A well-equipped home is a guarantee of a comfortable family life. This is important in winter, when pipes for water supply and heating must be insulated from the cold and protected from cooling of the coolant. Owners of buildings in the private sector in the cold season have problems with those sections of the pipeline that are laid in the cold basement and attic, in open areas adjacent to general communications. Water freezes in a system made of any material if thermal insulation of the pipelines has not been installed in advance.
The method of installing thermal insulation depends on the type of material and the method of laying the pipeline
The main tasks of thermal insulation of pipelines
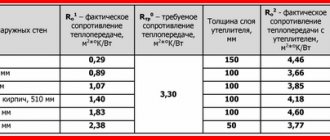
Based on building regulations, when installing any pipeline, it is recommended to use insulation that is suitable for a certain type of communications. These documents also regulate the thickness of the thermal insulation of heating pipelines. Insulating materials are produced in ready-made form, convenient for use:
- cylinders, half-cylinders;
- winding;
- film;
- insulating paint;
- sprayed insulation.
The latest generation of thermal insulation materials minimize heat loss in the coolant and increase the efficiency of the pipeline. Convenient forms of insulation release facilitate the installation of thermal insulation of pipelines.
During installation, it is important to properly lay and insulate all communications, excluding “cold bridges” and unprotected areas. Some parts of the pipeline require double or triple protection with various insulating materials, especially at joints.
The main mistakes leading to heat loss or freezing of the pipeline:
- lack of knowledge of installation technology;
- incorrect calculation of the thermal insulation layer of pipelines;
- incorrect choice of material for insulation.

When choosing an insulating material, you should take into account its properties, thickness, as well as the diameter of the pipes that are planned to be insulated
Each thermal insulating material has its own advantages and disadvantages. One pipe insulation has a longer service life, the other is less protected from moisture, so they are often combined for greater efficiency. The most important tasks that competent installation of pipeline insulation helps to solve:
- mechanical protection of pipes from deformation and corrosion;
- increasing efficiency when transporting coolant;
- reduction of heat loss;
- increasing the period of uninterrupted operation of pipes that does not require repairs;
- minimizing heat exchange with the external environment;
- protection against temperature changes and moisture.
When choosing materials for thermal insulation of pipelines, it is important to consider their parameters:
- resistance to chemicals and mechanical stress;
- thermal conductivity indicators of insulation;
- resistance to increased temperature loads;
- moisture resistance, vapor permeability;
- maintaining the integrity of the coating under compression, tension, and increased load;
- fireproof properties.
Note! If part of the pipeline will be located on the surface in winter, outside the heated room, the thickness of the thermal insulation of the heating pipelines or the number of layers should be maximum.

Pipes laid in unheated rooms and along the street must be insulated with the thickest material with a moisture-proof layer
In some sections of the pipeline, an alternative to expensive “shelling” can be used. If there are wide sewer or plastic pipes left, they can be cut lengthwise to wrap around metal pipes. Fill the intermediate space with leftover mineral wool or polyurethane foam (through cleared holes). The outer layer should be well secured with construction tape or other reliable winding, preferably foil.
It is impossible to name any one universal insulation material, since the construction market offers different thermal insulation materials for pipelines with many advantages. On the Russian market you can find imported and domestic thermal insulating materials from well-known brands:
- Knauf;
- Ursa;
- Isover.
Isolation of these firms is considered the most practical and effective.
Requirements for thermal insulators
The materials used for thermal insulation must meet the following conditions:
- To be environmentally friendly, not to cause harm to human health, not only in normal conditions, but also in the event of heating from insulated pipelines.
- Have a high service life when used not only indoors, but also outside in the open air or underground.
- The main requirement for any materials for thermal insulation of pipes is the lowest possible thermal conductivity coefficient.
- The material must be biologically stable. This prevents the formation of mold and mildew on it, as well as damage from insects and rodents.
- Heat insulators are often used on pipelines transporting hot water and steam with temperatures above 100 °C. Their material must withstand such thermal loads as well as significant negative temperatures throughout their operational life.
- The heat insulator must be corrosive and chemically resistant when used in an aggressive environment, which includes laying in the ground.
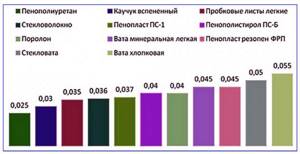
Rice. 3 Thermal conductivity of thermal insulators in W/(m °C)
Related article:
What kind of thermal insulation is there for heating pipes - types of materials and installation . In a separate article, in addition to expanded information about everything for thermal insulation of pipes, we reveal in more detail the types of thermal insulation that are used to insulate household heating pipes. Read it, I'm sure it will be interesting!
- Thermal insulation materials used underground are subject to increased requirements for rigidity and strength.
- It is desirable that thermal insulators do not absorb water and do not absorb moisture from the environment. This leads to a sharp increase in their thermal conductivity.
- Some pipelines made of polymer materials for hot water supply and heating are laid in screeds or grooves under the plaster walls. When hot water flows and after the pipes cool, deformations occur in the main due to the thermal expansion of the materials. To compensate for them, damper heat-insulating shells are used, which reduce to zero the risk of cracking of the plaster or screed when the geometric dimensions of the pipeline change.
- It is important that heat-insulating materials are not flammable or do not support combustion. When used indoors in residential premises, the absence of harmful gases in combustion products of thermal insulators plays an important role.
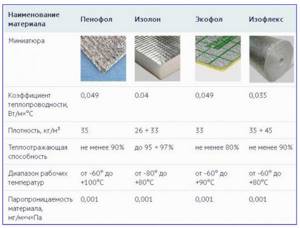
Rice. 4 Physical characteristics of different brands of polyethylene foam
- Thermal insulators should be easy to install without the formation of cold bridges. It is desirable that the material has good maintainability and that it can be easily dismantled in the event of an emergency on the pipeline.
- As with all building materials, the cost of thermal insulators plays an important role, which should be affordable to any consumer with low or average income.
Insulation based on basalt (mineral) wool
The main form of release is a cylindrical wrapping for pipes based on mineral raw materials. Durable and reliable insulation that does not harbor insects and mice, which is important for installation in basements and attics. Despite the appearance of mineral wool, the thermal insulation of pipelines using it guarantees long-term and flawless operation. Ready-made molded elements are sold for pipes of different diameters, so when purchasing it is important to know the plumbing parameters. In case of probable mechanical impacts on the external part of communications, rolls of basalt wool should be protected with a layer of reflective foil. There are offers with a ready-made protective layer, for example, made of foil insulation or glassine.
Installation: The pipes are covered with ready-made fragments, secured with tape, sometimes plastic ties or tapes are used.
Pipeline repair with replacement of external insulating coating
CLEANING METHODS: mechanical; chemical; thermal. The use of the last two when performing repair work on existing pipelines is prohibited. In practice, only mechanical cleaning methods are used.
TYPES OF MECHANICAL CLEANING:
— cutting off old insulation using cutters (knives), chains, brushes, cables;
— cleaning by dynamic impact on the insulation using sandblasting, shot blasting and shot blasting;
— hydrodynamic method (the surface is cleared of insulation as a result of exposure to water injected under high pressure). Insulation work is carried out during major repairs in the same way as during the construction of a new pipe. Repair of insulating coatings is carried out: with lifting of the pipeline in the trench; with lifting and laying the pipeline onto trench beds; without lifting, maintaining the position of the pipeline.
Selection of types and areas of major repairs of pipelines.
— examination (flaw detection) of the pipe wall and the condition of the insulating coating, as well as data for the entire period of operation of the pipeline, condition assessment;
— clarification of the location of the defective area, additional examination of detected defects;
—planning measures to prevent possible disruptions to the oil pipeline;
— the choice of type and method of repair depends on the following indicators: the condition of the insulating coating and the pipe wall; size and relative position of corrosion damage to the pipe wall; the number and nature of the distribution of dangerous and potentially dangerous defects in the pipe wall; specific conditions for the pipeline; actual and predicted oil pipeline load indicators; technical and economic indicators by types and methods of repair.
— establishing the timing of repairs depending on the nature of the defect, taking into account the workload of the oil pipeline at the moment and in the future;
— drawing up long-term and current plans for major repairs of the oil pipeline.
Classification and characteristics of accidents on main pipelines.
An accident is a sudden release or outflow of oil as a result of complete destruction or partial damage to a pipeline, its elements, tanks, equipment and devices, accompanied by one or more of the following events:
1. Ignition of oil or explosion of its vapors;
2. Pollution of any watercourse beyond the limits established by the water quality standard, causing a change in the color of the surface of the water or banks or leading to the formation of an emulsion below the water level, or to the precipitation of sediments on the bottom or banks;
3. The leak volume was 10 m³ or more.
4. Fatal injuries to people.
5. Injury to people with loss of ability to work.
TYPES OF ACCIDENTS
Category I - accidents characterized by a violation of the pipeline tightness with a loss of the pumped product of more than 100 tons or pipeline downtime for more than 24 hours;
Category II - accidents with loss of pumped product of less than 100 tons or pipeline downtime from 8 to 24 hours.
Violation of the tightness of the pipeline with loss of the pumped product up to 1 ton and downtime of the pipeline for up to 8 hours are classified as damage.
Category III - accidents in this category are characterized by a leak in tightness with a loss of oil product from 1 to 10 tons or downtime from 0.5 to 8 hours.
METHODS AND TOOLS FOR ACCIDENT DETECTION:
—visual (visible output);
— pressure control (pressure gauge readings): a decrease of more than 0.15 Pa indicates a leak or damage; — graphic-analytical;
—balance sheet accounting of oil;
— analysis of changes in the load of electric motors.
Methods for repairing defects in the pipe body.
DEFECTS: dents, corrugations, scuffs, cracks, metal loss, ovality, scratches, risks, corrosion, delamination, etc.
REPAIR METHODS
— grinding: [corrosion, risks, delamination];
—welding: [corrosion pits, risks];
— installation of a repair structure (couplings, pipes): [corrosion, dents, cracks, delaminations, risks and their combinations];
— cutting out the defect (replacing the “coil” or replacing the section); with this repair method, the section of pipe with a defect (coil) must be cut out from the oil pipeline and replaced with a defect-free coil [extended crack, deep dent with crack or corrosion].
Fiberglass insulation
The most affordable material produced on the basis of quartz sand, but obsolete “glass wool” is prohibited in many countries. This insulation is inexpensive, but over time this insulation becomes compacted and its effectiveness decreases. On the outside, additional winding is required, for example, with fiberglass.
Attention! Microscopic glassy threads are dangerous for the skin, so when installing such insulation it is important to take care of protecting the skin of the hands, face, and entire body.
Installation: A small layer of glass wool is placed over the heating pipes and covered with a non-hygroscopic material. The outside is wrapped with foil and roofing felt.
Use of thermal insulation materials in specific conditions
When solving the problem of insulating pipes using modern materials, it is necessary to take into account not only their properties, but also take into account environmental conditions . When insulating communications in the attic, it should be taken into account that high airflow and a significant level of humidity prevail in these rooms. During a sudden cold snap, subzero temperatures may be present in the attic floor. For this reason, preventing the appearance of “cold bridges” becomes an important task.
Using basalt wool or sprayed polystyrene foam in the attic is the most optimal option for insulating communications. An important task is to perform a proper vapor barrier on the attic floor.
If we talk about aluminum foil, it is not used separately as thermal insulation due to its high thermal conductivity. However, it is often used as an additional layer or used for winding. This solution makes it possible to maintain the temperature parameters of coolants transported through pipes.
When installing thermal insulation of pipes during the construction of light-duty country buildings on soils that are unstable, the materials are required to be light in weight. For example, such a popular thermal insulation material as basalt wool is heavier than its quartz counterparts. For this reason, it is often called “stone” wool. Polystyrene foam is a lighter heat insulator compared to it. Therefore, for thermal insulation of communications laid in light wooden country houses, it should be used.
To avoid difficulties when insulating pipes in a private house, it is best to use insulated pipes and self-adhesive insulation when laying communications. In order to eliminate errors made when performing thermal insulation work, you can use an additional winding. Experts often use aluminum tape.
The market offers a wide range of rigid semi-cylindrical insulation materials. Their peculiarity is that they can be used for pipes of a certain shape. Therefore, using them for wide and narrow pipes is quite problematic.
When choosing a material for thermal insulation of pipes that are located in adjacent areas, for example, between heating systems, plumbing and chimneys, experts in the field of thermal insulation recommend using insulation such as mineral wool. This material should be used in the most convenient form for the owner of the object.
Expanded polystyrene shell
This is an improved type of foam used for pre-insulated pipes or insulation in the form of cylinders and half-cylinders. Reuse is possible if it is necessary to open the pipeline to eliminate a leak or dismantle it. Available with or without an outer protective layer.
Installation: Laying the shell is the easiest thing to do, thanks to the well-designed release form. Expanded polystyrene cylinders are suitable for ground communications and underground (channel) pipe laying. They are covered with shell halves that fit the width of the pipe and secured. Foil tape is applied in a spiral in tightly adjacent layers.
To ensure “overlapping” of shell fragments when installing thermal insulation of pipelines, it is better to move the halves relative to the second part. After wrapping with foil tape, the insulation can be considered complete.
It is important to know! Similar to polystyrene foam shell halves, molded half cylinders made from other materials such as foam rubber or polystyrene foam are laid. Foamed polyethylene is produced in the form of a multicomponent base for foil insulation. And without an additional layer, it gradually deforms, cakes and creeps at the junction.

The factory “shell” made of polystyrene foam is easy to install, thanks to special grooves on each segment
Everything for pipe insulation and its application
For thermal insulation of pipelines, a wide range of synthetic and natural materials are used, produced by many domestic and foreign industrial enterprises. The basic principle of operation of the vast majority of heat insulators is that close to a vacuum and, to a lesser extent, atmospheric air are very poor heat conductors. That is, if a material has a large number of air chambers in its structure, its thermal conductivity is much less than if there are none.

Rice. 5 Foamed polyethylene tubes, regular and with a protective PE sheath
Indoors
Since indoor materials are not exposed to precipitation, their water resistance does not play an important role. Also, due to the lack of pressure on the outer shell, there are no requirements for their rigidity and strength. And finally, environmental friendliness is of great importance if heat insulators are used in residential buildings and apartments. The following types of insulators are most often used for internal thermal insulation of pipes:
Made from foamed polyethylene. Polyethylene (PE) is classified as an environmentally friendly and safe self-extinguishing material. For temperature insulation of pipelines, tubes 2 m long are produced with a longitudinal or intended line for cutting to the outer diameters of pipes from 15 to 160 mm. The shell thickness of the tubes ranges from 6 to 25 mm.
Operating parameters of foamed polyethylene:
- temperature range: from - 60 to + 75 ° C;
- thermal conductivity: 0.35 - 0.5 W/(m °C);
- water absorption: about 0.8% of volume;
- vapor permeability: 0.001 mg/m·h·Pa;
- flammability: groups G-1 and G-2 (slightly or moderately flammable).
PE pipe insulation is produced by a wide range of manufacturers with the brands Energoflex, Izokom, Isodom. Sometimes roll insulation of the Penofol, Izolon, Ecofol, Isoflex brands is also used to cover pipelines. Its advantages are the presence of a foil layer, which reduces losses from infrared radiation.

Rice. 6 Everything for thermal insulation of foam rubber pipes
Foamed rubber. This heat insulator in the form of tubes 2 m long with different diameters and wall thicknesses (similar to foamed PE tubes) is produced under the Energoflex and K-Flex trademarks. Basic physical and operational characteristics of foam rubber:
- thermal conductivity: 0.036 - 0.045 W/(m °C);
- flammability group: G-1 (slightly flammable);
- operating temperature range: from -200 to +150 °C;
- water absorption: 0.15% by volume;
- vapor permeability: 0.00012 mg/m·h·Pa.
Spray polyurethane foam
Convenient form of release - a two-component mixture is sprayed from a special device through a nozzle. It is used on any inclined surface or in hard-to-reach places in warehouses, attics and other auxiliary rooms. The use of foam materials such as sprayed polyurethane foam when laying underground communications is not advisable. The porous material is compacted under soil pressure, therefore losing its properties and becoming ineffective
Installation: Thermal insulation by spraying in the form of snow foam can be performed not only on the surface of pipes, but also on any freezing surface. Dense white foam forms excellent adhesion to metal (steel) pipes.
Advice! You can do this work yourself (if you have basic skills) or entrust it to a specialized company. In the absence of experience, there will be a large consumption of foam and an uneven layer during application. It is advisable to practice on a few square meters of area before fully thermally insulating the pipeline.
Thermal insulation paint
An innovation on the domestic construction market is a white or gray paste based on a multicomponent mixture of acrylic and synthetic fillers. It tolerates temperature changes well and perfectly protects metal from corrosion and condensation.
Installation: Apply with a special spray in several layers to ensure better insulation. It is advisable to treat well-cleaned pipes with a primer for painting metal.
With any method of pipe processing, it is important to check the tightness of communications, clean the pipes from rust, you can apply a primer and treat them with insulation according to all installation rules. Insulating the pipeline with high-tech materials guarantees that a private home will be provided with an uninterrupted supply of cold water and efficient heating.