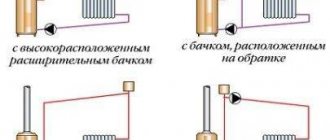
The associated radiator connection scheme (Tichelman loop) is called both “very stable” and “very gentle” - it does not tolerate inaccuracies and deviations from the rules during installation. Why are there conflicting estimates? It is not uncommon for several central radiators in this system to not heat up (perform poorly). It happens that one radiator does not work, regardless of location. What's the matter?
Troubleshooting a passing circuit is very easy
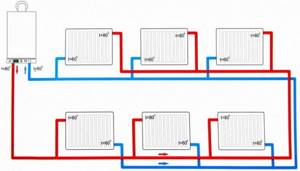
If you look at the hitchhiking diagram (Tichelman loop), you can note that all radiators are connected between the supply and return lines in parallel.
Moreover, there are usually more than 10 such heating devices. When their number is smaller, a cheaper dead-end circuit is often used.
Along the way, the coolant should be distributed approximately evenly between all radiators.
But this is ideal when the hydraulic resistance of the supply and return pipelines is small, “zero”. And the hydraulic resistance of the radiators is significant and noticeable.
Then the pressure graphs in the associated circuit look approximately as shown in the figure. The point here is the following - the highest pressure is on the outer radiators, the lowest on the central ones, but this is not at all critical - the flow through all devices is large enough for their stable operation and maximum power output.
Therefore, eliminating violations and malfunctions in the ride, first of all, involves proper installation according to the instructions. But in practice, there are a wide variety of nuances in installations, due to which this scheme does not work. Let's take a closer look.
Saving money is not for the Tichelman loop
The main increase in the cost of the Tichelman loop is the need to lay a ring of large-diameter pipelines. Typically an internal diameter of 25 mm is required. Fittings for such pipes cost a pretty penny; the design turns out to be 30 percent more expensive than the shoulder design.
If you save money and place pipes in the middle of the ring (say from 3 in the supply to 3 in the return, with 15 connected devices) with an internal diameter of 20 mm, then the hydraulic resistance of the pipelines (supply and return) compared to radiators will immediately increase and begin to affect .
The entire principle of this heating system will not be followed - the pressure on the radiators will vary too much for the circuit to work stably. At the extremes it is still large, but in the center problems will begin.

How is pressure distributed in a non-working associated circuit?
The issue with a thin pipeline will become even worse if radiators with almost zero self-resistance and a large internal cross-section are used - aluminum or cast iron. And these are not rarely used.
Then the increased resistance of the ring pipelines will noticeably affect the distribution of coolant through the radiators.
In fact, on the outer radiators the pressure drop will be large, but on devices inside the ring there will simply be no pressure - the entire flow will go through the outer ones in the ring.
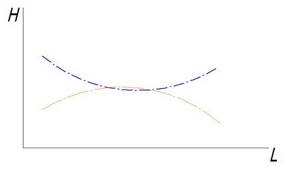
The pressure graphs along the length of the pipeline in such a scheme for supply and return are parabolas that almost converge in the middle, or even completely converge (the pressure drop across the central radiators is 0), or even overlap each other.
It also happens that several radiators in the center do not heat, but for some reason the most central one works. Because in it the coolant stream is completely overturned, the movement of the liquid occurs in the opposite direction (the graphs overlap each other).

How to fix the problem
It is clear that the problem with central radiators in a hitch, with a thin ring pipeline, can be easily solved. You just need to increase the hydraulic resistance of the outer radiators, and the flow will begin to move through the central devices. Those. use balancing valves on the inlets to turn off those that are working.
Then the total resistance of the radiators relative to the pipelines increased, we returned to the classical formulation of the question, and the circuit works.
But all this is eliminating an emergency situation, and not a complete solution to the issue.
How should a Tichelman loop be created?
The diameter of the pipes throughout the entire ring should be optimal, so that at the end sections a low coolant velocity is ensured, within the norm, up to 0.6 m/sec.
If you take the opposite route - save on pipes and plug the outer radiators, then the overall resistance of the system simply increases. The circulation pump is loaded and it absorbs more electricity. The difference in the price of electricity offsets the savings on pipe diameters.
Causes of failure and solutions
At the initial stage, you should check that the bypass is installed correctly. This element looks like a tube installed in front of the heating radiator. Using a bypass, two pipes connected to the battery are connected. One pipe is responsible for the supply of coolant, and the other for its return movement. Very often the reason that the last radiator does not heat is the installation of a bypass at a distance from its structure.

Often the heating battery, which is the last one in the overall design, stops heating due to its large size. If the radiator has more than 12 sections, the pressure may not be enough to distribute the coolant evenly. In this case, it is recommended to change the battery or cut off some sections.
It is better to entrust such work to a specialist. Also, before cutting, you need to make sure that the coolant supply is turned off. Therefore, it is preferable to carry out repair work during the warm season.
The third reason is improper balancing. Due to this, the coolant is distributed unevenly among the sections. To ensure the operation of the equipment, it must be installed in the correct position. It is also important to make sure that the wall on which the radiator is mounted has a flat surface.

Blockage in the heating system

The reason for the insufficient heat of the battery may lie in a blockage. The blockage is explained by the fact that after a long period of heating operation, the internal diameter of the pipes could be significantly reduced due to the appearance of rust. As a result, it may turn out that there is no room in the pipe for the circulation of coolant flow. In such cases, it will be necessary to carry out work to clean the battery or completely replace it. To clean or replace the radiator, shut off the coolant supply to the bypass. In this case, the entire system will continue to work. If you can get by with just cleaning, you can use the tips below:
- It is important to remember safety, as the coolant can be very hot.
- Cleaning should only be carried out under high water pressure.
- Before reinstalling the radiator, you should check the pipe connections; there may also be a blockage at the joint that can be cleaned.
- It is recommended to clean the radiators all at once.
Local reasons
In some cases, the battery may stop heating due to local breakdowns.
- Airing the general heating system in the house;
- Poor quality of the liquid acting as a coolant;
- Poor quality or old radiator.

To make the use of heating radiators as efficient as possible, it is necessary to regularly monitor their technical condition, clean them, check the position in which they are installed and remove stagnant air masses.
Why don't the batteries heat up?
You have noticed that the last battery in the home heating circuit is cold. What to do? Experts advise first determining the nature of the breakdown. It can be both global and local in nature. In the first case, you need to pay attention to the correct installation of the bypass and the heating element itself. The breakdown can be eliminated only by redoing the heating wiring in the house.
Local breakdowns include air pockets and contamination inside the heating element. They are the main reason why the middle or last battery in the heating system is cold. These problems can be fixed by a person without professional skills. But the help of specialists will not hurt here.
Often on construction forums people complain about heating systems - the bottom of the radiator is cold and the top is hot. It is worth noting that any radiator on top is warmer than on the bottom, but if the gap between these temperatures is too large, then most likely there is something wrong with the system. Moreover, this means that the battery produces less thermal energy than it should. After all, everyone knows that the efficiency of heating devices directly depends on the uniform heating of their surfaces.
Incorrect installation of heating system elements
Bottom feed connection is incorrect.
The following types of heating pipe connections are now common: diagonal analogue, bottom connection, side installation.
Please note! It is very common that the radiators on the top floors of apartment buildings are hot, but below they are only slightly warm. Here the problem is obvious - poor design and installation of the heating system. You can’t handle this on your own; you will need to consult an independent heating engineer.
It should be noted that the number of sections in any type of heating system should not exceed the standard limit.
Low coolant speed
If hot water moves through the pipes quickly enough, it will transfer heat more evenly along the entire length of the system. Otherwise, at the end of the line the radiators will be much colder than at the beginning.
Regarding high-rise buildings : the problem can be solved by connecting the battery in a diagonal pattern. This will ensure uniform fluid flow throughout the radiator.
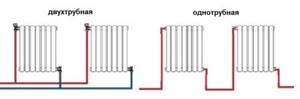
Diagonal battery connection
In a private home, a problem of this kind may occur due to a breakdown or absence of a circulation pump. You should check its correct operation. If the system is built on the gravitational principle of fluid movement, then it is recommended to install an additional pump. This will ensure uniform heating of radiators throughout the house.

Circulation pump in the heating system
Another reason that the bottom of the battery is cold and the top is hot can be a narrowing of the pipeline. This also leads to a low coolant flow rate. The pipeline becomes narrower if :
- The plastic pipes were poorly soldered, and part of the passage is blocked by a melted structural element.

Poor welding of plastic pipes. Too much deposits have formed on old iron pipes.

The bottom of the battery is cold and the top is hot due to deposits
- The control valve is equipped with a narrowed internal cross-section.
The article discussed the main problems that lead to insufficient heating of the lower part of the battery. The majority of problems can be solved independently and require little effort. However, some system flaws, such as deposits on pipes, may require replacement of the entire pipeline.
Air jams
The presence of air in the system is the main reason why the bottom of the battery is cold and the top is hot. Most often, this nuisance occurs among residents of apartment buildings on the upper floors. The air in the system tends upward, so if you live in the upper part of the building, you should install Mayevsky valves or drains.
You can read about how to bleed air from a cast iron battery here.

Mayevsky crane
The sequence of actions will be as follows:
- Shut off the pipe that supplies hot water to the battery. The “return” must remain open.
- Open the bleeder and wait until the air is completely out of the system.
- Close the drain and resume water supply to the radiator.
In a private house you can use an alternative scheme:
- Turn off the heating supply.
- Open the drain at the highest point of the heating system.
- Use back pressure to remove any accumulated air.
If these recommendations do not bring the expected result, it is better to call a specialist to diagnose the entire system as a whole.

Air bleeder in new batteries
Airy radiator
The presence of a large air bubble in the system is an obstacle to the normal circulation of coolant through the system of pipes and heating devices. The symptom is cooling of the entire radiator or the far upper part of it when the riser is hot.
Complicating the situation is the possibility of the simultaneous existence of obstacles of this kind. In centralized heating systems, automatic air exhaust systems are installed to prevent such situations.
Interesting fact: this type of malfunction is most often found in single-pipe systems of the Leningradka type, due to the peculiarities of connecting the radiator - the pipe is only at the bottom.
In private homes and autonomous heating systems, the “Mayevsky tap” serves the same purpose. “De-airing” of an autonomous system, if available, can, as a rule, be carried out on its own. Taking a small container or a cloth, turn the tap, release the air until the first drops appear, and close it by turning it to the previous position.
Battery clogged
Taking into account the low quality of the coolant supplied to heating systems, clogging becomes a very common cause of poor heating. The issue becomes especially relevant during the start of the heating season. In private homes, the system is autonomous, and clogging can only occur through an open expansion tank.

Battery clogged
To clean the battery, disconnect it from the pipes and rinse it. The first time hot water is poured in, then special solutions can be used.
Low pressure
The bottom of the battery may be colder than the top due to insufficient pressure in the system. If the main system is designed for cast iron pipes, then the water supply force in it is quite low. Installing bimetallic batteries means that the coolant is simply not forced through the narrowed passages inside the radiator.
In a private house with a membrane expansion tank, the pressure in the system can be raised manually. Residents of apartment buildings will have to contact their service provider to resolve the issue. Also, repair work may be carried out on the central highway, after which everything will return to normal.

Pressure gauge showing system pressure
Often the bottom of the battery is cold, and the top is hot, which can occur due to unlawful actions of neighbors of an apartment building :
- Installation of water-type heated floors.
- The bypass was mounted on a common heating supply pipe.
- The volume of radiators was increased without the approval of the technicians.
No circulation, heating failure - why
Failure in the heating system, deficiencies, imperfections, all lead to cold radiators. If there is no coolant circulation, then the reason needs to be determined. Most often, the answer to why the heating does not work is on the surface, obvious.
Let's look in order at the main causes of heating malfunctions, why water does not circulate through the pipes, and what needs to be done first.
Let's start with the simplest and most obvious reasons.
clogged, clogged
Every heating system must have a coarse filter. A very small device with a fine mesh and a sump (installed downwards! or at least to the side) saves equipment, pumps, and the boiler from coolant contamination that will be present in any system. Wood shavings, broken threads, rust, water sediment…. everything is retained by the mesh in the filter.
The sedimentation tank must be periodically untwisted and the mesh cleaned.
If the circulation in the heating system of a private house is disrupted, then the first thing you need to do is check the filter, which should be installed on the return line in front of the boiler.

Air in the system, airing
Airing can occur in any closed piping system where air removal measures have not been taken. Air is always present in the coolant, including in a dissolved state, is released during pressure changes, and accumulates at the highest points. Including in the boiler.
Automatic air vents are installed at characteristic, highest points of the system, as well as on collectors and special separators - the normal circuit is equipped with a special air catching device in which air bubbles are released from the coolant.
We recommend: Ventilation diagram for a private house - do-it-yourself supply and exhaust system
In addition, Mayevsky valves (manual air vents) should be on each radiator, and also possibly in other elevated places.
Checking the air supply, bleeding the air, installing air vents are common actions if circulation stops and the batteries are cold.

The circulation pump does not work
In private homes, the reason why the heating system stops working is a breakdown of the electrical equipment that controlled the movement of the coolant through the pipes.
If the heating suddenly stops working, then you need to check the functionality of the circulation pump near the solid fuel boiler or the pump in the automated boiler. In addition, the same unit can be installed in each circuit, which must work properly.
Bad polypropylene pipes
Often the consumer (customer) believes that polypropylene pipes are absolutely reliable and cannot cause heating problems or cold radiators.
But polypropylene is much more insidious than old steel or metal-plastic pipelines. Each place of soldering (welding) is a potential increased resistance in the system or a cause of cessation of circulation (weakened movement of water through the batteries), due to deposits of material inside.
It is impossible to control the quality of connections from the outside; all that remains is to cut out pieces, resolder, and remake polypropylene pipes.
Poor performance of a polypropylene system is a real problem for the home installer. Good professionals don’t take on this material at all.

Bad project
It is not uncommon for poor circulation to occur where there is poor design. Typically, the batteries are not connected correctly, according to some sequential circuit, where the last battery in the circuit receives much less coolant.
Another bad design is single-pipe circuits, where it is also difficult to establish the necessary coolant circulation through each battery.
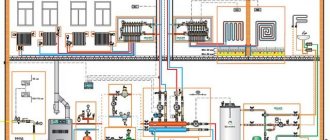
If the radiators do not heat up evenly, or there is poor coolant circulation on individual heating devices, first of all you need to consider how the connection corresponds to the classic circuits - shoulder, associated, radial. It is necessary to bring home heating to normal design standards, and then expect good circulation and uniform heating of the radiators.
Small diameter, overgrown pipes
Old steel pipes become overgrown with rust and deposits from the inside, their throughput capacity decreases significantly over time, and there is only one solution - they need to be replaced with modern ones.
But even during installation, for the sake of economy, mistakes can be made with the choice of pipeline diameter - on highways, on groups of heating devices, diameters of mm can be set. The result is noise in the pipes, excessive consumption of electricity, and insufficient coolant flow.
What pipe diameters should you choose?
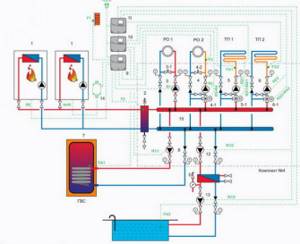
A complex system
A type of bad design is an incorrectly designed complex heating system consisting of many heating circuits and several boilers. Here entire circuits will not work correctly if the work of one affects the neighboring one.
As a rule, one boiler (the backup one does not count) and three circuits - boiler, radiators, heated floors with their pumps are coordinated normally, and no questions arise. But if you connect another working boiler plus a circuit (for example, heating a garage and greenhouse), then the system will become complex. It is difficult to say how the coolant will circulate in it without equalizing the pressures at the connection points.
In complex systems, a competent design is important, installing a hydraulic arrow or an equal pressure ring; more information about the hydraulic separator can be found here
No balancing
Many home heating schemes involve balancing; balancing and control valves are installed in them. For example, between floors, between shoulders, and for each radiator. The taps cover the direction with less hydraulic resistance; accordingly, more coolant will flow to other points.
Children can play with the taps. Or the system is initially unbalanced. Setting up, as a rule, is no problem, you just need to find this tap... How to set up home heating

Neighbors don't provide heat
But complex heating project schemes are of little concern to residents of high-rise buildings, who have a separate riser for each radiator in the apartment. And if any radiator stops heating up normally, it means there is no circulation through the riser, therefore...
You need to contact the heating network, housing office (service organization) to adjust the power in the risers, and if this does not help, then with the requirement to check the neighbors.
Often, unauthorized connection or replacement of radiators and pipes in central heating systems leads to a redistribution of pressure, circulation through individual batteries decreases and disappears.
No circulation in gravity system
In gravity systems, the pressure difference is low; they are especially sensitive to air pockets, pipe diameters, and gaps in radiators.
In old circuits, gradual deposits occur in radiators and pipes; circulation may decrease over time, and the only cure for this is replacing everything with a more modern one.
You also need to pay attention to the correctness of the circuit itself - the middle heating line is below the cooling line (the boiler heat exchanger is below the radiators), and also - the hot feed rises up to the highest point, and from there it drops to the radiators... Read more about gravity flow circuits below

Various breakdowns in heating systems
The taps and valves are closed - check that everything is open to ensure circulation. There is a leak in the system - there is not enough coolant, check the pressure, eliminate the leak. Installation with flexible pipes - the pipe is pinched. Failure of automatic equipment - thermal heads on mixing units, radiators, the mixing units themselves - silting, failure, it is necessary to check the correct operation. Also – electronic failure. Incorrect balancing on the distribution collector - in beam circuits, complex systems, collectors with balancing and tuning equipment can cause a lack of circulation anywhere due to breakdowns and incorrect settings. Low pressure, no air in the expansion tank - check the pressure in the pipes and the pumping of the tank; automated units will not work at all without the required pressure. Violation of the circuit, excess bypass - check that the installation complies with the design, the logic of the circuit, whether there are any short circuits in the jet, parallel branches to radiators and circuits.
We recommend: Types of socket boxes for concrete
Source: teplodom1.ru