In the process of designing a frame house, many people wonder what kind of insulation should be installed in the walls. In the article you will find information about the density of various heat-insulating materials, and a number of characteristics that will help you make a choice and build a heat-saving structure that allows you to maintain a comfortable temperature regardless of the time of year.
The comfort and emotional state of all people living in it depends on how warm the house is. In addition, the correct temperature in the house allows you to stay healthy and get sick less often, this is especially important if there are small children in it all the time. In order to maintain a comfortable temperature, and at the same time not pay a lot of money for the energy consumed, when building a house, due attention must be paid to the insulation installed in the walls.
For different structural elements of a building, the density indicator for insulation should be different. For a sloping roof, the insulation density should be at least 30–40 kg/m3. Otherwise, the thermal insulation will sag over time. For interior partitions, insulation with a density of 50 kg/m3 is chosen to ensure good sound insulation. For external insulation of a facade, the density of insulation for the walls of a frame house can reach up to 80 kg/m3.
Floor insulation using joists: materials for thermal insulation + insulation schemes
Regardless of whether there is a screed under the floor or just a filling of expanded clay, or maybe there is even damp earth under the floor, in order for the floorboards of a wooden floor to be warm, the space under the top flooring will need to be insulated.
For this, the well-known and most common method is used: insulating the floor along the joists.
What logs are and what insulation is best suited for thermal insulation of wooden floors, as well as what schemes are best to implement this will be discussed in our material.
General information
Selecting the type of insulation that is best suited for your room is only 50% of the job, success. It is important that the thickness of the insulation in the floor of the house is sufficient, because even the best material does not provide sufficient thermal insulation if it is laid in a thin layer. On the other hand, a very thick insulating layer will reduce the height of the ceiling in the room and is an unjustified waste of money.
It is extremely important to understand that the required insulation thickness will depend on the climate conditions in your area. It becomes obvious that when using the same insulating material in typical houses in Norilsk and Sochi, completely different layer thicknesses are required. For this reason, it is important to take into account that all the advice, as well as recommendations from the article, are given for the normal climate of central Russia, where in winter the temperature rarely drops below -25 degrees. If you live in a harsher or milder climate, it is recommended to adjust it down or up. We invite you to consider the main types of insulation, as well as data on layer thickness when used in different types of floors.
| TP - heated floor (factors) | Thickness of insulation material |
| TP above a room that is heated and the temperature is at least +18 degrees | 3 cm |
| TP above a heated room with an air temperature of +10…+17 degrees | 5 cm |
| TP above a heated room, where the temperature is 0...+10 degrees | 7 cm |
| TP above a room that is not heated | 10 cm |
| TP on the ground in the basement/ground floor with a recess of at least 1.5 meters | 12 cm |
| TP on soil in the basement/ground floor, the depth of which is 1.5 meters or more | 6 cm |
Types of floor insulation
The range of insulation materials is wide and varied, but three types of floor insulation are most often used.
- Floor insulation with mineral wool . For this purpose, glass wool and stone (basalt) wool are used. The materials are similar in their properties; they have very low thermal conductivity, while the vapor permeability of the material is high. Over time they do not cake and do not release hazardous compounds. Glass wool is easily restored under mechanical stress, but has one drawback that is not characteristic of stone wool. Glass wool easily absorbs moisture, after which the target qualities are lost. Additional material protection is required.
- Floor insulation with penoplex. An analogue of foam plastic, obtained using a slightly modified technology, due to which the material is absolutely resistant to moisture. Insulation is allowed for any floor. The disadvantage of penoplex is its flammability, although manufacturers are actively fighting this disadvantage by adding carbon dioxide to the composition.
- Floor insulation with expanded clay . Expanded clay is baked clay, a completely natural bulk material. It differs in grain size, thermal conductivity also varies depending on the granules. To insulate the floor, it is optimal to select the size of expanded clay up to 1 cm. The disadvantage of expanded clay is that it easily absorbs moisture, which causes it to lose its heat-insulating properties. When using expanded clay, an additional layer of moisture insulation is required.
User reviews
1: When purchasing, I didn’t pay attention to the smell from the thermal insulation. After insulation with polystyrene foam, it was impossible to enter the room.
2: We bought ecowool and liked the price. It turned out that it perfectly protects our house from the unwanted neighborhood of mice and cockroaches.
3: Lay basalt heat insulator between the joists, put on rubber gloves and a respirator. There was almost no waste left, unlike glass wool. The cutting was done with a regular knife.
Thus, to select the optimal insulation for a particular structure, it is necessary to find the best combination of density, mass, thermal insulation properties and, of course, the price of the material. Today there are many competing manufacturers on the market, and each of them offers various profitable options from which the consumer can choose the most suitable one for himself.
Insulation thickness
Let's consider how to correctly calculate such an important indicator responsible for maintaining heat in a house as the thickness of the insulation.
It should be noted that for each specific house this indicator is calculated individually - and the thickness of the material that is suitable for a house in southern latitudes may differ radically from the thickness of the material for a northern cottage. This calculation also includes other features.
To calculate the optimal insulation thickness suitable for your home, you need to use the formula prescribed in SNiP “Thermal protection of buildings”. The formula is: insulation thickness = R x A.
On the video, the thickness of the insulation for the floor in a wooden house:
What do these mysterious letters mean:
- R is the level of thermal resistance of the structure. This level is different for each climate zone. You can find it out from the application map that is attached to the SNiP.
- A is the coefficient of thermal conductivity of the insulation. Each type of insulating material has its own. You can see it on the packaging of the material. Some coefficients are also indicated in SNiP.
Using this formula, you can accurately determine what thickness of insulation is suitable for you, so that you are guaranteed not to freeze and achieve the optimal temperature in the house.
Attention: if according to the formula it turns out that the insulation layer in your house should be thin, then experts recommend in this case using expanded polystyrene or rolled materials. Such insulation can best protect the house, even if the layer is not too thick.
How to calculate insulation yourself
To calculate how thick the insulation should be, you need to know the minimum thermal resistance value . It depends on the climate. When calculating it, the duration of the heating period and the difference between internal and external (average for the same time) temperatures . So, for Moscow, the heat transfer resistance for the external walls of a residential building must be no less than 3.28, in Sochi 1.79 is sufficient, and in Yakutsk 5.28 is required.
The thermal resistance of a wall is defined as the sum of the resistance of all layers of the structure, load-bearing and insulating. Therefore, the thickness of the thermal insulation depends on the material from which the wall is made . Brick and concrete walls require more insulation, while wooden and foam block walls require less. Pay attention to how thick the material chosen for load-bearing structures is and what its thermal conductivity is. The thinner the supporting structures, the greater the thickness of the insulation should be.

Thermal conductivity
The ability of a material to transmit heat is determined by its thermal conductivity. Wood, brick, concrete, foam blocks conduct heat differently. Increased air humidity increases thermal conductivity. The inverse of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistance. To calculate it, the value of thermal conductivity in a dry state is used, which is indicated in the passport of the material used. You can also find it in tables.
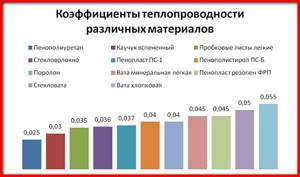
However, it must be taken into account that in corners, joints of load-bearing structures and other special elements of the structure, thermal conductivity is higher than on a flat surface of the walls. “Cold bridges” may appear, through which heat will escape from the house. The walls in these places will sweat. To prevent this, the thermal resistance value in such places is increased by about a quarter compared to the minimum allowable.
What is the basis for calculating the thickness of thermal insulation?
Even those readers who are not comfortable with physics and mathematics will be able to independently make such a calculation. Moreover, we invite them to take advantage of the built-in online calculator.
What is the basis for determining the required thermal insulation thickness?
The fundamental principle of the implementation is this: the total thermal resistance (or, more correctly, heat transfer resistance) of the enclosing building structure should not be less than the established value. This value is called normalized, and it is calculated for all regions taking into account their climatic characteristics. In addition, this indicator also takes on different values depending on the type of structure - there are standards for walls, coverings and ceilings.
It’s easy to find out this normalized value for your region of residence. Such information is probably available at any local construction organization. But it will be even easier to take the value from the schematic map below, covering the entire territory of Russia.
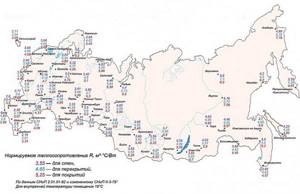
Normalized values of thermal resistance for building structures of residential buildings by regions of Russia
So, the normalized thermal resistance is known, but what does this tell us? The fact is that this total value is the sum of the thermal resistance indicators of each of the homogeneous layers of the structure.
If we look at a wooden floor by floor beams or joists, it will look something like this:
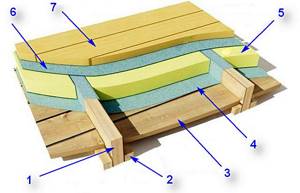
Schematic diagram of insulation of a wooden floor on joists or floor beams
1 – floor beams or joists – load-bearing parts of a wooden floor.
2 – cranial bars or support boards. Necessary for laying subfloors.
3 – subfloor boards. They can be mounted as a continuous flooring or sparsely. Sometimes, instead of boards, sheet material is used, for example, OSB boards or plywood. In some cases, for example, when thermally insulating the floor with rigid polystyrene foam blocks, the subfloor is completely abandoned - only a few jumpers are left to support the insulating layer.
4 – windproof membrane, which must have the property of vapor permeability - for the free release of moisture into the atmosphere. Not used when insulating with vapor-tight and wind-resistant materials, for example, extruded polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam.
Properties of mineral wool affecting its quality
In order for insulation, such as mineral wool, to meet the necessary requirements, its density must be determined. Naturally, the higher it is, the better, but this affects the cost, increasing the price. This is easy to explain, since the density is influenced by the number of fibers contained in the material. In production, to achieve a higher level of density, you will have to increase material consumption.
Properties of mineral wool
The density of mineral wool as insulation is traditionally determined by the weight of 1 m3 of material. Today, different representatives supply products of varying densities to the construction market. What does this depend on? From the technological features of production used.
That is why, when choosing an insulation material, it is worth considering not only the thermal properties that must be observed, but also the features of the frame building itself or the house where the walls will be soundproofed and thermally insulated.
For example, if it is necessary to insulate a multi-storey residential building, mineral wool with a property of 35 to 40 kg/m3 will be used. For production facilities, denser materials are used. Professional architects and builders use special formulas with which they can calculate the required density of mineral wool, which will allow for high-quality insulation of a frame house.
What densities exist:
- Mineral mats – from 100 to 200 kg/m3,
- Mineral fiber – 100-150 kg/m3.
- Semi-rigid slabs – 70-300 kg/m3.
- Rigid mineral wool slabs - 100-400 kg/m3.
The higher this property, the better the thermal insulation. For example, due to their high density, rigid mineral boards are used to insulate walls and ceilings of residential buildings in difficult climatic conditions. The thermal conductivity of mineral wool depends on the density. The process of mineral wool insulation is discussed step by step here.
The second indicator is thickness. The higher the thickness, the better the heat-saving properties.
Special mention should be made of such material as isover. Its properties are described in the tables below:
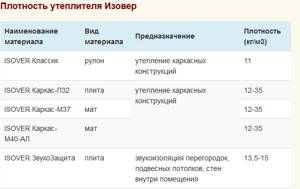
Characteristics of isover
table 2
Cork
In an era of environmental concern, it is not surprising that many people opt for natural materials. The bark of the cork tree has excellent thermal insulation properties. Cork differs from other natural materials in its honeycomb structure, which includes large and small cells filled with air.

Technical cork absorbs sound and vibration well, it is strong and durable. Available in the form of rolls, it has a small thickness and good density. The small thickness of the product allows you to insulate floors in rooms with maximum height. It is easy to install on any surface. Like any natural material it has a high cost.
This loose cellulose-based material is used to insulate even hard-to-reach places. It is poured automatically or manually with a layer of 15-20 cm, which in terms of thermal characteristics corresponds to a layer of expanded clay of 80 cm.
Ecowool has soundproofing and heat-insulating properties and is completely safe. But such material is afraid of moisture. Therefore, it is laid only in places where there is no likelihood of increased humidity levels. It is used most often when laying wooden floors.
Peculiarities
The density of a material refers to the weight of a given substance in one cubic meter of material. The unit of measurement is kg/m3 (kilogram per cubic meter). Another name for the density parameter is the specific gravity of the material.
Density indicators are determined by the quality of the connection between the molecules of the material. The stronger the insulation elements are connected, the higher its strength.
The easiest way to understand what density is is by looking at mineral wool insulation. It can be loose and noticeably soft, disintegrating into fibers (material with low density, the molecules of which have weak bonds). You experience completely different sensations when touching mineral wool mats - their fibers are stiffer, but most importantly, they seem to be pressed together (higher insulation density).

Overview of polymer materials
It is important to study specific insulation materials and compare them with each other.
Polystyrene foam thickness
This material is usually called polystyrene foam, but this is not entirely true, since foam plastics are a huge group of polymer foam materials.

Expanded polystyrene boards are one of the most effective insulation materials
- Pressless, suspension - marked as PSB. The most inexpensive of the others. The price per square meter with a thickness of 20 mm is only 40 rubles. The structure consists of large granules glued together. When broken, it begins to crumble. Such expanded polystyrene is not dense, you can’t make a screed on it, it is flammable and can easily be turned into dust by rodents. It can be used as insulation for the floor of a wooden house, but low quality will not give the desired result.
- Pressed polystyrene foam (PS) has closed cells. During production, some brands of latex PVC and blowing agents are added. It retains heat perfectly, has a stronger and denser structure, and is not afraid of mold. But it is not used primarily for insulating floors, but the next type.
- Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) - is obtained by squeezing the molten mass through holes of a certain shape. It has a dense structure, all cells are closed, which means the material does not absorb water and tolerates mechanical loads - it can be used for plastering and concrete screeding.
The material can be purchased in different thicknesses - from 5 to 100 mm. If you need to install 10 cm of material for insulation, take not a slab of comparable thickness, but two layers of 5 cm each, and install them overlapping. This approach eliminates cold bridges formed at the seams.

Expanded polystyrene boards 10 cm thick
Individual slabs have profiled edges for easy joining. Heat loss is also reduced.
Advice! When installing expanded polystyrene boards, it is additionally recommended to coat the seams with polyurethane foam. By the way, this material also belongs to foam plastics.
The thermal conductivity coefficient of non-pressed polystyrene foam is 0.05 W/m o C. The extruded one has a lower indicator - 0.04 with a density of 40 kg/m 3, despite the higher density.
Frame building walls
The wall of a frame house is a structure of several layers. It is based on a frame made of wooden or metal elements. They are knocked down so that the walls are rigidly fixed, for which jumpers, struts and strapping are used. The beam for the house is 15 cm wide, and thermal insulation is laid end-to-end between it. On one side of this layer a waterproofing material is placed, most often a film, less often a more expensive membrane. It protects the inside of the wall from excess moisture coming from outside.
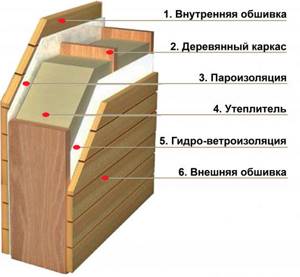
Wall of a frame house schematically
On the other side, a vapor barrier membrane is laid, which prevents moisture from entering the wall from inside the premises, but at the same time removes water vapor into the room from the wall.
OSB or other boards are placed on both sides.
Read about insulation technology here.
About the Canadian house - here, and about Finnish technology - here.