Lawyer Anisimov Representation and defense in court
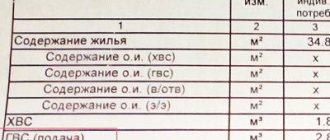
Article 15 of the Housing Code of the Russian Federation recognizes a residential premises as an isolated premises, which is real estate and is suitable for permanent residence of citizens (meets sanitary and technical rules and regulations, and other legal requirements). The total area of a residential premises consists of the sum of the areas of all its parts, including premises for auxiliary use, intended to satisfy citizens' household and other needs related to their residence, with the exception of balconies, loggias, verandas and terraces. In accordance with the Rules for the provision of utility services to owners and users of premises in apartment buildings and residential buildings (Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011 No. 354), when calculating the amount of payment for heating, the total area of the residential premises is taken into account. Thus, the balcony and loggia are not included in the heated area of the living space, but the bathroom and toilet are. According to the “Rules for the provision of gas supply services to the population” (as of 03/02/2015), “heated area is the total area of the apartment (house) excluding the area of loggias, balconies , terraces, as well as the area of premises where there are no heat-releasing surfaces (radiators, registers , walls of furnaces, pipelines of heating systems, etc.), which are not directly connected to the heated premises by doors and other openings” (clause 2 of the Rules).
Document overview
In cadastral activities, the area of the building and premises is important. The Russian Ministry of Economic Development has established how to determine it.
So, to determine the area and total area of a building (room), you need to refer to the area of the simplest geometric figure (rectangle, trapezoid, right triangle, etc.). Or divide such an object into the latter and sum up their areas.
The corresponding value is expressed in square meters, rounded to the nearest 0.1. The measured distances used for these purposes are meters, rounded to the nearest 0.01.
The area of the building is calculated as the sum of the areas of all above-ground and underground floors (including technical, attic, and basement). At the same time, we do not forget about the area of mezzanines, galleries and balconies of auditoriums and other halls, verandas, external glazed loggias and galleries. The area of open, unheated planning elements of the building is also taken into account separately.
The area of a room is the sum of the areas of all its parts, calculated by their sizes, measured between the finished surfaces of walls and partitions at a height of 1.1-1.3 m.
The total area of a residential premises and a house consists of the sum of the area of all their parts. This also includes the area of auxiliary premises that satisfy the needs associated with living in residential premises (except for balconies, loggias, verandas and terraces). We are talking about kitchens, corridors, baths, toilets, built-in wardrobes, storage rooms, as well as the area occupied by the internal staircase.
The distances used to determine the total area of housing are measured along the entire perimeter of the walls at a height of 1.1-1.3 m from the floor.
Heated area of apartments or usable area of premises, m2;
Heated volume of the building, m3;
D
– degree-day of the heating period, °С day (1.1).
Specific consumption of thermal energy for heating buildings >
must be less than or equal to the standardized value
≤
. (5.2)
5.1 Determination of heated areas and volumes of the building
This item is carried out in the section of the diploma project for residential and public buildings.
1. The heated area of the building should be defined as the area of the floors (including the attic, heated basement and basement) of the building, measured within the internal surfaces of the external walls, including the area occupied by partitions and internal walls. In this case, the area of staircases and elevator shafts is included in the floor area.
The heated area of the building does not include the area of warm attics and basements, unheated technical floors, basement (underground), cold unheated verandas, unheated staircases, as well as a cold attic or part of it not occupied as an attic.
2. When determining the area of the attic floor, the area with a height to a sloping ceiling of 1.2 m with a slope of 30° to the horizon is taken into account; 0.8 m - at 45° - 60°; at 60° or more - the area is measured up to the baseboard.
3. The area of residential premises of the building is calculated as the sum of the areas of all common rooms (living rooms) and bedrooms.
4. The heated volume of a building is defined as the product of the heated area of the floor and the internal height, measured from the floor surface of the first floor to the ceiling surface of the last floor.
With complex shapes of the internal volume of a building, the heated volume is defined as the volume of space limited by the internal surfaces of external enclosures (walls, roofing or attic floor, basement).
5. The area of external enclosing structures is determined by the internal dimensions of the building. The total area of the external walls (including window and door openings) is determined as the product of the perimeter of the external walls along the internal surface and the internal height of the building, measured from the floor surface of the first floor to the ceiling surface of the last floor, taking into account the area of window and door slopes with a depth from the internal surface of the wall to the inner surface of a window or door block. The total area of windows is determined by the size of the openings in the light. The area of the external walls (opaque part) is determined as the difference between the total area of the external walls and the area of windows and external doors.
6. The area of horizontal external fences (covering, attic and basement floors) is determined as the floor area of the building (within the internal surfaces of the external walls).
With inclined surfaces of the ceilings of the last floor, the area of the roof, attic floor is determined as the area of the inner surface of the ceiling.
The calculation of the areas and volumes of the space-planning solution of the building is carried out according to the working drawings of the architectural and construction part of the project. As a result, the following main volumes and areas are obtained:
Heated volume Vh
,m3;
Heated area (for residential buildings - total area of apartments) Ah
,m2;
Total area of the building's external enclosing structures, m2.
5.2 Determination of the standardized value of specific heat energy consumption for heating a building
The normalized value of the specific heat energy consumption for heating a residential or public building is determined from the table. 5.1 and 5.2.
Standardized specific heat energy consumption for heating single-apartment detached and semi-detached residential buildings, kJ/(m2 °C day)
Table 5.1
| Heated area of houses, m2 | With number of floors | |||
| 60 or less | ||||
| 1000 or more | ||||
| Note - For intermediate values of the heated area of the house in the range of 60-1000 m2, the values should be determined by linear interpolation. | ||||
Standardized specific heat energy consumption for heating buildings, kJ/(m2 °C day) or [kJ/(m3 °C day)]
Table 5.2
| Building types | Number of floors of buildings | |||||
| 1. Residential, hotels, hostels | According to table 5.1 | for 4-story single-apartment and semi-detached houses - according to table. 5.1 | ||||
| 2. Public, except those listed in pos. 3, 4 and 5 tables | ||||||
| 3. Clinics and medical institutions, boarding houses | ; ; according to the increase in number of storeys | |||||
| 4. Preschools | ||||||
| 5. Service | ; ; according to the increase in number of storeys | |||||
| 6.Administrative purposes (offices) | ; ; according to the increase in number of storeys | |||||
Heated area of the building
the total area of the floors (including attic, heated basement and basement) of the building, measured within the internal surfaces of the external walls, including the area of stairwells and elevator shafts; for public buildings, the area of mezzanines, galleries and balconies of auditoriums is included. (See: TSN 23-328-2001 of the Amur Region (TSN 23-301-2001 JSC). Standards for energy consumption and thermal protection.)
Source: “House: Construction Terminology”, M.: Buk-press, 2006.
Construction Dictionary.
Housing and communal services in Russia
3.36. The area of an apartment in a residential building is determined as the sum of the areas of living rooms and utility rooms WITHOUT taking into account loggias, balconies, VERANDAS, terraces and cold storerooms, vestibules (this area is also called the heated area - note Yu.K.) utility rooms include the area of kitchens, corridors , baths, toilets, built-in wardrobes, storage rooms, as well as the area occupied by the internal staircase. Note: The concept of “total area”, previously used in official statistical accounting of the housing stock, is equivalent to the concept of “apartment area” (SNiP 2.08.01-89*). 3.37. The total area of the apartment is determined as the sum of the areas of its premises, built-in wardrobes, as well as the areas of loggias, balconies, verandas, terraces and cold storage rooms, calculated with the following reduction factors: for loggias - 0.5, for balconies and terraces - 0.3, for verandas and cold storage rooms — 1.0"
Easy ways to calculate heat load
Any calculation of the thermal load is needed to optimize the parameters of the heating system or improve the thermal insulation characteristics of the house. After its implementation, certain methods of regulating the heating heat load are selected. Let's consider non-labor-intensive methods for calculating this parameter of the heating system.
Dependence of heating power on area
Table of correction factors for various climatic zones of Russia
For a house with standard room sizes, ceiling heights and good thermal insulation, you can apply a known ratio of room area to the required thermal power. In this case, 1 kW of heat will need to be generated per 10 m². A correction factor must be applied to the result obtained, depending on the climate zone.
Let's assume that the house is located in the Moscow region. Its total area is 150 m². In this case, the hourly heating load will be equal to:
15*1=15 kW/hour
The main disadvantage of this method is the large error. The calculation does not take into account changes in weather factors, as well as the features of the building - the heat transfer resistance of walls and windows. Therefore, in practice it is not recommended to use it.
Integrated calculation of the thermal load of a building
A larger calculation of the heating load is characterized by more accurate results. Initially, it was used for preliminary calculation of this parameter when it was impossible to determine the exact characteristics of the building. The general formula for determining the heating load is presented below:
Where q° is the specific thermal characteristic of the structure. The values must be taken from the corresponding table, a is the correction factor mentioned above, Vn is the external volume of the building, m³, Tin and Tnro are the temperature values inside the house and outside.
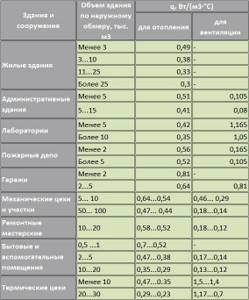
Table of specific thermal characteristics of buildings
Let's assume that it is necessary to calculate the maximum hourly heating load in a house with a volume along the external walls of 480 m³ (area 160 m², two-story house). In this case, the thermal characteristic will be equal to 0.49 W/m³*C. Correction factor a = 1 (for the Moscow region). The optimal temperature inside the living space (Tvn) should be +22°C. The outside temperature will be -15°C. Let's use the formula to calculate the hourly heating load:
Q=0.49*1*480(22+15)= 9.408 kW
Compared to the previous calculation, the resulting value is smaller. However, it takes into account important factors - temperature indoors, outdoors, and the total volume of the building. Similar calculations can be made for each room. The method for calculating the heating load using aggregate indicators makes it possible to determine the optimal power for each radiator in a separate room. For a more accurate calculation, you need to know the average temperature values for a specific region.
This calculation method can be used to calculate the hourly heat load for heating. But the results obtained will not provide an optimally accurate value of the building’s heat losses.
Heated area of the apartment: was it calculated correctly?
The methodology for planning, accounting and calculating the cost of housing and communal services, approved by Decree of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated February 23, 1999 No. 9, explains that “to determine the heating fee per 1 square meter of housing, the area of an apartment or individual house is determined as the total the area of living rooms and utility rooms excluding loggias, balconies, verandas, terraces and cold storage rooms, vestibules.” How do you look at the above problem through the prism of the above link to the current regulatory legal document? I answer:
See the main answer above. Currently, the calculation of the heating fee is based on the total area of the living space. An exception is made only for balconies, loggias, verandas and terraces - their areas are not included in the total and heated area. The storage area, if it is included in the total area of the apartment according to the technical passport, will also be considered a heated area. However, if the pantry is divided between several owners, then they must pay the costs for it in proportion to the total area of their apartments (based on the Housing Code of the Russian Federation).
Please note => Does a person with one sighted eye have the right to disability
Consider the calculation method for rooms with high ceilings
However, calculating heating by area does not allow us to correctly determine the number of sections for rooms with ceilings higher than 3 meters. In this case, it is necessary to apply a formula that takes into account the volume of the room. To heat each cubic meter of volume, according to SNIP recommendations, 41 W of heat is required. So, for a room with a ceiling height of 3 m and an area of 24 sq.m, the calculation will be as follows:
24 sq.m x 3 m = 72 cubic meters (room volume).
72 cubic meters x 41 W = 2952 W (battery power for heating the room).
Now you need to find out the number of sections. If the documentation of the radiator indicates that the heat transfer of one part of it per hour is 180 W, you need to divide the found battery power by this number:
2952 W / 180 W = 16.4
This number is rounded to the nearest whole number - it turns out 17 sections to heat a room with a volume of 72 cubic meters.
Using simple calculations, you can easily determine the data you need.
Heated area of the apartment according to the laws of the Russian Federation
In everyday life, any person may suddenly need to get an answer to the question of whether the balcony is included in the total area of the apartment. Ordinary people not involved in housing construction or the provision of real estate services hardly asked such a question without being faced with the need for clarification directly. According to clause 3.37 of the Instructions, the total area of an apartment is defined as the sum of the areas of its premises, built-in wardrobes, as well as the areas of loggias, balconies, verandas, terraces and cold storage rooms, calculated with the following reduction factors: for loggias - 0.5, for balconies and terraces - 0.3, for verandas and cold storerooms - 1.0.
Simple area calculations
You can calculate the size of heating batteries for a specific room based on its area. This is the easiest way - to use plumbing standards, which stipulate that a thermal power of 100 W per hour is needed to heat 1 sq.m. We must remember that this method is used for rooms with standard ceiling heights (2.5-2.7 meters), and the result is somewhat inflated. In addition, it does not take into account such features as:
- number of windows and type of double-glazed windows on them;
- the number of external walls in the room;
- the thickness of the building walls and what material they are made of;
- type and thickness of insulation used;
- temperature range in a given climate zone.
Is the balcony included in the total area of the apartment?
3.37. The total area of the apartment is determined as the sum of the areas of its premises, built-in wardrobes, as well as the areas of loggias, balconies, verandas, terraces and cold storage rooms, calculated with the following reduction factors: for loggias - 0.5, for balconies and terraces - 0.3, for verandas and cold storage rooms - 1.0. The same is said in the mandatory Appendix No. 2 to SNiP 2.08.01-89. Paragraph 2 of the Appendix states “The total area of apartments should be determined as the sum of the areas of their premises, built-in wardrobes, as well as loggias, balconies, verandas, terraces and cold storage rooms, calculated with the following reduction factors: for loggias - 0.5, for balconies and terraces - 0.3, for verandas and cold storage rooms - 1.0.”
Accurate heat load calculations
But still, this calculation of the optimal thermal load for heating does not provide the required calculation accuracy. It does not take into account the most important parameter - the characteristics of the building. The main one is the heat transfer resistance of the material used to manufacture individual elements of the house - walls, windows, ceilings and floors. They determine the degree of conservation of thermal energy received from the coolant of the heating system.
What is heat transfer resistance ( R )? This is the reciprocal of thermal conductivity ( λ ) - the ability of the material structure to transmit thermal energy. Those. the higher the thermal conductivity value, the higher the heat losses. This value cannot be used to calculate the annual heating load, since it does not take into account the thickness of the material ( d ). Therefore, experts use the heat transfer resistance parameter, which is calculated using the following formula:
R=d/λ
Calculation of walls and windows
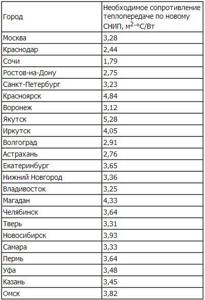
There are standardized values of heat transfer resistance of walls, which directly depend on the region where the house is located.
In contrast to the enlarged calculation of the heating load, you first need to calculate the heat transfer resistance for the external walls, windows, ground floor floor and attic. Let's take the following characteristics of the house as a basis:
- Wall area – 280 m² . It includes windows - 40 m² ;
- The material used to make the walls is solid brick ( λ=0.56 ). The thickness of the external walls is 0.36 m . Based on this, we calculate the TV transmission resistance - R=0.36/0.56= 0.64 m²*C/W ;
- To improve the thermal insulation properties, external insulation was installed - polystyrene foam 100 mm . For him λ=0.036 . Accordingly, R=0.1/0.036= 2.72 m²*C/W ;
- R value for external walls is 0.64 + 2.72 = 3.36 which is a very good indicator of the thermal insulation of a house;
- The heat transfer resistance of windows is 0.75 m²*C/W (double glazing filled with argon).
In fact, heat losses through the walls will be:
(1/3.36)*240+(1/0.75)*40= 124 W at a temperature difference of 1°C
We will take the same temperature indicators as for the aggregate calculation of the heating load +22°C indoors and -15°C outdoors. Further calculations must be made using the following formula:
124*(22+15)= 4.96 kW/hour
What is included in the total area of an apartment in Russia in 2021
It is possible to calculate the full cost of real estate Correctly estimate the purchase price Drawing up an explication, technical passport for the apartment As well as other accompanying documents for real estate This parameter will be needed when selling In order to justify the value of real estate to a potential buyer When carrying out redevelopment You will need to make the calculation yourself
- object of housing rights;
- living space;
- apartment area;
- unsuitable for habitation;
- auxiliary premises.
Object of housing rights Premises that are recognized as residential. Accordingly, in order for an apartment to be recognized as a residential premises, it must have the main features of such and meet standard requirements. They are determined for each type of real estate. Apartment area. Standard parameter that is taken into account primarily when calculating the cost of housing. Unsuitable for habitation. The condition of the premises when it cannot be used for its intended purpose. Moreover, there must be a recognition as unsuitable in the standard manner established
Please note => Write-off of fixed assets in RB transactions 2019
Total area and living area of the house
Due to the fact that the size of utilities depends on the area
, it is necessary that the area in the documents corresponds to reality. Sometimes this requires ordering a new technical passport for the residential premises. Based on the data contained in it, a cadastral passport is drawn up, and information from it is indicated in the certificate of ownership.
People often confuse concepts such as total area and living area; the main thing is to be guided by documents when determining the area, however, if you need to know the size of the area for specific purposes, it would be a good idea to consult a lawyer who, knowing the legal features of a particular issue, will help you not only in word, but also in deed.
Is the balcony area included in the total area of the apartment according to Russian law?
This fact must be known when purchasing/selling or re-registering residential real estate. When calculating the final total footage, the existence of balconies/loggias/terraces leads to an increase in the price of real estate, since it is calculated for each square meter. Living rooms include all premises suitable for living. All of these will need to be taken into account. Because otherwise, difficulties may arise with the Bureau of Technical Expertise. All technical documentation must be completed correctly - especially if there will be a sale of real estate in the future. Since buyers always pay especially close attention to this.
Correct calculation of heating - based on room volume
Should I calculate heating based on the volume of the room or limit myself to calculations based on area? Let's look at how calculating heating based on the volume of a room in a house is preferable and better than the common figures of “1 kW for every 10 square meters of area.”
So, if you calculate heating by the volume of a room, you include three quantities in it - the area of the room, the height of the ceilings and the thickness of the ceilings. In addition, not only thickness is involved in the calculation, but the floor material will also be important. Why? Let's explain a little below.
When you calculate heating based on the area of the room, only one indicator is involved in your calculations = the area of your premises. Why is the first option more accurate and why is it preferable?
Include a balcony in the total area of the apartment and legalize it with autonomous heating
Many people dream of making the balcony a full-fledged part of the apartment. It would seem that the most direct way to this is to place a radiator on the balcony. Can this be done legally? And is it possible to avoid punishment if the law does not work out? What does the law say about moving heating to the balcony? According to the Housing Code of the Russian Federation (Article 25, paragraph 1), “Installation, replacement or transfer of utility networks (including heating ones) ... refers to the reconstruction of residential premises.” It is allowed when you are renovating the residential part of the premises and you have permission to do so. The cost of housing primarily depends on the area. In order for all transaction processes to be carried out without deception and without errors, you should check the accuracy of the designated area specified in the purchase and sale agreement of the premises yourself. And here you will need knowledge of the law and calculation rules.
Calculation of heating by room area - detailed analysis of methods
If you have a need to replace old, failed radiators, or you are going to install a new system in a house under construction, you should know how to calculate heating based on the area of the room.
In order for the system to operate effectively, the number of sections of radiators to be installed must be accurately determined so that heat transfer and heating are optimal.
If there are not enough sections, then the room will never warm up properly, and a large number of them will lead to wasteful and excessive consumption of heat, and accordingly will have a detrimental effect on your finances and budget. The needs of premises of a standard type and layout can be determined using fairly simple calculations, and in order to achieve greater accuracy, it is necessary to take into account some additional parameters and features.
What is included in the total area when calculating heating fees?
Svetlana! The rules for calculating the amount of payment for were approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated May 6, 2011. To calculate the size of the heating fee in your case, this is formula 3 of Appendix 2 of the above rules. But it is not clear what exactly you are not satisfied with in the management company’s response. The formula indicates that for the calculation, in your case, the area of residential premises, that is, apartments, is taken. The area of common areas is not used in the formula, but this does not mean that when distributing the volume of thermal energy that your house consumed in all rooms, you do not have to pay for heating that is consumed in common areas - entrances, staircases, etc. d. Hello! For the calculation, the area of residential premises in your case is taken, but it must be taken into account that your house has a common house meter installed, which reflects the readings of thermal energy consumed in all rooms of the house, that is, in apartments and common areas, therefore, despite the fact that Since the calculation formula only indicates the area of residential premises, in fact your heating payment will include the thermal energy consumed both in your apartment and part of the thermal energy consumed on inter-apartment landings, stairs and basements.
Please note => Enrollment in a university with a certificate of loss of a breadwinner
Climate zones are also important
It’s no secret that different climatic zones have different needs for heating, so when designing a project it is necessary to take these indicators into account.
Climatic zones also have their own coefficients:
- central Russia has a coefficient of 1.00, so it is not used;
- northern and eastern regions: 1.6;
- southern stripes: 0.7-0.9 (minimum and average annual temperatures in the region are taken into account).
This coefficient must be multiplied by the total thermal power, and the resulting result divided by the heat transfer of one part.
conclusions
Thus, calculating heating by area does not present any particular difficulties. It’s enough to sit a little, figure it out and calmly calculate. With its help, every owner of an apartment or house can easily determine the size of the radiator that should be installed in the room, kitchen, bathroom or any other place.
If you doubt your abilities and knowledge, entrust the installation of the system to professionals. It’s better to pay professionals once than to do it wrong, dismantle it and start work again. Or do nothing at all.
A heated loggia is included in the total area of the apartment
Sometimes the developer misleads participants in shared construction, claiming to buyers that he is guided by the housing legislation of the Russian Federation. For example, it imposes information on clients - buyers that certain additional rooms in the apartment do not belong to the living space, although this space is paid for when purchasing. The total area of an apartment should be considered (according to a certain article of legislation) the total amount of area of all the premises that are included in it. Additional premises that satisfy the needs of apartment residents are also taken into account when calculating the total area.
How to correctly calculate the area of a house in 2021
- future housing is being designed;
- it is necessary to carry out construction and it is necessary to calculate the amount of material required in this case;
- carrying out finishing work indoors - usually the consumption of materials is calculated based on square meters;
- for registration of home ownership in the authorities of Justice;
- if it is necessary to rent out housing;
- repair work both indoors and outdoors;
- execution of a housing purchase and sale agreement;
- preparation of a special technical plan for the Bureau of Technical Expertise.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem , contact a consultant:
What is included in the total living area of the apartment?
According to the current rules for designating the total footage, the total area of your apartment must be understood as the result of the addition of all square meters of its heated and unheated rooms and premises, as well as those calculated using reducing indicators. An accurate understanding of how the reduction factor is used when calculating the square footage of individual premises will save you from misunderstandings and unpleasant surprises. If you were unable to protect yourself from such shortcomings, then only an appeal to the judicial authorities can restore justice.
Climate zones are also important
It’s no secret that different climatic zones have different needs for heating, so when designing a project it is necessary to take these indicators into account.
Climatic zones also have their own coefficients:
- central Russia has a coefficient of 1.00, so it is not used;
- northern and eastern regions: 1.6;
- southern stripes: 0.7-0.9 (minimum and average annual temperatures in the region are taken into account).
This coefficient must be multiplied by the total thermal power, and the resulting result divided by the heat transfer of one part.
Thus, calculating heating by area does not present any particular difficulties. It’s enough to sit a little, figure it out and calmly calculate. With its help, every owner of an apartment or house can easily determine the size of the radiator that should be installed in the room, kitchen, bathroom or any other place.
If you doubt your abilities and knowledge, entrust the installation of the system to professionals. It’s better to pay professionals once than to do it wrong, dismantle it and start work again. Or do nothing at all.
Continuing the topic: high-quality interior doors from www.dveri-tmk.ru will help keep your home or apartment warm. And simplify calculations for heating area.
Heated area of the apartment according to the laws of the Russian Federation
Thus, a balcony is a fenced area protruding from the plane of the facade wall. May be glazed. A veranda is a glazed, unheated room attached to or built into a building that has no depth limitation. A loggia is a built-in or attached room, open to the outside space, fenced on three sides by walls (on two sides in case of a corner location) with a depth limited by the requirements of natural light in the room to the outer wall of which it adjoins. May be glazed. Based on the definition itself, it becomes clear that a balcony cannot be included in the total footage when calculating fees for heating services, for example, since according to the Rules for the provision of utility services dated May 23, 2006. The area of unheated premises is not taken into account when calculating the amount of charges. As for the “rent,” it is calculated in direct proportion to the square footage of the entire apartment, but for an apartment with a balcony, a reduction factor of 0.3 must be used.
21 Dec 2021 marketur 1600
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Are there Benefits for Veterans Arriving in Moscow?
- Benefits for Perm war children
- Property tax benefits for disabled people of group 3
- How to mark the kindergarten number in state services
CALCULATION OF HEATED AREA AND VOLUMES OF A BUILDING
5.4 Thermal insulation of external walls should be designed to be continuous in the plane of the building facade. When using combustible insulation, it is necessary to provide horizontal cuts from non-combustible materials at a height of no more than the height of the floor and no more than 6 m. Fencing elements such as internal partitions, columns, beams, ventilation ducts and others should not violate the integrity of the thermal insulation layer. Air ducts, ventilation ducts and pipes that partially pass through the thickness of external fences should be buried to the surface of the thermal insulation on the warm side. It is necessary to ensure a tight connection of the thermal insulation to the through heat-conducting inclusions. In this case, the reduced heat transfer resistance of the structure with heat-conducting inclusions must be no less than the required values.
5.11 It is recommended to design the filling of gaps at the junctions of windows and balcony doors with external wall structures using foaming synthetic materials. All window and balcony doors must have sealing gaskets (at least two) made of silicone materials or frost-resistant rubber with a durability of at least 15 years (GOST 19177). It is recommended to install glass in windows and balcony doors using silicone mastics. The blind parts of balcony doors should be insulated with heat-insulating material.
What documents are needed when increasing the heated area in a private house?
It is worth noting that the process may be a little more complicated if the building belongs to the list of cultural or historical heritage sites. In this case, interested parties will have to visit several authorities, including the territorial department responsible for the protection of architectural monuments.
The application must be accompanied by a technical passport for each room. The process of approving redevelopment in a private house does not differ from the procedure for registering changes to premises in apartments in multi-storey buildings.