');> //–> The volume of water in a pipe is a quantitative characteristic of the space occupied by water inside the pipe.
The mass of water in a pipe is a quantitative characteristic of the mass of water located inside the pipe.
Volume calculation formula:
V = π * d 2 * l / 4
l – pipe length; d – internal diameter of the pipe.
The relationship between volume and mass is determined by a simple mathematical formula:
v – volume; m – mass; p – density.
In the calculation, the density of water is taken to be 1000 kg/m3.
You can quickly perform this mathematical operation using our online program. To do this, enter the initial value in the appropriate field and click the button.
This page presents a program for calculating the volume and mass of water in a pipe in accordance with the internal diameter of the pipe and its length.
Volume of water in polypropylene pipe
| diameter | 20 | 25 | 32 | 40 | 50 | 63 | 75 | 90 | 110 |
| water volume m3 | 0,14 | 0,22 | 0,35 | 0,55 | 0,87 | 1,38 | 1,96 | 2,83 | 4,20 |
For any questions you are interested in, please contact our office Teploprofi Company Russia, Penza region, Penza, st. Nekrasova, 46. Tel., fax, mobile Website: Teploprofi
We will professionally select and install
Russia, Penza region, Penza, st. Nekrasova, 46.
Sometimes it is very important to accurately calculate the volume of water passing through the pipe. For example, when you need to design a new heating system. This raises the question: how to calculate the volume of a pipe? This indicator helps to choose the right equipment, for example, the size of the expansion tank. In addition, this indicator is very important when antifreeze is used. It is usually sold in several forms:
The first type can withstand temperatures of 65 degrees. The second one will freeze at -30 degrees. To buy the right amount of antifreeze, you need to know the volume of coolant. In other words, if the volume of liquid is 70 liters, then you can purchase 35 liters of undiluted liquid. It is enough to dilute them, maintaining a proportion of 50–50, and you will get the same 70 liters.
What formula is used to calculate
To get accurate data, you need to prepare:
First, the radius is measured, designated by the letter R. It can be:
The first allows you to calculate how much liquid can fit in the cylinder, that is, the internal volume of the pipe, its cubic capacity.
The outer radius is necessary to determine the size of the space it will occupy.
To calculate, you need to know the pipe diameter data. It is denoted by the letter D and is calculated using the formula R x 2. The circumference is also determined. Denoted by the letter L.
Calculation of polypropylene pipes
In order to install the optimal heating or plumbing system in a particular room, a preliminary calculation of its operating parameters is made. The most important point here is the correct choice of pipe diameter. Such calculations ensure future energy savings and at the same time efficient operation of pipeline systems. These calculations are made using special formulas, as well as using previously developed tables. This work is called hydraulic calculation.
During this calculation, the amount of pressure loss to suppress hydraulic resistance inside the pipeline is determined. This resistance occurs at connections, branches and turns of the pipeline. However, the strongest pressure resistance occurs in places where there is a transition from a larger diameter pipe to a smaller diameter pipe. At this point, a throttling effect occurs, which is always accompanied by resistance to the main flow. Hydraulic losses can be calculated using this table.
As we said at the beginning of the article, the internal diameter of the pipes is perhaps the main factor in ensuring optimal operation of the pipeline. The total volume of water circulating in the system per unit of time depends on it. The main parameter in hydraulic calculations is the internal, not the external, diameter of the pipes. Correct calculation of the internal diameter of pipes is especially important when installing heating and plumbing systems in multi-storey buildings. An error in calculations may result in residents of the upper floors being left without water and heat. The required internal diameter and permeability of polypropylene pipes is determined by the formula
where Qtot is the maximum water flow, Pi is a coefficient of 3.14, V is the water circulation speed in the pipeline.
Such calculations are not needed for private houses. Experience shows that the optimal diameter of plastic pipes for houses and cottages is 20 millimeters.
How to calculate cross-sectional area
If the pipe is round, the cross-sectional area should be calculated using the formula for the area of a circle: S = π*R2. Where R is the radius (internal), π is 3.14. In total, you need to square the radius and multiply it by 3.14. For example, the cross-sectional area of a pipe with a diameter of 90 mm. We find the radius - 90 mm / 2 = 45 mm. In centimeters this is 4.5 cm. We square it: 4.5 * 4.5 = 2.025 cm2, substitute it into the formula S = 2 * 20.25 cm2 = 40.5 cm2.
The cross-sectional area of a profiled product is calculated using the formula for the area of a rectangle: S = a * b, where a and b are the lengths of the sides of the rectangle. If we consider the cross-section of the profile to be 40 x 50 mm, we get S = 40 mm * 50 mm = 2000 mm2 or 20 cm2 or 0.002 m2.
Soldering of polypropylene pipes
For this, a special soldering iron is used, on which nozzles are installed that can heat pipes of different diameters. One side of the nozzle heats the pipe from the outside and from the end; it is shaped like a small glass, and the second heats the connecting element (tee, angle or coupling).
The task is to simultaneously melt the outer part of the pipe and the internal cavity of the transition. It is at this moment that many novice plumbers make one significant mistake - they must not overheat the pipe and connector. This is fraught with the fact that the small internal hole intended for the flow of water is, at best, almost halved, which reduces the throughput of the pipe, and at worst, it seals it tightly. And then look for where it happened, it’s good if you haven’t had time to wall it up yet.
We insert the pipe and the “connector” into the nozzles, forcefully press them into it until it stops, count two or three seconds, remove the pipe from the soldering iron and connect the two elements together. Here you need to understand that the larger the diameter of the pipes being connected, the more time it takes to warm them up. Let's just say that 2-3 seconds of warming up is an axiom for a pipe ø20 (in the old days it is ½ inch), and for the subsequent diameter (ø25 or ¾ inch) the warming up time increases to 5-6 seconds. And so on with each diameter.
READ ALSO: What Could Be Swollen Cones on Polypropylene Pipes
Then another nuance arises. Firstly, the elements to be joined must be held with force until the polypropylene hardens - as a rule, this is 15-20 seconds. Secondly, at the moment the polypropylene hardens, you need to hold it firmly and securely so as not to turn or move the pipe in the connector. If you disturb the joint at this moment, you're guaranteed to leak.
Droplets of water that may remain in the plumbing system during its repair or the addition of any elements have the same detrimental effect on the joint. The steam generated at high temperatures simply will not allow the polypropylene to combine into a single whole. In this case, ordinary bread crumb is used. It is packed into the pipe and gives several additional tens of seconds, during which you need to have time to solder everything. Subsequently, the crumb is completely dissolved by water, and there can be no talk of any plugs.
If you are soldering polypropylene pipes for the first time, it would be good to invite a person who has already done similar work as an assistant. Experience is of great importance, and in some moments, competent advice on how to properly solder polypropylene pipes can be very helpful.
At first, when mastering this type of work, soldering propylene pipes will not be done quickly at all. But you shouldn’t rush, because if you rush, the quality will suffer. Do you need leaks?
By gaining experience, you will learn to work more efficiently, and the time spent on soldering polypropylene pipes will be reduced.
Who knows, over time, having learned how to solder propylene pipes, you may want to improve not only the plumbing in your home, but also the sewerage and heating systems, and you will be able to help your friends in repairing communications.
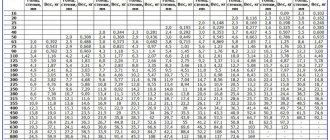
Internal volume of a linear meter of pipe in liters - table
The table shows the internal volume of a linear meter of pipe in liters. That is, how much water, antifreeze or other liquid (coolant) is needed to fill the pipeline. The internal diameter of pipes is taken from 4 to 1000 mm.
| Inner diameter, mm | Internal volume of 1 m running pipe, liters | Internal volume of 10 m linear pipes, liters |
| 4 | 0.0126 | 0.1257 |
| 5 | 0.0196 | 0.1963 |
| 6 | 0.0283 | 0.2827 |
| 7 | 0.0385 | 0.3848 |
| 8 | 0.0503 | 0.5027 |
| 9 | 0.0636 | 0.6362 |
| 10 | 0.0785 | 0.7854 |
| 11 | 0.095 | 0.9503 |
| 12 | 0.1131 | 1.131 |
| 13 | 0.1327 | 1.3273 |
| 14 | 0.1539 | 1.5394 |
| 15 | 0.1767 | 1.7671 |
| 16 | 0.2011 | 2.0106 |
| 17 | 0.227 | 2.2698 |
| 18 | 0.2545 | 2.5447 |
| 19 | 0.2835 | 2.8353 |
| 20 | 0.3142 | 3.1416 |
| 21 | 0.3464 | 3.4636 |
| 22 | 0.3801 | 3.8013 |
| 23 | 0.4155 | 4.1548 |
| 24 | 0.4524 | 4.5239 |
| 26 | 0.5309 | 5.3093 |
| 28 | 0.6158 | 6.1575 |
| 30 | 0.7069 | 7.0686 |
| 32 | 0.8042 | 8.0425 |
| 34 | 0.9079 | 9.0792 |
| 36 | 1.0179 | 10.1788 |
| 38 | 1.1341 | 11.3411 |
| 40 | 1.2566 | 12.5664 |
| 42 | 1.3854 | 13.8544 |
| 44 | 1.5205 | 15.2053 |
| 46 | 1.6619 | 16.619 |
| 48 | 1.8096 | 18.0956 |
| 50 | 1.9635 | 19.635 |
| 52 | 2.1237 | 21.2372 |
| 54 | 2.2902 | 22.9022 |
| 56 | 2.463 | 24.6301 |
| 58 | 2.6421 | 26.4208 |
| 60 | 2.8274 | 28.2743 |
| 62 | 3.0191 | 30.1907 |
| 64 | 3.217 | 32.1699 |
| 66 | 3.4212 | 34.2119 |
| 68 | 3.6317 | 36.3168 |
| 70 | 3.8485 | 38.4845 |
| 72 | 4.0715 | 40.715 |
| 74 | 4.3008 | 43.0084 |
| 76 | 4.5365 | 45.3646 |
| 78 | 4.7784 | 47.7836 |
| 80 | 5.0265 | 50.2655 |
| 82 | 5.281 | 52.8102 |
| 84 | 5.5418 | 55.4177 |
| 86 | 5.8088 | 58.088 |
| 88 | 6.0821 | 60.8212 |
| 90 | 6.3617 | 63.6173 |
| 92 | 6.6476 | 66.4761 |
| 94 | 6.9398 | 69.3978 |
| 96 | 7.2382 | 72.3823 |
| 98 | 7.543 | 75.4296 |
| 100 | 7.854 | 78.5398 |
| 105 | 8.659 | 86.5901 |
| 110 | 9.5033 | 95.0332 |
| 115 | 10.3869 | 103.8689 |
| 120 | 11.3097 | 113.0973 |
| 125 | 12.2718 | 122.7185 |
| 130 | 13.2732 | 132.7323 |
| 135 | 14.3139 | 143.1388 |
| 140 | 15.3938 | 153.938 |
| 145 | 16.513 | 165.13 |
| 150 | 17.6715 | 176.7146 |
| 160 | 20.1062 | 201.0619 |
| 170 | 22.698 | 226.9801 |
| 180 | 25.4469 | 254.469 |
| 190 | 28.3529 | 283.5287 |
| 200 | 31.4159 | 314.1593 |
| 210 | 34.6361 | 346.3606 |
| 220 | 38.0133 | 380.1327 |
| 230 | 41.5476 | 415.4756 |
| 240 | 45.2389 | 452.3893 |
| 250 | 49.0874 | 490.8739 |
| 260 | 53.0929 | 530.9292 |
| 270 | 57.2555 | 572.5553 |
| 280 | 61.5752 | 615.7522 |
| 290 | 66.052 | 660.5199 |
| 300 | 70.6858 | 706.8583 |
| 320 | 80.4248 | 804.2477 |
| 340 | 90.792 | 907.9203 |
| 360 | 101.7876 | 1017.876 |
| 380 | 113.4115 | 1134.1149 |
| 400 | 125.6637 | 1256.6371 |
| 420 | 138.5442 | 1385.4424 |
| 440 | 152.0531 | 1520.5308 |
| 460 | 166.1903 | 1661.9025 |
| 480 | 180.9557 | 1809.5574 |
| 500 | 196.3495 | 1963.4954 |
| 520 | 212.3717 | 2123.7166 |
| 540 | 229.0221 | 2290.221 |
| 560 | 246.3009 | 2463.0086 |
| 580 | 264.2079 | 2642.0794 |
| 600 | 282.7433 | 2827.4334 |
| 620 | 301.9071 | 3019.0705 |
| 640 | 321.6991 | 3216.9909 |
| 660 | 342.1194 | 3421.1944 |
| 680 | 363.1681 | 3631.6811 |
| 700 | 384.8451 | 3848.451 |
| 720 | 407.1504 | 4071.5041 |
| 740 | 430.084 | 4300.8403 |
| 760 | 453.646 | 4536.4598 |
| 780 | 477.8362 | 4778.3624 |
| 800 | 502.6548 | 5026.5482 |
| 820 | 528.1017 | 5281.0173 |
| 840 | 554.1769 | 5541.7694 |
| 860 | 580.8805 | 5808.8048 |
| 880 | 608.2123 | 6082.1234 |
| 900 | 636.1725 | 6361.7251 |
| 920 | 664.761 | 6647.6101 |
| 940 | 693.9778 | 6939.7782 |
| 960 | 723.8229 | 7238.2295 |
| 980 | 754.2964 | 7542.964 |
| 1000 | 785.3982 | 7853.9816 |
Polypropylene pipe PN25 according to GOST
How to stretch a cable in a HDPE pipe
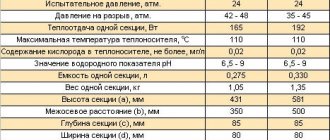
Modern polypropylene pipes are highly reliable, durable and have an affordable price. The polypropylene pipe with a nominal pressure of PN25 is not subject to corrosion, is resistant to temperature changes, is easy to install and is made of environmentally friendly materials. The main properties in accordance with GOST are given in the table.
| GOST | Parameter | Index |
| DIN52612 | Thermal conductivity, at +20 °C | 0.24 W/cm |
| 15139 | Density | 0.9 g/cm3 |
| 23630 | Heat capacity at +20 °C (specific) | 2 kJ/kgf |
| 21553 | Melting | +149 °С |
| 11262 | Tensile strength (at break) | 34 ÷ 35 N/mm2 |
| 18599 | Yield Strength Elongation | 50 % |
| 11262 | Yield strength (tensile) | 24 ÷ 25 N/mm2 |
| 15173 | Expansion coefficient | 0.15 mm |
Read material on the topic: Types of polypropylene pipes
Internal and external cross-section of plastic pipelines
Table of internal and external diameters of pipes
A wide range of plastic pipes contributes to their increasing popularity as a material for the installation of various pipelines for both domestic and industrial purposes.
And now, where previously exclusively steel pipes were used, they are being replaced by plastic ones, which are not only cheaper, but often more durable than their steel counterparts. But their advantages are not limited to these indicators.
There are a number of other important advantages:
- hygiene and environmental safety of pipes - due to its smoothness, lime deposits and colonies of microorganisms do not form on the inner surface of plastic pipes, and the pipe material is safe for the human body,
- low heat and sound conductivity ensure low heat losses and quieter operation of pipelines,
- the low weight of plastic reduces the load on structures, facilitates the installation of pipes and their transportation,
- visual appeal and no need to paint pipelines,
- no corrosion that reduces the strength of the plastic.
Basically, at a given time, several types of plastic pipes are used.
These are pipes such as:
Each type of pipe has its own advantages and features of use, which must be taken into account when purchasing them, based on the purpose of the future pipeline.
What is the difference between the designations of metal and plastic pipes?
But it is equally important to know that the diameters and designations of metal and plastic pipes differ. If metal pipes are designated based on their internal diameter, then the outer diameter is always indicated in the marking of plastic pipes
If metal pipes are designated based on their internal diameter, then the outer diameter is always indicated in the marking of plastic pipes.
In addition, inches are used to designate the diameters of metal pipes, while for plastic pipes the metric system is used, indicating the pipe size in millimeters.
How can this be done? In order to correctly replace one pipe with another, it is necessary to focus not on the diameter of the pipe, but on the nominal diameter.
What is a “nominal pipe bore”? The nominal bore of both pipes and connecting parts means the average internal diameter of the pipe (in the clear), which is designated as DN with the addition of a digital designation equal to the nominal bore expressed in millimeters (for example, DN90).
The nominal diameter of plastic pipes is calculated by the formula:
DN=Dnar – e,
where Dout is the outer diameter of the pipe (mm),
e – pipe wall thickness (mm).
If it is necessary to replace a steel pipe with a plastic one, the nominal diameter of the plastic pipe must be no less than the nominal diameter of the steel pipe.
Internal and external cross-section of plastic pipelines
The advantages of plastic pipes, their types, designations of the diameters of metal and plastic pipes, nominal diameter, table for selecting a plastic pipe instead of a steel one,
How to connect PPR PN25 pipes
Pipe welding is carried out using the thermal polyfusion method. The parts to be welded must be heated and quickly connected. A special soldering iron is used for heating. Some models have two heating elements at once, the power of which is designed to heat pipes of a specific diameter, but this does not always have a positive effect on the quality of welding.
Important! The use of two elements at once can lead to overheating of the plastic and overload of the electrical network. Therefore, the second heater should be used when the first one becomes unusable. The heating time depends on:
Heating time depends on:
- pipe diameter;
- welding belt width;
- ambient temperature - it should be within normal limits.
After heating, the material does not retain its plasticity for long. The connection must be fixed within a few seconds, without allowing distortions. The optimal temperature for heating is considered to be +260 ˚С. For a reliable connection, the pipe material must be very heated. But excessive heating can cause the shape to change. To avoid this, it is necessary to control the execution time of this operation. It should not exceed:
- 8...9 seconds for pipes with a cross-section of 20 millimeters;
- 9…10 seconds when welding a pipe with a diameter of 25 millimeters;
- 10...12 seconds for pipes with a diameter of 32 millimeters, etc.
Heated and already connected pipes must cool down. Fixing takes the same amount of time as heating. If the required time is not maintained, deformation of the connection will occur. Welding polypropylene pipes is a relatively difficult process. The quality is affected not only by the heating time, but also by violation of soldering rules. They are as follows:
- During operation, the welding machine must be constantly heated;
- Marks must be applied to the pipes in order to ensure the proper depth of the weld seam;
- The elements being connected must be heated simultaneously.