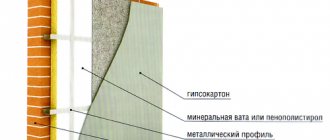
Aerated concrete itself is an effective heat insulator. So is it necessary to insulate an aerated block if its heat transfer resistance coefficient is 3-4 times higher than that of a brick? It turns out that to maintain a comfortable microclimate in the rooms at a given energy consumption, it is enough to install walls made of aerated concrete 400 mm thick. But to get the same result in a brick house, you need walls with a section of 1.7 meters.
About the need for insulation
The structure of aerated concrete is a complex system of many open cells (voids) filled with air. This structural feature determines two useful properties of the material:
- Good thermal insulation . The manufacturer claims that the porous structure of aerated concrete brings its thermal insulation properties closer to wood, and is three to four times superior to brick. In the middle zone, according to SNiPs, the thickness of external walls of 400-500 mm will be sufficient without additional insulation if a block of a grade no lower than D500 is used. These calculations are correct, but do not take into account the second property of aerated concrete.
- Gas permeability . Open pores mean that the material is able not only to transmit, but also to accumulate moisture, which is what happens during the operation of the house. Walls that have absorbed a certain amount of moisture become denser (water accumulates in the pores, like in capillaries). The thermal conductivity of such walls increases, and the ability to retain heat decreases, which is especially noticeable in regions with harsh winters. And if in the south (where the winter temperature difference between inside and outside the building is small) country houses do not need insulation, then to the north the walls must be protected.
The properties of aerated concrete are determined by its structure Source pinterest.com
Calculation of the “Dew Point” for the walls of your cottage
On the Internet you can find corresponding online calculators for heating engineering of enclosing structures. We recommend the following:
www.smartcalc.ru/thermocalc
Calculation example at the link: Region: Ekaterinburg, Sverdlovsk region; Premises: Residential; Construction type: Wall; Construction layers: Autoclaved aerated concrete D400, 400 mm thick (one layer, without finishing and insulation)
It is enough to select a region and enter information about the construction of the walls (layer by layer). Next, open the “Moisture Accumulation” tab. If the conclusion appears that “The enclosing structure satisfies the standards for waterlogging” - that’s it, the calculation is completed!
Please note: when calculating the “dew point”, the average temperature during the heating period is considered. In the Sverdlovsk region it is about -7°C. If within a few days the temperature drops to -35°C, the amount of steam that will fill all the pores will not have time to pass through the wall, the moisture will turn into ice, and the ice will “tear” the material. Especially if the walls are made of Twin Block - its frost resistance (F) is 100 cycles.
The lower the temperature, the lower the air humidity both outdoors and indoors. Thus, the probability of steam turning into water is low.
Summary: the “dew point” in the wall itself is not as dangerous as we are often afraid of. Risks arise only due to the accumulation of moisture in the walls during the heating period as a whole.
Principles for choosing insulation
When choosing a suitable material for insulating aerated concrete walls, three factors are taken into account:
- Physical properties of the material . Aerated concrete can regulate the humidity in the room: the walls breathe, allowing water vapor to pass out. The external cladding should not impede this diffusion.
- Properties of insulation . It should not just be vapor permeable; vapor permeability should be higher than that of aerated concrete blocks.
- Insulation rule . It says: the vapor permeability of each subsequent layer of facade insulation should increase. If the selected material cannot easily allow air to pass out, then a ventilated gap must be installed behind it.
Compliance with these conditions helps to shift the dew point beyond the walls. If the masonry is not protected by anything, the moisture accumulating inside will inevitably freeze in severe frost. This leads to noticeable heat loss; after several cycles of freezing and thawing, the destruction of the surface layer of the blocks may begin.
Good to know! The dew point is a plane in the thickness of the wall where, due to the difference in external and internal temperatures, water vapor condenses into dew. With proper organization of external insulation, the dew point moves outward and cannot harm the walls.
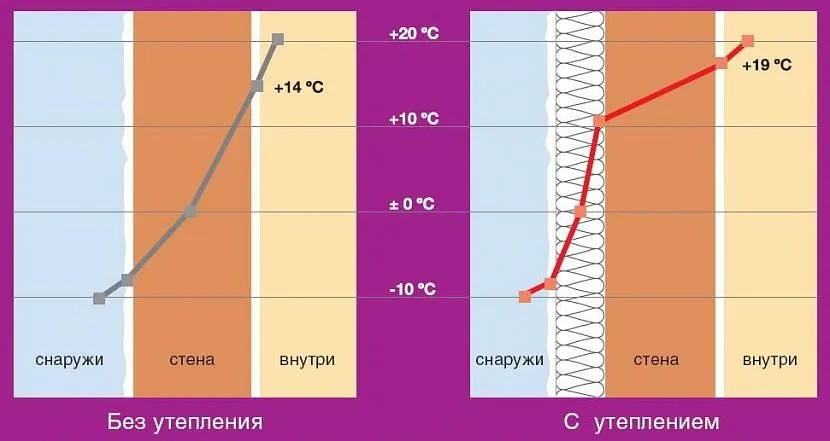
The energy efficiency of a house is affected not only by correctly selected insulation, but also by the quality of wall masonry.
If the interblock seams are made incorrectly (too thick), even high-quality insulation will not give the desired effect. Glue joints with a thickness of 1.5-2 mm are considered optimal. Laying blocks on cement-sand mortar with a seam of 10-12 mm will increase heat loss (and heating bills) by 20-20%.
Is outside and inside required at the same time?
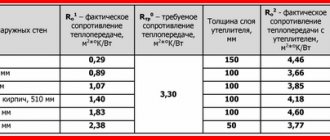
In accordance with SNiP, the minimum thickness of an aerated concrete wall structure to achieve a sanitary air temperature of 18-25 C is taken to be at least 400 mm. In cases where this requirement is not met, thermal protection is installed with a layer that will complement the missing width.
For example , for a 350 mm wall, the insulation must be at least 50 mm, for 300 mm, 100 mm insulation, and for 200 mm, 200 mm insulation. In the latter case, it is almost impossible to install a 200 mm thermal protection layer on one side, so it is installed on both sides.
This situation occurs when the owner of a personal plot decides to change the characteristics of the utility rooms and make, for example, a summer kitchen or garage insulated.
When choosing a location for installing thermal protection, the preferred option is external . If for some reason it is impossible to perform it, for example, expensive finishing of the house has been installed, there is a ban from architectural authorities on external insulation of a house in a historical building of the city, or for other technical reasons, then internal thermal protection is performed.
Types and advantages of facade insulation
There is an alternative possibility - insulating the building from the inside. This option is less preferable for several reasons:
- Living space will decrease.
- effective ventilation system will need to be installed .
- There will be a high risk of mold formation , as the dew point will shift inside the home. Moisture and heat are optimal conditions for unpretentious microorganisms and fungi.
How is aerated concrete insulated with plaster?
Another way to insulate aerated concrete walls is to plaster them. For this purpose, you can use special facade plasters; it is enough to apply a layer of 3 cm.
In addition, to insulate an aerated concrete cottage, you can use a simpler plaster prepared with slag sand. However, the last layer must be moisture-resistant and heat-resistant plaster. This will make the surface of the walls more protected and smooth, and due to the presence of polymers in the composition, such a facade will be highly resistant to any temperature changes.
Given the large area of work, it is best to plaster aerated concrete by machine:

To insulate walls made of aerated concrete, only light plaster mixtures are used. Before you start insulating the wall, you need to thoroughly clean and work the interblock seams with a metal spatula so that grooves form in them. Thanks to this, the adhesion of the plaster to the wall will be more reliable.
Video description
About mistakes when insulating aerated concrete in the following video:
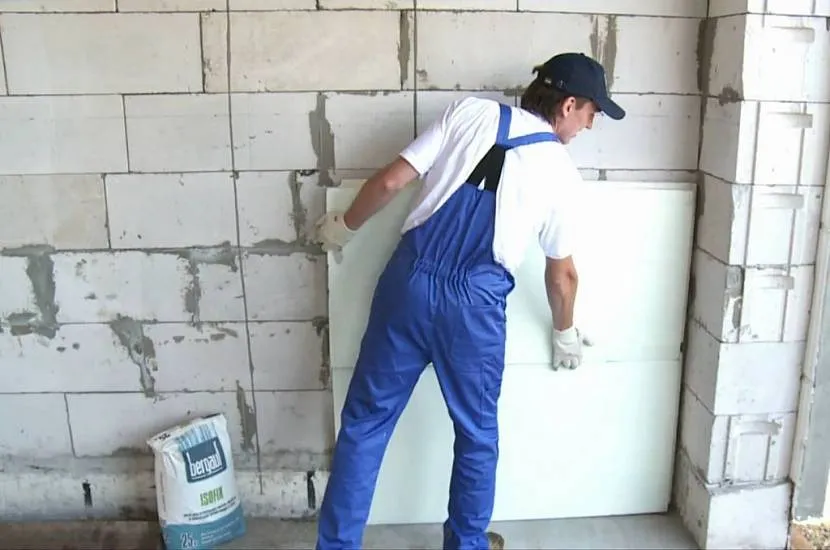

Internal insulation reduces the usable area of housing Source makemone.ru
Considering different options for how to insulate a house made of aerated concrete from the outside, many opt for ordinary or mineral plaster; the latter is specifically designed for aerated concrete walls. The insulation layer can be sheathed with several finishing materials:
- Siding or clapboard .
- Face brick or decorative stone .
- Plaster.
- Grouting the joints followed by the use of vapor-permeable facade paint .
Installation of an insulating layer on the outside has the following positive aspects:
- The energy efficiency of the building increases and heating bills decrease.
- Load-bearing walls are not exposed to natural forces, which increases the service life of a country house.
- Along with improved sound insulation of walls, living comfort increases .
- The appearance of facade walls improves .

See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in insulating country houses.
Which aerated concrete does not need to be insulated?
The required thermal resistance is provided by the following options for single-layer aerated concrete walls: D300(300mm), D400(375mm), D500(500mm).
If you are a self-builder, then we would advise you to take high-quality aerated concrete brand D400 (375 mm), which just meets the requirements for thermal protection and does not require additional insulation.

The D400 is quite durable for two-story buildings, and its thermal efficiency is very high, making it optimal in all respects. D300 is too brittle and often cracks, and D500 is too heavy and expensive for 500mm thick masonry.
Video description
We will dwell in more detail on insulating a house with polystyrene foam. Find out how safe polystyrene foam is in our video:
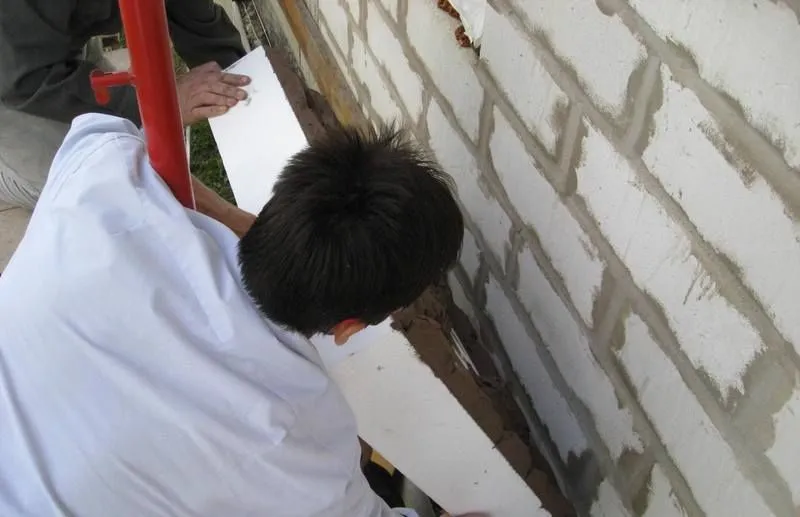

Foam insulation Source beton-house.com
- Installation of foam plastic . It is placed in the spaces between the frame elements, additionally secured with foam or glue.
- Fixing the slabs . The foam sheathing is additionally reinforced with plastic dowels (metal dowels are not suitable, as they create cold bridges).
- Decorative finishing . A primer is applied to the foam layer, a fiberglass mesh is fixed on top, then reinforcing glue is applied. After the glue has dried, finishing is done with decorative or warm plaster.
See also: Catalog of projects of houses made of aerated concrete blocks presented at the exhibition “Low-Rise Country”.
How is the sheathing for insulation made?
In order to insulate aerated block walls with mineral wool, it is necessary to install a sheathing of wooden beams on the façade of the building. They are attached to the aerated concrete masonry using dowels. The distance between the beams must clearly coincide with the width of the mineral wool sheets to prevent the formation of cold bridges.

After installing the insulation, it must be secured with slats, which are located horizontally between the beams. The mesh of slats is covered with sheets of asbestos cement and then plastered.

The thickness of the wooden beams, between which the mineral wool sheets are located, can be made slightly greater than the thickness of the insulation sheets. This creates an air gap that will increase the thermal protection of the facade.
Insulation with mineral wool
Mineral wool is presented on the market in the form of slabs and rolls. It is actively used for insulating facade walls; basalt slabs are a special case of mineral wool, with similar qualities and performance characteristics. The widespread use of mineral wool is due to its many positive qualities:
- Good vapor permeable properties .
- High strength and immunity to biohazards. Materials are available in different hardness categories.
- Fire resistance (in case of fire it does not burn, but melts).
- Environmental friendliness . The basis of mineral wool is natural components that are not hazardous to human health.

Installation of mineral wool on the facade is carried out in the following order.
- Facade preparation . The wall is cleaned and leveled using cement mortar. Then the surface is primed and, if necessary, additionally leveled with vapor-permeable plaster.
- Frame installation . The guides of the frame structure are fixed taking into account the size of the material used (roll or rectangular mats). Thanks to the frame, a ventilation gap is formed, sufficient for air circulation along the wall and steam removal.
- Fastening mineral wool . It is carried out using glue applied to the slab material. Additional fixation is provided by plastic umbrella dowels.
- Preparing for finishing . The mineral wool layer is reinforced with mesh and glue.
- Finishing . The walls are coated with primer and plastered; The second common option is to cover it with putty and paint it. When finishing, do not use acrylic plaster, which has moisture-proof properties; such a coating will cause condensation to form.
What materials are used for thermal insulation
What is the best way to insulate a house? The most common materials used as insulation for gas silicate blocks are foam boards and mineral wool mats.
Foam insulation involves the use of flat slabs consisting of polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, produced in the form of plates of various thicknesses and sizes. Foam plastic is easy to cut, saw, and drill. When using correctly selected glue, it adheres well to a wall made of gas silicate blocks.
Mineral wool is produced under different brands, such as ISOVER, KNAUF, URSA in rolls or slabs with a thickness of 45 to 200 mm, sizes: width - from 60 to 1200 mm, length - from 1170 to 10000 mm. Insulation with mineral wool and its fastening to the facade is usually carried out using special dowels for gas silicate blocks.
Sometimes cement-sand or cement-lime plaster with a porous filler - perlite or vermiculite sand, having a bulk volumetric weight of up to 50 kg/m3, can be used. Foamed foam granules are used as the porous component. When using such plaster, before painting the facade, it must be treated with deep penetration impregnation.
Another way to properly insulate gas silicate is to arrange a so-called ventilated façade. This is a type of finishing of the external walls of a house when the facing panels are fixed to an installed metal frame, the profiles of which can be made of galvanized sheet, stainless steel, or aluminum. A gap of at least 5 cm is left between the finishing sheets and the wall. Ambient air moves freely through it, which removes and dries condensation and moisture formed as a result of temperature changes from the wall of the building.

When using ventilated façade systems or fiber cement panels of the KMEW type, it should be taken into account that they can create additional load on the foundations and soil base. Therefore, before starting work, it is better to consult with specialists and perform a verification calculation of the load-bearing capacity taking into account changing forces.
Expanded polystyrene
Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) is one of the types of foam plastic. Expanded polystyrene is produced by foaming the starting ingredients at high temperature and pressure. The production method determines the physical properties of the material - it is mechanically strong, frost-resistant and can have different densities. The higher the density (and strength) of EPS, the higher the thermal conductivity. Vapor and air permeability are always at the same (low) level, and water absorption is minimal. The combination of qualities makes it possible to widely use EPS as an insulating facade material.
An undesirable property of polystyrene foam for aerated concrete walls - low vapor permeability, leading to the appearance of a thermos effect and a shift in the dew point - is avoided by installing a ventilation gap. As in the case of using polystyrene foam, the second option is possible - installing powerful supply and exhaust ventilation. Installation of the insulating layer and decorative finishing is carried out according to the same scheme as for foam plastic.

Expanded polystyrene boards Source ko.decorexpro.com
Why insulate
Sometimes insulation of gas silicate walls from the outside is required if the reason for additional thermal insulation is that during the construction of the building the thickness of the external walls was incorrectly selected and freezing occurs, leading to inefficient consumption of thermal energy and associated economic losses.
Another reason may be that during renovations, the owner of the building decides to transfer the not very effective thermal insulation of the premises from the inside of the facade walls to their outer surface. The installation of external thermal insulation is not allowed without external finishing, which, in addition to its decorative properties, serves as its protection from mechanical damage and aggressive atmospheric influences. Therefore, thermal insulation is usually installed in parallel with the exterior finishing of the building. An additional advantage is the increase in the internal volume of the premises adjacent to the external walls.
Polyurethane foam (PPU)
The material refers to sprayed substances; its application requires special equipment, which makes it not the most popular choice in private housing construction. After spraying, a homogeneous sealed layer with the following properties is formed on the wall:
- PPU penetrates the porous surface layer of the aerated concrete facade and forms a strong bond with it that does not collapse over time.
- The thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam, depending on density, is intermediate between polystyrene foam (minimum thermal conductivity coefficient) and mineral wool.
- The required thickness of polyurethane foam is determined by the type of material and ranges from 5 to 10 cm (in the middle band). The service life of such coating is at least 25 years.
- The vapor permeability of polyurethane foam after hardening is comparable to that of reinforced concrete; the filtration of air and water vapor completely stops. To remove water vapor accumulating in the premises, an effective ventilation system is organized.
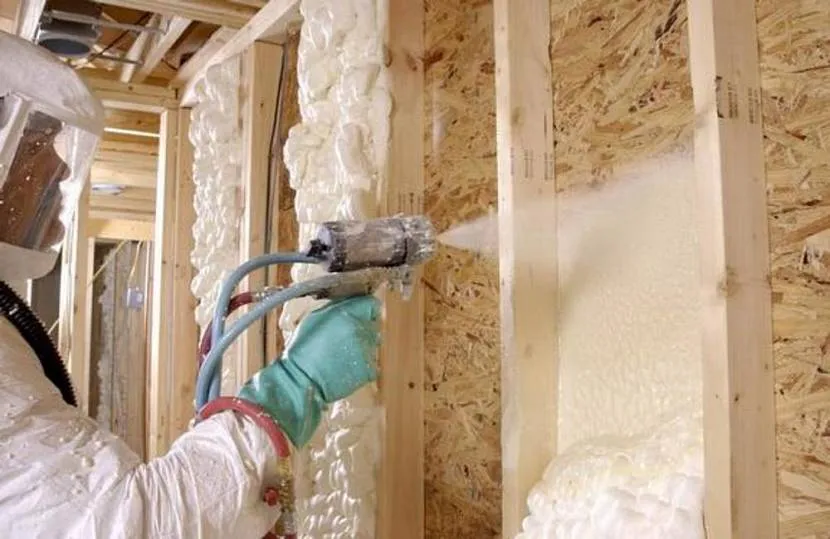

The principle of creating a polyurethane foam layer Source stroyfora.ru
- If polyurethane foam (as well as polystyrene foam or EPS) is chosen as the external insulating layer, a finish is selected for the premises that does not allow steam to penetrate into the aerated concrete . Cement plaster and alkyd paints are suitable for this role; ceramic tiles and vinyl wallpaper are often used.
Processes affecting thermal insulation
Why is it better to insulate walls from the outside rather than from the inside? This is due to a process called vapor permeability. While a person is in a room, steam is released mainly from his breath. If the building envelope is vapor-tight, steam, instead of passing through the walls, condenses on them, creating a humid environment that adversely affects the walls and their interior decoration or cladding. However, the most active exchange of steam-air gases through external walls occurs in the winter season.

Migration of vapor occurs in the direction from heat to cold. If the insulation is located inside, when the walls freeze, condensation also accumulates at the border of the insulation and the aerated concrete block. It is absorbed by the insulating material, which also usually has a porous structure and sharply reduces its protective properties.
The placement of thermal insulation on the outside and the use of special film vapor-permeable, but at the same time waterproofing membranes allow the most effective use of the desired properties of aerated concrete blocks and the material chosen for additional insulation.
Methods of attaching insulation to the facade
In practice, three technologies are used to insulate external gas-block walls.
- Curtain façade . It is a wooden or metal frame structure, the pitch of which is equal to the width of the heat-insulating material. The insulation is placed in the cells of the frame, and a decorative layer is mounted on top.
- Wet facade . The aerated concrete surface is cleaned. The selected thermal insulation material is attached to the adhesive and additionally secured with dowels. Then the wall is plastered in 2 layers using a reinforcing mesh.
- Wet façade with reinforcement . If brick or natural stone is chosen as the finishing facing material, hooks are used to fix the insulation. Then the surface is reinforced with mesh and plastered. After the plaster has dried, cladding is carried out; The method allows you to do without strengthening the walls and foundation and in many cases is preferable.
What thickness of insulation to choose
If you decide to insulate your home using aerated concrete from the outside, you need not only to choose the right materials, but also to decide how thick it will be. When determining it, it is important to take into account the region of construction, the final value of thermal resistance and the thickness of the walls, as well as the density of the material at their base.
Last but not least, attention should be paid to economic feasibility. The material should be selected taking into account your budget and the ability to carry out work without the involvement of specialists.
Methods for insulating aerated concrete facades
- The easiest way is to increase the thickness of the main wall. If the width of the foundation allows, this is the fastest, technically simplest and most cost-effective option.
- If the foundation width is limited, we recommend insulating the outside of the house with the most reliable insulation available today - low-density aerated concrete D100-D200. It has good thermal insulation characteristics and high vapor permeability, while being a stone material. This guarantees the durability of the thermal insulation layer compared to other materials applicable for insulation.
- What to do if it is impossible to increase the thickness of the wall, you are not going to refuse to add additional insulation to the house, but you don’t have enough money for insulation for aerated concrete? In this case, you have only one technically correct option - to insulate the house with mineral wool. It, in turn, also has excellent characteristics in terms of vapor permeability and thermal insulation, but is inferior to aerated concrete material in service life.
Cost of work on insulating the facade of an aerated concrete house
Construction organizations offer services for insulation and plastering of the facade of aerated concrete houses, the price of which is determined by several factors. The exact estimated cost of the work is determined during a direct inspection of the house. The cost of work is affected by the following parameters:
- Home inspection (the service is free in most cases if a contract is signed).
- Geometric features of walls, number of storeys and surface area.
- Consultation with a specialist on choosing optimal thermal insulation.
- Drawing up an .
- Purchase and delivery of materials.
- Carrying out work on insulation and finishing of the facade.
- Removal of construction waste .
Is it necessary to insulate a house made of 400 mm gas silicate blocks?
Most regions of our country are located in difficult climatic conditions, characterized by winters with severe frosts, as well as very hot summers. If the home owner wants to save money, he can accept any thickness of external walls in his home. Including 400 mm, that is, 1 block. If we compare this with most brick houses, their walls are 500mm thick (2 bricks). If the walls of the house freeze in the winter, and those living in it will suffer from the heat in the summer - the choice was made incorrectly. The thickness of the walls of buildings also depends on the number of floors, the wind rose and their intensity. Studying your mistakes from your own experience is a thankless task. Therefore, before carrying out work, it is better to contact a construction organization that employs specialists in the field of construction physics. They will perform thermal engineering calculations and give recommendations on wall thickness based on the specified parameters.
Service life and other advantages of insulation
The service life of mineral wool thermal insulation ranges from 25 to 40 years. Other advantages of this insulation include:
- environmental friendliness is not relevant in this case, because the insulation is located outside and inside the “pie” of the wall;
- non-flammable , the material does not support combustion;
- no smoke formation under the influence of open fire;
- low hydrophobicity, does not absorb moisture, but lets it out;
- low deformation, the insulation does not lose its shape over time;
- biological and chemical stability, inertness.
Expert opinion Vitaly Kudryashov builder, aspiring author
Ask a Question
The characteristics and quality of mineral wool largely depend on the manufacturer. Mineral wool " TechnoNIKOL ", "Rockwool", "Parok", "Ursa" is considered good
What factors should you pay attention to when choosing an insulator?
Different materials can be used to insulate aerated concrete houses. Such insulators differ according to the following characteristics:
- degree of thermal conductivity - some materials can protect buildings from the cold better, others - worse;
- vapor permeability;
- fire resistance - there are materials of this type on the market that are flammable and non-flammable;
- moisture resistance - some species are afraid of water, others are not.
Since aerated concrete itself, unlike wood, is not subject to fire, you can choose both fire-resistant and combustible materials for covering such walls. In terms of thermal conductivity, almost all modern insulators have good characteristics. In this regard, almost any material can be used for foam concrete.
Average cost and calculation of materials
In order to correctly calculate the thickness of the insulation and the amount of materials, you will have to contact specialists. It is better to do this at the design stage of the house. According to state standards, each climate zone has its own conversion factor. In addition, certain data is needed:
- thickness of building material;
- density of aerated concrete;
- height above ground level;
- method of heating the house;
- planned insulation and cladding.
It will be difficult to cope with such calculations on your own. Of course, you can also use an online calculator on one of the websites of construction companies.