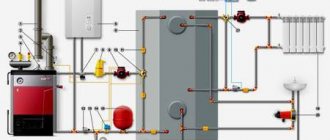
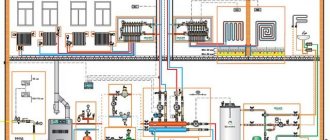
General overview of radiator types and their dimensions
There are several main groups of heating batteries, differing in design features:
- Sectional.
- Panel made of steel and bimetallic.
- Convector.
- Author's models , made to order, having unique shapes, but performing their functions.
The photo shows the original heating device
The material used and the design features of the heating devices determine:
- resistance to water hammer;
- corrosion;
- clogging and scale deposits;
- heat transfer intensity and other components of success.
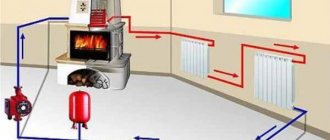
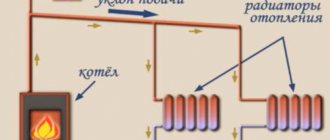
As for the size, the difference in height between the upper and lower collector (center distance) affects the possibility of installing the heating device. Most often they are installed in niches under windows; if the window opening is large enough, then the high battery simply will not fit.
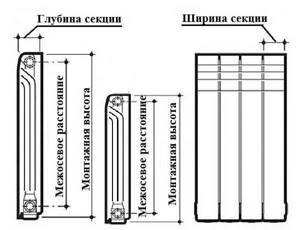
The diagram shows the center distance
This parameter is especially important for systems with natural circulation. The fact is that the pressure in the system is created due to the difference in height between the water supply to the battery and the boiler; the greater this value, the greater the natural pressure in the pipes.
Note! For example, it makes sense to choose a center-to-center distance of 250 mm for heating radiators only for very low window sills. In this case, it will be possible to install batteries even under a window sill 50-60 cm high.
Example of a battery in a room with large windows
Panel heating devices are an all-welded structure with a coolant coil between two ribbed panels with a gap between them of up to 1 cm. Such a surface increases the area of the heated surface and its heat transfer - radiation plus convection. The meager capacity promotes rapid heat transfer - the efficiency reaches 75%, but they also cool down quickly.
The disadvantage of panel products is:
- their vulnerability to water hammer, which makes them unsuitable for use in central heating systems;
- corroded by acidic water;
- You cannot drain water for a long time due to the same corrosion, but in contact with oxygen.
Sectional batteries are good for the possibility of their design changes - increasing/decreasing the number of sections to change power or repair. Traditional brittle but durable cast iron with high inertness has been replaced by bimetallic devices.

In the photo - the device of a bimetallic heater
In them, the coolant passes through steel tubes with aluminum fins, which have high thermal conductivity.
A bimetallic battery is the embodiment of two advantages in one product, namely:
- steel can withstand unstable pressure and aggressive environments;
- aluminum reacts with lightning speed to temperature changes.
Note! The only drawback that can be noted is the cost. The price of a bimetallic radiator can be 2-3 times higher than an analogue made of cast iron or steel.
When choosing bimetallic batteries, you also have to take into account the diameter of the vertical and horizontal channels, and not just the interaxal distance. As for the dimensions, the most popular models can be considered those with a difference between the nipple holes of 500 mm (the total height of the heating device is 570 mm).

The photo shows the horizontal and vertical channels; if the quality of the coolant is poor, they should not be too narrow
But in vacuum batteries the concept of “center distance” simply does not exist. The fact is that they use only 1 flow pipe through which the coolant circulates, and uniform heating of the surface is achieved through the evaporation of a low-boiling liquid.
Tubular battery registers are superior to sectional ones in compactness and variety of shapes. The absence of leaks at the joints is ensured by welding the fragments; they can withstand operating pressures of up to 15 atm, but thin walls do not withstand water hammer well. It is quite possible to make the registers yourself by choosing an arbitrary pitch between the pipes.
What is the difference between a 500/100 radiator and a 500/80 radiator?

In Russia today there are many types of heating equipment. When choosing a heating radiator (battery) for your apartment or private house, the first argument should be the type of heating of the house:
Autonomous heating of a private house up to 500 m2 Autonomous heating of premises over 500 m2 (roof boiler rooms) Centralized heating in apartment buildings or non-residential premises of any size.
Why do these three types affect the choice of a 500/100 or 500/80 radiator?
Each version of this type of heating operates according to different parameters and the composition of the coolant in the pipeline and radiators. Autonomous systems up to 500 m2 - the pressure in the system cannot be more than 3 Bar (kilogram) and the coolant, if desired, can be filled without unnecessary chemicals that accelerate the aging process of equipment.
Autonomous systems over 500 m2 - roof boiler room for residential apartments in a multi-storey building, the pressure depends on the height of the building, but not more than 6 bar (kilogram) with a conventional coolant (tap water).
Centralized heating of apartment buildings and non-residential premises is the most problematic heating system throughout our homeland, the pressure in such systems reaches 9 Bar (kilogram) with a coolant that contains chemical reagents and a lot of dirt.
All of the above affect the durability of your batteries and the connections (pipes and taps) to them. Knowing the system and the factors of their problems, consider the heating devices themselves, and in the next article we will decide which pipes and taps to install.
These devices are available to choose from:
Cast iron - irrelevant, ugly and ineffective in terms of heat transfer 160 W per 1 m2. Aluminum - modern, beautiful, efficient 199 W per 1 m2 for a burst of up to 25 Bar. Bimetallic - modern, beautiful, 187 W per 1 m2, but with a burst power reserve of up to 40 Bar.
A steel panel radiator is modern, efficient, reliable, but not always affordable.
Cast iron batteries do not need discussion!
Aluminum radiators:
The most common type of heating equipment today, so much has already been said and written about them, but aluminum radiators are still worthy of attention. Their technical data for all manufacturers is almost the same if we consider the 500/100 model, since the properties of aluminum are unchanged. A good manufacturer improves the design and convection of the device for greater heat transfer to each section. The working pressure of the radiators is 16 Bar (kilogram), the burst pressure is 25 Bar.
Heating radiator sizes
Based on the type of material, radiators can be bimetallic, steel, aluminum or cast iron. The dimensions, general parameters and weight of the batteries directly depend on this, which must be taken into account when choosing the appropriate option.
Bimetallic
In appearance, bimetal batteries resemble aluminum devices, while their output and input collectors, as well as vertical heat-conducting channels, are made of stainless steel with an aluminum housing placed on top.
Devices of this type do not rust and are resistant to water hammer, so they are often installed in apartments that are connected to a central heating system. The list of advantages includes a high level of strength, reliability, resistance to environmental influences, and compatibility with all heating systems. Section dimensions:
- Center distance: 200 mm, 350 mm, 500 mm.
- Height: 415 mm, 570 mm.
- Width: 80 mm.
- Depth: 75 mm, 85 mm, 90 mm, 100 mm.
Radiators have high heat transfer, do not require a large number of thermal media, and their service life reaches 20-25 years. They also have their drawbacks, for example, creaking that occurs due to the difference in the expansion coefficients of steel and aluminum. Vertical channels can become clogged, so their cleanliness must be monitored separately; in addition, bimetallic channels are more expensive than analogues made from other materials.
Aluminum
Dimensions of aluminum radiators
Radiators of this type can be extruded or cast; the second option is more popular, since such devices are highly durable and not subject to corrosion. Aluminum batteries provide optimal thermal output, they are easy to install and transport due to their low weight, and they are also able to heat up as quickly as possible.
The models are available in a variety of designs and represent the optimal combination of cost and heat efficiency. The downside is the potential for damage due to water hammer. There are devices on the market with a gap between the axes from 200 to 800 mm, the most popular options being 350 and 500 mm.
Aluminum units can only be operated if there is no oxidized environment in the coolant, so they are not recommended for installation in buildings with a central heating system.
Steel
Appliances made of steel, including those with side connections, are tubular or panel.
Panel-type radiators are a system of 1, 2 or 3 panels with or without fins made of special U-shaped plates. Each panel includes a pair of steel sheets with channels that are connected to each other by welding. The advantages of such radiators include increased heat transfer, convenient installation, resistance to damage, safety, reasonable cost and impressive design. Tubular radiators consist of inlet and outlet manifolds, which are connected to each other using several rows of tubes with a thickness of at least 1.0-1.5 mm. All parts are connected by welding, which leaves no seams. The list of advantages of tubular radiators includes accelerated heating, resistance to aggressive environments and mechanical loads, water hammer, the ability to choose the shape and color of the battery, safety and environmental friendliness, and no problems during operation.
The distance between the centers of the radiator fittings is 300 or 500 mm. The depth of the product section is from 40 to 115 mm. The thickness of the steel does not exceed 1.5 mm.
Panel devices may not withstand water shocks during system checks and are often subject to corrosion. The disadvantages of tubular radiators include reduced heat transfer, the formation of leaks in welding areas and high cost.
Cast iron
Cast iron batteries are still popular due to their good resistance to high temperatures, lack of corrosion problems and durability. Devices of this type have extended channels that ensure ideal circulation of the coolant even during clogs. Cast iron radiators provide an accumulating effect and remain warm for a long time after the coolant supply has been stopped.
What is center distance?
The technical passport for the heating device indicates all the main characteristics, including the inter-nipple distance. Usually this parameter is also in the model name (indicated by numbers). Sometimes experts call it not only the inter-nipple distance, but also the center-to-center or connection distance.
But all these are just different “names” of a quantity that determines the distance between the centers (axes) of the input and output collectors of a device or a separate section.

How tall are aluminum radiators?
The actual height of the heating radiator often does not correspond to that indicated in the specifications, instructions or data sheet. The fact is that manufacturers usually indicate the center-to-center distance between the centers of horizontal channels (see figure).
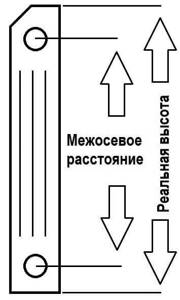
Height of the heating radiator and center distance.
It is important to know the center-to-center distance in order to design the location and installation of pipes. The actual height of an aluminum radiator is important when you are going to install it in a niche or under a window. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the height tolerances at the top and bottom. Read more about this in the article on the correct installation of heating radiators.
There are several standard center distance options for aluminum radiators:
- 30-35 cm;
- 50-55 cm;
- 60 cm;
- 90 cm.
The height of the section of an aluminum heating radiator may be 7-15 cm larger, depending on the design, manufacturer, etc. In addition, some models may have a non-standard center-to-axle distance, for example, 58.5 cm. But to determine which option is needed, approximate values will be enough.
Description of radiator center spacing characteristics

The center-to-center or inter-nipple distance of the radiator is a value indicating the gap between the central parts of the output and input collectors of the entire battery or each of its sections. It is indicated in the specification for the radiator, where its main characteristics are presented, and is indicated by numbers in the name of the device model. This indicator is of particular importance in private homes where water is naturally contained in the heating system. If the gap is large, liquid will not stagnate in such a radiator, due to which the efficiency will begin to increase.
Values of 300, 350 and 500 mm are considered standard; many modern manufacturers produce batteries of this type. There are models with other intervals, for example, 200, 400 or 600 mm; in designer batteries this value reaches 2000 mm. For radiators with the same center spacing, the installation height may be different and depends on the design features of the battery, the material from which it is made, as well as the design and brand. These values should not be confused, which is especially important when installing radiators in openings under windows or niches.
In Soviet or post-Soviet houses, appliances were more often installed with an interval of 500 mm; for this reason, options with this indicator are still more popular in Russia.
Aluminum radiator width
The width (length) of an aluminum radiator depends primarily on the number of sections. And the width of the aluminum radiator section is not a constant value. It depends on the model and manufacturer. And varies from 8 to 10.5 cm.
The width of the battery section determines how efficiently it will heat. The lower the temperature of the water or coolant in the system, the worse it warms up the aluminum feathers. Accordingly, the section should be narrower.
When connecting sections to each other, nipple nuts are used. Sometimes gaskets are installed at the joints or coated with sealant. Their thickness has virtually no effect on the overall dimensions of the radiator.
That is, to find out the dimensions of an aluminum heating radiator for 10 sections, it is enough to know its center distance and section width. Add 7-15 cm to the center distance - you will find out its real height. Multiply the width of the section to find out its length.
What are the dimensions of heating devices?
There are generally accepted standard sizes: thickness - 9 cm, width - from 40 cm, height - 76, 94 and 112 cm. However, the linear parameters of heating radiators can vary significantly. Their dimensions depend on the material from which they are made and their design.
By thickness (depth)
The thickness of heating radiators depends on the materials from which they are made and their shape:
- If you want to install thinner devices, then cast iron and bimetallic devices are clearly inferior in terms of material: the former due to fairly thick walls, and the latter due to the double layer of metal.
- The shape also affects the thickness. Panel devices are the thinnest: the thickness of steel and aluminum panels does not exceed 1 cm.
Width
The width of the battery can also be different: both small (less than 40 cm) and much larger - up to 1.5 m, which can be very convenient when planning a room with space restrictions for their placement.

An original solution for “wide” heating
Remember! To maintain the thermal balance in the room when the width of the heating apparatus is reduced, its height or the number of installed sections must be increased.
By height
Here, the sizes of radiators vary in the widest range - from 15 cm to 3 meters. They differ:
- Standard. The height of standard cast iron batteries is 588 mm, aluminum sections are 575 mm, bimetallic sections are 550-580 mm.
- Low. The height of “low” cast iron batteries can be about 35 cm, and aluminum ones – 15 cm. They have the enviable advantage of being placed under low window sills. An innovation is the so-called “plinth” radiators offered by some companies, the height of which can be only about 2 - 3 cm.
- Tall, or vertical with a small width, can reach 2 or 3 meters in height. They are installed in places where there is no suitable space for standard heating, but large volumes of air need to be heated. They are considered decorative and have wide design possibilities.
Interesting! Lower units have slightly greater heat transfer. This occurs due to the minimization of contact of warm air with the top of the device and the large heat flow from the fin surface.
Connecting dimensions of aluminum heating radiators
All sections that make up the heating radiator are identical. Traditionally in heating, diameters are measured in inches. There are several standards for connecting sizes:
| Inches | Millimeters |
| 1/2 | 12.7 |
| 3/4 | 19 |
| 1 | 25.4 |
| 1 1/4 | 31.7 |
| 1 1/2 | 38.1 |
The most common radiators are for connecting to pipes with an outer diameter of 3/4 and 1 inch. They provide optimal water flow rate.
If you install a radiator with a small cross-section of pipes, the fluid flow rate will be too high and it will not have time to release heat. If the cross-section of the pipes is large, then the flow rate will be low and the radiator will silt up - particles of dirt from the water will accumulate in its lower part.
Important! The diameter indicated in the technical specifications of the radiator is internal. The outer diameter of the heating pipe or fitting must correspond to it.
Terminology
Often in descriptions and specifications there is the concept of “center distance”. Sometimes the terms “internipple” and “intercenter” or connecting dimensions are used. These are different names for the same quantity. It is defined as the distance between the centers of the inlet openings of a section or radiator.
In the technical characteristics of radiators, such a concept as interaxle distance is often encountered.
This parameter is important if the supply pipes are in good condition and there is no need to change them. In this case, in order not to overcook the liner, you can choose a model with the same center distance as the old radiators.
The overall dimensions of the section or radiator itself are described by the following parameters:
If the radiator has a sectional structure, then the depth and width refer to the dimensions of the section. Moreover, the depth of the radiator will be the same, and the width of the battery depends on the required number of sections (you need to add about 1 cm more to the gaskets that are laid to seal the connections).
The names of radiators often contain numbers: RAP-350, Magica 400, Rococo 790 or RAP-500. The numbers are the center distance, indicated in millimeters. This makes it easier for both the buyer and the seller to navigate. The fact is that with the same center distance, the installation height can differ significantly. Therefore, the most accurate value is set in the specification.
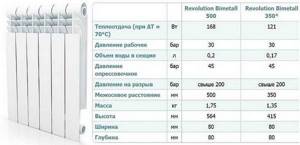
Example of technical characteristics. This is the Revolution Bimetall model
Radiator parameters that may need to be taken into account include the volume of water in the section. For apartments connected to centralized heating, this characteristic does not affect anything, but for individual systems it can be important: when it is necessary to calculate the volume of the system (to determine the performance of the boiler or the characteristics of the pump).
And perhaps the most important parameter is thermal power. It is worth noting that the highest power is not always necessary. Increasingly, apartments and houses with good thermal insulation require heating devices of medium power, and not huge ones.
When selecting the thermal power of one section, you need to remember that the radiator under the window must cover at least 75% of the width of the window opening. Then the room will be warm, there will be no cold zones and the glass will not “sweat”. That is why it is better to take 10 less powerful sections than 6 pieces with high thermal output.

Such a radiator may produce the required power, but there will be clearly cold and warm zones in the room
The standard window width is 1100-1200 mm. Accordingly, 75% is 825-900 mm. This is how long or longer your battery should be. Looking ahead a little, let's say that the average width of one section of an aluminum radiator is 80 mm, which means you will need 10-12 sections.
Dimensions of aluminum radiators from various manufacturers and their models
The tables below show both the size of the aluminum radiator section and the dimensions of the assembled radiators.
Aluminum radiators ROVALL
This company, part of the Sira Group, makes aluminum batteries with a distance between the collectors of 50, 20 and 35 cm. The kit for their installation (which is purchased separately) should include adapters, plugs, nipples with gaskets (for connecting sections), brackets for wall mounting and Mayevsky crane.
Country of origin: Italy.
Main parameters:
- Maximum operating pressure – 20 bar.
- The pressure when testing the device is 37.5 bar.
- The water temperature limit is 110 °C.
Characteristics of Rovall Alux 200 - distance between axles 200 mm:
ModelDimensions (H/D/D), mmPower of the entire radiator, WNumber of sections
| ALUX 200/1 | 245 / 100 / 80 | 92 | 1 |
| ALUX 200/4 | 245 / 100 / 320 | 368 | 4 |
| ALUX 200/6 | 245 / 100 / 480 | 552 | 6 |
| ALUX 200/8 | 245 / 100 / 640 | 736 | 8 |
| ALUX 200/10 | 245 / 100 / 800 | 920 | 10 |
| ALUX 200/12 | 245 / 100 / 960 | 1104 | 12 |
| ALUX 200/14 | 245 / 100 / 1120 | 1288 | 14 |
| ALUX 200/16 | 245 / 100 / 1280 | 1472 | 16 |
* All data is taken from official sources of manufacturers.
Characteristics of Rovall Alux 350 - distance between axles 350 mm:
ModelDimensions (H/D/D), mmPower of the entire radiator, WNumber of sections
| ALUX 350/1 | 395 / 100 / 80 | 138 | 1 |
| ALUX 350/44 | 395 / 100 / 320 | 552 | 4 |
| ALUX 350/6 | 395 / 100 / 480 | 828 | 6 |
| ALUX 350/8 | 395 / 100 / 640 | 1104 | 8 |
| ALUX 350/10 | 395 / 100 / 800 | 1380 | 10 |
| ALUX 350/12 | 395 / 100 / 960 | 1656 | 12 |
| ALUX 350/14 | 395 / 100 / 1120 | 1936 | 14 |
| ALUX 350/16 | 395 / 100 / 1280 | 2208 | 16 |
* All data is taken from official sources of manufacturers.
Characteristics of Rovall Alux 500 - distance between axles 500 mm:
ModelDimensions (H/D/D), mmPower of the entire radiator, WNumber of sections
| ALUX 500/1 | 545 x 100 x 80 | 179 | 1 |
| ALUX 500/4 | 545 x 100 x 320 | 716 | 4 |
| ALUX 500/6 | 545 x 100 x 480 | 1074 | 6 |
| ALUX 500/8 | 545 x 100 x 640 | 1432 | 8 |
| ALUX 500/10 | 545 x 100 x 800 | 1790 | 10 |
| ALUX 500/12 | 545 x 100 x 960 | 2148 | 12 |
| ALUX 500/14 | 545 x 100 x 1120 | 2506 | 14 |
| ALUX 500/16 | 545 x 100 x 1280 | 2840 | 16 |
* All data is taken from official sources of manufacturers.
Aluminum radiators Climatic Control Corporation LLP
The brainchild of this company is BiLUX AL radiators with excellent heat output, which are made taking into account all the nuances of individual heating systems. Their surface area is very significant, and the cross-section of the vertical pipe is optimally calculated. The factory for the production of these radiators is located in China. The distance between the axes of the collectors can be 30 cm (BiLUX AL M 300) or 50 cm (BiLUX AL M 500).
During the manufacturing process, the injection-molded upper parts are connected to the bottom, which is made using a special welding technology. After assembly, the batteries are processed chemically and mechanically. They are then tested to see how tight and durable they are. Batteries are painted in several stages. After cleaning, they are exposed to an electrostatic field. At this time, enamel based on epoxy resin is sprayed. Then, by heating to a high temperature, the surface of the product is polymerized.
Construction of bimetal radiators
This type of radiator is the result of combining two metals. The internal part (base) of the product has the shape of a steel frame, inside of which the coolant itself is installed directly, from which heat enters the atmosphere. The strength of steel allows it to withstand powerful pressure in the heating network, and its coating protects the product from corrosion.
The outside of the frame is covered with an aluminum shell (casing). Aluminum has good thermal conductivity, heats up quickly and conducts heat coming from the heating network. The outer shell is made up of fins to direct warm air into the room.
Types of bimetallic radiators
There are two main types:
- Cast or monolithic. The heater body is cast in a special mold.
- Sectional or prefabricated. The structure is assembled from separate sections using threaded connections.
The dimensions of the prefabricated radiator can be expanded by adding additional sections. A cast (monolithic) radiator cannot be expanded, but there are ready-made options with a wide range of sizes, so you can choose the right one.
On a note! Cast models, unlike prefabricated ones, cost an order of magnitude higher!
To choose a reliable radiator for an apartment, you need to know the structure of the heating network itself. In modern high-rise buildings it is better to install monolithic heaters. They are more resistant to pressure surges in pipes. A sectional model may not withstand such loads due to its special design. However, this type of radiator can be equipped with additional sections, which is necessary in some cases. In addition, it is much easier to maintain.

Semi-metallic radiators
This type of radiator is different in that its base is made not only of steel, but also some of its parts are made of aluminum, which makes the product less durable than the original. Because of this, the quality of the product and durability are sharply reduced. The junction between a steel pipe and an aluminum pipe wears out quickly due to the different degrees of expansion of these two metals when heated. Therefore, semi-bimetallic radiators are much inferior in quality to bimetallic ones.
Semi-bimetallic radiators can be identified by their lightweight. When choosing a radiator, it is worth considering this parameter. Such heaters are more suitable for installation in country houses, as they are similar to aluminum ones.
What is center distance
All bimetallic radiators have a distance between the inlet and outlet. The most common size is 350 mm or 500 mm, but batteries with a distance between the axes of 200 mm or 800 mm can be found on sale.
Product material
The internal frame of bimetallic radiators is made of durable steel alloy, and the outer shell is made of aluminum. The steel base can withstand high pressures in pipes and water hammer. High-quality steel is not subject to corrosion, and the outer casing made of aluminum heats up well and quickly distributes heat throughout the room. High carbon steel has special strength and durability.
Section calculation method
To determine the required number of elements, you need to determine the power. There are several rounded values calculated for a room with a ceiling height of 2.7 meters:
- For a standard room you need 100 watts.
- For each window add 10.
- If it is angular, the value is multiplied by 1.2.
- If the ceilings are higher or the windows are larger than usual, add 10%.
- Heating weakens from the upper floors to the lower ones, so another 2% should be added for each.

The resulting standard power is multiplied by the area of the room . The result is a total value calculated with a margin.
Then the number is divided by the passport indicator of one section , rounding up. An example calculation looks like this:
- (100 + 10) * 1.2 * 1.04 = 137.28 , where the extreme multiplier is chosen for the apartment on the third floor from the top.
- 137.28 * S = 151 * 18 = 2471, where S (18) is the area.
- 2471 / 190 = 13. In this case, with a power of one section of 190 Watts, 13 pieces will be needed.
Tall and narrow
Tall radiators, even in their usual design, look unusual. And if you paint it in a non-standard color, give it an unusual shape, and combine it with a mirror or shelf, it generally looks more like a designer item than a banal heating device.
Let us immediately upset cast iron lovers: the tallest cast iron radiator is around a meter. Haven't seen it higher. The same can be said about bimetallic ones - they don’t come above a meter. And in general, all that is in bimetal is 760-860 mm or so.

One of the most attractive models is the Arbonia Entreetherm vertical tubular radiator
Steel panel batteries as standard come in heights of up to 900 mm. But there are also special models that can reach two meters and higher. For example, Kermi has two models Verteo Plan and Verteo Profil - the maximum they can be up to 2.2 m. Purmo also has giants: Kos V, Faros V, Tinos V, Narbonne V and VT, Paros V. They differ in the type of front panel (smooth or profiled) and depth. But they all only have a bottom connection.
Steel tubular radiators are available with a height of up to 3000 mm. Moreover, if necessary, some manufacturers can make it higher. There are tall models from any manufacturer: everyone on the market offers such non-standard options “to order.” Here we will list only the most interesting from a design point of view: Entreetherm, Planterm from Arbonia, Dekor series from Kermi, Harmony from the Russian KZTO, Charleston from Zender.
Other types do not have tall radiators. The choice, it must be said, is considerable. Don't get confused.
Radiator weight
Aluminum is a lightweight metal. Products made from this material are lightweight, which makes them easier to move and reduces the strength . It should be noted that in the manufacture of batteries, metal is fused with silicon. This slightly increases the severity.
The average weight of one section is 1.25 kg. The value varies from 1 to 1.35, which depends on the dimensions and wall thickness. For example, to install a radiator of 10 units with a small margin, 15 kg of fasteners are sufficient.
Important! Of all types of radiators, aluminum ones are the lightest. This makes them easy to transport.
Standard height
When talking about standard height, we mean an interaxle distance of 500 mm. These were the connecting dimensions of the well-known cast iron “accordion” of Soviet times. And since they have a long service life, these batteries are still used in heating networks. Only now they are being replaced with new ones. Moreover, they often do not want to redo the system, so they look for heating devices of the same size. What's good: they are in almost every group.
Today, not only “accordion” is made from cast iron, although it exists and is popular. There are also retro-style radiators with a center distance of 500 mm, made in a modern style:
- “Accordion” is called MS-140, MS-110, MS-90 and MS-85. These modifications have different depths: 140, 110, 90 and 85 mm, respectively. The width also varies. Moreover, it differs from different manufacturers of the same model. So the MS-140 from the Minsk plant has a width of 108 mm, and from Bryansk and Novosibirsk - 93 mm.
- Cast iron radiators in retro style with a center distance of 500 mm will have completely different appearance and dimensions. Let's say the Modern 500 model. Sections with legs dimensions 645*100*45 mm, without legs 572*100*45 mm, thermal power 93 W. And the other DERBY M 500 has dimensions of 660*174*63 mm and a heat output of 118 W (where the dimensions are designated height*depth*width).
- The new type of cast iron batteries also have a decent range of parameters. Turkish Demrad Ridem 3/500 - 572*98.2*60 mm, Demrad Ridem 4/500 - 572*134*60 mm. Czech Viadrus Style has the following dimensions: height 580 mm, width 60 mm, depth is not indicated due to its nonlinear shape (narrower at the top, wider at the bottom).

Cast iron batteries can have such dimensions today
Aluminum
The dimensions of aluminum radiators are more standardized. Here we can even talk about average values. With an interaxial distance of 500 mm, the average section height is 570-585 mm. The almost standard width is 80 mm. There are options for depth. There are almost flat ones: Russian-made Thermal radiators have a depth of only 52 mm. These are the flattest aluminum batteries. For all others it is 80-100 mm.
Bimetallic
Here the situation is even more standard. There were no flat radiators in this category. On average, the dimensions are as follows: width 80-87 mm, depth 80-95 mm, height 565-575 mm.

The lowest radiator at Global Gl-200/80/D has a height of 200 mm
Steel panel radiators are rarely produced with a center distance of 500 mm. But still, there are some. For example, the Kermi campaign made the following connecting dimensions specifically for replacement: they are available in the Plan-K and Profil -K line. The Russian one also has standard size radiators: model RSV-1.
Tubular radiators come in a variety of models and sizes. It is quite easy to find the required sizes here. The Russian manufacturer has KZTO, and the Europeans have it. In this category, they operate more with the overall height - the mounting one, since many people prefer the bottom connection.
Subtleties of choosing a radiator model - expert advice
When choosing a battery, the consumer must take into account several other important parameters. In some inexpensive models, the steel insert is made only in vertically located channels. Therefore, radiators of this class have less protection against corrosion, and accordingly, their service life is reduced. In addition, such a design will not provide high strength. Therefore, these heating devices are called pseudo-bimetallic.
In practice, two main types of heating radiators are used: monolithic and collapsible. The first are a non-demountable structure, based on a stainless steel system. These radiators are designed to operate in systems where sudden pressure surges are acceptable, for example, in high-rise buildings. Collapsible devices are a certain number of sections, the number of which can be increased or decreased, but they are not adapted to sudden changes in pressure (hydraulic shock).

Adding additional sections to a bimetallic radiator
By the way, many experts recommend installing collapsible structures in autonomous heating systems, which can be found in low-rise or country houses. Boiler equipment installed in such buildings produces constant operating pressure and stable temperature. These parameters are set by the homeowner when setting up the system.
Heat dissipation and power
These two characteristics of aluminum radiators are almost always given as identical values and are used as synonyms in many articles. At the same time, each of them still has its own nuances, which follow from their physical definition:
- Heat transfer
is a thermodynamic process that involves the transfer of heat from a solid body (radiator surface) to the environment through a coolant; - Power
is a physical quantity that shows how much heat a particular device can produce per unit time. The more powerful the radiator, the larger the area it can heat.

An aluminum radiator installed in an apartment. In fact, an aluminum radiator performs useful work in heating a certain area, which depends on its power, due to the phenomenon of heat transfer. Both quantities discussed are measured in watts (W) or kilowatts (kW) and are often equated. Although it would be more correct to use the concept of power, which determines the amount of energy transmitted, and not the transmission process itself. We will use both expressions, according to recent practice.