Heating an individual house is one of the main conditions for long-term residence of residents in it; the level of comfort for people in the premises, ease of maintenance and financial costs for fuel depend on its normal functioning and structural design. To prevent negative consequences in emergency situations in cold weather associated with power outages and freezing of water in the system, antifreezes act as the heat supply medium, and the consumer should know how to fill a closed-type heating system with antifreeze.
Anti-freeze agents are classified as products that have a limited service life; during operation, pipes, heat exchange devices and fittings gradually accumulate contaminants. Therefore, during operation, it is necessary to repeatedly drain and fill the circuit with an antifreeze composition after flushing or temporary decommissioning of pipelines and branches of heated floors, boilers, and radiators.
Rice. 1 Closed system nodes
Types of individual heating systems
In private residential buildings, two types of heating systems are installed; how to fill the coolant depends on their design.
Open gravity
In houses with a height of no more than two floors, when installing only heat exchange radiators to heat the premises, they usually install a gravity heating system with a large capacity tank at the top. Circular circulation of the coolant along the circuit occurs by gravity due to the pushing out of less dense hot water heated in the boiler by cold water masses. The pipeline is laid with a slight slope towards the boiler in such a way that the liquid from the return line flows into the heater by gravity.
The heating main has only one point open to external access in the form of an expansion tank, through which antifreeze is usually poured into the heating system of the house. After evaporation or leaks, you can also add water through the tank. The option of bottom filling of the coolant into the gravity system through a drain pipe with a shut-off ball valve mounted at the lowest point of the pipeline cannot be ruled out. However, with this method, you will have to supply the liquid with pressure, for which you will need special water pressure equipment - an electric pump or its manual equivalent, a pressure testing device.
Rice. 2 Designs of gravity and closed systems
Closed
In high-rise buildings with extended heating circuits for underfloor heating, a gravity-flow system cannot cope with large volumes of coolant pumping and high hydraulic resistance of the line. In these cases, to ensure the movement of liquid through a long pipeline, an electric circulation pump is added to the main line (for heated floors, another additional unit is installed), the circuit is closed and a sealed hydraulic accumulator is installed instead of an open storage tank.
Water is poured into a closed-type heating system through the drain pipe at the bottom of the pipeline; to create the required water pressure in the line, the coolant is supplied by an electric pump or pressure tester.
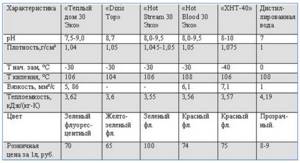
Rice. 3 Comparison table of water and glycol parameters
Related article:
Scheme of a closed heating system with forced circulation . A separate article describes in detail about a closed heating system, its elements, and provides a diagram for independent design and installation!
Recommendations on when to use water as a coolant
- when you live in the house permanently and the heating system is under your 24-hour control
- if you have a telemetry system installed in your home, which will quickly and promptly notify you of an emergency situation in your home, and you can just as quickly and promptly eliminate it
- when you have no risk of power outages in your home
For example, a gas generator is installed, which automatically turns on in the event of a power outage. Your heating system continues to operate as normal.
Comparison of water and antifreeze
Filling the heating system with water is the most popular method for the following reasons:
- Water is a generally accessible and inexpensive type of heat carrier; it is a natural source, so its use is environmentally friendly and safe.
- The highest heat capacity of water, 4200 J/kg∙K, means that it takes a long time to heat up and release thermal energy. This property allows it to be transported over long distances with low thermal energy losses.
- In comparison with other heat-transferring liquids, the viscosity of water at 1.006 m2/s∙10-6 at 20 °C is the lowest and falls with increasing heating temperature. This factor leads to a decrease in hydraulic resistance when it moves through the pipeline and, accordingly, to an increase in heating efficiency.
- The temperature coefficient of linear expansion of water is quite low; relative to a temperature of 0 ° C at +80 ° C, it increases in volume by only 2.8%.
- Water is neutral in chemical composition and does not have a destructive effect on pipelines made of thermoplastics widely used in household communications - ordinary, cross-linked, heat-resistant polyethylene, polypropylene or their varieties with an aluminum shell - metal plastics.
- The disadvantages of water include the corrosive effect on metals and the presence of salts in the composition, which, when heated, form scale, which reduces the efficiency of equipment and leads to blockages and failure of heat transfer elements (heating elements). To avoid the negative effects of scale, the circuit is filled with distilled water instead of the usual one.
- The main disadvantage of water, in which antifreeze is poured into the heating system of a house instead, is its high crystallization temperature of 0 ° C. With strong cooling of the aquatic environment, ice with low density is formed, growing in volume by approximately 10%. This leads to rupture of ice-frozen pipes, heat exchange batteries, and boiler equipment components.
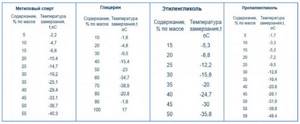
Rice. 4 Crystallization temperatures of aqueous solutions of non-freezing liquids
To avoid freezing of water in emergency situations, antifreezes are added to it, which have the following distinctive features:
- Anti-freezes have a 10% lower thermal capacity, so their use leads to a decrease in heating efficiency.
- The viscosity of antifreeze is 5 - 7 times greater than water, which means that to push them through pipes, more power of the electric pump will be required, and the hydraulic resistance will increase.
- Anti-freeze agents have a higher fluidity than water, so during their operation it may be necessary to replace gaskets or seals at the joints of pipelines and connected fittings with other denser materials.
- The thermal expansion of glycols is 1.5 times higher than water, so a hydraulic accumulator with a larger working chamber capacity may be needed.
- Factory antifreezes are usually designed to last 5 years (heating seasons), after which their composition is subject to decomposition with sedimentation. If the coolant in the heating system is not replaced in time (the disposal time is determined by the change in the color of the glycol), a poorly soluble sediment may appear in the circuit along with the pipes, boiler and radiators.
- Most glycols function up to +115 °C, but it is not recommended to increase the operating temperature above +70 °C. When overheated, their composition decomposes with the formation of a sparingly soluble precipitate.
- A significant advantage of glycols relative to water is the absence of expansion of the material during crystallization; the drug turns into a mobile slush of the same volume, which, when heated, again turns into a liquid state.
- Many antifreezes contain additives that reduce foaming and their corrosiveness - this significantly reduces the amount of rust when they are in lines with metal pipes and fittings.
- After draining used antifreezes, one of the problems is their disposal.
- One of the main disadvantages of antifreeze is the refusal of warranty service by many boiler manufacturers when any type of antifreeze is poured into their equipment.
How is the frequency of coolant replacement determined?
Coolant replacement should be carried out in the following situations:
- Planned event - the service life of antifreeze has expired, which is no more than 5-6 years, regardless of its type, manufacturer and other factors;
- There was a violation of operating rules - water was added to the system, dirt got in during maintenance, it was severely overheated or was not used for a long time;
- The old network with natural circulation is being modernized - new equipment and pipes are being installed.
It is also necessary to monitor performance indicators during system operation. The first signs of accumulation of deposits inside heat exchangers and pipes are an arbitrary increase in pressure, a decrease in efficiency, heat transfer with increasing energy consumption, and uneven heating of radiators. It is important to detect even minor deviations in operation in a timely manner, so periodically you need to monitor the readings of the pressure gauge, thermometers, and flow meters. This will avoid emergency equipment replacements.
In our company, experienced professionals deal with the problem, so replacement of the coolant with comprehensive cleaning is carried out within one working day, even at the height of the heating season.

Antifreezes for heating and their features
Currently, several types of anti-freeze products are most popular among the average consumer; they are usually sold in plastic canisters with a capacity of 10, 20 or 50 liters. The maximum negative temperature of the solution is indicated on the packaging; it can be used in finished form or before use water is added to it, guided by special tables (the dependence of the crystallization temperature on the volume of antifreeze in the liquid is nonlinear).
Any anti-freeze product contains an active substance with varying percentages (usually about 60 - 65%), distilled or deionized water (30 - 35%), additives, corrosion inhibitors (3 - 4%).

Rice. 6 Cost of 10 liters of ethylene glycol packaging
Ethylene glycol
The retail chain sells red ethylene glycol in canisters of 10 and 20 liters with a freezing point of -30 or -65 °C. The drug has a sweet taste, is poisonous if it enters the human body, and prolonged inhalation of ethylene glycol vapor can also cause short-term health problems.
Poisonous ethylene glycol can be used in closed circuits, where it cannot have a harmful effect on human health upon evaporation. The service life of ethylene glycol is 5 years; before use, the drug is diluted with water to a concentration that requires obtaining the desired freezing point.
Propylene glycol
Anti-freeze made of green polypropylene with the additional commercial name ECO, unlike its ethylene glycol analogue, is not only non-toxic, but also serves as an additive to food products. Propylene glycol is produced in the same containers as ethylene glycol with a freezing point of -20, -30 or -40 ° C, its price is almost 2 times higher than its ethylene glycol analogue.
In terms of its physical parameters (fluidity, thermal expansion, crystallization point), propylene glycol is close to ethylene glycols, with the exception of viscosity, which is 2 times greater. Propylene glycol can be safely used in both open and closed heating circuits.

Rice. 7 Propylene glycols in 10 kg packaging and their price
Glycerol
On sale you can find anti-freeze products based on glycerin with a crystallization temperature at a price slightly higher than or equal to the cost of ethylene glycol, the main properties of the drug:
- Glycerin is harmless and is used in closed and open systems.
- When the temperature limit of 115 °C is exceeded, glycerin decomposes, releasing toxic gas.
- If the content of the water component in the solution decreases, glycerin begins to burn and decompose.
- Has high viscosity.
- It has a less corrosive effect on metal parts than water due to the inclusion of rust inhibitors.
- Subject to foaming, which is removed by introducing a composition of special additives.
- The glycerin solution has increased fluidity and requires the use of dense paronite or Teflon seals.
- Its temperature instability makes it difficult to adjust the boiler.
- Decomposes over time with the formation of a sparingly soluble precipitate and chemically active components that have a negative effect on metals.
- The drug is prohibited for use in the European Union.
Taking into account the above-mentioned features of glycerin, it is not recommended to use it in heating circuits - this will not bring significant financial savings, and eliminating the problems that arise with its use can result in a much larger sum.

Rice. 8 Glycerin anti-freeze
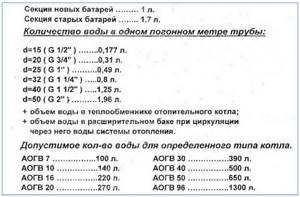
Antifreeze volume calculation
When purchasing expensive anti-freeze units, in order not to overpay, before filling the heating system, you should know the required volume of coolant. The easiest way to accurately determine it is to pump water into the main line with a pressure of 1 - 1.5 bar, and then drain it and measure the resulting amount. You can add 10% to the mass of the liquid for airing and evaporation of the coolant.
If experimental filling to determine the required volume of coolant is not feasible for some reason, you can use a simple formula for adding the volumes of the main components of the system: radiator heat exchangers, boiler, expansion tank capacity and pipeline:
V (system) = V (boiler) + V (cistern) + V (batteries) + V (pipes)
The working volume of the boiler and expansion tank is determined from the passport data for the equipment provided by the manufacturer. In the same way, the capacity of radiators is determined from the operating instructions by multiplying the indicators of one section by their number. In the absence or loss of passports for the boiler, hydraulic accumulator or radiator heat exchangers, the necessary information is obtained from Internet sources.
The volume of the working fluid in the pipeline is determined by multiplying its cross-sectional area by its length according to the well-known formula:
V (volume) = S (area) x L (length) , where
S (area) = 3.14 (pi) x R2 (radius squared).
Rice. 9 Example of calculated data for finding volume
How to fill a closed heating system with antifreeze
Before pouring antifreeze into pipes, a number of preparatory operations are carried out. These include draining waste coolant, washing pipes and equipment, purchasing antifreeze and auxiliary water supply units.
Choice of anti-freeze
Before filling the heating system in a private home with antifreeze, purchase the required reagent, taking into account its physical characteristics, quality indicators, cost and reviews of the manufacturer.
Since all popular anti-freeze products based on ethylene and propylene glycol are made from imported raw materials, their cost will be relatively high. In order not to incur extra costs, it is better to pour ethylene glycol into a closed circuit; in an open circuit there is no worthy alternative to propylene glycol.
You should refuse to choose cheaper analogues in the form of automobile antifreezes; for example, the well-known Antifreeze is produced using a completely different, obsolete Soviet-era technology than its modern glycol analogues, therefore it is absolutely unacceptable in the heating circuit. Antifreeze has completely different additives, designed to work in car radiators and useless in the heating circuit; its service life is significantly lower than glycols and the drug will have to be changed more frequently.
Domestic-made non-freezing liquids presented in the trading network are made from imported reagents, so their cost is approximately equal, they also all have a service life of 5 years and typical crystallization temperatures of the composition are -30 or -65 ° C; products with a freezing point of -20 are less common °C, -40 °C.
Owners who use anti-freeze products are well aware of such brands as Thermagent, Sintec, Sintoil produced by Obninskorgsiintez, Dixis trademarks, Warm House from Forward Group, Hot Blood from VintHim. All listed products have approximately the same cost and identical parameters.
Glycerin
Reviews about coolants of this group are the most contradictory, from the most enthusiastic to the sharply negative.
Positive characteristics of glycerin antifreeze:
- Complete safety for the human body and the natural environment. This is the safest coolant for the heating system of all antifreezes.
- Significant range of operating temperatures. The lower limit of crystallization is 30 degrees, the boiling point is the same as that of water (sometimes higher). Freezing of glycerol is not accompanied by its expansion. An increase in temperature not only liquefies, but also completely restores all the characteristics of the substance.
- Resistant to zinc. In this regard, it is one of a kind among other antifreezes.
- No aggressive effects on the sealing gaskets of the system are observed.
- Absolute fire safety.
- Before pouring glycerin antifreeze, the heating system does not need to be thoroughly rinsed, even if another substance was poured into it before.
- Durability. If you follow the operating rules, coolants of this type can last up to 10 years.
- The level of thermal characteristics here is comparable to propylene glycol. At the same time, glycerin coolants are 20-25% cheaper.

Disadvantages of glycerin:
- Outdated version. Glycerin antifreezes are the most “ancient”: it was in order to improve their performance characteristics that all of the above substances were developed.
- High density and viscosity. Pumps experience significant difficulties pumping glycerin coolant through the heating circuit. As a result, equipment wears out much faster.
- Low heat capacity. In this regard, glycerin is inferior not only to water, but also to propylene glycol.
The heat resistance and environmental safety of the substance deserve special consideration:
- Upon reaching a temperature of +90 degrees, significant foaming of glycerin is observed. To reduce this effect, special additives are usually used.
- The same temperature level triggers the process of chemical decomposition of the liquid. As a result of precipitation, the solid substance gradually layers inside the pipes, and the gas released, acrolein, has a very unpleasant odor, being a weak carcinogen.
- When overheated, water evaporates from glycerin, which makes the liquid very viscous. As a result of this, it loses its characteristics, turning into a jelly-like substance already at a temperature of +15 degrees. It is clear that normal operation of the heating system in such conditions is impossible.
As studies have shown, the main component of counterfeit antifreeze coolants for heating systems is most often glycerin. This is explained by its cheapness, which gave unscrupulous manufacturers the idea to use the material instead of propylene glycol, passing off their products as environmentally friendly high-quality propylene glycol antifreezes
Therefore, when purchasing non-freezing coolants, it is necessary to exercise some caution, requiring quality certificates. It should be noted that in Europe, coolants based on ethylene glycol have long been discontinued, but local companies are in no hurry to return to glycerin.