Ease of use of the calculator
Regardless of the type of highways, they are all subject to insulation. Usually they try to lay pipes underground. But in private construction, it is not uncommon for some fragments of engineering systems to pass along the street, through a basement, attic or unheated room. External installation becomes a forced decision if, for example, it is necessary to install a water supply or heating main to an auxiliary or technical building, and the boiler room is located in a residential building.
Such a section of the highway must be protected differently than underground communications: from the physical effects of natural phenomena (freezing), corrosion, and also to minimize thermal energy losses. All these problems are solved with the help of additional thermal insulation. It is worth saying that calculating the volume of pipeline insulation on a calculator is convenient for three reasons:
- Optimizes costs.
- Saves your time.
- Offers additional features. For example, when calculating mineral wool cylinders, linear meters are converted to volume (m³). This allows you to understand which vehicle is suitable for transporting the material.
Thermal insulation is the path to savings Source jhmrad.com
Correct calculation will allow the work to be completed correctly, and the pipes will be maintained in proper condition. The choice of material also plays an important role, because it not only prevents heat loss, but also prevents corrosion, and, therefore, helps to extend the life of the system.
Pipeline insulation options
Finally, we will consider three effective methods of thermal insulation of pipelines.
Perhaps one of them will appeal to you:
- Insulation using a heating cable . In addition to traditional isolation methods, there is also an alternative method. Using the cable is very convenient and productive, considering that you only need to protect the pipeline from freezing for six months. In the case of heating pipes with cables, there is a significant saving of effort and money that would have to be spent on earthworks, insulation material and other issues. The operating instructions allow for the cable to be located both outside and inside the pipes.
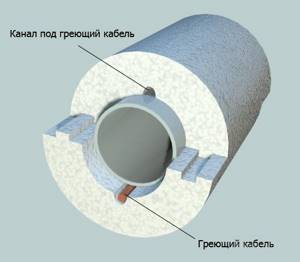
Additional thermal insulation with heating cable
- Air insulation . The mistake of modern thermal insulation systems is this: they often do not take into account the fact that soil freezing occurs according to the “top to bottom” principle. The freezing process is met by a flow of heat emanating from the depths of the earth. But since insulation is carried out on all sides of the pipeline, it turns out that I also insulate it from rising heat. Therefore, it is more rational to install insulation in the form of an umbrella over the pipes. In this case, the air gap will act as a kind of heat accumulator.
- "Pipe in pipe" . Here, more pipes are laid in polypropylene pipes. What advantages does this method have? First of all, the advantage is that the pipeline can be heated in any case. In addition, heating is possible using a device for suctioning warm air. And in emergency situations, you can quickly extend the emergency hose, thereby preventing all negative aspects.

Insulation based on the “pipe-in-pipe” principle
Materials: optimal options for pipelines
Thermal insulation is used for all types of pipelines, regardless of the temperature of the coolant. As a rule, it consists of the following components:
- The main layer of thermal insulation. It protects the insulated pipe from heat loss.
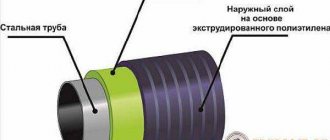
- External covering. It protects the thermal insulation layer from moisture, mechanical damage, and exposure to aggressive environments. External protection requires special strength and preservation of integrity during operation.
- Fastenings. Holds materials in the correct position.
Several types of materials are used to construct insulation. They differ in the method of application to the surface and the thickness of the resulting layer, but must have the following qualities:
- Do not belong to the class of flammable substances.
- Do not be aggressive towards metal elements of the system.

See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in water supply, sewerage and related work
According to the scope of application, the following types of insulation are distinguished:
- For elements of production lines.
- For sewer, waste and drainage pipes.
- For ventilation ducts and air conditioning systems.
- For underground pipelines with hot and cold water.
Calculation of thermal insulation of pipelines in calculators is carried out on the basis of another classification of insulation - their shape. According to this parameter, sprayed, slab, rolled materials and insulation in the form of cylinders are distinguished. The following types of thermal insulation are common in private construction:
- Mineral wool and mineral wool mats with fiberglass (stitched).
- Low-density mineral wool slabs with synthetic binders.
- Sovelite slabs (asbestos-cement).
- Plates of increased rigidity.
Foil coatings, polymer films, glass wool of various thicknesses, plaster coatings, and fiberglass (for waterproofing) are also used. A separate class consists of polymer-bitumen compositions, durable and economical; liquid polyurethane foam is less commonly used.

Insulation of a chimney pipe Source oboiman.ru
Methodology for calculating a single-layer thermal insulation structure
The basic formula for calculating the thermal insulation of pipelines shows the relationship between the amount of heat flow from an existing pipe covered with a layer of insulation and its thickness. The formula applies if the pipe diameter is less than 2 m:

Formula for calculating thermal insulation of pipes.
ln B = 2πλ [K(tт - to) / qL - Rн]
In this formula:
- λ — thermal conductivity coefficient of insulation, W/(m ⁰C);
- K is the dimensionless coefficient of additional heat loss through fasteners or supports, some values of K can be taken from Table 1;
- tt is the temperature in degrees of the transported medium or coolant;
- to—outside air temperature, ⁰C;
- qL—heat flow value, W/m2;
- Rн - heat transfer resistance on the outer surface of the insulation, (m2 ⁰C) / W.
Table 1
| Pipe laying conditions | K coefficient value |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, through channels, tunnels, open indoors on sliding supports with a nominal diameter of up to 150 mm. | 1.2 |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, through channels, tunnels, open indoors on sliding supports with a nominal diameter of 150 mm or more. | 1.15 |
| Steel pipelines are open along the street, through canals, tunnels, and open indoors on suspended supports. | 1.05 |
| Non-metallic pipelines laid on suspended or sliding supports. | 1.7 |
| Channelless installation method. | 1.15 |
The thermal conductivity value of the insulation λ is a reference value, depending on the selected thermal insulation material. It is recommended to take the temperature of the transported medium tt as the average throughout the year, and the temperature of the outside air tto as the average annual temperature. If the insulated pipeline runs indoors, then the ambient temperature is set by the technical specifications for the design, and in its absence it is taken equal to +20°C. The indicator of heat transfer resistance on the surface of a heat-insulating structure Rн for outdoor installation conditions can be taken from Table 2.
table 2
| Rн,(m2 ⁰C) /W | DN32 | DN40 | DN50 | DN100 | DN125 | DN150 | DN200 | DN250 | DN300 | DN350 | DN400 | DN500 | DN600 | DN700 |
| tt = 100 ⁰C | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.017 | 0.015 |
| tt = 300 ⁰C | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.015 | 0.013 |
| tt = 500 ⁰C | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.016 | 0.014 | 0.012 |
Note: the value of Rн at intermediate values of coolant temperature is calculated by interpolation. If the temperature is below 100 ⁰C, the value of Rн is taken as for 100 ⁰C.
Indicator B should be calculated separately:
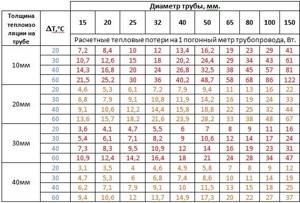
Table of heat losses for different pipe thicknesses and thermal insulation.
B = (diz + 2δ) / dtr, here:
- diz - outer diameter of the heat-insulating structure, m;
- dtr — outer diameter of the protected pipe, m;
- δ—thickness of the thermal insulation structure, m.
Calculation of the thickness of pipeline insulation begins with determining the indicator ln B, substituting into the formula the values of the outer diameters of the pipe and thermal insulation structure, as well as the thickness of the layer, after which the parameter ln B is found using the table of natural logarithms. It is substituted into the main formula along with the indicator of the normalized heat flow qL and make a calculation. That is, the thickness of the pipeline insulation must be such that the right and left sides of the equation become identical. This thickness value should be taken for further development.
The considered calculation method applied to pipelines with a diameter of less than 2 m. For pipes of larger diameter, the calculation of insulation is somewhat simpler and is carried out both for a flat surface and using a different formula:
δ = [K(tт - to) / qF - Rн]
In this formula:
- δ—thickness of the thermal insulation structure, m;
- qF is the value of the normalized heat flow, W/m2;
- other parameters are the same as in the calculation formula for a cylindrical surface.
Selecting a calculation method
High-quality pipeline insulation calculators have the ability to calculate the insulation in accordance with the final goal:
- What kind of thermal insulation should be in order to ensure a certain (specified) temperature on the surface. Such thermal insulation is in demand when it is necessary to reduce heat generation in a room or to comply with safety requirements and protect people from burns. Materials with a reflective surface are suitable for such purposes.
- What kind of insulator should be in order to protect the liquid circulating in the pipes from freezing at sub-zero temperatures. This problem is solved for pipeline sections located in the open air. It is especially relevant for small-diameter pipes that are not able to accumulate heat well.
- What thickness of thermal insulation should be so that moisture does not condense on its surface. The calculation is performed for pipes located indoors if cold water flows through them (the water temperature is lower than the air temperature). The calculation is not carried out for a system located outdoors.

Thermal insulation for water supply pipes Source odstroy.ru
- What should be the thickness of thermal insulation for a two-pipe underground installation.
Any insulating material has a thermal conductivity lower than pipes, so the heat flow density through it decreases, and therefore heat loss is reduced. All insulation calculations allow you to select the optimal thermal insulation thickness to save energy and maintain the performance of the system. When the required task is selected, all that remains is to enter the initial data.
General information
What is taken into account during the calculation:
1.what temperature are the insulated pipes?
2.range of temperature difference outside.
3.level of mechanical impact, for example, vibration, linear expansion.
4. maximum permissible loads on the pipeline.
5. loads experienced by the pipeline from the ground or transport passing from above.
6.indicator of thermal conductivity of insulating material.
7. resistance of thermal insulation to various types of deformation.
Reference! According to SNiP 41 – 03 – 2003, all thermal insulation materials have different characteristics that are suitable for insulating different types of pipelines and can withstand different operating conditions. Pipelines with a temperature of less than twelve degrees must have a vapor barrier layer.
Working with an online calculator
To calculate the thickness of pipeline insulation, enter the following initial data into the calculator fields:
- Outer diameter of the pipeline (in mm).
- Insulation material. Typically the field looks like a drop-down list where you can select the appropriate option. Some calculators are more specific, and are designed for only one heat insulator (for example, a mineral wool cylinder).
- Average coolant temperature. The indicator may include two numbers (readings in the forward/return pipeline), for example, 65/50, 90/50, 110/50.
- Temperature of the insulated surface (in °C).

Insulation of underground communications Source znatoktepla.ru
- Type of protective coating, metallic or non-metallic.
- Time until water freezes when the system is stopped: 0.5 hours, 0.75 hours, 1 hour, 1.25 hours.
To calculate the volume of thermal insulation of pipelines, additional parameters are entered into the calculator:
- Insulation thickness (in mm).
- Pipeline length (in m).
- The material from which the pipe is made (plastic or metal).
- The specific gravity (density) of the insulation, its thermal conductivity coefficient (sometimes it is enough to select a name from the list).
Some insulation calculators allow you to calculate the amount of thermal insulation for round bends. In this case, it is necessary to specify the bending radius (curvature of the center line) and the number of bends.
As a result, you will get the thickness or volume of thermal insulation suitable for your conditions. For any parameters, it is not recommended to purchase thermal insulation of greater thickness, “with a margin”. Such a modification will not bring a fundamental improvement, but the increase in the cost of the material, compared to insignificant optimization, will be significant.

Pipeline insulation on the street Source pinimg.com
Calculation of pipeline insulation materials
It is not difficult to carry out insulation calculations for pipelines; for convenience, it is recommended to use special calculators. There are a number of actions that allow you to preliminarily determine the volume of materials. Before starting calculations, you should immediately decide what type of insulation will be used. Insulators differ not only in appearance, but also in installation conditions and properties.
Painting agents can be used to insulate pipelines.
The quality of the materials is high, the layer is thin but durable, fully performing all functions. The calculation is done as follows:
- The formula for calculating the area of the cylinder is S=2πr(h+r), where r is the radius of the base of the pipe, h is the pipe length parameter, π is a constant, the approximate value for this case is 3.14.
- The resulting value is the coloring area. Next, according to the manufacturer’s instructions, determine the material consumption.
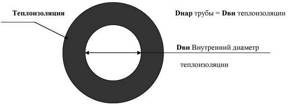
Scheme for calculating thermal insulation for a pipe.
When using conventional insulating materials, calculations are much simpler. It is necessary to determine the volume for the inside and outside of the pipe. To do this, use the formula V=πr2h, where:
- V is the volume of the pipeline;
- r — radius value (external or internal);
- h—pipe length;
- π is equal to 3.14.
The value of the internal and external radius is calculated separately, the resulting difference will be equal to the volume of the entire pipeline insulation material. Wrapping is an option for external insulation. In this case, the calculation is performed similarly using the first formula indicated, but it is necessary to take into account the thickness of the material, since it affects the quantity.
Briefly about the main thing
An online pipeline insulation calculator allows you to quickly calculate the thickness and volume of heat-insulating material. Thanks to the use of technology, you will save time, optimize costs and protect yourself from errors that are common in manual calculations with their cumbersome formulas.
Calculations may differ slightly depending on the task being set. For example, protection against heat loss, condensation or freezing of pipe contents. Accordingly, the data required to enter may vary.
Ratings 0