How to choose?
The selection of an expansion tank must be approached very responsibly, since this product plays one of the most important roles in water heating systems.
Let us highlight a few simple tips that will allow the buyer to choose a suitable model of good quality.
Experts recommend choosing membrane or closed containers. Despite the fact that these types of tanks are usually expensive, the heating system that contains them can last a very long time. This is explained by the fact that in this design the coolant and oxygen do not “meet” each other in any way
But this is only advice - the choice, one way or another, remains with the owner of the home. Always pay special attention to the material from which the rubber partition is made in closed models.
- If you are going to use the tank in conjunction with a central heating system, then the membrane rubber should have increased strength characteristics and resistance to high temperatures. This is because central heating in most cases does not involve significant pressure drops, but the temperature will still be quite high.
- A tank with a membrane characterized by increased elasticity can be safely purchased for a private heating system, since sudden pressure surges are common for this heating option.
- In order to use the expander not only in the heating system, but also in the system responsible for the water supply, the rubber from which the membrane is made must be food-grade. This is necessary so as not to detract from the positive qualities of the water.

When choosing between non-replaceable and replaceable types of membranes, it is recommended to choose the former, since if a non-replaceable part is damaged, you will have to replace the entire unit instead of one element. Before purchasing an expansion tank, it is recommended that you carefully read its technical characteristics. Ask the seller for all necessary quality certificates
If the product does not have them or they do not want to present them to you, it is better to refuse the purchase. Don't forget to fill out the warranty card. Please note that one of the most important parameters that you should pay attention to when choosing a tank is its resistance to diffusion and temperature changes. In addition, all elements of the unit (from the housing to the membrane) must be made of high-quality materials.

Purpose of an additional tank of a double-circuit boiler
As a rule, built-in compensation tanks in gas boilers have a volume of about 6-8 liters. They are designed to compensate for the expansion of 120 liters of coolant circulating in the heating system. Under normal operating conditions, such an expansion tank is enough for a small apartment or house.

If the heating area is large, heated floors are installed or there are many radiators in the rooms, the volume of the standard built-in tank will be small, since more water is used.
When heated, excess coolant completely fills the tank. And since there is no free space left in the tank, the water pressure increases in the heating system itself and an emergency release occurs by the safety valve. After this, it is unlikely that the gas boiler will be able to start working automatically.
To avoid such negative consequences, an additional expansion tank with a membrane is installed in the heating system in a design for a double-circuit gas boiler. When the standard tank is completely filled, the water goes into the reserve hydraulic tank. After cooling, the liquid returns to the radiators.
Common problems
Expansion tanks, like any other heating units, are subject to a number of specific problems. Let's get to know them.
The most common breakdown of such units is the rupture of the membrane part. As a rule, this occurs due to too high pressure (above normal) or uneven loads. Please note that replaceable elements break much more often than compressed ones, since stronger materials are used for the latter, because they can be changed at any convenient time.
The problem of a damaged membrane can lead to many unpleasant consequences. For example, this often causes water to leak from the air valve.
If the membrane is not replaced in time, its rupture will lead to the fact that over time the tank will simply fail. This is due to the fact that liquid gets on the inner surface of the tank, after which it can become covered with rust and become unusable.
Also, users quite often encounter damage to the tank body. If such a problem occurs with your equipment, it is better for you to seek help from a specialist. Do not attempt to repair damaged cabinet elements yourself, especially if you have never encountered such work before.
There are also cases when the expander boils. Most often, this problem occurs in homemade open-type structures. The main essence of this problem is the lack of circulation speed (or its complete absence).
Here are the main reasons for such breakdowns.
- Reduced wiring diameter. The main single-pipe heating circuit is usually installed with a pipe that is no less thin than DN 32.
- No slope. After the heating boiler, you need to make a so-called accelerating manifold. To do this, the pipe must be raised to the upper section of the circuit, where the expander is installed. The remaining part of the contour should be laid with a downward slope.
Many users are wondering how to fix such a serious problem without completely dismantling and reinstalling the heating system. The answer is simple - you need to install a circulation pump. This part works great in many systems (especially the open type). The pump must be placed on the return line directly in front of the boiler.
Another problem with expansion tanks is air blockage in the heating system circuit. To avoid colliding with it, you need to monitor the volume of water.
Types of expansion tanks
Next we will look at the types of expansion tanks for heating. They all have a similar design, differing in internal structure, volume and shape. Let's look at their structure and find out some distinctive features.
Expansion tanks for open systems
The expansion tank for an open-type heating system is a simple tank without any internal filling. Its task is to absorb the expanding and increasing coolant from the heating circuit, preventing it from being damaged. This is where the air generated during heating operation is removed. Installed at the highest point of the circuit, it holds up to several liters of liquid. In order to prevent foreign particles and dust from entering the coolant, the tank is closed with a lid. However, it is not airtight.
You can make the simplest expansion tank for heating with your own hands - there is nothing complicated about it. In open-type heating systems, various metal cylinders, plastic barrels and much more are used as such tanks. You can also weld it from sheet iron, giving it any shape (for example, rectangular - this is the simplest and most compact option). The expansion tank is connected to the system using a regular pipe of small diameter.
Cisterns for closed systems
Closed-type heating uses slightly different tanks. They are built in a closed circuit; the coolant in them does not communicate with atmospheric air. The general principle of operation of an expansion tank in a heating system is as follows: heating up and expanding in volume, the coolant under its own pressure enters the tank, filling part of its volume (it is limited by a membrane or a rubber balloon/bag). When cooling, the coolant is forced out in the opposite direction - into the heating circuit. Another essence of expansion is to maintain a certain pressure in the system.
A membrane heating tank is nothing more than a closed expansion tank. But the membranes used in their design can be of two types - in the form of a diaphragm or in the form of a rubber balloon (bag). Membrane tanks for heating systems are divided in two by a durable rubber (sometimes made from alternative materials) membrane. The second half is filled with air or pure nitrogen. When coolant enters, the membrane bends, compressing the gas filling. As soon as the coolant cools down and its volume decreases, the membrane will squeeze it back into the circuit.
Some users and experts call such tanks vacuum, but this is not entirely the correct terminology - there is no trace of vacuum here.
At the upper end of membrane expansion tanks for heating we can see valves for precise pressure adjustment. Pumps and pressure gauges are connected here. If the tank creates excessive pressure in the system (with the correct volume selected), the safety valve will begin to operate. If this happens, you should bleed a little gas from the gas part. Otherwise, we connect the pump here and start pumping air until the pressure recommended by the manufacturer is reached (indicated in the data sheet).
To check the pressure in the expansion tank of a boiler for heating a private home, use an ordinary car pressure gauge.
By the way, the housings of expansion tanks for heating private houses and many other buildings are made of plastic or metal. As for the membranes inside, they are often made removable - this is necessary for prompt repairs without replacing the entire structure.
Built-in tanks
There are also expansion tanks for boilers that are installed inside heating equipment - these are tanks for double-circuit boilers, in which all the piping is located directly on board. In most cases, their volume varies from 6 to 8 liters, which is quite enough for heating apartments and private households (and for proper heating operation). For example, such tanks are installed in boilers Baxi, Buderus, Protherm and many others.
Types of fasteners
There are certain requirements for installation and operation of each specific model. In particular:
- Installation is carried out in a room where the temperature is kept no higher than zero all year round.
- The container is installed above the boiler. The connection to it must be vertical.
- Emergency overflow is provided.
- There must be constant access to the air valve, drain tap, and nameplate.
- The reducer is placed after the water meter.
The structure can be attached using the 8-35 membrane tank mounting kits.
Standard brackets

This type of fastening is suitable for almost all container options. They have a standard shape. As a rule, they are made of metal. The kit includes everything you need - washer, gaskets, etc. It is important to choose a quality-made mount.
Adjustable brackets

The option is a metal bracket with a retractable console. The design includes a locking bolt(s). The holder is made by contact electric welding.
An adjustable bracket is used to mount the tank directly to the wall. It comes complete with a polystyrene foam gasket and a stainless steel washer.
Bracket with steel clamp

Designed for attaching the expansion tank to the wall. It is also used for floor mounting of the container. The length of the bracket can be adjusted independently.
Why do you need an expansion tank for heating?
When the heating system operates, the coolant often changes its temperature - it either heats up or cools down. It is clear that the volume of liquid changes. It either increases or decreases. Excess coolant is forced out into the expansion tank. So the purpose of this device is to compensate for changes in the volume of coolant.
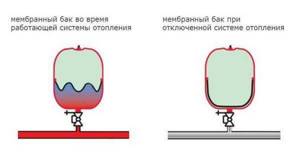
Operating principle of an expansion tank for heating
Types and device
There are two water heating systems - open and closed. In a closed system, coolant circulation is provided by a circulation pump. It does not create additional pressure, it simply pushes water at a given speed through the pipes. In such a heating system there is a closed expansion tank for heating. It is called closed because it is a sealed container, which is divided into two parts by an elastic membrane. In one part there is air, in the other the excess coolant is displaced. Due to the presence of a membrane, the tank is also called a membrane tank.
Closed type
An open heating system does not require a circulation pump. In this case, an expansion tank for heating is simply any container - even a bucket - to which heating pipes are connected. It doesn't even require a lid, although it may have one.
Open type
In the simplest version, it is a container welded from metal, which is installed in the attic. This option has a significant drawback. Since the tank is not sealed, the coolant evaporates and it is necessary to monitor its quantity - top up all the time. This can be done manually - from a bucket. This is not very convenient - there is a risk of forgetting to replenish water supplies. This threatens to cause the system to become airy, which can lead to its breakdown.
Automated water level control is more convenient. True, then, in addition to the heating pipes, you will also have to run a water supply into the attic and also somewhere to route the overflow hose (pipe) in case the tank overflows. But there is no need to regularly check the amount of coolant.
Installation of membrane device
A hydraulic accumulator of this type is installed where there is a minimum probability of coolant turbulence, since a pump is used for normal circulation of water flow along the circuit.
Correct container position
When connecting the expansion tank to a closed heating system, be sure to take into account the location of the air chamber of the device.
The rubber membrane periodically stretches and then contracts. Due to this impact, microcracks appear on it over time, which gradually increase. After this, the membrane has to be replaced with a new one.
If the air chamber of such a tank remains at the bottom during installation, the pressure on the membrane will increase due to gravitational influence. Cracks will appear faster and repairs will be needed sooner.
It makes more sense to install the expansion tank in such a way that the compartment filled with air remains on top. This will extend the life of the device.
Features of choosing an installation location
There are a number of requirements that must be taken into account when installing a membrane expansion tank:
- It cannot be placed close to the wall.
- The device should be freely accessible for regular maintenance and necessary repairs.
- The wall-hung tank should not be positioned too high.
- A shut-off valve should be placed between the tank and the heating pipes, which will allow you to remove the device without completely draining the coolant from the system.
- When installing on a wall, the pipes connected to the expansion tank must also be attached to the wall in order to remove possible additional load from the tank pipe.
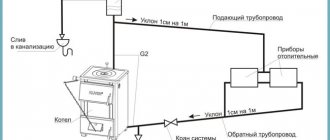
For a membrane device, the most suitable connection point is the return section of the line between the circulation pump and the boiler. Theoretically, it is possible to install an expansion tank on the supply pipe, but high water temperatures will negatively affect the integrity of the membrane and its service life.
When using solid fuel equipment, such placement is also dangerous because steam can enter the container due to overheating. This will seriously disrupt the operation of the membrane and may even damage it.
In addition to the shut-off valve and the “American” connection, it is recommended to install an additional tee and tap when connecting, which will allow you to empty the expansion tank before disconnecting.
Setting up the device before use
Before installation or immediately after it, it is necessary to correctly configure the expansion tank, otherwise called an expansion tank. This is not difficult to do, but first you need to find out what pressure should be in the heating system. Let's say an acceptable value is 1.5 bar.
Now you need to measure the pressure inside the air part of the membrane tank. It should be less by about 0.2-0.3 bar. Measurements are carried out with a pressure gauge with a suitable gradation through the nipple connection, which is located on the tank body. If necessary, air is pumped into the compartment or excess air is vented.
The technical documentation usually indicates the operating pressure, which is set by the manufacturer at the factory. But practice shows that this is not always true. During storage and transportation, some air may escape from the compartment. You must take your own measurements.
If the pressure in the tank is not set correctly, this can lead to air leakage through the air removal device. This phenomenon causes a gradual cooling of the coolant in the tank. There is no need to pre-fill the membrane tank with coolant; simply fill the system.
Tank as additional capacity
Modern models of heating boilers are often already equipped with a built-in expansion tank. However, its characteristics do not always correspond to the requirements of a specific heating system. If the built-in tank is too small, you need to install an additional tank.
It will ensure normal coolant pressure in the system. This addition will also be relevant if the heating circuit configuration changes. For example, when a gravity system is converted into a circulation pump and the old pipes are left behind.
This is true for any systems with a significant volume of coolant, for example, in a two- or three-story cottage or where, in addition to radiators, there is a heated floor. If a boiler with a small built-in membrane tank is used, installing another tank is almost inevitable.
Types - Open tanks
Open expansion tanks are characterized by the fact that they must be installed exclusively at the highest point of the heating system. Such a place could be, for example, an attic. But preventing the expansion of the coolant is not the only function of this type of device, since they also prevent water from boiling in the pipes and replenish its reserves in cases where for some reason a leak has occurred.
The tank can be used with both natural and forced circulation.
- If the circulation is natural, then the tank must be connected to the main line, which is why it will also “double-take” as an air collector.
- If the coolant moves through the system forcibly, then the tank is connected to the return pipe so that the water in the system does not boil.
In general, an open tank is a reservoir from which four tubes emerge:
- Expansion.
- Circulation.
- Overflow.
- Signal.
An expansion tube, which is located at the top of the tank, leads to the heating system. There is also an overflow tube, which is necessary in cases where the container overflows and you need to drain the water into the sewer. At the bottom, accordingly, there is a signal tube equipped with a lock, and a circulation tube is needed so that the coolant in the tank does not freeze, and so that the overall temperature is maintained permanently. If desired, you can take one more additional measure that would “insure” the circulation pipe - insulate the tank with thermal insulating material.
Important! Today, such tanks are practically not used in heating systems due to a large number of shortcomings. Among these shortcomings I would like to highlight the following:
Among these shortcomings I would like to highlight the following:
- Such systems are not adapted to high pressure.
- Their design is very bulky and large.
- Due to the fact that the system is open, along with water, air also enters the pipeline, which has the most negative effect on the surface of the pipes - corrosion will soon form on them. The same applies to other metal elements.
- Such tanks should be installed only at the highest point, and this, you see, is an additional expense.
How to properly install and secure the tank in different types of heating systems
For heating systems of various types, there are different principles for installing expansion tanks.
How to put in open
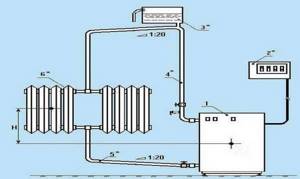
An open heating system is a single vessel of complex shape in which natural circulation of liquid occurs. Contact with air is made through an expansion tank, which is an open container of large volume with a lid; it is only needed to prevent debris from getting inside. Such tanks are installed in the attic and water is periodically added as it evaporates.

Photo 1. Expansion tank installed in an open heating system. The product is located at the highest point of the heating circuit.
The expansion tank is mounted at the top point of the circuit, because hot water, like air bubbles, tends to the top, and the cooling liquid drains by gravity. In the absence of an attic, this is the highest point of the accelerating manifold of a single-pipe system. The containers are not equipped with membranes or shut-off valves, so their installation will not require large financial costs.
How to install indoors
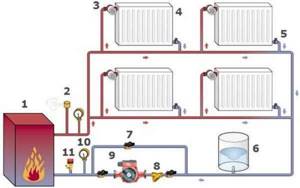
Selecting a container for a closed system is somewhat more difficult, because here you will have to rely on calculations and the volume of the heating circuit. In this case, the correct location is chosen relative to the section of the calmest fluid flow inside the circuit, without mixing flows or turbulence. The optimal area for this is in front of the circulation pump. Here the tank serves as a thermal expansion compensator and dampens water hammer.
When installing an expansion tank in a closed circuit, it is necessary to install a safety valve that will relieve excess pressure. If, when purchasing the boiler, an expansion tank was included in the kit, but after installation it turned out that its volume is not enough (it should be at least 10% of the total volume of water), this is usually indicated by too frequent operation of the pressure relief valve, you can purchase an additional tank and connect it is parallel to the first.
For a closed system, membrane expansion tanks are designed, which are best positioned vertically. In this case, the coolant enters the container from above, displacing all the air from the water compartment.
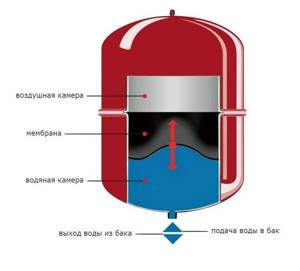
Photo 2. Diagram of the membrane type expansion tank. Arrows show the components of the structure.
The structure of the membrane tank is as follows: inside the space is divided into two compartments, separated by an elastic membrane. When liquid accumulates in the tank and pressure increases, the water presses on the membrane and the air in the upper section is compressed. The vertical position in this case is considered optimal; it makes it easier to compensate for excess pressure and extend the service life of the membrane.
Types and functions of heating expanders
An expansion tank is needed to compensate for the effect that an increase in the volume of coolant during heating has on the heating system. An additional container connected to the circuit becomes a storage place for the resulting excess water. When the temperature drops, part of the coolant leaves the tank and returns to the pipes.
The process is repeated with each heating and cooling cycle. If there was no such reservoir in the system, then when the water inside the pipes was heated, the pressure would increase and then decrease.
Such differences negatively affect the state of the system. They lead to leaks at the junctions of devices and pipes and can even cause equipment failure.
The expansion tank is selected depending on the characteristics of the heating system. For closed circuits, you need a special closed capsule with a membrane, and for open circuits, an unsealed container of a convenient configuration and the required size is suitable.
You should choose a membrane tank that is designed for contact with hot water. Typically, the body of such devices is painted red. You can make a container for installation in an open circuit yourself, for example, weld it from sheet metal. But it is important not only to choose the right device, but also to install it correctly.
Types of heating systems
There are two schemes for building heating networks - open and closed. An open (gravity) heating system is used in centralized heating networks and allows water to be directly withdrawn for hot water supply needs, which is impossible in private housing construction. Such a device is located at the top point of the heating system circuit. In addition to leveling pressure drops, the heating expansion tank performs the function of natural separation of air from the system, since it has the ability to communicate with the outside atmosphere.
Thus, structurally, such a device is a compensation tank of the heating system, not under pressure. Sometimes a system with gravitational (natural) circulation of a heat-carrying fluid may be mistakenly called open, which is fundamentally incorrect.
Sometimes such a device can be called a vacuum expansion tank for heating, which is also true. Such a system provides for forced circulation of the coolant; air is removed from the circuit through special taps (valves) installed on the heating devices and at the top of the system pipelines.
Selecting the location for installing the expansion tank
Installation of the expansion tank depends on the type of heating system and the purpose of the tank itself. It is better to install a closed compensation tank on the return line in front of the heating boiler and circulation pump.

Options for placement and installation of the expansion tank
If it is located on the supply line, the service life of the membrane will decrease due to constant exposure to a higher coolant temperature. In addition, in this case, if an emergency occurs, steam may penetrate into the expansion tank, as a result of which the diaphragm will no longer compensate for the coolant pressure, since the mixture of air and steam is a compressible medium.
Basic functions of the tank
The main function of the reservoir is to remove excess coolant and excess pressure for storage while the engine warms up. This happens due to the fact that during heating the volume of liquid and pressure in the entire system increases. By heating the liquid, antifreeze or antifreeze expands, the pressure increases and begins to rise to the top point of the system according to the same principle as in the heating system of a house.
The highest point of the system, as already mentioned, is this expansion tank. It should be noted that the liquid increases only while it is heated by the engine; after it cools down again after stopping the engine, it will all drain into the radiator. In order not to overfill the liquid, there are special marks on the body of this plastic container. You need to fill according to the following principle. You cannot fill liquid above the maximum mark and below the minimum mark, this can lead to various problems.
The second function of this device is to remove steam that accumulates as a result of evaporation of liquid. This is done by the lid, which has a special valve that, if necessary, releases and sucks in air.