Types of registers
The most common type is registers made of smooth pipes, and most often electric-welded steel ones. Diameters - from 32 mm to 100 mm, sometimes up to 150 mm. They are made of two types - serpentine and register. Moreover, register ones can have two types of connection: thread and column. A thread is when the jumpers through which coolant flows from one pipe to another are installed either on the right or on the left. It turns out that the coolant sequentially runs around all the pipes, that is, the connection is sequential. With a column connection, all horizontal sections are connected to each other at both ends. In this case, the movement of the coolant is parallel.
Types of registers made of smooth pipes
When used in systems with natural circulation, it is necessary to maintain a slight slope towards the movement of the coolant of the order of 0.5 cm per meter of pipe. Such a small slope is explained by the large diameter (low hydraulic resistance).
This is a serpentine heating register
These products are made not only from round, but also from square pipes. They are practically no different, only they are more difficult to work with, and the hydraulic resistance is a little higher. But the advantages of this design include more compact dimensions with the same volume of coolant.
Square tube registers
There are also registers made of pipes with fins. In this case, the area of contact between the metal and the air increases, and heat transfer increases. In fact, builders still install just such heating devices in some budget new buildings: the well-known “pipe with fins.” Although they don’t look the best, they warm rooms well.
A register with plates will have a much higher heat transfer
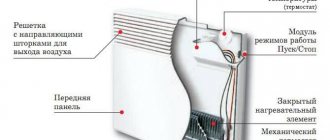
If you insert a heating element into any register, you can get a combined heating device. It can be separate, not connected to the system, or used as an additional heat source. If the radiator is insulated with heating only from the heating element, it is necessary to install an expansion tank at the top point (10% of the total coolant volume). When heated by a domestic boiler, the expansion tank is usually built into the structure. If it is not there (often happens in solid fuel boilers), then in this case it is necessary to install an expansion tank. If the material for the registers is steel, then the tank needs a closed type.
Electric heating can be useful in the most severe cold weather, when the boiler power is not enough. Also, this option can help out in the off-season, when there is no point in loading a long-burning solid fuel boiler and running the system to full speed. You just need to warm up the room a little. This is not possible with solid fuel boilers. And this backup option will help keep you warm in the off-season.
By adding a heating element to the register and installing an expansion tank, we get a combined heating system
Calculation of the number of ribs
Heating registers must be calculated before purchasing them. The diameter of the pipes is very important: experts believe that pipes with a cross-sectional diameter in the range from 3 cm to 8 cm are suitable for a private house. This decision is determined by the fact that a conventional heating boiler is not capable of producing a larger amount of heat, so too large surfaces will not warm up completely .
When making calculations, you need to pay attention to the length of one register rib and the heat transfer per meter of this length. For example, a meter-long pipe with a 6-centimeter cross-section can heat one square meter of area
When calculating the required number of edges, the result must be rounded up. The calculation of the number of heating registers must also take into account the characteristics of the building. For example, if a building has a large number of windows and doors, or if the walls are thin and poorly insulated, then the number of registers can be increased by 20-50%.
Related Posts
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- What kind of pipes are used for the gas pipeline?
- Which pipe to choose for heating
- Dismantling of heating systems
- Which rehau pipes are best for heating and water supply?
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- Leningrad heating system for a private house
- At what temperature of the coolant is the heating system turned off and turned on in an apartment building according to GOST
- Features of using PVC sewer pipes with a diameter of 50 mm
- Pipe box
- Tichelmann loop
- Do-it-yourself gas heater: options for the best homemade products
- Rules for laying sewer pipes
- How to make steam heating
- Decorative overlay for a heating pipe: what is better to choose to make it look beautiful?
- What are polyurethane foam pipes and where are they used?
- Cross-linked polyethylene pipes for water supply: material features, areas of application, installation technology
- Choosing between metal-plastic and polypropylene pipes
- What sizes of sandwich pipes are best to use for a chimney?
- Thin-walled metal pipe for electrical wiring
- How to choose high-quality pipes for water supply in an apartment
- Trenchless pipe laying options
- Heating system of a one-story private house
- Comparison of heating radiators by heat transfer
- Effective methods of thermal insulation of sewer pipes
Read with this
- Disadvantages of polypropylene pipes in home heating
- What kind of pipes are used for the gas pipeline?
- Which pipe to choose for heating
- Dismantling of heating systems
- Which rehau pipes are best for heating and water supply?
- Which pipes for heated floors to choose: characteristics and installation methods
- Leningrad heating system for a private house
- At what temperature of the coolant is the heating system turned off and turned on in an apartment building according to GOST
- Features of using PVC sewer pipes with a diameter of 50 mm
- Pipe box
Work order
- The jumpers are fixed in place and secured by welding at 2-3 points.
- Having positioned the structure vertically, the jumpers are finally welded. It is recommended to first make a thin seam at low current, which will allow the gaps to be filled well. Next, a thick main seam is performed at increased current.
- The internal space of the register is cleared of metal debris and slag.
- The plugs are applied, tacked and welded to the ends of the profile pipes.
- Welding seams are processed. The protruding parts are knocked down with a hammer, then each seam is cleaned with a grinder.
- Holes in the register are drilled depending on the selected connection diagram. In this case, it is better to place them not in the center of the ends, but slightly higher or lower.
- Connecting pipes are welded to the holes.
- The seams are cleaned and all holes except one are plugged. The register is filled with water under pressure and the welding quality is checked. The seams must withstand pressure up to 13 atm.
- The outer surface is cleaned, degreased and painted with heat-resistant paint.
- A fitting is welded to the top row and a Mayevsky valve is installed.
Construction of heating registers
Despite the fact that such heaters are considered outdated and do not have a very attractive appearance, they continue to be widely used in a variety of areas, for example:
- for heating production premises of industrial enterprises;
- as an autonomous heater in garages;
- as a water heating element built into a brick oven.
By design, heating devices are divided into 2 types: sectional and in the form of a coil. In the first case, the role of 1 section is played by each horizontal pipe, the flow of coolant through them is ensured by vertical jumpers. They are made of smaller diameter pipes in order to create artificial resistance to flow and increase heat transfer from each section. The pipes from which the sectional heating register is made are plugged at the ends, and the coolant is supplied according to the “top to bottom” scheme.
The design of the heater in the form of a coil is clear from its name. Here the diameters do not narrow; water flows freely through the entire device, changing direction several times. The heat transfer of this register is lower than that of a sectional one, but the hydraulic resistance is less and it is somewhat simpler to manufacture.
Heating registers from smooth pipes of round and rectangular cross-section are welded. However, the generally accepted design is ordinary round pipes made of low-carbon steel such as St3, St10 and even St0. If the battery is intended to work with a steam system, then St20 steel is used. It is not recommended to make sections with a rectangular cross-section; they are less washed by the convective air flow, which means they will give off less heat. For garage heating, autonomous registers are made, filled with antifreeze or transformer oil, and an electric heating element is built into the lower section at the end.
Radiator connection diagrams
How well the radiators will heat depends on how the coolant is supplied to them. There are more and less effective options.
Radiators with bottom connection
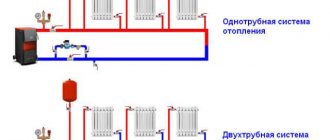
All heating radiators have two types of connection - side and bottom. There can be no discrepancies with the bottom connection. There are only two pipes - inlet and outlet. Accordingly, coolant is supplied to the radiator on one side and removed from the other.
Bottom connection of heating radiators for single-pipe and two-pipe heating systems
Specifically, where to connect the supply and where the return is connected is written in the installation instructions, which must be available.
Heating radiators with side connection
With a lateral connection, there are many more options: here the supply and return pipelines can be connected into two pipes, respectively, there are four options.
Option #1. Diagonal connection
This connection of heating radiators is considered the most effective, it is taken as a standard and this is how manufacturers test their heating devices and the data in the thermal power passport for such a connection. All other connection types transfer heat less efficiently.
Diagonal diagram for connecting heating radiators with a two-pipe and one-pipe system
This is because when the batteries are connected diagonally, the hot coolant is supplied to the upper inlet on one side, passes through the entire radiator and exits from the opposite, lower side.
Option #2. Unilateral
As the name implies, pipelines are connected on one side - supply from above, return from below. This option is convenient when the riser runs on the side of the heating device, which often happens in apartments, because this type of connection usually predominates. When the coolant is supplied from below, this scheme is used infrequently - it is not very convenient to position the pipes.
Lateral connection for two-pipe and one-pipe systems
With this connection of radiators, the heating efficiency is only slightly lower - by 2%. But this is only if there are few sections in the radiators - no more than 10. With a longer battery, its farthest edge will not heat up well or will remain cold at all. In panel radiators, to solve the problem, flow extenders are installed - tubes that bring the coolant a little further than the middle. The same devices can be installed in aluminum or bimetallic radiators, thereby improving heat transfer.
Option #3. Bottom or saddle connection
Of all the options, saddle connections for heating radiators are the least effective. Losses are approximately 12-14%. But this option is the most inconspicuous - pipes are usually laid on the floor or under it, and this method is the most optimal from an aesthetic point of view. And so that losses do not affect the temperature in the room, you can take a radiator a little more powerful than required.
Saddle connection of heating radiators
In systems with natural circulation, this type of connection should not be made, but if there is a pump, it works well. In some cases, it’s not even worse than the side one. It’s just that at a certain speed of movement of the coolant, vortex flows arise, the entire surface heats up, and heat transfer increases. These phenomena have not yet been fully studied, therefore it is not yet possible to predict the behavior of the coolant.
Types of heating registers
There are 3 types of registers considered:
- Sectional in the form of the letter “P”.
- Serpentine, the shape of which is S-shaped.
- Mixed.
Pipes made of steel or stainless steel are used for production, the diameter of which ranges from 25 to 200 mm. Industrial premises with administrative or economic purposes are heated through the use of pipes with a diameter of 25 to 100 mm. As for registers with a larger diameter, reaching 200 mm, they are installed in production workshops and at sports facilities of varying scale, for example, swimming pools.
As applied to private households, their installation significantly reduces heating efficiency.
When assembling registers, almost any number of sections can be used, which is determined only by the area of the room and the required amount of heat transfer.
When connecting sectional registers, jumpers are used that have a smaller diameter compared to the pipes that are part of the type of device under consideration. To calculate the optimal distance between heating pipes, use the formula D+50 mm, where D should be understood as the pipe diameter. Compliance with the distance calculated in this way makes it possible to minimize the infrared radiation of the pipes in relation to each other, which ensures an increase in heat transfer.
The connection of coils is possible due to bends, the diameter of which is identical to the diameter of the pipes. They are installed at the ends of the connected device. Because of this connection method, the cost of connecting registers increases, but not significantly. In this case, the increase in costs is compensated by an increase in operating efficiency, which provides a larger working surface area. Also, the coil register has such a positive aspect as lower hydraulic resistance compared to that present in the sectional version of such a heating device. This allows the use of circulation pumps with lower power and lower price.
End caps installed on pipes come in a variety of shapes: flat, round and elliptical. Plugs having an elliptical shape are used in systems where the coolant is supplied under high pressure. They are also used to give heating appliances a certain attractiveness. If there is a need, it is possible to equip the upper segment of the register with a fitting designed to install a degassing valve.
The variability in the design of heating registers does not end there; for example, there are devices of this type that are complemented by a heating element. The result is a device that does not require connection to the heating system, since the heating medium is heated by a built-in electrical appliance in the form of a heating element.
In the process of designing such devices, the power of heating elements is calculated in a certain way, which depends on how large the surface area of the device is. If the register overheats, this will lead to excessive activity of the expansion process and the coolant will flow out through the emergency valve. Otherwise, that is, if there is insufficient power, the efficiency of the heating element will be reduced to a minimum.
The autonomous register must be equipped with a fitting installed in the upper segment of this heating device. It is used to fill the coolant before putting it into operation and to install an emergency valve, which can be supplemented with an expansion tank, due to the need to compensate for the expansion of the coolant.
How to make a homemade register from profile, smooth steel pipes
Welding work, which forms the basis for the manufacture of registers for a heating system, requires a certain number of different tools and materials.
DIY tools and materials
In addition to the welding machine, you will need the following equipment:
- for cutting: grinder, plasma cutter or gas torch (cutter);
- tape measure and pencil;
- hammer and gas wrench;
- building level;
Welding materials:
- electrodes if electric welding is used;
- wire, if gas;
- oxygen and acetylene in cylinders.
Work order: how to weld the structure?
Depending on the type of design chosen (sectional or coil), the assembly of the registers will differ dramatically. The most complex ones are sectional ones, because they have the most joints of elements of different sizes.
Before moving on to assembling the register, you need to make a drawing and understand the dimensions and quantity. They depend on the heat transfer of the pipe. For example, 1 m of pipe with a diameter of 60 mm or a section of 60x60 mm and a thickness of 3 mm is intended to heat 1 m² of heated room area, taking into account that the ceiling height does not exceed 3 m.
The first thing to do is to cut sections from the selected pipe in accordance with the estimated length of the sections. The ends must be ground and cleaned of scale and burrs.
Before assembling the sectional devices, you need to put markings on them along which the jumpers will be installed. Usually this is 10-20 cm from the edges of the sectional pipes. A mark is made right there on the top element where the squeegee for the air vent (Maevsky tap) will be installed. It is located on the opposite side and along the edge of the section and along the outer plane.
- Using a gas torch or a plasma cutter, holes are made in the pipes according to the marks so that the jumper pipe can fit into them.
- The jumpers themselves are cut out from pipes of smaller diameter, 30-50 cm in size.
- Sections of the same length as the pipe jumpers are cut from the metal profile. They will be installed in the form of supports under the section pipes on the opposite side from the installation of the junction element.
- Plugs are cut from sheet metal 3-4 mm thick in the shape of the main pipe (circle or rectangle). In two of them, holes are made for drains, to which the supply and return circuits of the heating system will be connected through shut-off valves.
- First of all, plugs are welded to the sections.
- The leads are welded to the latter.
- Welding of jumpers with pipe sections is carried out.
- Supporting elements made from cut steel profiles are also attached by welding.
- The pipe for installing the Mayevsky tap is welded.
- All seams are cleaned with a grinder and a sanding disc.
It is better to carry out the assembly and welding process on a flat plane, on which two or three wooden blocks are laid (they can be replaced with steel profiles: an angle or a channel). It is on the bars that the pipe sections are laid out parallel to each other, taking into account the distance between the sections. As soon as the structure is assembled with tacks, you can begin welding all the seams, rotating the device so that welding is carried out only in the horizontal plane.
Regarding the installation of registers. Depending on which plane they will be attached to, it is necessary to consider the fasteners. There are several commonly used options.
If the device will rest on a floor base, then legs are installed under it. If it is attached to the wall, then use ordinary brackets with hooks bent upward.
After the register is completely assembled, it must be checked for tightness of the seams. To do this, one of the outlets is closed with a threaded plug, and water is poured through the second. Welding seams are checked. If a leak is detected, the defective area is boiled again and cleaned. After all operations performed, the device is painted.
Making a coil register is much simpler. Firstly, bends are ready-made factory parts that are selected according to the diameter of the pipe section. Secondly, they are cooked together in the same way as with a pipe.
First, connect two branches to each other. The resulting C-shaped fitting is connected in series to the ends of the two pipes, combining them into a single structure. At the two free ends of the register, plugs are installed, in which holes are pre-made, and the bends are welded.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before you start making heating registers, you need to evaluate all the pros and cons of these heaters, so that your expectations are not disappointed later. So, first about the advantages:
- low cost and ease of manufacture;
- low hydraulic resistance: thanks to this, the heater can be used in the “tail” of any system;
- reliability and durability: a register, qualitatively welded from ordinary pipes, will quietly serve for at least 20 years;
- resistance to pressure drops and water hammer;
- The smooth surface facilitates easy removal of dust when cleaning premises.
Unfortunately, a home-made heating register also has a lot of disadvantages. The main one is low heat transfer with a significant mass of the device. That is, in order to provide a comfortable temperature in a medium-sized room, the register must be of decent size. Let's give a simple example taken from technical literature. If the temperature difference between the coolant and the room is 65 ºС (DT), a register welded from 4 DN32 pipes 1 m long will deliver only 453 W, and from 4 DN100 pipes – 855 W. It turns out that, based on heat transfer per 1 m of length, any panel or sectional radiator is at least twice as powerful.
Other negative aspects of smooth-tube registers are not so critical, although significant:
- holds a large volume of water: the disadvantage does not play a big role if there are 1-2 such heating devices for the entire system;
- During operation, it is very difficult to increase or decrease the power of registers made of smooth pipes. You can’t do without dismantling the welding machine;
- are susceptible to corrosion and require periodic maintenance with painting;
- They have an unpresentable appearance: the defect can be corrected; if necessary, the heater is hidden behind a decorative screen.
Having analyzed the advantages and disadvantages of smooth-tube devices, we can conclude that their scope of application in private housing construction is very limited. As already mentioned, registers can be used for heating various rooms with low requirements for comfort and interior design.
When selecting materials, you need to decide what pipe diameters to take and what their total length should be. All these parameters are arbitrary; you can make a heater from any pipes, and take its length convenient for placement in the room. But in order to supply the required amount of heat, it is necessary to ensure a sufficient heat exchange area. To do this, it is recommended to perform an approximate calculation of the register based on the surface area.
Making such a calculation is quite simple. It is necessary to calculate the outer surface area of all sections in m2 and multiply the resulting value by 330 W. Proposing this method, we proceed from the statement that 1 m2 of register surface will give off 330 W of heat at a coolant temperature of 60 ºС and room air temperature of 18 ºС.
For a person who has welding skills, it will not be difficult to independently weld the register according to the available drawings. It is necessary to prepare and cut pipes into sections and lintels, and cut plugs from a steel sheet. The assembly sequence is arbitrary; after welding, the heater should be checked for leaks. When manufacturing and installing registers, consider the following recommendations:
- you should not take pipes with too thin or thick walls: the former will cool faster and last less, and the latter will take a long time to warm up and are difficult to adjust;
- do not forget to build a Mayevsky valve into the end of the upper section for bleeding air;
- when welding coils, the rotating section can be made from two ready-made elbows if it is not possible to use a pipe bender;
- Place a tap at the coolant inlet and a valve at the outlet;
- remember that the registers are installed with an invisible bias towards the connection of the supply pipe. Then Mayevsky's crane will be at the highest point.
Types of registers
The problem of replacing heating system radiators arises for many owners of apartments and private houses. I want to respect the design of the room, save money, and provide warmth and comfort. To achieve these goals, you should choose reliable, safe and durable radiators. The issue of cost also cannot be cast aside.
Heating systems, including radiators and registers, can be domestic or imported, stationary or portable. They can be made from different materials. Registers are made of aluminum, cast iron, and bimetallic. They all have their advantages, but each also has its disadvantages.
Bimetallic radiators are made of 2 different metals. Inside there are copper or steel pipes. From the outside they are covered with an aluminum casing, which is why they look like aluminum. It's easy to confuse them. From the outside it all looks like a single monolithic structure. Plus - high heat transfer. Aluminum coatings can have a variety of patterns. The downside is the high price.
- Aluminum radiators are very similar in appearance to bimetallic ones. They are cheaper, but are not intended for installation in a central heating system. Their purpose is to heat a private home. Reason: aluminum has direct, harmful contact with chemical inclusions in the central heating water. Aluminum radiators can be decorated with elegant cast patterns on the outside. Pros: the price is slightly lower than bimetallic and cast iron radiators. Disadvantages: predisposition to corrosion, some restrictions in use.
- Panel radiators are relatively new heating devices. Very popular in the USA and in a number of European countries. They are distinguished by a large heat transfer area and a high degree of reliability.
Types of registers for heating systems
Devices are divided into two categories. The technical characteristics of the system as a whole depend on the first. From the second - coolant circulation through the pipeline.
By material: steel, iron, aluminum and cast iron pipes
There are four types, although many other substances and their alloys can be used in production.
Steel

It is used more often than other metals.
This is due to several factors:
- cheapness;
- ease of processing;
- widespread;
- a wide variety of shapes.
Welding technology is used to create it.
Important! Sometimes registers are made of galvanized or stainless steel. It should be borne in mind that both options are expensive, and the first one is also difficult to process.
Smooth
Iron pipes with a high carbon content have this characteristic. To put it simply, the base is steel. To obtain a smooth surface, electric welding is used. They hold much more pressure than regular ones, while being nicer and a little more expensive. Similar registers are described in GOST 10704-91.
Aluminum

It is quite rare because welding requires special equipment that is not easy to find. This is their only disadvantage: the material is cheap, conducts heat well, almost without losing the latter.
Some registers are made from an alloy of steel and aluminum. Bimetallic devices are difficult to obtain, but they have better characteristics than their analogues.
Cast iron
They are almost never used because the registers are bulky and heavy. It is not advisable to create racks specifically for them. In addition, the metal is fragile and is capable of splintering or cracking from impact. Accordingly, you need to purchase protective covers that will reduce thermal conductivity. They are difficult to install, although they are reliable, and operation does not depend on the chemical composition of the pipes.
An almost identical description can be given to copper. It should be noted that it is much more expensive, but it transmits the temperature to the room 3-5 times better. Accordingly, a small harness is required. Among the disadvantages:
- fragility;
- poor compatibility with other metals;
- high requirements for coolant;
- mandatory grounding.
The material should be chosen according to personal preference, but it is also important to carry out calculations. They will help you calculate in advance the required installation dimensions for each type of metal.
By design: sectional, coil

Sectional registers are made from sections of large diameter pipes. They are connected by pipes to admit water. The latter are made of the same metal, and their size must correspond to the supply harness.
It is recommended to install the devices together with a circulation pump, since they create excess hydraulic resistance.
Creating sectional devices is not difficult. A grinder is used to cut out several registers and the connections between them. The system is assembled in one of two ways. In a continuous transition, transitions are made from each edge, and in a stepped transition, alternating. In the latter case, racks in the form of metal plates are placed at parallel sides.
Coil pipes are made from a single section of pipe. It is bent, which makes the creation process difficult. This applies to independent work: such devices are not uncommon in production. To speed up the work, the extreme sides, near the turns, are connected to each other.
For safety, small plates are installed between the bends to support the upper parts.
Sectional ones are slightly better for circulation, and are much easier to manufacture. Coil ones look a little more aesthetically pleasing and go well with a tubular electric heater.
Features of installation of ion boilers
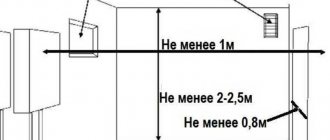
A prerequisite for installing ion heating boilers is the presence of a safety valve, pressure gauge and automatic air vent. The equipment must be placed in a vertical position (horizontal or at an angle are not allowed). At the same time, about 1.5 m of supply pipes are not galvanized steel.
The zero terminal is usually located at the bottom of the boiler. A grounding wire with a resistance of up to 4 ohms and a cross-section of over 4 mm is connected to it. You should not rely solely on RAM - it cannot help with current leakage. The resistance must also comply with the rules of the PUE.
If the heating system is completely new, there is no need to prepare the pipes - they must be clean inside. When the boiler crashes into an already operating main, it is necessary to flush it with inhibitors. The markets offer a wide range of products for removing deposits, salts and scale. However, each manufacturer of electrode boilers indicates those that it considers best for its equipment. Their opinion should be followed. By neglecting flushing, it will not be possible to establish the exact ohmic resistance.
It is very important to select heating radiators for the ion boiler. Models with a large internal volume are not suitable, since 1 kW of power will require more than 10 liters of coolant
The boiler will constantly work, wasting some of the electricity in vain. The ideal ratio of boiler power to the total volume of the heating system is 8 liters per 1 kW.

If we talk about materials, it is better to install modern aluminum and bimetallic radiators with minimal inertia. When choosing aluminum models, preference is given to primary type material (not remelted). Compared to the secondary one, it contains fewer impurities, reducing the ohmic resistance.
Cast iron radiators are the least compatible with an ion boiler, since they are the most susceptible to contamination. If it is not possible to replace them, experts recommend observing several important conditions:
- The documents must indicate compliance with the European standard
- Installation of coarse filters and sludge traps is required
- Once again, the total volume of coolant is produced and equipment suitable in terms of power is selected