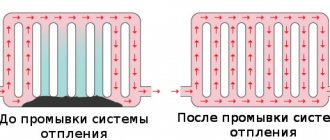
When is heating flushed?
Let us immediately note that individual heating systems of apartments and country houses very rarely require flushing. Typically, deterioration in heating is associated with other reasons, for example, airing. Let's explain:
- You filled the network with fresh water or antifreeze, expelled the air, and started the boiler.
- After 2-3 weeks, the coolant “breaks in” - a precipitate of salts falls in the heat exchanger, solid particles are captured by a mesh filter. During this period, the mud trap needs to be cleaned frequently.
- Since the amount of impurities in the supply water is limited, sedimentation soon stops. There is simply nothing for heat exchangers, pipes and batteries to become clogged with.
That is, a closed system can work quietly without any cleaning. If it is constantly fed from the water supply network, the amount of salt sediment will increase indefinitely. Over the years, the pipelines will become half overgrown, and silt will settle in the radiators.
Options for clogging cast iron batteries depending on the connection method
A similar effect occurs due to the penetration of oxygen into the coolant. Air bubbles cause corrosion of metal pipes and fittings from the inside, forming iron oxide (rust) particles, which are constantly found in the mud pan. The cause may be low-quality plastic pipes without a protective oxygen barrier.
Reference. A “used-in” coolant often takes on a dark or even black color; this is quite normal. Brown water indicates a large amount of rust.
So, in what cases is heating flushing carried out:
- The heating devices, one or more, stopped heating normally. The battery sections heat up unevenly, the bottom remains cold. At the same time, you eliminated all possible faults, but did not get any results.
- For various reasons, you constantly replenish the system with fresh coolant. For example, to operate electrode boilers you need water with a certain amount of salts, which decompose during a chemical reaction. You have to add salt to the coolant or fill in a new one.
- Oxygen penetrates into the network water, the filter often gets clogged (almost every day), the radiators do not heat well, the boiler operates at maximum mode.
The conclusion is simple: flushing is done when there is a problem with the water heating system; no frequency needs to be observed. There is a different approach to the centralized heat supply of multi-apartment residential buildings, where the radiator network is flushed annually, after which pressure testing is performed (in accordance with the requirements of SNiP).
How often do you clean the heat exchanger in a gas boiler?
The frequency of cleaning the heat exchanger depends primarily on the type of coolant and the design features of the unit itself. It is least common to service single-circuit boilers in heating systems that use purified water as a coolant. To keep them in good condition, it is enough to carry out preventive maintenance once every 4 years.
If untreated water circulates in the system, the boiler should be flushed once every 2-3 years. If the water is hard, then the cleaning regime is once every 2 years. The secondary heat exchanger of a double-circuit boiler must be washed with the same frequency, because unfiltered tap water with impurities flows through it.
Most often, maintenance is required for equipment in heating systems where antifreeze is used as a coolant. It should be washed at least once every 2 years. In addition, you have to monitor the expiration date of antifreeze and replace it in a timely manner. Otherwise, the efficiency of the system will decrease and heating costs will increase.
When cleaning heat exchangers, pay attention to the appearance of the boilers and nozzles and, if necessary, carry out repair work. You should also monitor the condition of chimneys and clean them of soot in a timely manner. These simple measures extend the life of heating equipment and prevent breakdowns.
About price tags
The price of flushing a gas boiler heat exchanger depends on the method chosen. The cheapest is mechanical. You can do it yourself. But you need to act extremely carefully. A stiff metal brush is used.
The second method is hydrodynamic. It uses jets of powerful pressure water. Special settings apply. They develop line pressure up to 1500 bar.
The effectiveness of the method is very high. But the price tag too -...
The third method is chemical. A booster is used - a special device. With its help, a composition for acid cleansing is introduced. This composition circulates in the heat exchanger for several hours and effectively cleanses it. Even carbonate scale is removed.
Example of a device before and after surgery.

Disadvantages of this method:
- high price tag of the reagent,
- metal wear,
- a lot of toxins are formed.
How to flush the system - 3 available methods
Without the use of specialized equipment, you can do the washing in the following ways:
- local cleaning of radiators;
- simple flushing of pipes and heating appliances with tap water;
- chemical (otherwise known as hydrochemical) cleaning of heating pipelines.
Reference. Centralized heating networks of apartment buildings are flushed using the hydropneumatic method. A powerful compressor is connected to the elevator unit located in the heating point. A mixture of water and air is pumped through the radiators and pipes of all apartments, tearing off particles of solid deposits, and even more so silt. The dirt is then dumped into the sewer.

Most homeowners do not have compressor units. In addition, you will need a mixing chamber and experience in performing such activities, otherwise you risk breaking the tightness of the joints. This means that the hydropneumatic method is of little use for self-flushing the system. We recommend starting by cleaning dead batteries.
Radiator cleaning
Identifying a problem battery is quite simple - with the heating running, feel the entire surface with your hand or measure the temperature at different points with a contact/non-contact thermometer, and then compare with the temperature of the supply line. If the sections heat up unevenly, flush the radiator.
In an apartment with central heating, flushing the battery is done as follows:
- We close the shut-off valves on the connections to the heating device. Using a gas wrench, unscrew the top plug with the Mayevsky tap, substitute the basin, and drain part of the coolant.
- Carefully open the tap on the supply line so that the water pressure throws debris out of the radiator. Of course, keep your basin under the stream. When the light coolant flows out, close the valve and put the plug in place.

- Similarly, we repeat the listed manipulations with the bottom plug. After rinsing, tighten the plug, open both taps, and bleed the air.
The described technology is applicable in private houses with automatic heating from the water supply. Just before flushing, it is better to close the valves on the boiler and expansion tank. In other cases, you need to remove the radiator and wash it separately. Connecting a cold water supply hose to the heating network is a risky option; when water is supplied “to a closed valve”, high pressure of 3...6 Bar can break the tightness of the system.
Disconnecting the battery gives one plus - the opportunity to look inside the supply pipes. Having seen deposits there that cover 1/3 or half of the flow area, it is easy to decide on further flushing of all heating pipelines.

In the photo on the left is the removal of sludge from a cast iron radiator, on the right is a horizontal line clogged with sediment
Note. In an open system we have an expansion tank communicating with the atmosphere. If it is not possible to cut off the container with a tap, then it will not be possible to flush the battery through the recharge; the water will trample over the top and begin to drown the house.
Cast iron radiators that have served for more than 10 years will definitely have to be removed and cleaned with some kind of chemical, for example, a caustic soda solution (see the video below). The sediment at the bottom of each section rarely remains liquid and is unlikely to be removed using running water.
Rinsing with running water
The essence of the method is to remove dirt from the system using a large flow of water from the centralized water supply network. Let us immediately note the disadvantage of this option: only liquid sludge and suspended particles traveling along with the coolant can be washed out of pipes and heating appliances. If there are hard deposits in the batteries, it will not be possible to remove them.
How is this hydroflushing done:
- We connect the water supply hose to the make-up fitting. As you know, this pipe is cut into the lower point of the heating return line. We connect the drain hose to a break in the supply line (for example, instead of a circulation pump or at the junction of a faucet) and lead it to the sewer or to an area near the house.
- We clean the mud trap, open all radiator taps and balancing valves.
- The boiler must be isolated from the system using taps and must be washed separately. You should not drive all the dirt through its heat exchangers, especially for double-circuit heat generators.
- Open the water valve, gradually increasing the water flow. As you understand, backwashing begins, that is, the flow moves towards the coolant flow in operating mode.
- When the stream from the drain hose becomes transparent, turn off the water, swap the hoses and flush the heating in the other direction - along the movement of the coolant.
- At the end of the hydraulic cleaning, we refill the system, start the boiler, check the operation of the batteries and do balancing.
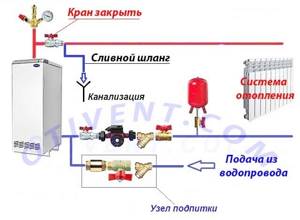
An important nuance. It should be understood that flushing is carried out due to the high flow of water through the heating pipelines, and not due to high pressure. You cannot supply water “to a closed valve”, only through an open drain hose. The heating network is not designed for water pressure.
A system with an open tank must first be prepared for flow rinsing. There are 2 options: cut off the expansion tank with a tap or plug the overflow tube. The second method is suitable for tanks without a top cover. If this is not done, the water will overfill the tank and flow out, leaving the area of the system left unwashed.
Chemical cleaning option
This is the most affordable way to thoroughly flush the heating system with your own hands. To implement it you will need:
- vibration pump of a submersible household series, for example, “Rucheek” (or similar);
- a water filter in the form of a flask with 2–3 replaceable cartridges;
- special means for flushing heating networks and radiators;
- container for chemical solution;
- connecting fittings.
The procedure is carried out in 3 stages - preliminary removal of contaminants with running water, then chemical cleaning itself, and finally - final rinsing. The first and third stages are done using the technology described above using water supply; the second stage uses a submersible pump and filter.

How to flush the heating system chemically (stage 2):
- Prepare the washing solution in the barrel according to the instructions on the package. The amount of liquid corresponds to the volume of coolant in the heating network plus the container itself. We wrote how to choose the right chemical at the end of the article.
- Connect the pressure pipe of the pump to the heating supply, immerse the device in the barrel. The filter is placed on the drain line, which is directed into the same container, as shown in the video below.
- Remove the mesh from the standard mud pan and screw the empty plug back on. Otherwise you will have to clean it every 10 minutes.
- Turn on the pump, pump the reagent into the system. Make sure that the solution flows into the barrel from the drain hose and that there are no leaks.
- Flush heating lines until the water stream becomes lighter. Heavily contaminated filter cartridges must be replaced during the cleaning process.
- Wash the remaining chemicals from the radiator network with running water (stage 3).
Reminder. Chemical cleaning should only affect pipes, radiators and heated floors (if necessary). It is not recommended to pump the reagent through the boiler; it is better to clean the unit separately. An open type expansion tank should be cut off from the pipeline network or sealed.
How to flush the system of a country house, watch the video: