Today, polyurethane has become an integral part of our daily lives. It is often used to replace products made of rubber, steel and other materials. In construction, polyurethane is widely used for thermal insulation of buildings. This material is also often used in various industries, including light industry, footwear, furniture, etc. In particular, polyurethane is used to make fillings for mattresses, armchairs, car seats, and much more.
Polyurethane belongs to a group of synthetic polymers that are obtained from high molecular weight alcohols (polyols) and polyisocyanates. In addition, various dyes and additives are added to the material during the production process. Therefore, experts have been arguing for a long time whether polyurethane is harmful to human health. To understand this issue, we should consider its composition in more detail.
History of the material
The birth date of polyurethane foam can confidently be called 1937, when a small group of scientists from a laboratory in Levenkusen synthesized a material with unusual properties. Depending on the mixing ratio of the components of the new material and how quickly the reaction took place, the properties of polyurethane foam were radically different. On the one hand, the material was elastic and flexible, but rather weak to resist tensile loads. On the other hand, strength, hardness, density, but brittleness when bending. The material had extremely broad prospects, but the Second World War significantly slowed down their implementation. However, starting from the 60s of the last century, the production of polyurethane foam began to develop at a rapid pace.
conclusions
Of course, we have not listed all the negative opinions and not all the arguments in favor. But I hope we were able to make it clear that many concerns are related to ignorance or unsubstantiated rumors.
However, there is no smoke without fire. Probably, someone has encountered unscrupulous or inexperienced contractors, perhaps even defective raw materials from which the polyurethane foam was obtained, or non-compliance with work regulations. If your Mercedes is broken, this does not mean that all Mercedes cars are bad. Perhaps you just needed to change the oil on time.
In this regard, we recommend that you carefully select a supplier of raw materials and a contractor. Choose only proven, experienced teams with high-quality equipment for spraying polyurethane foam. Get feedback from their clients. Make sure that the contractor used raw materials with the stated requirements, ask for certificates. It is also not difficult to determine the density of the resulting polyurethane foam and its flammability right at the work site using a kitchen scale and a lighter. If in doubt, conduct a professional examination. It is better to do all this before the work begins or at the very beginning - it will save a lot of time and nerves.
The good news is that polyurethane foam continues to gain popularity and consumer confidence, while at the same time occupying an increasing share of the market. More and more experts agree that polyurethane foam is the future in the field of energy-saving construction technologies.
For more information on this topic, see:
- Spraying polyurethane foam – what is it?
- Thermal insulation (thermal insulation, thermal insulation)
- Density of polyurethane foam
Discussion
Please enable JavaScript to view the comments powered by Disqus.
Component composition of polyurethane foam
The main components included in polyurethane foam and necessary for the formation and attachment of polymer chains are polyol (component A) and polyisocyanate (component B). Sometimes domestic manufacturers can add another component to the polyol - a catalyst. The main components of polyurethane foam have a specific odor and are a liquid of a fairly thick consistency with shades from light yellow to dark brown.
During long-term storage, the polyol tends to exfoliate, so it is recommended to mix it before use. Polyisocyanate interacts with water - upon contact, crystallization begins. During long-term storage in the open air, a film forms on the surface of the material. According to its component composition, polyurethane foam can be of two types - for spraying and for pouring.
Polyurethane foam and harm to health: how to avoid negative consequences?
There are three main mistakes made when working with PPU:
- Failure to comply with operating requirements
- Ignoring protective equipment in direct contact with liquid foam mixtures
- Using low-quality sprayers
Pro Tip To minimize inhalation of spray fumes or their settling on interior surfaces, it is recommended that the area being treated is well ventilated.
Our article about polyurethane foam spraying technology will help you avoid the first two mistakes. Regarding the sprayer, it is preferable to use high-pressure apparatuses, which ensure uniform mixing of both phases of the mixture with 100% completion of the chemical reaction, due to which the question of whether the components of polyurethane foam are harmful disappears. In addition, this spraying ensures guaranteed quality of the coating.
Biogenic properties
Polyols and polyisocyanates used for the production of polyurethane foam are petroleum products. However, it is known that polyurethane foam components can also be produced from vegetable oils. The best option for this purpose is castor oil. The polyol component can also be obtained from sunflower, soybean, and rapeseed oils. However, the cost of these raw materials is quite high and production is not economically feasible. Biogenic polyurethane foam materials are produced in small volumes and are used to solve very narrow specific problems.
Pros and cons of polyurethane mattresses
The advantages of polyurethane mattresses are obvious:
- The optimal combination of quality and price.
- Has orthopedic properties.
- Hygienic (does not rot, is indifferent to pests).
- Do not cause allergic reactions.
- Completely safe filler.
- Long-term operation and preservation of quality.
- Easy to care for and clean (not afraid of water).
While sleeping on a polyurethane mattress, the filler seems to adapt to the contours of the person’s body, supporting it and relaxing the muscles. Despite this, the mattress is quite elastic; it properly supports the spine, improves blood circulation, thereby eliminating congestion in the body. Polyurethane mattresses are recommended for overweight people, bedridden patients during postoperative periods, or during periods of illness, as they prevent the occurrence of bedsores.

Undoubtedly, it is pleasant that a polyurethane mattress will not stick together, deform or wrinkle. If there is a need for transportation, it can be easily rolled up and transported to the desired location, after which it will again take its original shape.
With such significant advantages, polyurethane mattresses also have disadvantages. Namely:
- Quickly absorbs liquid, even evaporation.
- Cheap polyurethane mattresses quickly wear out and become deformed.
- Requires careful care (ventilation, cleaning).
- Relatively short service life of up to 10 years.
After its service life (more than 10 years), polyurethane gradually deteriorates, it becomes deformed, and this immediately affects its orthopedic properties, comfort of sleep and rest. The disadvantages of polyurethane mattresses are insignificant and they are fully compensated by its advantages, but whether to buy it or not, everyone must make their own choice.
Related Posts
- Steel x12MF for knives: characteristics, pros and cons
- Eucalyptus blanket: pros and cons of choice
- Steel 110x18 for knives: pros, cons and features
- Pros and cons of vacuum packaging
- Satellite TV: advantages and disadvantages
- Hoverboard: pros, cons and what you need to know
- Electric stove: advantages and disadvantages
- Solid fuel boilers - pros and cons of choice
How to make a foam mattress with your own hands
Experts recommend using exclusively orthopedic mattresses in everyday life; in addition to comfortable rest, it also prevents diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Unfortunately, the price of factory-made mattresses is quite high and not everyone can afford it. Meanwhile, making a foam mattress with your own hands is not such a difficult task.
The structure of a factory orthopedic mattress
When sewing a mattress, you can go in two ways:
- simplify the task as much as possible and use a thick layer of highly elastic material as a filler. After cutting, all that remains is to process the edges of the material, cover it with fabric and place it in a case. A 10 cm foam mattress created in this way will be quite convenient and comfortable;
- You can complicate the task and try to combine a layer of foam rubber and a spring base in the mattress. In this case, the output will be an analogue of factory-made orthopedic mattresses.
One of the best options is a spring base with independent springs. In this case, a person is guaranteed to be able to take a comfortable position. In the proposed design, the spring base will be placed in a box glued together from pieces of foam rubber. For the side edges, you can use foam rubber with a thickness of about 30 mm, but for the top and bottom parts - at least 50 mm. You will also need felt, fabric for covering the mattress and sewing a cover, and braid.
Main part of the mattress
The base of the mattress is a structure consisting of two layers of foam rubber, two layers of felt and a spring base located between them. After cutting the foam rubber and felt, a layer of foam rubber is first laid on any horizontal surface, then there is felt, a spring base, again a layer of felt, and this “pie” is covered with a layer of foam rubber. Felt is used here to prevent springs under load from damaging the surface of the polyurethane.
The structure of the future mattress
The free space on the sides should be covered with inserts made of the same polyurethane, and the result should be a closed box. It is better to use special glue to glue the elements of the box. You can get by with regular PVA or liquid nails, but, firstly, the drying time of the adhesive layer will increase, and secondly, a hard crust will form at the gluing site, which will simply crack when deformed.
Glued mattress base
There is no need to additionally fix the felt and spring base. They will not move during use.
For additional strength, when gluing, you can place a wide board on the foam rubber and place a load on it.
Instructions for sewing a cover
For the cover you will need batting and fabric; when cutting, you just need to take into account the dimensions of the foam “box”. And, of course, leave a reserve for finishing the edges.
In the first stage, the batting is sewn to the fabric. On a flat surface, the batting and fabric are aligned with each other and hand stitched along the long side of the rectangle several times. After this, you can proceed to processing the edges.
First, the excess batting that protrudes beyond the fabric is cut off, after which the part of the future cover is stitched around the perimeter with an overcast stitch. After this, you can sew the narrow parts of the cover into one whole.
Large pieces should be sewn on using decorative tape to hide the seam. First, the braid is sewn along the perimeter of the large part, then the edge of the narrow part is applied to the same braid, the braid is folded and stitched. Using the same principle, a zipper is also sewn on so that the mattress can be taken out when washing the cover.
Ready mattress
Properties of polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam produced by domestic and foreign manufacturers has a number of both positive and negative characteristics.

The low thermal conductivity of the material (0.019 - 0.03 W/m), almost complete vapor tightness, and water resistance make polyurethane foam an excellent heat and water insulator. The same can be said about sound insulation. The high adhesion coefficient makes it possible to apply polyurethane foam to almost any surface.
However, polyurethane foam is not characterized only by its positive qualities. Harm to human health can be caused during the burning of polyurethane foam (in the presence of a direct source of fire, the material burns). In addition, polyurethane foam releases toxic substances into the atmosphere - formaldehyde. Polyurethane foam, the components of which interact with air and water, is not resistant to sunlight. Over time it darkens and falls off.
What is it and application
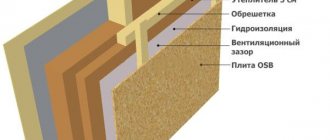
PIR insulation is a foamed polyisocyanurate, actually a direct analogue of polyurethane foam, with a similar structure and composition, but the proportions of the main components differ, as does the list of catalysts and fillers. It is a rigid foam material with extremely low thermal conductivity. According to the manufacturer, the thermal conductivity value reaches 0.020 W/m*K.
The method of manufacturing PIR insulation also differs from PUR (polyurethane foam). Greater temperature and pressure are applied at which reaction and foaming occurs. The output is a closed cellular structure with minimal vapor permeability.
The cell size is calculated in micrometers, as is the wall thickness, as a result the density of the material is reduced to 45-60 kg/m3, but at the same time strength is maintained, which is characterized by values even higher than polyurethane foams. Only 3% of the volume of the finished insulation is occupied by polyisocyanurate foam, the rest of the space is occupied by gas.
Polyisocyanurate is mainly used in industry and construction as insulation in sandwich panels, a structural element with an additional coating. PIR boards are often additionally coated with kraft paper, sheet steel foil or polymer films.
This is necessary not only to expand the scope of application, but also as additional protection, a barrier between the insulation and the environment.
This is necessary not only to preserve the integrity of the material, but also to isolate the environment from it, since the question of the toxicity and safety of the material still remains open.
The performance characteristics, as well as methods of use, are similar to those for sheet polyurethane foam and extruded polystyrene foam (EPS).

It is suitable for insulation:
- buildings, including private houses with plaster or ventilated facades;
- floors;
- roofing (mostly flat roofing);
- climatic equipment (air conditioning, ventilation systems) subject to the permissible operating temperature.
PIR insulation gains in efficiency due to the unconditional presence of an additional outer layer of:
- Kraft paper – increases the adhesion of adhesives, forms a ready-made base for further finishing;
- Aluminum foil is a heat shield that can significantly increase the thermal insulation properties of the material;
- Sheet metal - increasing strength, including structural strength, is used to form fences that do not require additional reinforcement at rated load.
A significant operational disadvantage of PIR insulation is shrinkage, which occurs during the first years after installation. Judging by the Technical Specifications from the manufacturers, the shrinkage should not exceed 2%, although in practice much depends on the accuracy of the installation.
It is difficult to lay the material in reserve, like mineral wool, or to provide functional gaps for further sealing as it shrinks.
In this case, manufacturers focus on the method of joining polyisocyanurate sheets.
The slabs are produced with a lock along the edge, moreover, on two or four sides at once:
- Quarter;
- Tenon and groove;
- Lock with overlapping surface layer (wave for roofing insulation).
Scope of application of polyurethane foam

This modern building polymer has found wide application in various areas of human activity. Its widest area of application is in construction: thermal insulation, acoustic and waterproofing of civil and industrial facilities for any purpose (residential, country houses, workshops, warehouses, hangars, etc.). Due to low thermal conductivity, polyurethane foam is used to insulate not only roofs, but also walls, both inside and outside buildings. Sandwich panels made of polyurethane foam are indispensable in the construction of prefabricated construction projects.
Polyurethane foam with a density of 30-86 kg/m³ (rigid polyurethane foam) is used as a noise and heat insulation material. Material with a density of 70 kg/m³ has a dense structure, does not allow water to pass through and is successfully used for waterproofing work.
In the production of refrigeration equipment, polyurethane foam is used as a cold insulator. The shoe industry uses the material to make various shoe elements and instep supports.
However, there are areas where the benefits of using a material such as polyurethane foam are very questionable. Lining material and fillings for upholstered furniture, mattresses, pillows, etc. can be harmful to health. (polyurethane foam with a density of 5-40 g/m³ - soft foam blocks). Although PU foam manufacturers claim that the material is environmentally and biologically neutral, its use as a filler for children's toys can also make parents think about the health of their children.
Production of polyurethane foam and flammability of elastic polyurethane foam for furniture and mattresses
Two-component polyurethane. Sprayed thermal insulation - what is it and where is it used?
The production of polyurethane foam in the sector of production of elastic polyurethane foams is associated with their use in the production of upholstered furniture, mattresses, office chairs and armchairs, in the automotive and textile industries. The production of polyurethane foam uses technologies for the production of elastic polyurethane foams in the form of blocks or molded polyurethane foams. High quality elastic block polyurethane foam is usually produced in a continuous manner using a conveyor and modern equipment. In case of low requirements for the quality of the material, elastic block polyurethane foam is obtained by periodically pouring the foaming composition into a box. Modern box installations have vacuum chambers, which makes it possible to produce elastic polyurethane foam of low apparent density up to 20 kg/m3 without the use of methylene chloride, as well as elastic polyurethane foam of standard and lower than standard rigidity.
The production of polyurethane foam for furniture use is associated with the unique useful physical and mechanical properties of elastic polyurethane foams, including low apparent density, elasticity, virtual absence of odor, and the ability to quickly restore size and shape after deformation. That is why the production of polyurethane foam is used in the manufacture of upholstered furniture and mattresses. Elastic polyurethane foam for furniture is obtained by reacting a polyol with a diisocyanate in the presence of foaming agents, catalysts, surfactants, antioxidants, dyes, and fire retardants. The fire safety of elastic polyurethane foam is one of the most important characteristics of these materials, since it largely determines the safety of upholstered furniture and mattresses.
PUF ignites when exposed to a sufficiently powerful heat source, and the combustion characteristics of elastic PUF include such indicators as ease of ignition, smoldering ability, flame spread rate, heat release rate, smoke formation, and toxicity of combustion products. The fire safety of elastic polyurethane foam can be improved by changing the composition of the polymer matrix and adding fire retardants to the formulation. The production of polyurethane foam and the use of elastic polyurethane foam in combination with various furniture upholstery fabrics can significantly affect the flammability of the final product.
Cigarettes, dry alcohol tablets, newspapers, and gas burners are often used as ignition sources for testing the fire hazard of products with PU foam filler. Such tests show the dependence of the flammability of upholstered furniture on the type of shell used, the configuration of the final product, the formulation of elastic polyurethane foam, and the combustion source. To predict the behavior of a complex product in a specific fire situation, one does not limit oneself to the results of laboratory flammability experiments, but conducts appropriate large-scale flammability tests of finished products.
Sleeping in the arms of PPU...
We will talk about such bedding items as polyurethane foam mattresses. Harm, quite serious, can be caused by inhaling fumes of complex volatile chemical compounds (about 30 types), the most dangerous of which are phenol and 2-ethylhexanoic acid. Moreover, new mattresses filled with polyurethane foam emit 5-6 times more hazardous substances into the atmosphere than old ones. The concentration of vapors of these substances is comparable to emissions from a new laminate flooring.
Assurances about the safety of mattresses filled with polyurethane foam are questionable for the simple reason that at the stage of their manufacture resins, catalysts, solvents, and active chemical components (phenol!) are used.
Is polyurethane harmful in everyday life or not?
For domestic purposes, polyurethane is used for insulation of residential premises, as well as as a filler for mattresses and upholstered furniture. In this case, foam material is used, which, after complete drying, does not pose a danger to human health.
However, polyurethane is still classified as a potentially hazardous material, since if it is used incorrectly, toxic fumes can be released into the environment. So, if the thermal insulation coating did not have time to dry completely or violations were committed during its installation, then in the future phenol-formaldehyde derivatives will be released into the living space, which can lead to the development of symptoms of chronic poisoning for the residents. In general, completely dried polyurethane foam does not pose a danger to human health. Therefore, manufacturers often classify polyurethane as environmentally friendly materials.
Thus, we can conclude that if all operating rules are followed, polyurethane products do not pose a danger or harm to human health. However, experts do not recommend using polyurethane products in children's rooms, as they can cause allergic reactions, headaches and other symptoms in children.
The modern construction market is ready to offer its consumers both materials that have many years of use and a strong reputation, as well as a whole list of polymers that came to the market not so long ago and are still gaining recognition from buyers. It is this group that includes polyurethane foam.
Is phenol a big threat?
Phenol is considered a toxic substance because it emits toxic fumes, and this process can continue for years without reducing or losing toxicity. This chemical element can cause disruption of the most important systems of the human body: respiratory, nervous, cardiovascular. The consequence may be headaches, loss of consciousness, and impaired coordination of movements. Kidney and liver function may also be affected. Constant contact with phenol and its vapors can cause the appearance of such serious diseases as asthma, infectious pulmonary pathologies, and allergies.
According to scientists involved in research in this area, the use of polyurethane foam for the manufacture of children's furniture, mattresses, and toys is unjustified. Polyurethane foam may well be replaced with safer materials. If parents are concerned about the health of their children, they need to be very careful when choosing toys and mattresses for them, in which polyurethane foam can be used as a filler. The majority of civilized countries have banned the use of phenol for the manufacture of everyday goods.
Flammability of polystyrene foam
Due to this property, polystyrene foam in the form of pre-foamed granules was used as a component for napalm bombs to burn enemy armored vehicles. Expanded polystyrene melts and its melt burns at temperatures above 1100ºС. This is the only polymer that burns at such a high temperature. Therefore, when a building in which there is a significant content of polystyrene foam catches fire, everything burns, even metal structures.
In turn, when polystyrene burns, its thermal degradation occurs, which releases a significant amount of substances hazardous to humans. Therefore, back in the Soviet Union, under a unified system of sanitary and chemical control of the use of polymer materials, the USSR Ministry of Health banned the use of expanded polystyrene in construction.
In connection with the above, in Western Europe 20 years ago, expanded polystyrene was completely removed from residential buildings. The main peaceful use of expanded polystyrene in northern Europe and Canada is for insulation of road and railway tracks. To give the road durability, slabs of this material are added to the body of its “layer cake”. Moreover, it is not foamed, but extruded polystyrene foam (technology developed by BASF, Germany) that has a hard and durable shell that is used. This makes it possible for expanded polystyrene not to become saturated with moisture, maintain its thermal insulation ability and prevent freezing of the road surface - which is the main reason for its rapid destruction. The use of expanded polystyrene in greenhouses is also effective, especially in the northern regions. Studies have shown that toxic STYRENE is not released into a humid environment, but remains in polystyrene foam without causing any harm. In addition, under a layer of sand, gravel or soil, there is no question of the fire hazard of polystyrene foam. This is where this material belongs.
What else is harmful?
Polyurethane foam products are widely used in many areas of human life. Polyurethane foam and foam board based on polyurethane foam have a negative effect on the lungs, skin, and eyes. Thermal insulation boards made from polyurethane foam release toxic polyisozoanate compounds into the air, which can cause allergies or asthma. When PPU boards are heated by heating batteries or sunlight, the release of polyisocyanate increases.
When a fire occurs, polyurethane foam burns and releases toxic gases, which is an additional source of danger and threat to life. However, it is worth noting that recently non-flammable types of polyurethane foam, obtained by introducing special additives into their composition, are increasingly being used. Such polyurethane foam practically does not cause any harm to health.
Is a polyurethane foam insulation layer harmful for residential premises?
This question concerns the vast majority of amateur builders, since very often special additives are a production secret, and it is not possible to find out how harmful polyurethane foam is. Any mixture produced undergoes the most stringent tests to confirm its non-toxicity under different operating conditions. So the actual harm to polyurethane foam is zero if you use a mixture from a trusted manufacturer that has all the necessary quality and safety certificates.

So where is the truth?
Polyurethane foam - what is it? Is it harmful or beneficial? The huge number of places where polyurethane foam is used in various spheres of human life does not allow us to give an unambiguous answer to this question. For the construction industry, this is certainly a benefit, and a huge one. The ability to make a mixture and apply polyurethane foam to the insulated surface directly at the construction site reduces associated costs and allows you to create a monolithic polyurethane foam surface without cracks during installation and cold bridges. Thermal insulation of main pipelines, insulation of low-temperature pipelines in the chemical industry is also currently hardly possible with the same efficiency that polyurethane foam provides.
However, the use of this material in the production of goods for people (and for children in particular) seems to many specialists in this field not entirely justified. The release of toxic substances can have a negative impact on human health. Even before 2003, the manufacturing technology of domestic components for the production of polyurethane foam included the use of highly volatile ether compounds. Today, manufacturers claim that this technology has been abandoned. Within 3 days after application, the material is freed from a small amount of gases remaining after the reaction of the components, and after that the polyurethane foam is environmentally friendly.
In general, in each specific case, before using products made from polyurethane foam, you need to take a sensible approach to assessing all the pros and cons of using this material in a particular area of life.
Fire hazard of polyurethane foams (“Release of a full set of chemical warfare agents”)
Unlike expanded polystyrene, rigid polyurethane foam is an inert polymer with a neutral odor. For this reason, it is widely used in refrigerators for food storage. Polyurethane foam does not create toxic emissions that cause human illness or death.
But as a result of the combustion of polyurethane foams and polyisocyanurate foams, a mixture of low molecular weight thermal decomposition products and their combustion products is always formed. The composition of the mixture depends on temperature and access to oxygen.
The process of dissociation of polyurethane foam into the initial components - polyisocyanate and polyol - begins after heating the material to 170-200°C.
With prolonged exposure to high temperatures above 250 ° C, most thermosetting plastics, as well as rigid polyurethane foams, gradually decompose.
When the isocyanate component is heated above 300°C, it decomposes with the formation of volatile polyureas (yellow smoke) in the case of elastic polyurethane foams or the formation of non-volatile polycarbodimmides and polyureas in the case of rigid polyurethane foams and polyisocyanurate foams. Thermal decomposition of the polyisocyanate and polyol occurs.
At temperatures exceeding 300°C, the destruction of polyisocyanurate foam begins, which, unlike polyurethane foam, contains a more stable isocyanurate cycle. Temperature at which sufficient quantities of flammable decomposition products are formed that can be ignited by flames, sparks or combustible surfaces, for rigid polyurethane foams from 320 ° C.
For rigid polyurethane foams based on special grades of polyisocyanate, the decomposition temperature with the release of flammable gases ranges from 370 °C to 420 °C. In addition, during the decomposition of various polyurethane foams when heated to 450 °C, the following compounds were identified: carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide), butanediene, tetrahydrofuran, dihydrofuran, butanedione, water, hydrocyanic acid and carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide).