The rate of the chemical reaction and the mixing ratio of the components determine the subsequent characteristics of the resulting polyurethane foam:
- Flexible springy material has elasticity, but is characterized by low tear resistance. Everyone knows foam rubber from this category.
- The dense and durable version is hard, but fragile when bent.
- Foamed polyurethane foam has a wide range of advantages.
As a rule, polyurethane foam is obtained from petroleum products, but it is possible to produce it from components of plant origin. Castor, soybean, rapeseed and sunflower oils are excellent for these purposes. Since the production of polyols from plant raw materials is less profitable, this method of production is impractical and is used extremely rarely.
Polyurethane foam release forms
Depending on the percentage of mixed components and the rate of chemical reactions, polyurethane foam is divided into two types:
- Soft (up to 40 kg/m3);
- Solid (up to 86 kg/m3).
Soft polyurethane foam includes the well-known foam rubber. The industry produces several types of foam rubber, which differ in degree of rigidity:
- soft (HS);
- standard (ST);
- highly elastic (HR);
- hard (HL);
- increased rigidity (EL);
- special purpose (highly elastic and fireproof), (CMHR).
Important! Foam rubber (except for special CMHR) is a highly flammable and highly flammable product. It is characterized by combustion with the release of toxic substances. Due to these features, soft polyurethane is not used in the construction industry.
Builders use solid polyurethane foam in their work. The industry produces this material in several forms:
- Sheet polyurethane foam. It has, as a rule, a rectangular shape and a thickness from 5 to 1000 mm;
- Rolled. This is not too thick (from 2 to 30 mm) material, which is sold in rolls and is also used for insulation. One side of the polyurethane foam roll has a synthetic or fabric backing;
- Blocky. The very name of polyurethane foam indicates that this material is produced in blocks with a hard surface coating. A striking example is sandwich panels;
- Acoustic. This polyurethane foam has a figured relief, thanks to which it has an increased ability to absorb sounds;
- Contour. This is shaped polyurethane foam, which is poured into special molds. This includes, for example, car headrests, backrests or armrests.
- Liquid. Liquid polyurethane foam is understood as polyurethane foam. It is successfully used for installing door frames and window frames in high-rise buildings and private houses.
By the way, the foaming mixture sprayed onto flat surfaces or into openings is also divided into 2 types:
— Open-cell polyurethane foam. This material is often used indoors, where there is no need to withstand humidity, because due to the open cells, such polyurethane foam accumulates moisture. However, its lightness and low cost speak in its favor, despite the fact that in its properties such polyurethane foam is not inferior to mineral wool. They also resort to open-cell polyurethane foam in cases where it is necessary to achieve good sound insulation in the room.
— Closed cell polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam with a closed cell is used to insulate the external structures of buildings, thermal insulation of walls and unused roofs. It is denser and heavier, but in most respects it outperforms open-cell polyurethane foam. By the way, if we talk about the durability of the material, then this quality directly relates to closed-cell polyurethane foam.

Characteristics
There is also no clarity about the characteristics of the material.
Thermal conductivity
When advertising their products, sellers indicate very low thermal conductivity values of polyurethane foam. Rarely, you can find a coefficient of 0.017 W/(m×°K), more often - 0.020-0.022 W/(m×°K). But this is from the realm of fantasy. Even in laboratory conditions, where all requirements for the quality of components and their formulation can be met, it is rarely possible to obtain a thermal conductivity index of 0.022 W/(m×°K).
Similar values are achieved only with the use of freon r141b as a foaming agent, which is prohibited for use in Europe (and therefore is not produced). The use of other foaming agents increases the value of the coefficient, and therefore in European countries a thermal insulation layer with a thermal conductivity of 0.028 W/(m×°K) is considered high quality.
In Russia, the real figures are 0.030-0.035 W/(m×°K) (the specific value depends on the experience of the performers).
However, consumers should not be upset. Even if the technology is violated, the actual thermal conductivity of the insulation deserves respect, since it is one of the best and comparable to basalt wool.
Density
The density of the insulation determines the bending strength (fragility), the weight load on the structure and the thermal insulation properties.
Two-component, closed-cell polyurethane foam, can be obtained in different densities, combined into 3 groups.
- 1 group. Low density - 28-32 kg/m3. The main scope of application is ceilings and walls from inside the room, onto which the material is applied in a thin layer. Thermal conductivity coefficient is from 0.028 to 0.032 W/(m×°K). Vapor permeability at the wood level is 0.05 mg/(m*h*Pa), which makes it possible, albeit conditionally, after detailed calculations, to use polyurethane foam for insulating the walls of wooden houses (more on the problem below).
- 2nd group. Average density - 32-40 kg/m3. A classic representative of the species. The components are sold separately, in cylinders. Used to insulate all structural elements of a building. It has the lowest percentage of moisture absorption among all types of insulation.
- 3rd group. High density - 40-80 kg/m3. Achieving such density using portable equipment is theoretically possible, but practically impossible. It is used in places with high mechanical load on the heat-insulating layer, but only after special surface treatment, which experts call armoring.
Life time
Manufacturers of polyurethane foam consider their products to be durable, with a service life of 30-50 years. These figures are confirmed by the experience of using this insulation in the USA and Europe. However, in Russia, in the first years of using the new product, they were faced with the fact that the insulation from the facades of multi-storey buildings began to fall off in layers after 5-6 years of operation.
At first, the root of the evil was seen in the poor adhesion of polyurethane foam to the wall material. When the lag became widespread, they began to study the problem seriously and turned to Western experience. It turned out that the reason is in a completely different plane - the sun's rays. The material does not tolerate ultraviolet irradiation, ages, or in the language of scientists: it is subject to UV destruction. The aging rate is about 1 mm per year.

The worst enemy of polyurethane foam is the sun.
Simply painting the insulating layer with fade-resistant paint or mastic protects the material from destruction, extending its service life to 30 years when the facade is open. If the insulated facade is finished with siding or porcelain stoneware, you don’t have to worry about the safety of the insulation at all.
Adhesion
Foamed polyurethane has excellent adhesion to all types of building materials, with the exception of polyethylene film. For example, in order to tear polymerized insulation from concrete, you will have to apply a force of at least 2.5 kg/cm2, and for steel - 1.5 kg/m2. These are very large numbers. No wonder the best types of glue are polyurethane based. But such adhesion is possible only if the insulation is sprayed onto a clean and dry surface.
The insulation will not adhere to whitewash and “boiling” plaster; it will fall off along with them under minor mechanical loads due to low bending strength.
Scope of application of polyurethane foam
Considering the variety of types of this material, it is not surprising that polystyrene foam has become widespread in a wide variety of industries. Here are some examples:
— Construction of industrial facilities (insulation of buildings with sandwich panels, as well as thermal insulation of roofs with sprayed polyurethane);

— Construction, as well as major repairs of residential buildings, cottages and private houses (insulation of external walls and foundations of the house, doors and windows, internal insulation of attics and balconies);

— Pipeline communications (thermal insulation of oil pipelines and fuel oil pipelines);
— Transportable refrigeration units (cold insulation of automobile and railway refrigerators);

— Refrigeration equipment (cold insulation of domestic and industrial refrigeration units, as well as food storage warehouses);
— Heating networks for serving the population (thermal insulation of hot and cold water supply pipelines during installation, as well as major repairs);

— Automotive industry (car interior decoration with the formation of elastic and semi-rigid elements);

— Radio electronics and electrical engineering (ensuring vibration resistance of various electrical appliances);
— Light industry (production of synthetic leather);
— Furniture industry (production of foam rubber for upholstered furniture, as well as cabinet and decorative elements of their polyurethane);
— Mechanical engineering (products and mechanisms made of polyurethane and polyurethane foam);
— Aircraft and carriage building (vehicle products with elasticity, increased fire resistance, as well as heat and noise insulation).
Kinds
Most enterprises can produce different types:
- • liquid – sold in spray containers;
- • hard – sheets, shells and panels;
- • foam rubber – mats and rolls of finished products.
Thickness and protective properties can vary depending on the purpose. The characteristics allow it to be prepared directly on the construction site. When the proportions of components change, the features change.
Foam rubber
It has a low density from 5 to 35 kg/m3. The scope of application is very wide - from furniture filler to linings in shoes and clothes, they are used to make washcloths and gaskets for doors and windows.
PPU hard
The main place of use is construction. More often it is produced directly on site - this saves resources. Using special equipment, workers mix the components in the required proportions.
This produces ready-made polyurethane foam, which is not afraid of petroleum products and water, but is afraid of organic solvents and other mineral acids. There are more than 30 brands of different purposes and densities. Polyurethane foam can be used in one form for insulation, or in combination with analogues of a different frequency.
The scope of application is wide - from noise and heat insulation of buildings to the insulating layer in refrigeration equipment. Extremely positive reviews.
Liquid
Used for spraying on walls and ceilings. Thanks to its thinner consistency, it became possible to spray it onto walls under pressure to provide insulation. Indispensable if you need to work without weighing down the structure.

Thickness table
| Name | Thickness, cm | ||||||
| 2,0 | 3,0 | 4,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 8,0 | 10,0 | |
| Uncoated/paper | 37,8 | 42,6 | 52,2 | 61,2 | 71,2 | 92,3 | 119,8 |
| Foil | 42,7 | 47,5 | 57,1 | 66,1 | 76,1 | 97,2 | 124,7 |
| Armofol | 37,5 | 41,2 | 49,3 | 56,8 | 65,0 | 82,6 | 105,5 |
| On one side - fiberglass | 51,6 | 56,4 | 66,0 | 59,8 | 68,0 | 85,6 | 108,5 |
Comparison with mineral wool
This is the closest analogue, more popular, cheaper and inferior in a number of properties. The compressive strength of polyurethane foam is at the level of 0.3; for mineral wool it is not calculated, since it is a very flexible and obedient material.
Polyurethane foam can absorb no more than 10% of water; mineral wool is not designed for such a load and itself has a constant 4% humidity. It will not resist swelling from liquid, so it is not recommended to use it in residential buildings.
Let's talk about maximum service life. The foam will last at least 40 years, and the level of other substances does not exceed 10. Caked mineral wool simply becomes a harmful gasket that is of no use.
Polyurethane foam does not contain dangerous fumes, formaldehydes and phenols, like its cheaper analogue with 6% of unwanted compounds, and is completely safe. It is resistant to aggressive environments and has excellent resistance to rodents and insects. Polyurethane foam does not release fibers into the air; mineral wool contains an allergen for many people and azone-depleting gases.
Parameters of sprayed insulation
It’s worth saying right away that, as with any other insulation, it is preferable to insulate the walls of buildings from the outside. If you insulate from the inside, the outer wall will freeze. How many defrosting/freezing cycles it will withstand depends on the material, but rarely will such a house last more than 10 years.
When insulating the outside with polyurethane foam, a final exterior finish is required - the surface has a very unattractive appearance. But there are no problems with freezing of the walls, the building will last a long time.
There are no problems with the roof at all. Roofing materials are designed to withstand repeated freezing, so roof insulation with polyurethane foam can be done from the inside, spraying it directly onto the “underside” of the roofing material or onto the sheathing.

Sprayed thermal insulation can be applied to any surface, and the roof can be insulated from the inside
Whether to insulate the house from the outside or from the inside, we figured it out. Now a little about the layer thickness. Insulation with polyurethane foam is usually made of large thickness. This is not due to the fact that small is not enough. Usually, just according to thermal characteristics, an insulation thickness of 2-3 cm is required, but they make it at least 5 cm. This is so that under any conditions the dew point ends up in the thickness of the thermal insulation, and not in the wall material. Since polyurethane foam is non-hygroscopic, it cannot get wet, condensation simply does not occur, and excess moisture is removed naturally due to the vapor permeability of the material.
How is it different from foam rubber?
Foam rubber is a type of elastic polyurethane foam.
The cellular porous structure provides good air, vapor and moisture permeability. The degree of elasticity is regulated by the addition of different types of polyol during production.
When choosing consumer goods, it is necessary to remember that “foam rubber” is the trade name of polyurethane foam , which was registered in the Soviet period by a Scandinavian company of the same name.
Foam rubber is mainly used in the light and furniture industries. Furniture upholstery, fillings for mattresses and pillows, soft toys, mannequins - this is a list of the most common uses of this type of polyurethane foam.
The material is characterized by different thicknesses and, accordingly, different rigidity. It is mainly produced in the form of sheets or blocks.
Different types of foam rubber are combined in the furniture industry, which improves the quality of the products.
For example, a more rigid sheet is used for a sofa seat than for the backrest.
Orthopedic products, as a rule, should not be soft. They are designed to ensure that the body is positioned correctly and comfortably. For this purpose, a new type of foam rubber with a “memory effect” was developed. It is able to return to its original shape after deformation. During operation, such material follows the contours of the body of the person lying on it, which allows you to relax as comfortably as possible.
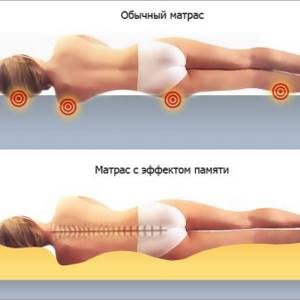
The main mechanical characteristics of foam rubber, on which the service life of furniture products depends:
- rigidity;
- density;
- strength;
- elasticity;
- cell size;
- support coefficient.
For example, the support coefficient and cell size are decisive in highly elastic types of polyurethane foam.
Furniture foam rubber is subjected to significant loads, so conscientious manufacturers use the material with the highest density. It can easily withstand long-term dynamic loads and static weighting.
Review of manufacturers
Polyurethane foam insulation has become popular recently. Therefore, new manufacturers of these products are appearing on the market, as well as contractor companies providing installation services.
Reputable PU foam suppliers produce components under their own brands. The rest, as a rule, are resellers, purchasing components from well-known brands. Some firms use local oil refineries.

Using consumer reviews, we can identify several reliable polyurethane foam manufacturers:
- Basf is a German chemical concern with branches in 160 countries. The brand produces a wide range of products. More than 7 thousand items, 60% of which are sold on the European market, about 22% of sales are in the United States of America, the rest is distributed between the markets of South America, Asia, Africa and the Pacific. In Russia, the company has several subsidiaries, including BASF Construction Systems LLC, BASF Vostok LLC, Wintershall Russland. One of the well-known joint ventures producing polyurethane foam products is. The company produces polyurethane systems that are available to consumers of any level and for various applications.

- Synthesia Internacional SLU is a Spanish chemical company founded in 1964. The main direction since 1966 is the production of polyesters, as well as polyurethane systems for various industrial sectors, for example, thermal and acoustic. Since 1970, polyurethane foam for sandwich panels, construction and refrigeration systems first appeared in the product range. Today the company produces products for different market segments. The most famous distributor of products in Russia is Global Therm LLC. This company provides direct deliveries, carries a certain supply of products in a warehouse in Moscow, guarantees a flexible payment system and consultations with technical specialists.

- Sipur (Poland) is one of the largest manufacturers of sprayed polyurethane foam insulation. Thermal insulation products are characterized by low thermal conductivity, which allows the insulation to be applied in a thinner layer (spray thickness up to 6 cm). The company guarantees a service life of polyurethane foam of about 50 years. Thanks to its closed-cell structure, thermal insulation not only retains heat, but also helps strengthen structures and protect them from moisture. The density of the insulation is 18-22 kg/m3, the degree of air permeability is about 0.0045 kg/(m2*hour), the temperature range for operation is from -70 to +100 degrees. The modern innovative material is patented, developed specifically for the CIS market, and therefore combines reasonable prices and high quality characteristics.
- Icynene (Canada). The brand produces energy-efficient polyurethane foam insulation for private and industrial construction. More than 300 countries have confirmed the quality of the produced material with certificates. Guaranteed period - 25 years. The company has appeared on the polymer insulation market since 1986.
- Wanhua (China). The company began production in 1998 and today has achieved worldwide recognition. The company's product range includes several high-quality types of polyurethane foam, aromatic polyamines, and polyisocyanate (MDI). The latter is produced at two factories with a total capacity of up to 500 thousand tons per year.
burning ppu video
Polyurethane Foam Review
Home » News and Articles » Review of Polyurethane Foam
Today, polyurethane foam is widely known not only to specialists in the construction industry, but also to a wide range of consumers. Many of us are probably familiar with this material. Any home owner who has at least once considered the issue of insulation is guaranteed to have heard about polyurethane foam and considered it as one of the thermal insulation options. Spraying polyurethane foam has become very widespread and is used almost everywhere - being a kind of standard for quality and durability. So, what is polyurethane foam or as it is also called PUF for short - in its structure it is a porous, fine-celled material belonging to the group of plastics, which in its structure consists of 85-90 percent of the gas sphere. It would first be developed in the laboratory of IG Farben (in Leverkusen) by a group of scientists led by the then little-known Otto Bayer. The synthesized material had a set of unique, very interesting physical and technical properties that predicted a great future for it.
Distribution of polyurethanes in various fields
And indeed, compounds based on polyurethane are used very widely in the modern world: furniture production, molding of car seats, stucco production, filling soft children's toys, cold insulators in industrial refrigerators, fillers for pillows and other areas. Polyurethane and its variety polyurethane foam had a number of interesting consumer properties that found their application in various areas of human activity... PPU immediately attracted the attention of the construction industry due to its outstanding thermal insulation characteristics (0.019 - 0.03 W/(m K)) which along with the unique properties of adhesion to almost any surface including: brick, wood, concrete, glass, metal, paper, various varnish coatings - make this insulation one of the most popular and in demand by both construction companies and ordinary consumers.
Characteristics and properties of polyurethane foam
It would not be entirely correct to consider the characteristics of polyurethane foam in isolation from its structure - in this regard, it is advisable to begin considering polyurethane foam with the issue of the chemical structure of this insulation. For the industrial production of polyurethane foam, the petrochemical compound of polyol and polyisocyanate (also commonly known as component A and component B) is used. When a chemical polymerization reaction occurs, short units of identical and homogeneous polymers appear at the ends of molecular groups. Depending on the speed of the chemical reaction, the length of the chain also varies, on which the final properties of the resulting polyurethane foam largely depend. Conventionally, foamed polyurethane or PUF can be divided into two significant groups: - soft polyurethane foams - which are mainly used in light industry and also as furniture fillers. — solid polyurethane foam with a density of 35 kg/m3, which has found the widest application in the construction industry. You can see the main characteristics of solid polyurethane foams used in construction as acoustic and thermal insulation in more detail in the following table:
| Indicators | Fork of values |
| Density, kg./m. Required voltage to destroy the PU foam structure, no less Thermal conductivity, W/m*K, no more. Number of closed pores in the structure of the material (per cm3), not less than Water absorption, % volume Flammability group of the material | 35..150 at compression 0.15..1.0 MPa; at bending 0.35..1.9 MPa 0.019..0.03 85-97 1.2..2.1 GOST-12.1.044 (low-flammability) |
Practical aspects of using polyurethane foam
If we focus not just on the characteristics of polyurethane foam, but on the practical aspect of using these properties, we can name the following strengths of this insulation:
— Due to its low weight, polyurethane foam will not create additional load on insulated surfaces, which is especially important when carrying out roofing thermal insulation work. — The applied layer of polyurethane foam gives additional mechanical stability to the surfaces on which the spraying was carried out. “It is not susceptible to significant seasonal temperature changes and can operate successfully over a wide temperature range. From minus two hundred to plus two hundred degrees Celsius. — With the use of this insulation, a completely insulated monolithic surface is achieved without joints and seams, which are so characteristic of sheet and panel heat-insulating materials. — Polyurethane foam has exceptional durability, confirmed by the practical experience of its many years of use. — It is not susceptible to aggressive environments and microorganisms, which makes it suitable for use in difficult and particularly difficult environmental conditions.
Of course, these are not all the positive aspects of polyurethane foam - professional builders can easily name dozens more points, but this is the topic of a separate article entirely devoted to the issue of considering the properties of polyurethane foam insulation!
Areas of application of polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is widely used in the insulation of residential apartment buildings, where it is used as the middle layer of thermal insulation structures, and in the insulation of country houses, cottages, hangars, warehouses and other objects - where, as a rule, polyurethane foam spraying technologies are used. At the same time, by spraying polyurethane foam, not only is it possible to save money on transportation costs, but it is also possible to achieve a completely monolithic thermal insulation layer. Foamed polyurethane applied using this technology creates an ideal heat and noise insulating barrier over the entire applied surface! Unlike all kinds of insulation in the form of plates and rolls, the material applied using this technology is not characterized by divergence of joints and uneven fit - which has a positive effect on the overall efficiency of thermal insulation of structures. It is also worth noting that the applied surface is given additional mechanical stability - which is especially important for roofing thermal insulation work, as well as for insulating hangars.
Economic aspect of using PPU thermal insulation
Let's consider the issue of insulating a house with polyurethane foam from the perspective of an ordinary consumer. Here we get a not entirely unambiguous picture - that is, on the one hand, polyurethane foam insulation of a house is more expensive than some competing materials. However, if when choosing insulation you are guided not only by the price factor, but also take into account other related aspects - such as service life, environmental friendliness, solidity and low conductivity of the resulting thermal insulation. It turns out that the choice of polyurethane foam is reasoned, justified and appropriate. And yet, having once spent on comprehensive insulation of your house with polyurethane foam, in the future you will no longer be concerned about this issue - since the service life of this insulation, confirmed by laboratory tests, is more than 50 years. In houses and buildings where complex thermal insulation work was carried out, costs during the heating seasons were reduced by more than 2 times. And in the hot season, there is a significant saving in electricity spent on maintaining comfortable living conditions. Thus, the initial costs of insulating the house will be fully recouped after just one, maximum two heating seasons - in the future, due to the reduction in costs, enviable regular financial savings will be observed.
Weaknesses of polyurethane foam
There are not many disadvantages of polyurethane foam - but they still exist, although in all kinds of advertising brochures they are usually unobtrusively silent about them. One of the nuances of the chemical structure of polyurethane foam is that it is prone to accelerated destruction under the influence of direct ultraviolet rays - which, of course, affects the service life of the material. This problem has a very simple and logical solution - when carrying out external thermal insulation work, polyurethane foam needs to apply a protective layer. A laconic solution can be the usual painting of surfaces, which also gives an additional aesthetic appearance. Another point of using polyurethane foam is the flammability group G-2; polyurethane foam belongs to the class of low-combustible materials. Under the influence of high temperatures, the outer surface of the polyurethane foam structure smolders - therefore this insulation cannot be used for insulation work in places that are exposed to extremely high temperatures and open flames. When the source of high temperatures is removed, the smoldering of the outer layer of polyurethane foam stops instantly.
Conclusions As we see, the list of advantages of Polyurethane Foam is much more voluminous and broader than its weaknesses, which for the most part can be attributed to the nuances and specifics of the use of this insulation. Of course, it was the qualitative superiority of the totality of all consumer properties that played a key role in the emergence of Polyurethane Foam as a kind of gold standard for the quality and reliability of thermal insulation!
Polyurethane foam - myths and reality
The volume of use of polyurethane foam (PPU) for thermal insulation of various objects is continuously growing. From 1999 to 2021, the consumption of components for polyurethane foam in Russia has increased almost 5 times.
The use of PPU could have been wider if not for existing myths and simply incorrect information about PPU. A survey conducted at construction sites, bases and building materials supermarkets showed: 1,500 respondents regarding polyurethane foam have the following opinions: 1. Polyurethane foam is a flammable material - 56%. 2. PU foam releases toxic substances - 73%. 3. PU foam absorbs moisture like a sponge - 22%. 4. Polyurethane foam darkens over time and falls off -17%. 5. Polyurethane foam is a good insulation material, but expensive - 9% 6. They know nothing about the properties of polyurethane foam - 15%. 7. Excellent insulation - 2%. When asked how they knew this, the respondents (except for points 6 and 7) found it difficult to answer. Let's try to deal with each opinion.
1. PPU is a flammable material
All main PU foam systems, as is known, are low-combustible materials, i.e. are resistant to open flame and thermal radiation: flammability group G2, GZ according to GOST 12.1.044-89. This group also includes ALL insulation materials, including polystyrene foam, expanded polystyrene, foamed polyethylene, etc. The exception is non-flammable insulation based on basalt fiber, but it is characterized by increased hygroscopicity. Another non-flammable insulation material is expanded clay. However, the scope of its application is quite limited and to obtain a noticeable effect of thermal insulation, a layer of expanded clay of at least 30 cm is required. It turns out that polyurethane foam is the same moderately flammable material as all the others, but, unlike expanded polystyrene, polyurethane foam contains a fire retardant in its composition , which prevents the flame from spreading and transfers polyurethane foam into the category of self-extinguishing materials. Simply put, there is an external source of fire - the PU foam burns, there is no source of fire - the PU foam does not burn. PUF is produced from two components - polyol component A (contains polyols, stabilizers, catalysts and blowing agent) and isocyanate component B. Until 2003, component "A" did not contain a fire retardant - trichlorethyl phosphate (TCEP), because this reduced the shelf life of the component. It was supplied with the "A" component separately and the spray crew had to add TCEP to the "A" component immediately before using it. Thus, the fire-fighting properties of thermal insulation depended on the performers. It was more profitable for the spraying team not to add a fire retardant to component “A” at all, because it slows down, although slightly, the process of foaming foam. At the same time, the consumption of components increases, and, accordingly, the cost of work increases. As a result, a room treated from the inside with polyurethane foam without a fire retardant or with an insufficient amount of it could catch fire during electric welding work, improper handling of open fire, etc. Currently, such components no longer exist. Modern components “A” contain effective flame retardants, which make polyurethane foam self-extinguishing, i.e. not burning outside the flame of a third-party fire source.
2. PU foam releases toxic substances
Generally speaking, all objects made of plastic emit harmful substances to some extent. It's no secret that even the Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision standards establish a minimum amount of harmful substances that are considered safe for health. For example, the familiar smell of a new car is caused by harmful volatile chemical compounds that evaporate from plastic parts over time. Inexpensive furniture emits toxic formaldehyde, because... Chipboard contains a large amount of it. OSB boards, which are used for wall cladding in frame housing construction, are even more toxic because... they contain more formaldehyde. Only natural materials can be considered absolutely environmentally friendly: stone and wood, not treated with antiseptics. Among insulation materials, the leader in environmental friendliness is mineral wool, because... It does not itself release volatile chemicals. But it releases the same formaldehyde contained in the adhesive base, which allows the fibers to retain their shape for some time. In addition, mineral wool is an allergen. Therefore, it is prohibited for use in children's and preschool institutions. As for polyurethane foam, the release of volatile chemicals actually occurred before. It happened that a characteristic odor remained in the room after spraying polyurethane foam for several weeks. The reason for this is component “A”, which has already been discontinued. Modern components do not have highly volatile ether fractions, and when checked three days after applying polyurethane foam, no harmful substances are detected in the room. Within two to three days, depending on the thickness of the layer, the polyurethane foam is freed from a small amount of residual reaction gases and is then completely environmentally safe.
3. PPU absorbs moisture like a sponge
To determine the ability of a material to absorb moisture, the method of saturating the sample with water and control weighing “before” and “after” is used. To compare the hygroscopicity of different materials, you need to weigh samples of the tested materials, then place them in a chamber over a stream of steam, and after a certain time, remove them from there and weigh them again. Test results:
| Material | Density, kg/cub.m. | Moisture saturation. % | |
| 1 | Minvata | 15 | 15-18% |
| 2 | Penoizol, Ecopen | 15 | 12-13% |
| 3 | Expanded polystyrene | From 15 to 30 | 9-10% |
| 4 | PPU, Penoplex | From 20 to 35 | 5-7% |
| 5 | PPU | From 40 to 60 | 2-4% |
| 6 | PPU | From 60 to 80 | 1-2% |
You see: of all the tested materials, polyurethane foam is the least hygroscopic. Moreover, the higher the density of polyurethane foam, the lower its hygroscopicity. It is more profitable for contractors to work with polyurethane foam of lower density due to lower consumption of components. Taking advantage of the fact that the customer does not realize or is not able to check the density of polyurethane foam, some contractors use material that does not meet the technical requirements. It happens that low-density polyurethane foam is in direct contact with water for a long time, which inevitably penetrates its structure over time. But other thermal insulation materials will be saturated with water much earlier. This doesn't mean the material is bad. This means that you need to choose the right density of polyurethane foam, comply with the requirements of SNiP and... control the performers.

4. Polyurethane foam darkens over time and falls off
Due to exposure to direct sunlight, unprotected polyurethane foam is destroyed to a depth of approximately 1 mm per year. Simple painting with water-based façade, oil-based, alkyd paint or mastic of any brand will reliably protect the polyurethane foam and extend its service life to 25-30 years. If the polyurethane foam falls off the insulated surface, it means that it was applied to a damp, rusty or oily surface. If the surface is clean and dry, then the adhesion of polyurethane foam is from 1.5 to 2.5 kg/sq.cm, which is equal to the rate of gluing two smooth, grease-free surfaces using polyurethane glue.
5. PPU is a good insulation material, but expensive
Indeed, at first glance, insulation with polyurethane foam is more expensive than insulation with polystyrene foam or mineral wool. Let's try to figure it out. Firstly, usually, when calculating the costs associated with insulation, the costs of installing insulation are not taken into account, and this constitutes a significant part of the total cost when insulating with thermal insulation sheets (plates). PPU does not require installation; the price includes the entire range of work. Secondly, polyurethane foam does not require the use of moisture-wicking membranes, like sheet and roll insulation, because it does not have an air gap between the insulation and the surface, therefore, the dew point is inside the heat-insulating layer and condensation does not appear. Thirdly, the service life of polyurethane foam is disproportionately higher than that of other types of thermal insulation. It is generally accepted that heat losses of buildings and structures increase every year by an average of 6%. This is due to the loss of thermal insulation of its original properties. Over time, heat losses increase to 40 - 50% and even 60% of the original level, depending on the types of insulation. Polyurethane foam does not crumble, does not absorb moisture and does not allow condensation to appear, therefore it can be used for up to 50 years, and its properties after 50 years remain almost the same as at the beginning. Over time, PUF's intermolecular bonds weaken slightly, which only slightly changes the mechanical characteristics of PUF. Unfortunately, only a few are aware of this problem; for the majority it simply does not exist, i.e. it is not obvious. The presence of insulation inspires confidence, although in fact the effectiveness of such insulation drops by half after 6-10 years. If you follow the recommendations and change the insulation at least every 10 years, then the cost of polyurethane foam will be much lower, because PPU insulates once and almost forever. In one of the outskirts of London there is a factory where the walls and roof of one of the workshops were insulated with polyurethane foam back in 1957. This building is considered the first building in the world to use PPU thermal insulation. In 2005, the building was demolished. Experts from the BASF concern took the insulation for analysis and, after studying it, issued a short conclusion: “The mechanical and heat-insulating properties of polyurethane foam have remained virtually unchanged.” Imagine how many years have passed and how much the world has changed since 1957. And all these years, PPU has saved the plant owners a lot of money on heating costs - and this despite the fact that the lowest winter temperature in England is only minus 5 degrees Celsius.
«Dusty Mystery" Mineral wool.
“Mineral particles, which make up the bulk of house dust, were until recently considered its safest component,” says Nadezhda Logina. — These were mainly particles of local soil and universal dust formed by volcanoes and other geological disasters. But recently, the composition of mineral dust particles has begun to change, and components harmful to health appear among them. First, asbestos particles were detected, and now also mineral fibers - products of the decomposition of mineral wool. A lot of insulation materials are produced on its basis, and many even line the inside of the house with it, which should not be done under any circumstances: the mineral fibers formed during its decomposition go straight into the home. External ventilated facades, which are made today even for high-rise buildings in cities, are “dusted” with these fibers, and they enter apartments through ventilation and windows - in the summer, when they are open, this happens especially actively. Mineral fibers, like asbestos particles, remain in the lungs, contributing to the development of asthma, bronchitis and other inflammatory diseases of the respiratory system. We are already seeing such patients turning to doctors immediately after major repairs have been carried out in their homes. But most importantly, mineral fibers are officially recognized as carcinogens by the World Health Organization. It is no coincidence that mineral wool is banned for residential construction in many European countries. In addition, in the production of mineral wool, special resins are used, which, when evaporating, release carcinogens phenol and formaldehyde. Since these same substances are actively released from home furniture and other finishing materials, their concentration in homes can increase significantly. They are also harmful to the nervous system and cause irritation of the respiratory tract and mucous membranes.
Table 1. Technical characteristics of polyurethane foam
| Thermal insulator | Average density (kg/m3) | Thermal conductivity coefficient (W/m*K) | Porosity | Service life (years) | Operating temperature (°C) |
| PPU hard | 30-150 | 0,019-0,03 | Closed | 30 | -160..+150 |
| Cork board | 220-440 | 0,5-0,6 | Closed | 3 | -30..+90 |
| Expanded polystyrene | 40-150 | 0,04-0,06 | Closed | 15 | -100..+80 |
| Min. cotton wool | 55-150 | 0,052-0,058 | Open | 5 | -40..+120 |
| Foam concrete | 250-400 | 0,145-0,160 | Open | 10 | -30..+120 |
Table 2. Chemical resistance of polyurethane foam
| Chemical compound | PPU reaction |
| Sea water, soap suds | Racks |
| Benzene, toluene, xylene, gasoline, kerosene | Racks |
| Vegetable oils and animal fats | Racks |
| Methylene chloride, carbon tetrachloride | Swells |
| Alcohol, acetone, styrene, ethyl acetate | Swells |
| Concentrated hydrochloric acid | Swells |
| Concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids | Dissolves |
Table 3. Adhesion of polyurethane foam with some materials
| Aluminum | 1.0 kg/sq.cm |
| Steel | 1.5 kg/sq.cm |
| Wood (plywood) | 1.5 kg/sq.cm |
| Cast iron, galvanized iron | 2.0 kg/sq.cm |
| Concrete | 2.5 kg/sq.cm |
Table 4. Comparative characteristics of thermal insulation with polyurethane foam and mineral wool
| Indicators | Polyurethane foam (PPU) | Mineral wool |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | 0,019-0,03 | 0,034-0,045 |
| Coating thickness | 30-70 mm. | 120-220 mm. |
| Availability of fasteners | No | Yes |
| The need for vapor barrier | No | Yes |
| Presence of cold bridges | No | Yes |
| Water absorption | 1% | 10-15% |
| Shrinkage | No (dense polyurethane foam) | Yes |
| Effective service life | 25-30 years | 5 years |
| Moisture, aggressive environments | Stable | Properties are lost |
| Structure | Closed cell | Open cell |
| Fire safety | G2, G3, V3, D2, T3, GOST 12.1.044 (low-flammability) | G1, NG according to GOST 30244 |
| Ecological cleanliness | Safe. Approved for use in residential buildings by the Ministry of Health of the RSFSR No. 07/6-561 dated December 26, 1986 | Allergen |
| Actual heat loss | 1.7 times lower than standard SNiP 2.04.14-88 | Exceeding the normative SNiP after 12 months of operation. |
| Manufacturing jobs | From +5C to +30C | From +5C to +30C |
| Operating temperature, 0C | -150+120 | -70+250 |
Table 5. Comparative table of materials by coating thickness
| Polyurethane foam | 25 mm. |
| Expanded polystyrene | 45 mm. |
| Cork | 50 mm. |
| Mineral wool boards | 60 mm. |
| Tree | 140 mm. |
| Foam concrete | 250 mm. |
| Expanded clay concrete | 500 mm. |
| Brickwork | 650 mm. |
Advantages of polyurethane foam
The popularity of polyurethane foam is largely due to its advantages over other construction insulation materials.
Here are just a few of them: - Durability . Considering that the service life of polyurethane foam reaches 50 years, we can say with confidence that this is one of the most durable insulation materials.
— High adhesion . One of the most important qualities of this insulation is its excellent adhesion to any surface, be it wood, metal, brick, glass or concrete.

— Savings on fasteners . This material is fixed independently, without fasteners and adhesives, which significantly saves money on installation.
- Absence of “cold bridges”. A huge advantage of polyurethane foam is that the insulation is seamless. It has no joints, which means there are no “cold bridges” that other materials suffer from to preserve heat.
- Does not depend on temperatures. It is impossible not to note the resistance to high and low temperatures of this material. This may seem surprising, but polyurethane foam can withstand temperatures from -100°C to +100°C.
Important! Experiments show that the material in question has a high frost resistance (up to 1000 cycles). This means that once you foam all the cracks, frames and slopes, you will never need another insulation.
— Anti-corrosion protection. Here, again, the adhesive properties of polyurethane foam play a decisive role. Polyurethane foam adheres so tightly to metal surfaces that they gain reliable protection against corrosion for many years. And if necessary, the foam can be easily removed.
— Inertness to salts and acids. Expanded polystyrene is resistant to almost all known salts, alkalis and acids (not afraid of gasoline, alcohols, diluted acids and plasticizers). Thanks to this feature, polyurethane foam perfectly withstands exposure to aggressive environments.
- Environmentally friendly. PUF is made from synthetic materials, but in its finished form it is absolutely non-toxic, i.e. does not emit harmful compounds and does not emit odor.
Important! Polyurethane foam is also supported by the fact that manufacturers in all countries of the world, without exception, use the material in question to make food refrigerators.
- Fire resistance. From a fire safety point of view, solid polyurethane foam has no equal. PU foam does not burn, and even when it melts, it tends to self-extinguish. Thanks to this feature, such material is economically profitable to use in industrial premises with a high level of fire hazard.
- Lightness. An important advantage of polyurethane foam is that the insulation in question is extremely lightweight, and therefore does not weigh down the structure and does not require the construction of a more massive base.
— Soundproofing. The material in question boasts high soundproofing properties. In this indicator, polyurethane foam is superior to both mineral wool and foam concrete. PPU is ideal for insulating houses built near airports, busy highways and industrial enterprises.

— Low moisture absorption. Polyurethane foam practically does not absorb moisture, which means it does not allow mold and mildew to spread throughout the house. In terms of moisture resistance, polyurethane foam is superior to all known insulation materials. For example, the moisture resistance of foam concrete is 15-20%, while polyurethane foam is only 0.5-1.5%.
Important! Polyurethane foam is also unique in that it can be used to fill any hard-to-reach cracks and spaces that cannot be insulated with other materials. In this regard, PPU is indispensable.
Thermal conductivity indicators should be separately compared. This indicator of polyurethane foam is 0.02 W/m*K, while the thermal conductivity of mineral wool is 0.048 W/m*K, expanded clay concrete is 0.14 W/m*K, and reinforced concrete is 1.69 W/m* TO. In terms of thermal conductivity, polyurethane foam is second only to expanded clay and foam glass.
About the advantages of PPU
1. Polyurethane foam “sticks” perfectly to any materials, be it brick, glass, wood, concrete or metal. The shape of the surface and its deviation from straightness do not matter. Thanks to good adhesive properties, there is no need to be tricky with additional fasteners. By the way, there is no need to treat the surface with anything before spraying.

Polyurethane foam has excellent adhesion to almost all building materials.
2. This insulation is made directly on site, and the volume of initial components is minimal. Therefore, transport costs are low.
3. Polyurethane foam is incredibly lightweight; it does not weigh down the surface. This is very important when insulating a roof.
4. When applying a layer of polyurethane foam, we not only insulate the walls and partitions, but also make them more durable.
5. Polyurethane foam coating does not respond to warming and cooling throughout the year. It feels great at temperatures from minus 200 to plus 200 degrees Celsius.
6. Unlike panel and sheet insulation, this type of thermal insulation is a single whole that tightly fits the structure. There is no joint anywhere, not a small seam where the cold wind can blow.

You can install PPU anywhere and without the use of fasteners.
Disadvantages of polyurethane foam
Having chosen this material, it is worth studying its disadvantages. These include:
- Negative effects of sunlight. Polyurethane foam is destroyed under prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation. This means that if you want this wall insulation to serve you as long as possible, it must be hidden under the sheathing.
Important! Modern production of PPU panels has already resolved the issue of exposure to ultraviolet radiation by producing panels with a metal frame (a striking example is sandwich panels).
- Smolders under the influence of fire. We have already mentioned that polyurethane foam does not burn. However, its smoldering in an open flame affects the strength of the thermal insulation, and therefore this material should not be used for insulating baths and saunas. In addition, the release of harmful substances during smoldering polyurethane foam can affect health.
— Do not apply to wet surfaces. Polyurethane foam can only be applied to dry and warm surfaces. In this regard, use in winter on open construction sites is not allowed.
How safe is polyurethane foam?
Answering this important question, let’s say that in its finished form, PUF is completely harmless and does not emit toxic substances into the atmosphere. It is only important to protect yourself from foam particles when spraying it. In this regard, it is necessary to work with such material in a protective suit, gloves, a respirator and safety glasses, observing all safety measures. In addition, it is important to use properly maintained equipment and certified liquid polymers. Then there will be no questions about the safety of polyurethane foam.
About the disadvantages of PPU
This article is by no means an advertisement, so we will also list the negative properties of polyurethane foam. However, there are very few of them, more precisely, two.
1. The negative impact of ultraviolet radiation can lead to rapid wear of the material. In order to prevent destruction of the insulation, it is necessary to provide for its protection. Plaster, various panels or ordinary paint can serve in this capacity, which will not only protect from the sun, but will also make the surface of the polyurethane foam more attractive.
2. As already mentioned, polyurethane foams are considered low-flammability materials. According to the classification, they have a flammability group of G-2. This means that when exposed to high temperatures, fire will not occur, but the insulation will begin to smolder. This process will instantly stop as soon as the material is cooled. But where the surface heats up too much or may catch fire, polyurethane foam should not be used.
Tips and tricks from professionals
Despite the fact that polyurethane foam appeared on the Russian market relatively recently, professionals have managed to thoroughly study its properties and features of use.
They give some advice to novice masters:
- If a section of insulation is damaged, it must be cut out with a sharp knife and foamed again.
- To ensure that polyurethane foam lasts at least 30 years, it is protected from ultraviolet radiation. To do this, you can use polymer mastic or polyurea.
- For self-spraying PU foam on a small surface area, you can use disposable installations. Today they can be found in large construction stores. They will be much cheaper than professional equipment.
Polyurethane foam is a modern safe material with excellent thermal insulation properties. It is universal, suitable for processing any surface. Spraying polyurethane foam is a complex process, so it is better to entrust it to specialists.
Installation methods

Spraying a thermal insulating coating made of polyurethane foam is a fast and high-quality installation method. To successfully spray thermal insulation you need:
- Dry, clean work surface;
- Lack of precipitation (rain, snow, fog);
- Wind no stronger than 5 m/sec;
- Working surface temperature from +10°C;
- Mixture temperature +18-25оС;
- The thickness of the sprayed layer is 3-5 cm.
The work is carried out in a protective suit and mask, in a ventilated room, starting with hard-to-reach areas (pipes, ventilation hatches, etc.). The sprayed layer in one pass is about 15 mm; for reliable insulation, the surface is treated several times.
How to insulate yourself?
The process of wall insulation can be divided into two types: internal and external.
Internal
From the name it follows that the work is carried out indoors. Most often, corners, loggias or balconies are insulated.
Polyurethane foam allows you to treat even problem areas such as the bathroom and kitchen.
The material has good moisture-resistant properties. To eliminate hygroscopicity, a vapor barrier with a foil layer must be laid on top of the polyurethane foam, which should be located inside the room.
When insulating loggias or attics, polyurethane foam will help avoid heat losses and save heating costs.

Technology for insulating balconies and loggias
In order to insulate a small balcony or loggia, it does not require a lot of time and expense. Typically, these purposes require a standard set of tools and materials:
- aluminum profile for lathing (from any construction supermarket);
- self-tapping screws with dowels;
- drill;
- PPU components (it is better to purchase a ready-made set);
- dispenser gun - if you buy a ready-made kit, then the equipment is already in it;
- personal protective equipment – gloves, goggles, respirator;
- building level.

At the preparatory stage, the walls and ceiling are cleaned of old coating, peeling plaster and other debris. If there are deep cracks in the joints between walls or in corners, it is better to fill them with pieces of foam plastic and putty. There is no need to eliminate minor defects, since foam will handle this task.
The second stage is to install the sheathing. To do this, the profiles are attached along the walls at regular intervals, fastening them with perpendicular jumpers. Experts advise lathing all openings, windows and doors, around the entire perimeter. Next, you should cover all double-glazed windows, door panels and communications with polyethylene so as not to spoil them during the application of insulation.
The third stage is spraying. According to the instructions for the insulation components, the gun, supply hoses, and nozzles are assembled. The cylinders are shaken well before use. First of all, it is necessary to foam the cracks in the joints between the ceiling and walls, corners and process openings. A narrower nozzle is used for these purposes. Next, it is better to use a wider sprayer to evenly apply polyurethane foam to the surfaces of the ceiling and walls. In places with minor defects or unevenness, the insulation is applied in a thicker layer to level it out. After finishing the work, excess polyurethane foam must be removed from the sheathing.
The final stage is finishing. Drywall is attached to the sheathing if in the future you plan to paint the walls, cover them with plaster or wallpaper. Finishing using plastic or wooden panels is often practiced.
It must be remembered that in the case of plastering, it is necessary to strengthen the reinforcing fiberglass mesh before applying the finishing layer.
Basement
Damp basements are especially in dire need of insulation and waterproofing. Stages of work:
- The procedure for isolating a surface from excess moisture. To begin with, the floor is covered with roofing felt. It should be remembered that the sheets are laid overlapping; 20 centimeters are placed on the walls. To ensure high-quality tightness, the roofing material is coated with mastic around the perimeter; it is also better to do the same with the joints. In case of low humidity in the basement, the walls are also treated with mastic to a height of 10-15 cm from the floor. The screed will help prevent deformation of the protective coating.
- The application of polyurethane foam insulation begins from the corner to the exit. It is better to make 3-4 layers, clearly monitoring the level over the entire floor area.
- A concrete screed is evenly applied on top of the polyurethane foam. The rule is to equalize the thickness. The minimum permissible thickness is 5 cm.
- Finishing. After the screed has dried for at least two to three days, the floor is covered with tiles, panels, linoleum or any other material.
Attics and attics
Working with polyurethane foam insulation in the attic depends on the method of subsequent finishing.
- If the attic space, after insulation, is planned to be covered with eurolining or plasterboard, then the foam should be applied between the rafters. In this case, there is no need to cover the floor beams with waterproofing, antiseptic or primer.
- If the finishing involves decorative plaster, then polyurethane foam should be applied to all surfaces, including beams.
You need to start work with the joints and seams between the walls and roof. It is important to monitor the uniformity of the insulation layer. It is convenient that finishing can be started in a short amount of time, since the insulation hardens almost instantly.
External
External insulation of the facade of a building allows not only to retain heat, but also to avoid dampness, mold, and other harmful microorganisms.
For outdoor work, self-foaming modifications of polyurethane foam are most often used. They are applied evenly, without seams, filling all defects and unevenness of the walls. In addition, the material has excellent adhesion and is suitable for insulating both a wooden house and structures made of concrete and brick. PPU hardens quickly.
Due to the fear of sunlight, it must be covered with a finishing decorative and protective layer.
There are two ways to insulate a roof or walls with polyurethane foam, depending on the type of insulation used:
- Using polyurethane foam with an elastic structure. The plastic material has a porous structure and is characterized by low density. In this regard, such insulation makes it possible to insulate the roof while simultaneously providing sound insulation.
- Using hard polyurethane foam. The material is most common in construction because it has a high density.
This results in the following performance characteristics:
- moisture resistance – protection of the roof from water;
- resistance to deformation, thanks to which the insulation can withstand significant loads;
- the light weight of polyurethane foam reduces the overall load on the foundation;
- ease of installation - thermal insulation does not require disassembly of structures or additional preparation.
When constructing private houses, the first method is more often used; when insulating large structures, the second method is used.

The main stages of applying polyurethane when insulating a low-rise building with your own hands:
- Cleaning the base and eliminating major defects on it. At this stage, it is necessary to clean the walls, necessary areas of the floor or ceiling from dust, old coating and various dirt. The procedure will improve the adhesion of polyurethane foam to the surface. At the same time, experts note that it is not necessary to level the bases.
- Application of a polyurethane foam layer using special equipment. Spraying is carried out on cleaned substrates. The thickness of the polyurethane foam layer will depend on several factors. Less material will be needed on leveled surfaces. The type of insulated floors themselves will also affect. A preliminary calculation of heat loss will help you avoid unnecessary costs by providing the necessary protection.
- Reinforcement with a special screed. As a rule, fiberglass mesh with small holes is used as reinforcement. Professionals advise not to lay a reinforcing layer less than 6 cm.
- Finishing. To protect polyurethane foam insulation, you can use any materials: brick, plaster, artificial or natural stone, facade paint, siding and others.
Large companies working in the construction of large buildings and structures often use rigid polyurethane foam. This reduces time and financial costs.
In addition, it is economically profitable to cover the insulation of a hangar, warehouse or high-rise building with just such polyurethane foam, since it is more durable, faster to apply, and does not require additional costs for leveling the walls.
You can apply polyurethane foam using two methods:
- Spraying. The process takes place using special equipment in the form of a gun, into which two components and water are supplied. A chemical reaction occurs, the result is polyurethane foam, which lies in an even layer on the open surface.
- Filling. In this case, the components are mixed in advance and the resulting mixture is poured into the hole. The method is suitable for closed and hard-to-reach places, complex architectural forms (niches, arches, various projections, corners, columns), old buildings.
Application conditions and surface preparation
Even with good adhesion, which is characteristic of polyurethane foam insulation, surface preparation will not be superfluous. First of all, you need to remove everything that is crumbling - and first of all the old paint. Grease stains must also be removed and neutralized. They shouldn't exist.

Polyurethane foam is applied to dry, grease-free surfaces
Everything that should not be covered with foam should be covered with polyethylene secured with tape. It must be secured carefully, without gaps - it is difficult to remove the foam.
When insulating a roof with polyurethane foam, there are two ways to apply thermal insulation. The first is to make a permanent continuous sheathing onto which foam is poured. The second is to make a temporary frame consisting of two parallel planes.
If the outer walls of a building are insulated with polyurethane foam, a finishing finish is assumed. And after cleaning the surface, you need to make sure that you can strengthen it with something - it won’t work with foam. To do this, most often, wooden or metal strips are placed on the walls, to which the exterior trim is then attached. This completes the preparation. But applying polyurethane foam is only possible on a completely dry surface, at temperatures above +10°C. There are no other conditions.
Polyurethane foam insulation technology
There are two methods of insulation using this material:
- Spray insulation;
- Pouring polyurethane foam.
Let's consider the features of these processes.
Insulation by spraying polyurethane foam
The simplest, and at the same time the most common way to work with polyurethane foam is spraying. To apply the foam, a spray gun is used, in which the main ingredients (isocyanate and polyol) are mixed with air.

Applying polyurethane foam in this way is very similar to spray painting, because an operator with a spray gun sprays yellowish foam in an even layer onto the desired surface (floor, wall, ceiling or pipe), without missing a single centimeter of the surface. The main reaction begins after the liquid mixture hits the surface. Under the influence of air, a chemical reaction begins in liquid polymers with the release of heat and carbon dioxide, which provokes abundant foaming of the material and filling of all voids with foam.
Comparing with other methods, we can highlight a number of advantages that spraying polyurethane foam has:
- due to the ideal filling of all cracks and penetration of foam into hard-to-reach places, the appearance of a dew point is eliminated, which means a place where moisture collects;
- a layer of polyurethane foam leaves no joints or seams, which means it eliminates heat loss through possible breaks in the insulation;
- in terms of its ability to adhere to surfaces on which liquid polyurethane foam is applied, this material is comparable, perhaps, to professional construction adhesive;
- Cooling of the material occurs gradually, thereby eliminating cracks and tears that could affect the material’s ability to retain heat.
It should be noted that despite its apparent simplicity, working with spraying polyurethane foam has a number of subtleties that only experienced specialists know. Practice shows that producing high-quality polyurethane foam spraying the first time is a difficult task, and therefore it is better to entrust this work to professionals.
Important! In Europe, polyurethane foam spraying operators are classified as highly qualified workers, each of whom completes 1.5 year courses in this specialty. Therefore, when hiring a contractor to insulate your own home, be sure to inquire about his qualifications, and do not hesitate to look at the documents on completion of the courses.
Pouring the insulation of the structure with polyurethane foam
In the case when two ingredients are mixed without access to air, the mixture turns out mushy, which means smooth and dense. With such a mixture you can easily fill the niches between the load-bearing wall and the facade of the building; you can pour the mixture under the subfloor, under the roof, or into any other limited cavity. 20-25 minutes after pouring, the material will increase in volume and fill the entire space.
By the way, this technology allows you to pour polyurethane foam into three-dimensional forms and obtain products of any configuration. This is how you get:
- sandwich panels, as well as thermal panels and panels with cladding;
- heat-insulating shells for pipes;
- beehives;
- decorative interior elements (stucco molding, baguettes);
- elements of refrigeration chambers;
- elements of air ducts and ventilation systems.
By the way, facade panels with clinker tiles are produced on the basis of polyurethane foam. The polyurethane foam panel here serves as insulation, and the clinker tiles exactly replicate the noble clinker stone.
Let's just say that pouring polyurethane foam is a process no less complex than spraying foam. Without experience, it is incredibly difficult to carry out this filling efficiently. The operator must not fill the niche completely, and make the mixture not too dense, so that when expanding, it fills the entire internal space, but does not damage the outer cladding. The point is that it is not possible to visually check the result of filling, and all inaccuracies in the work will “come out” later, during the operation of the house.
List of materials for utility networks:
| Steel pipes in polyurethane foam insulation (PPU pipes) with an outer polyethylene sheath with an ODK (Operational Remote Control) system with a pipe diameter of 15-720 mm with an outer sheath diameter of 100-900 mm. |
| Steel pipes in polyurethane foam insulation (PPU pipes) with an outer shell of galvanized steel with a pipe diameter of 15-720 mm and an outer shell diameter of 100-900 mm. |
| Steel bends in polyurethane foam (polyurethane foam insulation) /30 o, 45 o, 60 o, 90 o/, tees in polyurethane foam, transitions, pipe elements for fixed supports, end elements. |
| Supports for pipelines: NShchO fixed reinforced concrete 2-pipe panel with polyurethane foam insulation and movable sliding clamps. |
| Reinforced concrete components for heating mains: non-passing channels KN-1, KN-2, KN-3, KN-4, KN-5, KN-6, KN-7, trays, floor slabs, support pads OP-1, OP-2, OP-3, OP-4, thermal chambers. |
| KSO bellows expansion joints , SKFT units in polyurethane foam insulation . |
| Thermal tape (heat-shrinkable tape) , cuffs and PPU shells for insulating pipeline joints without coating and foil, kits for sealing KZS joints (heat-shrinkable sleeve + mounting foam package, brackets for ODK), galvanized protective casings. |
| Bitumen-rubber mastic MBRKh, MBRG for waterproofing and corrosion protection of pipeline connections. |
Pre-insulated PPU pipes are divided into:
1) according to the material of the outer shell of polyurethane foam insulation into two types:
- in a galvanized shell (for networks laid externally by “air” method)
- in a polyethylene sheath (for networks laid underground)
2) according to the thickness of the polyurethane foam insulation into two types:
- type 1 ordinary (for areas with temperate climates)
- type 2 reinforced (for areas with cold climates)
In St. Petersburg, type 1 is usually used, in the Leningrad Region and the North-West of the Russian Federation - type 2.
Insulated PPU timber
Let’s talk separately about a new product that has gained enormous popularity in Europe today. It consists of two lamellas, between which a layer of polyurethane foam is poured. Foaming, polyurethane foam glues the boards together, creating an imitation of real laminated veneer lumber.
Practice shows that a structure assembled from two lamellas and fasteners in the form of polyurethane foam is no different in appearance from a wall made of laminated veneer lumber, but in terms of characteristics, it is many times superior to it. Insulated PPU timber is three times lighter, cheaper and warmer than solid wood. The internal filling of the wall made of polyurethane foam enhances the thermal insulation properties of the timber, and the house does not require additional insulation, which saves money on heating.
Having familiarized yourself with the advantages and disadvantages of polyurethane foam, having considered the types and technology of applying the material, it will be easier for you to make the right choice in terms of insulating your home and soundproofing it. Make the right choice, and your home will delight you with warmth and comfort for many years!