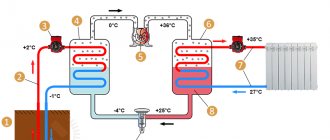
Water and antifreeze: pros and cons
The debate about which is better - ordinary water or antifreeze liquids for water heating systems - lasts approximately as long as the antifreezes themselves are used. And although there is no consensus on this matter even among recognized experts, the list of arguments has been compiled quite detailed.
Standard coolant packaging
To make it easier for you to familiarize yourself with them, we have presented them in table form:
| Advantages | Flaws | |
| Water |
|
|
| Antifreeze liquid |
|
|

The photo shows the consequences of freezing water in the battery
As can be seen from the table, non-freezing liquids for heating systems have both advantages and disadvantages. And if you still decide to use such tools, we recommend that you carefully study the following sections.
What is antifreeze for?
As we said earlier, inhibitors are added to heating fluids, which can affect the following qualities:
- Corrosion.
- Acid-base properties.
- Formation of deposits on the walls.
- Foaminess.
All these parameters are very important to ensure that your heating system lasts for more than a year or two. Therefore, when choosing antifreezes, take into account these qualities; they must comply with GOSTs.
For example, when such a liquid is used in equipment with high temperatures and high pressure, it is important to take into account the foaming index and scale index. Of course, if you don’t want to start renovations at your home in the near future and reconsider the heating system as a whole
The photo shows an example of what can happen if you are careless about this issue.

Such deposits on the pipe walls will lead to expensive repairs of the entire system.
Characteristics and properties of antifreeze
An important nuance of antifreeze is the presence of components such as inhibitors. Such elements affect the fragility of polymers, for example, in pipes such as polyethylene.
There are other nuances that may cause inconvenience in using a coolant such as anti-freeze for heating:
Compared to water, a coolant such as an anti-freeze agent in a home heating system heats up more slowly and also does not accumulate heat as effectively. In order to use antifreeze as a coolant, you will have to install a fairly powerful boiler into the system. This will entail not only the initial financial investment, but also the cost of purchasing fuel. Antifreeze liquid for heating systems has a higher viscosity compared to water
For antifreeze you will have to install a circulation pump with more power. Antifreeze has a higher ductility, so special attention should be paid to sealing various butt joints during installation.

Technical characteristics of antifreeze
Do not forget that antifreeze for the heating system must be diluted with water. The percentage of coolant directly depends on the freezing point of the antifreeze.
The amount of water added also plays an important role. Manufacturers recommend using water for dilution with a hardness value of no more than 6 units.
If non-freezing coolant for heating systems is diluted with too hard water, this can lead to the formation of sediment. Such an unpleasant factor can affect the efficiency of the heating system, and can cause a breakdown of one of the components of the heating system.
If we compare price categories, antifreeze in a home heating system will cost more than water. The financial side of the issue, as reviews show, also plays an important role in the process of organizing a heating system.
Most emergencies in heating systems in winter arise due to initially incorrectly selected coolant and the owner’s desire to save money on its purchase. As a rule, having decided to buy an antifreeze liquid for the heating system of private houses, the owners do not spend a lot of time searching for a suitable product, but purchase the first composition they come across on the market that has a suitable freezing point and a more or less affordable price.
But this approach to the issue of choice promises many troubles in the future. Of course, after the equipment stops functioning, the perplexed owner will still turn to a specialized company whose specialists are able to solve the problem. However, such requests are often belated - after all, additional funds have to be spent on restoring the functionality of the heat supply system, the size of which is not even comparable to the cost of the most expensive imported coolant.
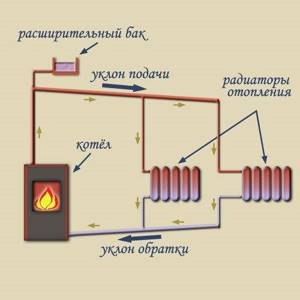
How to fill the coolant into the system
If you have a heating system with natural circulation, then the coolant must be placed in an expansion tank, which is best placed slightly above the highest point of the system and connected with a strong hose.
There are two main points to consider here:
- Release the air (check all installed valves, but if you use float valves that release air automatically, then simply monitor the filling);
- Make sure that the container is not empty, because then an air lock will form in the system and the liquid will have to be drained again.
Thus, if ordinary taps are used, then it is better to fill it together - one person makes sure that the container is filled all the time, and the second checks the taps. If you have automatic taps, you can pour liquid into the structure yourself.
If you operate an installation with forced circulation, then the coolant must be supplied under pressure using a pump with a bottom water intake. Connect a strong hose to it and secure it well at the joints. Place it in a container with antifreeze and turn on the pump.
There are also nuances here:
- Since the pump empties the container quite quickly, you must ensure that it is filled to avoid the formation of an air lock;
- Monitor the pressure in the system (so that it does not rise above 2-3 atmospheres), turn off the pump in time;
Before pumping in antifreeze, it is better to fill the installation with water a day in advance to make sure it is tight. Detecting a leak after the “anti-freeze” is in the system is undesirable, since it is toxic and can get into the living room. Yes, and draining the liquid to troubleshoot problems is problematic.
If water was previously used for heating, then you should definitely pay attention to the fact that it has greater expansion properties than antifreeze. And before using them, it is necessary to change all seals at the joints to avoid leaks
It is also worth considering that it will not be possible to drain all the water from the system, and then additional dilution of the antifreeze will occur. To avoid loss of density, you need to mix the antifreeze solution with the concentrate approximately 1:1.
Antifreeze liquids are not used if:
- You have galvanized pipes installed. This will entail chemical reactions resulting in the formation of a lot of salt deposits, which will block the operation of the heating system;
- They are made on an ethylene glycol basis, and you are using a double-circuit boiler. In this case, it is possible that antifreeze from the heating cycle may enter the water supply circuit, and this is dangerous to human health.
- You have an open heating system, since the antifreeze may evaporate, and its vapors are toxic.
How to make anti-freeze: main points
Whatever composition you prepare, it should:
- clean the windshield from dirt and ice;
- remain liquid at subzero temperatures;
- be safe for both humans and machine parts.
That's all, perhaps, nothing more is required from the washer.
As a rule, the base of non-freezing liquid includes ordinary distilled water, alcohol and some additives for fragrance, coloring and improving cleaning properties. Among the alcohols used in production are methyl, ethyl and isopropyl.
Methyl alcohol is harmful to health, so anti-freeze products based on it are prohibited in Russia. And even if you have a canister of this substance lying around somewhere in your garage, you should not pour it into your car.
Isopropyl alcohol is extremely rare among people; this technical liquid has a pungent odor. You can ask someone who repairs and cleans office equipment at home. True, such a master usually doesn’t have more than half a liter in stock. And by the way, it costs much more than ethanol.
Ethyl alcohol is the most affordable option. Many people have a bottle of medical, technical or even food grade ethanol at home. However, no one has canceled our favorite vodka either, because in essence it is an aqueous solution of ethyl alcohol.
To make anti-freeze in the washer at home, many also use salt, acids, and detergents. But first things first.
Methods for filling the system with coolant
The issue of filling usually arises only in the case of a closed-type system, since open circuits can be filled without problems through an expansion tank. Coolant is simply poured into it, which, under the influence of gravity, spreads along all contours
It is important that all air vents are open
There are several methods for filling a closed heating system with coolant: by gravity, with a submersible pump or using special pressure testing equipment. Let's look at each method in more detail.
By gravity. Although this method of pumping coolant for a heating system does not require equipment, it takes a lot of time. You have to squeeze out the air for a long time and also gain the required pressure for a long time. By the way, it is pumped up with a car pump. So you will still need equipment.
You need to find the highest point. Usually, this is one of the gas vents (it needs to be removed). When filling, open the tap to drain the coolant (lowest point). When water runs through it, the system is full:
- When the system is full (water runs out of the drain tap), take a rubber hose about 1.5 meters long and attach it to the entrance to the system.
- Select the inlet so that the pressure gauge is visible. Install a check valve and ball valve at this point.
- Attach an easily removable adapter for connecting a car pump to the free end of the hose.
- After removing the adapter, pour coolant into the hose (keep it up).
- After filling the hose, use an adapter to connect the pump, open the ball valve and pump liquid into the system. You need to make sure that air is not pumped in.
- When almost all the water contained in the hose has been pumped in, the tap is closed and the operation is repeated.
- On small systems, to get 1.5 Bar, you will have to repeat it 5-7 times, with larger ones you will have to tinker longer.
With this method, you can connect a hose from the water supply, you can pour prepared water into a barrel, raise it above the entry point and then pour it into the system. Antifreeze is also added, but when working with ethylene glycol you will need a respirator, protective rubber gloves and clothing. If the substance gets on fabric or other material, it also becomes toxic and must be destroyed.
Using a submersible pump. To create working pressure, the coolant for the heating system can be pumped with a low-power submersible pump:
- The pump must be connected to the lowest point (not the system drain point) through a ball valve and a check valve; a ball valve must be installed at the system drain point.
- Pour coolant into the container, lower the pump, and turn it on. During operation, constantly add coolant - the pump should not drive air.
- Keep an eye on the pressure gauge during the process. As soon as its needle moves from the zero mark, the system is full. Until this point, manual air vents on radiators can be opened and air will escape through them. As soon as the system is full, they must be closed.
- Next, you need to increase the pressure while continuing to pump the coolant for the heating system with the pump. When it reaches the required level, stop the pump and close the ball valve
- Open all air vents (on radiators too). The air comes out, the pressure drops.
- Turn on the pump again, pump up a little coolant until the pressure reaches the design value. Bleed the air again.
- Repeat this until air stops coming out of their air vents.
Next, you can start the circulation pump and bleed the air again. If the pressure remains within normal limits, the coolant for the heating system is pumped. You can put it to work.
Pressure testing pump. The system is filled in the same way as in the case described above. In this case, a special pump is used. It is usually manual, with a container into which the coolant for the heating system is poured. From this container, liquid is pumped through a hose into the system.
When the system is filled, the lever moves more or less easily, but when the pressure rises, it becomes more difficult to work. There is a pressure gauge both on the pump and in the system. You can follow where it is more convenient.
Next, the sequence is the same as described above: pump up to the required pressure, deflate the air, repeat again. Do this until there is no air left in the system. After that, you also need to start the circulation pump for about five minutes and bleed off the air. Repeat this several times.
Which pipe should I pour antifreeze through?
This is what the feed tap looks like
Before you get started, you need to know how to fill your heating system with antifreeze. There are two types of heating circuits. In one, the coolant is in contact with air, and in the other, circulation takes place in a completely closed circuit. The operating principle of these circuits is different, but they are united by the fact that antifreeze can be used in both. To pour antifreeze into the heating circuit you will need a pump. Coolant can be poured into open circuits in buckets, but in the case of non-freezing liquid this will take too long.
Antifreeze is poured into the heating system, in theory, through a make-up valve, if one is available. If it is not there, then the following options are possible:
- through the battery plug;
- through a pipe under a closed expansion tank;
- through the boiler.
To fill the heating circuit with antifreeze through the radiator plug, you need to unscrew it and screw in a tap instead.
A pump is connected to this tap, thanks to which antifreeze enters the pipes. After filling the heating system with antifreeze is completed, the tap remains at the end of the battery. This will allow you to recharge the system during operation, as well as use it as a drain when you need to empty the circuit of coolant.
In closed circuits there is a membrane expansion tank, for which there is a separate pipe. When the system is full, it is recommended to temporarily remove the expansion chamber. Is it possible to fill the heating system with antifreeze when the tank is not removed? It’s possible, but most likely, after this the expanzomat will still have to be removed and reconfigured. The expansion tank is installed both up and down.
The second method is more preferable, and the valve is installed on the pipe in different ways. Some installers install American valves with a tap in such a way that the shut-off valves remain on the circuit, while some, on the contrary, install them in such a way that the tap is removed together in the expansion chamber.
Antifreeze (propylene glycol liquid)
Non-toxic varieties of antifreeze have been known for only a couple of decades. They are made from propylene glycol and are almost completely harmless to humans. Thanks to this quality, propylene glycol liquids will be the best option for a double-circuit system in a private home. They are easy to fill with your own hands.
According to the instructions, such compounds can be used until the outside temperature reaches -35 degrees; at a lower level, antifreeze can freeze.
The harmlessness of propylene glycol is proven by the fact that this material is included in the list of approved food additives as E1520 and is often found in confectionery products, where it is used to soften and retain moisture. At the same time, propylene glycol antifreeze may also contain quite dangerous substances - additives that can affect the heating system.
They are necessary to avoid foaming or oxidation of pipelines and radiators, but make the liquid dangerous for people. Antifreeze for heating of this type is identified thanks to the green dye specially added to it.
Disadvantages of Propylene Glycol
The disadvantage of propylene glycol-based antifreeze is its relatively high cost. Moreover, its density is less than that of ethylene glycol coolant, and its thermal conductivity is worse. Therefore, such non-freezing liquid is used very rarely in heating systems of apartments or houses.
Types of non-freezing liquids
The modern antifreeze market is replete with a variety of these specific products. The range of formulations is very wide due to increased demand.
Antifreeze is based on various chemical compounds:
- ethylene glycol;
- propylene glycol;
- glycerol;
- bischofite solution;
- saline solution
The most popular household antifreezes are water-based with a solution of glycerin, ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. Since these compounds have a high degree of aggressiveness, additional substances - additives - are added to them to prevent corrosion, the formation of foam and scale inside the circuit.
Let's look at the most common types of low-freezing liquids in more detail:
- Ethylene glycol compounds are the most used, and they have the lowest cost. However, few people think about their highest toxicity. Ethylene glycol is prohibited from being used in dual-circuit systems, as there is a high probability that the mixture will enter the water supply, causing harm to human health. When the coolant temperature rises above 110 degrees, the substance forms a sediment that can damage some parts of the heating line.
- Propylene glycol liquids have similar properties, but they are not harmful or dangerous to human health and heating system elements. Experts recommend pouring propylene glycol into the circuit.
- Glycerin substances also have zero toxicity and are completely environmentally friendly; they provide maximum protection for pipes, boilers and radiators from corrosive processes. Glycerin does not increase in volume when it becomes a solid composition, and to restart the heating processes it is only necessary to heat it.
- Bishofite solutions are produced on the basis of natural materials and have unique physical and chemical properties. Bischofite antifreeze perfectly tolerates high boiling temperatures, low freezing temperatures, and has greater heat transfer and thermal capacity than water, which is not typical for the vast majority of antifreeze products.
- Salt anti-freeze products are made on the basis of various mineral salts and their compounds. A significant disadvantage of compositions made of magnesium, calcium and sodium is the high degree of corrosion processes in pipelines and heating equipment.
Low-freezing liquid for heating a private home is sold in two forms - diluted mixtures ready for pouring (for temperatures from -20 to -25 degrees) or a concentrate that needs to be diluted with your own hands. For temperatures down to -30 degrees, the concentrate is diluted in a ratio of 9:1, for freezing down to -65 degrees - in a ratio of 6:4.

Calculation of fluid in the heating system
To purchase the required amount of “anti-freeze”, you must first set the capacity of the heating system as accurately as possible. This procedure is simple, but time-consuming. It is necessary to measure the lengths of all lines and connections to the batteries, distributing them by diameter. Then, for each diameter, calculate the flow area (using the formula for the area of a circle) and multiply the result by the length of the pipe.
Having calculated the volume of liquid in the pipelines, the volume of water contained in the radiators and boiler must be added to the result obtained. This data is available in the technical data sheets for the products. Well, then, when purchasing antifreeze, recalculate the entire volume taking into account dilution with water. The ratio of liquid and water for different temperatures is indicated in the instructions on the manufacturer's packaging.

Instructions for use
If your system previously ran on water, switching to antifreeze will not be easy. Theoretically, radiators with a boiler can be emptied and filled with cold-resistant coolant, but in practice the following will happen:
Addition. After filling the liquid, the old connections sealed with flax and paint are guaranteed to flow.
In order for heating to function normally using a chemical coolant, you need to calculate in advance or remake the existing system according to the new requirements:
- Select the capacity of the expansion tank at the rate of 15% of the total volume of liquid (water was 10%);
- The pump performance is assumed to be 10% more, and the generated pressure is assumed to be 50% more. Let us explain with an example: if previously there was a unit with a working pressure of 0.4 Bar (4 meters of water column), then use a 0.6 Bar pump for antifreeze.
- In order to operate the boiler in optimal mode and not raise the temperature of the coolant, it is advisable to add 1-3 (depending on power) sections to each battery.

- Pack all joints with dry flax or use high-quality pastes - sealants such as LOCTITE, ABRO or Hermesil.
- When purchasing shut-off and control valves, consult with the seller about the resistance of rubber seals to glycol mixtures.
- Pressure test the system again by filling the pipes and heating equipment with water.
- When starting the boiler unit at negative temperatures, set the minimum power. Cold antifreeze needs to be warmed up slowly.
Advice. The total amount of coolant is easy to calculate - the cross-sectional area of the pipe is multiplied by its length, the capacity of the boiler and radiators is indicated in the product data sheets. Find out how to properly place and connect the expansion tank in our separate publication.
The concentrated coolant must be diluted with water, ideally with distillate. Do not rely on an excessive reserve of frost resistance - the more water you add, the better the heating will work. Recommendations for preparing coolant:
- For heating elements, electric and gas double-circuit heat generators, prepare the mixture at minus 20 degrees. A more concentrated solution may foam upon contact with the heater, and carbon deposits will form on the surface of the heating element.
- In other cases, mix the components at freezing point according to the table below. Proportions are indicated per 100 liters of coolant.
- If there is no distillate, first conduct an experiment - dilute the concentrate in a jar with plain water. If you see a precipitate of white flakes - a product of the decomposition of inhibitors and additives, this water should not be used.
- A similar check is done before mixing antifreeze from two different manufacturers. It is unacceptable to dilute ethylene glycol with propylene composition.
- Prepare the coolant immediately before pouring.
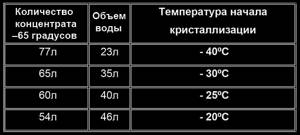
To find out the amount of ingredients for a volume of 150 liters, multiply the given figures by a factor of 1.5. The maximum service life of any non-freezing substance in pipes and heating radiators is 5 years. At the end of the specified period, the liquid is drained, the system is flushed twice and filled with fresh antifreeze.
Selection of coolant by heating type
Some will decide to use ethylene glycol as a coolant. This liquid is dangerous when exchanged between several coolants. Why? Ethylene glycol is not recommended for use in boilers with two circuits, since any damage to the exchanger wall will immediately lead to negative consequences. It also cannot be used in systems that use an opening type with an expansion tank.
Today, a large number of antifreezes are based on ethylene glycol. At the same time, its price is quite low. It is also distinguished by its ability to have good thermophysical properties. Its freezing point ranges from -35°C to -65°C depending on the concentration.
Antifreeze based on propylene glycol has great advantages because it is non-toxic. Therefore, it is allowed for use as a coolant for heating systems. Propylene glycol has a low crystallization temperature - -40°C. For example, Gulfstream antifreeze is produced on the basis of propylene glycol, as well as glycerin.
Its positive properties are as follows:
- Eco-friendly.
- High physical characteristics.
- Low freezing point.
But, despite all these advantages, not everyone can afford to buy it due to the high price. That is why some refuse to use it and look for alternative sources of coolant.
An alternative circulating fluid may be water containing ethyl alcohol (40-55% alcohol). This solution crystallizes at -30°C. The use of this antifreeze is limited only to a closed system, which is equipped with forced circulation. If you use it with an open system, the alcohol will evaporate very quickly. Moreover, a clear disadvantage is the low boiling point, which ranges from 85°-90°. Most heating heaters heat the liquid to 95° and under such circumstances, water with ethyl alcohol is not suitable. Moreover, if automation is used, which regulates the air temperature, but not the temperature of the coolant in the heating system.
Choosing an “anti-freeze” for heating
Tip number one: buy and fill in antifreeze only in extreme cases - for periodic heating of remote country houses, garages or buildings under construction. Try to use water - regular and distilled, this is the least troublesome option.
When choosing a frost-resistant coolant, follow the following recommendations:
- If your budget is limited, take ethylene glycol from any well-known brand - “Teply Dom”, Dixis, Spektrogen Teplo Coolant, Bautherm, Termo Tactic or “Thermagent”. The cost of the concentrate -65 °C from Dixis is only 1.3 USD. e. (90 rubles) per 1 kg.
- If there is a danger of antifreeze getting into household water (for example, through an indirect heating boiler, double-circuit boiler), or you are very concerned about the environment and safety, buy harmless propylene glycol. But keep in mind: the price of the chemical is higher; a ready-made Dixis solution (minus 30 degrees) will cost 100 rubles (1.45 USD) per kilogram.
- For large heating systems, we recommend using premium class HNT coolant. The liquid is made on the basis of propylene glycol, but it has an increased service life of 15 years.
- Do not buy glycerin solutions at all. Reasons: sedimentation in the system, too high viscosity, tendency to foam, a large number of low-quality products made from technical glycerin.

In the light of the flashlight, tiny white flakes are visible - a sediment of technical glycerin
- Electrode boilers require a special liquid, for example, HNT-35. Before use, be sure to consult with a representative of the manufacturer.
- Do not confuse automobile antifreezes with chemicals used in heating systems. Yes, both formulations are glycol-based, but the additive packages are completely different. Engine coolant is not compatible with residential water heating.
- For open and gravity-flow heating systems, it is better to use water, or, in extreme cases, propylene glycol diluted at minus 20 °C.
- If the heating distribution is made with galvanized pipes, there is no point in purchasing glycol mixtures. The substance will deal with zinc, lose the package of additives and quickly degrade.
Clarification. It is not profitable to use frost-resistant liquid for an open heating system. Hot antifreeze will evaporate into the atmosphere through the expansion tank, the antifreeze will have to be constantly topped up, and money will be spent. It is unacceptable to pump in ethylene glycol, since its vapors are toxic.
There is a lot of debate about the harmfulness of ethylene glycol compounds, including on the pages of construction forums. Without denying the harmful effects of the chemical on human health, let us draw attention to a convincing fact.
Homeowners whose closed systems are installed well have been using inexpensive glycol for years without any problems. Let's listen to the expert's opinion in the video:
Recommendations from experts
- Antifreeze is best used in house systems that are rarely visited in winter and the system does not work for most of the time.
- It is necessary to use equipment that is designed to work with antifreeze.
- The power of radiators should be 30-40% greater than that of conventional ones.
- Due to the high level of antifreeze viscosity, pumps must be used with enhanced hydraulics.
- In the case when it is necessary to make a solution from a concentrate, only distilled water should be used.
- You cannot mix different types of antifreeze; it is best to use one. But in the case when this is the only way out, it is recommended to mix them in a container and observe the precipitation.
- The use of automobile antifreeze for heating systems is not allowed, due to the fact that it contains elements whose use in residential buildings is unacceptable.
- A concentrate whose freezing threshold is -65°C cannot be used in its pure form, as this may cause overheating of the heat exchanger and decomposition of additives.
- And if you use a solution whose freezing point is not higher than -25 ° C, and the temperature has dropped below (which is quite unlikely), then there is no need to worry. The heating installation will not be damaged at all. The antifreeze will thicken, and as soon as the temperature rises to a certain value it will return to its original state without any loss of its properties.
- In order to prevent leaks at the sealing joints, you can use automotive sealant.
To summarize, I would like to note that there are different types of coolants. Before purchasing antifreeze for a heating system, you should consider a number of points: the material from which the pipes and radiators are made, the conditions of use and the possibility of periodic maintenance. The choice is also influenced by the financial side of the issue.
Thus, everyone can afford imported antifreeze for heating systems, the cost of which is much higher than ordinary distilled water. In this case, a high-quality domestically produced product is recommended. It must be remembered that the system requires timely flushing. This directly affects its efficiency and long-term operation.
When can't you use anti-freeze?
Despite the large number of advantages, not every antifreeze can be used for heating boilers. Improper operation can, over time, cause destruction of the heat exchanger and rapid breakdown of expensive equipment.
In addition, there are some other restrictions that must be remembered when using antifreeze for heating systems.
Antifreeze must not be used if:
- The system uses galvanized pipes. This can lead to chemical reactions that create a large amount of salt deposits that block the operation of the heating system.
- The antifreeze is based on ethylene glycol, and the system uses a double-circuit boiler. In this case, there is a high probability of antifreeze from the heating system getting into the water supply circuit, which is harmful to human health.
- The heating system is an open type, so there is a possibility of evaporation of the “anti-freeze”, and these fumes are quite toxic and can cause serious harm to health.
Antifreeze concentrate should only be diluted with distilled water. Ordinary running water is not suitable for these purposes - due to the large number of third-party elements, an undesirable chemical reaction can be caused.
Features when starting the heating system
Different compositions of solutions affect the operation of the heating system. Thus, the presence of ethylene glycol affects the initial stage of system startup. The heating process must be started at low power, then gradually increased to the required level. This method will reduce the toxic effects of this substance.
A product based on propylene glycol does not require such adjustments when starting heating equipment.
When all the requirements are met, then there is no need to be afraid of using “anti-freeze” as a coolant. It will solve a lot of problems if used skillfully.
Prices for non-freezing liquid vary, and so does the quality. The policy here should be this: when it is not possible to buy a good product, it is better to stick with water. In this case, you must ensure that the coolant is drained from the system before the onset of frost, or turn on the heating devices on time.
Water or anti-freeze?
Water is the standard, most accessible and widespread coolant for a heating system. Most heating equipment is designed to use water. It is inexpensive, environmentally friendly and completely non-toxic liquid. Even if a breakthrough occurs or a leak forms, nothing threatens human health.
At the same time, there are disadvantages to long-term use of water:
- If the system is at rest and the temperature drops to sub-zero values, the water will turn into ice, which will cause rupture of pipes, radiators and damage to the boiler.
- With prolonged use of water, scale deposits on the parts, which increases energy costs by up to 25%.
- Constant contact of metal pipes with water leads to corrosion.
We have already discussed the advantages and disadvantages of antifreeze. Its use is justified when a private house is rarely visited in winter and heating does not occur regularly, but is started only when people are in the room.
Thus, despite all the disadvantages of using water, when permanently living in a country house, it is still better to use ordinary water as a coolant.

How to calculate the required quantity?
To purchase the required amount of antifreeze liquid, you need to know the exact capacity of the system. This information may be available to the specialists who created the project or carried out the installation. If the data is lost, you can still find out the parameters, although you need to spend some time.
First you need to measure the total length of the lines and distribute them according to the diameter. After this, the flow area is calculated. All this is multiplied by the total length. The volume of water in the radiators is added (data can be found in the relevant technical documentation). This will give you the required total volume of coolant.
The required amount of anti-freeze can be found out at the time of purchase. The ratio with which antifreeze should be diluted with water is indicated on the packaging.
Using your home allows you to forget about the danger of coolant freezing and future repairs. The use of antifreeze has its advantages and disadvantages, which must be taken into account when choosing and during operation.
How to protect pipes from freezing
In some cases, defrosting of the heating system may not be noticed. When defrosting, pipes may burst, and as a result, the basement may flood. Of course, after such a situation you will have to carry out repairs, which will require large expenses. To prevent this situation, it is recommended to use modern systems that can prevent the coolant from freezing.

A good system is to de-ice pipes. In such a system, a resistive cable is laid along the pipe. The cable should be located next to the pipe. To protect short sections of pipe, you can use a resistive cable that is equipped with an additional thermostat. The cable can be used for long sections of pipe. It is more profitable to use a self-regulating cable.
The pipe anti-icing system is also used in drinking water pipes. The only difference is the cable routing. In this case, it is placed inside the pipe.