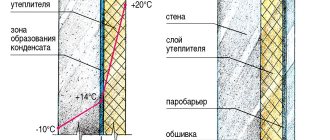
Dew point position
The place where air humidity decreases due to the precipitation of moisture on the surface in the form of drops of condensation, at the same time a physical phenomenon with a variable value, which is measured in degrees , is the dew point.
If you calculate the dew point value for a specific room, taking into account climatic features and several parameters: relative humidity, pressure, outside and inside temperatures, then you can calculate where moisture will fall on a surface point having a temperature below the dew point value. And where this point will be (its position) depends on the thickness and material of the main structures, on the thickness of all the layers forming the wall pie, on the insulation. Where warm air hits a surface that is below the dew point, the surface becomes wet.
Moisture from the air converted into condensate has detrimental consequences for structures. Ideally, it should be retained in the insulation and then removed. If the main structures get wet, then mold and destruction are inevitable. Fungal spores continuously increase colonies and have a detrimental effect on the health of the inhabitants of the house. Prolonged wetting of the insulation leads to a decrease in the declared properties - it simply loses its thermal insulation properties.
Damage to dew point for house walls
We figured out that the dew point can be located in three different parts of the wall:
- in external wall insulation
- in the wall, closer to the outside
- in the wall, closer to the inside
In each of the listed places, the dew point will manifest itself differently. If in one place it is harmless, then inside the house or in the wall it will have certain destructive consequences on the integrity of the wall. Below, we will analyze the behavior of the dew point in each of the listed places.
Dew point in external insulation
This is the most harmless dew point for your home. In this case:
- When the dew point occurs, condensation forms directly in the insulation itself.
- The insulation is not hygroscopic, therefore moisture is not retained in the wall structure and evaporates when the air temperature changes.
- Due to the vapor barrier properties of the insulation, the moisture that is formed when condensation evaporates goes outside and does not interact with the wall of the house.
- The walls of the house are dry throughout the year, both from the outside and from the inside
- The walls retain their strength and integrity for many decades
insulation on the outside
Dew point in the wall of the house, closer to the outside
- The behavior of a wall largely depends on the material from which it is made. Walls made of dense and heavy building materials such as brick, expanded clay concrete, stone, and wood can withstand dew point better. Because they are less susceptible to destruction and have a higher frost resistance coefficient.
- The walls of houses built from porous materials that absorb moisture well and allow steam to pass through. Such as foam blocks, gas blocks and similar materials, the effect of the dew point should be minimally short.
destruction of a wall due to moisture
- When condensation occurs inside the wall, the wall material becomes saturated with liquid. When the air temperature subsequently drops below zero, the accumulated liquid freezes and increases in volume. An increase in the volume of liquid destroys any wall material from the inside. This leads to the formation of both small and large cracks in the wall structure. The walls crumble and finally lose their strength.
- If the wall, in which the dew point is inside and is insulated from the outside, then the insulation will not prevent the accumulated moisture from escaping outside. Therefore, all the liquid will accumulate on the surface, between the insulation and the wall. This entails the formation of mold and mildew, with all the ensuing consequences that are harmful both to the building and to human health.
- If the wall of the house is not insulated from the outside, then the liquid will come out as the air temperature rises, but this will not protect the wall from internal destruction after the water freezes. We can observe similar evaporation of liquid from a damp wall in the form of a white coating on brick walls.
Factors influencing the dew point value
An important role is played by the ventilation and heating system, which creates an optimal microclimate with standardized humidity levels for residential premises. The higher the air humidity, the higher the dew point value. This can be visually represented as follows: room humidity is 60%, temperature is 20 degrees - condensation will fall on a surface with less than 12 degrees of heat. But, if at a similar temperature the room humidity is 40%, then moisture will not fall on the surface above six degrees. If a drop of dew is located next to the ventilation layer or the external environment, the consequences of this phenomenon will not affect the operational properties of the building.
Comfortable values for a person
For most people, conditions with a point value in the range of +10…+15℃ are optimal. If the indicator increases, then the person feels discomfort. When the point value is less than +10℃, the environment becomes dry, and from +15℃ humidity begins to be felt. If the indicator is above +20℃, it becomes stuffy. People with heart and respiratory problems are more susceptible to environmental parameters than others.
The dew point temperature determines the comfort level of living in the house
Insulation of walls inside structures
By choosing cellulose insulation Ecowool and insulating wooden structures with it, you can avoid a conflict of materials, since the fibrous structure of wood and similar ecowool will “breathe” evenly, regulating air humidity naturally - drawing in moisture and releasing it in one algorithm. In such a tandem there will be no sharp temperature limit, and therefore no prerequisites for the structures to get wet. For a frame house, filling the walls with ecowool along the width of the studs using the wet-glue method or by injection, under the pressure of fluffed ecowool in the cavity - that is, insulating the inner layer is a reliable protection of wooden structures from getting wet caused by the dew point. Unfortunately, this effect is difficult to achieve with insulation materials that do not absorb moisture - polyurethane foam, polypropylene foam, or cannot remove it. Mineral wool, having excellent declared properties, loses them when wet, and it is quite difficult to dry it.
Another point negates the insulation of cavities with roll and sheet insulation: the presence of seams. Even super-high-quality installation does not guarantee that there will be no cold bridges in the joints - cracks that deliver cold air to warm internal surfaces or warm and humid air to external ones. This is where an unplanned dew point may appear, nullifying all insulation efforts.
PENOPLEX: on the facades of country houses
For each of us, home is the place where we want to feel completely safe, regardless of whether there is a blizzard raging outside or pouring rain. In order to make this desire come true, you need to take timely care of the insulation of your own home. First of all, this applies to walls, which are one of the most vulnerable parts of any building.
Even the strongest walls are exposed to a number of destructive factors. These factors include precipitation, water vapor contained in the air, wind, and temperature changes. Most of the territory of Russia is located in a zone of harsh winter climatic conditions, when the thermometer often drops below -20 0C, and at such a temperature - and there is no need to deceive anyone - a wooden beam even 200 mm thick will be not just cold, but icy. That is why wooden beams are an excellent structural material, but not the best thermal insulation material, not to mention brick, aerated silicate blocks, foam concrete, aerated concrete and similar materials. And if we want to live in warmth and comfort, it is simply necessary to insulate the house.
The main function of thermal insulation of any structure is protection from unwanted heat exchange. It is from this point of view that it is necessary to insulate absolutely any walls: wooden and stone. Why is it so necessary to do this? Yes, because unwanted heat exchange is a negative process that causes a lot of inconvenience and unnecessary expenses. Insufficiently reliable thermal insulation of walls leads to the fact that the house loses up to 45% of its heat. But this is not only literally money thrown into the oven, it is also cold in winter and unbearable heat in summer...
Someone will argue that there is no need to insulate the walls of his house, because... they are very thick. The statement has a right to exist; all that remains is to answer the question: why do you need this? Why these colossal costs for monumental walls and an equally monumental foundation to support these walls? Wouldn't it be nicer to spend money on something more useful than building fortress walls that are not necessary?
Properly executed thermal insulation of a house in general and its walls in particular is not only coziness and comfort in the room at any time of the year, but also a way to actually save money during the entire life of the building. However, in order for thermal insulation to effectively perform its main function - protection from unwanted heat exchange, it is necessary to use effective thermal insulation materials, otherwise all efforts may be a waste of time, nerves and money.
Today, one of the most convenient and practical materials that can effectively solve the problem of thermal insulation of buildings throughout their entire service life is PENOPLEX® thermal insulation. As a new generation of thermal insulation material, PENOPLEX® has a number of obvious advantages compared to the thermal insulation materials of “yesterday” - glass wool, mineral wool.
The required thickness of the insulation is determined by the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient; this is the most important indicator of any thermal insulation material (see Table 1):
Cost savings on thermal insulation of buildings – low thermal conductivity.
The required thickness of the insulation is determined by the value of the thermal conductivity coefficient; this is the most important indicator of any thermal insulation material (see Table 1):
Type of thermal insulation material
Thermal conductivity coefficient in laboratory conditions W/m 0С (at 25±5 0С)
Thermal conductivity coefficient under operating conditions “A” (dry climate)
Thermal conductivity coefficient under operating conditions “B” (humid climate)
Table 1. Thermal conductivity coefficients of various thermal insulation materials in laboratory and real conditions
From a practical point of view, the data from the table means that to insulate the external wall of any building, you will need a smaller volume of PENOPLEX® , approximately 1.5 times less than the required thickness of mineral wool - and this is a significant saving of living space and, no less important, your financial resources .
Insulating the wall from the inside
When insulating walls from the inside, you need to be sure that the dew point will be in the thickness of the wall. Visually, this is determined simply - if the wall does not get wet during the cold season, then the dew point does not go inside the room and additional insulation will not cause the formation of dampness under the insulation and its wetting. But since we, by insulating the wall, block its heating from room heat, during periods of cold weather, this process can shift to the inner surface of the main structure and dampness with mold will become inevitable. There are no identical situations when determining where to choose wall insulation. Many factors are taken into account:
- Climatic conditions;
- operating mode;
- heating and ventilation systems;
- thickness of walls, quality of their material, construction;
- humidity and temperature inside and outside;
- degree of insulation of the floor, roof, etc.
But again, if the insulation is capable of taking moisture from the surface and releasing it (drying on its own), and natural insulation with a fibrous structure has such properties, then many issues are leveled out. The company Teploservis St. Petersburg carries out insulation with Ecowool, both internal surfaces and hollow structures inside walls. All control openings showed that in the case of such insulation, there is no dampness or mold in the house. A comfortable microclimate is maintained without additional ventilation systems.
Thermal insulation material
To protect buildings from heat loss, high humidity and point shifts, it is insulated with thermal insulation materials. In winter, insulation helps reduce heating costs, and in summer it keeps the room cool. Each product has its own areas of application and properties. Eco-friendly and easy-to-install materials are used in construction. The required type of insulation is selected for certain conditions.

With proper insulation from the outside, the dew point will be located inside the insulation
According to their form, materials are divided into:
- roll;
- leafy;
- bulk;
- single.
By structure:
- fiber;
- cells;
- grainy.
Raw materials can be organic, inorganic and mixed.
Main characteristics of insulating materials:
- thermal conductivity;
- moisture absorption;
- porosity;
- humidity;
- density;
- vapor permeability;
- specific heat;
- strength, etc.
Penoplex
Penoplex is also called expanded polystyrene. Unlike foam polystyrene, the material has a higher density and is less subject to mechanical damage. It almost does not conduct steam due to its low vapor permeability coefficient. However, it belongs to group IV of flammability (it ignites quickly).

Penoplex is recommended for external wall insulation
Penoplex of the “comfort” category is produced for insulating walls, terraces, loggias, and balconies. Its thermal conductivity coefficient is 9 times less than that of mineral wool. The material requires little time to heat the room after cooling due to its low heat capacity. The operating temperature range is -70…+70℃. Penoplex of this type does not have the best sound insulation, has the lowest density and lower tensile strength compared to other materials.
Penoplex for walls is suitable only if an effective ventilation system is installed in the room to maintain comfortable humidity.
A 2 cm wide layer of polystyrene foam retains heat almost as well as 40 cm of mineral wool or 37 cm of brickwork.
Styrofoam
Polystyrene foam is a material characterized by lightness and buoyancy. It is resistant to fire, but when exposed to fire it begins to melt. The material is easy to process and is not subject to infection by fungi and mold.
Polystyrene foam is obtained from foamed polymer raw materials: polystyrene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polyurethane. It consists of small identical balls that are fastened together. High-density rigid foam is used for insulation. The panels are easy to connect using rubber or epoxy adhesive.
The temperature range is not important for polystyrene foam, but the material is subject to mechanical damage.
Slabs 5 and 10 cm thick are used as thermal insulation. But, despite the structure, the material is sound-permeable.

Polystyrene foam is one of the most common materials for home insulation.
Mineral wool
Thermal insulation material consists of compressed fibers. Glass, basalt and slag are used as raw materials. The starting material is melted and spun into fibers. Their length is 2-60 mm. The air pores of the mats fill approximately 95% of the total volume. The product is easy to produce and has a low cost.
Mineral wool has many qualities suitable for home insulation.
Due to its porosity, cotton wool allows air and steam to pass through, maintaining air exchange. At the same time, it does not burn and is resistant to moisture, has good sound insulation. But the material has 2 drawbacks:
- contains phenol;
- Flying pieces of cotton wool, falling on human skin, cause itching.
External insulation
The position of the dew point in the insulation from the outside can be predicted only if the thickness of the insulation corresponds to the thermal engineering calculation. A smaller layer may cause more harm than heat. The dew point can be located in the middle of the wall and move to the inner surfaces during sudden cold snaps. The inside of the wall will get wet. But it’s worth repeating - there are no identical situations; the choice of insulation and insulation methods must be made taking into account all the features of the project, layout, structures, climate, operating conditions.
There are additional construction nuances when insulating, these are ventilation gaps, additional vapor barrier, wind protection, do not forget about them when starting to insulate the house. Having opted for natural cellulose insulation Ecowool, you can get any free advice from Teploservice specialists by calling 8 (812) 9999812. We will carry out insulation of any complexity at any stage of construction, repair and operation. Heating service works with certified cellulose-based insulation .
Possible consequences
Improper installation of thermal insulation can lead to unpleasant consequences. The material is applied only to the facade, since additional insulation from the inside is considered impractical for the following reasons:
- Living space is decreasing.
- The wall freezes because the heat from the room does not reach the ceiling. As a result, condensation penetrates inside the thermal insulation. The wall is wet and subject to corrosion.
Poor installation results in wall destruction. If the surface under the insulation is uneven and old, it will have to be reapplied, after making repairs. If the insulation on the outside is not additionally covered, then in one season it will become wet, become unusable and begin to move away from the walls. The thermal layer must be protected from the external environment.
Video: Removing the dew point from the wall
Dew point during bath construction
The dew point in a bath made of aerated concrete is calculated according to the same principle. The parameters of the desired temperature and humidity are entered into the program. Since the bathhouse is a place with increased humidity, construction must necessarily use insulation. The façade must be built with a ventilation gap so that the insulation has time to dry.
AltaiStroyMash offers to purchase conveyor lines or stationary plants for the production of aerated concrete blocks. You can set up such production for your own needs or produce gas blocks for sale. Company managers will help make your business profitable and efficient. Clients already have similar plants in different countries and cities: Russia, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and others. Information, product catalogs, photo and video materials can be viewed on the company’s official website.
Condensation on windows

Very often, manufacturers of modern windows have to accept complaints that their customers' windows are fogging up. The formation of condensation on windows is not only aesthetically unsightly, but also threatens the wooden structures with waterlogging and, as a result, the formation of mold. Let's look at the possible causes of condensation on windows.
Condensation is a liquid that has passed the dew point and fallen in the form of droplets on the window.
Well, if this happened on windows, then only the windows and their manufacturers are to blame. Logically this is correct, but if there is no water in the window itself and it cannot release it, where does the condensation come from?
Types of warm matter
The use of thermal insulation materials reduces space heating costs by 50%.
The use of thermal insulation materials not only combats dew point, but also creates a favorable microclimate in the room.
In cold weather, the walls will not freeze, the interior decoration will remain unchanged for a long time, and in the heat the house will not overheat, it will always be cool. The choice of thermal insulation materials on the construction market is very diverse. Depending on the raw materials from which they are made, they are divided into organic and inorganic.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool is a glassy fiber obtained by processing rock melts or metallurgical slags. This is the most common type of insulation. Due to its porous structure, mineral wool has low thermal conductivity.
The air pores of mineral wool make up up to 95% of the volume of the material.
At the same time, it has good sound and heat insulating qualities and does not deform under the influence of different temperatures. This is a particularly useful quality when insulating walls, because... the material will be constantly exposed to moisture, and mineral wool is highly resistant to deformation during its entire service life with minimal shrinkage possible. In addition, mineral wool is a non-flammable material and is environmentally friendly. The ease of installation also speaks in its favor. This material can be used for any type of insulation. Its only drawback is that it absorbs moisture well, but this property can be prevented with the help of hydro-repellent impregnation. Calculating the dew point of mineral wool is impossible without indicators of air temperature and relative humidity.
Condensation on entrance doors
The first reason for the formation of condensation on the front door is based on increased air humidity, when the indicator exceeds 55%. Then the condensate is collected on the surface, where the temperature is slightly below the “dew point”. In winter, such a surface is the front door.

It is important to maintain indoor air humidity of about 45% for the health of residents. The humidity of the internal climate is affected by both ventilation devices and the temperature of the heated air in the room. The second reason for condensation is hidden in low thermal insulation - a metal door is more prone to large amounts of condensation due to poor sealing between the metal sheet and the frame. In a typical version, there is not enough air outflow for those purposes to allow vapors to escape, but it is quite enough to deposit them on the surface.