-500 sq.m/shift);
The service life of polyurethane foam, according to manufacturer guarantees, is comparable to the “life” of the structure itself. About 20-25 years.
The material is interesting because it is non-toxic (its components are properly certified); Regarding the fire safety of polyurethane foam, one thing can be said: it does not support combustion, which is confirmed by various types of certificates and practice. Flammability group of polyurethane foams G2. Toxicity indicators during combustion of T3.
Spraying technology and polyurethane foam consumption
Spraying of polyurethane foam is carried out on site using a mobile foam generator .
A single pass gives only 5-10 mm of polyurethane foam, which is 0.5-1 kg/m2, so the required thickness is achieved in several passes after the previous layer has completely dried.
Foam polymerization occurs in 10-40 seconds, and the layer dries completely in 24 hours. The quality and speed of work are influenced by factors such as wind speed, ambient temperature, etc.
The spraying process consists of the following sequence of actions:
- equipment testing;
- cleaning the surface from moisture, dust, grease, rust, etc.;
- homogenization of components in barrels;
- mixing components in a foam generator;
- control spraying with measurements;
- spraying polyurethane foam onto the selected surface.
Material consumption depends on the density of polyurethane foam and layer thickness. Based on the above data, then every centimeter applied to 1 square. A meter of polyurethane foam weighs about 1 kg. From here it is easy to calculate the mass of the material for a given surface area and coating thickness.
There is also evidence that 20 mm polyurethane foam costs approximately 500 rubles per square meter. meter, 50 mm - 550 rubles, 100 mm - 600 rubles. Of course, prices may change over time and from company to company.
Polyurethane foam, mineral wool, penoplex or polystyrene foam: what is better to choose for insulation

When choosing decent insulation for your home or industrial building, you need to take into account a number of factors that will ultimately affect the time until the next major renovation, the costs of maintaining your home, industrial premises, quality of life and comfort.
We build and insulate once and for life.
The most common and popular insulation materials: mineral wool, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam. Let's compare polyurethane foam with other insulation materials and identify the differences between polystyrene foam, mineral wool and polyurethane foam. What is better and what is worse in operation for 50 years.
The nuances of performing work with polyurethane foam
During a work shift, at a flow rate of 1 l/min, you can produce up to 6 cubic meters of polyurethane foam for the necessary thermal insulation of pipes or something else. Technologists must competently structure the work process and, when developing it, select installations for the specific density of a particular brand of polyurethane foam. If it is necessary to thermally insulate walls, the density of the foam “coat” should be at the level of 30-50 kg/m3. When performing thermal insulation work on the roof, the density of polyurethane foam should be 45-70 kg/m3. When spraying the ceiling - up to 12.
A feature of the process of applying polystyrene foam to a surface at a low temperature is the implementation of the first layer in the form of a thin layer of primer (no more than 10-20 mm). Other layers may be much thicker. There are other nuances, in particular, the phenomenon of “diminishing” the previous ones with each subsequent layer of polyurethane foam, which increases the overall density of the entire coating.
THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY OF POLYURETHANE FOAM
Gas-filled polyurethane foam plastic has a set of excellent properties and excellent characteristics that make this material convenient and practical for thermal insulation and the manufacture of various products.
In this article, we will consider polyurethane foam as insulation. Let's figure out which insulation is more effective, how to determine the thickness of a particular material for thermal insulation. Based on the laws of thermophysics, let’s compare polyurethane foam with other building materials. Along the way, we will note the interesting properties of polyurethane foam and mention the restrictions on use.
Description of the properties of polyurethane foam
In the section Polyurethane foam - description, characteristics, we have already described polyurethane foam briefly. In everyday life, polyurethane foam is foam rubber; rigid construction grades are used to insulate walls, foundations, floors, roofs, and balconies.
There are two ways to install polyurethane foam: sheets and spraying. Better insulation is created by spraying using GRACO high-pressure equipment. Ours uses exactly this equipment.

The main advantages of polyurethane foam
- thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam is 0.02 - 0.03 lower than that of polystyrene foam, and 2 times lower than that of mineral wool;
- high moisture resistance, practically does not absorb water;
- temperature of use of polyurethane foam from -70 to +110 degrees;
- the official service life is more than 30 years, there are known cases - 60 years, this is 5 times longer than that of expanded polystyrene and mineral wool;
- there is no deformation or subsidence during operation;
- he is not afraid of mold and mildew;
- good sound insulation;
- continuous seamless coating and foam-filled cracks, thanks to the spraying of fine foam;
- no condensation, which means no mold;
- good adhesion to any surface;
- there are no installation costs due to the lack of vapor barrier, wind protection, counter slats, you buy the installation and the insulation itself right away;
- low load on structures due to low weight;
- flexibility and elasticity under loads;
- the fastest installation compared to other insulation materials and without waste
- Our prices include the cost of installation and materials. See what everyday problems PPU solves for people here.
Disadvantages of polyurethane foam
- higher price, this disadvantage is compensated by savings of up to 50% on heating and cooling of premises, there are no drafts on the floor;
- protection from the sun is needed, polyurethane foam must be covered with paint or a decorative coating, for example, siding.
Application technology
The two components are fed into the mixing tank. There they are mixed under pressure and sprayed onto the surface to be treated using a gun. After a few seconds, the mixture sharply increases in volume and quickly hardens.

Method of applying polyurethane foam
Important! To apply polyurethane foam, special equipment and personal protective equipment are required. Therefore, it is better to entrust this process to professional construction organizations.
Polyurethane foam is a quality material in all respects. Savings of time and money can be 50-70% compared to using traditional insulation. Work can be carried out all year round. Technologies do not stand still, so insulating building structures using polyurethane foam will become cheaper and more reliable.
Areas of application
Polyurethane foam is widely used in construction as a heat-insulating material. It can be used to insulate brick, concrete or wooden structures. It is used to treat foundations, roofs, and exterior walls of houses. In addition, due to the beneficial properties of this material, it is also in demand in other areas:
- in industry and instrument making;
- in cars, airplanes, ships;
- for insulation of pipelines, heating networks.
Elastic varieties of polyurethane foam are widely used in the production of furniture and bedding. Mattresses and sofa fillings made of polyurethane foam are popular due to its ability to retain shape, environmental friendliness, and durability.

Areas of application of polyurethane foam
Lifetime
Most manufacturers indicate a service life of 20-30 years. This is the warranty time during which the useful properties of the material are within acceptable limits. Recent studies by European scientists have shown surprising and encouraging results. When demolishing houses built 40-50 years ago using polyurethane foam, scientists found that its properties remained virtually unchanged. The structure and texture remained the same as originally. Further laboratory studies only confirmed the durability of this material.
Environmental friendliness
An important parameter that modern builders are paying more and more attention to. During the production process, polyurethane foam goes from liquid to solid in 30 seconds. After this, harmful fumes from its surface stop. If it is heated to 450 Cº, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide will begin to be released. However, the same thing can be observed when wood is heated.

Polyurethane foam does not emit compounds harmful to the human body
Insulation methods
We examined only the main advantages and disadvantages of this insulation. Many other pros and cons depend on the technology of polyurethane foam insulation - polyurethane foam can be used in the following ways:
Next, we will consider how polyurethane foam insulation is carried out using each of these methods, and what features these technologies have.
Sputtering
Spraying of polyurethane foam is carried out using special equipment - a torquet machine. The latter ensures the mixing of ingredients, as well as the supply of finished foam to the nozzle under high pressure.
Advantages:
- Versatility. The foam adheres reliably to any surface. In this way, it is possible to insulate the attic with polyurethane foam, pitched roof, external and internal walls, floors, ceilings, etc.;

The method of spraying polyurethane foam can insulate the roof
- No cold bridges. The insulation is laid on the surface in a continuous layer, thereby eliminating the appearance of cold bridges;
- High speed. The foam is quickly applied and hardens almost immediately. This allows you to begin finishing work immediately after insulation.

Spraying polyurethane foam requires expensive equipment
Flaws:
- Need for equipment. For this reason, it is impossible to do insulation with your own hands;
- Complexity of the process. Spraying polyurethane foam is a rather complex process that requires a highly qualified operator. Therefore, it is advisable to trust the work to well-known companies that provide a guarantee;
- Toxicity. Liquid foam is toxic. True, after hardening the insulation is absolutely harmless to health.
The well-known polyurethane foam is also polyurethane foam, only one-component and mixed with gas. The structure of the polyurethane foam is single-cell.
Price. Insulating a square meter of surface using this method costs about 500 rubles.
Fill
Pouring differs from spraying in that the mixing of PU foam ingredients occurs without exposure to air. The result is foam of a creamy consistency, which is supplied with minimal pressure. This allows you to pour polyurethane foam into cavities of various designs.

Foam is poured into frame walls through a hole after covering them.
Most often, this method is used to insulate frame walls, floors and ceilings. You can also insulate the attic with polyurethane foam or a regular pitched roof.
Advantages:
- Possibility of pouring polyurethane foam into molds. This technology is used to produce polyurethane foam shells for pipes and other products;
- No cold bridges. When filling wall cavities and horizontal surfaces, as in the previous case, cold bridges are eliminated. The only thing is that cold zones can arise as a result of incomplete filling of frame walls. Therefore, insulation must be carried out by specialists;

The pouring method can be used to insulate two-layer brick walls
Flaws:
- Limited application. It is impossible to insulate solid walls using this method;
- The need for vapor barrier. Before insulating frame walls and other structures from the inside, it is imperative to provide a hermetically sealed vapor barrier. Otherwise, wooden structures will quickly become unusable.
In addition, this technology has the same disadvantages as spraying.
Price. The price of one cube of polyurethane foam is in the range of 6000-7000 rubles.

PPU boards are ready-to-use insulation
Slabs
Insulating an object with polyurethane foam boards is the simplest and at the same time universal technology. The principle of installing slabs is no different from using any other slab insulation, such as polystyrene foam, penoplex or mineral wool.
In addition to versatility, the use of slabs has other advantages:
- High strength. This allows the slabs to be used for insulating floors under screed or even for insulating foundations;

PPU slabs can be used to insulate any surface of the house including the foundation
- Possibility of finishing insulated walls in different ways . House insulation with polyurethane foam boards can be done both for wet finishing (plastering/painting) and for sheet materials that are mounted on the frame;
- Possibility of self-insulation . The instructions for installing the plates are quite simple, which allows even a beginner to cope with the task.
Flaws:
- High price. If your choice largely depends on the cost of insulation, then PPU slabs will not suit you due to their high cost;
- Possibility of formation of cold bridges . During installation, the slabs must be laid close to each other, and the existing cracks must be foamed. Otherwise, the efficiency of insulation will be greatly reduced.
For these reasons, polyurethane foam boards are not widely used.

Extruded polystyrene foam is a cheaper alternative to polyurethane foam
Instead of polyurethane foam boards, you can purchase extruded polystyrene foam boards. They also have excellent characteristics, but at the same time they cost several times less.
Price. The price of one slab measuring 1200x600x60 mm starts from 750 rubles.