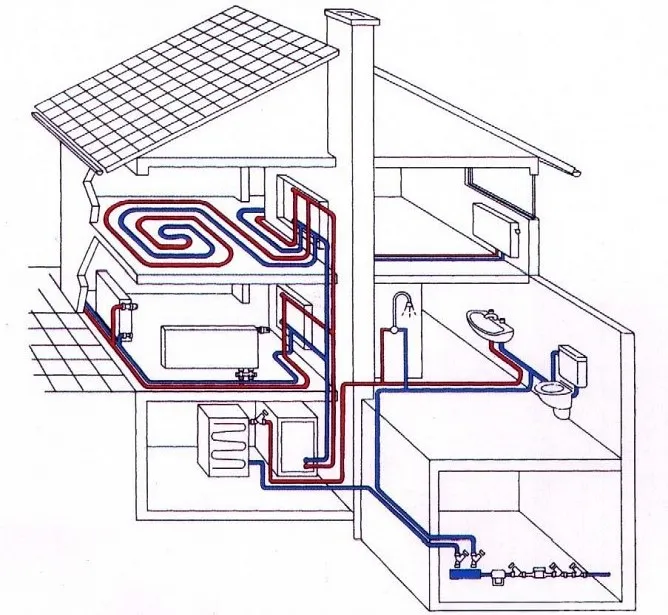
Comfortable living in a private two-story house depends entirely on the complex of communications, among which one of the main places is occupied by the heating network. Is not it? It is she who is responsible for maintaining optimal temperature conditions and the safety of the building itself. Agree, room temperature is one of the main components of ensuring comfortable living.
The choice of heat source and its correct connection directly determines whether you can maintain the temperature necessary for living. Here we will help you understand how the heating system of a two-story house functions, and which wiring diagrams are considered the most effective.
Here you will find information about the types of coolants, methods and features of their connection. For clarity, the material is accompanied by connection diagrams, as well as videos that will help expand knowledge about heating systems in private houses.
Efficiency of forced circulation schemes
The prevailing part of modern heating systems can function fully only when artificial circulation is created, that is, one in which the coolant moves within the network due to the operation of the circulation pump.
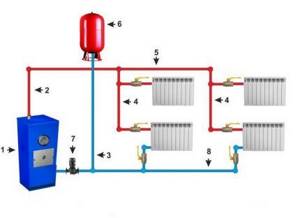
Diagram of a heating system with a gas boiler in a 2-story house: equipment and metering devices are installed on the first floor (in the basement, in the basement), in a specially equipped room with good sound insulation (+)
There are prerequisites for installing forced circulation in a building with several floors:
- installation of a pipeline with a smaller diameter, which facilitates the assembly of the wiring as a whole;
- providing zonal regulation (along with or instead of general regulation);
- the presence of 2nd and higher floors does not affect the heating efficiency;
- reducing the coolant temperature without changing heat transfer parameters;
- possibility of using inexpensive plastic pipes.
The disadvantages include the availability of power supply - interruptions are possible, but they can be easily avoided by using backup UPSs. The problem of louder noise can also be solved by installing a layer of sound insulation in the boiler room.
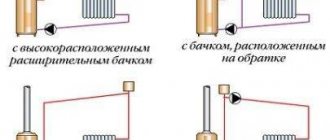
Scheme of water heating with forced circulation: 1 – gas or electric boiler; 2 – riser; 3 – pipe to the expansion tank; 4 – riser for draining; 5 – upper horizontal wiring; 6 – expansion tank; 7 – circulation pump; 8 – return line
The most suitable place for inserting the circulation pump is where the temperature drops to a minimum, that is, directly in front of the boiler, on the return line.
Pros and cons of single-pipe wiring
We will try to give an objective assessment and highlight the real advantages of single-pipe water systems:
- A closed circuit with a membrane expansion tank is easier to install. One pipe is laid faster than two.
- It is easier to hide a single main or riser in the walls than double-pipe branches (example in the photo below). The fly in the ointment: the ring manifold crosses doorways, making installation difficult.
- A heating network with risers is indispensable when it is necessary to organize gravity flow in a building of 2-3 floors. There is no point in passing two pipelines through the ceiling; one vertical line is enough.
- Installation is cheap in one case: when a gravity heating system is used in a one-story private house. Savings are achieved by laying one main line instead of two (remember, gravity flow a priori requires pipes of large diameters Ø48-57 mm).
- The closed type system can be automatically controlled using thermostatic radiator valves. Disclaimer: it is necessary to take into account the specifics of the operation of heating devices and choose the right fittings. We will return to this issue below.

The main problem of the Leningradka is the cooling of the coolant as it moves towards distant radiators. It is impossible to increase radiator sections and the cross-section of the main line indefinitely; the optimal number of devices is 4-5 pieces. on one circuit.
We list other disadvantages:
- Hydraulic instability is the effect of one battery on the operation of the others. If you close the first radiator valve, subsequent appliances will receive hotter water and begin to overheat the rooms.
- In order for the coolant to flow well into the radiators with a closed Leningrad circuit, it is necessary to use full-bore fittings on the branches. An increase in the hydraulic resistance of the line causes water to flow further in a straight line, and the coolant flow through the battery decreases.
- “Leningradka” and vertical wiring are more expensive than a two-pipe shoulder circuit. If we add the costs for additional radiator sections, then the cost of installation from cross-linked polyethylene will be comparable to a radial system, where fittings are not used, but there is a distribution comb.
- The circuit is complex to calculate and configure (balance). The power and heat transfer surface area of the batteries must be determined as accurately as possible.
An additional disadvantage of gravity distribution is the large diameters of pipes laid with a slope of 3-5 mm per linear meter. Risers coming out of the ceilings stick out in plain sight and spoil the interior of the premises. It is not always possible to wall pipelines into walls; you have to get sophisticated and make decorative boxes.
Natural circulation as an alternative
Nowadays, autonomous heating networks with gravitational circulation, that is, operating according to natural physical laws, can be found extremely rarely.
The principle of operation is explained by the difference in density of cold and heated water and the presence of an additional control device - an expansion tank, which is installed in the upper part of the hot water riser.
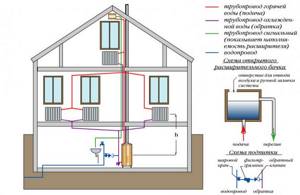
Diagram of a heating system in a two-story house with natural circulation: an accelerating vertical riser crosses both floors and ends in the attic, near the expansion tank, and the lower circuit is located in the basement or on the first floor (+)
A feature of the natural type network is the inclined arrangement of horizontal pipes (return and distribution) and the location of the boiler - it is installed at the lowest possible level. The coolant is supplied through the expansion riser, and the cooled water (or antifreeze) is discharged through the return riser.
The advantages of the gravity circuit are independence from electrical power, ease of installation, and the absence of noise produced by the circulation pump.
Wiring
To connect radiators, various pipeline laying schemes are used. Typically, coolant is supplied to the battery from below or from above, and it exits only through the lower outlet. Based on these characteristics, diagonal, side and bottom connections of heat exchange devices are distinguished.
Although the diagonal connection is considered the best in terms of heat dissipation, many experts argue that the bottom connection is no less effective and ensures uniform heating of the entire surface of the batteries.
When connecting radiators to the side, insufficient heating of the opposite side is often observed in heat exchangers with a large number of sections.
Single-pipe
With a single-pipe distribution, the coolant passes through one pipeline connecting the supply and return lines. Its typical representative is the Leningrad pipe, in which the heating fluid flows through one large-diameter pipe, forming a closed loop, and radiators are connected to it in parallel from below. Sometimes in Leningrad a diagonal battery connection scheme is used, but in this case the heat transfer is not much higher and the aesthetic appearance of the premises suffers.
There is a Leningrad line that is laid in individual private houses, the main pipe is taken with a diameter of 40 or 50 mm depending on the number of batteries, the bends for connecting them are made with a pipe of a standard diameter of 20 mm.
Single-pipe heating with lateral connection of radiators is often used in communal multi-storey buildings. At the same time, to ensure the possibility of disconnecting or repairing batteries with their disconnection from the line using ball valves, a bypass jumper is used. Water always passes through it, both in operating condition and when the radiator heat exchangers are disconnected.
When organizing a gravity system, a single-pipe heating system for a two-story house is also used, the diagram of which can combine both diagonal and side connection of radiators.
Typically, taps extend from the large-diameter upper pipe, laid from the expansion tank with a certain slope, to which a number of heat exchangers are connected. The return from each radiator is also collected in a common pipe and enters the boiler. In this way, a parallel connection of radiator heat exchangers in a private two-story house is realized with the possibility of independently adjusting the temperature regime in each of them.
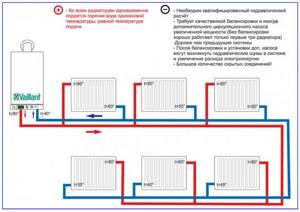
Rice. 14 Dead-end wiring, its pros and cons
Two-pipe
More often than others, when organizing autonomous heating, a two-pipe heating system for a two-story house is used, the main advantage of which is the ability to deliver coolant to the radiators at the same temperature as possible.
When connected, the heating fluid is supplied to the batteries through one pipe with a standard diameter of 32 mm, and returned back to the boiler through another, laid parallel to the supply.
This diagram of a two-pipe heating system for a two-story house, called dead-end, is used in most wiring due to the relative ease of installation. However, a dead-end heating system does not ensure uniform heating of all radiators, so when using it, a thermostat must be installed in each of them.
Without thermostats, the associated system allows achieving uniform heating of all heat exchangers. In it, the heating fluid is supplied to the first and subsequent radiators from the boiler; in the same way, the return line to the boiler is laid from the first to the last in the battery circuit (hence the name - passing).
As a result, the total length of the circuit, consisting of segments of the supply and return lines, is equal for each battery and, accordingly, the heating temperature of each heat exchange device is the same.
Despite such an obvious advantage of the associated or Tichelman scheme, which allows you to set the temperature parameters of all heat exchangers with one adjustment of the boiler heating temperature, it has not become widespread.
This is primarily due to the fact that the wiring according to the Tichelman scheme is not exactly two-pipe heating. During installation, the pipe flow increases by approximately 1/3 to direct the return to the boiler not from the first radiator closest to it, but from the last one. As a result of this, three pipes will be laid in a row on the wall if the circuit is not closed in a loop around the perimeter of the room, which significantly worsens the aesthetics of the appearance of the premises.
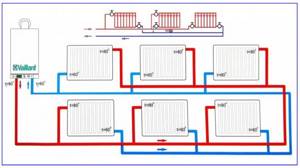
Rice. 15 Tichelman's passing route
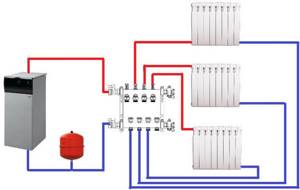
Beam or collector
The principle of such wiring is to connect all batteries from a central collector unit. In this case, each radiator has its own supply and return pipe. If a collector heating circuit is used in a two-story house, then the collectors are installed on 2 floors, respectively, connecting them through a central riser extending from the distribution comb.
The main purpose of the manifold circuit is to lay the pipeline under a screed or other floor covering; it is practically not used for its external installation.

Rice. 16 Example of intra-house collector distribution of heated floors
Related article:
Scheme of a closed heating system with forced circulation . A separate article describes in detail about a closed heating system, its elements, and provides a diagram for independent design and installation!
In heating systems for a two-story house, double-circuit gas boilers are widely popular, which usually heat water for domestic needs and heat exchangers. To heat the premises, water systems are used from a series of radiators or heated floors with a pipeline laid under the screed.
Features of a single-pipe heating system
The choice of one- or two-pipe heating does not depend on the number of floors of the house - both types are suitable, but for buildings with 2 or more floors, the installation of a circulation pump is required.
Heating with a liquid coolant (water or antifreeze) is considered the most effective, while for small one-story houses, for example, summer cottages, other options can be considered.
Operating principle and distinctive features
Heating radiators, according to a single-pipe scheme, are connected in series, that is, the coolant first enters one device closest to the boiler, from it through a pipeline to another, etc. The looped circuit, which is a network, is also suitable for a 2-story house, since it is conveniently located along the perimeter walls.
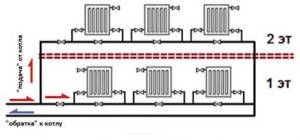
The simplest single-pipe heating scheme for a 2-story building: from the supply riser, the coolant flows into heating radiators connected in series order
The presence of shut-off valves can improve the use of the system. For example, the Mayevsky faucet is designed to remove air “locks” that often occur during downtime, that is, in the summer. In addition to it, various models of balancing valves, ball valves, and special regulators are used.
The forced circulation method in a single-pipe structure in the event of a temporary absence of electricity can be replaced by a natural one, but this requires the installation of a membrane tank and the placement of horizontal pipes at an angle of up to 5º.
Assessing disadvantages and advantages
The main advantage of single-pipe networks is considered to be easier drafting of the project and the installation itself. A minimum of pipes allows you not to rely on a complex room layout, but simply lay the pipeline strictly along the perimeters of both floors. Savings on purchasing fewer elements for a single main line - pipes, taps - are also appreciated.
One pipe takes up much less space than two, so it can be disguised under the floor covering, laid unnoticed in doorways, that is, installed without disturbing the interior.
One of the main disadvantages of a single-pipe system, relevant for a house with 2 floors, is the rapid cooling of the coolant during sequential movement through the radiators (+)
The disadvantages include the need to purchase a more powerful circulation pump, as a result of which the cost of electricity increases. It is more difficult to regulate the temperature level in a design with a serial connection: when the heating intensity in the nearest radiator decreases, the temperature in the entire line will automatically decrease.
Which heating scheme should I choose?
When choosing a specific type of heating system, you should be guided, first of all, by the characteristics of the building, pay attention to the availability of electricity and financial capabilities. If you have engineering documents, look at them, as a rule, all the necessary numbers are indicated. Otherwise, you will have to carry out all the measurements yourself. The required minimum is the floor area, the volume of the room, the thickness and material of load-bearing walls and partitions.
After this, it is worth analyzing the climatic features of the region, the cost and availability of various types of energy. Based on these data, a primary selection of options for organizing heating is made, after which the planned costs for their acquisition and installation, as well as future maintenance, are calculated. It is economic indicators, both short-term and strategic, that are decisive when choosing a specific type of heating.
If there are difficulties with finances, the availability of light is unstable, and the only energy source is coal, then perhaps you should look towards simple one-pipe heating systems. If there is gas, a stable supply of light and finances allow, then you can look towards two-pipe and radiant heating systems for a two-story house.
Common connection options
If you decide to install a single-pipe system, you will have to choose between two types:
- simple circuit without regulation;
- "Leningradka" with the ability to turn off individual radiators.
In terms of control method, the first option is clearly inferior to the second; its only advantage is its budget cost.
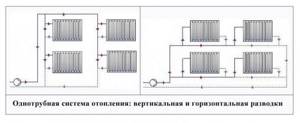
Installation of a simple single-pipe system of horizontal or vertical type is simple and reliable, but temperature control in the network is impossible (+)
Installing the Leningradka will cost a little more, since in addition to the pipes you need to purchase a set of shut-off valves. Using bypasses and valves, you can reduce/increase the amount of coolant supplied to the radiator.
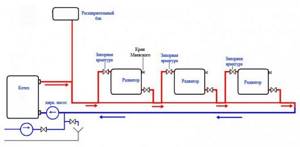
Diagram of the Leningradka device: using shut-off valves, you can temporarily turn off individual unnecessary radiators without changing the functional qualities of the entire system as a whole (+)
"Leningradka" is recognized by professional heating engineers as the best option for a single-pipe system for a 2-story residential building.
Complete set and installation of equipment
Standard equipment for system assembly:
- circulation pump;
- gas or electric boiler (power depends on the size of the house, characteristics of the coolant, etc.);
- expansion tank;
- pipes 20 mm and 25 mm;
- adapters, gaskets, plugs;
- set of radiators;
- Mayevsky cranes.
Along with steel pipes, polymer or metal-plastic pipes can be used, with the latter being preferred.
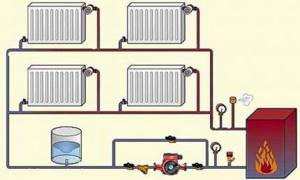
In heating circuits with closed expansion tanks, air is bled using automatic bleeders equipped with shut-off valves and floats, or Mayevsky valves supplying each radiator
First, they find a suitable place for the boiler and install it, then assemble the pipeline leading to the radiators. Tees are fixed in places of radiator branches and bypasses. The pump is installed on the return line, next to the inlet to the boiler, and connected to the power supply.
The installation location of an open expansion tank is the highest point of the system; a closed one can be mounted in any convenient place, for example, in a boiler room. Radiators are suspended from the walls using special fasteners and equipped with plugs and taps.
Common installation mistakes
Above are “Leningrad” diagrams of horizontal single-pipe floor circuits with radiators connected to a common main line by two tees. Only part of the total volume of coolant circulating through the circuit flows through each device. You may encounter an erroneous connection without a main pipe (see the outline of the first floor in the figure below).
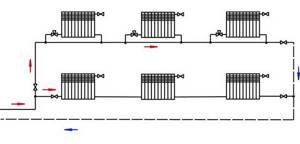
Types of connection of radiators in horizontal single-pipe circuits.
This method of connecting heating radiators is extremely cheap. Each radiator has one fitting for connecting a DN20 or DN25 metal-plastic pipe and a section of pipe between adjacent devices. Can't think of anything cheaper. But the price to pay for the cheapness is poor performance of half the radiators. The first of them (in the direction of the coolant movement) is heated to a temperature of 55 ° C, and the last one at N = 6-8 is heated to only 35 ° C, since the coolant, passing through the radiators, intensively cools down in them.
Two-pipe heating system for a 2-story house
Truly comfortable living conditions can only be achieved by installing a two-pipe heating system. Its design allows you to regulate the temperature in individual rooms and save energy resources.
How does a two-way circuit work?
Unlike a single-pipe circuit, a two-pipe circuit consists of a pair of lines with different purposes: one of them supplies coolant, the second returns it back. The radiators are connected not in series order, but in parallel. One circuit, with heated coolant, extends from the riser to the radiators of both floors, the second is mounted to the boiler outlet and is also distributed to both floors.
Radiators are equipped with thermostatic valves that allow you to set a comfortable temperature. If desired, you can reduce the heating intensity partially or completely block the flow of water into the device.
Some devices are fundamentally embedded in the return line, for example, a membrane tank that regulates pressure, a circulation pump and a safety valve are traditionally installed in front of the boiler
In modern 2-story houses, two-pipe structures are used, since they are much more efficient than single-pipe ones:
- reduce pressure loss;
- do not require a powerful pump;
- keep the coolant temperature the same for each radiator;
- allow you to use many different thermal devices within one system (for example, radiators, convectors and “warm floors”);
- make it possible to repair and replace parts without compromising overall functionality.
The main disadvantage is the difficulty of self-installation - during assembly, consultation and supervision of professionals is required.
Successful solutions for installing a two-pipe system
There are many incarnations of various schemes, but when drawing up a project you should start from individual requirements.
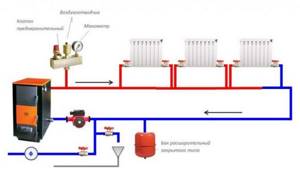
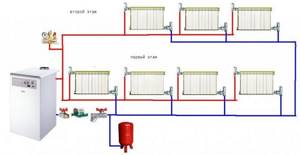
The simplest diagram for arranging a heating system in a 2-story house. It is characterized by the following points: 2 circuits for heating and hot water production, liquid coolant, forced circulation (+)
A number of universal schemes are suitable for providing heat to houses of various sizes and number of floors.
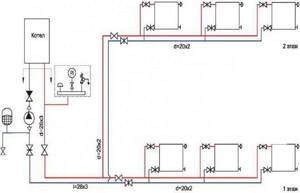
Detailed diagram of two-pipe wiring for a one-story house with a fully equipped basement. The problem of thermal insulation of the floor in the basement was solved by connecting a water-based “warm floor” system
If you install additional equipment, such as a membrane tank, the capabilities of the heating system will expand.
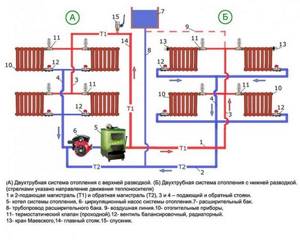
A and B – two variants of the wiring device, upper and lower type. Additional equipment: expansion tank, Mayevsky taps, overhead line (+)
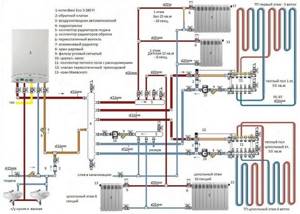
The following diagram combines the three most popular wiring diagrams.
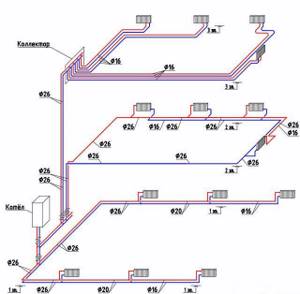
Level 1 – dead-end wiring with parallel installation of both circuits; Level 2 – counter wiring, characterized by two-way radiator connection; 3 – collector wiring with improved balancing
All of the above schemes are suitable for heating a 2-story building.
Advantages of water heating in a private house
When heating rooms in systems with almost any type of fuel or heat pumps, water is often used as a coolant, and this is due to its following features:
- Water has a high heat capacity, which means it takes a long time to heat up and releases heat slowly. Therefore, the loss of thermal energy during its movement through pipelines is much lower than that of other types of media.
- An alternative to water is heated air. To heat all the rooms in the house with it, you will have to install an air duct system and supply air masses through the ceilings. This will require the use of additional fans, will lead to energy costs and inefficient operation of the entire system, where heated air comes from above rather than from below. In addition to the fact that the air quickly gives off heat, all boiler equipment using various types of fuel is designed to connect water pipelines to them, and not air channels.
- The advantage of heating with water is that many boilers are equipped with indirect heating systems. They can simultaneously supply water to the heating pipeline and heat it for domestic needs, providing hot water supply.
- Water coolant is easy to obtain from any water supply system, its cost is reduced to zero.
- When using heating with water, it is relatively easy to set the temperature in each room, which cannot be said about air heating of several rooms from one unit.
- When using heated floors, even during a power outage, a massive cement-sand slab with a thickness of at least 50 mm will retain heat for a long period of time.
Choosing a suitable scheme
After familiarizing yourself with the heating systems used in two-story houses, it’s time to return to your draft project, where the types of radiators and boiler are selected, the arrangement of this equipment is determined, and wishes are listed. Next, select a scheme in accordance with the recommendations:
- If there are frequent power outages, the choice is small - you need a gravity system. If the house is heated with a brick stove, you should use it as a heat source and not buy a boiler.
- If you still don’t understand what you want, feel free to assemble a closed-type two-pipe dead-end circuit. It can be easily adapted to different conditions and equipment. Subsequently, install a solid fuel, gas or electric boiler - there is no difference, the heating will work.
- If you have increased requirements for interior design, start with manifold wiring. In order not to make a mistake with the size of the pipes, pull the diameter of 32 mm to the comb, and make connections to the batteries Ø16 x 2 mm (outer).
- Warm floors are installed if there are funds and desire. It is better to combine them with any system other than gravity.
In a small country house with 2 floors, it is worth making a one-pipe system from PPR pipes. With 3-4 batteries on each branch it will work flawlessly. We do not recommend using Leningradka in a large cottage. For more information about choosing a wiring, watch the video from an expert:

Watch this video on YouTube
Pipes for connecting radiators and heated floors
For homeowners without installation experience, we recommend the following options:
- If you want to save on materials, take reinforced polypropylene pipes (PP-R) with fittings. In addition, buy an inexpensive Chinese soldering iron - it will definitely be enough to assemble 1 system.
- Without special tools, you can install heating pipes from metal-plastic pipes on compression fittings, tightened with open-end wrenches. The disadvantage is the high cost of parts.
- The best solution is to assemble the system from cross-linked polyethylene or metal-plastic with press fittings. You will have to rent special pliers.

The structure of the polypropylene pipe - to prevent thermal elongation, aluminum reinforcement is laid between the layers of plastic
Polypropylene pipelines are welded according to technology, the main thing is to accurately maintain the heating time. It is strictly not recommended to wall PP-R joints in floors and walls to avoid the consequences of leakage.

On the left in the photo are pipes made of metal-plastic, on the right - cross-linked polyethylene
Open and closed heating systems
The operation of an open heating system is carried out in many apartment buildings. For this, a special expansion tank is used. During operation, excess ends up in this container. The system may not be tight, so the whole process is accompanied by evaporation of vapors. The open version does not include a built-in pump. The installation design is quite simple and easy.
- uniform heating of the room;
- ease of operation;
- durable;
- the system can operate even when the electricity is turned off;
- no need to install an additional pump;
The closed heating system is completely sealed and does not emit vapors during operation. The movement of the water flow is carried out using a pump. There is no natural circulation in this system. If excess water begins to appear, the valve is activated and the liquid evaporates to reduce the water level.
Advantages of the closed type:
- reliability and strength;
- the ability to adjust the pressure level in the system;
- availability;
- resistant to low temperatures;
- the ability to use additional heaters;
Basic system requirements
There are a number of important requirements that must be taken into account when designing a heating system.
- In general, the heating design of a two-story house must correspond to the architectural design of the building. The placement of the boiler requires certain structural and design conditions of the room in which it will be located. The installation locations of radiators, as well as the pipeline routes, should not violate the architectural rules for the arrangement of residential and technical premises. All this means that a qualified designer must draw up a plan for the heating system, based on the finished architectural design of the house.
- During operation, the system must provide all internal and external surfaces with the temperature required by building codes and regulations (SNiPs).
- The system must be quite economical to operate. If heating your home requires too much energy consumption, you should contact a specialist: perhaps some parts or components can be unified.
- The pipeline should have a minimum of bends and turns. If during its installation you need a large number of fasteners in different sizes, it means that the heating circuit is poorly designed.
It is always necessary to draw up and evaluate a preliminary scheme Source tapiart.ru
- During use, the system must be reliable, safe, convenient and silent. A good system allows home owners to easily control heating appliances and, if necessary, easily repair them.
- The aesthetic side is also important. Radiators and pipes connected to them must have a neat, attractive appearance. The less noticeable the heating elements are, the better.
Pipe laying options
Heat supply schemes for a two-story house using heating batteries are distinguished not only by the type of connection of the pipeline and radiators, but also by the methods of laying other elements of the system. When choosing a specific heating arrangement, the design and features of the property and the personal preferences of its owners are taken into account.
Option one
– performing pipe routing by concealed installation. They are laid in such a way that they are located in the cavities of the ceiling and walls. This method is convenient because it allows you to create an original interior, in which there are no details that violate the integrity of the design solution.
Option two
– location of pipes along the walls. This location is considered traditional, since it can be found in many houses, especially old ones. In this case, pipes and radiators are mounted to the walls of the room using special fasteners.
Related Posts
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- Leningrad heating system for a private house
- Dismantling of heating systems
- Which pipe to choose for heating
- What kind of pipes are used for the gas pipeline?
- How to make steam heating
- Tichelmann loop
- Heating system of a one-story private house
- Pipe box
- Rules for laying sewer pipes
- Which rehau pipes are best for heating and water supply?
- Choosing between metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes
- Features of using PVC sewer pipes with a diameter of 50 mm
- Decorative overlay for a heating pipe: what is better to choose to make it look beautiful?
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- Connection diagram for double-circuit gas boilers to the heating system
- What sizes of sandwich pipes are best to use for a chimney?
- Connecting and calculating a buffer tank to a solid fuel boiler
- A supply of hot water that is always at hand: how does an electric water heater for heating work?
- How to insulate an outdoor water pipe
- Effective methods of thermal insulation of sewer pipes
- Thin-walled metal pipe for electrical wiring
- How to install a chimney correctly with your own hands: all the nuances when installing a chimney
- Online calculation of the capacity of round and rectangular profile pipes
- Connection diagrams for bimetallic radiators
Read with this
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- Leningrad heating system for a private house
- Dismantling of heating systems
- Which pipe to choose for heating
- What kind of pipes are used for the gas pipeline?
- How to make steam heating
- Tichelmann loop
- Heating system of a one-story private house
- Pipe box
- Rules for laying sewer pipes
Why two-pipe
Why should the heating circuit be a two-pipe system?
Because, compared to the simpler single-pipe Leningrad, it allows for more uniform heating of the batteries. With a large single-pipe circuit, the temperature difference between the supply and return will inevitably become noticeable and will force an increase in the size of the radiators, which is unprofitable and not always applicable from the point of view of room design.

A multi-section battery is a dubious decoration for a living room.
Please note that a single-pipe system is cheaper to install (simply due to the shorter total filling length) and is more fault-tolerant. As long as there is a pressure difference at the ends of the filling, stopping the circulation in it is impossible in principle.
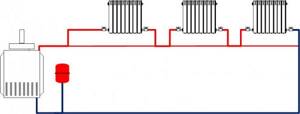
Single-pipe Leningrad is a leader in fault tolerance.