Pipe dimensional characteristics
Water supply pipes (regardless of the material from which they are made) have common dimensional characteristics:
- inner diameter;
- outside diameter;
- Wall thickness;
- total length.
In addition to these characteristics, when choosing, you should take into account the number of turns and connections when laying the hydraulic system.
The main indicator for water pipes is the internal diameter; the pressure and flow of water at the end points of the system, in taps, internal pressure in the pipelines, and the quietness of its operation depend on it.
Relationship between characteristics
Dimensional characteristics are interrelated. For example, if the pressure in the incoming pipeline increases, then, with a constant cross-section, the pressure in the hydraulic system will become higher, and troubles may begin: connecting fittings will leak, the water supply will become noisy.
How does the length of the water pipe affect the diameter of the pipes?
Standard sizes of pipelines, their diameters are measured in inches. 1 inch is equal to 25.4 mm. The inch is indicated in the literature and on diagrams by the double apostrophe symbol – “””. In domestic water supply systems, both houses and apartments use 0.5-inch or 3/4-inch calibers. They are designated as 1/2″ or 3/4″.
Table of pipe diameters for water supply.
The required diameter of the pipe elements is directly proportional to their total length. The diameter of the water supply pipes in the apartment does not exceed 20 mm.
The same section is used in a country private house with a small length, up to 10 m. If the length of the water supply in the building reaches 30 m, you need to take a pipe in a 25 mm crossbar; if the length is longer, then you should choose 32 mm.
The number of connections, turns and water points also affects the recommended diameter upwards. If you incorrectly select the capacity of pipelines for a sufficient number of consumption points, this can lead to the fact that, for example, opening a tap in one room will lead to a decrease in pressure and loss of water in another.
In a private house, the number of water points is greater than in a city apartment. The simultaneous use of most of them can even lead to the inoperability of household appliances, a washing machine or a dishwasher.
When designing and installing the system, it is better to use pipes with a spare cross-section, especially in a private house in the absence of a central water supply. Water risers have a larger diameter than the outlets going from the riser to the points of consumption.
Why does the diameter of the pipes determine the throughput of the water supply system?
According to the laws of hydrodynamics, the same amount of water passes through any section per unit time. With constant pressure and changing cross-sections in pipes, too small a cross-sectional size will lead to constantly high pressure in the system, which will reduce its reliability and can lead to breakdowns. It is inconvenient to use taps with increased pressure in the network.
To correctly calculate the water supply, it is necessary to take into account the throughput of the pipes. It must correspond to the number of consumption points, the amount of water consumed by a particular plumbing fixture. The water tap consumes no more than 5 liters of water per minute.
The table determines the pipe capacity.
When calculating the diameter of pipelines, you need to take into account:
- overall length;
- number of branches;
- number of joints and turns;
- water pressure created by a well pump
For a private country house, there is no point in making precise calculations using complex formulas and computer programs. This calculation is enough.
The water tap consumes no more than 5 liters of water per minute.
Up to 30 l/min can flow through a 25 mm pipe; with a diameter of 32 mm, the throughput increases to 50 l/min. For 10 water points, a 1-inch inlet pipe is sufficient. For greater accuracy, you can refer to the Shevelev tables. Another general rule: larger diameter - lower pressure.
The material from which the pipes are made affects the choice of their dimensional characteristics. To supply water to a home, pipes made of polymers can be used: plastic, PVC, metal-plastic, polyethylene. It is possible to create a water supply system made of steel, stainless steel or copper.
What diameter pipes are allowed to supply heat?
For the ideal design of a heating system, it is important not only to choose the pipe material according to the rules, but also to correctly calculate the pipe diameter.
This particular criterion specifies the pipe’s ability to pass through, determining the volume of coolant that can be transported through it per unit time. The pipe diameter directly affects the pipeline length and its potential “branching”, and also determines the number of heating radiators that can potentially be connected to the system. Heat loss can also be predicted based on the pipe diameter.
Types of heating pipes
All pipes for heating systems, figuratively speaking, can be divided into two options: - iron: stainless steel, ferrous metal, copper, brass, bronze; — polymer: PVC, metal plastic, polymer ethylene, polypropylene.
Metal-plastic pipes are easy to install, resistant to temperatures that rise for some time to 130 degrees, they are flexible and can be placed behind furniture. Polyethylene pipes stretch when heated, so auxiliary fasteners and compensation loops are used with them. Any plastic pipes do not make unnecessary noise, which is considered one of their positive qualities. Copper pipes are not at all inferior to their metal-plastic counterparts, and surpass them in most characteristics. The service life of a copper heating system can reach 100 years, and craftsmen believe this material is impeccable for a heating system. Copper has a high thermal conductivity, which is great for underfloor heating systems, but quite poor in other heating systems. And copper is not a cheap material at all. Stainless steel is more affordable than copper, but it is difficult to install, and it does not have the necessary thermal conductivity and flexibility.
Any of these materials has its own disadvantages and advantages, but it is better to avoid polyvinyl chloride pipes and polypropylene, as they are sensitive to high temperatures.
Types of heating systems
Heating systems can be centralized or individual. In a central heating system, such as is used in high-rise buildings, the pressure can rise to 16 atmospheres when the pipeline is cleaned. In a personal system, which is equipped in personal homes and cottages, the pressure will not exceed 2-3 atmospheres. Plus, heating systems can be single-pipe or double-pipe, with forced or convective circulation. Of course, the pipes must meet a specific heating system.
Forced heating system The pipe diameter for installing a forced system must be small, and here's why: - with a smaller diameter of heating pipes, a small amount of heated coolant is required, which saves money and time;
— the speed of movement of the coolant in the system is lower, the smaller the cross-section of the pipes; — small-diameter pipe installation is easier to do;
— a small-diameter pipeline is much more economically profitable.
Pipe diameter and efficiency of the heating system
The efficient functioning of the heating system is guaranteed only by a properly designed pipeline. Even at the planning stage, it is necessary to reduce the probable heat losses; otherwise, even with serious energy costs, the heating system will not fully operate and cope with its own tasks. An economical system with a high efficiency is created only taking into account all the nuances: the physical and chemical parameters of the material, the length and diameter of the pipes.
Types of pipe diameters
1) internal diameter (considered the main parameter determining the size of the product); 2) external diameter (gives the classification of pipes): - small diameter (5-102 mm); — average (102-406 mm); — large (406 mm or more); 3) symbolic diameter (diameter value rounded to the nearest whole number, expressed in inches).
The material from which the pipe is made determines the difference between the outer and inner diameter of the product. The outer diameter is always strictly taken into account when installing a heating system, since the choice of fasteners depends on it. The internal diameter is considered the main indicator for choosing a pipe for the system.
The choice of pipe diameter for a private country house depends on the method in which the coolant will be supplied to the system. If a country house is connected to the main line, then the calculations are similar to those for installing a pipeline in an apartment. If a country house is equipped with an independent system, the pipe diameter depends on the heating scheme and material. For example, gravitational circulation requires one diameter, and forced circulation requires another.
Standard solutions
To supply water from the well to the house, pipes made of HDPE - low-density polyethylene, metal-plastic, polypropylene and copper - are used.
Pipes made of HDPE - low pressure polyethylene
The material is easy to assemble; no tools are required. Only special inexpensive fittings are used, which are tightened by hand, ensuring tight connections.
HDPE pipes will not burst, even if the water in them freezes. Suitable only for cold water, therefore optimal for introducing water into the house.
Pipes made of low pressure polyethylene.
It is possible to make a complete water supply system from HDPE. This solution is suitable in the case of creating only a cold water supply system for cold water supply to premises.
In this case, electric water heaters are used to obtain hot water.
This water supply scheme is used in houses for seasonal residence or in non-residential buildings, such as a bathhouse, summer kitchen, etc. Other types of materials are used inside the house.
Metal-plastic pipes
One of the most popular is metal-plastic. It combines the lightness of plastic pipes and the strength of metal, does not rust, the outer surface does not conduct electricity, and the inner surface does not allow sediment to form. The price of such pipes is less than copper or stainless steel.
The flexibility of this material makes its installation simple; it is possible to ensure the minimum possible number of joints and connections; press fittings and an ordinary adjustable wrench are sufficient for it. Suitable for use in hot water systems
The disadvantages of metal-plastic include the need to periodically tighten threaded connections. Aesthetically, metal-plastic also cannot compete with pipes made of copper or stainless steel. Such pipes are additionally covered with decorative panels.
Polypropylene pipes
Another typical solution could be the use of polypropylene pipes. The durability of this material reaches 50 years. Available reinforced and non-reinforced.
Features of polypropylene pipes
Polypropylene pipes occupy a leading position in terms of the breadth of use in water supply systems of private houses and communal apartments. They have no worthy competitors in terms of cost, ease of installation and practicality when laying cold water supply (CW) mains. The main disadvantage of polypropylene is the high coefficient of linear expansion when heated, which is not an important factor in this case.
In hot water supply (DHW) pipelines, ordinary polypropylene is not used due to insufficient heat resistance and high linear elongation coefficient.
There it is better to use co-extruded material, which is a polypropylene pipe with an internal fiberglass shell. Fiberglass increases the heat resistance of the entire pipe and reduces its thermal expansion.
Polypropylene pipes are connected by soldering; if two sections of the same diameter are joined, a coupling, elbow or tee is placed on top of them, depending on the unit being mounted. This connection method is called socket connection. Thanks to this method, the flow area of the polypropylene pipeline remains unchanged in all sections. Thanks to the large number of different polypropylene fittings, almost any assembly can be soldered. When joining pipe sections of different diameters, transition couplings are used.
With the same external dimensions, the diameter of the passage channel of PP pipes is much smaller than that of metal or polymer analogues made of cross-linked polyethylene.
As for pressure characteristics, ordinary polypropylene can withstand pressure from 10 (PN10) to 20 (PN20) bar throughout its entire service life. A fiberglass-reinforced pipeline can operate for a long period at a working fluid pressure of up to 20 (PN20) or 25 (PN25) bar at elevated temperatures.
Rice. 3 Dimensions of polyethylene pipes
Errors when installing plumbing
Narrowed pipe section
. When replacing a riser, installing a narrowed pipe will inevitably lead to a decrease in the pipeline's capacity, as a result of which your repair will harm all residents of the upper floors. Sometimes a problem with a decrease in water supply can be observed inside the apartment itself, when the “grief masters” install a 3/4-inch pipe at the inlet with a maximum throughput of no more than 1.2 cubic meters per hour. If this pipe supplies water to two bathrooms and a kitchen, simultaneous use of plumbing will become impossible.
Reverse connection of the mixer
. When connecting the mixer to cold and hot water pipes, the correct connection option is as follows: the valve on the right side - to the cold water pipe, the valve on the left side - to the hot water pipe. Reconnecting the faucet will lead to inconvenience when using it and even burns if a person habitually opens a cold water tap and hot water flows out of it.
Suboptimal water distribution
.
When performing apartment renovations, owners traditionally create a water supply system with a sequential (tee) wiring diagram as the most economical and easiest to implement. However, later they often regret that they did not provide for a collector water supply scheme. The reason lies in the fact that the tee circuit has many disadvantages: it makes it impossible to selectively turn off the water supply without turning off the entire water supply; if there is a large number of working plumbing fixtures in the apartment, it leads to a decrease in pressure in distantly located devices; Numerous tee connections often lead to leaks. Tee pipe routing Manifold pipe routing
Violation of the welding process of polypropylene pipes
. The main violations are as follows:
a) misalignment of pipes in the vertical or horizontal direction, due to which, when attached to the wall surface at the soldering site, deflection or torsion forces act on the pipe; subsequently the soldering unit is destroyed; b) the overlap seam of the pipe and fitting is too large, which leads to a narrowing of the lumen in the pipe; c) too long a period of time between the moment the soldering iron is removed and the moment the pipes are joined, which leads to weak soldering, a deformed and short-lived seam; d) a change in the position of the seam at the end of soldering, which causes a displacement of the soldered layers, and subsequently the destruction of the seam.
Insufficient securing of pipelines
. Neglecting the rules for securing pipelines when laying hot and cold water supply systems can cause a breakdown of utility networks. Pipelines that are not secured along their entire length lead to their deformation and damage to the welds at the joints. When laying water supply networks, fasten pipes as follows: for pipes with a diameter of up to 32 mm - after 1 m, for pipes 32 mm and larger - after 1.5 m.
Installation of a double-circuit boiler in a house with an extensive hot water supply system
. The disadvantage of a double-circuit boiler is that the water in it is heated by a flow method, and with a high flow intensity it cannot heat the water to the required temperature. If there are two bathtubs installed in the house, then when using a double-circuit boiler, only one person will be able to wash with hot water, and the other will have to wait his turn.
Laying water pipes in the ground freezing zone
. According to the rules, water pipes are laid at a depth that is 10-20 cm below the freezing zone. Otherwise, during frosts, water will freeze in the pipes. If it is not possible to comply with this rule when laying a water supply system, then the pipes should be covered with thermal insulation material or a heating cable should be attached to them, which will prevent the water from freezing.
Inaccessibility of shut-off taps and water meters for maintenance
. These important parts must be located at a convenient height, and in such a place that the owners can not only take readings, but also replace meters and shut-off valves, without resorting to dismantling plumbing fixtures or destroying walls.
How to install water pipes
It’s worth noting right away that it is most convenient to install both the pump and pipes at once. At the same time, all the necessary calculations should be done in advance, otherwise you may encounter a lot of difficulties. The descent of the pump into the well should be smooth. Moreover, if the preliminary preparation is not carried out correctly, then you can receive an insufficient amount of water that is required to supply the house. The lack of pressure will affect the comfort of residents. As a result, they will have to choose between doing laundry, using the shower, or watering the garden. Carrying out side procedures simultaneously will become impossible.
Modern pumps are most often equipped with a flanged or threaded version for connecting a pipe. Although sometimes a coupling type of connection is used. Experts recommend first connecting the water-lifting element on one side, and only after that proceeding with the installation of the second part of the pipe. Lowering the structure to the ground is strongly discouraged. This may cause damage to important components or displacement of certain parts.
Find out how to choose the right diameter of a water pipe: 4 secrets of a plumber
Everyone inevitably has to understand how a water supply works, what throughput is and how these concepts are interconnected - breakdowns are not uncommon here. It also happens when a person has to quickly understand these matters - when building a house - an option is selected, the diameter of the pipe for the water supply is calculated, and a bunch of similar criteria. So we will pay attention to these kinds of nuances, understand the intricacies and understand what diameter of pipe should be used for water supply and what should not be used.

Generalized data
The construction of water supply systems in both private and multi-storey houses is carried out using metal options, which have different pipe diameter designations. They come in steel and copper, depending on the person’s wishes. The radius is also selected separately, the same applies to plastic or combined options.
It is worth understanding that the diameters of water pipes and other parameters depend on the source material. It turns out that the pipe capacity is calculated based on the following parameters:
- Internal plumbing radius;
- Transitional size;
- Nominal size;
- Outer radius;
- Thickness.
Previously, it was easy to calculate the diameter of a pipe - 15 years ago, identical cast iron pipes were common.
Carrying out installation
Features of installing pipes and pumps largely depend on the type of well. In some cases, installation of conventional devices will be very difficult. In such situations, it is possible to use flexible hoses that can replace water-lifting pipes. The main thing is that these elements are strong enough and safe for humans. Under no circumstances should they release harmful chemical compounds into the water. In addition, you should make sure that the pipes are reliable enough and that all fasteners are of high quality. Otherwise, the water supply will have to be repaired immediately after its first use.
Experts strongly recommend using only those options that have been developed and manufactured for these purposes as water-lifting pipes. You should not take nylon hoses or fire pipes, as they will quickly fail and may even damage the pump. As a result, you will have to spend money on purchasing a new set of expensive equipment.
Choose the appropriate size: from small to large diameter (external and internal)
As in other engineering activities, each millimeter of water supply can be calculated using formulas.
But in practice, during rapid construction I rarely resort to such methods; they use the standard diameter of metal-plastic pipes for water supply. Choose from these classic options:
- Diameter 1.5 centimeters;
- One centimeter.
The riser in multi-storey apartments is made based on the internal size:
- 5 centimeters;
- Size 2 centimeters.
Please note that the internal diameter of the water pipe is not chosen at random. If you plan to install a complex water supply system in your house and it is noticeable that the diameter of the water supply pipe will become narrowed, then choose options with a large diameter in advance. In this case, the pressure will be equal in each section of the water supply system and will not be able to change due to joints, turns and bends.
Please note that it is stupid to install a sewer system with an external size larger than the riser in the house - the pressure in the system will decrease and the pressure in the tap will drop. But even taking this factor into account, you rarely have to use complex formulas for engineering analysis.

Selecting casing size
Quite often, decisions about laying a different type of well structure occur when drilling a hole. The dredging process may reveal the need to use different pipe widths to create a more reliable and efficient water supply system. This is what leads to the fact that when forming a structure, pipes of various diameters are used, thanks to which the initial width of the deep-hole equipment column expands or narrows.
Some well drilling companies initially offer their customers to make narrow passages, which makes it possible to offer more favorable conditions in a competitive market. And in some cases, the owner of the facility himself decides to reduce the cross-section of the well, since it is cheaper
It is important to understand that the productivity of the well does not depend entirely on the width of the pipe, since to a large extent it is determined by the technical parameters of the filter components and the ability of the rocks to produce water.
In any of the options, it is very important that there is a gap between the casing pipe and the casing of the pumping equipment, allowing you to quickly and easily dismantle the pump along with the pipe and other parts. Most often, specialized documentation indicates that pumping equipment should be no less than 10 millimeters thinner, compared to the internal diameter of the pipe
This allows you to minimize damage from axial displacements, sagging welds, compression of the pipe under soil pressure, as well as other unpleasant factors.
That is why it is recommended to choose so that the gap is more than 10 mm.
Why the analysis is carried out: calculation for a private house and apartment
In addition to calculating the diameter of a water supply pipe, taking into account the throughput based on the volume passing through, you also need to not lose sight of the direct throughput. At the same time, pay attention to the plumbing used in the house, keep in mind that the radius does not differ greatly - you will damage the mechanisms inside. The dimensions of plastic pipes for water supply and the throughput should be taken into account even so that opening a tap in one room does not stop the water supply in another.
To correctly make the appropriate calculation, you will have to take into account the material, size of the pipeline and the number of points leaving the system. Bandwidth is considered by the following methods:
- Using a special derived formula;
- Selecting the appropriate option from the table of standard values;
- Electronic programs for pipeline calculations.
The main thing when carrying out calculations is to take into account the internal radius for each pipe section, take into account roughness and internal deposits in cast iron versions . If you carry out the calculations correctly, select the correct cross-section of pipes and install compensators and other technical elements in the right places, then water in the house will be able to flow constantly and without interruption. It is important that you get normal high-quality pressure, which is enough to serve the needs of the people living in the house. It is important to build the system so that when you open the faucet in the kitchen, the water in the faucet in the bathroom does not disappear, otherwise such troubles can constantly haunt you. Therefore, build the scheme correctly, work through every possible option available, so that later there are no inconveniences. The diameter of the water pipes must be selected based on the installation conditions of the main line.
Pipes for a pumping station at the dacha
Pipes used for a pumping station in a country house have the same requirements as for other options for using hydrophore.
It is worth paying attention to the diameter of the pipe. However, the calculation rules are common to all stations that we discussed above
But it’s worth talking separately about choosing a hydrophore for your dacha. To ensure your life at the dacha with an autonomous and reliable water supply at any time of the year, you need to automatically supply water to any point of water consumption. This is precisely why a pumping station is needed, which will be able to provide sufficient pressure in the water supply under any conditions, even when the pump is turned off. The main thing is to choose the optimal equipment and install it correctly on your own summer cottage.
Where is the best place to install a pumping station at the dacha? Let's name three main options for placing a hydrophore:
- directly next to a well or well;
- in one of the utility rooms;
- directly in a residential building.
When choosing a hydrophore (pumping station) for your dacha, you should pay attention to such characteristics as:
- engine power;
- created water pressure;
- hydrophore performance.
Many stations are equipped with safety devices that look like sensors that can turn off the device when it overheats or in so-called “dry mode” when there is no water in the system.
This increases the cost of the station, but will ensure its safer use in the country. The kit usually has a check valve and a water filter. If you don't have them, be sure to buy them and install them in the hydrophore circuit.
Diameter dimensions of water supply pipes for a private house
When choosing the diameter of pipes for installing water supply in a private house, it is recommended to take into account the following characteristics:
- water pressure force. When it is weak, the diameter of the pipes must exceed the standard one. Weak pressure + narrow pipes = weak stream from taps;
- total length of the plumbing system;
- how many water points are there in the house: the diameter of the pipes is directly dependent on their number;
- the same applies to the turning points of the pipeline - in general, any of them contributes slightly to a decrease in pressure. Do you have a “Cretan labyrinth” there? This means that the diameter - on any section of the pipeline - of the water pipe for a private house should be with some margin.
You should also take into account the temperature of the water - pipes for hot water supply and hot water supply can be purchased with the same diameter, but the walls of the “hot” ones must certainly be thicker.
How does the length of the water pipe affect the diameter of the pipes?
The general rule is: the longer, the more! So, how to correctly choose the diameter of a pipe for your home plumbing without going into puzzling calculations? In most cases, the standard recommendations are justified:
- short pipeline less than 10 m - 20 mm;
- less than 30 m - at least 25 mm;
- if the pipeline is long - more than 30 m - the optimal solution would be 32 mm.
Large linear extension
The polypropylene plastic pipeline has a large linear expansion. Under the influence of temperature, the pipe can expand, forming a wave. Linear expansion for polypropylene is 2.5 mm per 1 linear meter.
If you install them under plaster, the waves will not be visible, but external installation will not please your eye. Pipes that are smooth after installation may become wavy after a couple of days. Because of this, it will be necessary to attach the pipeline to the wall at a smaller pitch. However, even with frequent fastening, the pipe will not be level. Although linear expansion does not affect the performance of the product, it still spoils the appearance.
Standard solutions
- usual pipeline diameter is 10 and 15 mm;
- the riser will require a little more - 25.
You need to know: the purchased products are not created by jewelers, and “10 mm” pipes will easily turn out to be a couple of millimeters larger. Be sure to be guided by such a parameter as the thickness of the walls: you need to choose the diameter exactly inside (for this you need to subtract the wall thickness from the total) so that all the fittings fit!
The higher the level of complexity of future plumbing work in a household, the larger the diameter of all pipes, both long and short, should be. When a “complex” pipeline with many turning points, joints and expected pressure surges is expected, it is worth insuring yourself by increasing the diameter. You should also definitely take into account the maximum values of both pressure and temperature in your water supply so that it does not burst from the first water hammer.
The savings here are unjustified. Additional advice: in order for the plumbing system to perform flawlessly and be reliable in operation, you need to select high-quality products. This applies to pipes and small elements (fittings and couplings). It would be a shame to “ruin” a proven system with cheap fittings.
What should be the diameter of pipes in water heating systems?
To calculate the pipeline hydraulic resistance, you need to know the hydraulic resistance and coolant flow:
- S is the calculation of the cross-sectional area of the pipe (internal size);
- π – constant (3.14);
- Q – formula for calculating water flow in m3/s;
- V – formula for coolant flow velocity, m/s.
These formulas are applicable for liquids, but to calculate the required cross-section of a heating pipe, it is more convenient to use the formula:
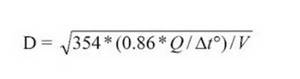
- D - formula for determining the diameter of the heating pipe, millimeters;
- ∆t° - difference between supply and return temperatures, °C;
- Q - required amount of heat to be transferred, kW
- V is the speed of the coolant, m/s.
For heating private houses and small cottages, it is appropriate to use in the calculations the required coolant speed of 0.2-1.5 m/s. The optimal speed, ensuring high efficiency and comfortable operation, is 0.3–0.7 m/s. Movement below the specified values leads to the formation and accumulation of air pockets; if the parameters are exceeded, cavitation noise occurs and energy consumption for pump operation increases.
In hydraulic calculations, reducing the diameter by half corresponds to an equivalent length of 0.5 for DN25 mm, 0.7 for DN40, 1.0 for DN50. For comparison, the equivalent length for a 90° angle in the same diameter is 0.3 for DN25 mm, 0.5 for DN40, 0.6 for DN50. Thus, a narrower diameter has a much greater impact on head loss than a 90° bend of the same diameter.
Calculation of heating pipes - heat supply in an apartment in the city and a privatized house
Whether we are replacing worn-out sections of risers and hoses in an apartment, or designing a heating system for a country house from scratch, over time we will need to buy materials. Heating devices, shut-off valves, fittings and... pipes. How not to miss the mark with their diameter?
This is what our publication is about.
The diameter of the pipes determines the operation of the heat supply no less than the type of batteries
Why are calculations needed?
Why not take the diameter by eye? Or, to be on the safe side, with a known reserve?
Here it is worth dividing two quite different cases.
- In an apartment in the city, when the diameter of the riser is underestimated, we get slower circulation in it. It will become colder for all your neighbors above and below. But with an excessive cross-section of the pipe, we do not get any bad consequences, apart from dubious aesthetics.
However: as the pipe diameter increases, its cost increases nonlinearly. A pipe with a diameter of 32 millimeters is almost four times more expensive than a pipe with a diameter of 16 millimeters. This is clear: its mass increases in proportion to the square of the diameter, and simultaneously with the mass, the costs of producing a linear meter also increase.
The cost of the pipe increases in proportion to the square of the diameter
- But in a private house, if the diameter is overestimated, we will suffer not only financially. The volume of the coolant becomes larger, and significantly so. Hence the greater inertia of the system: the heating devices, after lighting the boiler, will heat up very slowly.
If the piping is done in the basement or attic, heat loss will also increase: a thick pipe has a decent surface area.
Reducing the cross-section of the heating system is also the worst option: to maintain the proper temperature, the design of the radiators will have to make circulation in the system faster. And this leads to noise at bends and shut-off valves, not to mention throttling points.
Where to get diameter values from
Let’s say right away: the hydraulic calculation of pipelines is a rather complex engineering task that takes into account quite a few factors.
This includes:
- The pipe material and its roughness indicator, on which the hydraulic resistance depends.
- The degree of its wear.
- Coolant pressure.
- Number of turns and their angle.
- Number and type of shut-off valves.
- Planned operational period.
Clarification: the degree of wear affects the hydraulic resistance of profile pipes. The surface roughness inside polymer and metal-polymer pipes remains almost unchanged for some time. Which, however, does not make the calculation difficult.
To correctly calculate the heating systems of high-rise buildings and highways, engineers use, in other words, Shevelev’s tables and complex formulas; We need the most common solution possible.
In the case of standard high-rise building projects, simply reducing the pipe diameter by one step will provide the opportunity to save very large sums
Let's divide the problem into its components.
Apartment in the city
Here it is enough to learn a few simple rules:
- When replacing a heating riser, a pipe of the same diameter as that used by the builders is taken. There is no need to increase or decrease the diameter. The notable exception is the case of previous repairs carried out by unqualified professionals. If the cross-section of the riser in a short section changes from DN25 to DN15, it is better to cut it out by removing the transition in diameter.
- For connections to heat exchangers of various types, a DN20 pipe is sufficient. Narrowing of the pipe is allowed only after a jumper, which can be made with a DN15 pipe.
- If a throttle, thermostatic head, or even just a valve is installed in front of the radiator, the jumper is strictly required and has the same diameter as the riser.
If you do not want some of the heat to pass by the heating radiators during the peak of cold weather, put a valve on the jumper. Of course, if the throttling shut-off valve is not completely open, the valve on the jumper must be in the “open” position.
Only and exclusively modern ball valves are used. They are much more reliable when compared with morally old screw ones and in the “open” position they have little hydraulic resistance.
In the photo, all needs are met. The new riser is the same diameter as the outdated one; The jumper is made with the same diameter. The heating device is cut off by ball valves
Gravity heating system
Regardless of the number of floors of the house, the length of such a system is limited by the largest difference that can create a thermal expansion of the coolant. The outline cannot be long; The area of the room that is heated and the heating output of the boiler are also limited.
If so, the task can be made easier by giving exact diameter values.
- For a house with an area of up to 70-80 square meters, bottling is performed with a DN 32 pipe. For a larger area - DN 40 or even DN 50.
Important: do not confuse the symbolic diameter with the external one. DN is a parameter approximately equal to the internal cross-section of the pipe and introduced to unify the fittings and connectors. The external one can stand out significantly from it due to the decent thickness of the walls.
It is best to install shut-off valves on it; Chokes or thermostats for balancing the system will not be superfluous either. A common problem with convective circulation systems is that the heating devices closest to the boiler are much hotter than those further away.
The filling diameter is 40 millimeters, the liner diameter is 20. If necessary, the design of the radiator can be changed with valves. Strictly speaking, this is not true; but the scheme is quite workable
Forced circulation system
In order to calculate the required pipe diameter in any case with our own hands, we still have to get into the wilds. However, not very far: instead of a complex calculation, we will use a table.
The table makes it possible to choose the pipe size without too complicated calculations
How to use this table?
The instructions are not very complicated.
However, we need additional information about where to get the speed of movement of the coolant and the heat flow in watts that we need.
- The limits of water speed in pipes are 0.6 - 1.5 meters per second. At a lower speed, distant heating devices will noticeably cool down; with more, the background noise of the water at the fittings will become audible.
- The approximate amount of heat required for a privatized house can be calculated based on the norm of 60 watts per cubic meter of volume. For a warm region, the resulting amount is multiplied by 0.7 - 0.9, for the severe cold of Chukotka or Yakutia - by 1.5-2.0.
Let's take, as an example, a pipe for the heating circuit of a house with an area of 75 square meters somewhere in Krasnodar.
Ceiling height is 3 meters; We will not divide the heating system into several independent circuits; We will limit the speed of water in the pipes to 1 meter per second.
- We calculate the need for heat. The volume of the room is 75*3=225 m3. To supply it with heat during the peak of cold weather, you will need 225 * 60 = 13500 watts. The warm climate of Krasnodar will force us to reduce the need for heat to 13500 * 0.7 = 9450 watts.
- Now we are looking in the upper horizontal line for the speed of movement of water in the circuit that we need. Let us remind you that it is equal to 1 meter per second.
- Found it? We move vertically down the table until in the top line of the square we see a value greater than the required 9.5 kilowatts. Rounding here should only be done upward.
- In the fourth square from the top we find a value of 14370 watts, at which we can complete the search. As is easy to see, it corresponds to the internal diameter of the pipe 15 millimeters. This means that we can choose a half-inch pipe made of steel or polypropylene with an outer diameter of 20 millimeters.
With the same traffic capacity, the outer diameter of the profile pipe is smaller due to thinner walls
When using the table, you need to take into account that it gives values for the outlet temperature between supply and return of 20 degrees. Which, however, is considered quite common for local heating systems.
Useful little things
In conclusion, there is a certain amount of unsystematized information that may be useful to the reader when designing his own heating system.
- The advantage of a small cross-section of pipes - the low thermal inertia of the system - negates the use of cast iron radiators. Their parts have a large internal volume, and the heating devices themselves heat up for a long time due to their large mass and relatively low thermal conductivity. A good choice for local heating is aluminum batteries.
- But still, sometimes thermal inertia is considered a plus. If you live in the house regularly and use a solid fuel boiler that needs to be loaded with firewood or coal a couple of times a day, you will only be pleased that the batteries will cool down for a long time.
- A heat accumulator - an insulated tank with a volume of 300-2000 liters - will help to further expand the inertia of the system. Among other things, it will help to heat the house with electric current, using it at an inexpensive overnight rate. The tank is mounted at a very different point in the circuit and accumulates heat at night; During the day, the hot coolant in it transfers heat energy to the batteries.
- When distributing collectors from the collector, metal-plastic or polyethylene (of course, cross-linked polyethylene) pipes of very small diameter are used. An external cross-section of 16 millimeters is fully sufficient in this case.
With the collector circuit, a large diameter of the supply line is not required. Each insert feeds only one heating device
- Pipes of various types are placed in the screed only in one piece, without any connections - welded or fittings. The exception is polypropylene: its welded joints do not differ in durability and strength from a solid pipe; however, the material is not very flexible like metal plastic or rex pipe.
Conclusion
We hope that the proposed methods for selecting pipes will seem good to you. As in most cases, the video at the end of the publication will offer additional information on this interesting topic. Have mild winters!
What does narrowing the diameter of the pipeline lead to?
Consequences of narrowing the pipeline diameter:
- The pressure loss increases - according to the laws of hydrodynamics (along with turns, corners, tees). Therefore, when designing, an allowance for pipe narrowing is always taken into account.
- The formation of “blind spots”, vortices, which further narrow the cross-section of the pipeline.
- The larger the internal diameter of the pipe, the less pressure occurs in the system and vice versa. Thus, at the point of narrowing, the pressure increases sharply due to the need to pass the same volume through a smaller cross-sectional area of the pipe.
- The equivalent length increases, which is important when calculating the parameters of circulation or feed pumps.
- Cavitation noise may occur at the narrowing site.
- The speed of movement of the coolant or supplied liquid slows down.
The best option for installing a heating system is to use one standard size for the main line, and make branches from it smaller in diameter. This will make the coolant circulation more controlled and simplify calculations.
how to calculate, water speed in the system, consequences of narrowing, coolant
Before installing heating in a house, you must first correctly calculate the diameter of the pipes. The calculation will be considered on systems with forced ventilation. In such systems, the movement of the coolant is ensured by a constantly running circulation pump. When choosing the diameter of the pipes, it is taken into account that their main task is to ensure the delivery of the required amount of heat to the heating devices.
Data: how to calculate the diameter of a heating pipe
To calculate the diameter of the pipeline, you will need the following data: this is the total heat loss of the home, the length of the pipeline, and the calculation of the power of the radiators in each room, as well as the wiring method. The outlet can be one-pipe, two-pipe, have forced or natural ventilation.
Also pay attention to the markings on copper and polypropylene pipes of outer diameter. The internal one can be calculated by subtracting the wall thickness. For metal-plastic and steel pipes, the internal size is indicated when marking.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to accurately calculate the pipe cross-section. One way or another, you will have to choose from a couple of options. This point is worth clarifying: a certain amount of heat needs to be delivered to the radiators, while achieving uniform heating of the batteries. If we are talking about systems with forced ventilation, then this is done using pipes, a pump and the coolant itself. All that is needed is to drive the required amount of coolant over a certain period of time.
It turns out that you can choose pipes of a smaller diameter and supply the coolant at a higher speed. You can also make a choice in favor of pipes of a larger cross-section, but reduce the intensity of the coolant supply. The first option is preferable.
Selecting water speed in the heating system
High water speed and smaller diameter pipes are the most common choice. If you increase the diameter of the pipe, the speed of movement will decrease. But the latter option is not so common; reducing movement is not very beneficial.

When choosing pipes, you should also take into account the possible speed of water in the heating system
Why high speed and smaller pipe diameter are more profitable:
- Smaller diameter products cost less;
- It is easier to work with smaller diameter pipes at home;
- If the gasket is open, they do not attract attention so much, and if the installation goes into the walls or floor, then smaller grooves will be required;
- A small diameter provides less coolant in the pipe, and this, in turn, reduces the inertia of the system, which saves fuel.
Special tables have been developed to determine the size of pipes for a home. Such a table takes into account the required amount of heat, as well as the speed of movement of the coolant, as well as the temperature indicators of the system. It turns out that in order to select pipes of the required cross-section, the necessary table is found, and the diameter is selected from it. Today there may be a suitable online program that replaces the table.
Heating system wiring diagram and heating pipe diameter
The heating wiring diagram is always taken into account. It can be two-pipe vertical, two-pipe horizontal and single-pipe. A two-pipe system involves both upper and lower placement of lines. But the single-pipe system takes into account the economical use of the length of the lines, and is suitable for heating with natural circulation. Then the two-pipe system will require the mandatory inclusion of a pump in the circuit.
There are three types of horizontal wiring:
- Dead end;
- Beam or collector;
- With parallel movement of water.
By the way, in the diagram of a single-pipe system there may also be a so-called bypass pipe. It will become an additional line for fluid circulation if one or more radiators are turned off. Usually, shut-off valves are installed on every radiator, which allow you to shut off the water supply if necessary.
What could be the consequences: narrowing the diameter of the heating pipe
Narrowing the pipe diameter is extremely undesirable. When wiring around the house, it is recommended to use the same standard size - there is no need to increase or decrease it. The only possible exception would be a large length of the circulation circuit. But even in this case you need to be careful.
Many experts do not recommend narrowing the diameter of the pipes, as this can have a detrimental effect on the entire heating system
But why does the size become smaller when replacing a steel pipe with a plastic one? Everything is simple here: with the same internal diameter, the outer diameter of the plastic pipes themselves is larger. This means that the holes in the walls and ceilings will have to be expanded, and seriously - from 25 to 32 mm. But for this you will need a special tool. Therefore, it is easier to pass thinner pipes into these holes.
But in this same situation, it turns out that the residents who made such a replacement of pipes automatically “stole” approximately 40% of the heat and water passing through the pipes from their neighbors in this riser. Therefore, it is worth understanding that the thickness of pipes that are arbitrarily replaced in a heating system is not a matter of private decision; this cannot be done. If steel pipes are replaced with plastic ones, no matter how you look at it, you will have to widen the holes in the ceilings.
There is such an option in this situation. When replacing risers, you can pass new pieces of steel pipes of the same diameter into the old holes; their length will be 50-60 cm (this depends on such a parameter as the thickness of the ceiling). And then they are connected with couplings to plastic pipes. This option is quite acceptable.
Correct calculation of pipe diameter for heating (video)
If you are incompetent in calculating the diameter of pipes, return lines, diagrams and choosing a coolant, it is better to call specialists and ask them to comment on their work.
Happy projects!
Add a comment
heatclass.ru
Why is the diameter of pipes most often narrowed?
- Reduce installation costs and purchase of components;
- The diameter of holes in walls and ceilings decreases;
- Installation is simplified and accelerated;
- The volume of coolant in the pipes decreases;
- The thermal inertia of the heating system is reduced;
- Increasing the speed of coolant movement;
- The volume of concrete required for pouring pipes in the floor is reduced (special cases).
However, despite the existing advantages of narrowing the diameter, such a solution can cause failure of the heating system, breakdowns, accidents, failure to reach the designed capacity and other consequences. Each system must be designed taking into account the technical conditions and individual characteristics of the system, connected heating, pumping and other equipment, the selected piping system and other factors.
Heating system wiring diagram and heating pipe diameter
The heating wiring diagram is always taken into account. It can be two-pipe vertical, two-pipe horizontal and single-pipe. A two-pipe system involves both upper and lower placement of lines. But the single-pipe system takes into account the economical use of the length of the lines, and is suitable for heating with natural circulation. Then the two-pipe system will require the mandatory inclusion of a pump in the circuit.
There are three types of horizontal wiring:
- Dead end;
- Beam or collector;
- With parallel movement of water.
By the way, in the diagram of a single-pipe system there may also be a so-called bypass pipe. It will become an additional line for fluid circulation if one or more radiators are turned off. Usually, shut-off valves are installed on every radiator, which allow you to shut off the water supply if necessary.
GOSTs and SNiPs
Regarding the calculation of the diameter of pipelines, it is useful to use:
- SP 40-102-2000 - describes the general requirements for all types of installed pipelines made of polymer material;
- SNiP 41-01-2003 - contains building codes and regulations for heating, heat supply, and ventilation systems;
- SNiP 2.04.02-84 and its updated version SP 31.13330.2012 - addresses issues of standardization and design of water supply systems;
- GOST 34059-2017 - contains rules for performing work during the installation of heating, cold water and hot water, testing communications;
- GOST R 52134-2003 – standards for pressure pipes made of thermoplastics, the main regulatory document;
- SNiP 2.04.01-85 - rules for organizing internal water supply;
- SP 40-101-96 – rules for the design and installation of polypropylene pipes.
Low pressure polyethylene pipes
HDPE pipes are used for external laying of water pipes. They are produced in lengths and coils of diameters corresponding to the standard number series.
There are several grades of polyethylene depending on its internal structure; pipes are made from PE-80 and PE-100, the latter being the best.
Unlike polypropylene pipes, the wall thickness of HDPE pipes can vary within wider limits. For them, the dimensional ratio of the outer diameter to the wall thickness SDR is also established, and it can vary in the range from 2.5 to 41.
HDPE pipes are designed to transport water with a temperature not exceeding 40 °C. It is clear that they are used only in cold water supply systems.
As for the pressure characteristics, the pressure that a HDPE pipe can withstand ranges from 2.5 to 25 bar and directly depends on the SDR.
HDPE pipes are connected using external compression couplings, so that their internal diameter remains unchanged throughout the entire pipeline.
Related article:

What is HDPE pipe
A separate article explains what HDPE pipe is - the production process, application, joining methods, installation.

Rice. 4 Installation of polypropylene and polyethylene pipes











