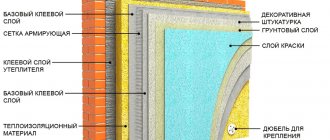
Insulating a house or any other structure with ecowool from the inside manually, with your own hands, does not require any specific preliminary preparation. The cellulose will be laid in the cavities of the insulated surface without exposure to a powerful air flow; the “lining” of the insulation will take place precisely during the process of laying the ecowool. The insulation that you put into voids with your own hands is essentially free-flowing. The heat insulator must be “closed” during the insulation process. The backing for this can be either sheet materials (plywood, OSB, gypsum board, etc.) or rolled vapor barrier “film” materials: kraft paper, Tyvek, isospan and others. Read about installation of roll materials here. In the case of insulating the walls of a country house from the outside, ecowool is sewn up with “wind protection” - film or board.
Do-it-yourself insulation of the floor and attic with ecowool
When insulating a horizontal plane with ecowool, the insulation is scattered over the surface between the joists, in a relatively even layer, with approximately 10% excess of the required thickness (height), after which the laid ecowool is “slammed” - compacting it to the level of the joists. Ecowool is covered with a light wind barrier or construction cardboard (if necessary), then the floor is laid.
The attic is insulated by backfilling the entire surface of the attic floor. Ecowool laid over the entire surface of the attic with the required thickness can remain in this open position for the entire service life.
General principles of thermal insulation
The correct technology for thermal insulation of floors consists of five main stages:
- dismantling old floors;
- installation of rough (technical) floor;
- laying insulation and securing it;
- laying a hydro-vapor barrier over the insulation;
- installation and securing of the finished floor.
Each specified stage must be carried out with the utmost care. If errors are made during the installation process, correcting them may require large amounts of time and money. Therefore, it is not recommended to carry out work without prior preparation, in a hurry and without due care.
Do-it-yourself insulation of walls with ecowool
The walls are insulated by filling the formed void with ecowool. At the same time, it is necessary to simultaneously create density in the insulation by compacting the layer. Hemming is done gradually from the bottom up, as the insulated space is filled with insulation.
The height of a solid ecowool column should not exceed 3 meters, since the weight of the laid material will put pressure on the bottom layer. Since there may be a risk of shrinkage under the pressure of its own weight, it is necessary to adhere to the reference material consumption. It is recommended to separate high vertical insulated cavities with “partitions” (cutoffs). When insulating walls, special attention should be paid to the corners, filling them completely and tightly with thermal insulation.
Wet styling
Wet ecowool has the ability to adhere well to any surface. This feature is used to insulate walls.
High adhesion is explained by the fact that ecowool contains the natural substance lignin. Lathing is attached to the walls to be treated.
Well-moistened ecowool is sprayed into the cells of the sheathing using a blow molding machine. At the exit of the nozzle, the fluffy cotton wool is wetted with water and sticks to any wall - wooden, concrete, brick.
This is clearly visible in the video. After the insulation dries, it becomes plastic and elastic. It is easy to cut to a given level. And the trimmings can be put back into use.
Do-it-yourself roof insulation
Insulation of a pitched roof is carried out by filling the space between the rafters with cellulose ecowool. Insulation occurs gradually, the formed empty space is filled from the bottom up. Roll or sheet materials are hemmed along the way. When insulating the roof, it is necessary to take into account the angle of the “slope”, that is, the greater the angle of the pitched roof, the correspondingly more density must be put into the insulation so that it does not shrink in the future (A pitched roof angle of more than 750 is equivalent to vertical structures). When insulating the roof, special attention must be paid to filling the “under-ridge” cavity (if a small attic is not provided). When thermally insulating the “slope”, the ecowool insulation should not come into contact with the roofing. To fulfill this condition, it is necessary to create a ventilated gap between the ecowool layer and the roofing.
Classification of insulation
Comparative table of characteristics, pros and cons of insulation materials.
| material | scope of use | pros | minuses | coefficient of thermal conductivity |
| sawdust | mounds in old attics, between walls | inexpensive material, easy to use, good air permeability, environmentally friendly | easily rots and burns | 0,070-0,093 |
| expanded clay | floors and attics of durable ceilings | does not burn, does not rot, holds heat well | very heavy | 0,085-0,160 |
| Styrofoam | walls, attics | inexpensive material, resistant to moisture and rotting | smoldering from fire with the release of toxic substances, creating a “greenhouse effect” | 0,047-0,065 |
| mineral wool | walls, attics | inexpensive, easy to use, holds heat well | unstable to moisture, shrinks and deforms | 0,048-0,070 |
| ecowool | walls, attics | breathes well, environmentally friendly material | not resistant to moisture | 0,032-0,041 |
Depending on the structure of the material, all ceiling insulation materials that are used in houses with cold roofs can be divided into several groups:
- Monolithic (massive) - these include artificial materials (foam plastic, polystyrene), which are laid on the ceiling in large blocks that reliably prevent heat loss.
At the same time, they block the removal of excess moisture from the air, as mentioned earlier. - Fibrous (porous) are materials with a developed internal structure, represented by numerous fibers.
These fibers form large internal spaces that fill air bubbles that reliably retain heat in the house. A classic example is mineral wool. Threads of mineral wool, as well as ecowool, are able to absorb and retain moisture, but at the same time the protective properties of ecowool are practically not reduced. At the same time, it has been experimentally established. that moistening mineral wool by even 1% of its mass leads to a decrease in thermal conductivity qualities by up to 8%. This is explained by the fact that loose fibers begin to disintegrate, so the material loses density. - Bulk insulation - for example, expanded clay and sawdust. They protect the house from cooling by creating a dense layer that retains heat well. The advantages of these materials are also that they allow the surface to “breathe” and do not create a greenhouse effect in the house.
Density of ecowool when insulating with your own hands
To determine the density of the ecowool being laid, it is necessary to take into account the material consumption. The density of the laid thermal insulation is determined by taking into account its direct consumption on the insulated area.
Ecowool consumption rates:
- for flooring – 35 kg per cubic meter
- for a wall – 60 kg per cubic meter
- for the roof – 50 kg per cubic meter
We recommend monitoring the density of laid ecowool using a mathematical method, dividing the insulated area of a particular element into separate sections (squares), thereby reducing the error in the consumption of ecowool insulation at the time of its installation.
Flaws
The disadvantages of cellulose wool include:
- an increase in thermal conductivity during operation, which is caused by two reasons: a decrease in volume due to shrinkage (starts from the second year of operation); increasing the humidity of the insulating layer (when wet, it dries, but not to its previous state);
- significant shrinkage on vertical and inclined structures, and therefore manufacturers recommend increasing the layer thickness by 25% compared to the calculated one, or increasing the insulation density to 65 kg/m3. Both options lead to increased consumption of material, and, consequently, to increased costs of repair work;
- weak rigidity, which requires the installation of gratings on the walls and roof of the attic;
- complex technology for performing work not only in the wet state, but also when blowing dry fibers - without special equipment it is practically impossible;
- long drying time when applied “wet” - up to 3 days;
- strong dependence of the quality of ecowool on the feedstock, which is difficult to control even among leading manufacturers.
Recommendations for do-it-yourself insulation
- To calculate the required number of ecowool packages (15 kg each), you can use an online calculator, or multiply the insulated area in cubic meters by the technological consumption of the material.
- Recommended insulation thickness: for floors - 15-20 cm, for interfloor ceilings - 10-15 cm, for insulation of pitched roofs - 15-20 cm, and for attic floors - 20-30 cm.
- Unified reference and technological standards imply a mechanical method of laying insulation. The process of insulating a house manually, as a rule, occurs with a “reserve”. When purchasing ecowool for self-installation, consider that its consumption may be slightly higher than the established standards (on average by 10%).
- Ecowool insulation is intended for insulation of wooden structures; in cases of insulation of elements made of other materials (iron, stone, brick, concrete), it is necessary to isolate them from the possibility of absorbing condensed moisture from ecowool, and “foam” all large cracks
- In case of expected shrinkage of ecowool under the pressure of its own weight, it is necessary to install horizontal dividing partitions in high vertical insulated cavities during installation of ecowool, this will reduce the weight of the insulation.
- When insulating the roof, it is necessary to protect the insulation from the possible penetration of excessive amounts of under-roof condensate into it.
- For the convenience of compacting ecowool, you can make a simple “tamper”.
- We recommend selecting insulating materials in such a way that their ability to transmit steam is directed from the room to the street.
For questions regarding the use of ecowool, preparation for insulation, as well as questions regarding the purchase or coordination of its delivery, you can contact our company by phone (812) 9999-812 , or, regardless of the time of day, simply write us an email using the feedback form . We process all requests without exception, answering questions.
Ecowool is a “loose” insulation based on cellulose, gray (light gray in color). Developed and intended as the most suitable for thermal insulation of wooden structures.
Ecowool composition:
- 81% - recycled cellulose (from recycled newspaper waste paper);
- 12% - antiseptic (boric acid);
- 7% - fire retardant (borax).
Ecowool is a chemically passive insulation material and does not cause corrosion to metals in contact with it.
Technical characteristics of ecowool:
G2 - moderately flammable (GOST 30244), B2 (DIN 4102) - moderately flammable (GOST 30402), D2 - moderate smoke-generating ability (2.14.2 and 4.18 GOST 12.1.044), RP-1 - flame spread over the surface “0” (DSTU B V.2.7-38-95) Air permeability - low, with a material density of 35.0-40.0 kg/m3 total (80-120)x10-6 m3/msPa, vapor permeability - 0.3 mg/(mchPa ), sorption humidification according to GOST 17177.5 for 72 hours - 16%. pH value = 7.8–8.3; The thermal conductivity coefficient of the material is 0.037-0.042 W/(m*K).
Methods of use
You can insulate a house using ecowool in various ways. Industrial options involve spraying slightly moistened ecowool directly onto the insulated surface, and laying dry ecowool in the frame, pumped using powerful compressors. You can also effectively insulate a small building, such as a garage or country house, manually, but this will take a little longer and increase material consumption.
Wet method
Wet application of ecowool
In the wet method, lignin acts as an adhesive. Moistened ecowool easily adheres to walls made of any material, forming a layer of insulation with a density in the range of 50-65 kg/m³. This option is excellent for insulating brick block buildings. It is enough to lath the walls using a metal profile or wooden beam, which is preferable, and apply the material using special equipment. In this case, the fluffy cotton wool is wetted directly at the nozzle exit with a small amount of water and fed to the surface under pressure.
This type of ecowool installation is the most productive and easy to use. The disadvantage is the need to use fairly expensive equipment.
For application on complex surfaces and suspended structures, as well as when insulating ceilings, adhesives are additionally added to the water below for moistening, which will enhance the adhesion of ecowool, in addition to lignin.
All excess material is cut off level and dried, after which it is ready for reuse. Actually, with any method of installing ecowool, there is no waste left, because it can be reused.
Video: applying ecowool using special equipment
Dry method
As a classic option, ecowool can fill prepared niches in walls and sheathing cells on floors in dry form. In this case, you need to fluff it up using a nozzle for stirring solutions and a drill in a bulk plastic container, and fill all the necessary places with bulk. It is enough to compact it until it begins to absorb forces. In order to comply with the rules and regulations for insulating ecowool with your own hands, you must adhere to a simple formula:
m – required mass of ecowool;
S – area of the insulated cell;
L – thickness of the insulation layer;
P – required density of insulation.
Insulation using a compressor
For horizontal distribution, the density is chosen to be 45 kg/m³, for vertical distribution – 65 kg/m³.
The industrial method of distributing ecowool involves pumping the fluffy material with a compressor. The sheathing is completely covered with sheathing material, film or craft paper. At the top point of the structure there is a hole for mounting the supply hose. Under the influence of pressure and air flow, ecowool is blown into all, even minor, recesses of the cell to the top. Once filling is complete, the hole is sealed.
Video: manual installation of dry ecowool
A little history about Ecowool
The properties of cellulose have been known for a long time
Research into the possibilities of paper material at the end of the 19th century interested manufacturers and led to the creation of ecowool production technology. At the beginning of the twentieth century - 1928, the first production facility producing cellulose insulation was opened. The championship belongs to Germany.
Since then, cellulose insulation has only victoriously gained popularity: in the USA, Canada, Europe, Japan and other eastern regions, it is recognized as the most environmentally friendly and inexpensive. In Russia, domestic cellulose thermal insulation material has appeared since 1993. The technology, equipment, and even the Russian name for this insulation came to us from Finland. In Finland, the share of ecowool (where it is called “Ecovilla”) among insulation materials for low-rise construction reaches 70%.
The production of ecowool and its use is only gaining momentum in the post-Soviet space: In Kazakhstan, the material has been produced since 1999, in Estonia - since 1990, in Lithuania - since 1994, and in Ukraine and Belarus - since 2007, and since 2012 production of “Ekovata-Nevskaya” was launched near St. Petersburg.
What kind of material is this
You can’t use who knows what for insulation. Therefore, it is worth understanding what ecowool consists of and what characteristics it has.
Ecowool consists mainly of recycled products, or more precisely, paper. 80 percent ecowool consists of recycled cellulose. The remaining 20 percent is a mixture of antiseptic and fire retardants. They do not allow the material to rot and prevent the possibility of combustion.
In fact, this type of insulation practically does not support combustion, which adds positive points to it. The borax included in the composition is responsible for this feature. Mold and rot are also not a problem for this insulation, since for this purpose, the list of components contains boric acid.
Despite the scary names of the components included, all of them are absolutely safe in terms of human health.