The most popular way to maintain heat in the rooms of a private house is heating associated with the movement of water through pipes. There are many types of structures that allow you to conduct and install heating in a house. Practical owners choose a double-circuit heating system for a private home. It fully pays for the money spent on it and effectively heats the premises.
In our article we will analyze in detail what two-pipe heating is, why people install this system, what heating installation schemes exist. We will also touch on the topic of installing a double-circuit boiler that runs on gas.
What is dual-circuit heating?
Double-circuit heating (two-pipe) is the most popular pipe layout for heating a house. A double-circuit heating system is better than a single-circuit heating system due to the rational and efficient distribution of the coolant.
The two pipes connected to the radiator perform different functions. Water heated by the boiler to the required temperature flows through one pipe. On the other, the cooled coolant is discharged. Then it goes back into the boiler for further heating, but does not flow into the next radiator. The water in both pipes often moves in the same direction, although with a certain installation design it can move in opposite directions.
A double-circuit heating system requires more pipes than a single-circuit heating system, but it is more efficient and much more practical.
Thanks to the two-pipe system, you can maintain a comfortable temperature in a specific room, and not in the entire house at once. It's also more economical. A two-circuit system can be automated so that it can heat a room to a certain temperature, turn itself off, and then turn on again when the temperature drops to a certain point. These are not the only advantages of such heating.
What is the difference between basic and detailed thermal circuits?
Thermal heat supply schemes can be basic, detailed and installation. The schematic diagram of the boiler room shows only the main thermal power equipment: boilers, heat exchangers, deaeration units, chemical water purification filters, feed, make-up and drainage centrifugal pumps, as well as utility networks that connect all this equipment without specifying the number and location. This graphic document indicates the costs and characteristics of coolants.
The expanded thermal diagram reflects the installed equipment, as well as the pipes with which they are connected, specifying the location of shut-off and control valves and safety devices. In the case when it is impossible to plot all the nodes on a detailed thermal circuit, then it is separated into its component parts according to the technological principle. The boiler room flow diagram provides detailed information on the installed equipment.

Why do people choose a dual-circuit system?
This type of wiring has advantages that need to be mentioned in order to understand why home owners choose it. These include:
- Parallel connection of radiators. This allows you to maintain different temperatures in a single room. This allows the system to be used in multi-storey buildings. Plus, if one or more radiators break down, the system will continue to function. With a single-circuit system this is impossible.
- Possibility of connecting a large number of radiators. The temperature of the water entering each radiator will be the same, regardless of how far it is located from the boiler.
- Possibility of installing a thermostat. The system monitors the temperature itself and automatically turns on when needed. The owner only needs to set the temperature range.
- Low heat loss. Almost all the heat generated is not lost, but is used to heat the room. In single-circuit systems it is wasted.
Of the minuses: many note the long length of pipes and the high cost of installing double-circuit heating in a private house. In fact, a double-circuit system is not more expensive than its single-pipe counterpart due to the small diameter of the pipes themselves. And there are much more benefits from it.
Beam system with collectors
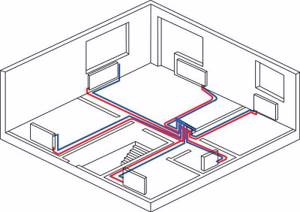
Radiant heating system using a collector.
This is one of the most modern schemes, which involves laying an individual line to each heating device. To do this, collectors are installed in the system - one collector is the supply, and the other is the return. Separate straight pipes diverge from the collectors to the batteries. This scheme allows for flexible adjustment of heating system parameters. It also makes it possible to connect heated floors to the system.
The radial wiring diagram is actively used in modern homes. The supply and return pipes here can be laid in any way - most often they go in the floors, after which they are suitable for one or another heating device. To regulate the temperature and turn on/off heating appliances, small distribution cabinets are installed in the house.
According to heating engineers, this scheme is ideal, since each heating device operates from its own mains and is almost independent of other heating devices.
Advantages and disadvantages of beam systems
There are many positive qualities:
- the ability to completely hide all pipes in the walls and floors;
- convenient system setup;
- possibility of creating remote separate adjustment;
- minimum number of connections - they are grouped in distribution cabinets;
- it is convenient to repair individual elements without interrupting the operation of the entire system;
- almost perfect heat distribution.

When installing a radiant heating system, all pipes are hidden in the floor, and the collectors are hidden in a special cabinet.
There are also a couple of disadvantages:
- high cost of the system - this includes the costs of equipment and installation costs;
- difficulty in implementing the scheme in an already built house - usually this scheme is laid out at the stage of creating a home ownership project.
If you still have to put up with the first drawback, then there is no escape from the second.
Features of installation of radiant heating systems
At the project creation stage, niches are provided for laying heating pipes, and installation points for distribution cabinets are indicated. At a certain stage of construction, pipes are laid, cabinets with collectors are installed, heating devices and boilers are installed, a test run of the system is carried out and it is checked for leaks. It is best to entrust all this work to professionals, since this scheme is the most complex.
Despite its complexity, a radiant heating system with collectors is one of the most convenient and efficient. It is used not only in private homes, but also in other buildings, for example, in offices.
Dual-circuit heating schemes
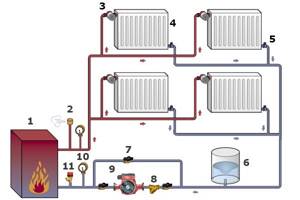
An example of a two-pipe heating scheme for a house
A double-circuit heating system can be installed in different ways. The choice depends entirely on the decision of the home owner. In order not to miscalculate and understand which of them is necessary in a given situation, we will dwell on them in more detail. The most common of them will be:
- Open wiring.
- Closed wiring.
- Upper wiring.
- Bottom wiring
- Dead end.
So, let's start in order.
Boiler room diagram when using solid fuel
Solid fuel boilers have a certain disadvantage, which is caused by high inertia of operation, due to the impossibility of fine adjustment of the combustion process of solid fuel.
In order to smooth out the disadvantage, a buffer tank is installed in the circuit, which gains temperature to heat the heating circuit and consumes heat over a long period of time.
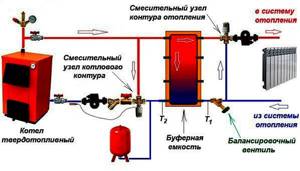
This thermal diagram of a solid fuel boiler house consists of:
- Heat supply source with a primary heating circuit: solid fuel boiler;
- safety group with safety valve;
- buffer capacity;
- heating circuit circulation pump;
- boiler circuit circulation pump;
- expansion tank;
- shut-off valves, drains, air vents;
- balancing valve;
- heating circuit mixing unit for automatically maintaining the temperature in the radiators;
- mixing unit of the boiler circuit, for optimal boiler operation;
- weather-compensated or customizable automation with emergency alarm.
Open wiring
This implies the presence of an expansion tank that is not sealed. It has a lid, but it does not close the tank tightly, which allows the liquid in it to communicate with the atmosphere.
Install it at the highest point of the system. It is located in attics or directly under the ceiling of a building. In the first case, it is necessary to maintain heat in the attic, otherwise the coolant may freeze, and in the second, such a design looks untidy. Installation at this point in the house is necessary to ensure that water does not overflow from it.
The tank can only be filled with water. Other coolant fluids will not work. The system communicates with the atmosphere and some of the water regularly evaporates. Owners of such heating systems must monitor the water level in open wiring. If there is insufficient coolant, the entire heating system will fail.
The system is the easiest to install, does not pose any particular threat to humans and does not require additional components.
How to do it yourself in a private house. Rules and scheme of actions
According to the PUE, in order to make grounding through an outlet directly yourself, it must be connected according to the diagram not to the panel board, but directly to the circuit.
One of the main requirements for the grounding loop is that the resistance of the system as a whole should not exceed 4 ohms. To do this, you need to correctly connect the circuit to the power panel using a conductor made of copper. One side of it is attached to the base of the house, and the other to the zero on the shield.
Photo 2. Ready-made kit for grounding a wall-mounted gas boiler with all the necessary components.
To independently implement a grounding device, you can use the following methods:
- Buy a ready-made kit for grounding a gas boiler. It includes all the necessary components. Installation is quite quick and does not take much time. You will need a small area of 0.5x0.5 m2. Grounding can be carried out in the basement or a few meters from the house itself.
- Make your own ground electrode. To do this you will need a welding machine and a steel angle. The created structure, in the form of a triangle or an inverted letter Ш, is dug into the ground to a depth of more than 1 meter.
Reference! Before starting work, it is necessary to install an independent external grounding loop near the house.
Tools and materials
The process is done thanks to the following tools:
- According to the markings made, a trench is dug with a shovel.
- Grounding conductors are driven into the drilled holes with a hammer.
- Using a motor drill, deep holes are drilled in the upper part of the trench.
- To connect the corners between the horizontal elements of the ground loop, a metal tape is used. Electric welding is required for connection.
- At the end of the conductor entering the room, an M6 or M8 bolt is welded. A wire ring is placed on it, which is responsible for the internal grounding of a private house.
Materials used:
- Metal corner (size 50x50x5 mm). The house grounding loop is an equilateral triangle, into the corners of which metal grounding conductors are driven.
- Steel strip 40 mm wide and 4 mm thick. In order to join the corners together, a metal tape is used.
- Metal wire rod with a diameter of 8–10 mm. It is laid in a trench and raised above the level of the blind area by 50 centimeters.
How to ground a circuit: work process
To properly and effectively ground a gas boiler, it is necessary to create an external circuit.
Contour manufacturing process:
- Markings are made at a distance of one meter from the house. An equilateral triangle with sides of 2 m is drawn.
- A trench 50 cm deep and 40 cm wide is dug along the drawn lines.
- Next comes the connection to the house using a trench of the same size.
- Deep holes are made with a drill.
- Grounding conductors are inserted into the pits. The distance to the bottom of the trench should be about 15 cm.
- The ground electrodes are connected to each other using metal strips 40x4 mm.
- They place a metal strip in the trench leading to the house.
- Weld a strip of metal to the base using a metal rod.
Attention! Such equipment of a grounding system is possible only if there is a sufficient amount of land near the house. If it is impossible to ground the boiler using a triangular circuit, linear grounding is used
Closed wiring
The system is based on an expansion tank. Inside it is divided transversely into two parts by an elastic partition, which is called a membrane. The required pressure is maintained in the upper part, and the volume of water is maintained in the lower part. The lower part is connected to the heating system through a pipe.
Water and any ethylene glycol-based liquid are suitable for filling a closed dual-circuit system. The advantage of the latter is that it does not freeze even at fairly low temperatures. Disadvantage: it is not egological and requires disposal. And there are problems with this in the CIS countries.
An expansion tank with a membrane can be installed anywhere in your home, not necessarily at the highest point.
A sealed tank is more dangerous than a leaking one. The pressure can increase greatly, and gases, having no outlet, accumulate. Therefore, a closed system must be carefully monitored and air vents installed.
Implementation options
Scenario 1
Given: a one-story house with an area of no more than 100 square meters. Several completely separate rooms, each of which requires the installation of a heating device. What will be the piping of a double-circuit heating boiler in this case?
The simplest to implement, fault-tolerant and problem-free scheme is the so-called Leningradka, a single-pipe barracks-type heating scheme. Another important argument in its favor is the low price of materials: one circuit will clearly cost less than two (in the case of a two-pipe circuit).
What does its implementation look like?
- The relatively small area of the house means that it has a small number of permanent residents. Therefore, hot water consumption is unlikely to be a serious problem. For the sake of increasing thermal inertia, we will not give up beautiful, inexpensive and well-heating aluminum radiators.
- However, it is still advisable to increase the volume of water in the circuit. The simplest and cheapest solution is to increase the diameter of the circuit pipe by one step. Let's say from DN40 to DN50. The volume of water in the pipe in this case will increase by (50/40)^2=1.5625 times (the internal volume of the pipe is proportional to the square of its cross-section).
- Each heating device runs parallel to the main circuit without breaking it. The inset pattern is bottom or diagonal. Each radiator is equipped with a throttle for balancing on the supply, a valve to completely cut off the radiator on the return, and an air vent (Mayevsky valve or a regular valve) in any of the upper plugs.
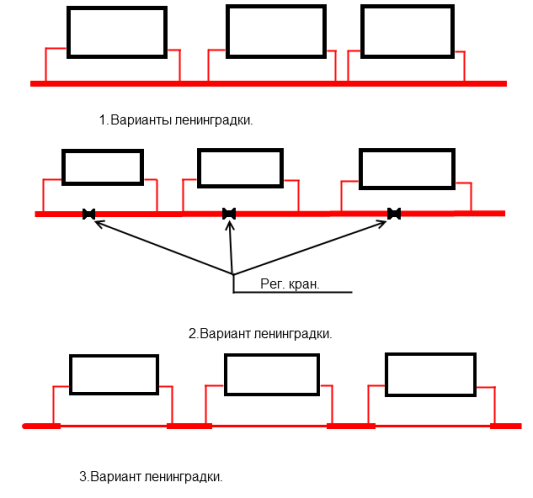
We need the first version. The main circuit should not open or reduce its cross-section.
- Immediately after the boiler, the pipe of the main circuit rises sharply, forming the so-called accelerating manifold. Then it is laid with a constant downward slope.
Such a complex (and, admittedly, not always aesthetic) wiring is needed so that when the circulation pump stops, heating of the heating devices is possible due to natural circulation.
- In front of the boiler, along the flow of water in the circuit, a membrane expansion tank is inserted, designed to compensate for changes in the volume of liquid when heated. The instructions for its selection and installation are standard: the volume of the tank is taken equal to 10% of the coolant volume; The tank is mounted with the hose facing up.
Read also about the features of the heating radiator piping process.
Scenario 2
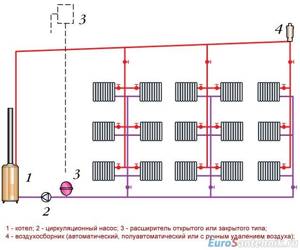
Given: a two-story house with a large number of separate rooms; double-circuit boiler. What will be the wiring diagram for a double-circuit heating boiler in this case?
We will not invent complicated ways: we will implement the classic two-pipe scheme with top filling and constant wiring of heating devices.
- Directly from the boiler, the heated water flows upstairs into the supply pipeline, which encircles the house in the attic or passes under the ceiling of the second floor.
- The coolant then passes through the risers to which the heating devices are connected. However, they do not open the riser completely: each radiator is equipped with a jumper and a throttle for adjustment.
The shut-off valve on the second line of the line will not harm, but the air vent is one for the whole house and is located to the expansion tank at the top point of the circuit.
- The coolant returns to the boiler through the lower outlet, which encircles the house along the floor of the first floor or basement.
The advantage of this scheme is that, if necessary, it can work due to natural circulation. The role of the accelerating manifold is performed by a pipe through which the coolant flows to the upper filling.

The circuit can work without a circulation pump. Without electricity you won't freeze.
How to increase the thermal inertia of a heating system?
- Again, increasing the diameter of the bottling pipes.
- By replacing aluminum heating radiators in the project with cast iron or steel tubular ones. They are characterized by a large internal volume, designed to compensate for the relatively low thermal conductivity of the material.
Don't be afraid of the ugly design of Soviet-style cast iron batteries. Yes, they are still in production; However, along with them, you can also find quite decent externally wall-mounted heating devices made of cast iron and designer floor radiators on the market.
Cast iron is also advantageous because, in addition to the thermal inertia of a large volume of coolant, it itself has a large heat capacity. With a weight of 100 - 150 kilograms, a floor-mounted cast iron radiator will not cool down quickly.

The 13-section Demrad Retro, with a height of about a meter, weighs 175 kilograms.
Tip: a situation often occurs when the second floor is used periodically in winter, during guests’ visits. In this case, a heating scheme with two boilers and independent single-pipe circuits for each floor will be more economical. Most of the time, one of the boilers will operate in economy mode, maintaining the room temperature only slightly above zero.
Universal solution
Finally, there is an extremely simple way to modify a finished heating system with your own hands, greatly increasing its thermal inertia. It is enough to include a heat accumulator in the circuit.
What it is?
A tank with a volume of 300 to 2000 liters with two connection pipes, reliably insulated to reduce heat loss. The idea is simple: it stores a large volume of hot water; When heating of the coolant stops, the reserve of thermal energy accumulated by the tank is consumed. The larger the tank volume, the slower the batteries will cool.

A heat accumulator is the simplest and most universal solution to the problems of a double-circuit boiler.
Where is it mounted?
At any point in the heating circuit. You can take it to the basement by opening the circuit running along the first floor with two pipes for connecting it. You can use the pantry to install it. You can make it the basis for a warm bed: it will inevitably dissipate some amount of heat.
How profitable is it?
- The heat accumulator will smooth out fluctuations in the temperature of the coolant when the double-circuit boiler heats hot water. The batteries will be warm all the time.
- The heat accumulator is especially beneficial when using electricity as a heat source and in the presence of a two-tariff meter. The main volume of coolant is heated to maximum temperature during the night tariff. During the day, the accumulated heat is consumed.
Does this solution have any disadvantages?
- The cost of the tank is quite high. An insulated container with a volume of 1 m3 will cost approximately 20-30 thousand, depending on the manufacturer.
- Let us repeat: despite the thermal insulation, the tank will inevitably dissipate some heat.
Upper wiring
Pipes supplying coolant are installed at the top of the room. Most often closer to the ceiling, above the windows. This contributes to the appearance of high pressure in them. The pipes supplying coolant back to the boiler run along the bottom of the room, as close to the floor as possible.
A two-pipe heating system for a private house with overhead wiring requires an expansion tank. Sealed or not is the owner's choice.
The disadvantage of the top wiring is that some of the heat goes up. It is not intended for heating large areas. But the coolant is transferred at high speed.
Boiler room diagram with 2 boilers
The use of two gas units for one heating system is a fairly popular solution among owners of autonomous heating systems with a system thermal power above 50 kW.
This may be a large heated area of the facility, or the presence of additional heat loads in the form of hot water or air-heated heating units.
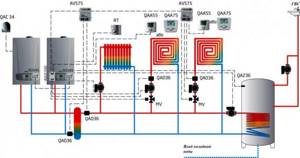
The use of two units per thermal circuit has a number of advantages compared to one source of equivalent power. First of all, because several small-sized units of less weight are much easier and more economical to place in a boiler room, which is especially important when constructing roof-mounted or semi-basement furnaces.
In addition, the installation of 2 units significantly increases the operational reliability of the heat supply system. In the event of an emergency stop of one of the units, it will continue to function with 50% thermal load.
This piping scheme significantly increases the working life of boilers, due to the fact that they are less loaded during the heating period of the year.
Bottom wiring
Here the coolant-conducting pipe is installed directly under the window sill, and the return pipe is installed near the floor.
The pressure in the pipes is not very high, so pumps have to be used. Airing is possible. To avoid this drawback, Mayevsky cranes should be installed on the floor. If the house is multi-story, then this tap should be located on each floor.
The wiring can be laid only to the doorway or two heating systems independent of each other can be installed on both sides of the door.
The expansion tank is easy to install anywhere. If it is closed, then it can be placed in rooms rather than in the attic, which is convenient. The lower wiring is not noticeable. This is important if you care about the wiring fitting into the decor of your room.
What is the difference between closed and open system schemes?
The main difference between an open or gravity heating system and a closed one is the complete absence of devices for forced movement of the coolant through the pipes. This process occurs only due to the thermal expansion of the heated liquid.
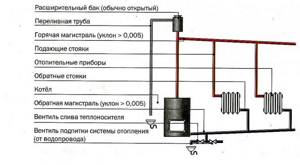
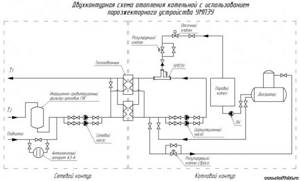
Composition of elements in the thermal circuit of a boiler house with an open heat supply circuit:
- The heating source is a hot water boiler operating on solid, liquid and gaseous fuel.
- Expansion tank for thermal compensation of the coolant.
- Temperature compensator overflow pipe.
- Supply (hot) line with heating risers.
- Heating appliances.
- Return line with heating risers.
- Coolant drain valve.
- Heating network feed valve.
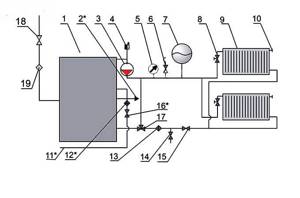
The circulation of the heating fluid in a closed boiler installation is carried out thanks to a circulation pump (3), which is installed on the water outlet line from the boiler (1), usually in its upper part, and an air vent (4) is also located here. Water, heating up in the boiler, enters the heating supply pipeline and is directed to the batteries (9) through a thermostatic valve (8).
An expansion tank (7) is installed on the supply line for temperature compensation of water during heating, a safety valve (6) for relieving emergency pressure in the network and a pressure gauge (5) for monitoring the working pressure of the medium.
A Mayevsky valve is installed on the heating device to release the air lock (10). Along the return flow of the coolant, a three-way valve (17), a water purification filter (13), a shut-off valve (15) and a drain valve (14) are installed.
Gas is supplied to the boiler through a gas valve (18) and a filter (19) to purify the energy carrier before the nozzle of the burner device. Make-up water in the water-heating boiler house circuit comes from the water supply system (11) through the valve (16) to the filter to remove suspended solids and hardness salts. The boiler is equipped with a hot water supply line for its own needs (2).
Heating the house with a double-circuit gas boiler

If you are looking for a universal way to provide your home with heat, then you should think about purchasing a double-circuit gas boiler. It can not only heat the room, but also heat water for domestic needs.
It is worth keeping in mind that boilers are not entirely suitable for large houses. The heating capacity of hot water in double-circuit boilers allows servicing only one point. If you plan to have several bathrooms, then the power will not be enough. In such cases, you should resort to indirect heating boilers or conventional heating element tanks.
Heating system installation
We will begin the description of installation work with the installation and piping of the boiler. In accordance with the rules, units whose power does not exceed 60 kW can be installed in the kitchen. More powerful heat generators should be located in the boiler room. At the same time, for heat sources that burn different types of fuel and have an open combustion chamber, it is necessary to ensure a good air flow. A chimney device is also required to remove combustion products.
The location where the heat generator will be located must be selected taking into account the minimum permissible distances to walls or other equipment. Typically these intervals are specified in the manual supplied with the product. If this data is not available, then we adhere to the following rules:
- passage width on the front side of the boiler is 1 m;
- if there is no need to service the unit from the side or rear, then leave a gap of 0.7 m, otherwise - 1.5 m;
- distance to the nearest equipment – 0.7 m;
- when placing two boilers next to each other, a passage of 1 m is maintained between them, and opposite each other - 2 m.
Double-circuit heating combined with heated floors
Closed options for double-circuit heating of a private house can be easily combined with a water heated floor system. It is important to consider that underfloor heating is a low-temperature system, and radiators are a high-temperature system. Therefore, it is necessary to provide underfloor heating so that the temperature drops from 60-80 degrees to a more comfortable 45-50.
If you want to heat all one room with a water floor, then this module will be useful to you:

The module has a thermal head, which, depending on the temperature, opens or closes the coolant supply to the system. The module is connected to the return of the dual-circuit system.
If you want to implement a solution: one floor has floors, another has radiators, then it’s worth distributing the coolant in the boiler room.
Boiler in the boiler room diagram
There are various options for connecting an indirect heating boiler to boiler units that can operate on any type of fuel: gas, solid and liquid fuel.
In this scheme with an indirect heating boiler, a water gun or distribution manifold is not installed. The installation of these elements is associated with certain difficulties, as it creates a very complex hydraulic system.

This scheme uses 2 circulation pumps - for heating and domestic hot water. The heating pump runs continuously when the boiler room is running. The DHW circulation pump is started by an electrical signal from the thermostat installed in the tank.
The thermostat detects a drop in the temperature of the liquid in the tank and transmits a signal to turn on the pump, which begins to circulate the coolant along the heating circuit between the unit and the boiler, heating the water to the set temperature.
This scheme is used for all modifications of heating sources installed in both hot water and steam boiler rooms.
A certain modification of the circuit is allowed when a low-power boiler is installed in it. The electric heating pump can be turned off by the same thermostat that turns on the pump to the boiler.
In this option, the heat exchanger heats up faster and the heating is stopped. With prolonged inactivity, the temperature in the room will drop.
In addition, after warming up in the boiler is completed, the pump in the heating circuit comes into operation and begins to pump cold coolant into the boiler, which causes the formation of condensation on the heating surfaces of the boiler and leads to its premature failure.
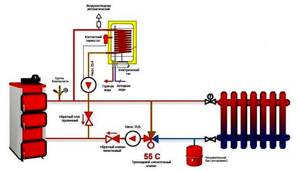
The process of condensation can also occur in the case of long pipelines laid to the batteries. With a large heat removal from heating devices, the coolant can similarly cool down greatly, and the low return temperature will harm the operation of the boiler.
To protect it from condensation and water hammer that occurs when cold water comes into contact with hot heating surfaces, the system is equipped with a protective circuit equipped with a three-way valve.
The diagram shows a temperature of 55C. The thermostat integrated into the circuit automatically selects the required flow rate to maintain the return coolant temperature.
What is boiler piping
Boiler piping is a complex of pipelines and external components that is installed on gas boilers and heating appliances. In addition, piping is usually called the process of installing the periphery that forms the external part of the heating circuit.
Since the boiler is a double-circuit boiler, together with the heating it is necessary to assemble the DHW wiring and connect it to the water supply devices. Installation is a responsible and important job that requires the involvement of competent, qualified specialists.
It is also possible to independently piping the system if the user has copper soldering skills or knows how to handle polypropylene pipelines.
In any case, the result depends on the thoroughness and accuracy of the contractor, his level of training in the creation of thermal systems.

What to do if the house is huge in area
- For a huge two-story building with a significant number of separate rooms, a two-pipe heating scheme is best suited. It must have a top spill and permanent radiator wiring.
- Directly from the heat generator, the heated water flows up the supply pipe. It goes around the building along its attic or along the ceiling of the upper floor.
- Then the water enters the risers, and batteries are connected to them. They do not completely open the riser. Any device is equipped with an adjusting throttle and a jumper.
- It is necessary to install a shut-off valve on the second branch of the supply pipeline. It is possible to install only one valve for bleeding air and screw it to the expansion tank in the upper section of the circuit.
- Through the second (lower) pipe, which goes around the building through the basement or floors of the first floor, water flows back into the boiler.
In other words, a system with such a circuit can operate without electricity-dependent units (for example, a pump). Based on this, if force majeure events occur, you will not freeze under any circumstances.
Increasing the thermal inertia of the system
You have the opportunity to increase the thermal inertia of the heating system with your own hands.
- It is convenient to do this by choosing a slightly larger cross-section of contour pipes than required by the project.
- In addition, it is possible to replace aluminum batteries with cast iron counterparts. They have an expanded internal number of sections, which increases the thermal conductivity and heat capacity of the material. There is a conclusion that all cast iron radiators for heating systems have an ugly design. But, this is not true. Yes, their obsolete Soviet-era models are still being produced. But besides them, the market also offers modern analogues. For example, beautiful floor radiators made of wrought iron or wall-mounted radiators with flat, aesthetic shapes.
- Often the attic or second floor of a house is needed only occasionally in the winter, for example, to accommodate guests. Then a good option is to use a heating circuit with two heat generators and separate single-pipe circuits for each floor.
- In this case, the boiler at the top will be operated most of the time in economical mode, i.e. Maintain temperatures around +5 degrees.
The most inexpensive method to overcome all troubles
- It is also possible to independently improve the heating network, repeatedly increasing its thermal inertia.
- To do this, you need to add a thermal energy accumulator (storage tank) to the circuit. It is a container with a volume of 300/2000 l, which has two connecting pipes. The tank should be well insulated to reduce heat loss.
- The container helps to accumulate huge volumes of heated water. If the boiler stops, the heat reserve from this tank is wasted. It is clear that the larger the tank, the slower the radiators will cool.
- The heat accumulator can be installed on any part of the heating system. It is possible to mount it in the basement. To do this, you need to open the lower circuit with two pipes. It is possible to place the unit in a storage room. An interesting option is to transform the device into a hot bed base. Since it will inevitably release some heat into the atmosphere.
- The battery will compensate for temperature changes in the coolant while the boiler warms the water for domestic hot water. It is very beneficial if the boiler runs on electricity.
Calculation of heating of a 2-story building
Calculation of energy efficiency, heat transfer and technical parameters of heating determines its performance characteristics, the amount of heat loss in the house, the power of the heat generator, the number of radiators, their location, etc.
The performance of a boiler, which provides efficient heating of a two-story house, is calculated based on the overall results of heat loss in the building. The initial data for calculations should include:
- The area of each heated room and the total area of all rooms in the house.
- Climatic and geographical features of the area.
- Thermal insulation of the building and each room.
- Building materials from which load-bearing walls, interior partitions, ceilings and other floors are built, as well as their thickness.
- Constructive solution of the roofing system, the presence or absence of an attic, attic, overhead technical space.
- Dimensions of windows and doors, quality of their insulation.

You can watch the video or download a video about different 2-pipe connection schemes here:
Which scheme is better to choose?
The selection of wiring is carried out taking into account many factors - the area and number of floors of a private house, the allocated budget, the presence of additional systems, the reliability of power supply, and so on. We will give a number of general recommendations for choosing:
- If you plan to assemble the heating yourself, it is better to opt for a two-pipe shoulder system. It forgives beginners many mistakes and will work despite the mistakes made.
- If you have high requirements for the interior of rooms, take the collector type of wiring as a basis. Hide the comb in the closet, and route the lines under the screed. In a two- or three-story mansion, it is advisable to install several combs - one per floor.
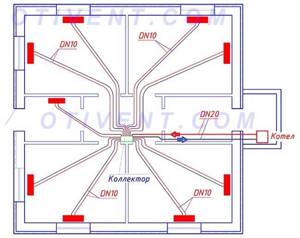
For radial wiring, it is advisable to place the collector in the center of the house - Frequent power outages leave no choice - you need to assemble a circuit with natural circulation (gravity flow).
- The Tichelman system is suitable for buildings with a large area and a large number of heating panels. It is not financially feasible to install a loop in small buildings.
- For a small country house or bathhouse, a dead-end wiring option with open piping is perfect.
Advice. Heating of a dacha for 2-4 small rooms can be organized using a single-pipe horizontal system with a lower distribution - “Leningradka”.
If the cottage is planned to be heated with radiators, heated floors and water heaters, it is worth adopting a dead-end or collector wiring option. The two indicated schemes can be easily combined with other heating equipment.
Equipment stages and operation
If you decide to make a heating circuit for a two-story house with your own hands, strictly follow the sequence of work.
- Calculation of the need for heat output from radiators for each individual room and total power. Information is needed to select a boiler and the number of batteries. The location of doors and windows relative to the cardinal directions, the area and degree of insulation of the floor, walls, and ceilings are taken into account.
- Drawing up a project - general and floor-by-floor, coordinating the installation locations of gas equipment with the supplying organization. Providing the required electrical power if electricity is used.
- Selection and purchase of a boiler, pipes, heat exchangers, components for assembling a single system.
- Pipeline layout.
- Assembling a single circuit, crimping.
- First launch and setup, eliminating leaks.
During further operation in operating mode, perform the following types of work:
- cleaning all components from dust and dirt;
- timely elimination of leaks;
- de-airing of radiators when the temperature of individual devices decreases;
- checking pressure, timely topping up coolant;
- maintaining the liquid level in the system throughout the year, including during the inter-furnace period.
Advantages over existing systems
1. There are no heaters at the central heating substation or electrical substation substation. 2. Hydraulic stability is many times higher. 3. Underproduction of electricity due to heat consumption is eliminated due to the absence of the need to maintain a temperature difference in heat exchangers. 4. Reservation of consumers is ensured in case of interruption of circulation along any of the circuits, respectively 25-30% or 75-70%. 5. The ingress of raw water into the network water through leaks in the heat exchangers is excluded.